Sports Psych
1/91
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
92 Terms
Anxiety
Negative emotional state caused because a situation is threatening
Trait anxiety + Inheritance
Easily become anxious - Genetically inherited
State anxiety
Situational
Competitive trait anxiety
Competitive situations as threatening
Stress
Negative psychological state + physiological responses where people perceive threats to wellbeing
Eustress
Positive - feeling of fulfilment + arousal
Distress
Negative - causes anxiety + apprehension
Stressors
Factors or situations which cause stress
When can stress cause anxiety
If stressor is bigger than ability
Stress process - Positive
Challenging
Increased motivation + energy
Increased performance
Stress process - Negative
Threatening
Increased anxiety
Decreased performance
Controlling cognitive anxiety (3)
Positive self talk
Imagery
Goal setting
Somatic ways controlling negative anxiety
PMR
Breathing control (centring)
Biofeedback
Personality
A persons unique patterns of traits
Eysenck’s trait theory
Placed on 2 contniua
Stable to neurotic
Extrovert to intovert
Social learning theory
DARMMM - Personality changes according to environment
DARMMM
Demonstration
Attention
Retention
Motor reproduction
Motivation
Matching performance
Interactionist approach to behaviour
B = F(PE)
BEHAVIOUR is a FUNCTION of a PERSON interacting with their ENVIRONMENT
Interactionist effect in strong situation
Environment dictates behaviour
Interactionist effect in weak situation
Personality traits dictate behaviour
Advantages of tests (1)
Cheap + Quick
Disadvantages of tests
Lying to create good impression
Responses change due to circumstances
Advantages of observation to measure personality
Subject tested in actual setting
Disadvantages of observation to measure personality
Know they are being watched so change
Different behaviours evaluated differently between observers
Difficult to gauge what is going on internally
Advantages of interview
In depth interactive understanding
Disadvantages of interviewing
Time consuming
May lie
Nerves may cause obscured results
Atkinson’s theory of achievement motivation
Individual’s drive to achieve success for its own sake
Desire to succeed - fear of failure
Factors affecting achievement motivation
Task difficulty
Incentive value of success
Motivation
The internal mechanisms and external stimuli which arouse and direct our behaviour
Negative effect of motivation
Too much extrinsic + tangible lead to loss in value and often lead to deviance
Goal setting
What a performer is trying to achieve in the future
Outcome goals
Concerned with end result
Performance goals
Related to behaviour / comparison of previous performance
Process oriented goals
How to become a successful team
SMART Goals
Specific
Measurable
Achievable
Realistic
Time bound
Agression
Any form of behaviour towards the goal of harming / injuring another being
Hostile agression
Primary intention to cause harm - outside the rules
Channelled agression
Behaviour that causes harm yet for a different aim / reason - outside the rules
Assertive behaviour
No intention to cause harm - Competitive drive within the rules
Instinct theory - aggression
Pent up aggression is released in a respectable way - CATHARSIS (cleansing the soul)
Social learning theory - links to aggression
Aggression is learned through observation
Frustration aggression theory
Blocking of goals leads to aggression
Aggressive cue hypothesis
Frustration leads to aggression
Because of socially learned cues or stimuli detected
Social facilitation
The influence of the presence of others on performance
Zajonc’s 4 types of audience
Audience
Co-actors
Competitors
Supporters
Zajonc’s theory on cognitive learners
Social inhibition
Zajonc’s theory on autonomous learners
Social facilitation
Zajonc’s theory on simple tasks
Social facilitation
Zajonc’s theory on complex tasks
Social inhibition
Zajonc’s link to drive theory
Presence of others leads to dominant response
Evaluation apprehension
Cottrell - Sense of anxiety caused by the feeling of being judged
Limitation to evaluation apprehension
Only experienced increased arousal if they perceive they are being evaluated
Attitude
Evaluation, positive or negative of people objects and ideas
Components of the triadic model
Cognitive - Beliefs
Affective - Feelings
Behavioural - Behaviour
Factors that influence attitudes (3)
Experience
Observation
Social roles / norms
Measuring attitudes
Questionnaire
Physiological tests
Interview
Observation
Elements in persuasive communication theory
Message - Clear and appropriate
Recipients - Need to want change
Situation - Time and place
Persuader - High status
Cognitive dissonance
When all 3 CAB elements are negative - coach will apply pressure to change one to positive
This causes dissonance
May cause the player to change the other elements
Groups
2 or more people who interact and influence each other
Characteristics of a group (6, I’s)
Interaction
Identity
Interpersonal relationships
Interdependence
Independence from other groups
Identical goals
Stages of group development (4)
Tuckman
Forming
Storming
Norming
Performing
Cohesion (Carron)
Groups stick together and unite in pursuit of its goals and objectives
Task cohesion
Where a team works together to achieve their goals or an end result
Social cohesion
Teams socialising together to build personal relationships
Carrons model of cohesion (PETL)
Personal
Environmental
Team
Leadership
Steiners model of group performance
Actual productivity = Potential productivity - Losses due to faulty processes
2 types of faulty processes
Motivation faults
Coordination faults
Ringleman effect
Average individual performances deceases with an increase in group size
Social loafing
Loss of motivation by an individual from a team
Group definition + Person
Barron
Process of influencing individuals and groups towards a set goal
Autocratic leaders
Dictatorship
Strong discipline
Useful in very favourable/unfavourable situations
Democratic leaders
Take into account other members
Person orientated
Moderately favourable situations
Laissez faire leaders
Figurehead
No leadership
Just get on with their stuff
Prescribed vs emergent leaders
Given authority
Leaders emerge from the group
Theories of leadership (3)
Great man theory
Social learning theory
Interactionist approach
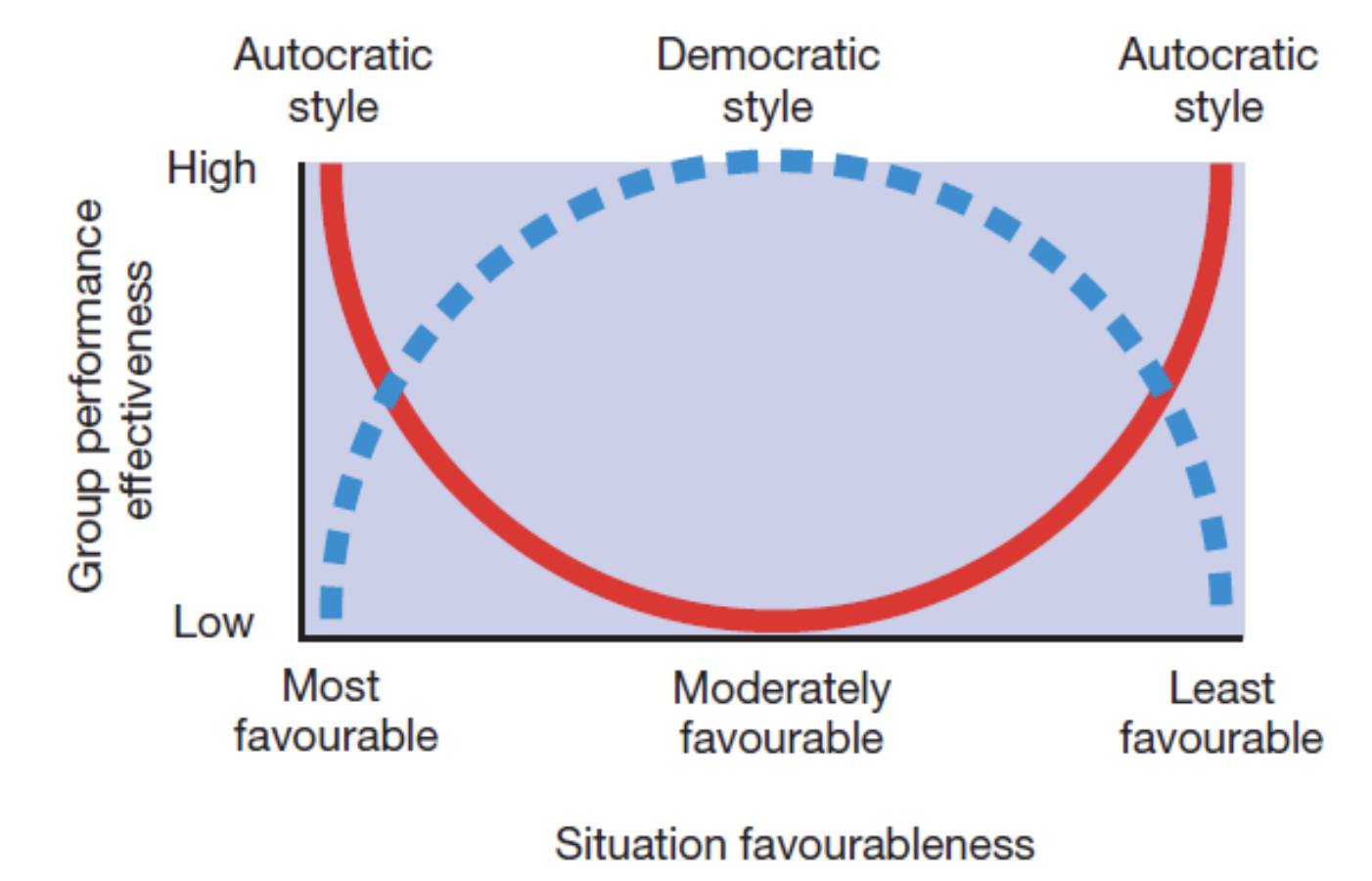
Fielders Contingency model
Task orientated approach in very un/favourable situations
Person orientated approach in moderately favourable
Chelladurai’s model (SLM RAP) + outcome
Characteristics - Behaviour
Situation - Required
Leader - Actual
Members - Preferred
Performance + satisfaction
Self confidence
General belief they can meet the demands of a situation
Self efficacy
Belief in ones ability in relation to a specific task in a specific situation
(situation specific self confidence)
What will self efficacy determine (3)
Choice of activity
Level of effort
Degree of persistence
Bandura’s theory of self efficacy
PAVE the way for the VP of the EA
Performance accomplishments
Vicarious experiences (modelling)
Verbal pursuasion
Emotional arousal
Attribution theory
Weiner - achievement is linked o the attribution we make:
Effort
Ability
Task difficulty
Luck
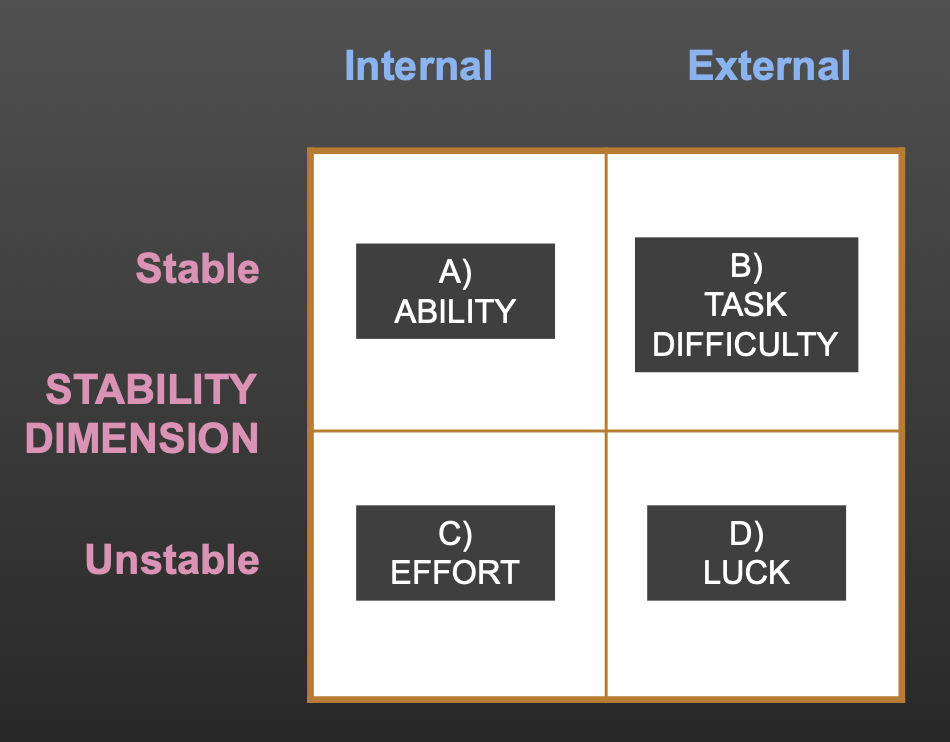
Weiners model of attribution
Locus of causality dimension - Internal or external
Stability dimension - is it changeable in short term
Self serving bias
Correct use of of attribution to increase confidence and self efficacy
Success due to internal reasons
Failures due to external
Learned helplessness
Performers see failure as inevitable
Failure due to internal
Success due to external
What do NACH personalities more likely refer to in terms of attribution
Self serving bias
What do NAF personalities most likely refer to in terms of attribution
Learned helplessness
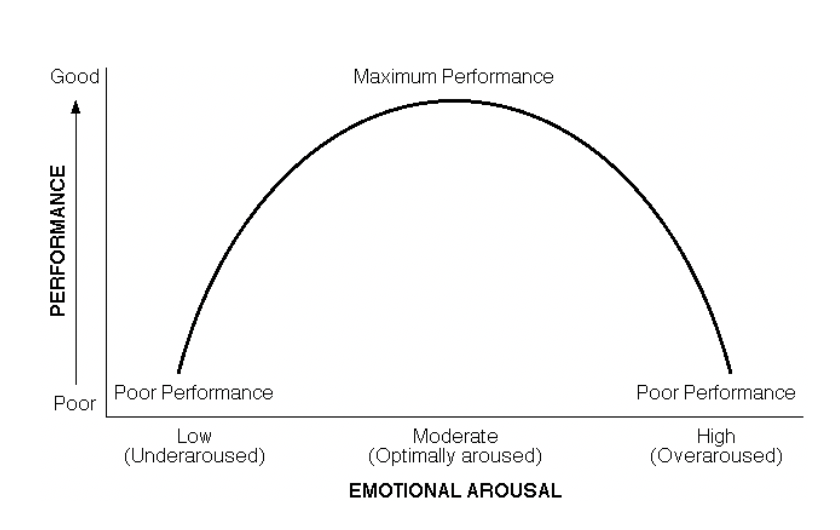
Arousal
State of alertness of an individual to perform a task on a continuum from deep sleep to extreme excitement
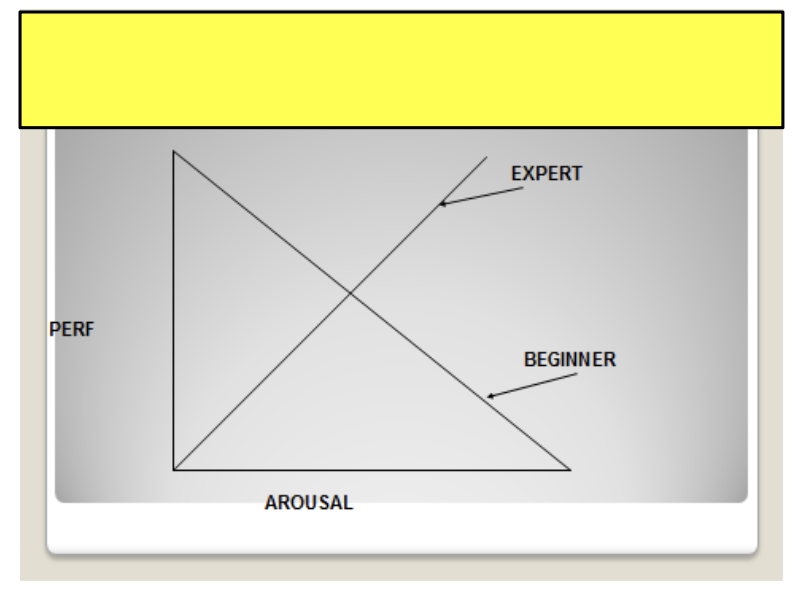
Hulls drive theory
As arousal increases, athletes dominant response occurs
Things that shift inverted U theory
Type of skill
Level of performer
Personality of performer
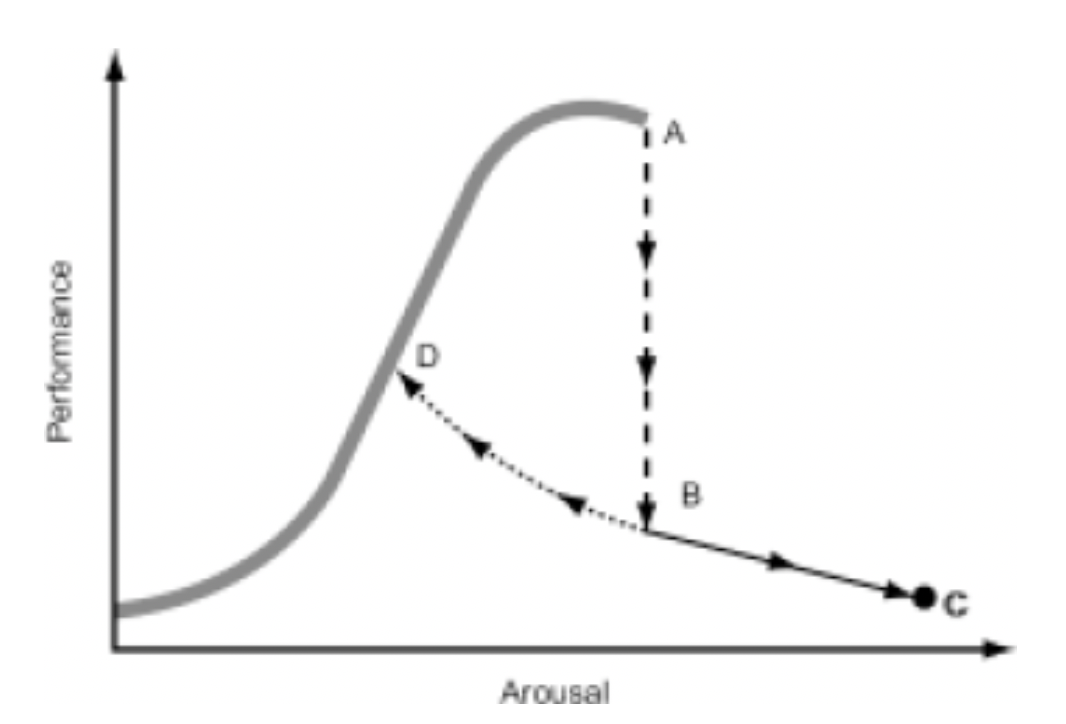
Catastrophe theory
When catastrophe happens, an athlete can either reduce arousal and go back to (D) or lose more control and performance deteriorate further