PD E2- Derm
1/130
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
131 Terms
what is meissner’s corpuscle?
contains unmyelinated nerve ending surrounded by Schwann cells; touch receptors; enriched in fingers and toes
localized in dermis bt epidermal ridges
what are lamellar corpuscles / pacinian corpuscles?
nerve endings in skin responsible for sensitivity to vibration and pressure; responds only to sudden disturbances
what is the epidermis?
most superficial layer of skin; NO blood vessels; outer horny layer composed of dead keratinized cells and inner layer is where melanin and keratin are formed
What are the 5 lays of the epidermis from superficial to deep?
stratum corneum
stratum lucidum (palms and feet)
stratum granulosum
stratum spinosum
stratum basale
what is the dermis?
lies below the epidermis; well supplied w/ blood; contains sebaceous glands, sweat glands, and hair follicles
what are the layers of the dermis?
papillary layer- contains caps and touch receptors, creates fingerprints
reticular layer- contains pacinian corpuscles/sensory receptors, sweat glands, lymph vessels, and hair follicles; causes cleavage lines pattern
what is the hypodermis?
subcutaneous tissue- loose connective tissue (adipose) that insulates the body; contains blood and lymph vessels, base of hair follicles and sweat glands
what are sudoriferous / eccrine glands?
secrete sweat to maintain body temp
what are apocrine glands?
become active during puberty; secrete pheromones
what are sebaceous glands?
found surrounding hair follicles; secrete sebum to keep hair and skin moist
what kind of pigmentation does carotene cause?
golden yellow pigment in SC fat; heavy in palms and soles
what kind of pigment does oxyhemoglobin cause?
bright red pigment; predominates in arteries and capillaries
what kind of pigment does deoxyhemoglobin cause?
blueish pigment (cyanosis); predominate in cutaneous blood vessels
what 3 things should you think of with skin exams?
bugs, drugs, and contact
what is tenting / decreased turgor a sign of?
dehydration
what is the mnemonic for describing skin lesions?
SPECL SCAB
size
pattern (if more than 1)
elevation
color
locaiton
shape
consistency
and
borders
what is annular?
ring shaped
what is arcuate?
partial ring shape
what is bizarre mean when describing shape of lesions?
irregular
what does confluent mean?
run together
what does discoid mean?
disc chape- no central clearing
what does iris mean?
circle w/in a circle
what does reticular mean?
marble like
What is the ABCDE mnemonic?
asymmetry of shape
border irregularity
color variation
diameter larger than 6 mm
elevation or evolving
what is a nevi / mole?
well circumscribed hyperpigmented papule or macule
what is a macule?
flat non palpable lesion < 1 cm
what is a patch?
flat non palpable lesion > 1 cm
what is a papule?
palpable lesion < 0.5 cm
what is a plaque?
palpable lesion > 0.5 cm
what is a nodule?
solid or cystic lesion < 2 cm
what is a tumor?
solid or cystic lesion > 2 cm
what is a vesicle?
circumscribed papule containing clear/serous or hemorrhagic fluid < 0.5 cm
what is a bullae?
circumscribed papule containing clear/serous or hemorrhagic fluid > 0.5 cm
what is a pustule?
circumscribed papule containing purulent material
what is a furuncle?
infection of the hair follicle; purulent material extends through dermis into SC tissue and small abscess forms
what is a carbuncle?
coalescence of several inflamed follicles into single inflammatory mass w/ pustular drainage from multiple follicles in the epidermis
what is an abscess?
collection of pus w/in the dermis and deeper skin tissues
what is cellulitis?
bacterial infx of skin
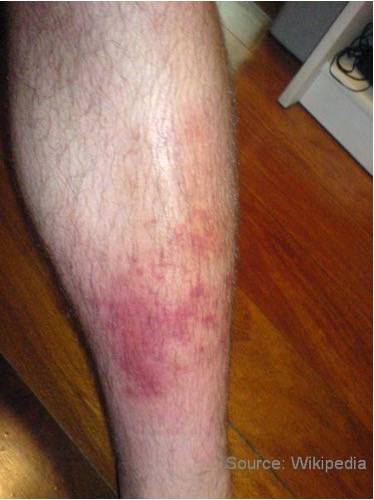
what is lymphangitis?
inflammation or infx of lymphatic channels
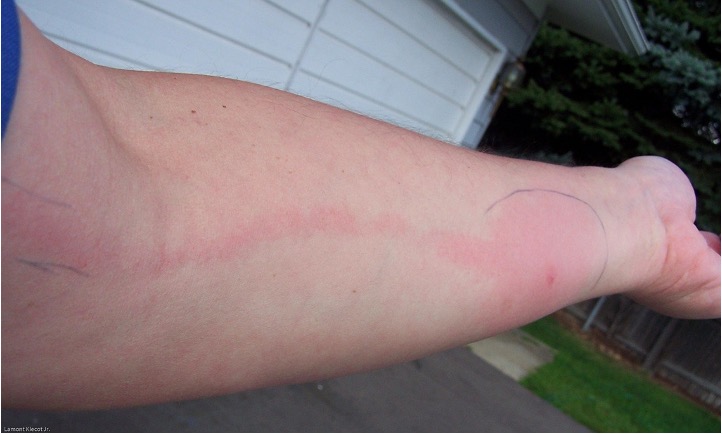
what are verrucae / warts?
small tumors of skin caused by HPV 16 and 18 → squamous intraepithelial lesions of anogenital and oral cavity
grey to flesh colored nodules raised from skin surface
rough, hornlike projections; cauliflower like in texture
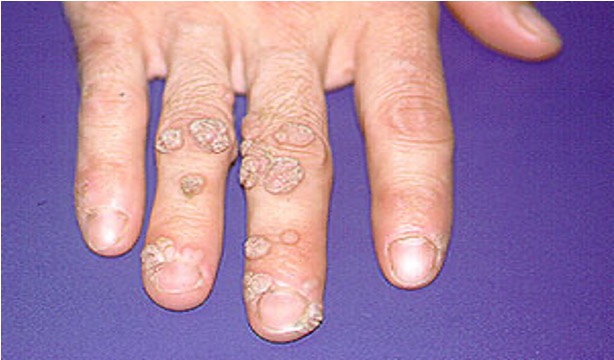
what is a corn?
conical structure of keratin pointing to dermis; occurs due to pressure on thin skin
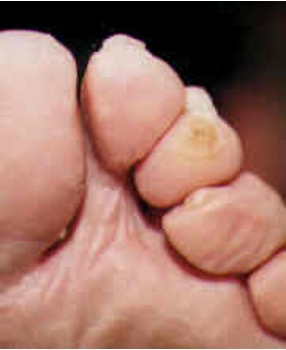
what is a callus"?
thickening of epidermal keratin; occurs due to pressure and friction
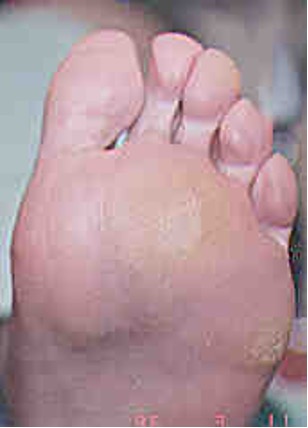
what is scaling?
exfoliated epidermis
seen in dandruff, psoriasis, etc
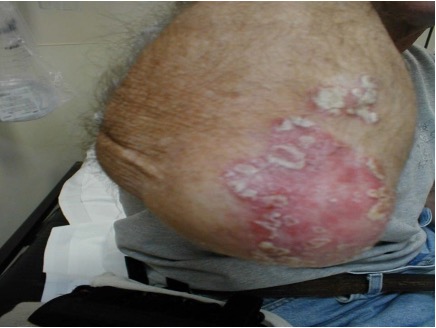
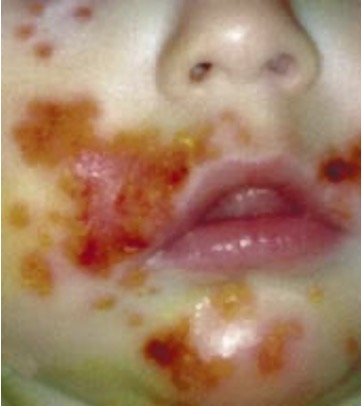
what is crusting?
dried residue of pus, serum, or blood
ex: scabs, impetigo
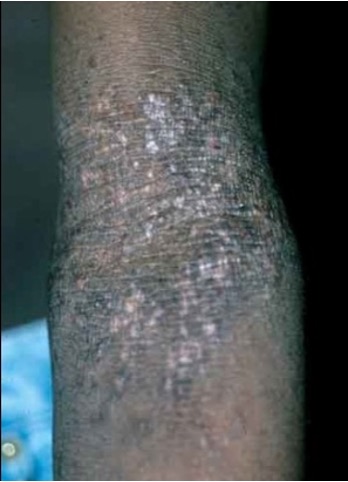
what is lichenification?
roughening/thickening of epidermis
ex- atopic derm
what is a scar?
replacement of destroyed dermis w fibrous tissue
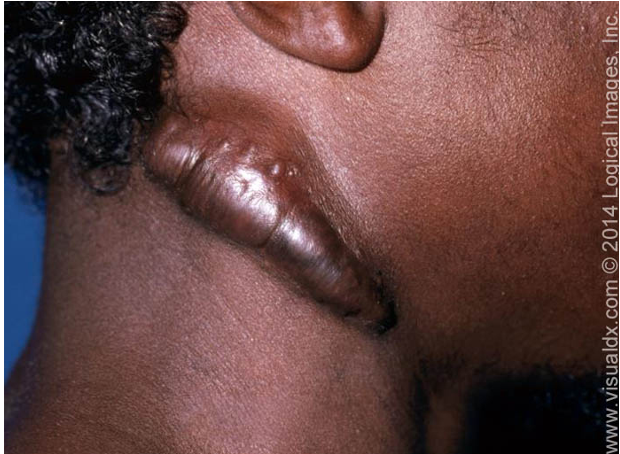
what is a keloid?
elevated scar that grows beyond the wound
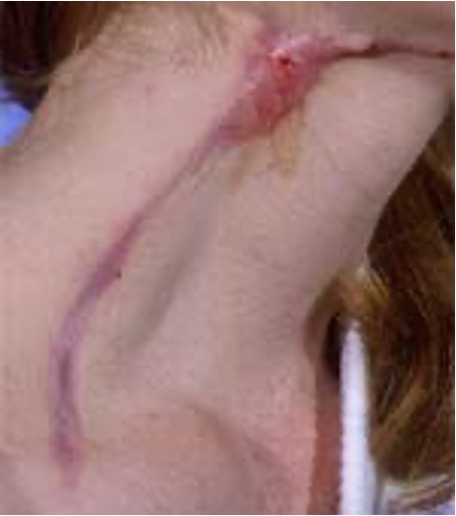
what is a burrow?
slightly raised tunnel in epidermis; ex- scabies
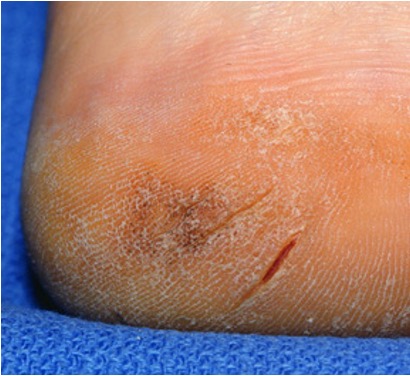
what is a fissure?
linear crack from epidermis to dermis; ex- cheilitis, athletes foot
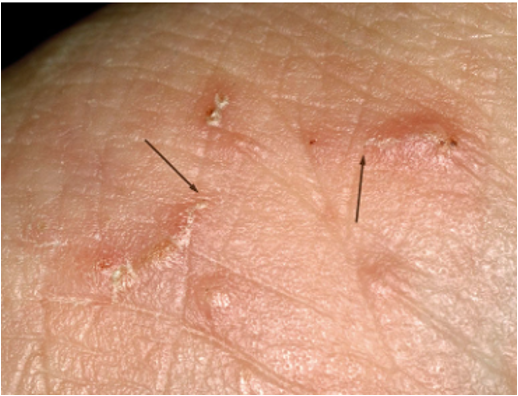
what is excoriation?
superficial linear traumatized area; ex- abrasion or scratch
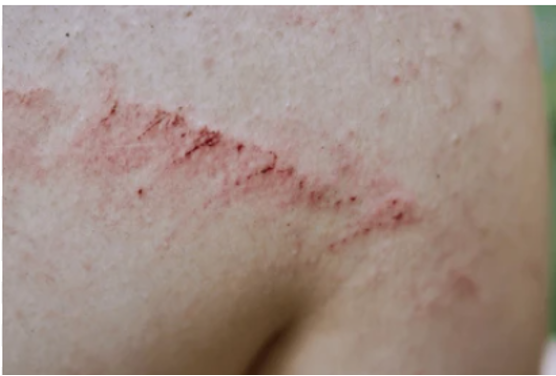
what is petechia?
reddish/purple macules < 2mm; do NOT blanch w/ pressure
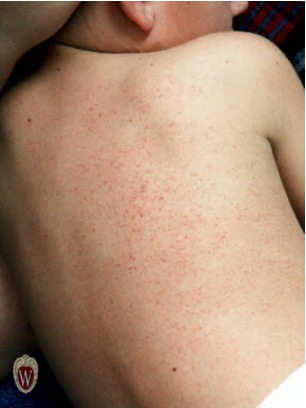
what is purpura?
reddish/purple macules > 2mm; does NOT blanch w/ pressure
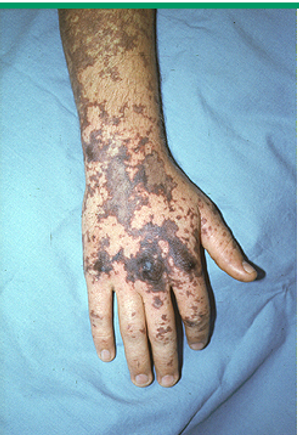
what is ecchymosis?
flat, non palpable, SC accumulation of extravasated blood; color evolves over time: purple/blue → red/brown → green/yellow
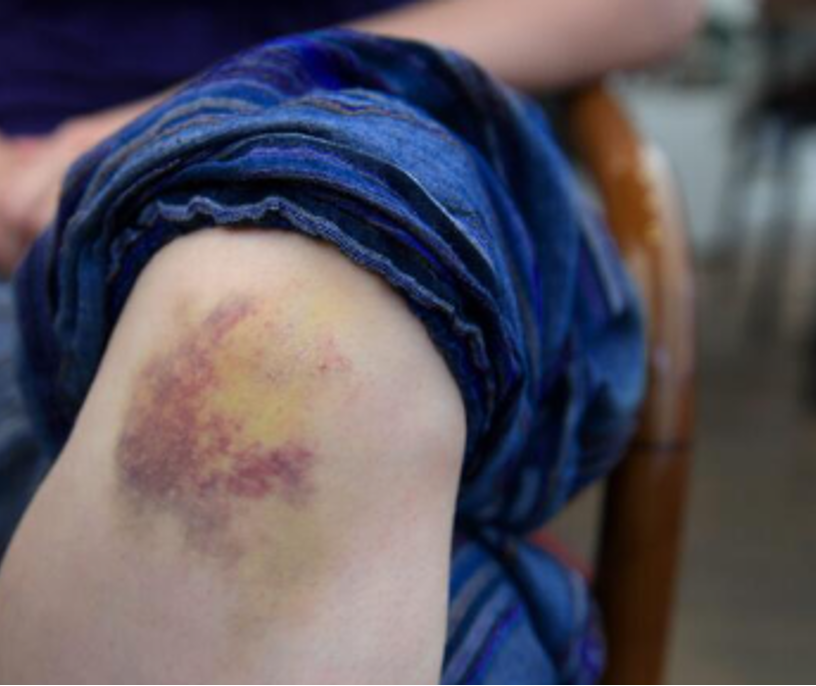
what is a hematoma?
palpable, SC accumulation of extravasated blood; color evolves over time: purple/blue → red/brown → green/yellow
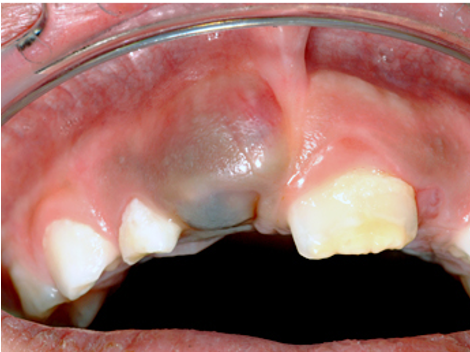
what is a telangiectasia?
fine, irregular blood vessel
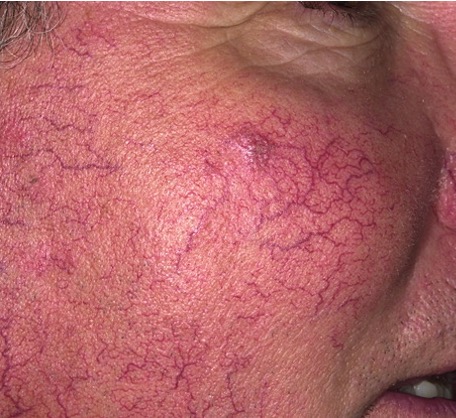
what is a spider angioma?
central red macule w/ radiating spider like arms
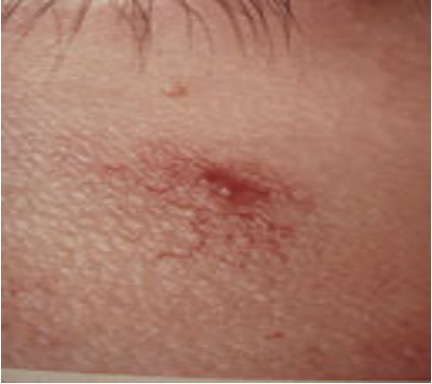
what is a cherry angioma?
small red papule
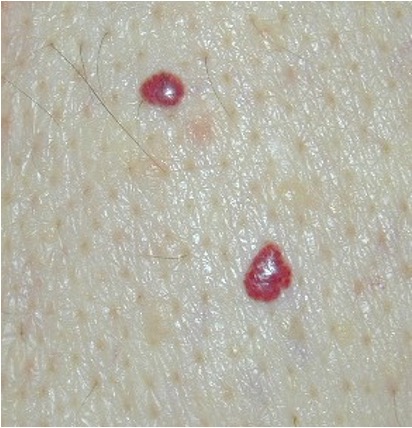
what is an erosion?
superficial, focal loss of part of epidermis
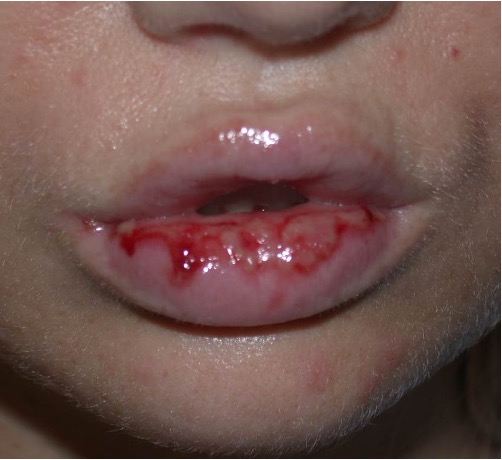
what is an ulceration?
focal loss of epidermis extending into dermis
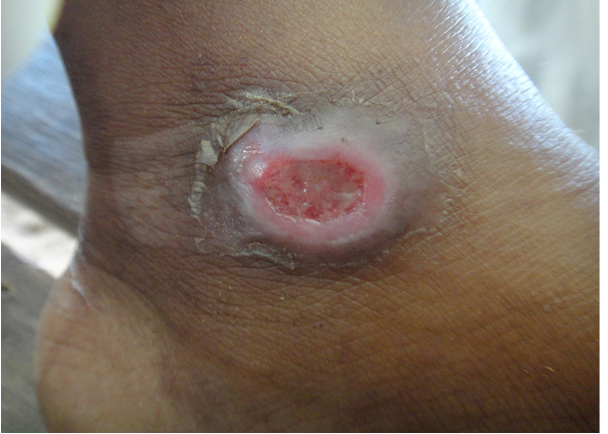
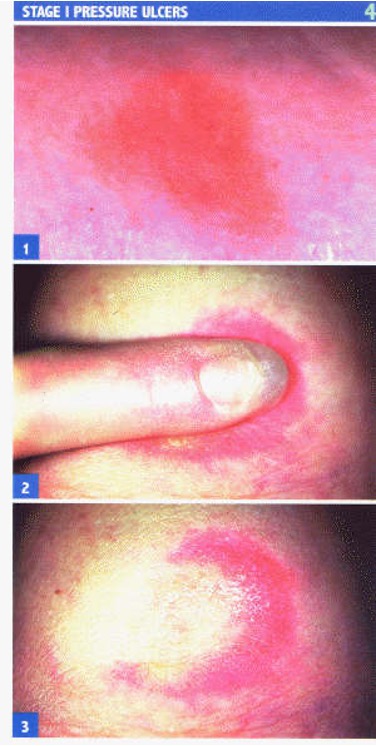
what is stage 1 pressure ulcer
alteration of intact skin
redness or purple stage to skin
inc warmth or coolness
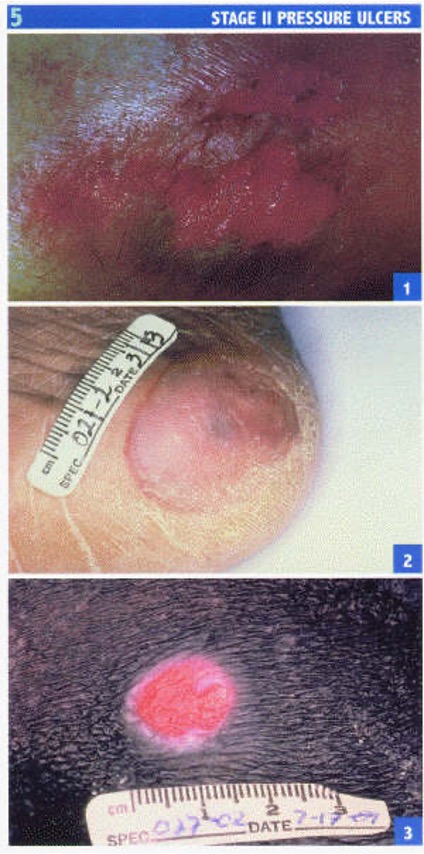
what is a stage II pressure ulcer?
partial thickness skin loss involving epidermis and/or dermis
what is a stage III pressure ulcer?
full thickness skin loss does not extend through fascia
doesnt involve muscle or bone
necrosis of SC tissue
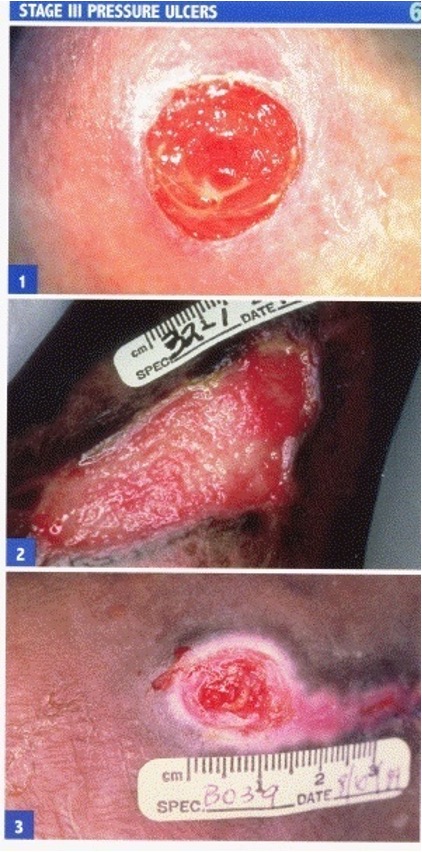
what is a stage IV pressure ulcer?
full thickness skin loss
destruction of tissue, muscle, and/or bone
sinus tracts (tunneling wounds) are common
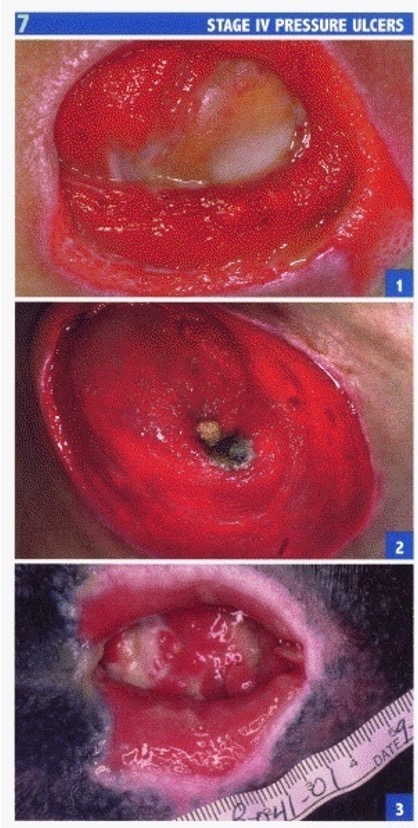
what is atrophy?
depression of skin caused by thinning of epidermis or dermis
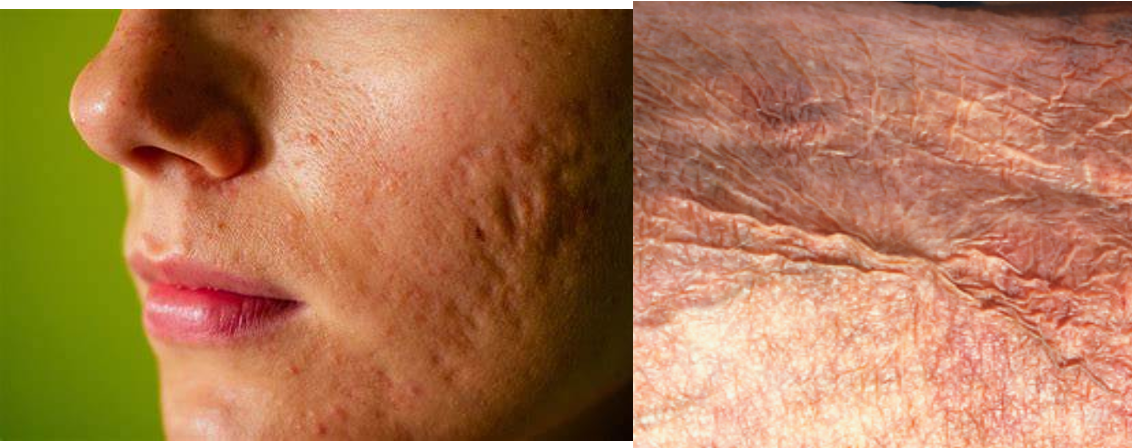
what is a patch test?
confirms substances that produce allergic contact dermatitis
what is auspitz sign?
bleeding after scales scraped off
what is nikolsky phenomenon?
shearing of blisters upon pressure to skin
what is darier sign?
scrape skin → red, swollen and possible wheal → urticaria pigmentosa
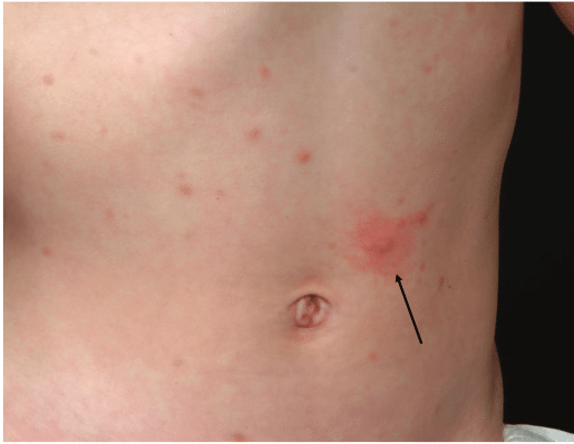
what is koebner phenomenon?
appearance of new skin lesions on previously unaffected skin secondary to trauma
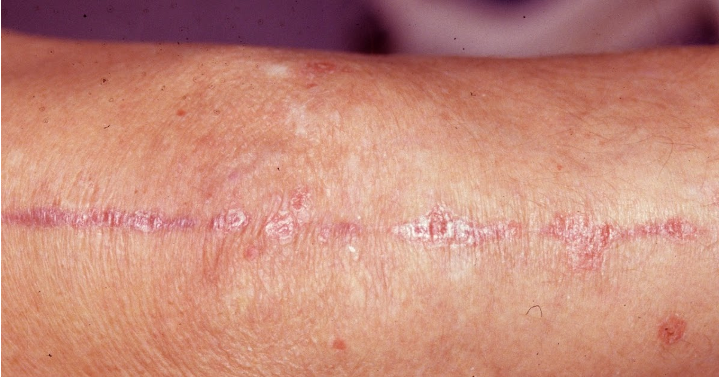
when should you biopsy?
question for malignancy
failure to heal
inc in size
bleed easily
ulcerate spontaneously
tumor or growth of uncertain nature
inflammatory condition
what is moh’s surgery?
high specialized method of excision that allows for histologically confirmed removal of tumor w/ smallest surgical margins and defect; guided by frozen section mapping in 3 dimensions
what is cryosurgery?
used for small, superficial non malignant lesions (warts)
NOT recommended for thick areas (palms/soles) or anatomically confined areas (nails) bc of severe pain
what is dermoscopy?
inspection of deeper layers of epidermis and papillary dermis w/ hand lens w/ built in lighting and magnification of 10-30x
distinguishes bt benign and malignant growth patterns in pigmented lesions
what is hirsutism?
inc hair growth; can be due to hormonal changes and increased androgen
ex: females w/ PCOS
what conditions are associated w/ decreased hair growth?
androgenic alopecia, alopecia areata, trichotillomania, hypothyroidism (queen Anne’s sign- loss of lateral eyebrow), tinea capitis, venous stasis
what is tinea capitis?
fungal infection of hair/scalp
what is koilonychia?
spooning of nails; nail plate thins and becomes inverted due to poor perfusion to nails
ex: iron deficiency anemia
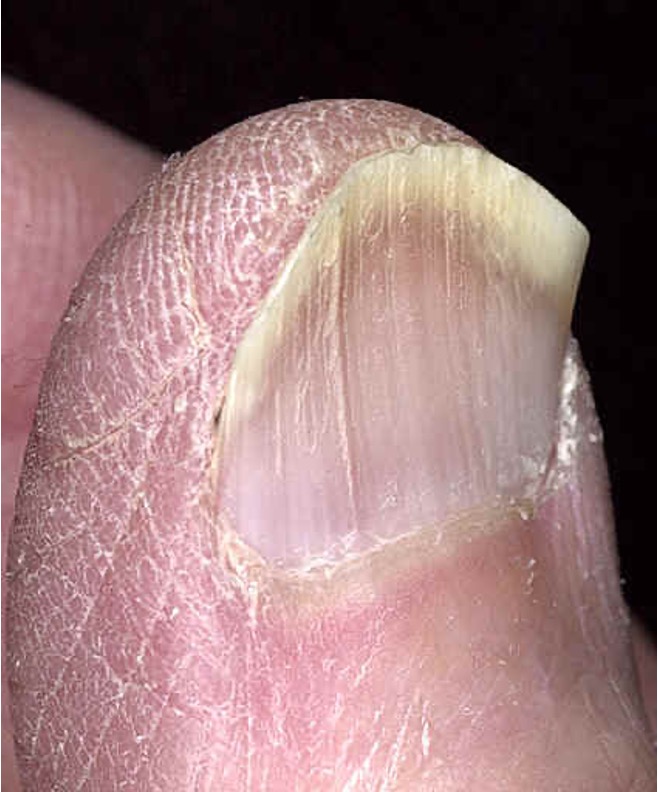
what is nail pitting?
dystrophy of nail plate; areas of small depression or “pits”
ex: autoimmune, psoriasis, FHx
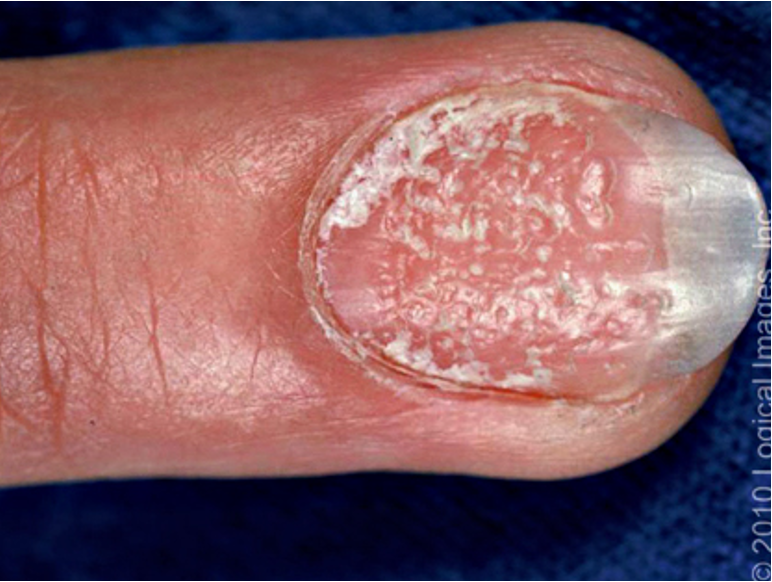
what are splinter hemorrhages?
bleeding from capillaries
ex: trauma, endocarditis
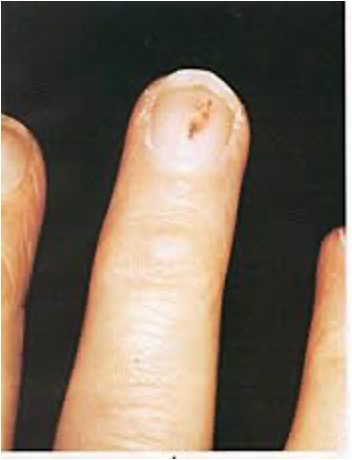
what is a subungual hematoma?
hemorrhage to nail plate
ex: trauma
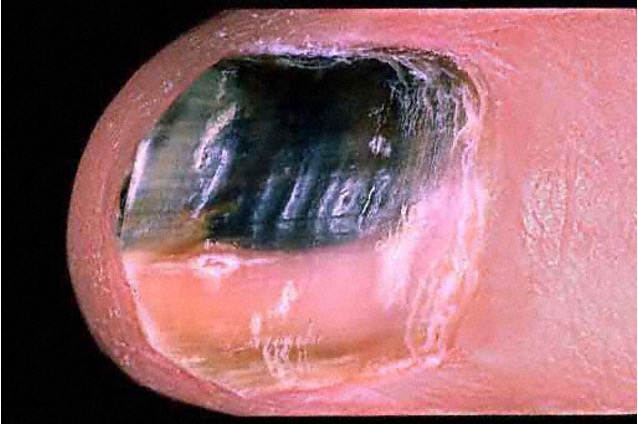
what are beau’s lines?
traverse depression of nail plate, usually bilateral; sign that systemic illness or injury disrupted nail growth
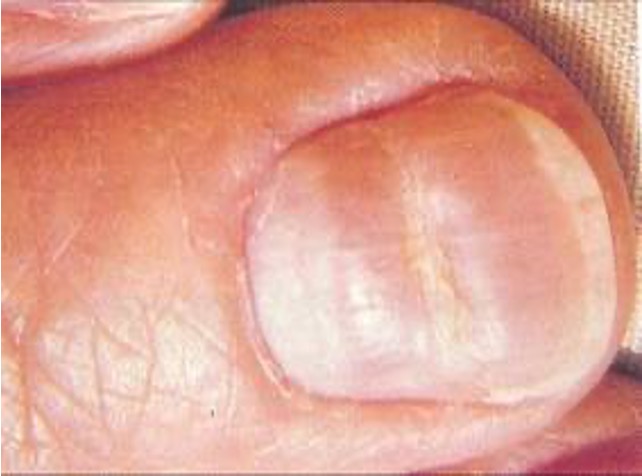
what are mee’s lines?
curving transverse white bands on nails
ex: arsenic poisoning, HF, Hodgkins, CO poisoning
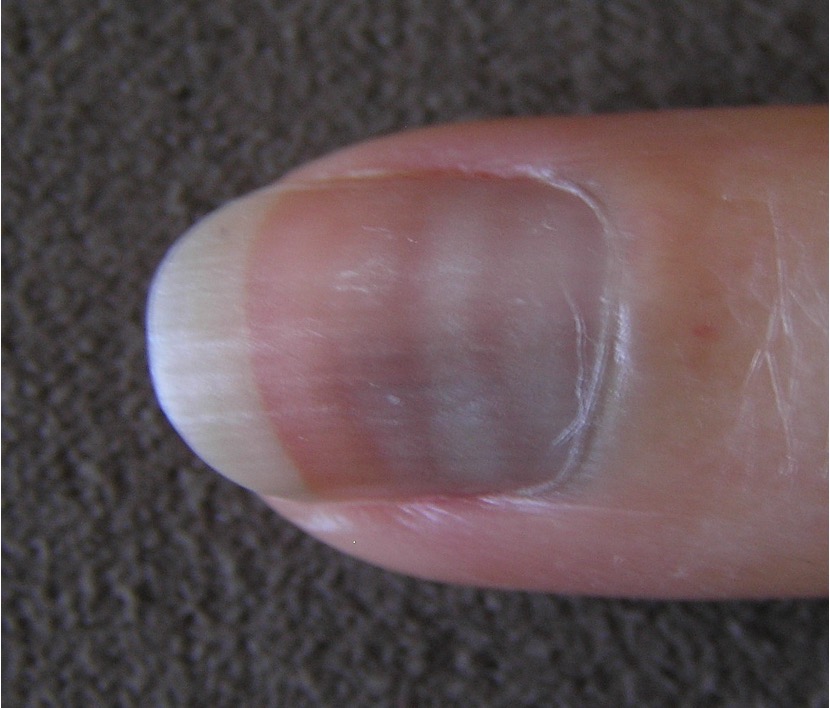
what is oncyholysis?
separation of nail plate from bed; starts distally
ex: trauma, excess manicuring, psoriasis, diabetes, drug reaction
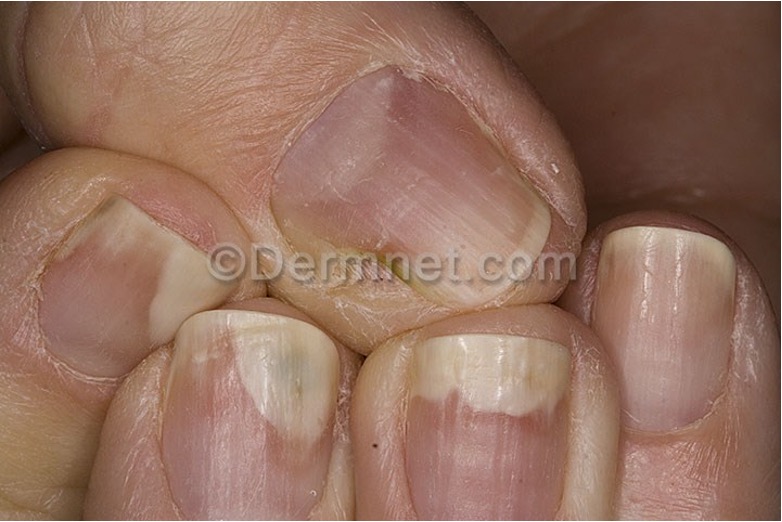
what are Lindsay’s nails?
half white / half brown/red/pink; suggests chronic renal failure
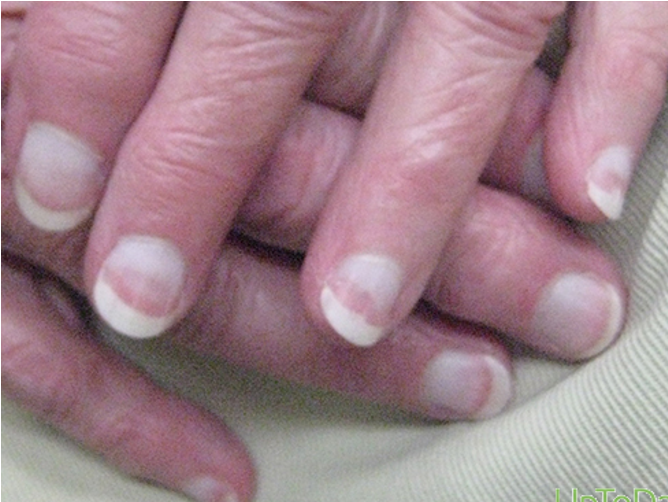
what are terry’s nails?
white nails; sign of HF
what do blue-green nails suggest?
pseudomonas infx
What drug causes brown-yellow discoloration of nails?
phenindion (anticoagulants)
what does brown/black nail discoloration suggest?
onychomycosis / paronychia
what is melanonychia?
line through nail; can be benign or malignant
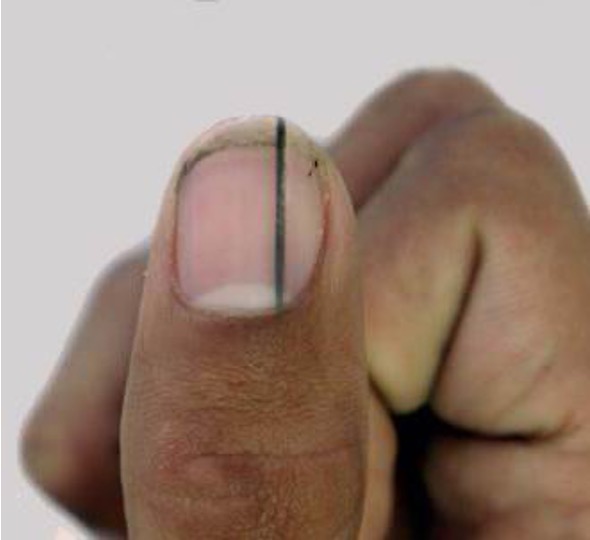
what is clubbing?
angle bt nail base and finger is > 180 degrees (lovibond’s sign); end of finger becomes rounded and bulbous
ex: chronic hypoxia
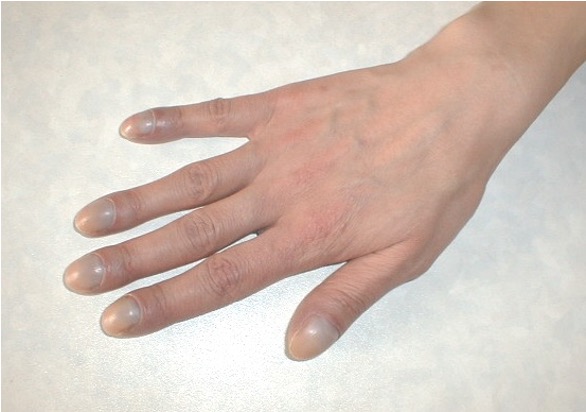
what is felon?
acute infx of fingertip pulp space
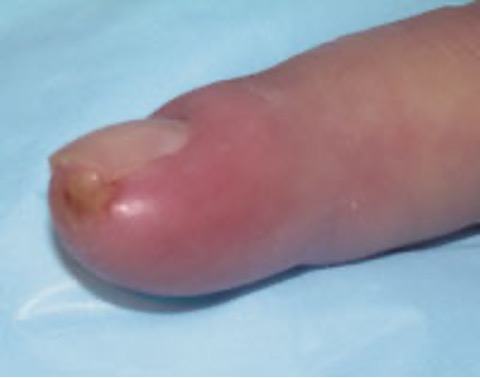
what is paronychia?
acute infx of nail fold
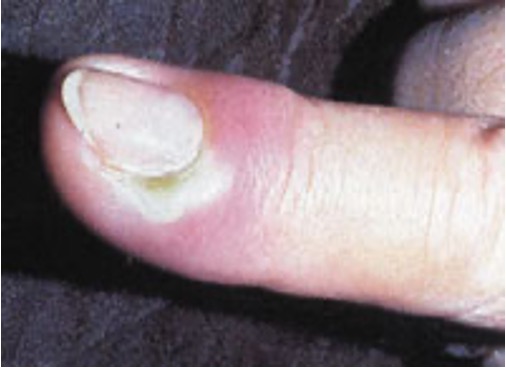
what is herpetic whitlow?
herpes infx of finger pad
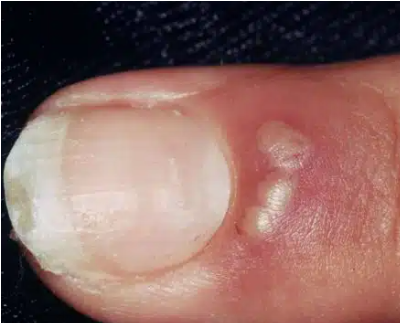
what is onychia?
fluctuant swelling beneath entire nail plate
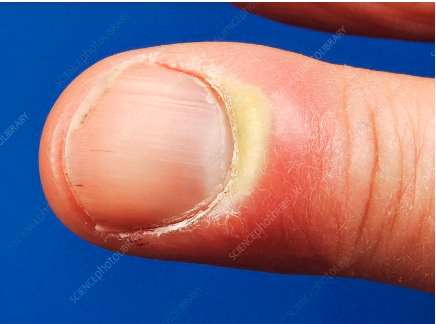
what do white or pale nail beds indicate?
anemia
what do white nail plates indicate?
severe liver disease
what does koilonychia indicate?
iron deficiency state or erythrocytosis
what should you think w/ a splinter hemorrhage that starts in germinal matrix and grows outward w/o any normal bed bt proximal end and germinal matrix?
malignant melanoma
what does nail biting increase risk of?
eponychium
splinter hemorrhages are usually caused by trauma, but may indicate _____
endocarditis