Intro to CNS Drugs (NOT DONE)
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
What protects the brain from foreign substances but also can affect the effectiveness of CNS drugs?
The Blood Brain Barrier
What is the BBB made of?
Tight endothelial junctions
Basement Membrane
Receptors
proteins
Pericytes
Astrocytes
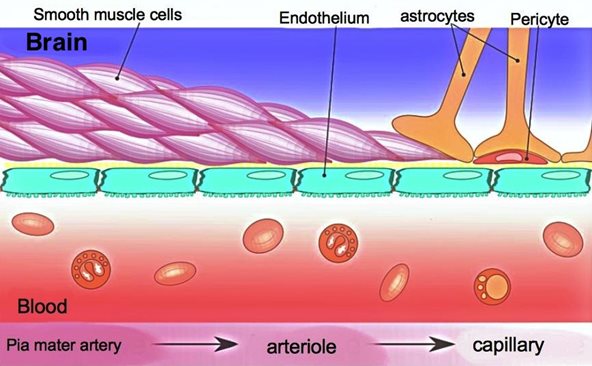
What does the BBB keep out?
Ionized compounds
Large Compounds
To cross the BBB a drug/molecule needs to be what?
Small
Lipid soluble
Poorly protein-bound
Non-ionized at the pH of cerebral spinal fluid (7.3)
What can cause increased solubility of the brain?
Inflammation
Site of Tumors
Neonates
Specific areas have increased solubility
Ex: 4th Ventricle
What receptors/proteins regulate the BBB by limiting the passage of molecules?
Solute carrier proteins
Carry essential molecules (glucose/vitamins) across the BBB
Receptor-mediated transcytosis
Transport important hormones (insulin/leptin)
Transcytosis=transport of biological molecules
ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporters
Move substances in both directions across BBB
P-glycoproteins and MDR1 are subtypes of this transporter
What is ABCB1?
The gene that encodes for P-glycoprotein, aka MDR1
Some drugs ____ or _____ p-glycoprotein
Inhibit/Induce
What is the difference between active/inactive P-glycoprotein?
Active
a protein in cell membranes that acts as an energy-dependent efflux pump, exporting a wide variety of substances like drugs, toxins, and xenobiotics out of cells
Inactive
More drugs cross the BBB
CNS drugs activate/inactivate specific _______
Neurons
What are the 6 CNS transmitters?
Glutamate
GABA
Dopamine
5HT
Ach
NE
Describe the function of Glutamate as a CNS transmitter
Primarily excitatory
Causes Na+ influx into postsynaptic neurons (causes signal)
Describe the function of GABA as a CNS transmitter?
Inhibitory postsynaptic
Influx of Cl- into postsynpatic neurons
Polarizes neuron (prevents signal)
Describe the function of Dopamine as a CNS transmitter?
Excitatory/Inhibitory
Emotion, reward system, motor control
Describe the function of 5-HT (serotonin) as a CNS transmitter?
Excitatory/Inhibitory
Feeding behavior, body temp, sleep
Describe the function of Ach as a CNS transmitter?
Excitatory
Arousal, memory, learning, movement
Describe the function of NE as a CNS transmitter?
Excitatory
Arousal, mood, cardiovascular region
T/F: Side effects are common to CNS drugs
True, most receptors are present throughout the brain, so by trying to treat one part you can trigger all parts
The ______ pathway of neurons is responsible for perception and localization of pain, and then sending that to the brain
Ascending
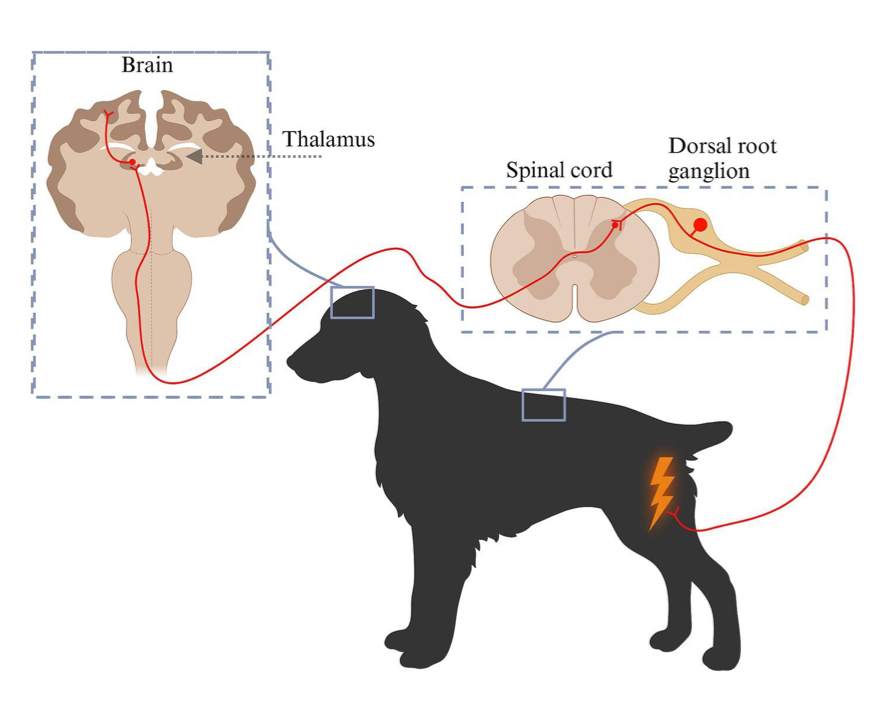
Harmful stimuli are first detected by specialized free nerve endings called __________
Nociceptors
Once a nociceptor is stimulated, the harmful stimulus is changed to an electric signal that is transmitted from the nociceptor to the brain via peripheral ______ nerves
afferent
Which neurotransmitter is used to inhibit postganglionic neurons and inhibit peripheral nerves and dorsal horn pain?
Serotonin
What are Analgesics?
Drugs that relieve pain
What are the 3 ways that we use anesthetics?
Topically
Injection into tissue
Injected into space
How do local anesthetics function?
Reversible competitive inhibitors of Neuronal Na+ Channels
Decrease polarization via blocking Na+ channels
Results in the blocking of the A.P initiation
Results in the blockage of nociception conduction (blocks pain signal so it doesn’t reach the brain)
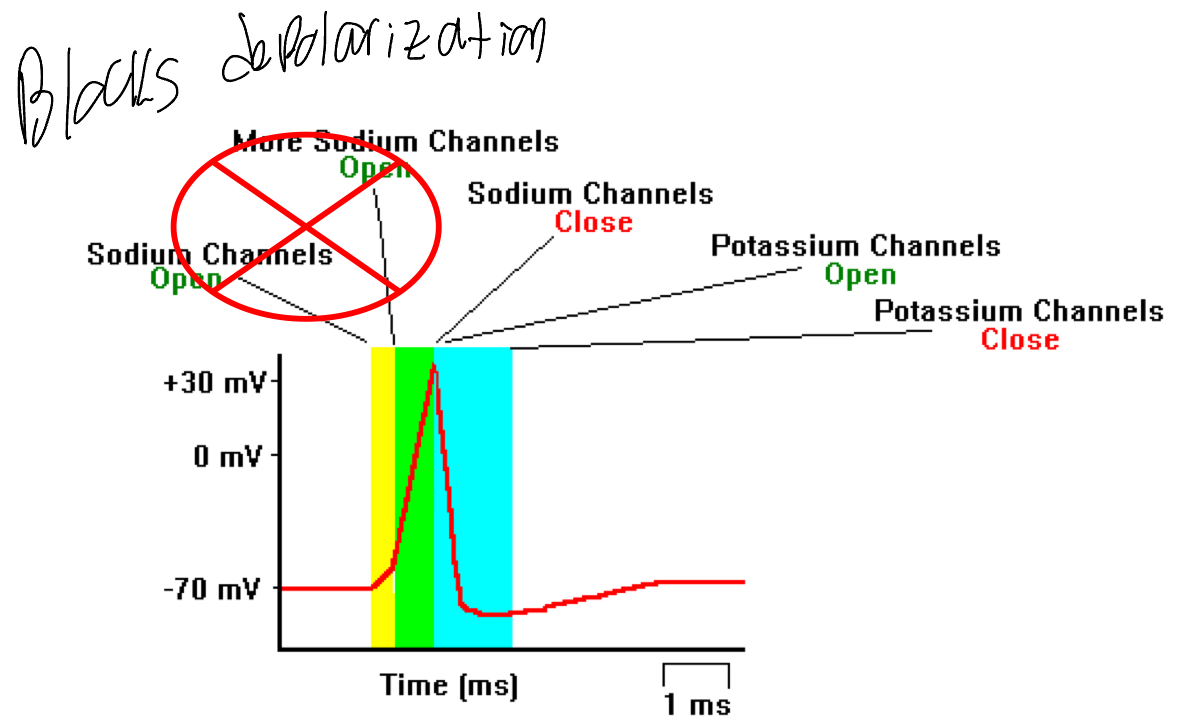
T/F: Local anesthetics induce unconsciousness
False
What are the different ways that local/topical anesthetics can be used?
As a sole analgesic
To improve anesthetic quality
Contribute to multimodal analgesia
Decrease the amount of required opioids
Local anesthetics are sometimes combined with ________ or an _________ to increase the duration of activity by preventing the drug from exiting the desired area of analgesia.
Epinephrine
Alpha-2-Agonist
Nerves vary in __________ to local anesthetics
Susceptibility
What are some factors that can affect a nerve’s susceptibility to local anesthetics?
Diameter of nerve
A small diameter is blocked more easily than large one
Sensory vs Motor (more resistant to blockage)
Touch/proprioception is less affected
Toxicity of Local Anesthetics are partly determined by ________ within cardiocytes and cells of the central nervous system.
Accumulation
What are some adverse effects of Local Anesthetics?
Tissue ischemia/necrosis
Caused by Decreased blood flow
Caused by Epinephrine or Alpha-2-Agonist
Systemic injections of high doses can cause
Seizures
Respiratory Depression
Hypotension
Cardiac Arrest
Cardiovascular depression
Allergic reactions
Ion trapping in pregnant animals
What are the Pharmacokinetics of Local Anesthetics?
High/Low protein bound
Metabolized where?
Acidic/basic?
Highly protein bound
Metabolized in liver
Weak bases
Trapped in low pH areas