Biosci 221 - Exam 1
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/75
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Chapter 1, Protists (algae and protozoa), fungi. and helminths
Last updated 10:18 PM on 3/8/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
76 Terms
1
New cards
Bacteria
cells lacking a nucleus
2
New cards
Archaea
nonbacterial cells that lack a nucleus
3
New cards
Protists
mostly unicellular eukaryotes
4
New cards
Fungi
chemoheterotrophic organisms that are usually nonmotile and grow by absorbing nutrients from their surroundings
5
New cards
Helminths
parasitic worms that are multicellular, eukaryotic, invertebrate animals, most are macroscopic but have microscopic life stages
6
New cards
Viruses
noncellular microbes that must infect a host cell
7
New cards
One or 2 sentences regarding any of the scientists included in the Ppt.
* Robert Hooke built the compound microscope and thus the first to observe cells
* Antonie van Leeuwenhoek was the first to observe single-cell microbes (bacteria and protists), documenting their size and shape for identification with a single lens microscope
* Antonie van Leeuwenhoek was the first to observe single-cell microbes (bacteria and protists), documenting their size and shape for identification with a single lens microscope
8
New cards
One or 2 paragraphs worth of info about Louis Pasteur and Robert Koch
* Louis Pasteur discovered:
* Discovered fermentation was caused by a single-celled, living yeast
* Developed the “swan-neck” flask that kept boiled contents free from microbes and used this flask to show that even without oxygen microbes can grow (disproving spontaneous generation)
* Was the first to recognize that attenuated strains of a microbe could still confer immunity to the disease. He learned that certain microbes required different treatments in order to be attenuated which led to his rabies vaccine.
* Robert Koch:
* Germ theory (specific microbe causes specific disease)
* Chain of infection (spread of disease; the infectious agent, source of infection, portal of exit, mode of transmission, portable entry, and susceptible host)
* devised techniques of __pure culture__ to study a single species of microbe in isolation
* Koch’s postulates
* Discovered fermentation was caused by a single-celled, living yeast
* Developed the “swan-neck” flask that kept boiled contents free from microbes and used this flask to show that even without oxygen microbes can grow (disproving spontaneous generation)
* Was the first to recognize that attenuated strains of a microbe could still confer immunity to the disease. He learned that certain microbes required different treatments in order to be attenuated which led to his rabies vaccine.
* Robert Koch:
* Germ theory (specific microbe causes specific disease)
* Chain of infection (spread of disease; the infectious agent, source of infection, portal of exit, mode of transmission, portable entry, and susceptible host)
* devised techniques of __pure culture__ to study a single species of microbe in isolation
* Koch’s postulates
9
New cards
Koch's Postulates
four criteria designed to establish a causal relationship between a causative microbe and a disease
10
New cards
Postulate 1
The microbe is found in all cases of the disease but is absent in healthy individuals.
11
New cards
Postulate 2
The microbe is isolated from the diseased host and grown in pure culture.
12
New cards
Postulate 3
When the microbe is introduced into a healthy, susceptible host, the same disease occurs.
13
New cards
Postulate 4
The same strain of microbe is obtained from the newly diseased host.
14
New cards
Importance of microbes to the Earth and people
Microbes act as decomposers, degrading biological waste and helping keep the environment clean
Some do nitrogen fixation, helping plants absorb nitrogen from the soil
Some do photosynthesis giving us oxygen
Some can be used in meds like penicillin
Microbes also live in our bodies; i.e. good gut bacteria protect against infection by pathogens and help digestive processes
Some do nitrogen fixation, helping plants absorb nitrogen from the soil
Some do photosynthesis giving us oxygen
Some can be used in meds like penicillin
Microbes also live in our bodies; i.e. good gut bacteria protect against infection by pathogens and help digestive processes
15
New cards
Types of scientists or fields of study in microbiology
agricultural microbiology (managing plant pathogens and plant-associated microbes) and forensic microbiology (analyzing microbial strains as evidence in criminal investigations)
16
New cards
Taxonomy
An ordered group of ranks used to classify organisms from general to specific (Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, Species)
17
New cards
Binomial nomenclature
Formal naming system for living things that all scientists use
18
New cards
How do you properly write scientific names?
The genus name is capitalized and the species is lowercase, italicized or underlined if you can't italicize; the abbreviated first letter of the genus is capitalized and the full name of the species is in lowercase (can only be abbreviated after it has already been written fully)
19
New cards
History of microbes on Earth
Hydrothermal vents in the ocean?
Some of the organelles in eukaryotic cells were once prokaryotic microbes; the larger cell engulfed or took in the smaller cell.
Some of the organelles in eukaryotic cells were once prokaryotic microbes; the larger cell engulfed or took in the smaller cell.
20
New cards
Endosymbiosis
A condition of living within the body or cells of another organism; explains the origin of mitochondria and chloroplasts
21
New cards
Prokaryotic cells versus Eukaryotic cells
cells that lack a nuclear membrane and have no membrane-bound organelles are called prokaryotes while eukaryotes are cells with a nucleus
22
New cards
Algae
photoautotrophic, usually have a cell wall
23
New cards
Protozoa
chemoheterotrophic, no cell wall but have a pellicle
24
New cards
What is the difference between algae and protozoa?
protozoa must find and ingest their food from their environment, while algae are photosynthetic and can make their own food
25
New cards
Chemoheterotroph
Carbon source = organic
Energy source = chemical breakdown of carbon source
Energy source = chemical breakdown of carbon source
26
New cards
Photoautotroph
Carbon source = inorganic
Energy source = sunlight
Energy source = sunlight
27
New cards
Paralytic Shellfish Poisoning (PSP)
caused by *Alexandrium*
eating shellfish that contain these toxins can cause paralysis
eating shellfish that contain these toxins can cause paralysis
28
New cards
Diatoms
eukaryotic single-celled algae
29
New cards
Dinoflagellates
eukaryotic group of single-celled algae
“red tide” gives off toxins
“red tide” gives off toxins
30
New cards
Harmful Algal Blooms (HABs)
when colonies of algae grow out of control and produce toxic or harmful effects on the environment
31
New cards
**two** of the important uses of algae
Spent biomass can be used as fertilizer
Its bioactive compounds can be used in pharmaceuticals
Its bioactive compounds can be used in pharmaceuticals
32
New cards
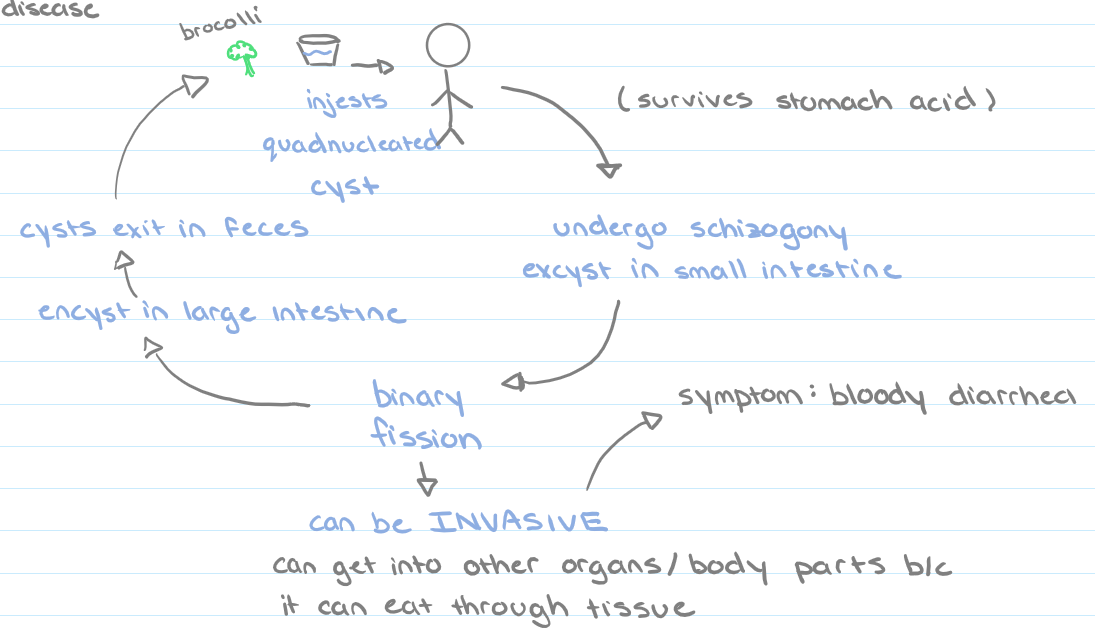
*Entamoeba histolytica* (life cycle)
1. ingested
2. undergo schizogony and excyst in small intestine
3. binary fission
4. encyst in large intestine
5. cysts exit in feces
33
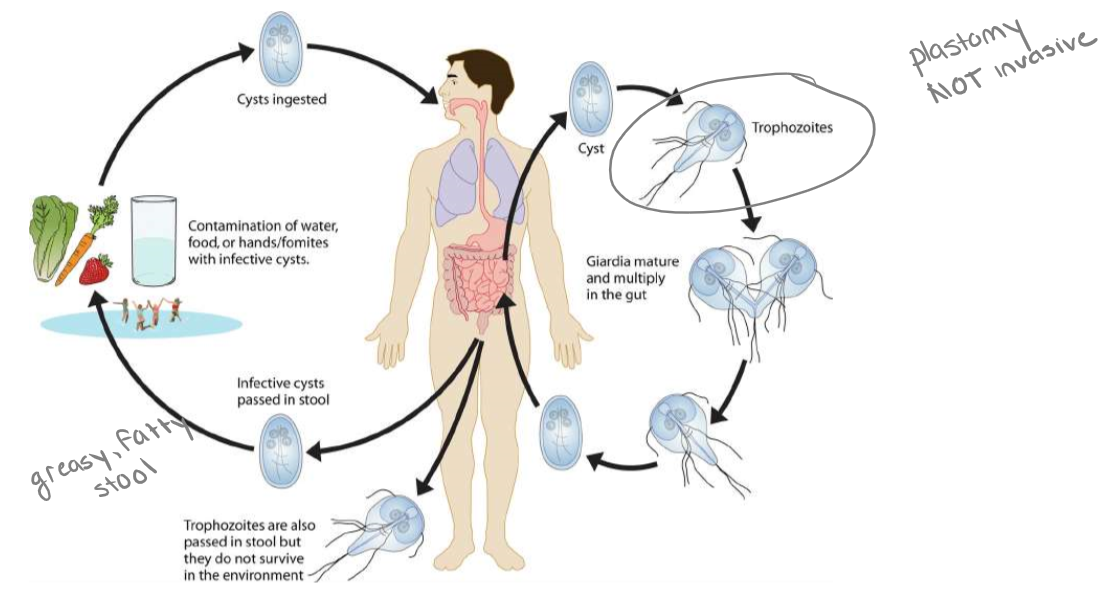
New cards
*Giardia* (life cycle)
1. ingested
2. undergo plasmotomy and excyst in small intestine
3. binary fission
4. encyst near colon
5. cysts exit in feces
34
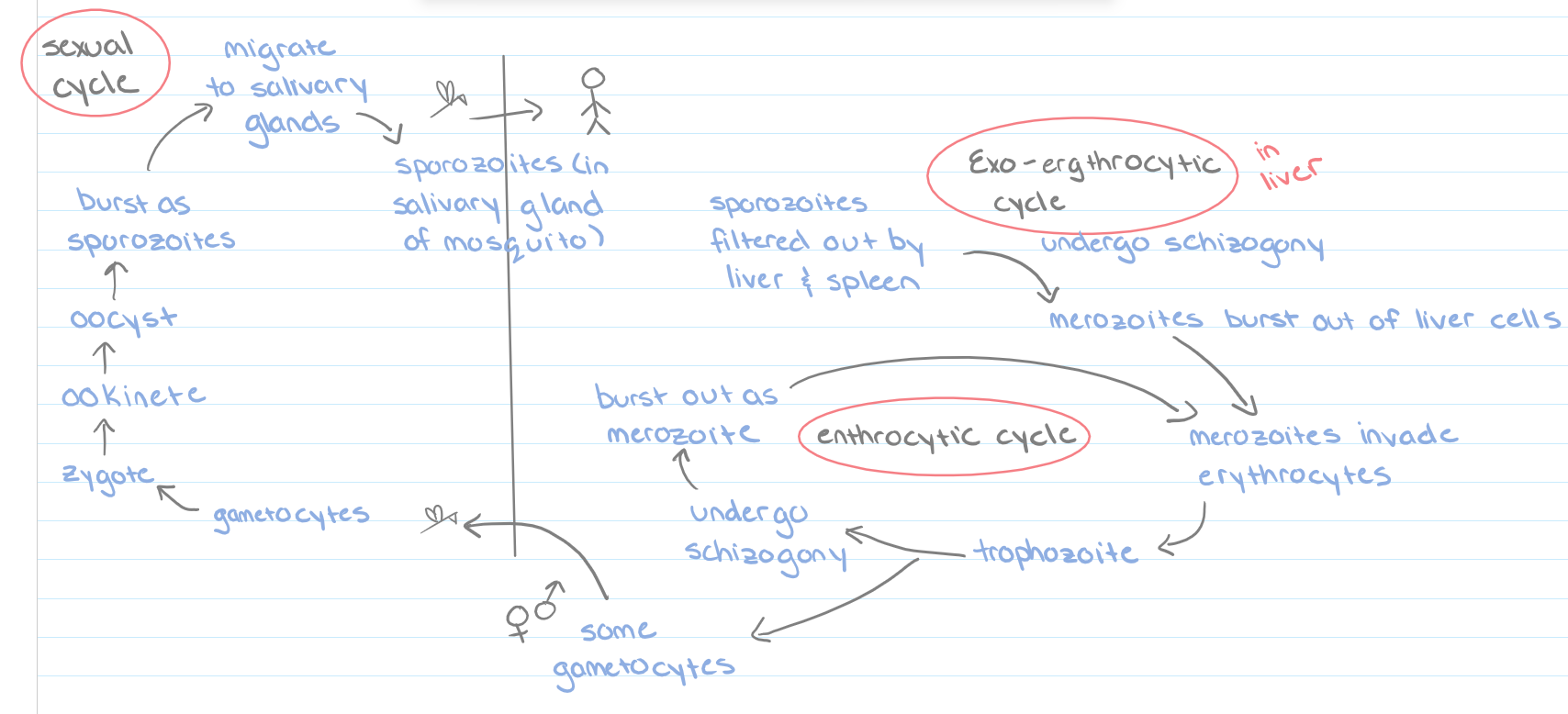
New cards
*Plasmodium* (life cycle)
(see picture)
35
New cards
*Trichomonas*
STI
does not form cysts
can be asymptomatic
does not form cysts
can be asymptomatic
36
New cards
*Giardia*
Diarrheal disease
cysts can survive hours in the pool
1-10 billion cysts released daily
infective dose approximately 10 cysts (low)
cysts can survive hours in the pool
1-10 billion cysts released daily
infective dose approximately 10 cysts (low)
37
New cards
*Trypanosoma cruzi*
Chagas’ disease
a neglected disease
vector = a reduviid bug bite
largest cause of preventable heart disease in the world
a neglected disease
vector = a reduviid bug bite
largest cause of preventable heart disease in the world
38
New cards
*Leishmania*
A neglected disease
vector = sand fly
3 different forms (cutaneous, mucocutaneous, and visceral)
vector = sand fly
3 different forms (cutaneous, mucocutaneous, and visceral)
39
New cards
*Naegleria fowleri*
This free-living protist gets into your sinuses
100% fatality
100% fatality
40
New cards
*Acanthamoeba*
Free-living amoeba which causes keratitis (corneal infection)
is caused by cleaning contacts with water
is caused by cleaning contacts with water
41
New cards
*Entamoeba histolytica*
Diarrheal disease
a very common protist infection worldwide
usually taken care of by water treatment
a very common protist infection worldwide
usually taken care of by water treatment
42
New cards
*Toxoplasma gondii*
Foodborne
congenital transmission (organisms cross the placenta)
potential inhalation of dried cysts
congenital transmission (organisms cross the placenta)
potential inhalation of dried cysts
43
New cards
*Plasmodium*
Malaria
Vector = mosquito
Vector = mosquito
44
New cards
*Cryptosporidium*
Diarrheal disease
fecal-oral route of transmission
can survive in the pool
cause of the largest waterborne outbreak in the U.S. (Milwaukee)
fecal-oral route of transmission
can survive in the pool
cause of the largest waterborne outbreak in the U.S. (Milwaukee)
45
New cards
Mycoses
fungal infections which can be caused by inhalation or contact with asexual spores
46
New cards
True pathogens
can cause disease in any susceptible host
47
New cards
Opportunistic pathogens
rarely cause disease in healthy individuals
48
New cards
Concerns about mycoses
Difficult to treat as there are a limited number (14) of antifungal agents known, most of which are relatively toxic
Is a frequent cause of **HAI**s, or healthcare-associated infections
Hard to develop a medication that could harm the fungal cell but not our cell b/c both cells are eukaryotic
Is a frequent cause of **HAI**s, or healthcare-associated infections
Hard to develop a medication that could harm the fungal cell but not our cell b/c both cells are eukaryotic
49
New cards
*Aspergillus flavus*
Produces **Aflatoxin B** (the most potent carcinogen known)
can infect crops, lethal to poultry and livestock
can infect crops, lethal to poultry and livestock
50
New cards
*Aspergillus fumatigus*
Farmer’s Lung
opportunistic pathogen
associated with people working outside in fields and agriculture
opportunistic pathogen
associated with people working outside in fields and agriculture
51
New cards
*Cryptococcus neoformans* and *C. gatti*
Neoformans are opportunistic while gatti is emerging
found in pigeon and chicken droppings and can therefore be found in the soil
the leading cause of death in AIDs patients in Africa
found in pigeon and chicken droppings and can therefore be found in the soil
the leading cause of death in AIDs patients in Africa
52
New cards
*Candida albicans*
Candidal intertrigo, candida thrush, candida meningitis
most common fungal HAI
50% fatality rate
most common fungal HAI
50% fatality rate
53
New cards
*Candida auris*
Urgent threat
highly antibiotic-resistant that has spread quickly around the world (and in healthcare settings)
highly antibiotic-resistant that has spread quickly around the world (and in healthcare settings)
54
New cards
*Coccidioides immitis*
Valley Fever
is a true pathogen
endemic (regularly occurring) in the U.S.
windy conditions help spread its fungal spores
often misdiagnosed
hardly reportable
is a true pathogen
endemic (regularly occurring) in the U.S.
windy conditions help spread its fungal spores
often misdiagnosed
hardly reportable
55
New cards
*Histoplasma capsulatum*
Spelunkers disease
a true pathogen
grows in humid, high nitrogen areas where there is bird and bat guano
endemic in the U.S.
not reportable in CA
often misdiagnosed
a true pathogen
grows in humid, high nitrogen areas where there is bird and bat guano
endemic in the U.S.
not reportable in CA
often misdiagnosed
56
New cards
*Blastomyces*
A true pathogen
acquired from the environment (inhalation) not person to person hardly reportable
acquired from the environment (inhalation) not person to person hardly reportable
57
New cards
*Sporothrix*
Cause of sporotrichosis (rose gardener’s disease)
from getting poked or scratched
from getting poked or scratched
58
New cards
*Trichophyton*
Trichophyton is a dermatophytic fungus, which is often responsible for nail, hair follicle, and superficial skin infections (i.e. Tinea pedis is athlete’s foot)
59
New cards
Dr. George Washington Carver
* Documented fungal diseases of plants
* He sent over 1000 fungi to the U.S National Fungus Collection
* This was essential in identifying fungi occurring in the U.S. to develop control measures such as breeding for the resistance to the diseases of the crops
* He sent over 1000 fungi to the U.S National Fungus Collection
* This was essential in identifying fungi occurring in the U.S. to develop control measures such as breeding for the resistance to the diseases of the crops
60
New cards
*Pneumocystis*
* Small, unicellular fungi that cause pneumonia (PCP)
* Forms secretions in the lungs that block breathing
* Opportunistic infection and used to be the leading cause of death in AID patients
* Forms secretions in the lungs that block breathing
* Opportunistic infection and used to be the leading cause of death in AID patients
61
New cards
*Stachybotris*
Sick building syndrome
“toxic black mold” found in water-damaged structures
“toxic black mold” found in water-damaged structures
62
New cards
*Claviceps purpurea*
* Ergot
* Plant pathogen (that grows on rye) that is responsible for significant toxic poisonings throughout history
* I.e. St. Anthony’s Fire — killed 1000s in the Middle Ages
* Now used in many meds as a vasoconstrictor
* Plant pathogen (that grows on rye) that is responsible for significant toxic poisonings throughout history
* I.e. St. Anthony’s Fire — killed 1000s in the Middle Ages
* Now used in many meds as a vasoconstrictor
63
New cards
Parasitic Helminths…
have a high rate of reproduction,
are usually host-specific
usually does not kill the host
have different methods to evade the immune system
are usually host-specific
usually does not kill the host
have different methods to evade the immune system
64
New cards
Class Trematoda
flukes
leaf-shaped
mollusks are usually the intermediate host(s)
the vertebrate is usually the definitive host
digestive system
leaf-shaped
mollusks are usually the intermediate host(s)
the vertebrate is usually the definitive host
digestive system
65
New cards
Class Cestoda
tapeworms
long/ribbon-like bodies
scolex for attachment (with reproductive segments called proglottids)
usually also require two or more hosts
no digestive system
long/ribbon-like bodies
scolex for attachment (with reproductive segments called proglottids)
usually also require two or more hosts
no digestive system
66
New cards
Phylum Nematoda (roundworms)
cylindrical
usually only one host
complete digestive system
very diverse and numerous group
usually only one host
complete digestive system
very diverse and numerous group
67
New cards
Intermediate (or Secondary) host
the host in which larval development occurs
68
New cards
Definitive (or Primary) host
the host in which mature organisms live and undergo sexual reproduction
69
New cards
*Clonorchis sinensis*
Chinese liver fluke
from consuming fresh water fish
from consuming fresh water fish
70
New cards
*Schistosoma*
Blood fluke
neglected disease
burrows into the skin
snail is intermediate host
neglected disease
burrows into the skin
snail is intermediate host
71
New cards
Cercarial dermititis
Swimmer’s Itch (bad rash)
72
New cards
*Taenia solium ** (and Cysticercosis)
Found in uncooked/undercooked pork
fecal/oral route
leading cause of epilepsy in the world
fecal/oral route
leading cause of epilepsy in the world
73
New cards
*Ascaris lumbricoides*
Ingested
fecal/oral route
invasive
most common helminth infection in the world
fecal/oral route
invasive
most common helminth infection in the world
74
New cards
*Necator americanus*
Hookwork (has cutting mouthparts)
burrows through the skin (in between the toes)
blood in stool and anemia
burrows through the skin (in between the toes)
blood in stool and anemia
75
New cards
*Enterobius vermicularis*
Pinworm
the most common infection in the U.S.
passes through fecal/oral route so its hard to control
the most common infection in the U.S.
passes through fecal/oral route so its hard to control
76
New cards
*Trichinella spiralisis*
from eating contaminated/undercooked pork
less common now b/c of regulations (can’t feed pigs trash)
most common in area where people eat wild game
less common now b/c of regulations (can’t feed pigs trash)
most common in area where people eat wild game