Bio 164: Urogential anatomy
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/55
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 3:45 PM on 2/20/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
1
New cards
scrotum
the sac that holds the testes
2
New cards
testis (pleural testes)
the organs that make sperm cells
3
New cards
epididymis
the series of hollow tubes that stores mature sperm cells
4
New cards
ductus (vas) deferens
the tubes sperm cells travel through during ejaculation, before the urethra. The sperm cells are suspended in salt water solution.
5
New cards
seminal vesicle
this gland secretes a sticky yellowish/whitish fluid which makes up about 60% of semen. The fluid enters the urethra via the ejaculatory ducts
6
New cards
urethra
transports urine from the bladder the outside of the body, and also transport semen from the reproductive organs to the outside of the body
7
New cards
ejaculatory duct
small paired tubes that carry sperm from the vas deferens and fluid from seminal vesicles into the urethra, they pass through the prostate gland.
8
New cards
bulbourethral gland
during arousal this gland secretes a small amount of slippery fluid into the urethra to neutralize any acidic urine and lubricate the glands
9
New cards
prostate gland
this gland secretes a thin, milky white fluid, which makes up about 30% of semen. This fluid enters the urethra as it passes through the prostate.
10
New cards
penis
made of 3 spongy tissue layers
* the paired corpora cavernosa
* single corpus spongiosum
* the paired corpora cavernosa
* single corpus spongiosum
11
New cards
glans of the penis
sometimes called the head, covered by a layer of skin called the foreskin.
12
New cards
bladder
the hollow sac that stores the urine formed in the kidney
13
New cards
spermatic cord
made up from ductus deferens, the testicular artery, and testicular veins. Travels from the testis of the scrotum, through the inguinal canal and into the abdominal cavity
14
New cards
ovary
the organ that makes oocytes (egg cells)
15
New cards
uterine tube
transports ovulated oocytes from the ovary to the uterus
16
New cards
uterus
a hollow structure that contains a thick layer of smooth muscle, and endometrium. Located in the pelvic cavity, but will expand into the abdominal cavity during pregnancy
17
New cards
myometrium
smooth muscle in the uterus
18
New cards
endometrium
tissue lining the smooth muscle in the uterus
19
New cards
fundus
the dome shaped superior aspect of the uterus
20
New cards
cervix
the narrow muscular opening to the uterus containing a sticky mucus to prevent the passage of bacteria and pathogens
21
New cards
broad ligament of the uterus
the “ligament” that is a fold of peritoneum that covers and supports the uterus
22
New cards
vagina
the hollow muscular tube that connects the uterus to the outside world, the external opening the vaginal canal is called the vaginal orifice
23
New cards
urethral opening
the walls of the vaginal canal secrete a fluid that lubricates the canal and orifice during sexual arousal
24
New cards
labia minora
two thin folds of skin that enclose the vaginal orifice and urethral opening
25
New cards
labia majora
two thicker folds of skin that enclose the labia minor and the glans of the clitoris
26
New cards
glans of the clitoris
structure containing a spongy erectile tissue
27
New cards
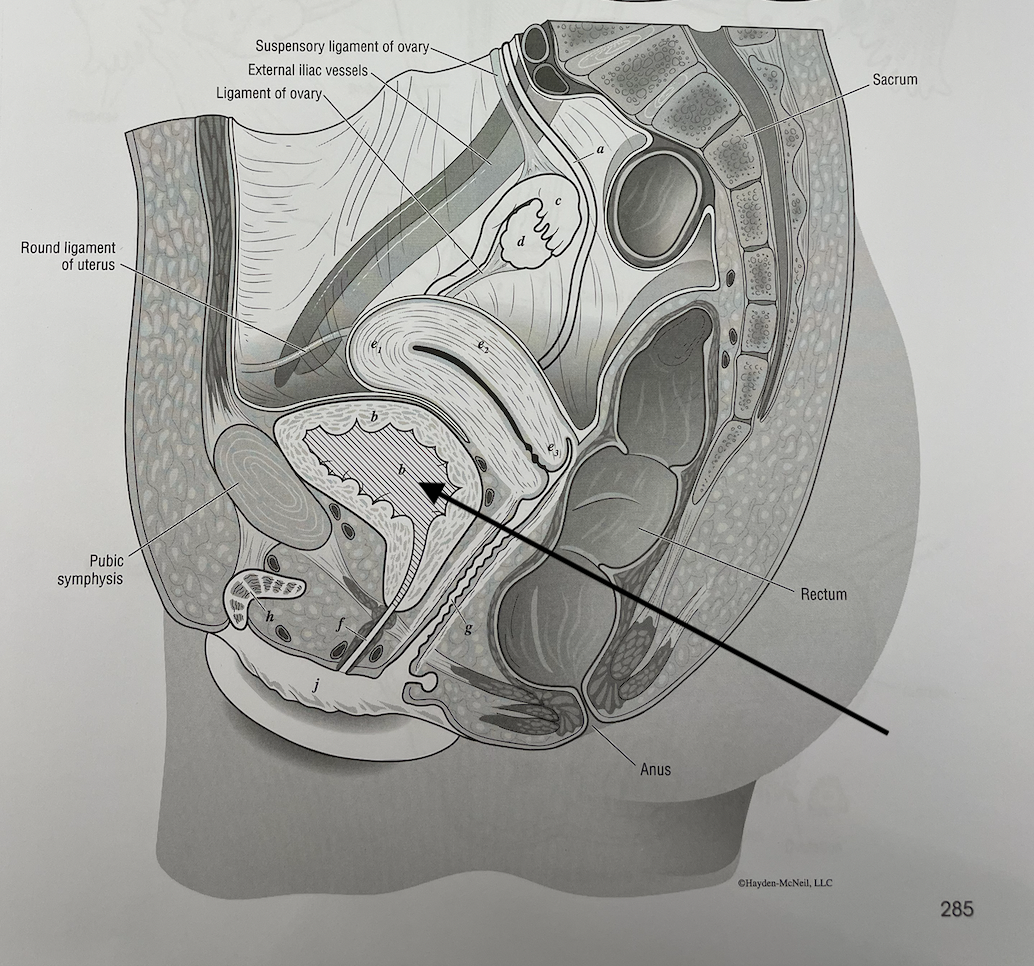
what structure is this
urinary bladder
28
New cards
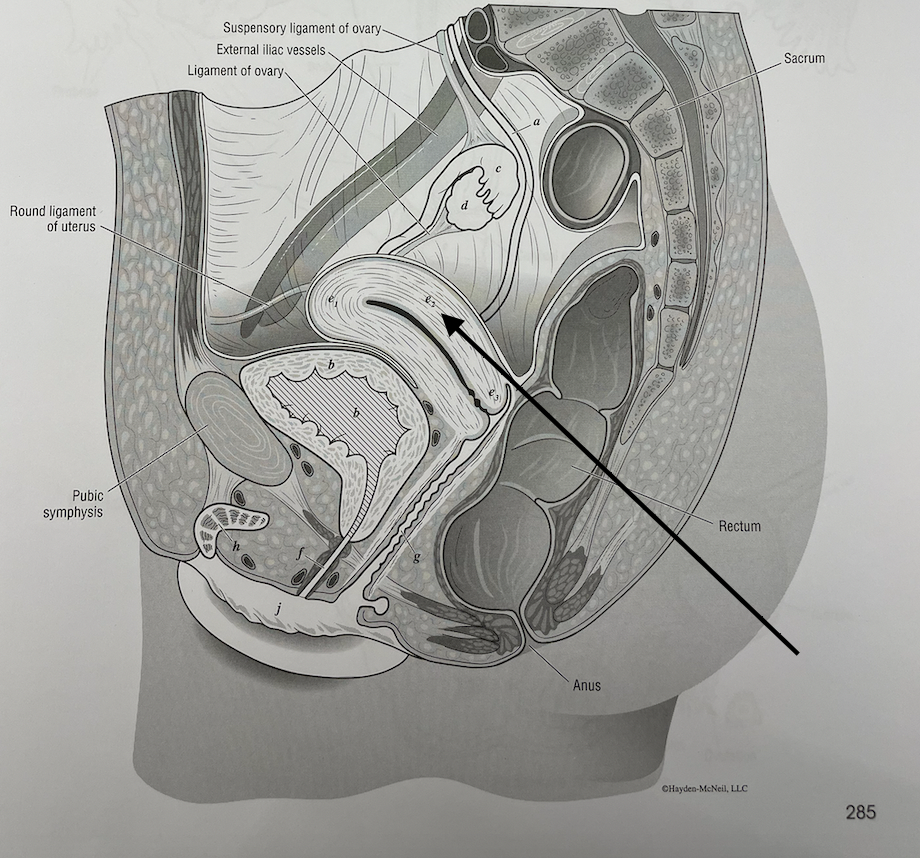
what structure is this
body of the uterus
29
New cards
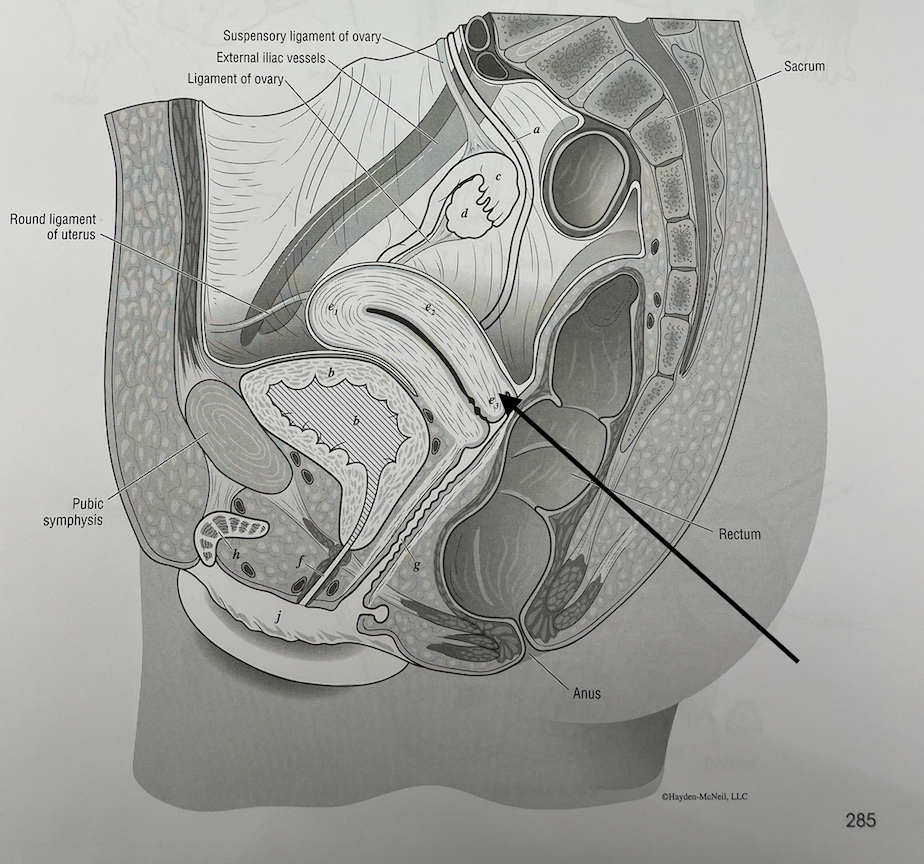
what structure is this
cervix of the uterus
30
New cards
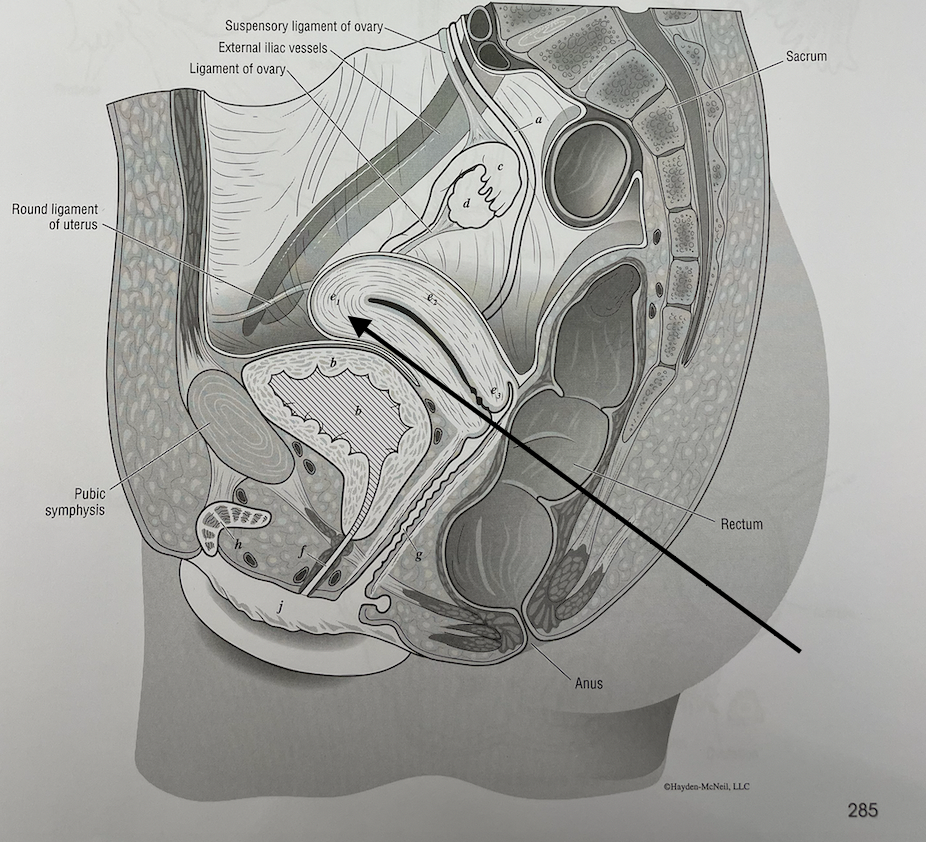
what structure is this
fondus of the uterus
31
New cards
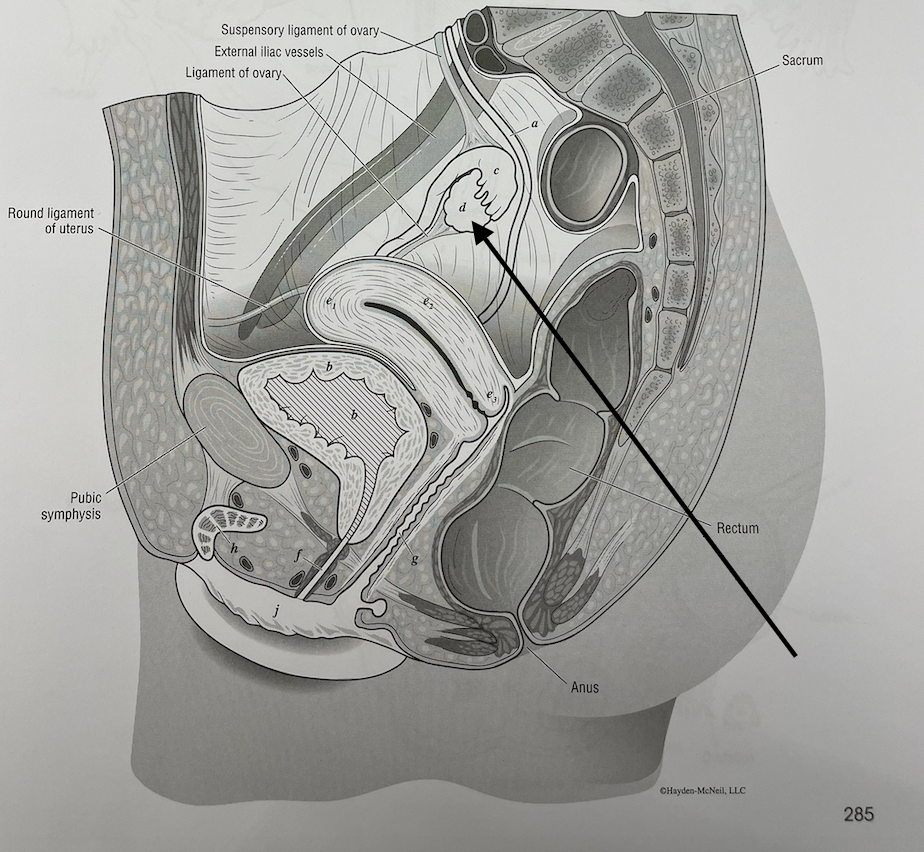
what structure is this
ovary
32
New cards
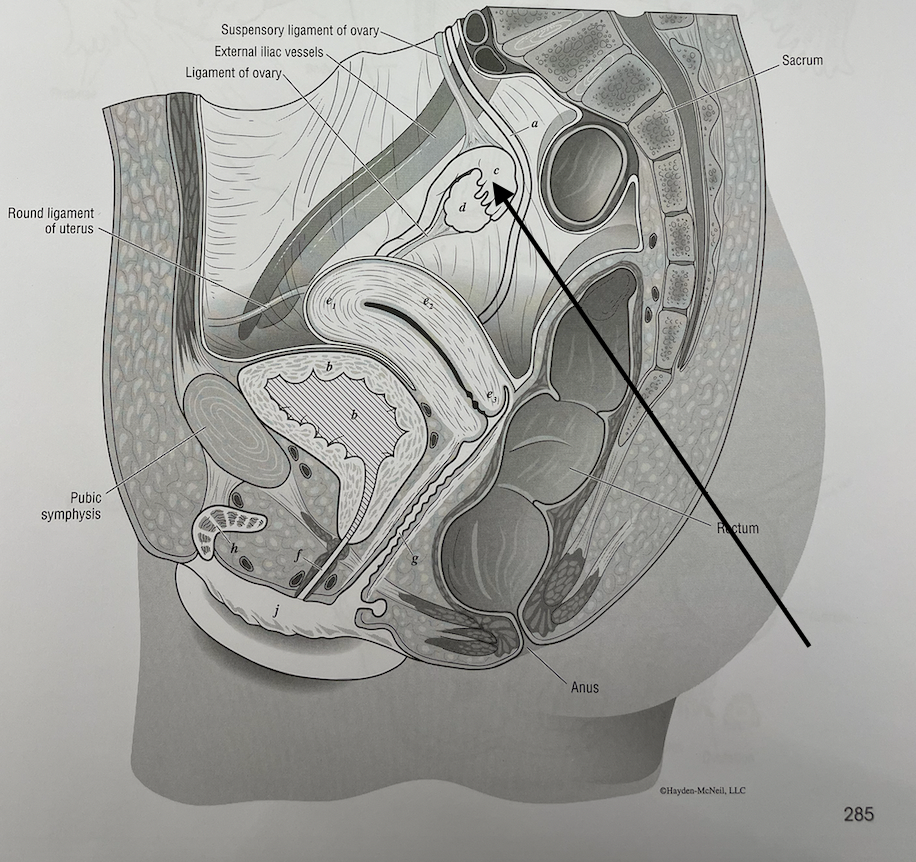
what structure is this
the Fallopian tube
33
New cards
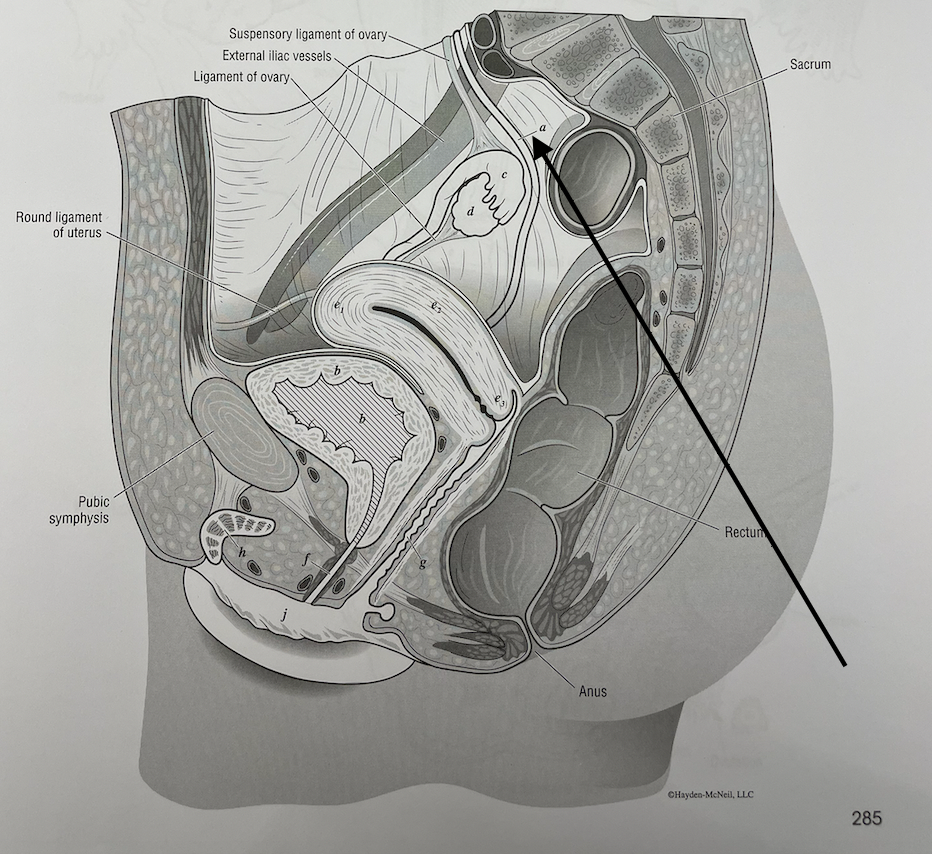
what structure is this
ureter
34
New cards
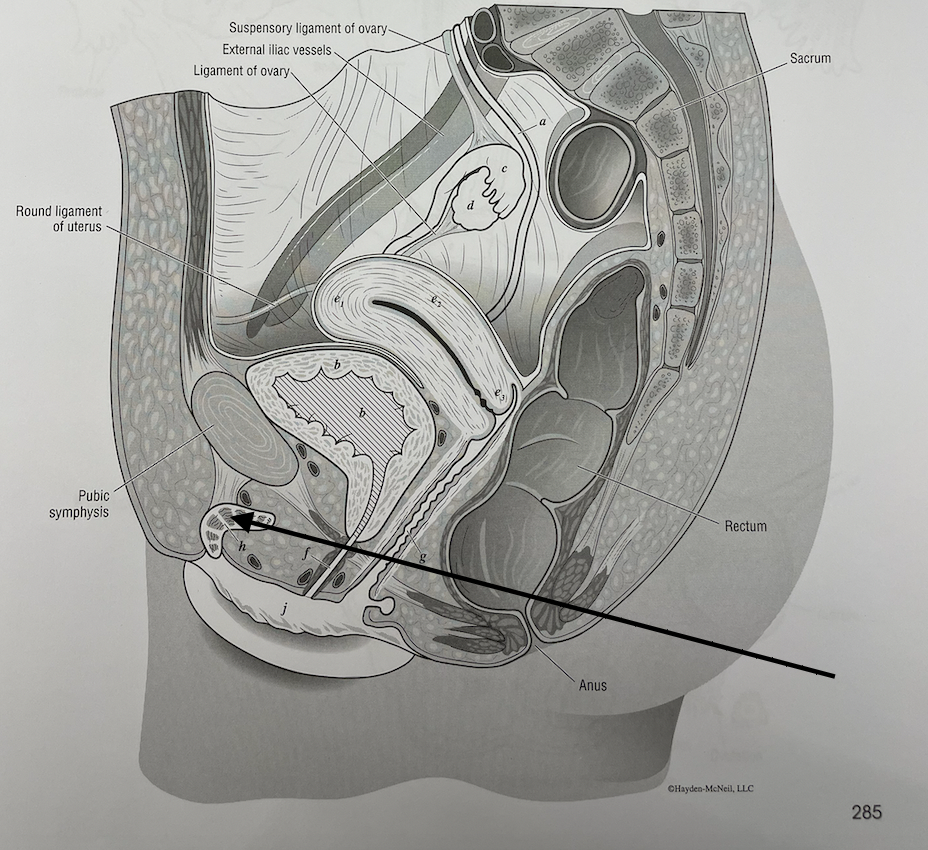
what structure is this
clitoris
35
New cards
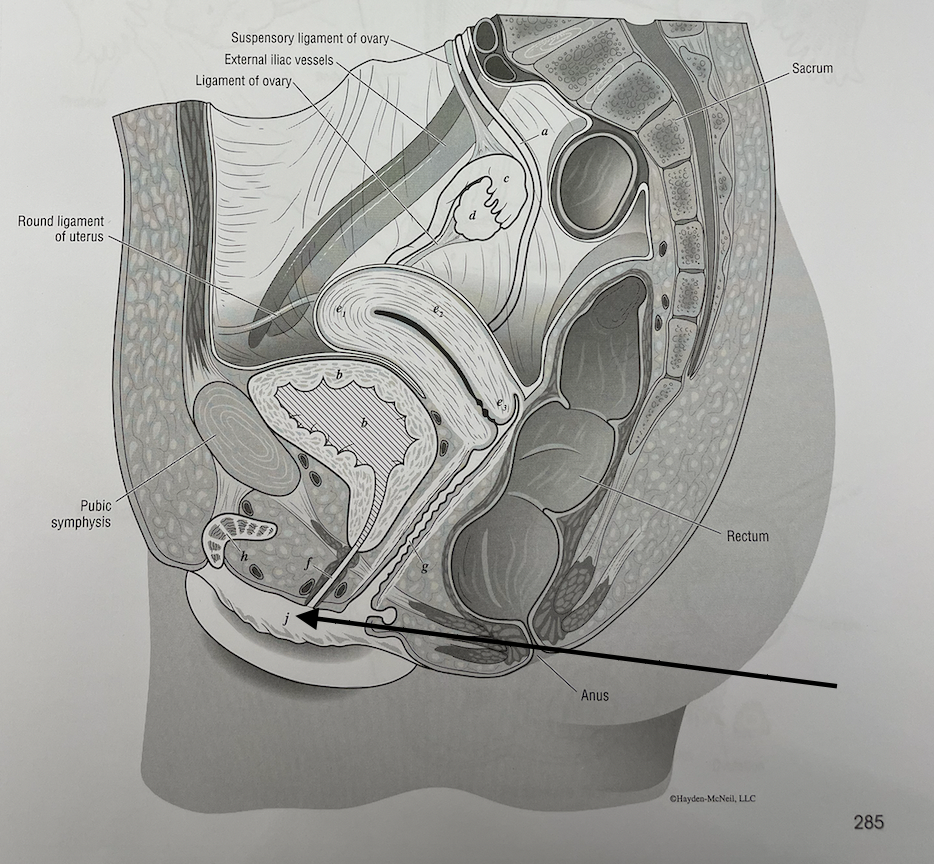
what structure is this
labia minora
36
New cards
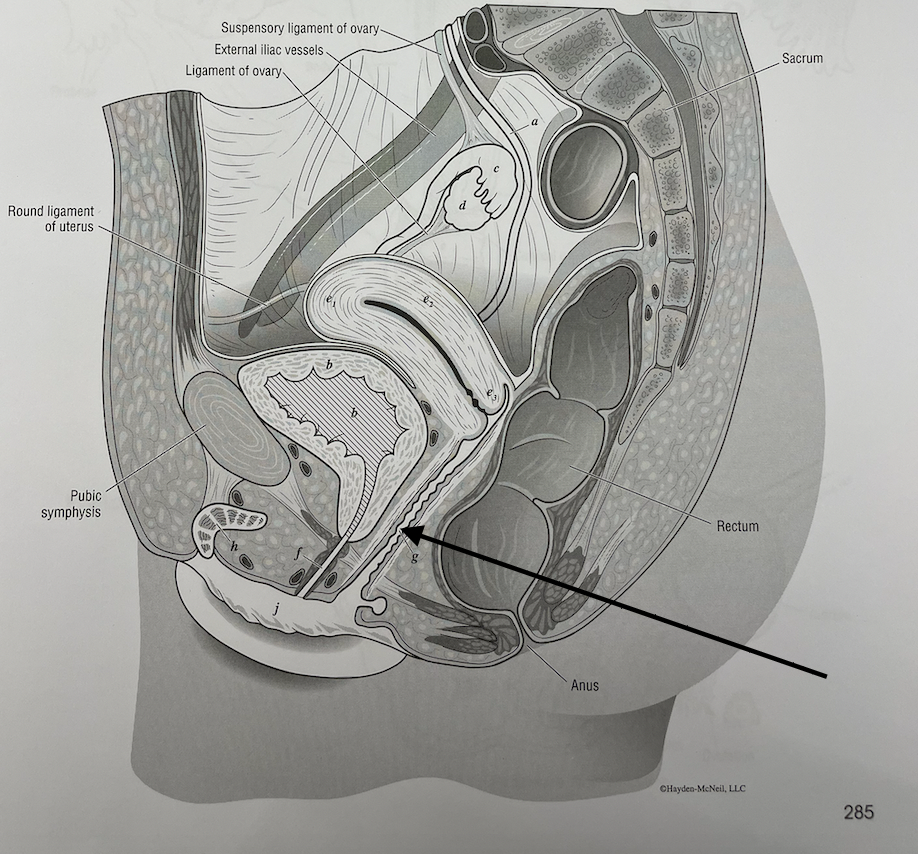
what structure is this
vagina
37
New cards
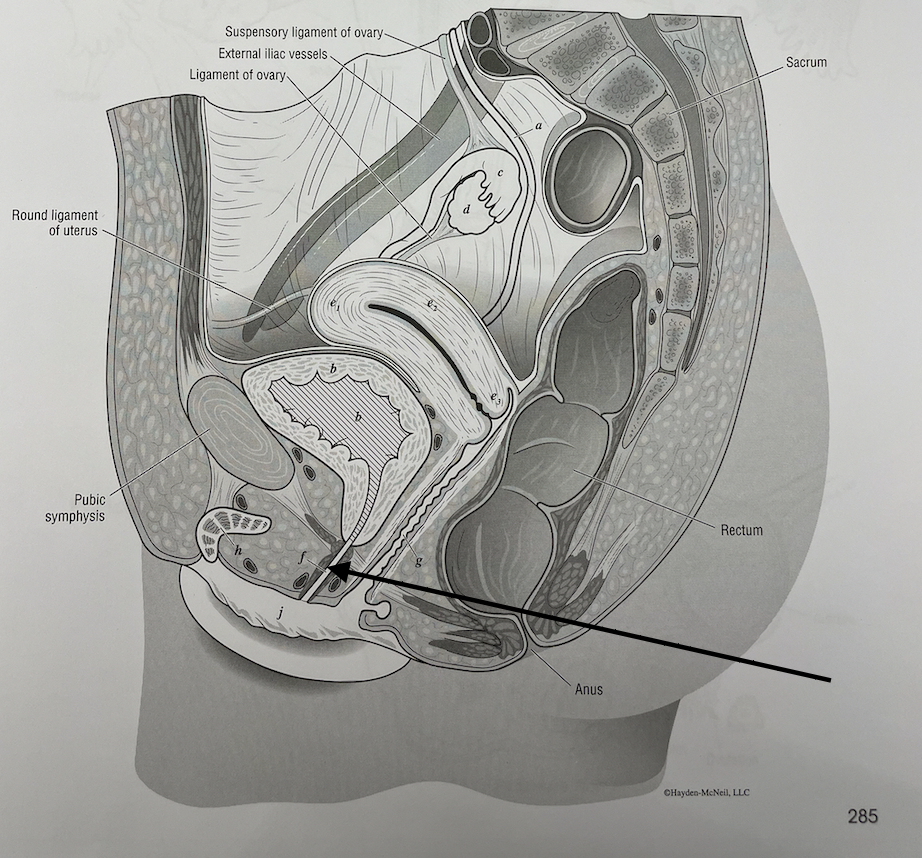
what structure is this
urethra
38
New cards
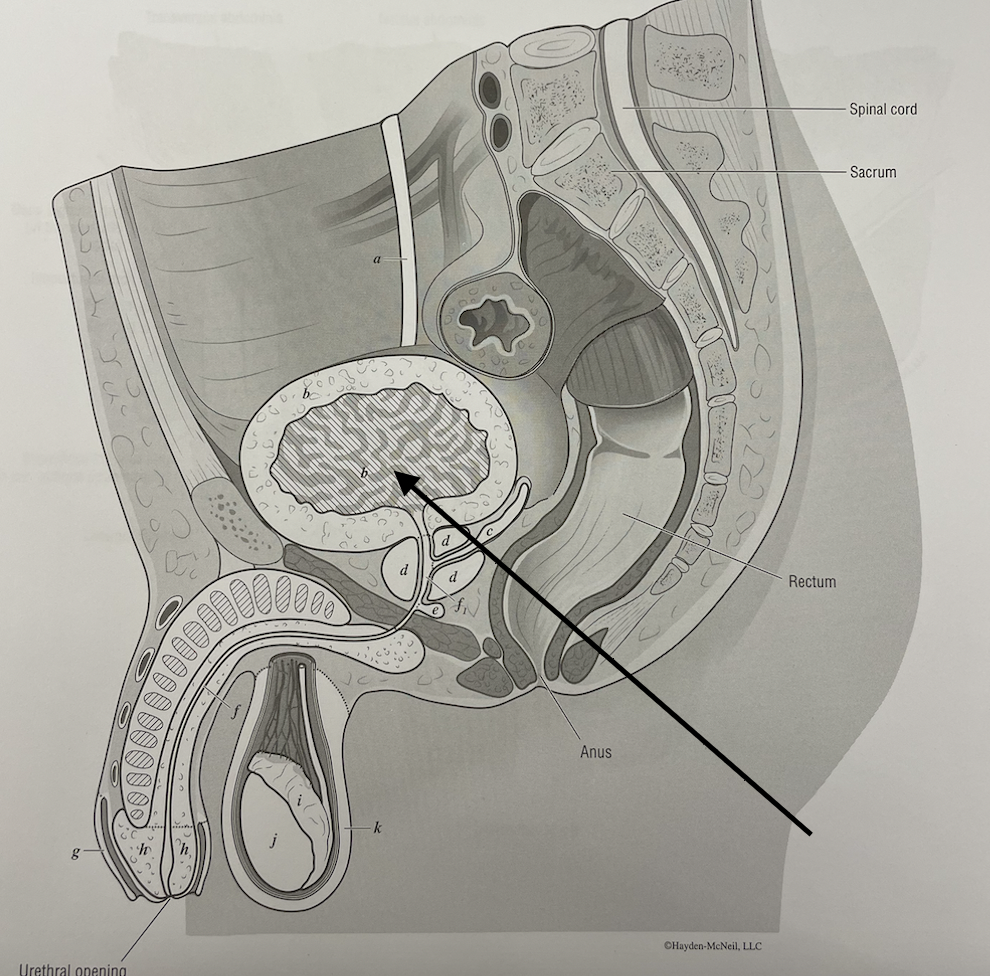
what structure is this
urinary bladder
39
New cards
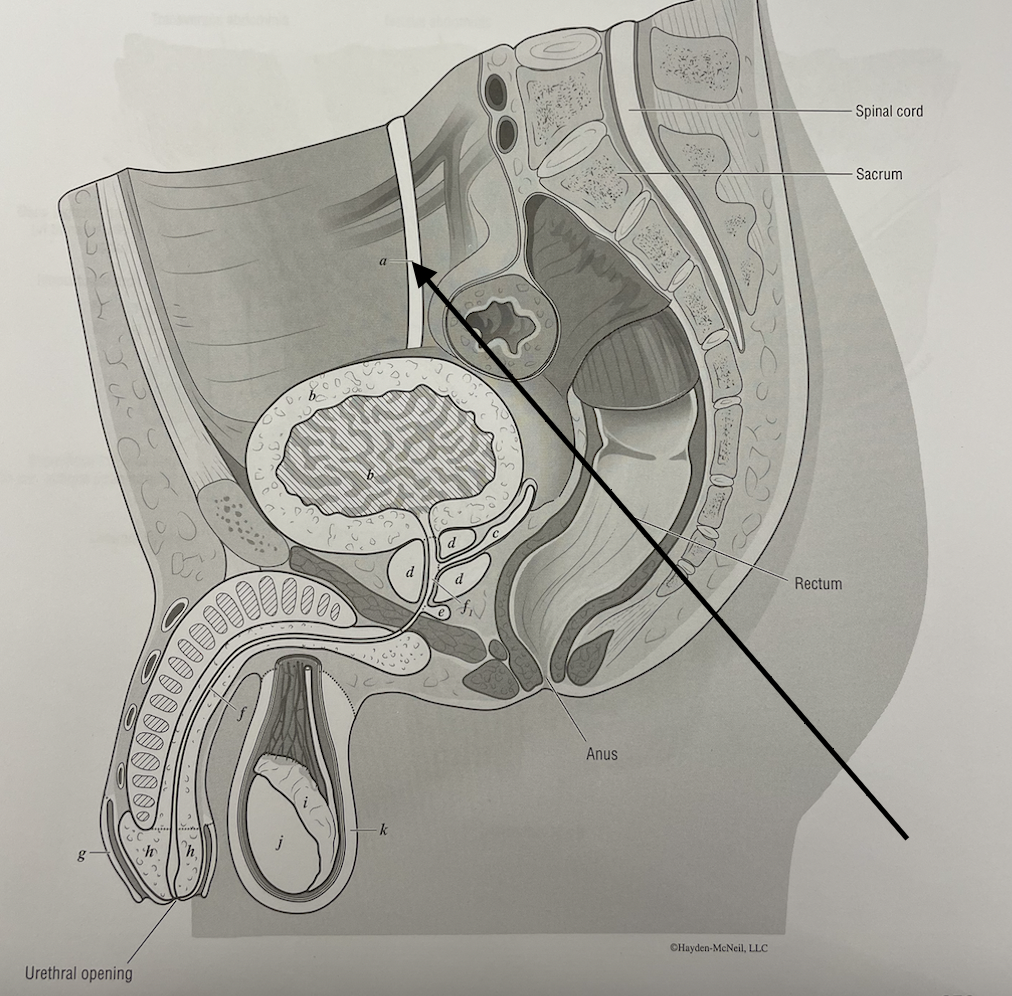
what structure is this
ureter
40
New cards
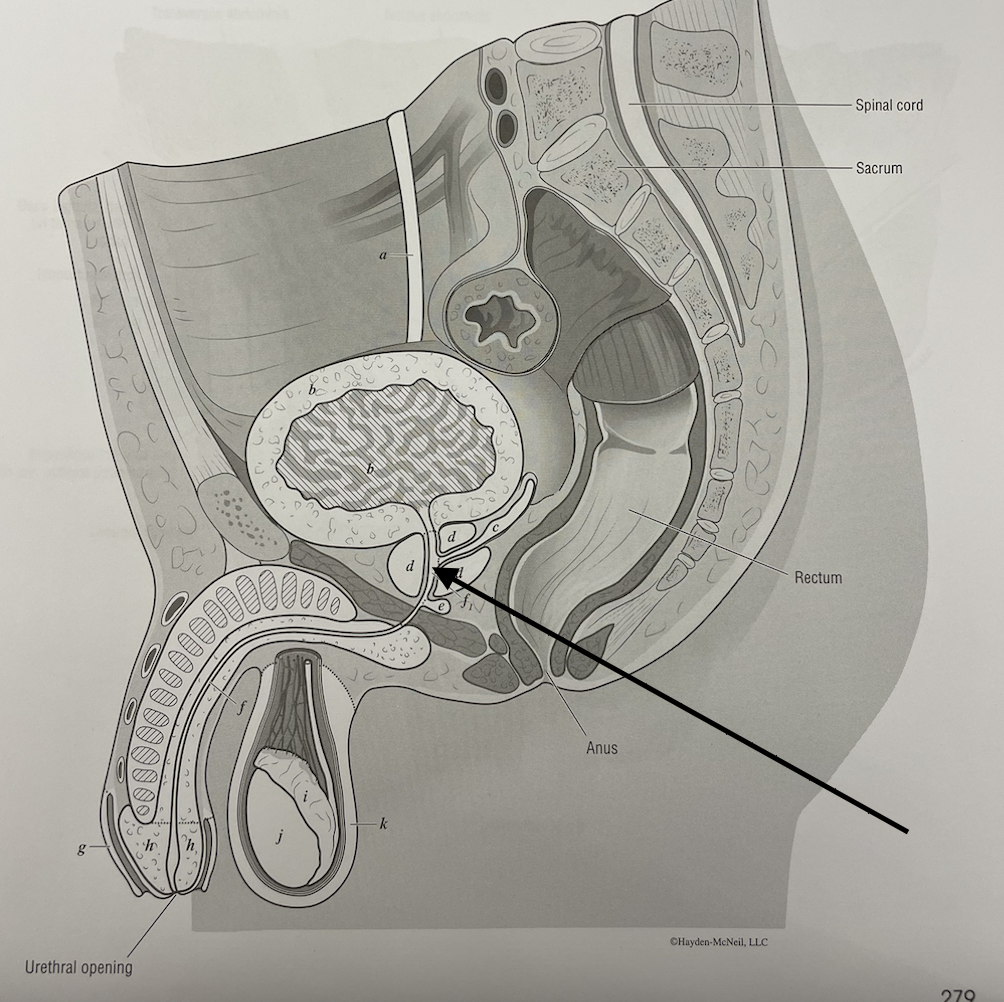
what structure is this
intermediate part of the urethra
41
New cards
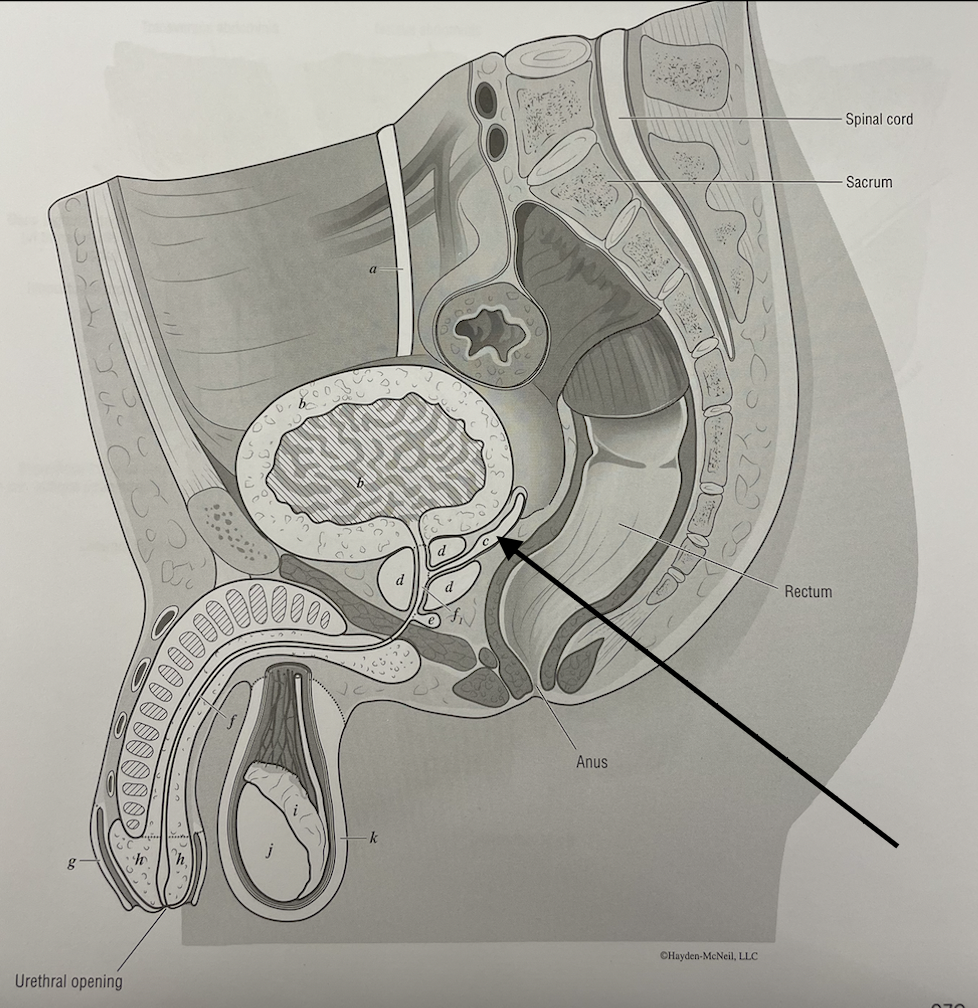
what structure is this
seminal gland
42
New cards
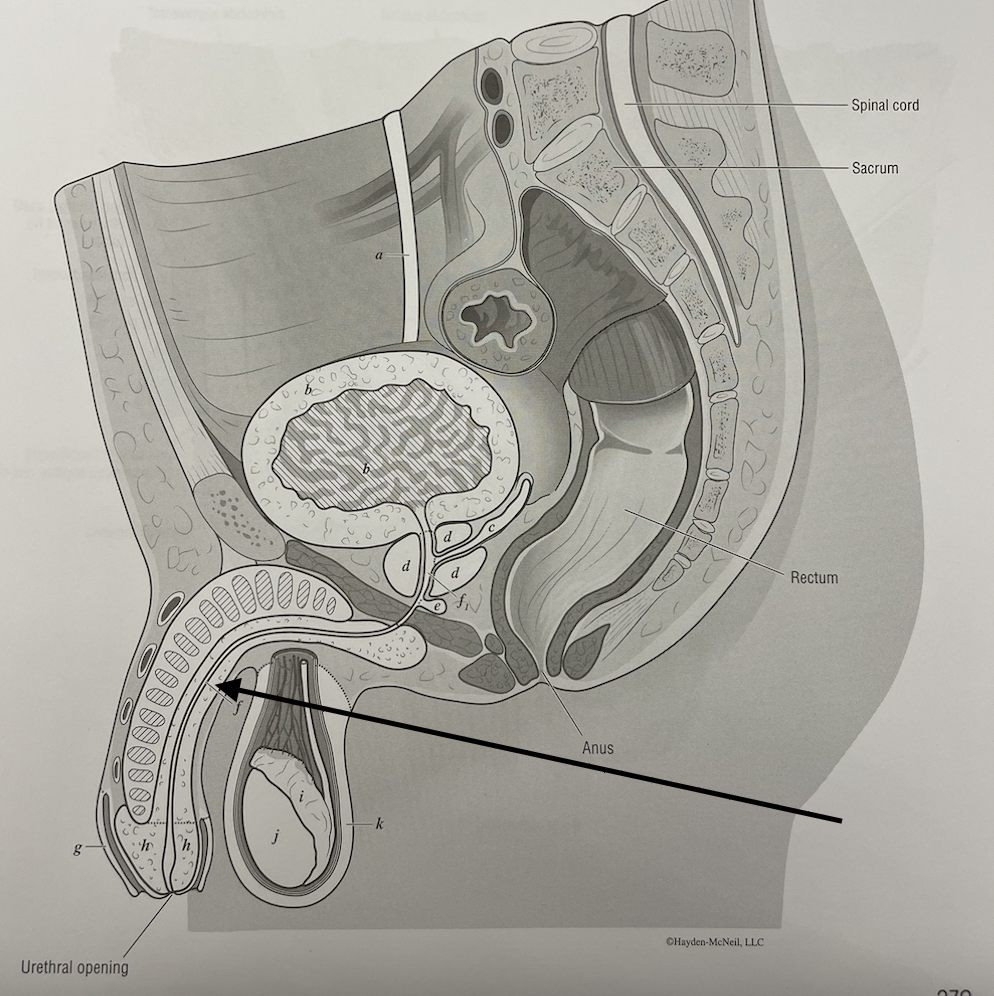
what structure is this
urethra
43
New cards
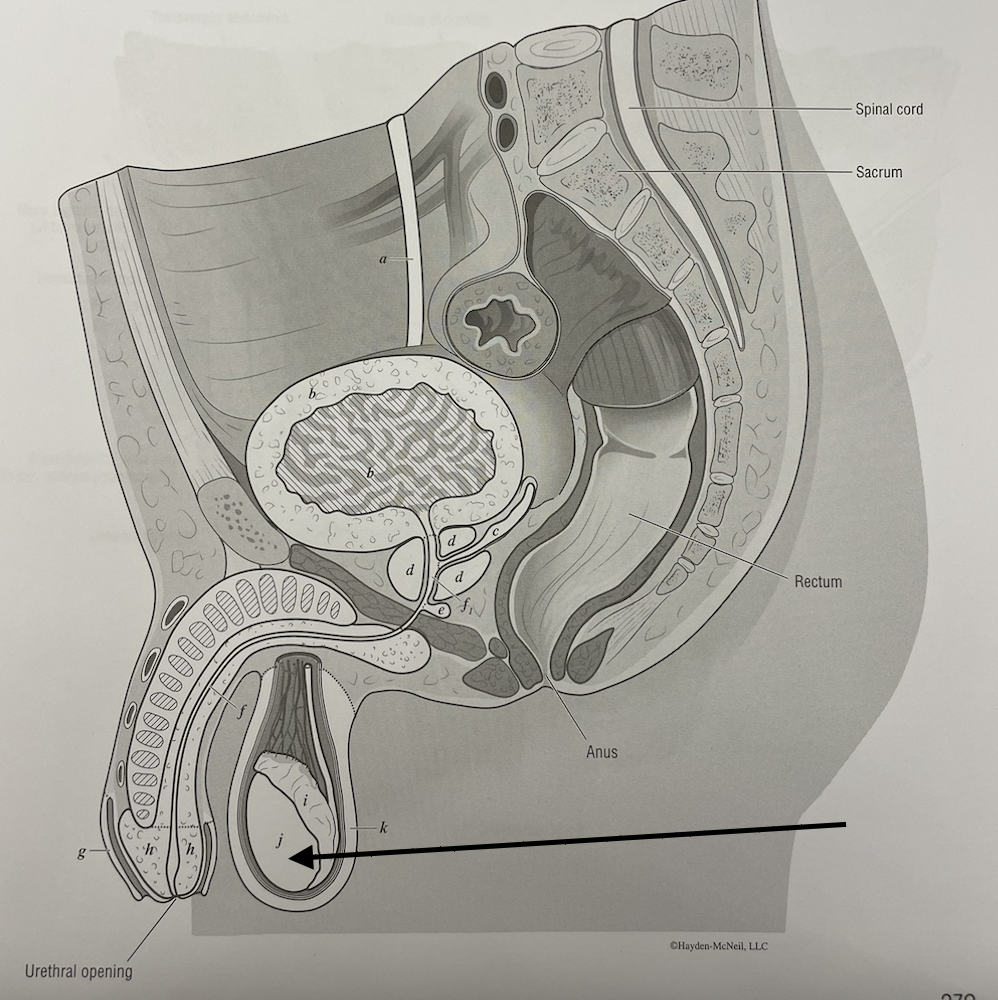
what structure is this
testis
44
New cards
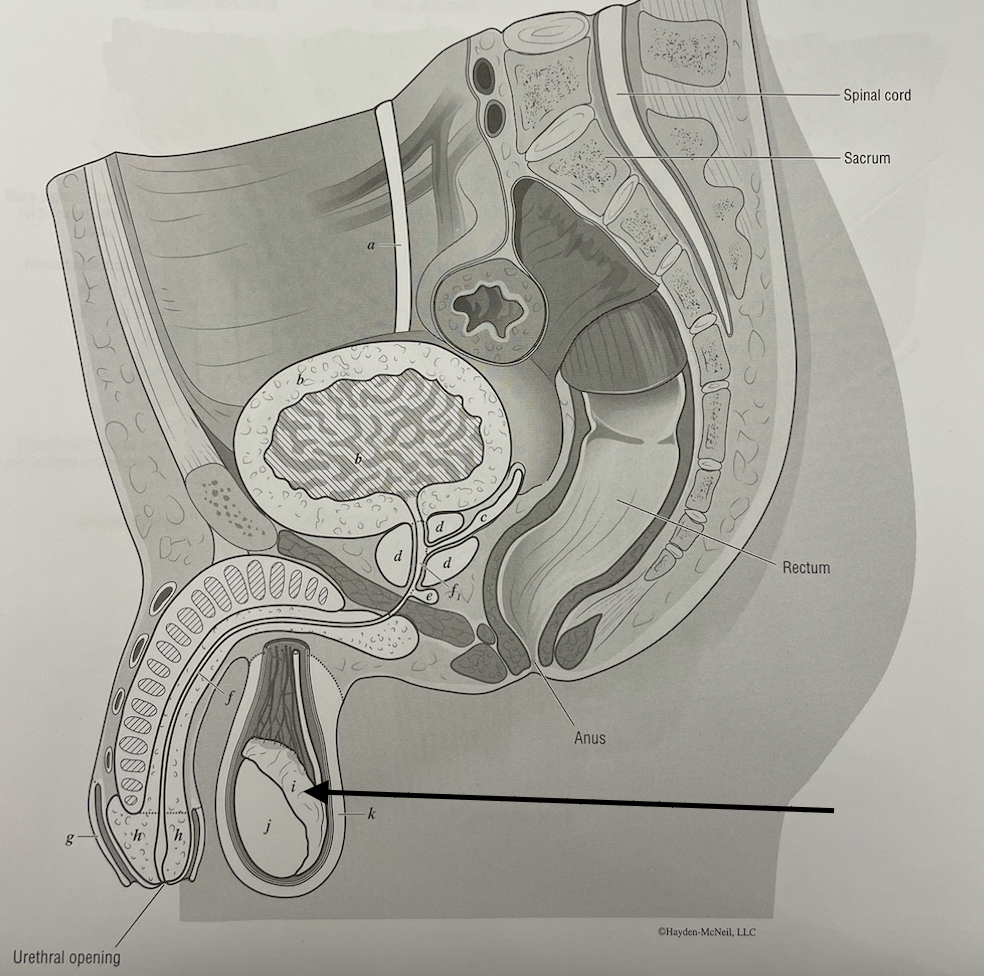
what structure is this
epididymis
45
New cards
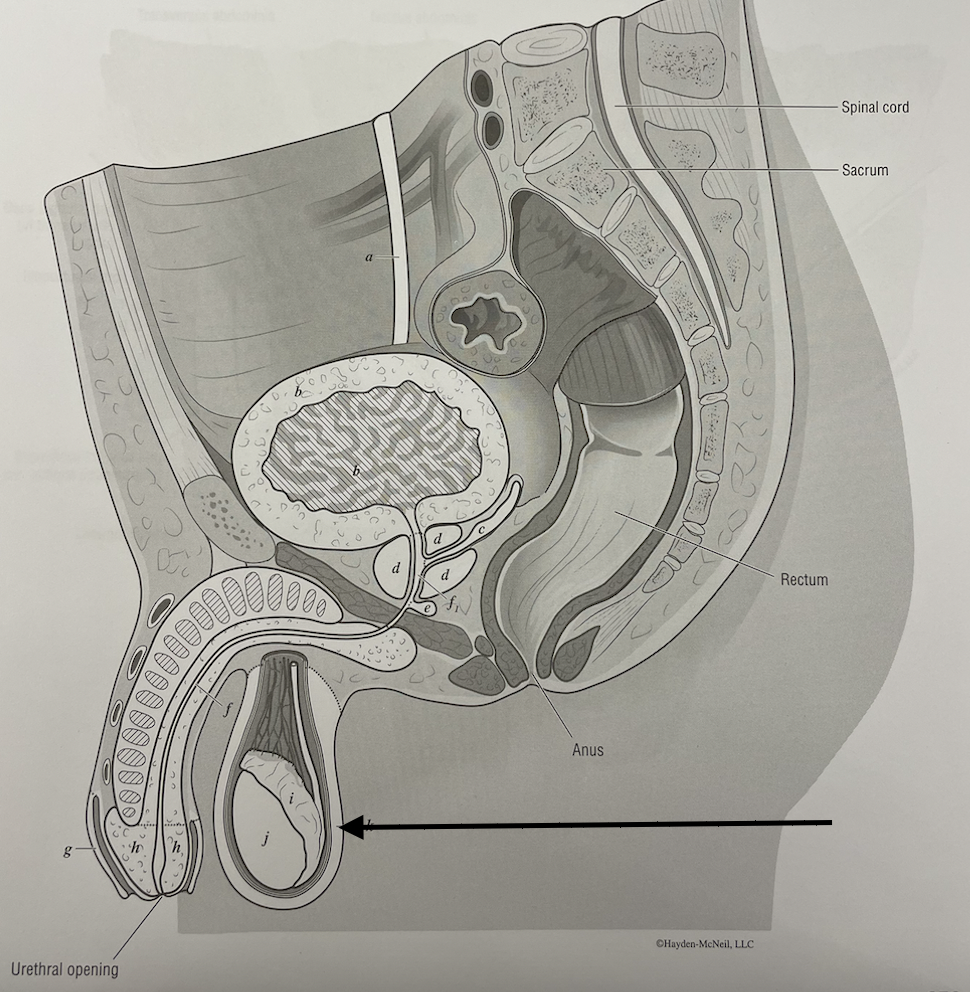
what structure is this
scrotum
46
New cards
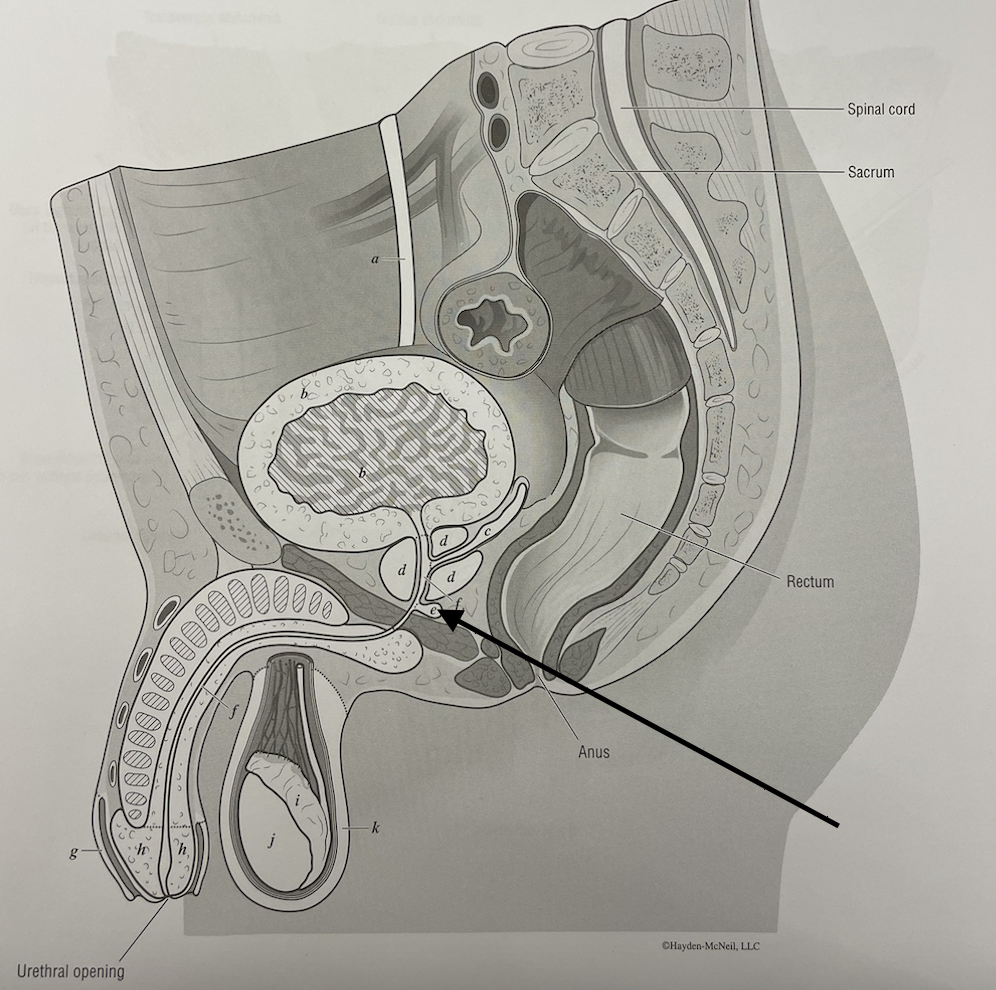
what structure is this
bulbo-urethral gland
47
New cards
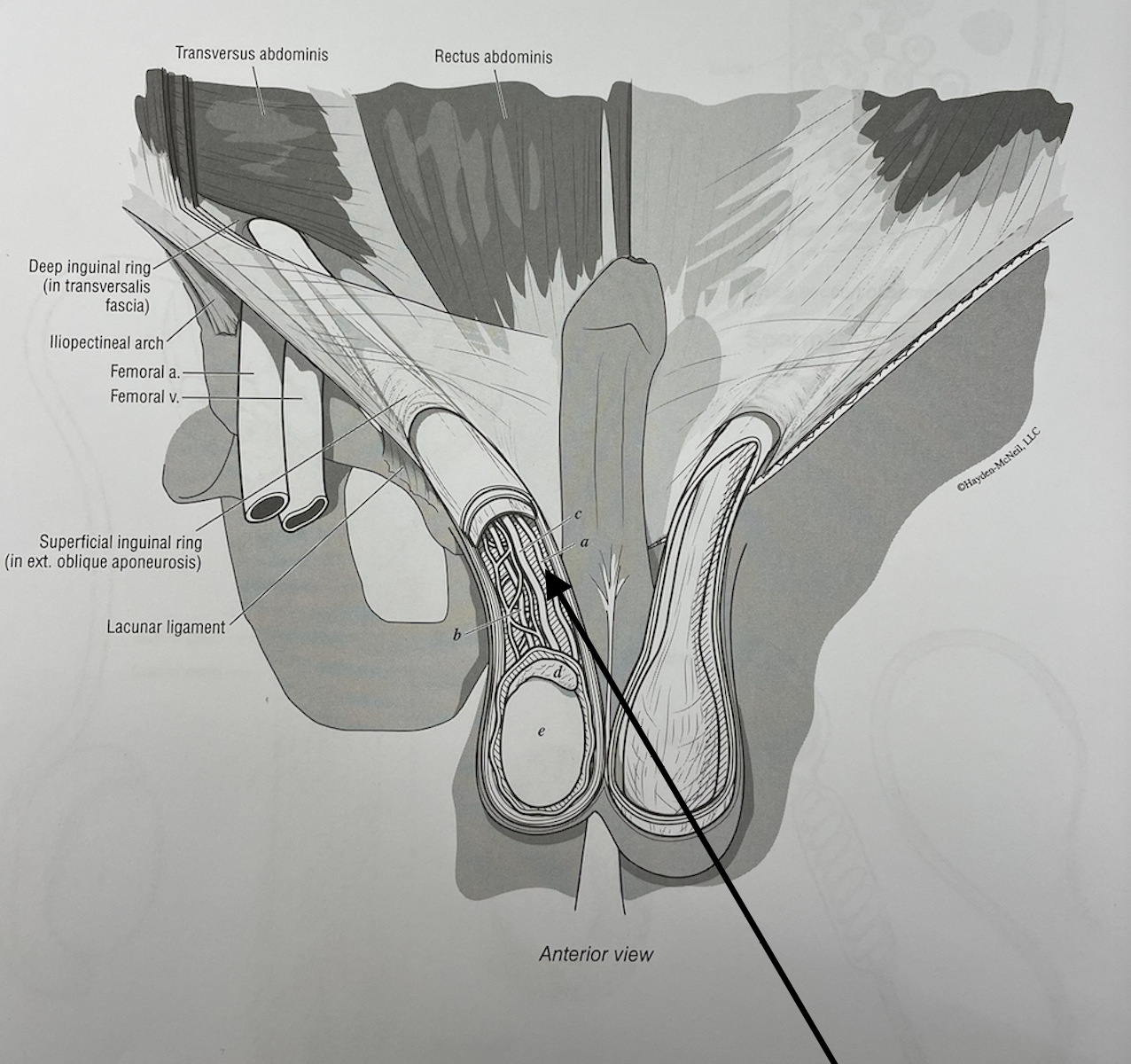
what structure is this
testicular
48
New cards
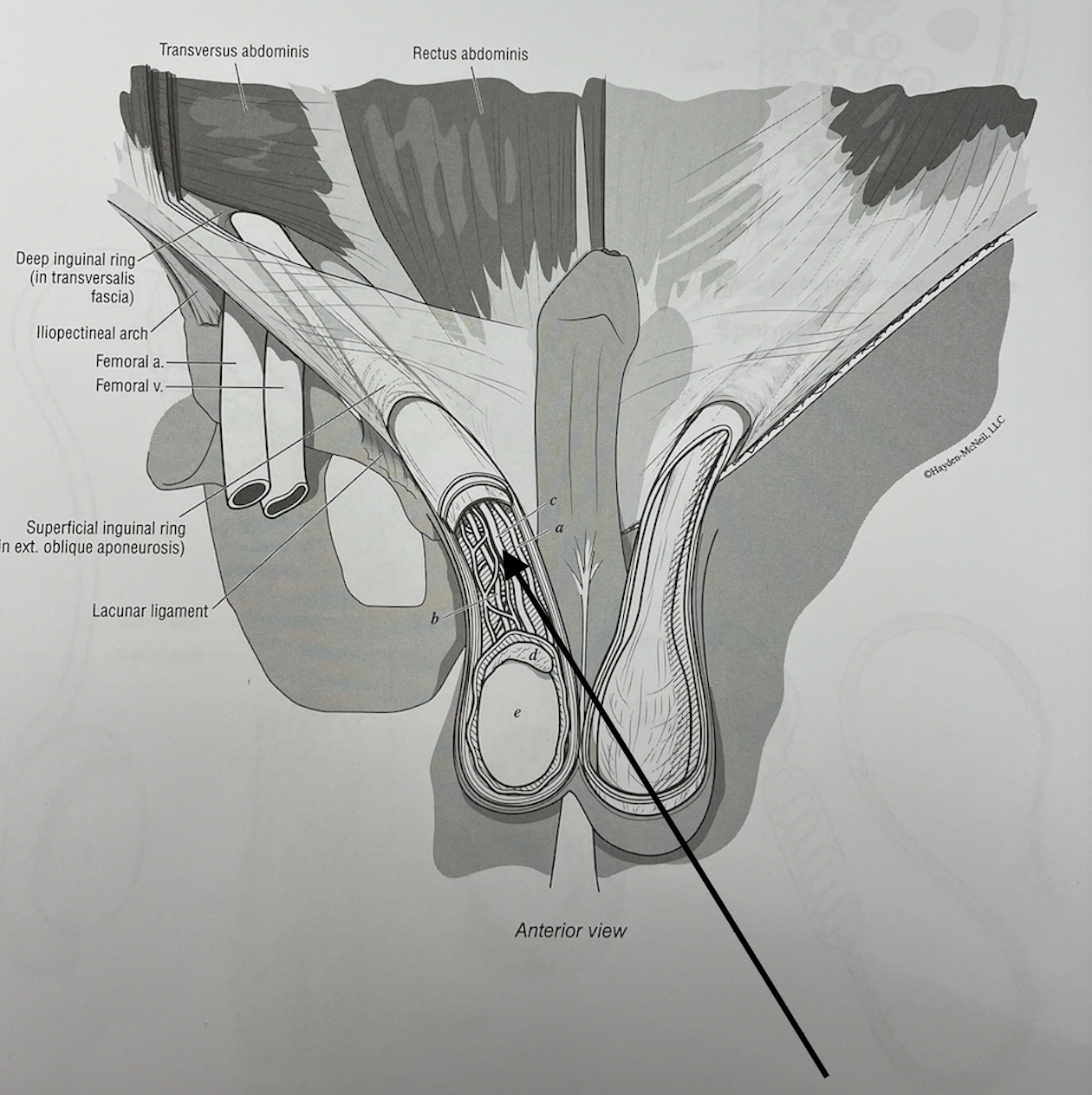
what structure is this
ductus referens
49
New cards
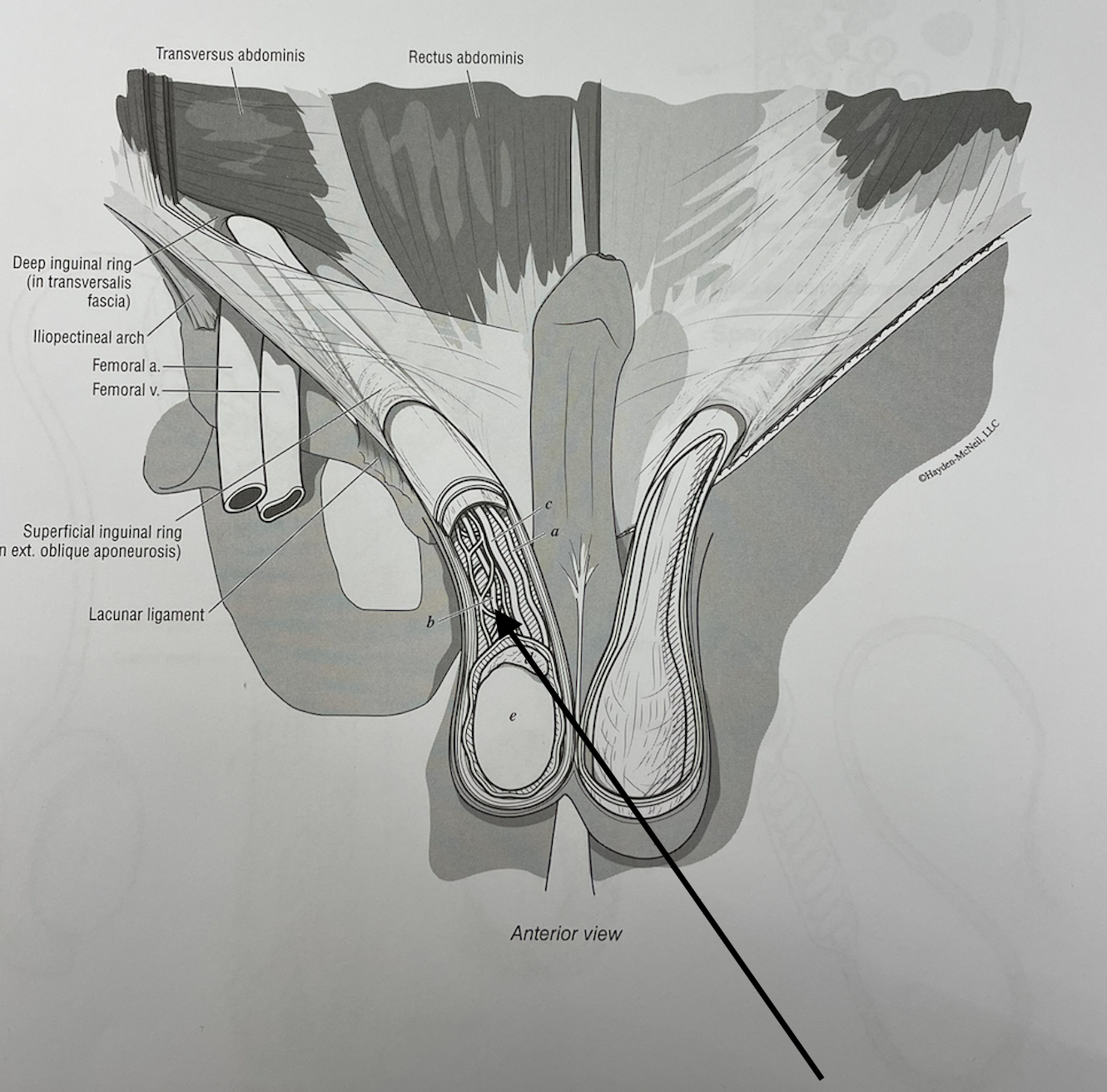
what structure is this
testicular a.
50
New cards
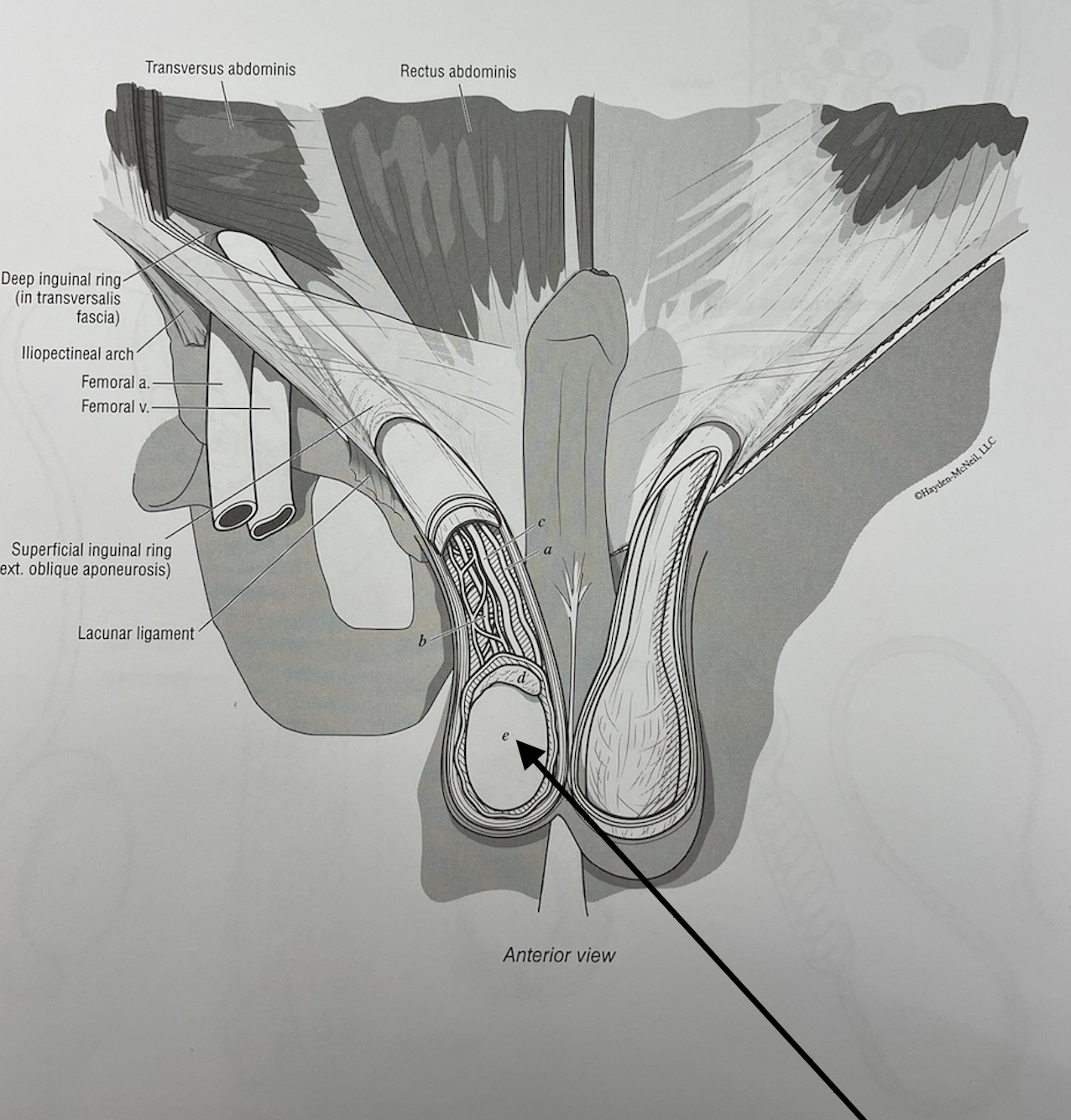
what structure is this
testis
51
New cards
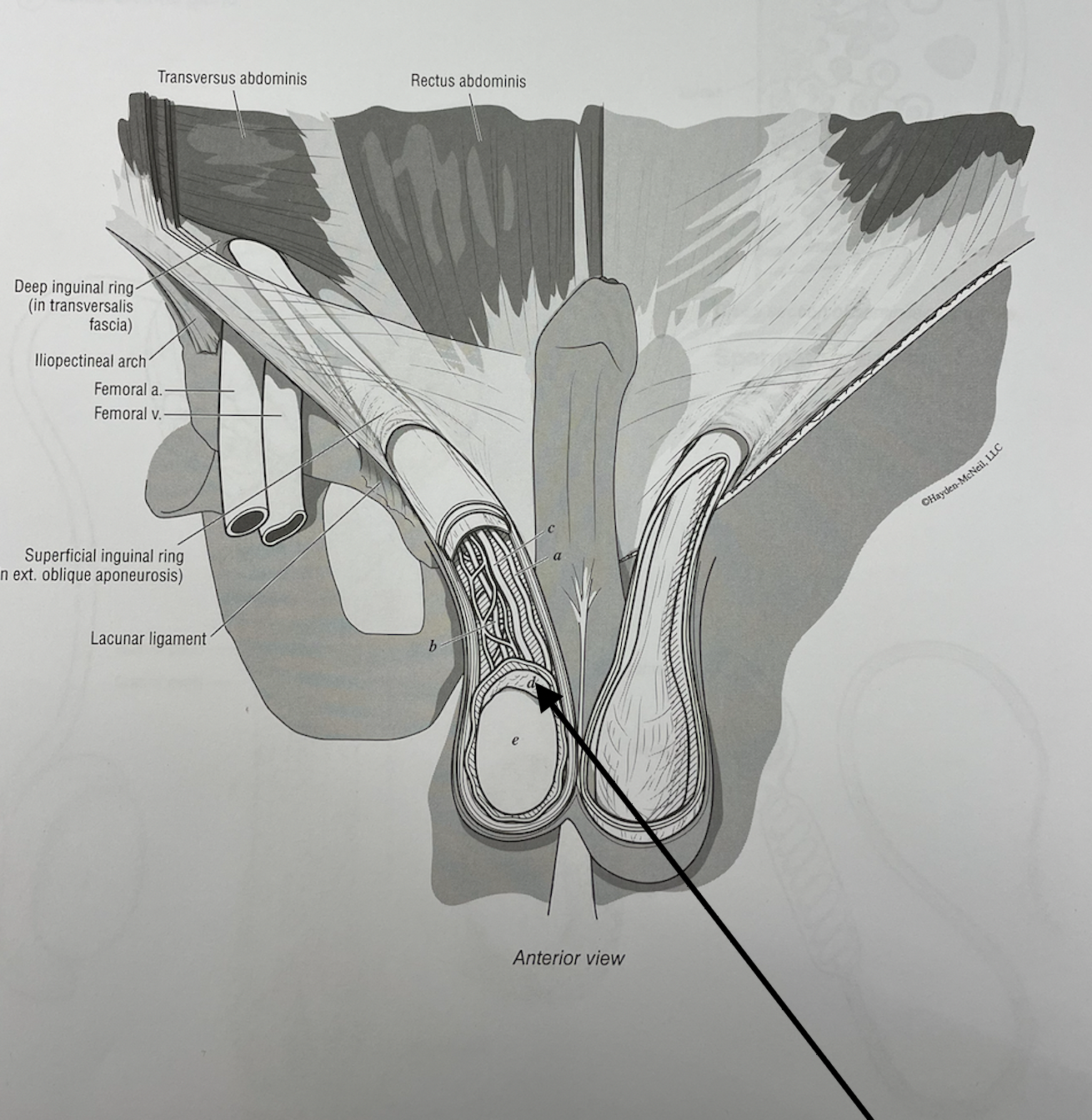
what structure is this
epididymis
52
New cards
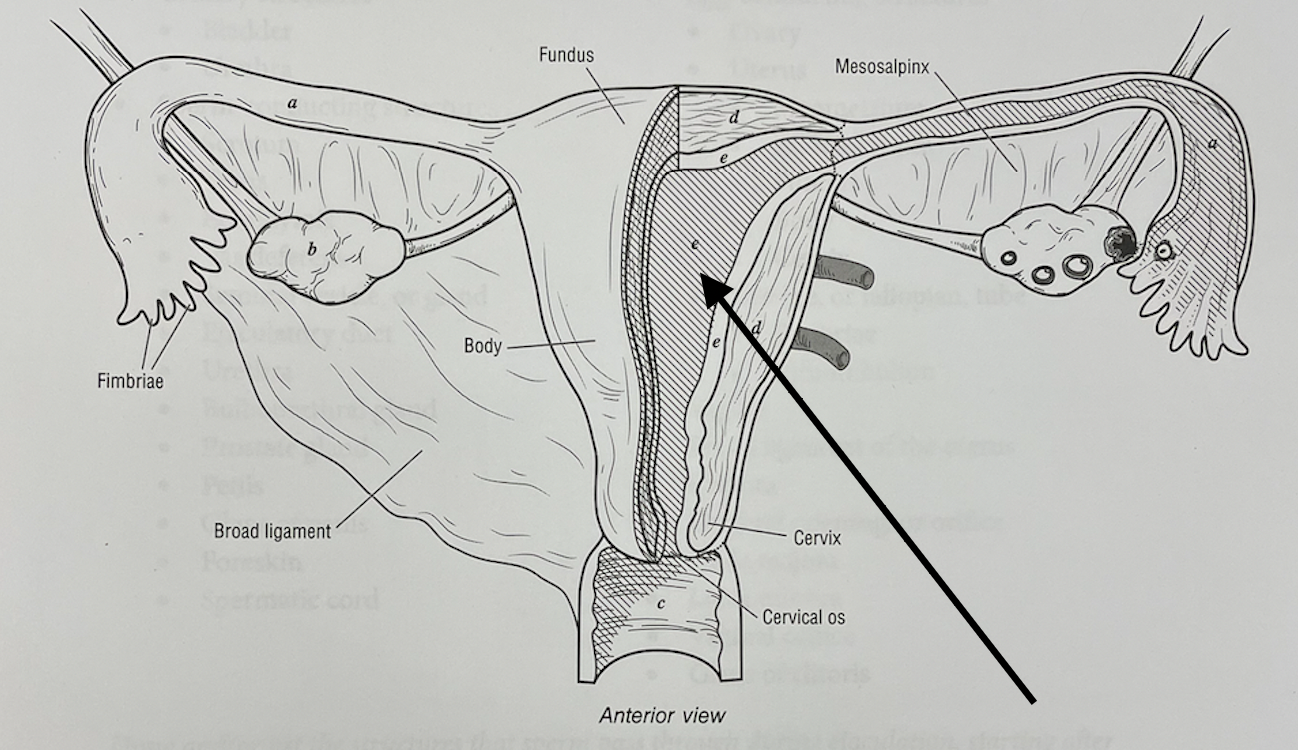
what structure is this
endometrium
53
New cards
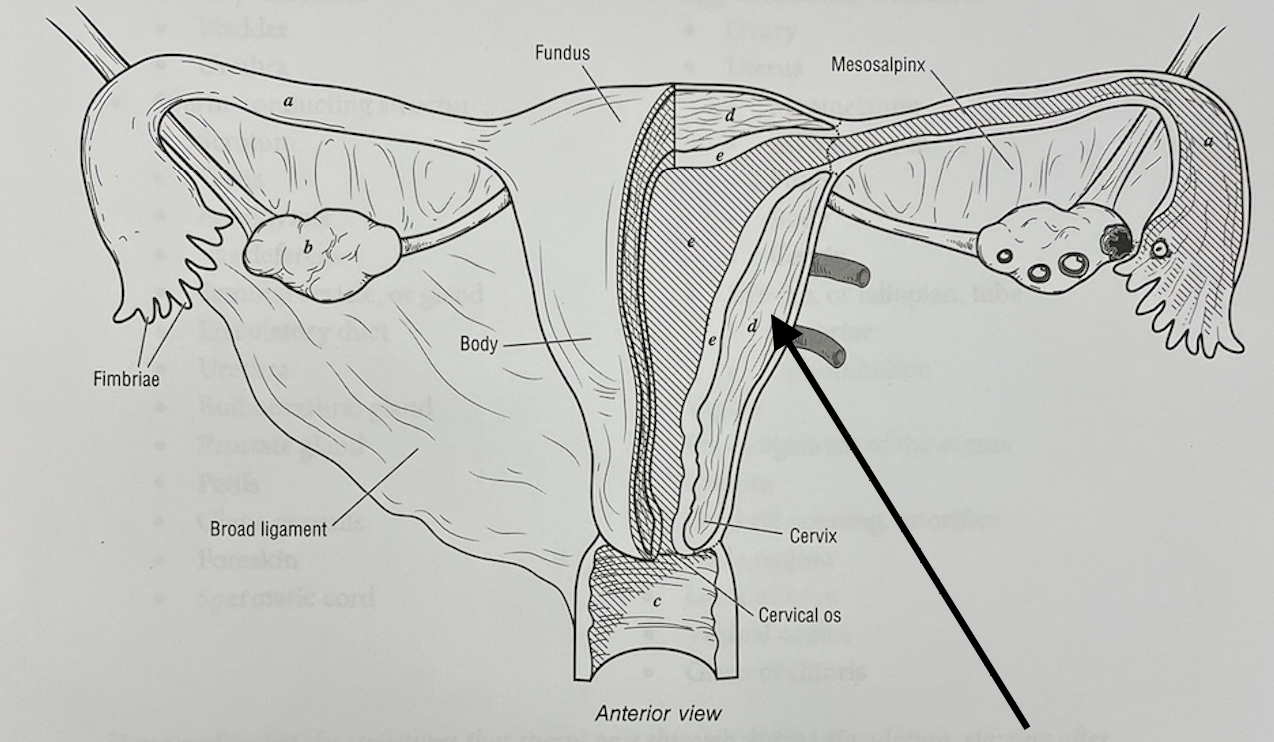
what structure is this
myometrium
54
New cards
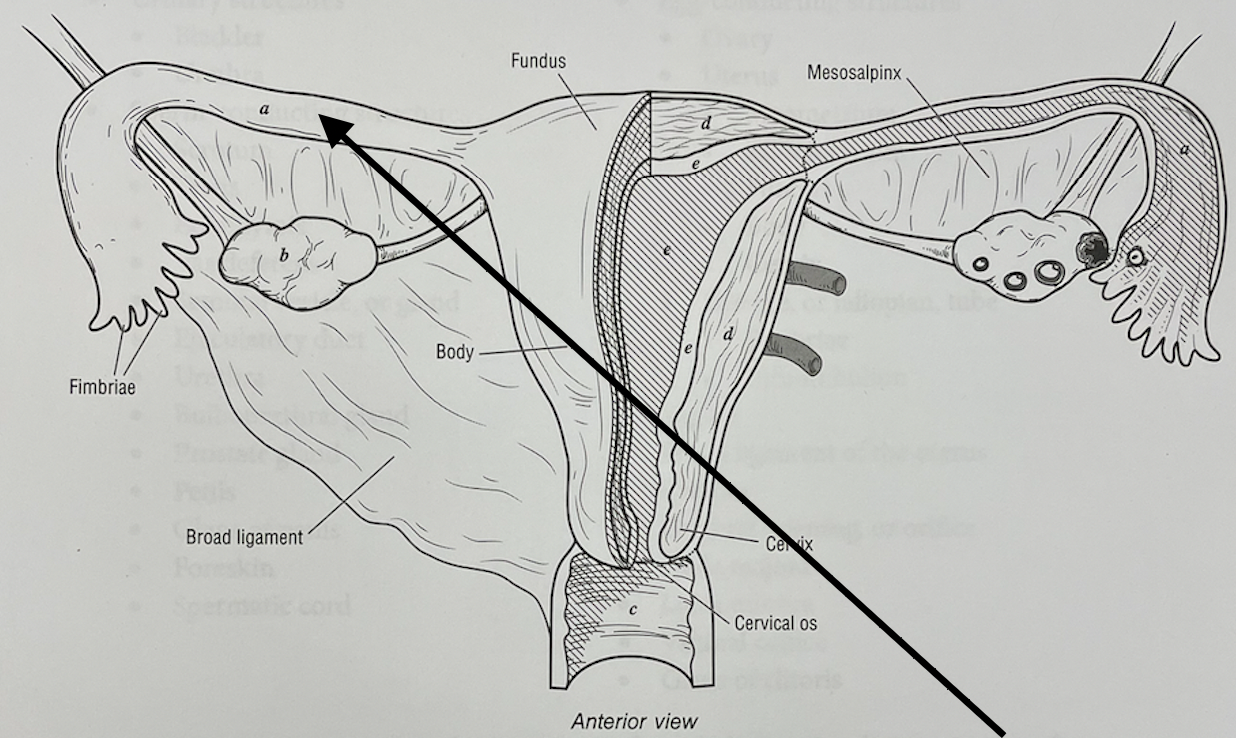
what structure is this
uterine (fallopian) tube
55
New cards
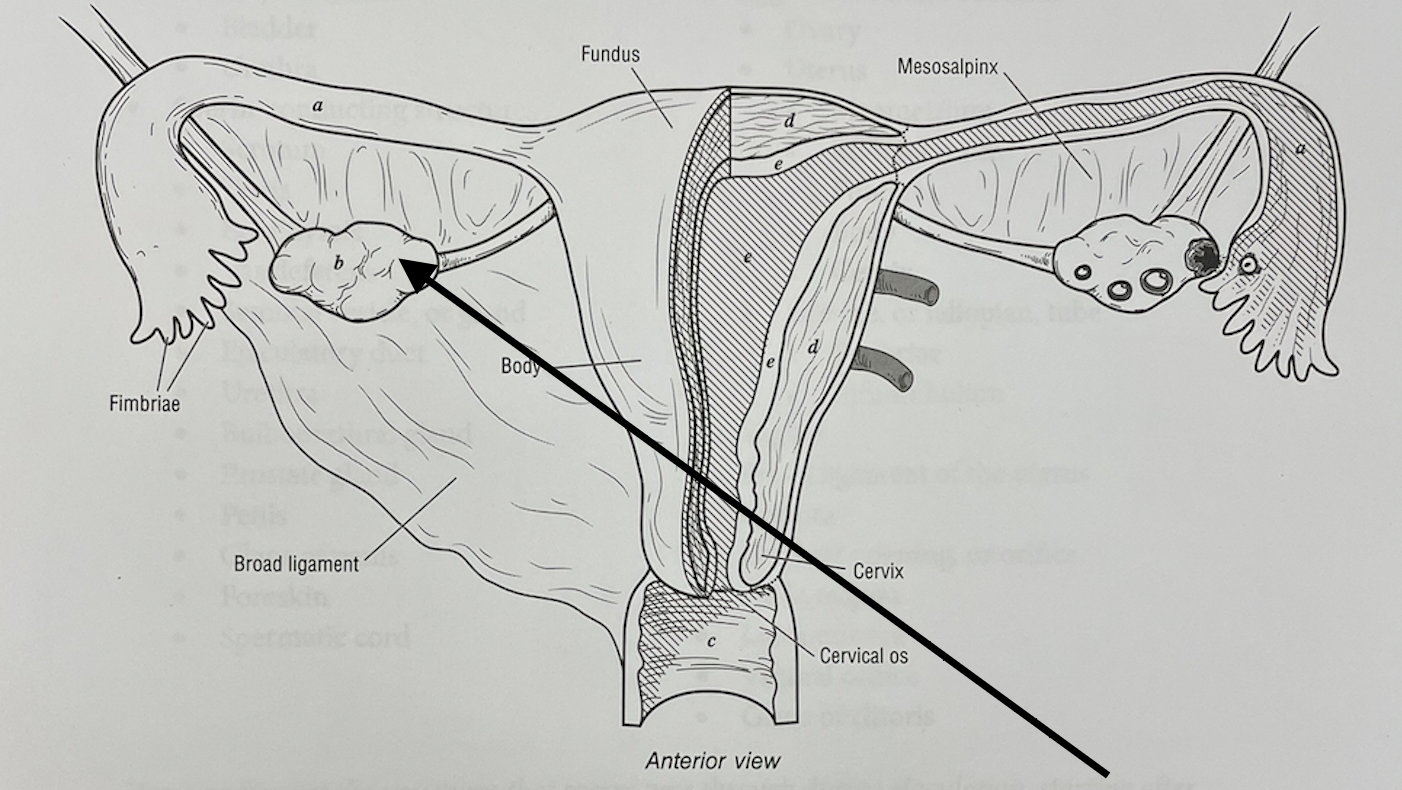
what structure is this
ovary
56
New cards
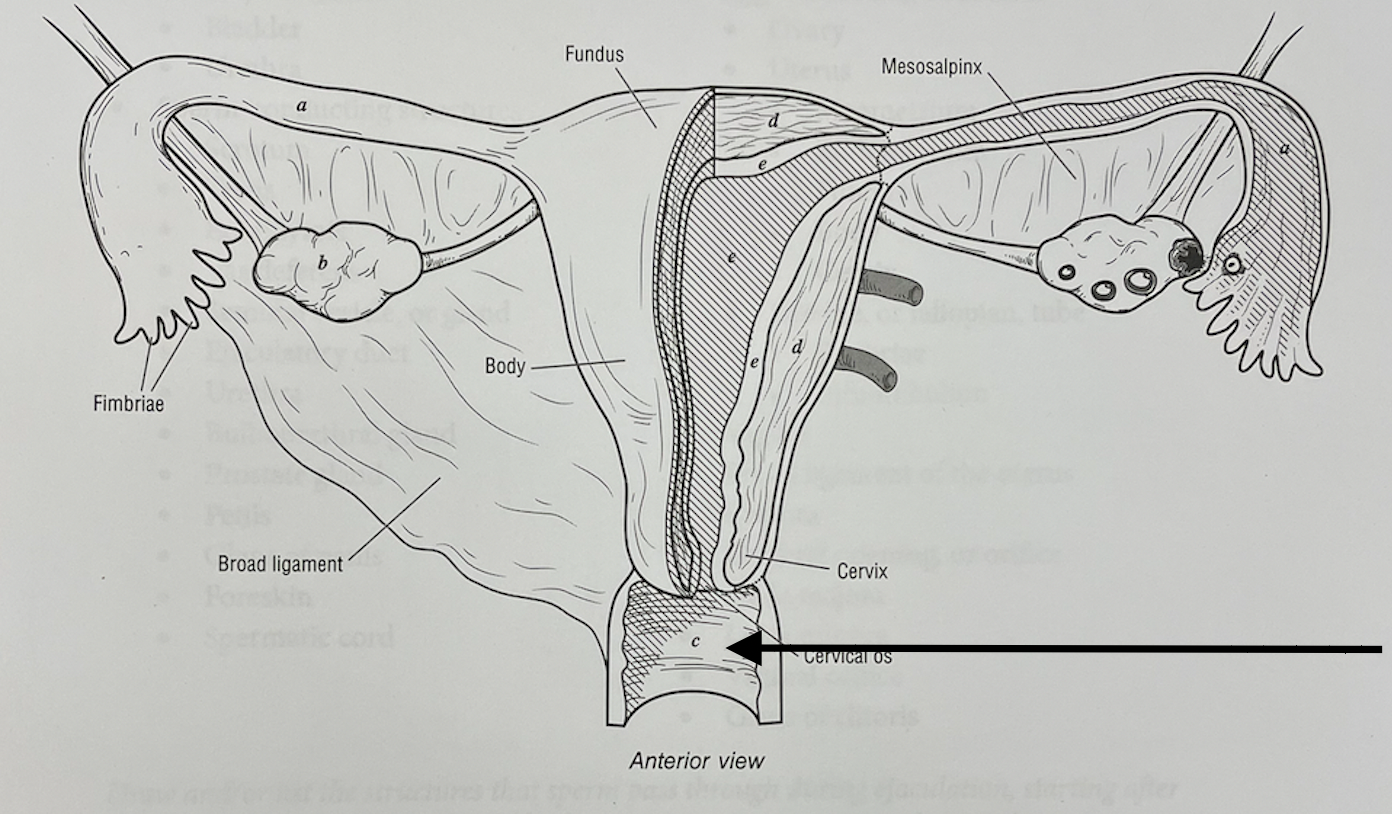
what structure is this
vagina