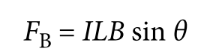MCAT Physics and Math - Electrostatics and Magnetism
1/41
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
Electrostatics
the study of stationary charges and the forces that are created by and which act upon these charges
proton
positively charged subatomic particle
electron
negatively charged subatomic particle
attractive forces
draw particles closer together, opposite signs
repulsive forces
push particles apart, same signs
ground
a means of returning charge to the earth
Static charge buildup/electricity
materials that are normally electrically neutral can acquire a net charge as result of friction; more significant in drier air because lower humidity makes it easier for charge to become and remain separated
coulomb (C)
SI unit of charge
fundamental unit of charge (e)
1.60 × 10−19 C
negative in electron, positive in proton
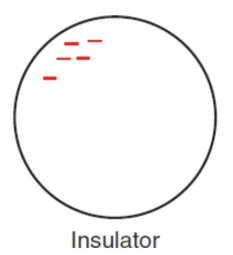
insulator
will not easly distribute a charge over its surface and will not transfer that charge to another neutral object very well; electrons tend to be closely linked with their respective nuclei
ex. most nonmetals
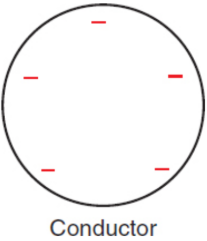
conductor
the charges will distribute approximately evenly upon the surface; able to transfer and transport charges and are oen used in circuits or electrochemical cells; nuclei surrounded by a sea of free electrons that are able to move rapidly throughout the material and are only loosely associated with the positive charges
ex. metals, ionic/electrolyte solutions
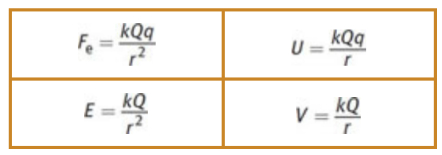
Coulomb’s law
quantifies the magnitude of the electrostatic force Fe between two charges
where Fe is the magnitude of the electrostatic force, k is Coulomb’s constant, q1 and q2 are the magnitudes of the two charges, and r is the distance between the charges
direction of the force may be obtained by remembering that unlike charges attract and like charges repel
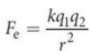
Coulomb’s/electrostatic constant (k)
depends on units
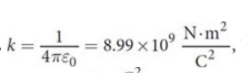
permittivity of free space (ε0)
a measure of how dense of an electric field is "permitted" to form in response to electric charges in a vacuum
8.8541878188(14)×10−12 F⋅m−1 (C2⋅kg−1⋅m−3⋅s2)
Electric fields
Every electric charge sets up; make their presence known by exerting forces on other charges that move into the space of the field; vector quantity
where E is the electric field magnitude in newtons per coulomb, Fe is the magnitude of the force felt by the test charge q, k is the electrostatic constant, Q is the source charge magnitude, and r is the distance between the charges
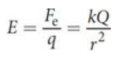
test charge
the charge placed in the electric field
source charge
creates the electric field
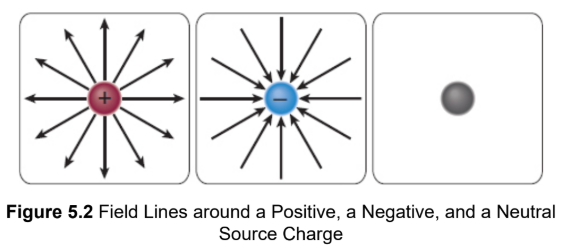
Field lines
imaginary lines that represent how a positive test charge would move in the presence of the source charge; drawn in the direction of the actual electric field vectors and also indicate the relative strength of the electric field at a given point; Where the field lines are closer together, the field is stronger; where the lines are farther apart, the field is weaker
electric potential energy.
a form of potential energy that is dependent on the relative position of one charge with respect to another charge or to a collection of charges
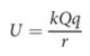
electric potential
the ratio of the magnitude of a charge’s electric potential energy to the magnitude of the charge itself
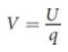
volts (V)
unit of electric potential, = J/C
Coulomb’s Law derivatives
From left to right, multiply by r; from top to bottom, divide by q
potential difference/voltage
exist between two points that are at different distances from the source charge
where Wab is the work needed to move a test charge q through an electric field from point a to point b.
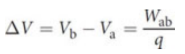
equipotential line
a line on which the potential at every point is the same; the potential difference between any two points is zero
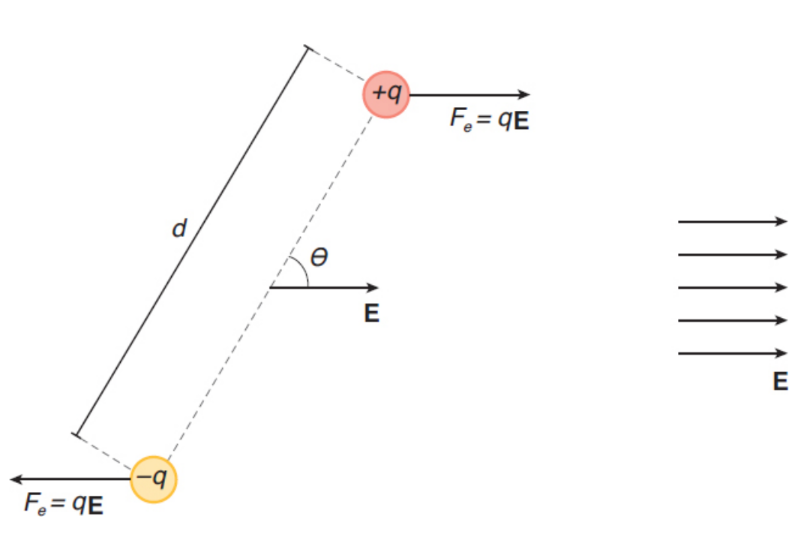
electric dipole
results from two equal and opposite charges being separated a small distance d from each other; transient or permanent
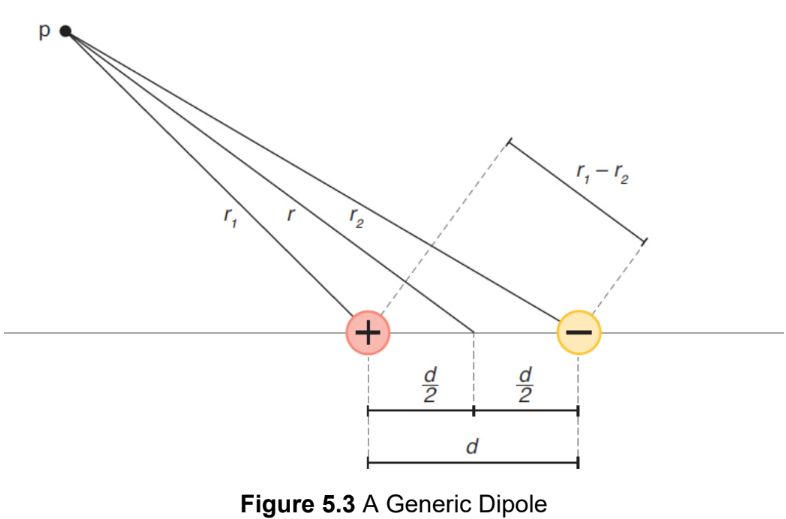
electric potential of dipoles
the scalar sum of the potentials due to each charge at that point
r1 - r2 ≈ d cos θ
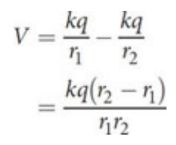
dipole moment (p)
product of charge and separation distance; SI units of C · m; vector from the negative charge toward the positive charge (chem: pos (w/ crosshatch) to neg)
p = qd
perpendicular bisector of the dipole
the plane that lies halfway between +q and –q; the electrical potential at any point along this plane is 0
electric field vectors at the points along the perpendicular bisector will point in the direction opposite to p
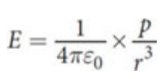
net torque about the center of the dipole axis
τ = pE sin θ
where p is the magnitude of the dipole moment (p = qd), E is the magnitude of the uniform external electric field, and θ is the angle the dipole moment makes with the electric field.
magnetic field
created by moving charge; may be set up by the movement of individual charges, by the mass movement of charge in the form of a current though a conductive material, or by permanent magnets
tesla (T)
the SI unit for magnetic field strength; N*s/m*C
gauss
1 T = 104 gauss
Diamagnetic materials
made of atoms with no unpaired electrons and that have no net magnetic field; slightly repelled by a magnet and so can be called weakly antimagnetic
ex. wood, plastics, water, glass, and skin
Paramagnetic materials
unpaired electrons; weakly magnetized in the presence of an external magnetic field, aligning the magnetic dipoles of the material with the external field; Upon removal of the external field, individual magnetic dipoles to reorient randomly.
ex. aluminum, copper, and gold
Ferromagnetic materials
unpaired electrons and permanent atomic magnetic dipoles that are normally oriented randomly; become strongly magnetized when exposed to a magnetic field or under certain temperatures; Field lines exit the north pole and enter the south pole
ex. iron, nickel, and cobalt
infinitely long and straight current-carrying wire magnet
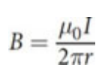
permeability of free space (μ0)
1.25663706127(20)×10−6 kg⋅m⋅s−2⋅A−2
right-hand rule
Point your thumb in the direction of the current and wrap your fingers around the current-carrying wire. Your fingers then mimic the circular field lines, curling around the wire.
To determine the direction of the magnetic force on a moving charge, first position your right thumb in the direction of the velocity vector. Then, put your fingers in the direction of the magnetic field lines. Your palm will point in the direction of the force vector for a positive charge, whereas the back of your hand will point in the direction of the force vector for a negative charge.
circular loop of current-carrying wire magnet
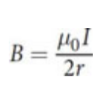
Lorentz force
the sum of electrostatic and magnetic forces
magnetic force
where q is the charge, v is the magnitude of its velocity, B is the magnitude of the magnetic field, and θ is the smallest angle between the velocity vector v and the magnetic field vector B; perpendicular component
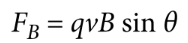
Force on a Current-Carrying Wire
where I is the current, L is the length of the wire in the field, B is the magnitude of the magnetic field, and θ is the angle between L and B.