Cell organelles and their functions
1/26
Earn XP
Description and Tags
key definititions + labelled diagrams
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
cell
the basic unit of a living organism composed of organelles suspended in a cytoplasm with a cell membrane surrounding it
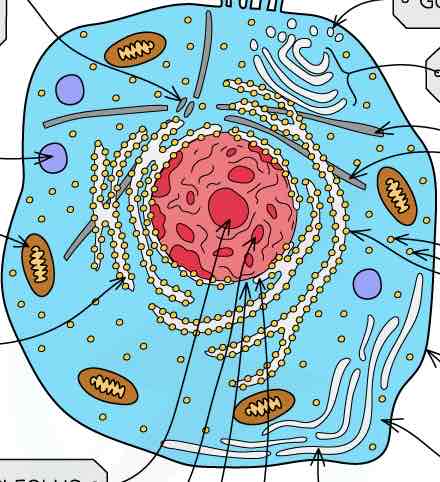
structure of a eukaryotic animal cell (labelled diagram)
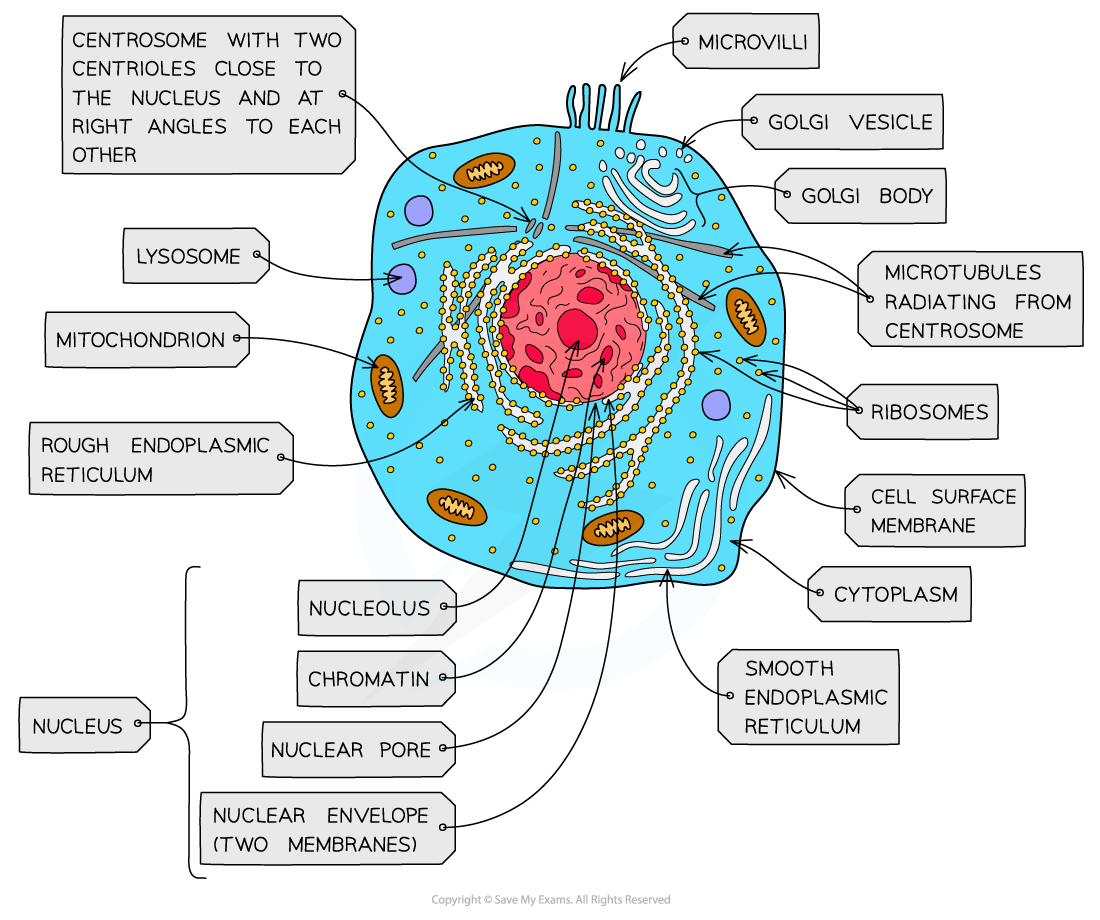
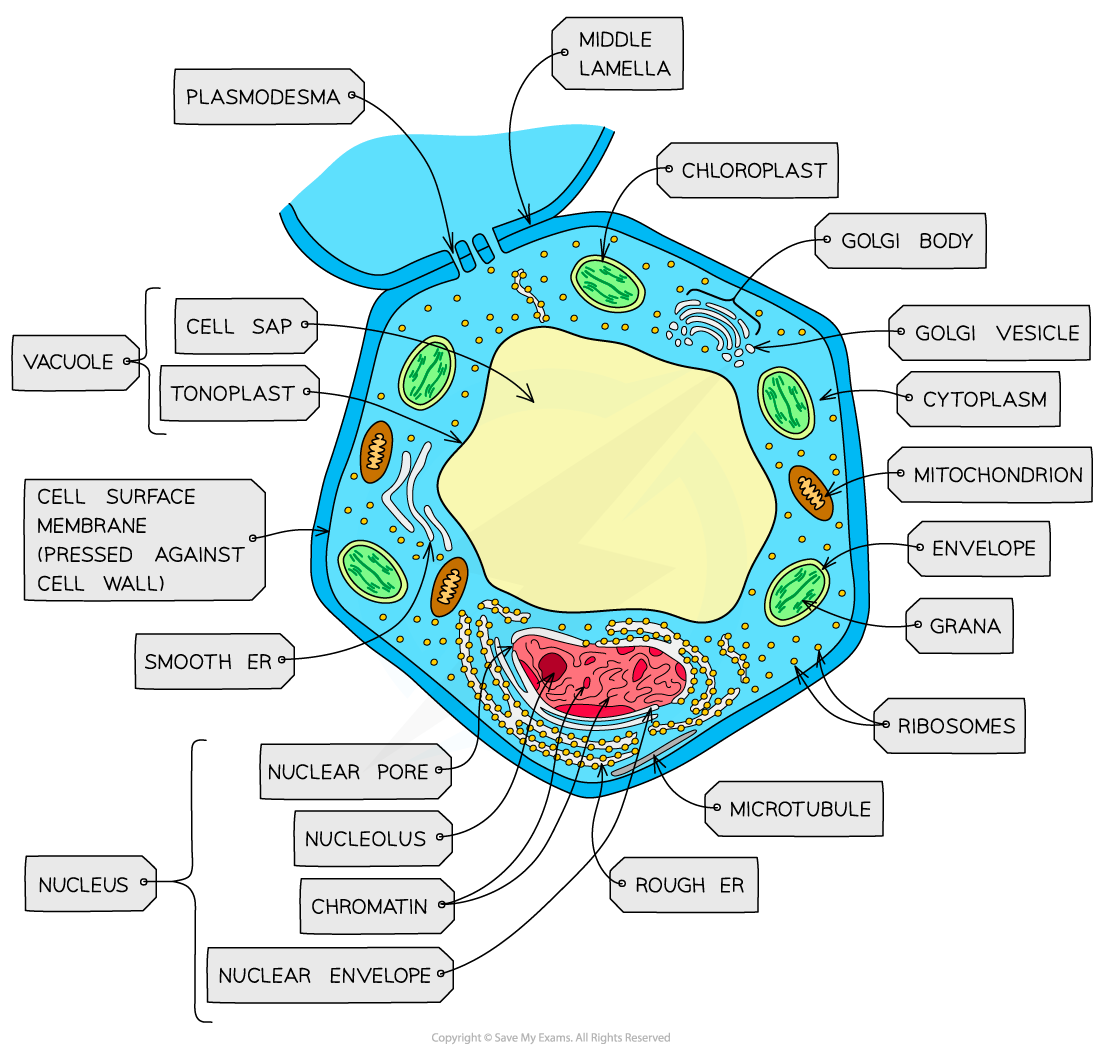
structure of a eukaryotic plant cell (labelled diagram)
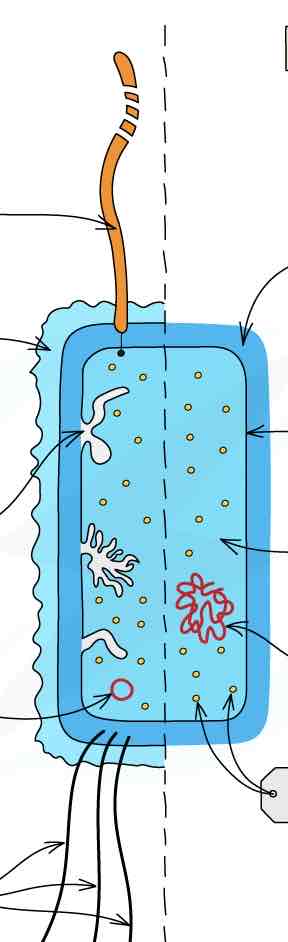
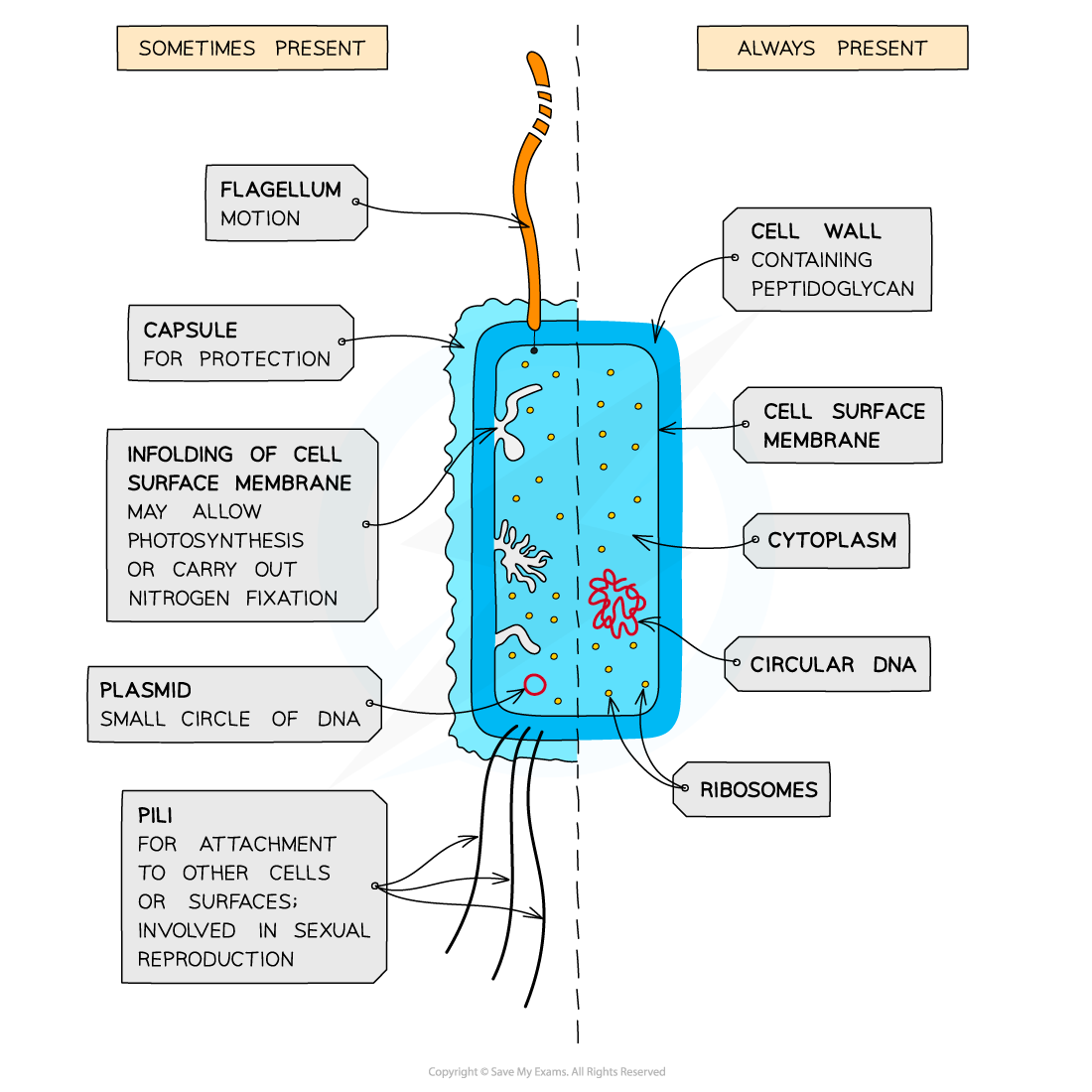
structure of a prokaryotic cell (labelled diagram)

function of the nucleus
contains chromosomes and nucleolus. chromosomes are made up of DNA, which contains genes and controls the synthesis of proteins
function of the nucleolus
dense body within the nucleolus where ribosomes are synthesised
function of the nuclear envelope
made of two membranes perforated by pores that allow mRNA to pass through
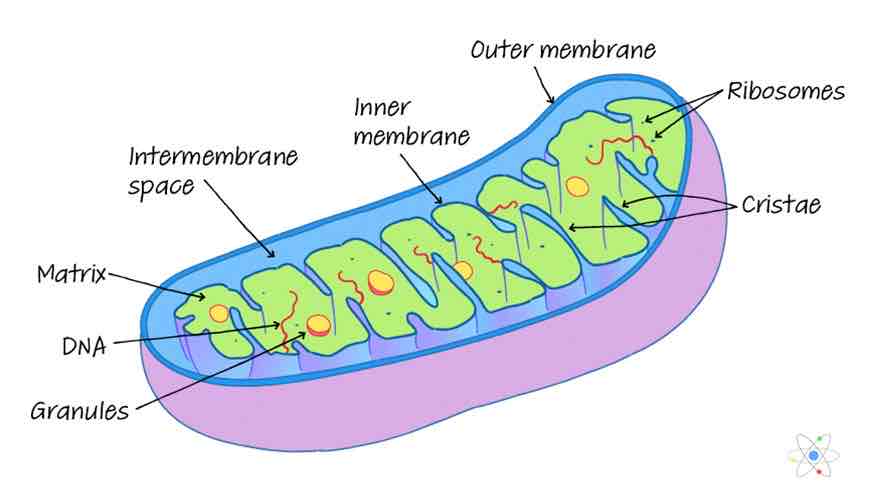
function of mitochondria
two membranes, the inner one is folded to form the cristae- site of the later stages of aerobic respiration
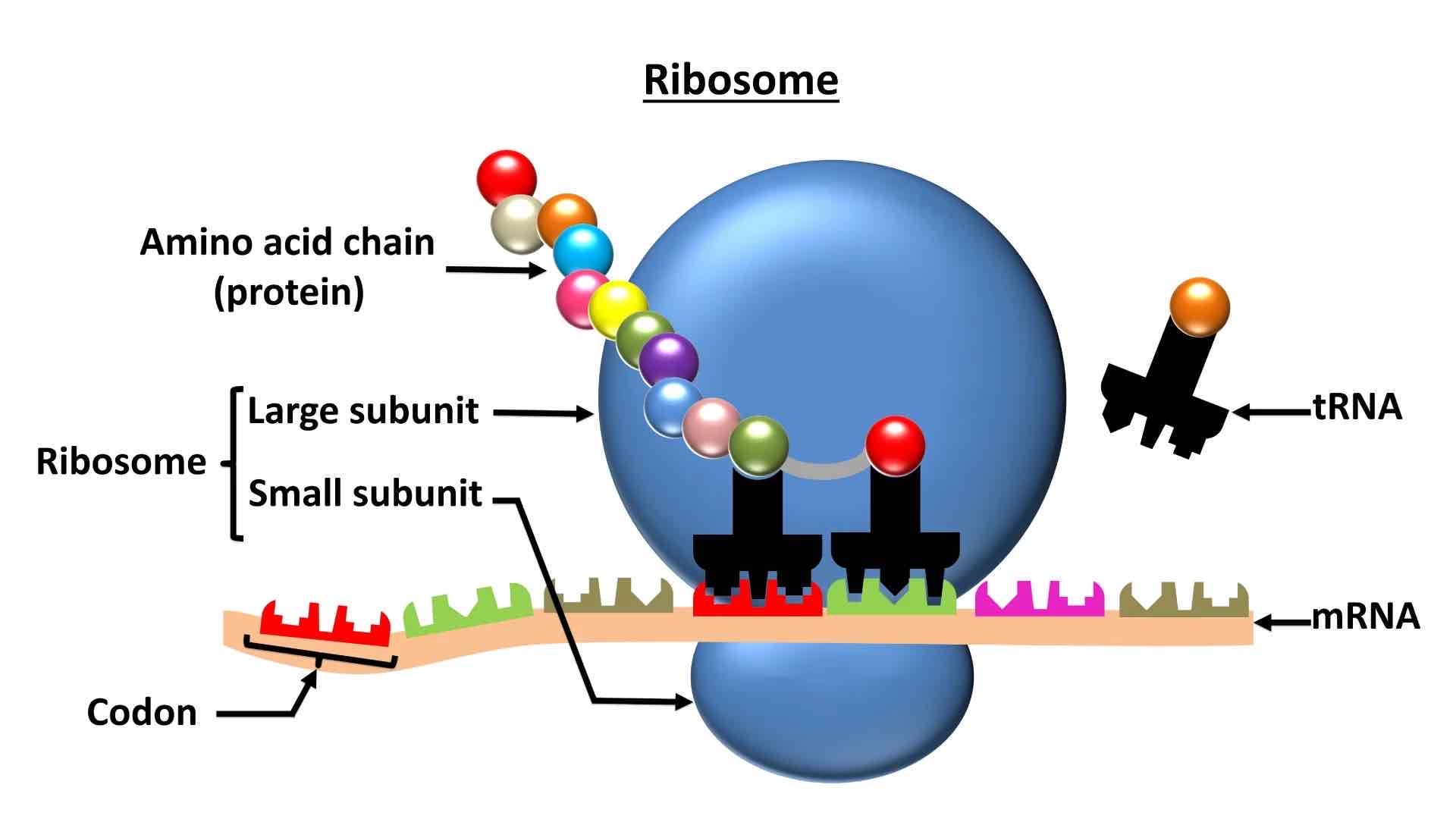
function of ribosomes
the site of protein synthesis
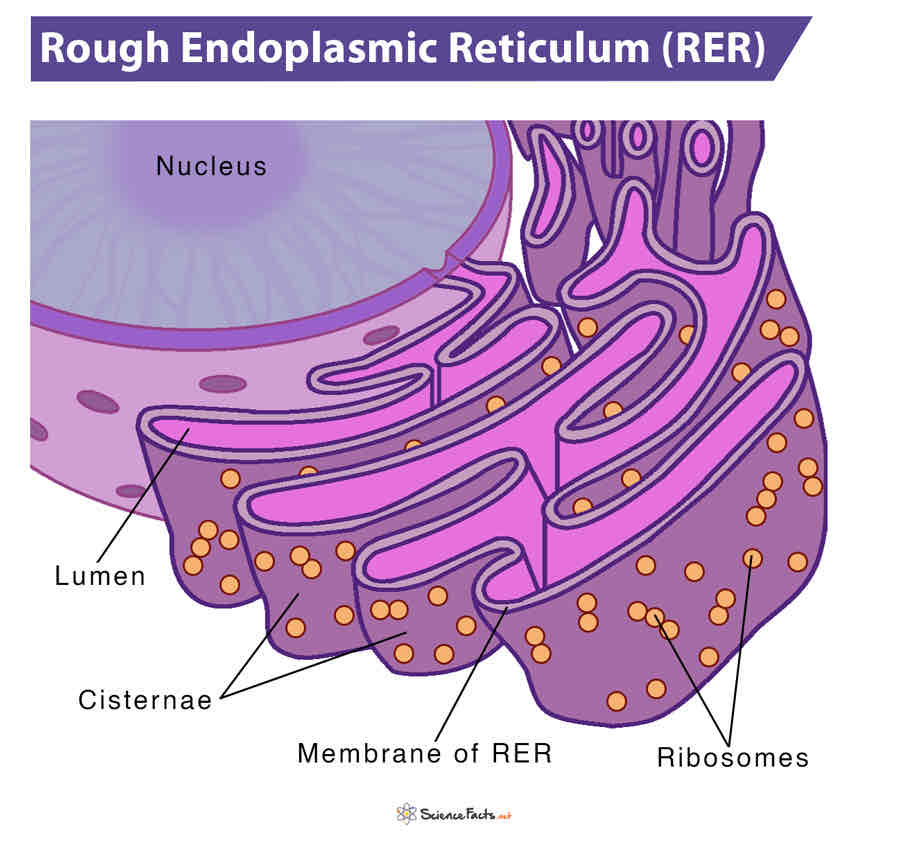
function of the rough endoplastic reticulum
system of interconnected membrane-bound sacs with attatched ribosomes. polypeptide chains formed on these ribosomes pass through the rough ER and assume secondary or tertiary structure
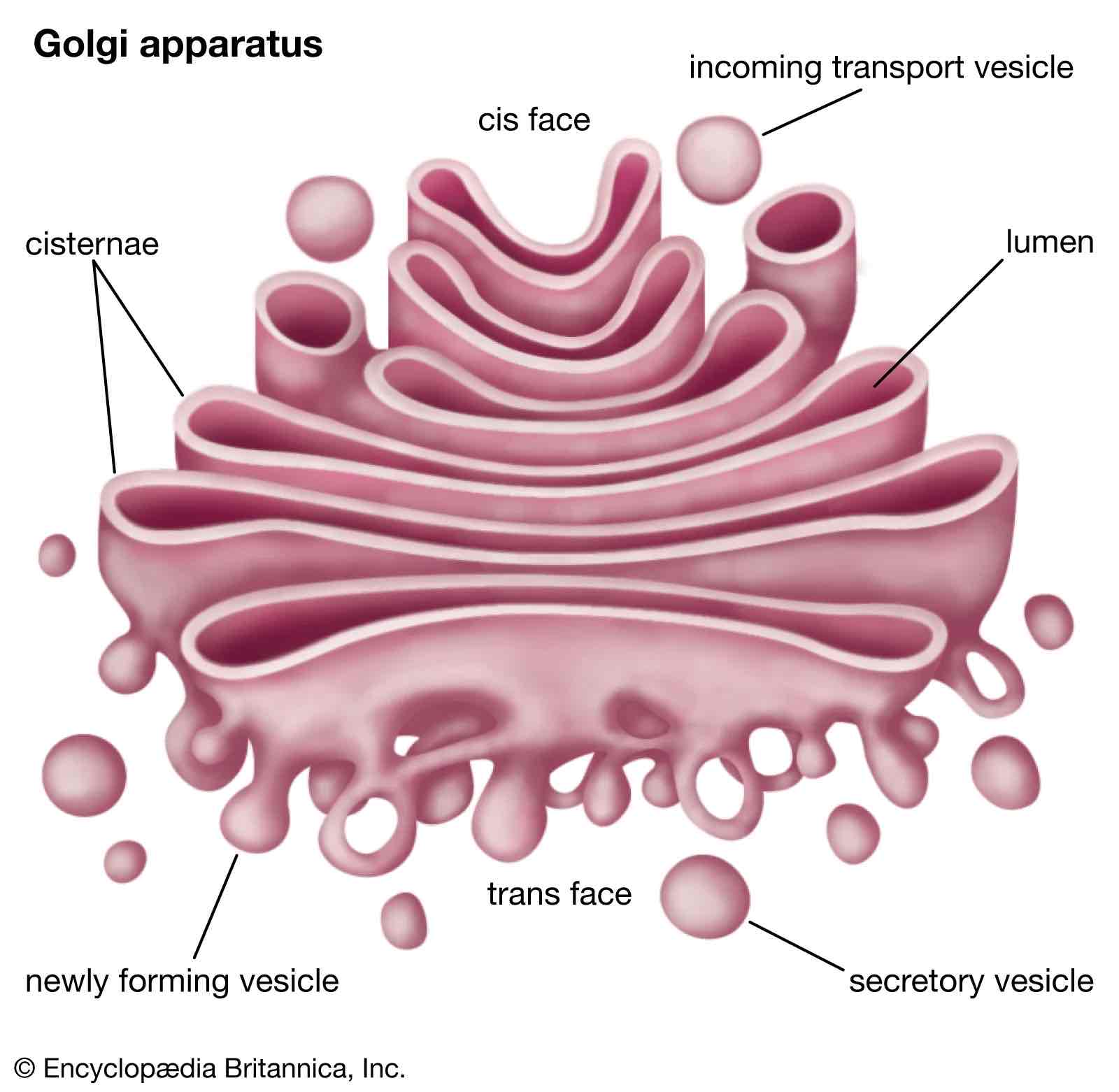
function of the golgi apparatus
flat membrane-bound sacs involved in modifying proteins and packaging them into vesicles for transport
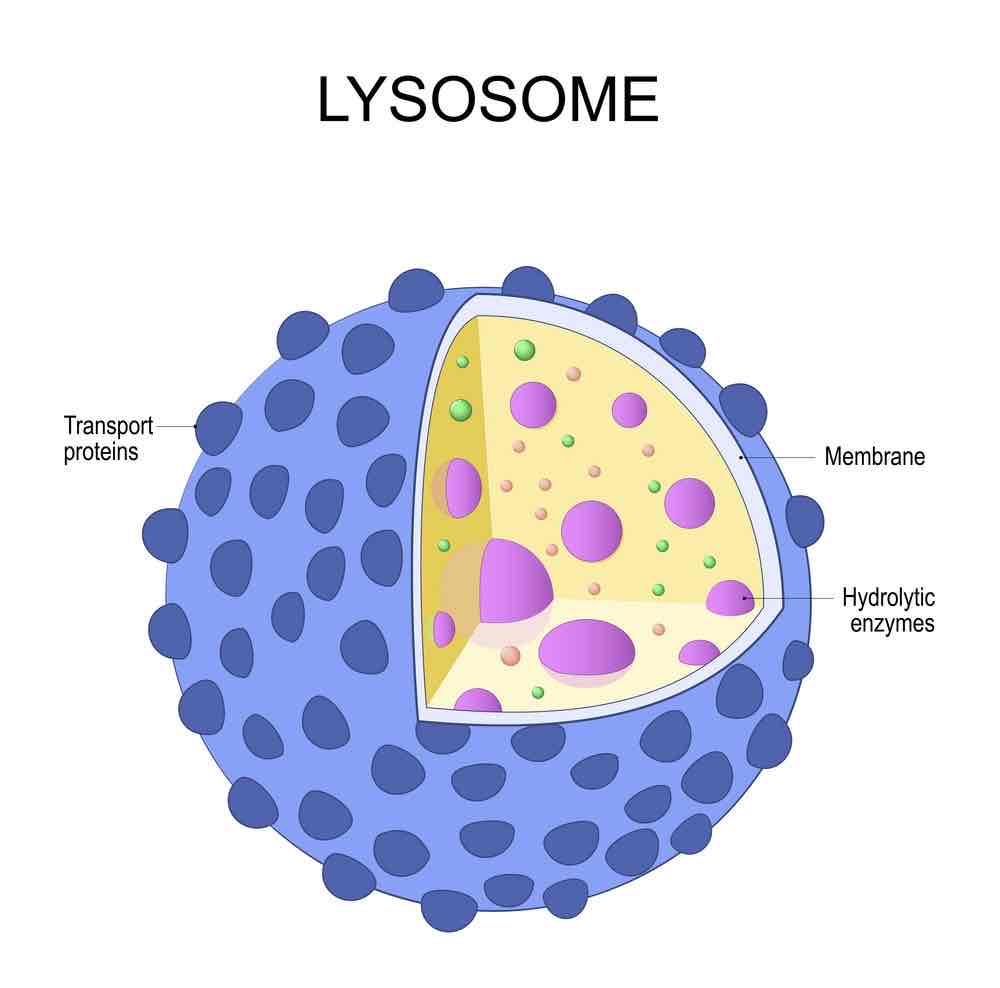
function of a lysosome
sacs containing digestive enzyme that carry out the breakdown of unwanted substances in the cell
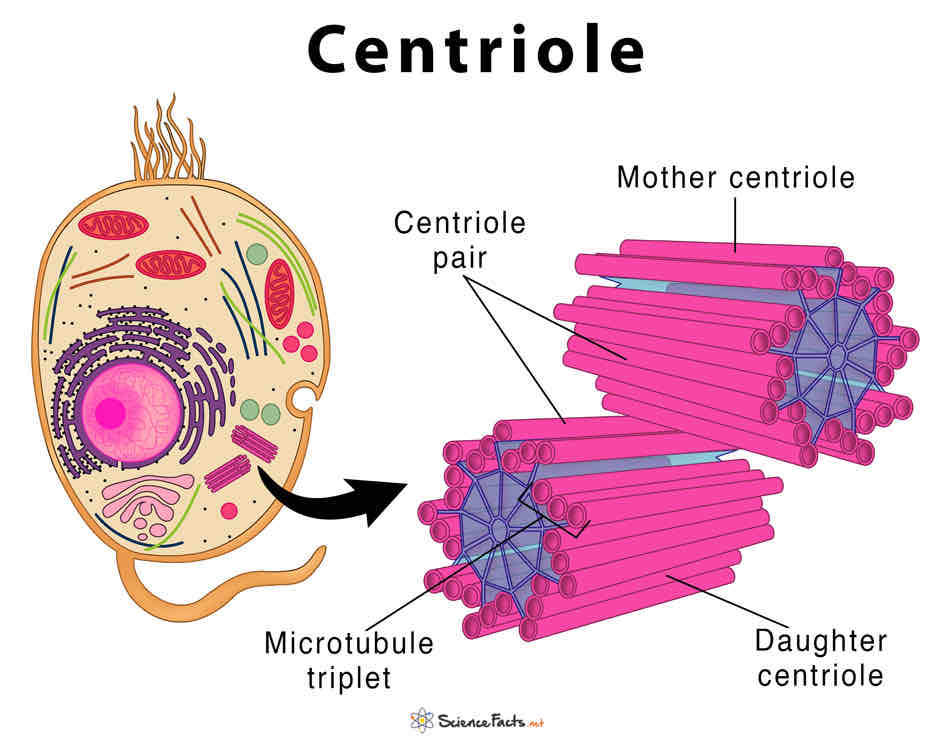
function of the centrioles
hollow cylinders made of protein microtubules, involved in formation of the spindle during nuclear division
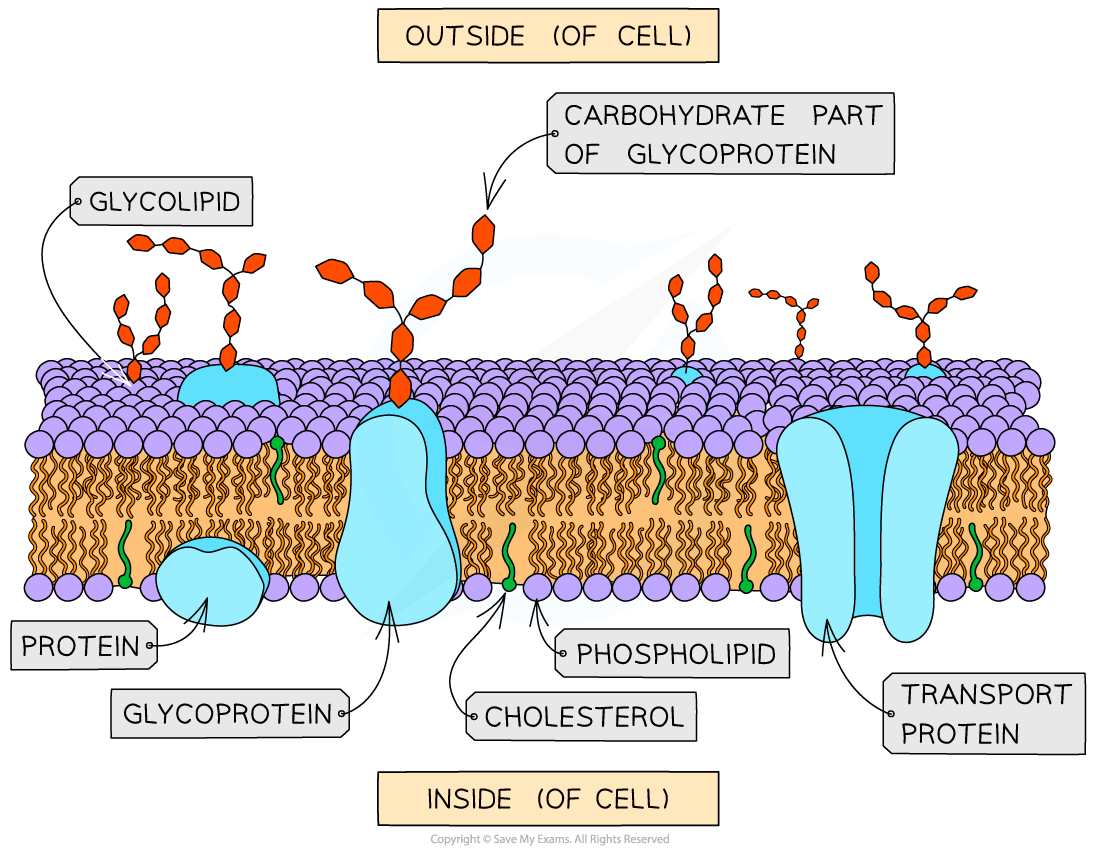
function of the cell surface membrane
phospholipid bilayer containing proteins, is responsible for entry and exit of substances in and out of a cell and is the site of cell communication via receptors
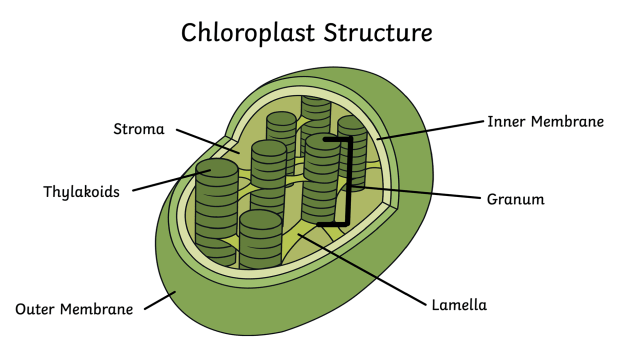
function of a chloroplast
site of photosynthesis
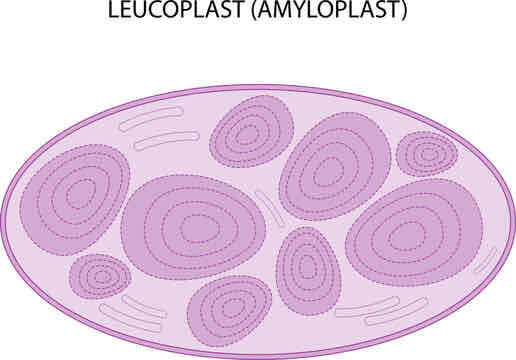
function of an amyloplast
stores starch
function of a tonoplast
membrane surrounding the vacuole that seperates its contents from that of the cytoplasm
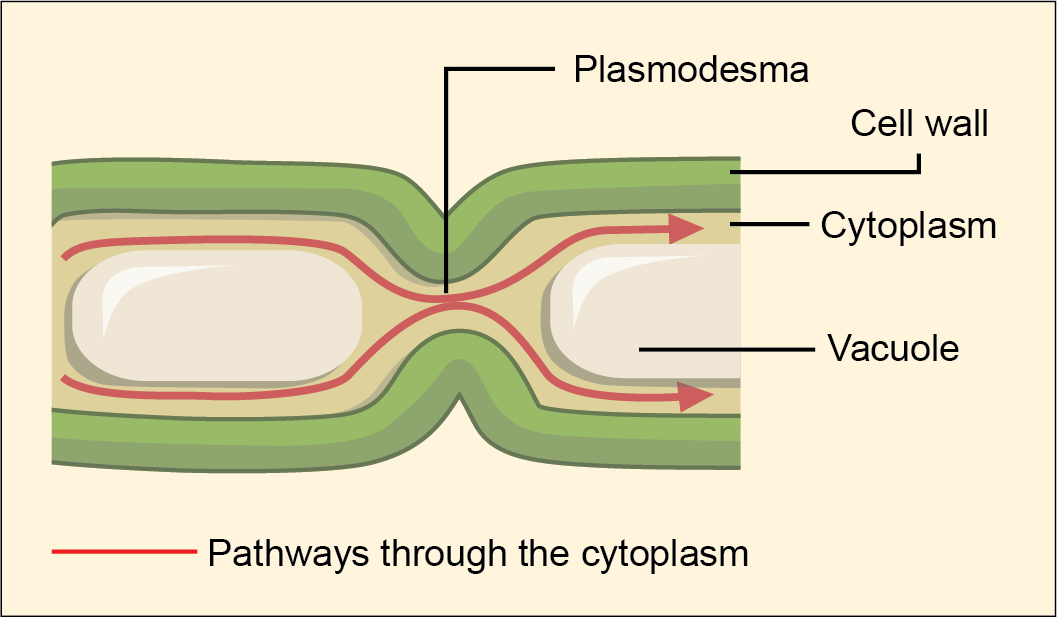
function of a plasmodesmata
channels between plant cells that allow the transfer of substances between adjacent cells
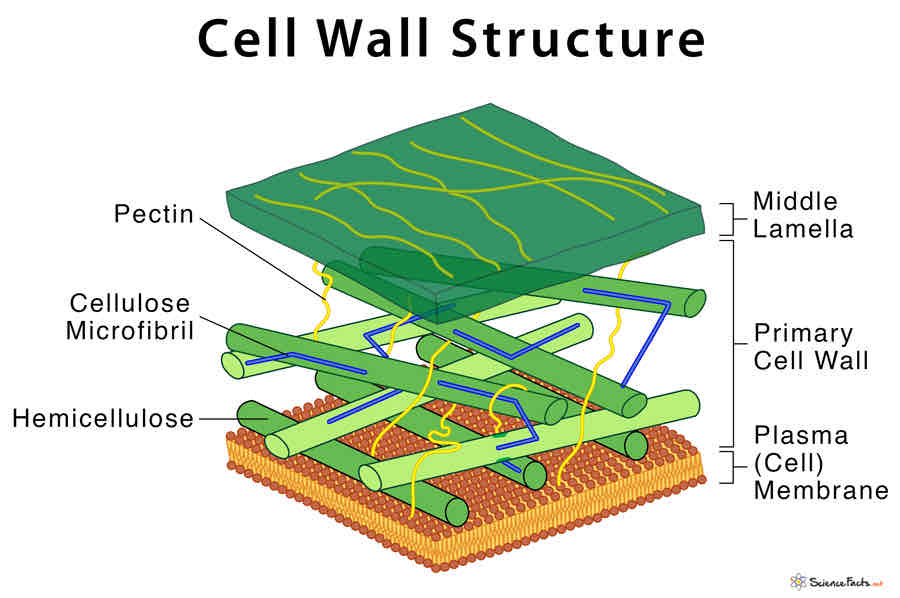
function of the cell wall (plant)
provides support and mechanical strength- made of cellulose
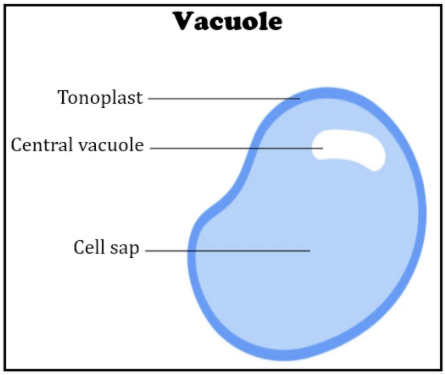
function of a vacuole
maintains cell structure and acts as a temporary energy store
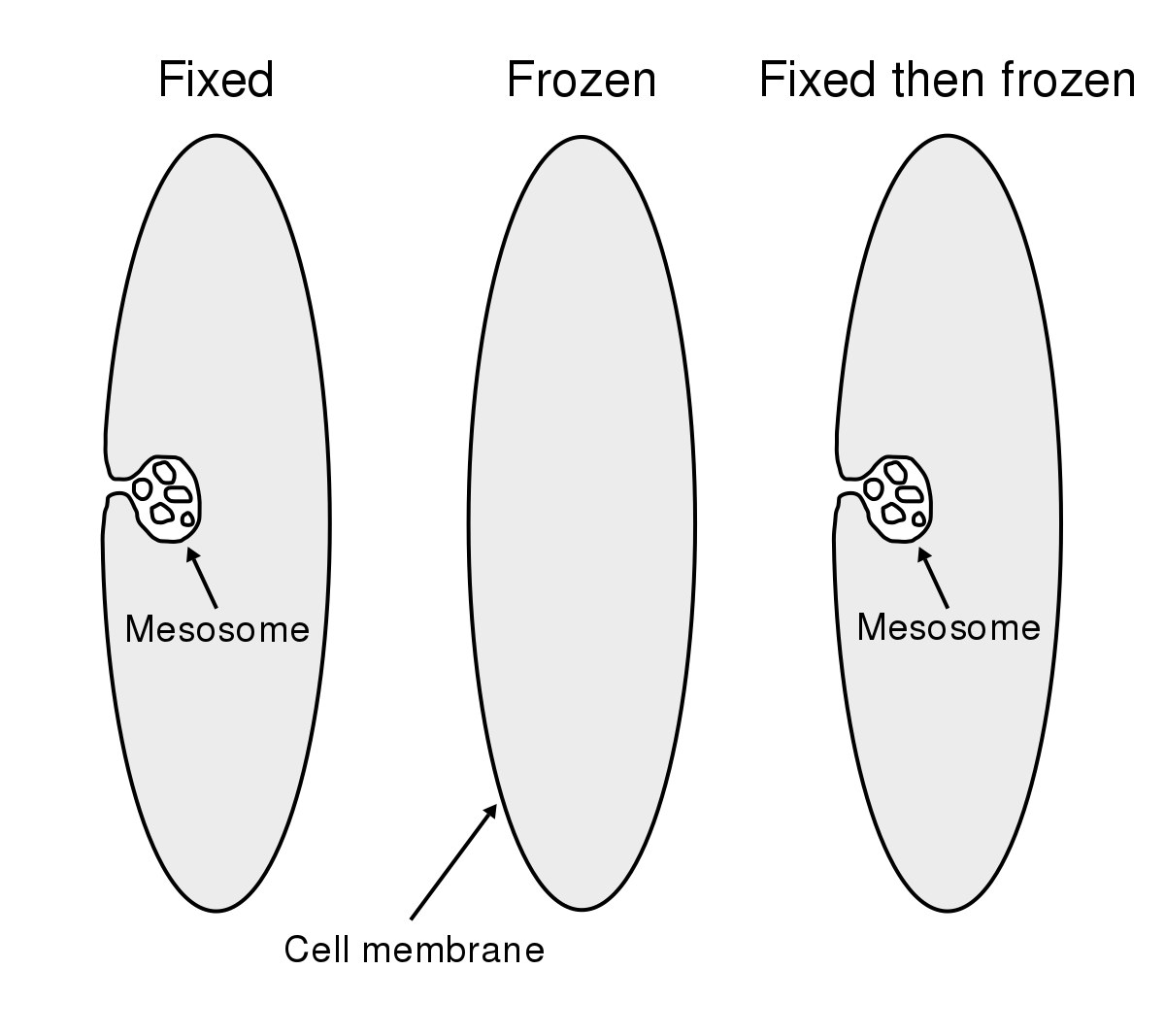
function of a mesosome
infolding of cell surface membrane- suspected site of respiration
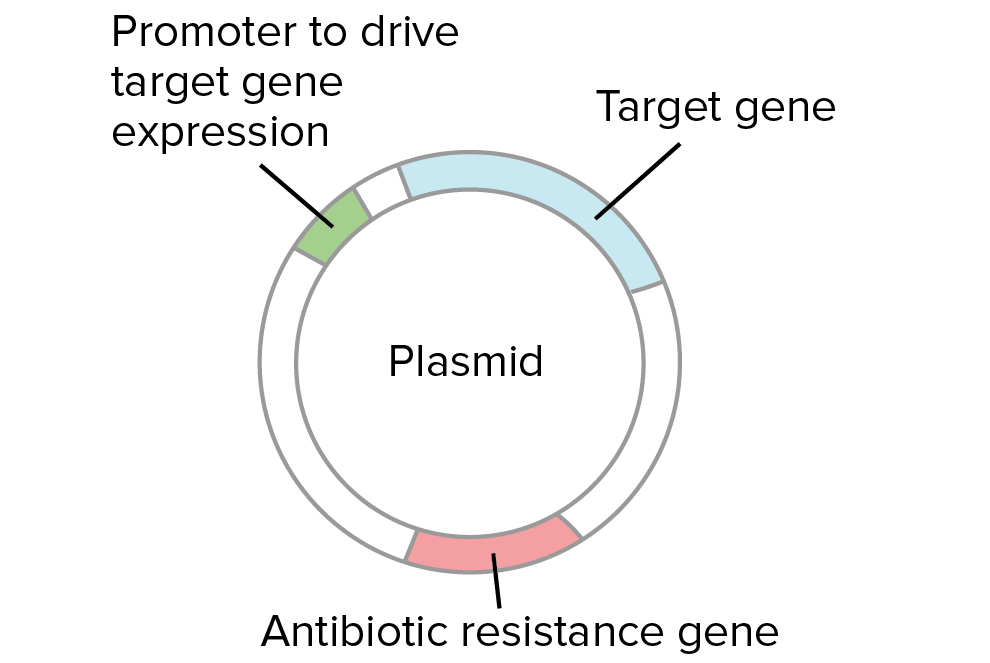
function of a plasmid
small circle of DNA
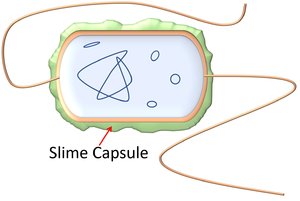
function of a capsule
slimy layer on surface for protections and to prevent dehydration
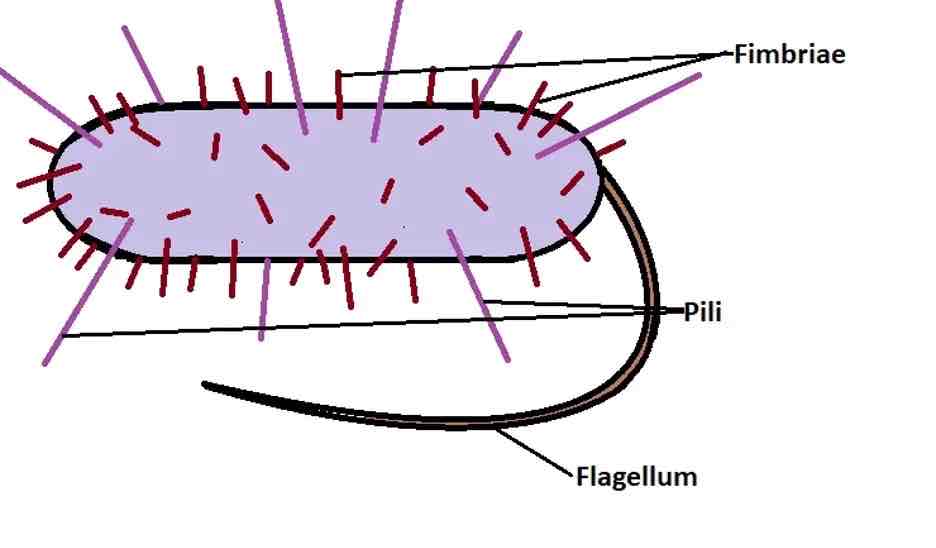
function of the pili
thin protein tubes that allow the bacteria to adhere to surfaces
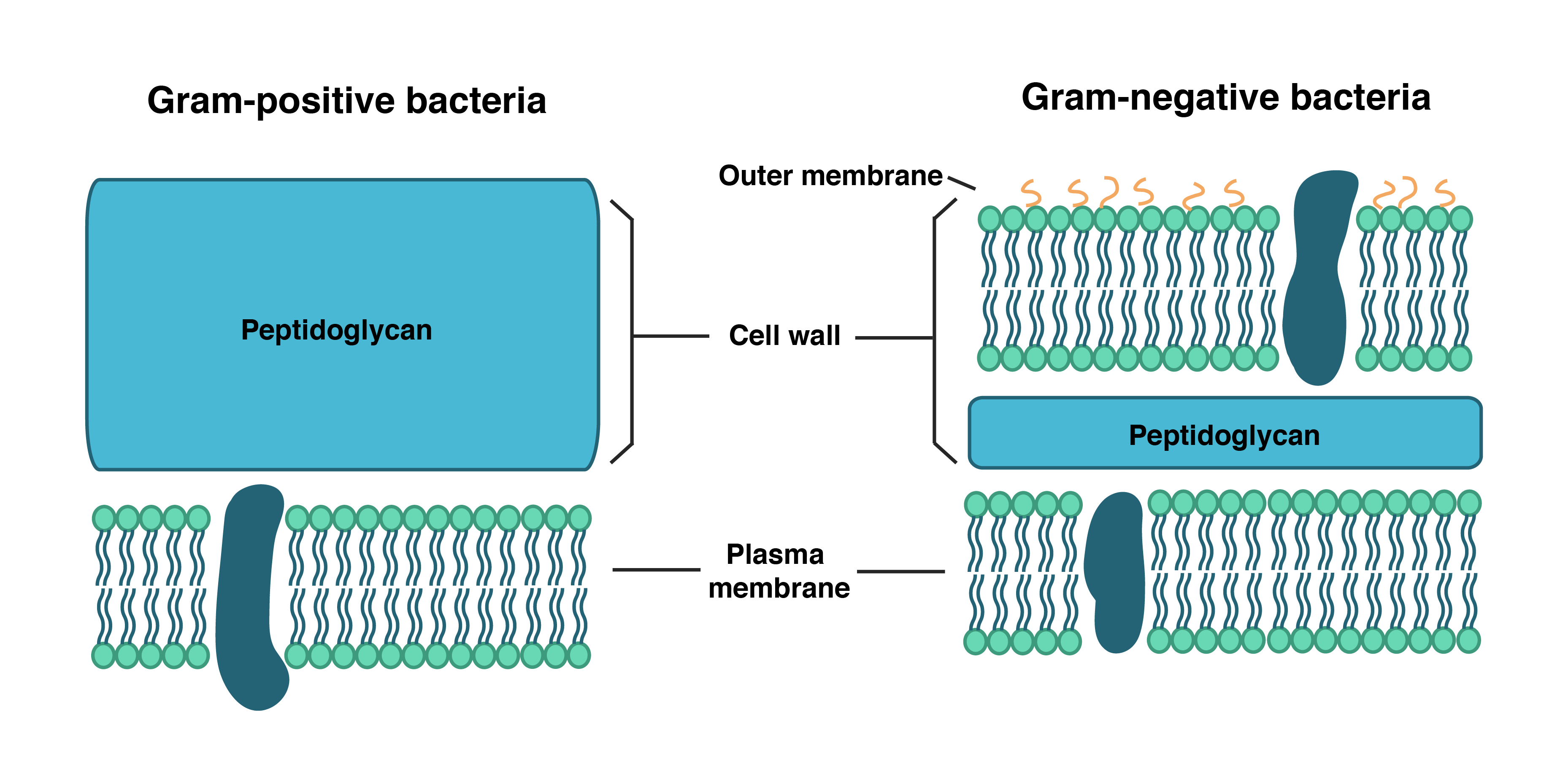
function of the cell wall (bacterial)
made of peptidoglycan- can be gram positive (no outer membrane nor periplasmic space and suseptable to peniciillin) or gram negative (thinner peptidoglycan wall, contains outer membrane, periplasmic space, murein proteins and exotoxins that block antibiotics)
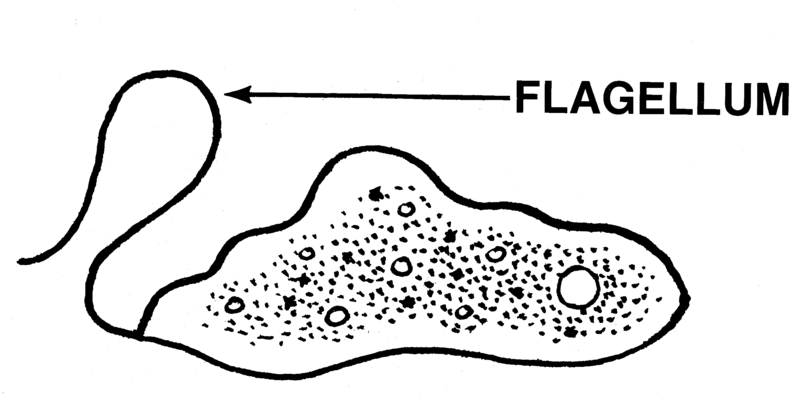
function of a flagellum
hollow cylindrical thread-like structure that rotates to move the cell
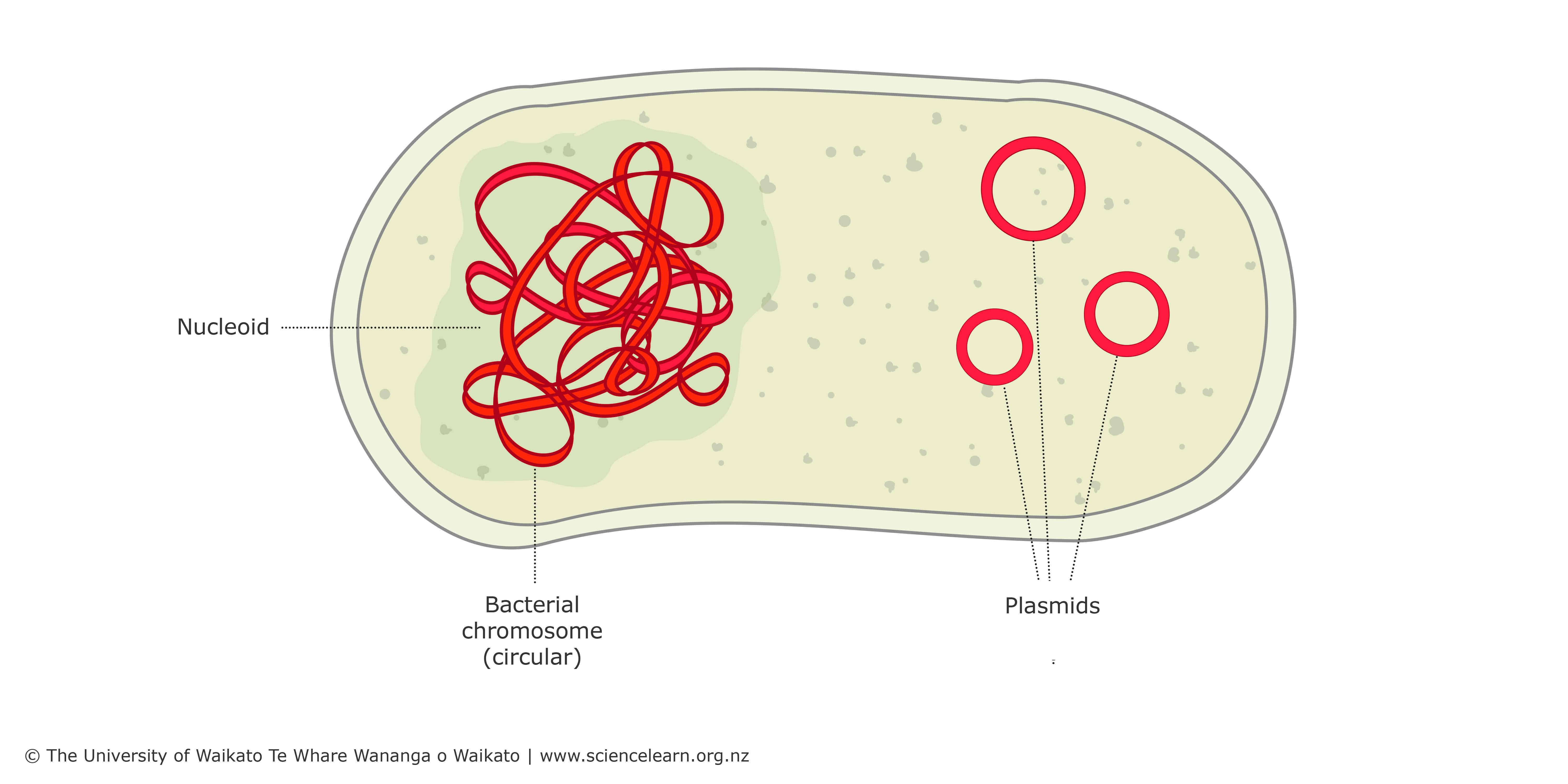
function of circular DNA
contains genes that control cell activity