Biology- in depth flash cards _ SUMMER STUDIES
1/134
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Revision in the summer so I do not str
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
135 Terms
What is a primary structure of a protein?
The order in which the amino acids are arranged in a protein chain
What is a secondary structure of a protein
When some chains coil up or fold into pleats that are held together by weak forces of chemical attraction
What does it mean when proteins have a tertiary structure
The coiled chain of amino acid is folded into a ball that is held together by weak chemical bonds and stronger bonds
What do you call a protein with a spherical shape?
globular protein
What type of bond holds together the secondary structure of a protein?
hydrogen bonds
What do Carbohydrates contain?
Carbon, hydrogen and oxygen
What are Monosaccharides?
The single units from which all the other carbohydrates are built
What are two examples of monosaccharides?
Glucose and fructose
How many forms does Glucose have?
Two forms
What are the two forms that Glucose has?
alpha and beta
How are Disaccharides formed?
When two monosaccharides are joined together by a chemical reaction . A molecule of water is also formed so it is a condensation reaction
What are two examples of disaccharides
Maltose and Sucrose
What are Polysaccharides?
They are polymers; large molecules made up of monomers. Monomers of polysaccharides are monosaccharides
What is Polysaccharides?
a starch
What are starch molecules made up of?
Two different polysaccharides- amylose and amylopectin [POLYMERS OF GLUCOSE]
Where is starch only found?
Plant cells
What can several cellulose molecules form?
microfibrils
Where is cellulose only found in?
Plants
What do the microfibrils do?
Strengthen the plant cell wall
What are lipids?
Oils and fats
What is ppant oil and animal fat mostly made up of ?
A group of lipids called Triglycerides
What does a triglyceride normally consist of?
a molecule of glycerol with three fatty acids attached to it
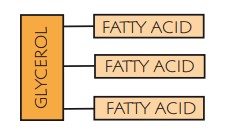
What is a fatty acid molecule made up of
a long chain of carbon atoms with an acid group of COOH at one end, Hydrogen atoms attached to the carbon atoms
What is meant by a saturated fatty acid?
When every carbon atoms in the chain is joined by a single bond.
What is meant by an Unsaturated fatty acid?
If one or more of the bonds is a double bond
What is meant by polyunsaturated?
A fatty acid with many double bonds
What are Phospholipids?
They have two fatty acids chains and a phosphate group with glycerol between the two
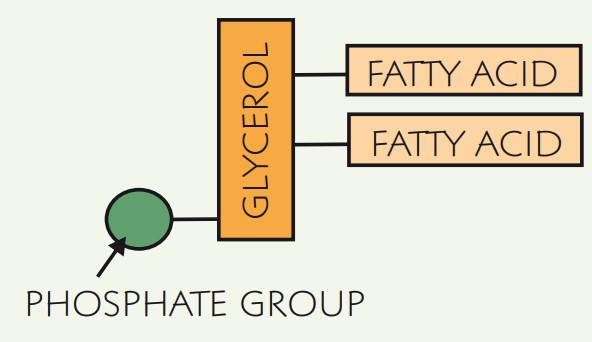
What are cell membranes made from?
a double layer of phospholipids
What is a metabolic pathway?
a series of connected chemical reactions that feed one another.
What do enzymes reduce?
The activation energy
What do digestive proteins do?
They help to break down food into smaller molecules in the digestive system
What shape are all enzymes?
Globular
What can enzymes be involved in?
breaking down molecules or building molecules
What is a substrate?
a substance that is acted upon by an enzyme
What is the active site?
A region on the surface of the enzyme molecule where a substrate molecule can attach itself.
What happens as soon as the enzyme substrate complex has formed?
The products of the reaction are released and the enzyme is ready to accept another substrate molecule.
What must happen to the substrate molecule in order for it to fit inside the active site?
It must be the correct shape
What happens as the temperature increases?
Enzyme reactions become faster due to the molecules having more energy
What could happen when the temperature is too high for the enzyme?
The atoms of the enzyme molecule vibrate more rapidly and break the weak bonds that hold the tertiary structure together.
What term is used when the shape of the active site changes and the substrate can no longer fit in?
The enzyme is said to be denatured
What else can affect enzyme activity?
pH
Describe the effect of pH on enzyme activity
Hydrogen ions (H+) in acids and hydroxyl ions (OH– ) in alkalis can disrupt the weak bonds and change the shape of the active site.
What are Prokaryotic organisms?
Single celled
What are Eukaryotic organisms?
Multicellular
What are Organelles?
Parts of cells that have specific functions
What is the Nucleus used for?
The nucleus contains genetic material that controls what the cell does
What does the Cytoplasm do?
The cytoplasm contains enzymes that are a catalyst for biochemical reactions
What is the Mitrochondria used for?
This is where glucose and oxygen are used in respiration to provide a source of energy for the cell
What is the Cell-surface-membrane used for?
It holds the cell together and controls what goes in and out
What is the cell wall used for?
It gives the cell support as it is made form cellulose
What does the Vacuole contain?
cell sap, a weak solution of sugar and salts
What does Chloroplast contain?
Chlorophyll for photosynthesis
What are bacterial cells?
Prokaryotic!
What does a Prokaryotic cell NOT contain?
nucleus
mitochondria
chloroplast
What are plasmids?
rings of DNA that floats freely in the cytoplasm
What is a flagellum?
a tail like feature that allows the cell to move and rotate
How much can a light microscope magnify objects?
Up to 1500 times
What does a light microscope allow you to see?
Individual animal and plant cells along with some of the organelles inside them
If the cell has been stained, what can you see?
You will be able to see the dark-coloured nucleus surrounded by lighter-coloured cytoplasm
What would also be visible?
Tiny mitochondria and the black line of the cell membrane
What would you be able to see if it were a plant cell?
The cell wall, chloroplasts and the vacuole
What can a light microscope also be called?
optical microscope
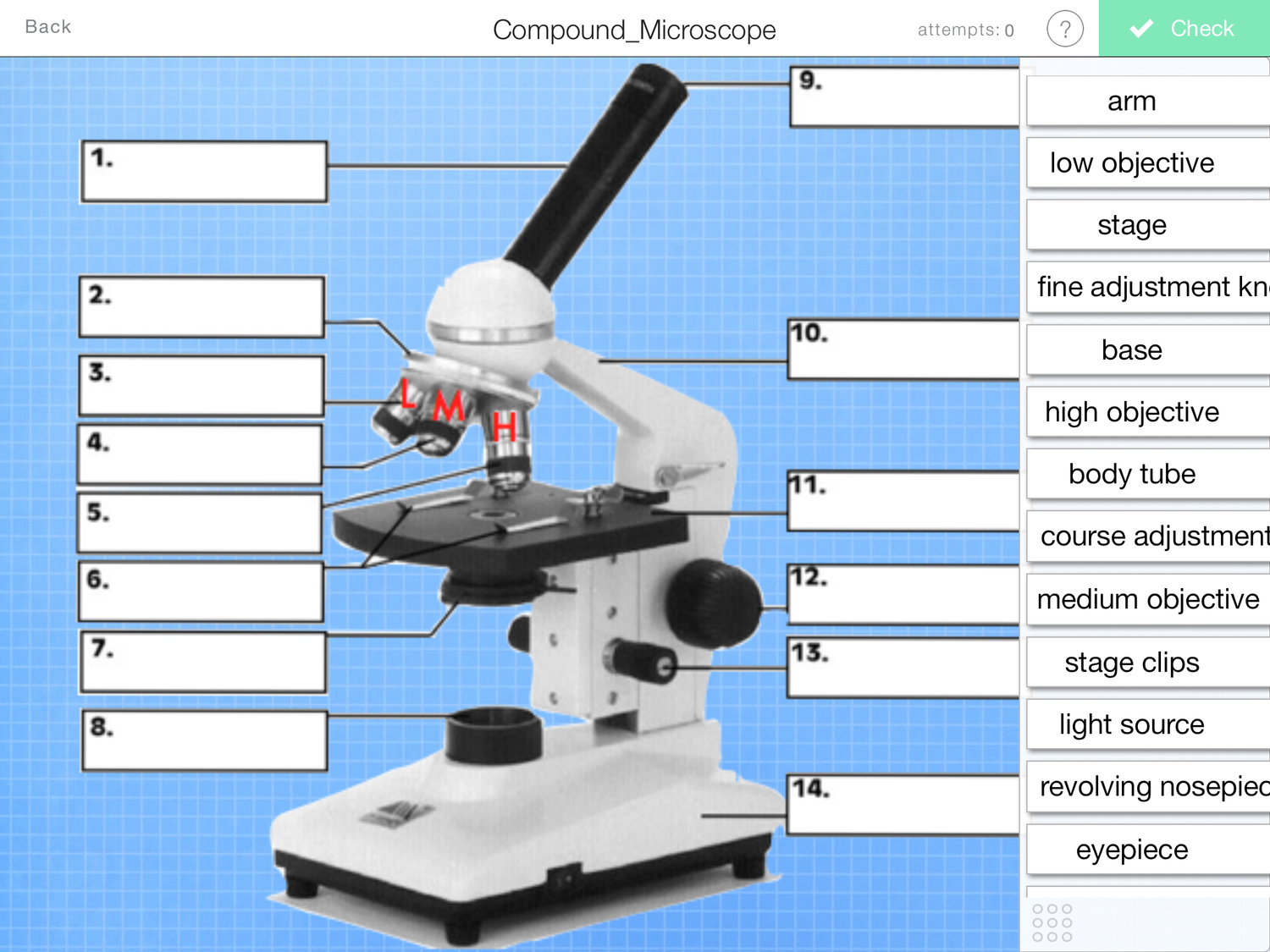
What is and what does number 11 on the photo do?
Stage- where you put the microscope slide
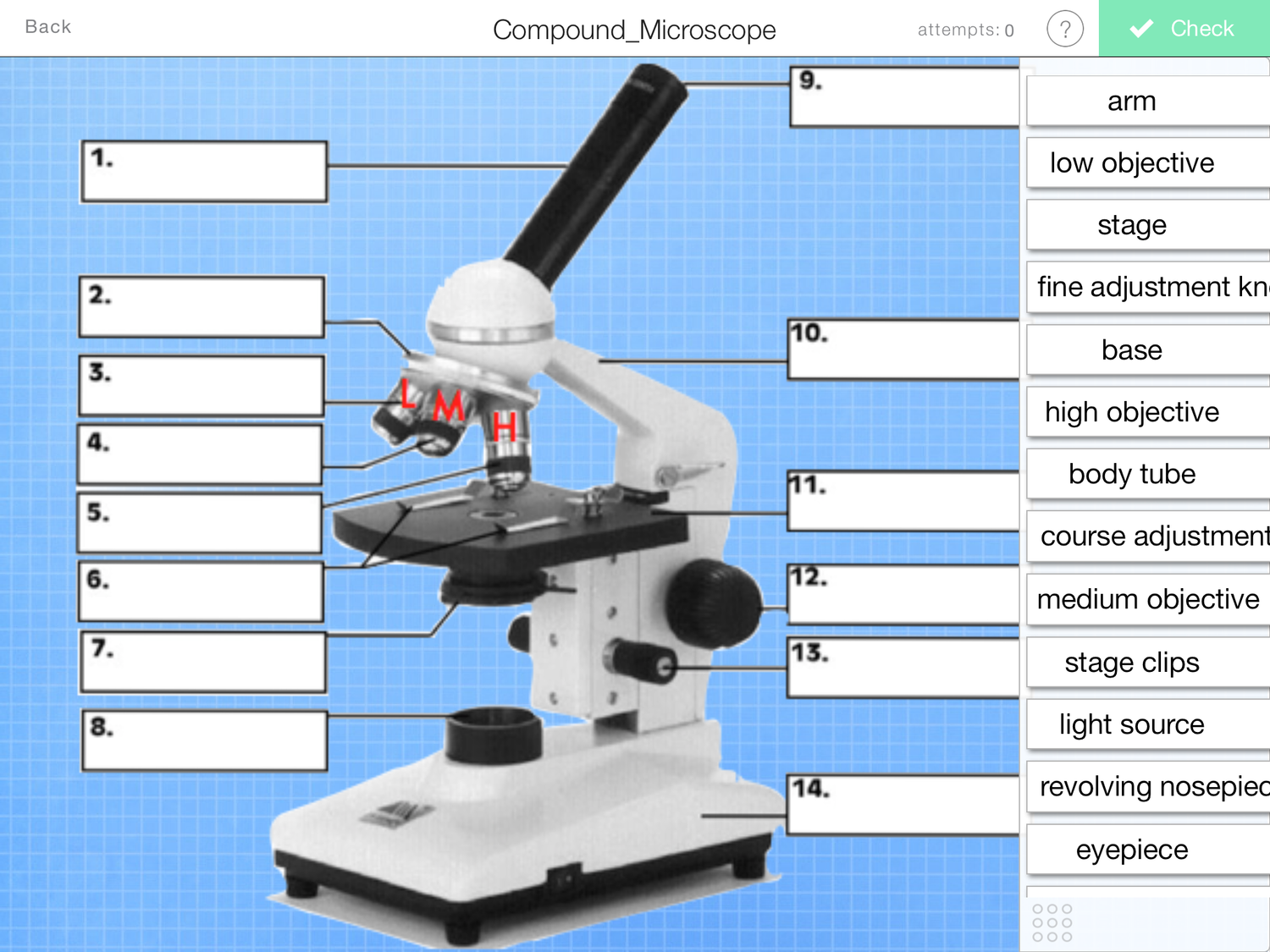
What is and what does number 1 on the photo do?
Eyepiece- you look down to view the specimen
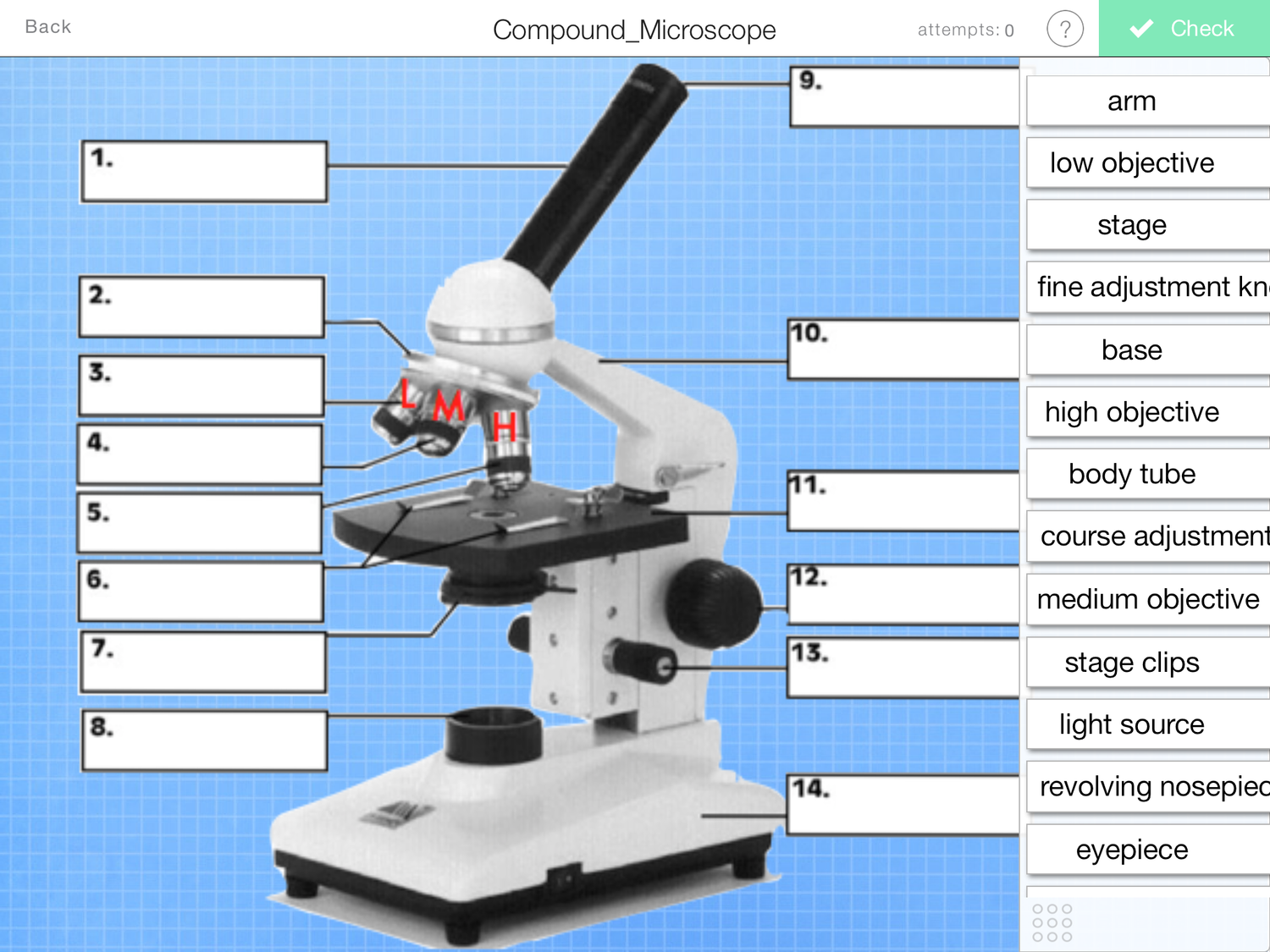
What is and what does number 12 on the photo do?
Coarse adjustment knob- to bring the specimen roughly into focus
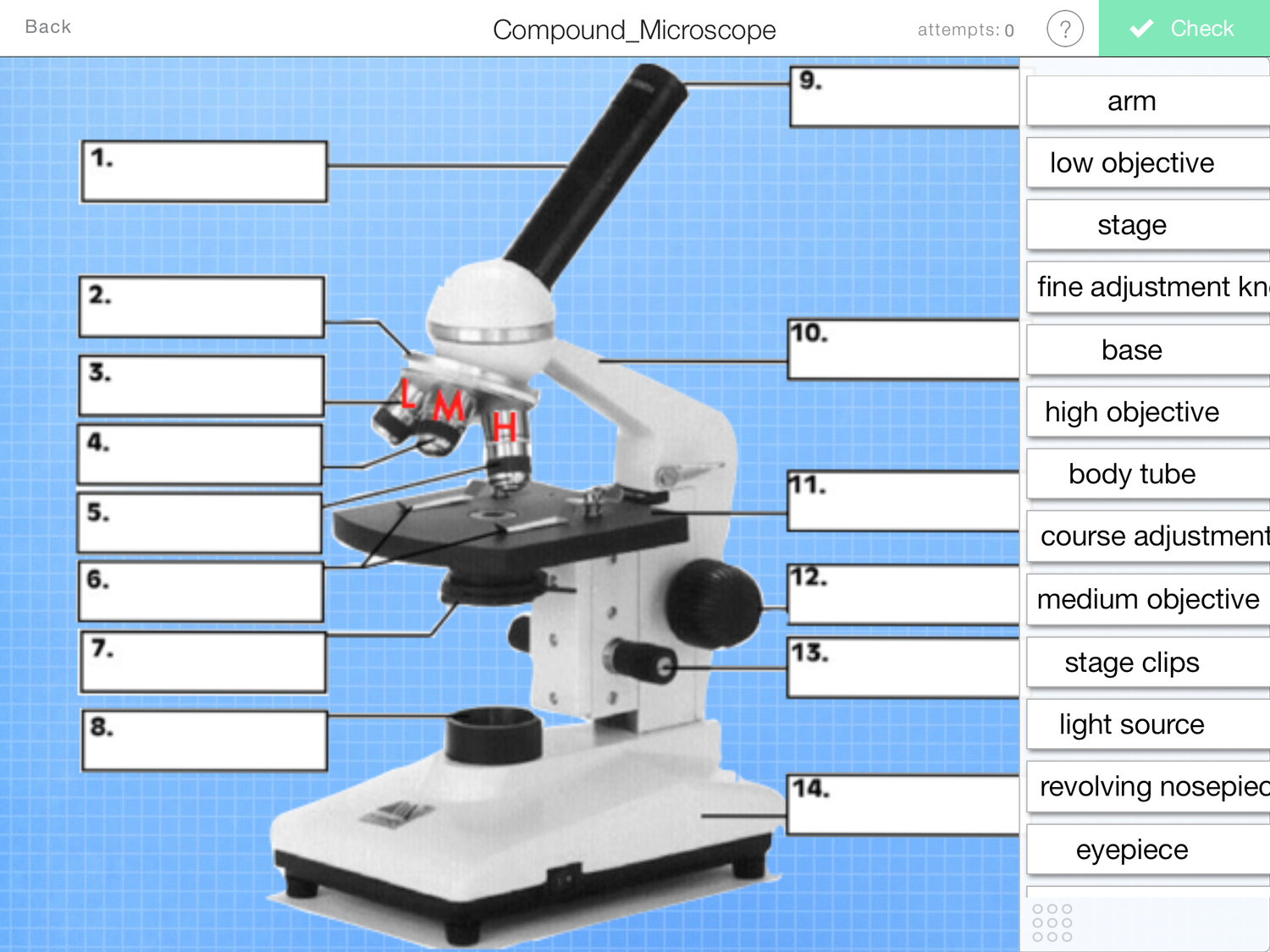
What is and what does number 8 on the photo do?
Light source- so you can see through the specimen
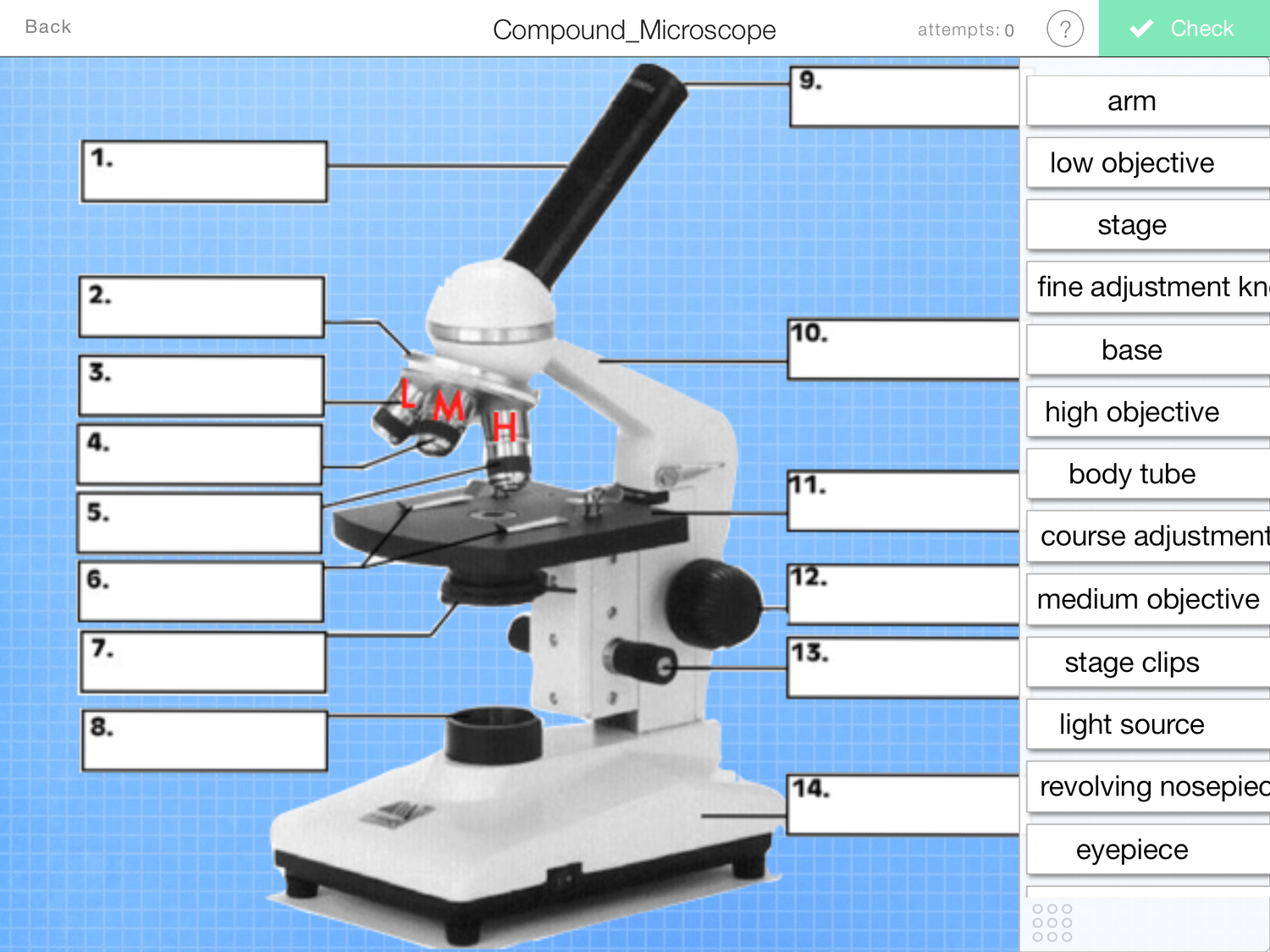
What is and what does number 4 on the photo do?
High and low power objective lenses- these magnify the specimen
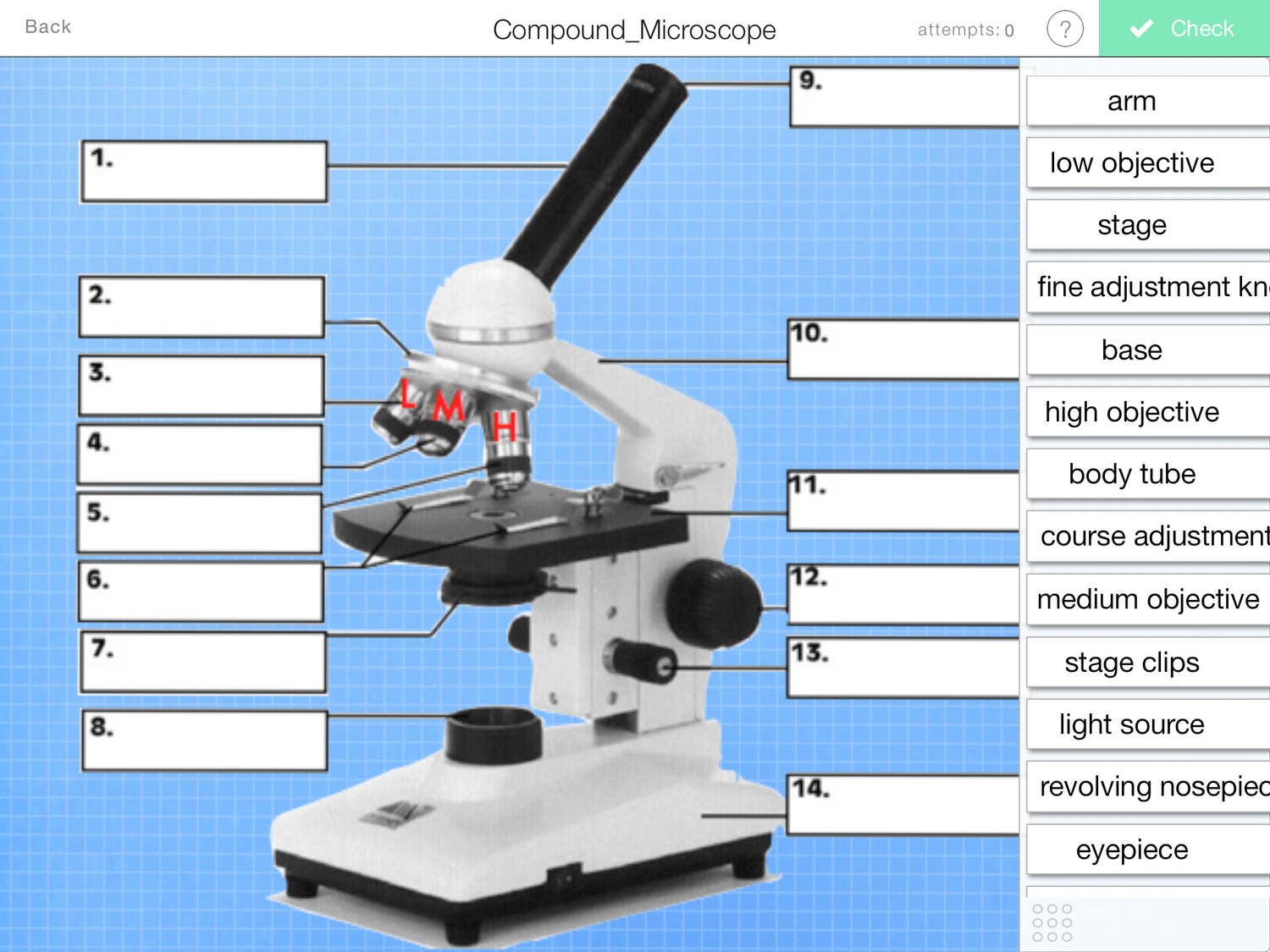
What is and what does number 13 on the photo do?
Fine adjustment knob- to finely tune the focus
When was a detailed ultrastructure of cells revealed?
In the 1950s after the electron microscope was invented
How much can an electron microscope magnify objects?
More than 500,000 times
How does seeing this clearly allow you to do?
See in greater detail than with a light microscope, you can see detailed structures inside organelles such as mitochondria and chloroplast.
When an image is recorded by an electron microscope, what is this called?
Electron micrograph
Where does aerobic respiration take place in?
The mitochondria
What microscope do you need to see mitochondria in detail?
Electron microscope
What does each mitochondrion have?
A smooth outer membrane and a folded inner membrane with a matrix
What is the job a mitochondrion?
To capture the energy in a form that the cell can use. To do this, aerobic respiration takes p,ace inside the mitochondria.
What is the word equation for aerobic respiration?
Glucose + Oxygen → Carbon dioxide + Water + Energy
What molecules does the energy released by respiration end up in?
Molecules of ATP
What does ATP stand for?
Adenosine Triphosphate
What is ATP used in cell for?
To provide energy for muscle contraction, active transport and building large molecules from small ones as well as many other processes.
What does a plant cell wall consist of?
Long straight cellulose molecules that lay side by side to form microfibrils