Lesson 9: Non Arthropod Ecdysozoans
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
Ecdysozoa
“to strip off” → moult
8 subphylum
nematoda
nematomorpha
lorichifera
kinorhyncha
priapulida
onychophora
tardigrada
arthropoda
Nematoda
roundworms
very abundant all over the world, very high human impact
most important of all parasitic animal groups
ecto and endo parasitic
reproduction results in 100, 000s of eggs
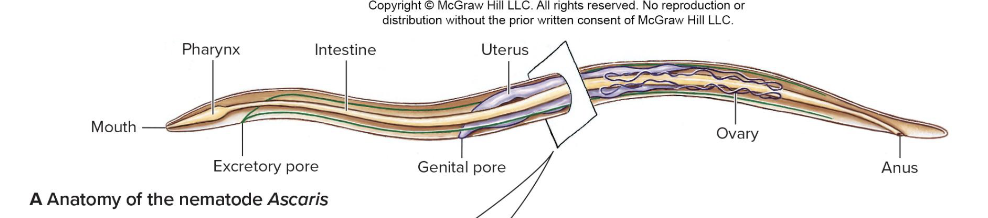
Nematoda structure
adapted mouth parks
thick cuticle made of collagen
fluid-filled pseudocoelom functions as a hydrostatic skeleton
no circular muscles
Common nematoda parasites
intestinal roundworms
~1 billion people infected
hookworms
~650 million people infected
pinworms
dont need an intermediate host
most common nematode parasite of developed countries
filarial worms
arthropod transmission
~200 million people infected
Caenorhabditis elegans
free-living, non hazardous, non parasitic, non infectious nematode
one of the most important experimental biological models
all 959 cells traced from zygote to adult
entire nervous system known
genome entirely mapped
Nematomorpha
horsehair worms
pseudocoelomate
semi-parasitic
adults are free living
juveniles are parasitic in arthropods
pathenogenetic reproduction
a form of asexual reproduction in which a new organism develops from an unfertilized egg, without a male's contribution
Panarthropoda
subsection of ecdysozoa which includes:
onychophora
tardigrade
arthropods
small coelom
ventrolateral appendages: walking pairs
homocoel and open circulatory system
blood + lymph = hemolymph
Onychophora
velvet worms
soft “velvelt-like” cuticle
repels water
14-43 pairs of unjointed legs with pad and 2 claws

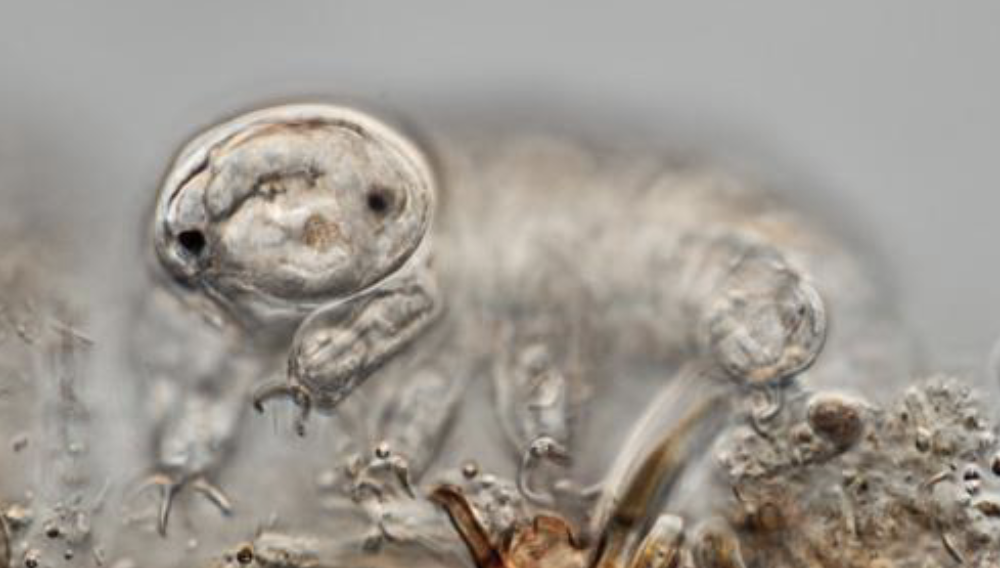
Tardigrada
water bears
8 unjointed legs with claws
pair of sharp stylets and sucking pharynx
used to pierce and suck plant juices/small invertebrates
parthenogenetic or sexual reproduction
cryptobiosis= tun state
a reversible state where an organism's metabolism temporarily ceases to survive extreme environmental conditions like freezing, desiccation, or oxygen deficiency

Nematoda organization
organ system
Nematoda symmetry
bilateral
Nematoda body cavity
pseudocoelomate
Nematoda development
Nematoda segmentation
no