3.4.2. Genetic diseases
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/42
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
1
New cards
Autosomal genetic diseases
Caused by a gene in an autosomal chromosome
2
New cards
Types of autosomal genetic diseases
Recessive, dominant and co-dominant
3
New cards
Recessive diseases
* Caused by recessive alleles
* Most common genetic disease
* Most common genetic disease
4
New cards
What phenotype develops the disease?
Individual must have two copies of the recessive allele in order to develop the disease
* Heterozygous
* Heterozygous
5
New cards
Carriers
Individuals who have one allele for the genetic disease and one dominant allele (i.e. heterozygous individuals)
6
New cards
Examples of recessive disease
Cystic Fibrosis
7
New cards
Cystic Fibrosis
Mutation to CFTR gene on chromosome 7
8
New cards
Normal role of CFTR gene
Codes for the production of chloride ion channels required for secretion of sweat, mucus and digestive juices
9
New cards
Effects of Cystic Fibrosis
Recessive alleles of affected gene produce malfunctioning chloride channels
* Sweat contains excessive sodium chloride, but digestive juices and mucus have insufficient sodium chloride
* Hence, not enough water moves into the secretions by osmosis, making them more viscous
* Sticky mucus builds up in the lungs, causing infections and respiratory failure
* Pancreatic duct is blocked (pancreatic cyst) so digestive enzymes secreted by the pancreas do not reach the small intestine
* Sweat contains excessive sodium chloride, but digestive juices and mucus have insufficient sodium chloride
* Hence, not enough water moves into the secretions by osmosis, making them more viscous
* Sticky mucus builds up in the lungs, causing infections and respiratory failure
* Pancreatic duct is blocked (pancreatic cyst) so digestive enzymes secreted by the pancreas do not reach the small intestine
10
New cards
Chances of both parents being carriers
1/400
11
New cards
Dominant diseases
* Caused by a dominant allele
* Small proportion of genetic diseases
* Small proportion of genetic diseases
12
New cards
What phenotypes develop the disease?
Only one dominant allele of the gene is required to develop the disease
* Homozygous dominant (100% chance)
* Heterozygous (50%)
* Homozygous dominant (100% chance)
* Heterozygous (50%)
13
New cards
Example of dominant disease
Huntington’s disease
14
New cards
Huntington’s disease
Caused by the dominant allele of the HTT gene on chromosome 4
15
New cards
Normal role of HHT gene
Produced a protein called Huntington, whose function is unknown
16
New cards
Effects of Huntington’s disease
* Dominant allele causes degenerative changes in the brain
* Symptoms usually start between 30 to 50 years old
* Changes to behavior, thinking and emotions become increasingly severe
* Life expectancy after the start of symptoms is 20 years
* Individual eventually dies of heart failure, pneumonia or other infections
* Symptoms usually start between 30 to 50 years old
* Changes to behavior, thinking and emotions become increasingly severe
* Life expectancy after the start of symptoms is 20 years
* Individual eventually dies of heart failure, pneumonia or other infections
17
New cards
Co-dominant diseases
* Caused by co-dominant alleles
* Very rare
* Very rare
18
New cards
Genotype affected
In individuals carrying one normal allele and one affected allele, both are expressed
19
New cards
Example of co-dominant disease
Sickle cell anemia
20
New cards
Sickle cell anemia
* Normal allele for hemoglobin is Hb^A and the sickle cell allele is Hb^S
* Phenotype of individuals with one Hb^A and one Hb^S (heterozygous) differ from those who have two copies of either allele, so the alleles are co-dominant
* Phenotype of individuals with one Hb^A and one Hb^S (heterozygous) differ from those who have two copies of either allele, so the alleles are co-dominant
21
New cards
Sex-linked genetic diseases
Caused by a gene in a sex chromosome
22
New cards
Sex linkage
When the ratios of inheritance for a disease are different in males and females
23
New cards
What causes sex linkage?
Sex-linked genes are only present on one sex chromosome and not the other, so the sex of an individual affects what alleles are passed onto offspring
24
New cards
What chromosome causes the majority of sex-linked diseases? Why?
X-chromosome
* Y chromosome is shorter and contains only a few genes, while the X is longer and contains genes not present in the Y
* Y chromosome is shorter and contains only a few genes, while the X is longer and contains genes not present in the Y
25
New cards
If the gene is on the X chromosome, how many copies will males vs females have?
Males (XY) → one copy
Females (XX) → two copies
Females (XX) → two copies
26
New cards
X-linked dominant inheritance
More common in females because if ither chromosome (maternal or paternal) carries a dominant allele for the disease, the female will have it
27
New cards
X-linked recessive inheritance
More common in males because they only have one copy of the gene, so if they have the affected allele, they will express the disease
28
New cards
Carriers of X-linked recessive
Males → cannot be carriers as Y chromosome cannot mask the disease
Females → since they do not inherit affected gene from an unaffected father, they can be carriers
Females → since they do not inherit affected gene from an unaffected father, they can be carriers
29
New cards
Example of X-linked recessive
Red-green colorblindness and haemophlia
30
New cards
Red-green colorblindness
Disorder in which the individual fails to discriminate between red and green
31
New cards
What causes red-green colorblindness?
A recessive allele of a gene that synthesizes photoreceptor proteins
32
New cards
Who is more affected by red-green colorblindness?
Males since the presence of an abnormal allele will necessarily given them the condition
33
New cards
Conditions for a female to be affected
Affected father + inherit the X-chromosome carrying the recessive gene from their mother
34
New cards
Conditions for a male to be affected
Mother is affected → 100% chance since mother must be homozygous recessive
Mother is carrier → 50% chance since mother is heterozygous
Mother is carrier → 50% chance since mother is heterozygous
35
New cards
Haemophilia
Disorder in which the body’s ability to control blood clotting is impaired
36
New cards
What causes haemophilia?
A recessive allele of a gene that codes for a protein called factor VIII, which is needed to make blood clots
37
New cards
Alleles of factor VIII gene
Dominant F → codes for normal factor VIII
Recessive f → lack of factor VIII
Recessive f → lack of factor VIII
38
New cards
Conditions for male vs female be affected
Same as red-green colorblindness
39
New cards
Pedigree charts
Used to investigate patterns of inheritance within a family
40
New cards
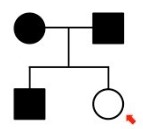
Autosomal dominant
* Cannot be recessive → two affected parents would not have unaffected offspring
* Parents must be heterozygous
* Cannot be recessive → two affected parents would not have unaffected offspring
* Parents must be heterozygous
41
New cards
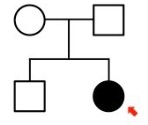
Autosomal recessive
* Cannot be dominant → two unaffected parents would not have affected offspring
* Parents must be heterozygous
* Cannot be dominant → two unaffected parents would not have affected offspring
* Parents must be heterozygous
42
New cards
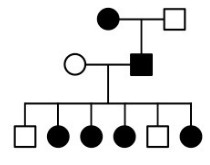
X-linked dominant
* Sex linkage cannot be confirmed
* 100% incidence of affected daughters from an affected father suggests X-linked dominance
* Sex linkage cannot be confirmed
* 100% incidence of affected daughters from an affected father suggests X-linked dominance
43
New cards
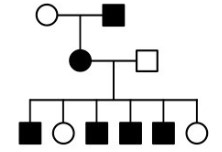
X-linked recessive
* Sex linkage cannot be confirmed
* 100% incidence of affected sons from an affected mother suggests X-linked recessive
* Sex linkage cannot be confirmed
* 100% incidence of affected sons from an affected mother suggests X-linked recessive