Lecture 14- cytoskeleton, actin, cell motility, muscle
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
Kartagener Syndrome
• cilia have defective or no what
movement
what motors associate with Actin filaments
Myosin
head domain binds what and hydrolyzes ATP to move in power stroke
actin
actin filaments= F-actin
microfilaments
what polymers of actin protein monomers (G-actin)
polarized
microfilaments assembly requires what
ATP
F-actin dynamics
• elongation is much faster than nucleation (like MTs) – need what to start
nucleus
subunits incorporated/released tend to be
what to the plus end, what from the minus end
added, released
the plus end has a what affinity for ATP-actin than the
minus end does
higher
at LOW ATP-actin concentrations, growth at what end
plus
nucleation is energetically what- must have nucleating proteins, ie, the Arp2/3 complex or Formins, also (Listeria) ActA
unfavored
Actin binding proteins can promote filament what
formation
cell biologists often use fluorescently labeled phalloidin to see the actin’s what
cortex
blocks plus ends
cytochalasin D
binds filaments and prevents breakdown
phalloidin
binds/sequesters free monomers
latrunculin
cytochalasin treated cells –predictions
what aspect of actin dynamics helps
to explain this result?
treadmilling of subunit addition/release
Actin binding proteins can what filament formation
decrease
monomer sequestering proteins alter what- to what-Actin equilibrium
G to F
Actin binding proteins can stabilize what or link them
filaments
monomer polymerizing proteins promote growth
Profilin
capping proteins can stabilize what of a filament
length
membrane-binding proteins connect the what to the cell surface
cytoskeleton
Actin filaments are linked into into what structures
3D
cross-linking and bundling proteins create what structures
(microvilli, stereocilia)
strong
filament-severing what can break filaments into smaller
filaments
proteins
Listeria capitalizes on host what
Actin
a migrating cell polarizes in response to the what
environment
the Rho family of monomeric GTPases promote what reorganization
actin
in an experiment, you bind myosin S1 fragments to a coverslip and add stabilized, labeled Actin filaments and ATP. what happens?
the actin binds but doesn’t move
unconventional myosins walk on actin filaments and can carry what
cargo
myosins I, V, and VI are associated with what vesicles
and organelles
cytoplasmic
smallest contractile unit
sarcomere
skeletal muscle and cardiac muscle cells are comprised of what
myofibrils
myosin II forms what that pull on actin filaments
filaments
Thick filaments
myosin
Thin filaments
actin
Thick (myosin) and Thin (Actin) Filaments Do or Do Not change their length- only the extent of overlap changes as sarcomere contracts/extends
Do Not
Tropomyosin molecule associates with # Actin subunits
7
Tropomyosin’s location along the Actin filament is what dependent
Ca2+
Troponin does what filament by association with Actin and Tropomyosin
stabilizes
the largest protein known – 38000 amino acids
Titin
may prevent overstretching; positions myosins
Titin
Nebulin may determine the size of the what
sarcomere
what binds ATP and releases F-Actin
Myosin
if you stretched a relaxed myofibril, which bands/zones would NOT change in size?
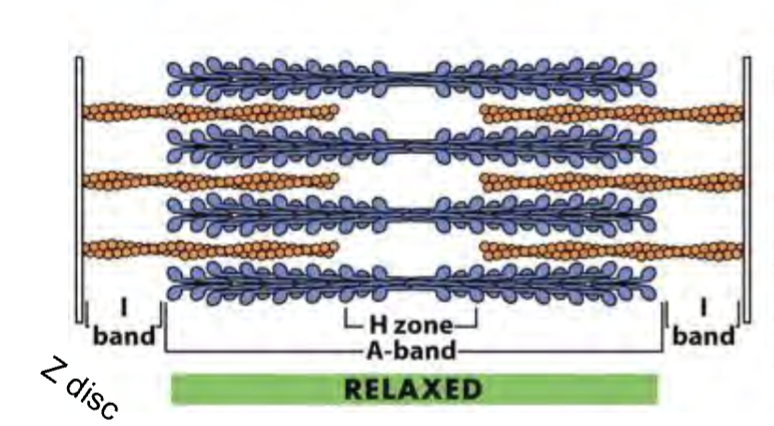
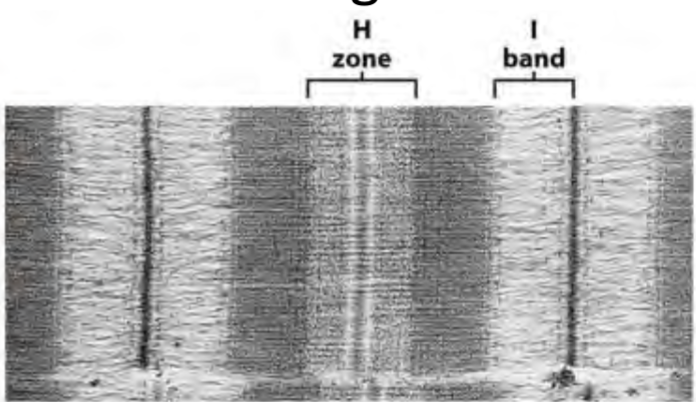
A band
in a stretched myofibril where sarcomeres are 50% longer, do you expect the contractile strength to be
reduced
for someone who was immobilized by the curse Petrificus Totalus, in which all the skeletal muscles stiffen, in which state would you expect most of the victim’s muscle myosin?
not bound to either ADP or ATP
motor neurons do what to a muscle at the neuromuscular junction
signal
impulse causes the sarcoplasmic reticulum to do what Ca2
release
high Ca2+ relocalizes Tropomyosin and allows what to bind Actin
Myosin
muscle contraction triggered by Ca++ release into what
cytosol