Neural Circuits & Behavior Quizzes
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
The resting membrane potential typically ranges from _______ to _______.
-40 mV; -90 mV
40 mV; 90 mV
0 mV; 90 mV
-90 mV; 90 mV
40 V; 90 V
-40 mV; -90 mV
Which of the following statements about action potentials is false?
They can transmit signals over long distances
They occur at threshold
They boost the spatial spread of electrical signals
They are elicited by hyperpolarization
They are all-or-none
They are elicited by hyperpolarization
The transmembrane potential is generated by
All of the above
high concentrations of specific leak channels
diffusion of ions down a concentration gradient
the selectivity of the membrane
ATP dependent pumps removing ions
All the above
Which of the following statements about electrochemical equilibrium is false?
For a given ion concentration gradient, the resulting potential is independent of the number of charges on the ion
The direction of the ion gradient determines the polarity of the membrane potential
Ionic gradients are necessary for the generation of the membrane potential
The size of the potential is proportional to the size of the ion gradient
Electrochemical equilibrium involves the movement of a relatively small number of ions
For a given ion concentration gradient, the resulting potential is independent of the number of charges on the ion
How will a neuron respond to an injection of negative current?
It will generate a single action potential
It will reach the threshold potential
It will generate multiple action potentials
It will have a positive electrical response
It will become hyperpolarized
It will become hyperpolarized
An action potential occurs if current injected into a neuron that _______ the neuron to reach _______ potential.
depolarizes; threshold
hyperpolarizes; synaptic
depolarizes; synaptic
hyperpolarizes; resting
hyperpolarizes; threshold
depolarizes; threshold
In a two-compartment model of a cell with a K+ permeable membrane, at K+ equilibrium potential, there is _______ flux of K+ ions
a large outward
a small outward
a small inward
no net
a large inward
no net
Typically, neurons firing action potentials encode a signal intensity by
sending signals of different sizes down different axonal branches
All of the above
firing at precise moments so as to signal different sized signals
changing the size of their action potentials.
changing the frequency of their action potentials
changing the frequency of their action potentials
The figure shows an electron micrograph of a chemical synapse in the cerebral cortex. Which statement about this synapse is accurate?
None of the above
A gap junction connects the two neurons via connexons that span the pre- and postsynaptic membranes.
Inside the presynaptic neuron are synaptic vesicles, which fuse with the membrane in the active zone
Inside the postsynaptic neuron are synaptic vesicles, which fuse with the membrane in the postsynaptic density.
Inside the presynaptic neuron are synaptic vesicles, which fuse with the membrane in the postsynaptic density
Inside the presynaptic neuron are synaptic vesicles, which fuse with the membrane in the active zone
What is the action of the neurotransmitter at a chemical synapse?
It transfers an action potential from the presynaptic neuron to the postsynaptic neuron.
It acts on receptors in the postsynaptic membrane.
It electrically activates the presynaptic neuron.
It depolarizes the postsynaptic membrane by delivering an electrical charge.
It crosses the postsynaptic membrane and then activates ion channels in the postsynaptic neuron.
It acts on receptors in the postsynaptic membrane.
In the sequence of events in neurotransmission, which event occurs just after the action potential arrives at the presynaptic terminal?
Fusion of the synaptic vesicles with the presynaptic membrane
Release of the neurotransmitter
Influx of Ca2+ into the presynaptic terminal
Packaging of the neurotransmitter
Delivery of the neurotransmitter to the presynaptic terminal
Influx of Ca2+ into the presynaptic terminal
Which event is the first in the series of events that take place during chemical synaptic transmission?
Synaptic vesicles fuse with the presynaptic membrane.
Voltage-gated Ca2+ channels open.
Neurotransmitter is released into the synaptic cleft.
Neurotransmitter binds to its receptors.
Influx of Ca2+ in the presynaptic terminal.
Voltage-gated Ca2+ channels open.
Which substances diffuse through connexon channels between pre- and postsynaptic neurons?
Small proteins
All of the above
Ions
Second messengers
ATP
All the above
The synaptic potential
All of the above
makes communication between nerve cells possible
propagates along axons
occurs only in response to external stimuli
determines the cells resting potential
makes communication between nerve cells possible
mall-molecule neurotransmitters are _______ for _______.
taken back into the presynaptic terminal; degradation
taken up by the postsynaptic cell; reuse
taken back into the presynaptic terminal; reuse
scattered in the synaptic cleft; reuse
taken up by the postsynaptic cell; degradation
taken back into the presynaptic terminal; reuse
Which structure can be found exclusively at an electrical synapse?
Synaptic vesicle
Neurotransmitter receptor
Presynaptic membrane
Connexon
Synaptic cleft
Connexon
Presynaptic and postsynaptic neurons that form _______ synapses are connected via _______.
chemical; connexons
electrical; the synaptic cleft
electrical; synaptic vesicles
electrical; gap junctions
chemical; neurotransmitter release
electrical; gap junctions
At which point during signal transmission at a chemical synapse is exocytosis occurring?
While Ca2+ enters the presynaptic terminal
During reuptake, as synaptic vesicles are reformed from the plasma membrane
During neurotransmitter release into the synaptic cleft
As neurotransmitter binds to its receptors
As voltage-gated Ca2+ channels are opening
How would application of a Ca2+ channel blocker affect the function of a synapse?
It would eliminate the postsynaptic potential but have no effect on presynaptic neuron.
It would increase the magnitude of postsynaptic potential.
It would eliminate the presynaptic Ca2+ current but have no effect on the postsynaptic potential.
It would decrease the magnitude of postsynaptic potential.
It would eliminate the postsynaptic potential and the presynaptic Ca2+ current.
It would eliminate the postsynaptic potential and the presynaptic Ca2+ current.
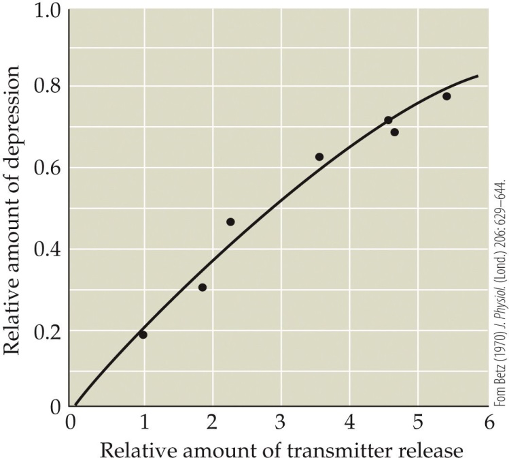
Which statement describes the depicted phenomenon most accurately?
Synaptic depression directly correlates with the amount of neurotransmitter released.
Synaptic depression directly correlates with the concentration of extracellular Ca2+.
Synaptic depression is inversely correlated with the amount of neurotransmitter released.
Synaptic depression depends on the rate of neurotransmitter release.
Synaptic depression depends on the concentration of neurotransmitter in synaptic vesicles.
Synaptic depression directly correlates with the amount of neurotransmitter released.
What causes synaptic facilitation?
Release of greater than usual number of synaptic vesicles
Stronger binding of Ca2+ to synaptotagmin 7
Buildup of Ca2+ in the presynaptic terminal
Release of synaptic vesicles loaded with extra neurotransmitter
Activation of synaptotagmin 7 by means of phosphorylation
Buildup of Ca2+ in the presynaptic terminal
Which type of short-term synaptic plasticity lasts the longest?
Potentiation
Depression
Augmentation
Post-tetanic potentiation
Facilitation
Post-tetanic potentiation
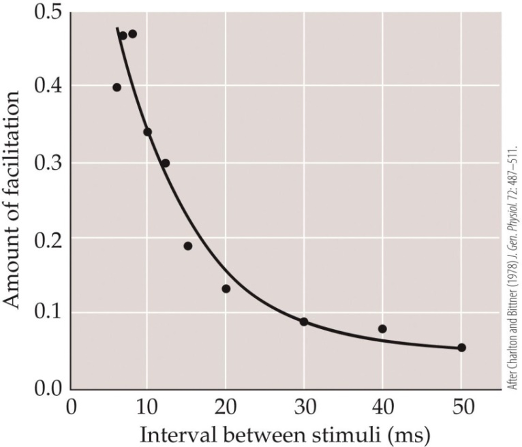
At which time interval would the postsynaptic membrane potential of the second stimulus be greatest?
20 ms
50 ms
8 ms
30 ms
15 ms
8 ms
What characteristic(s) make(s) Aplysia californica a practical model organism for studying the nervous system?
That it is aquatic
Its large neurons
Its great magnitude and variety of neurons
The random location of its neurons
All of the above
Its large neurons
Which condition(s) must be met to induce LTP?
Glutamate must open the postsynaptic AMPA receptors.
Mg2+ block must be expelled from NMDA receptors to allow Ca2+ influx.
The postsynaptic membrane must be depolarized for a period of time.
Glutamate must be released from the presynaptic terminal.
All of the above
All of the above
Complete the sequence of events that take place in the presynaptic enhancement underlying short-term behavioral sensitization: Serotonin is released from facilitatory interneuron; Ca2+ influx into the presynaptic terminal is enhanced; more neurotransmitter is released; synaptic transmission is enhanced
IP3 signaling keeps presynaptic K+ channels closed.
PKA signaling keeps presynaptic K+ channels closed.
IP3 signaling keeps postsynaptic K+ channels closed.
PKA signaling keeps presynaptic K+ channels open.
cAMP signaling keeps presynaptic K+ channels open.
PKA signaling keeps presynaptic K+ channels closed.
Which process differentiates long-term from short-term sensitization?
Changes in gene expression
Synaptic transmission between the facilitatory and sensory neurons
Production of cAMP
Changes in the synapses between the sensory and motor neurons
PKA activation
Changes in gene expression
What causes synaptic facilitation?
Release of greater than usual number of synaptic vesicles
Stronger binding of Ca2+ to synaptotagmin 7
Buildup of Ca2+ in the presynaptic terminal
Release of synaptic vesicles loaded with extra neurotransmitter
Activation of synaptotagmin 7 by means of phosphorylation
Buildup of Ca2+ in the presynaptic terminal