Pulmonary
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
91 Terms
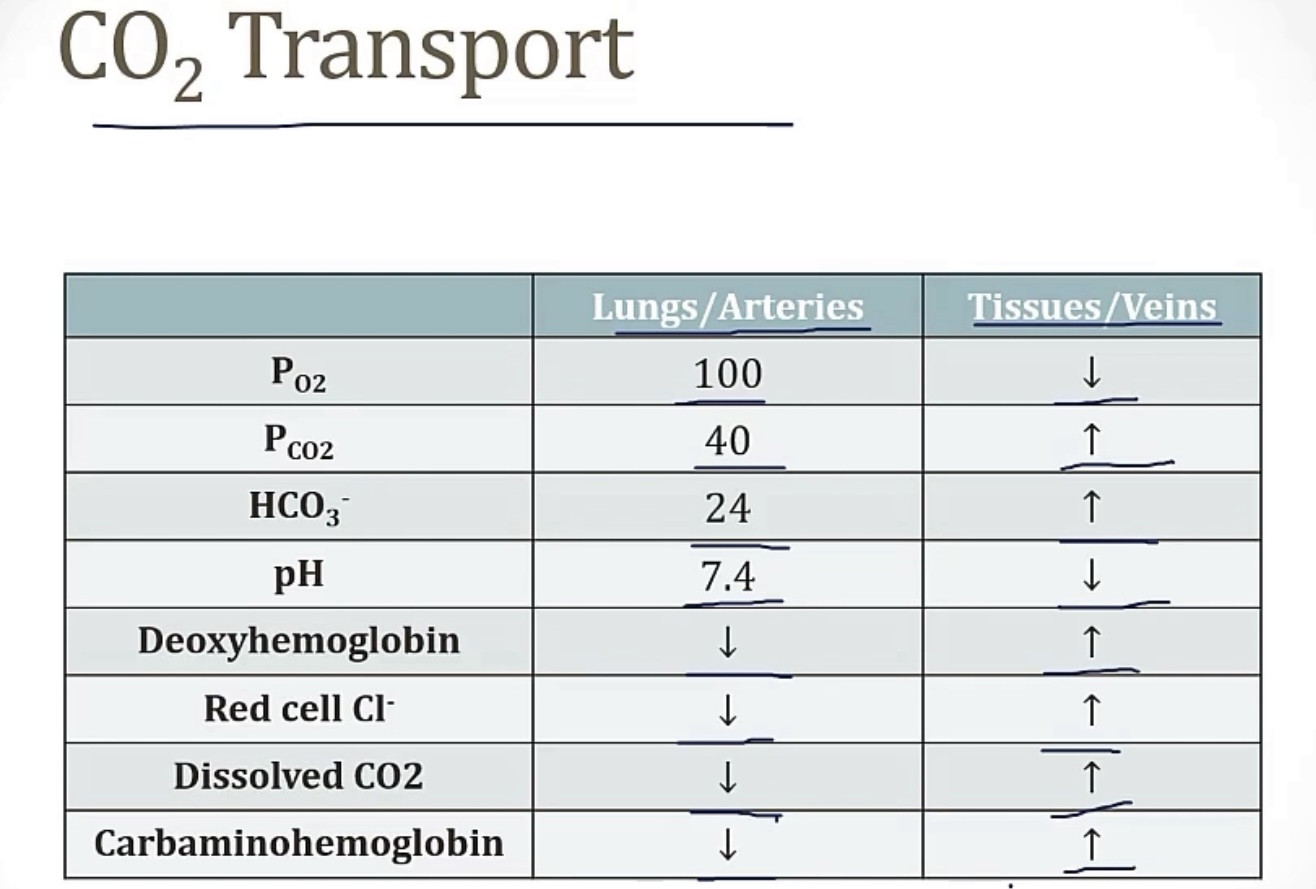
Carbon dioxide
-produced by what cellular process?
-the 3 ways CO2 is transported to the lungs are __, __, and __
DISSOLVED…
-this is determined by what law?
-based on PaCO2 and __
AS BICARBONATE…
-explain the physiology of RBCs, and movement of CO2, carbonic anhydrase, bicarb, chloride, and hydrogen/protons
BOUND TO HEMOGLOBIN…
-binds at the same sites, or different sites, as O2?
-how does this change the affinity of O2 with hemoglobin
-this principle determines 2 ‘effects’, which are the __ and __
-explain each
-cellular metabolism
-dissolved; as bicarbonate; bound to hemoglobin
DISSOLVED…
-Henry’s law
-solubility
AS BICARBONATE…
-RBCs have carbonic anyhdrase; CO2 can passively move into RBCs, then interact with carbonic anhydrase to make bicarbonate; this bicarbonate then leaves RBCs to go to the plasma, and Cl- comes in to take its place(and maintain electrical neutrality, since they’re both negative; this is the chloride shift) this is why you’ll have lots of chloride in venous blood. Meanwhile, the bicarbonate leaves H+ behind, which could theoretically raise the pH in RBCs, but deoxyhemoglobin is present(hemoglobin that has off-loaded its oxygen to the tissues), and binds to the free H+ to buffer and keep the pH in balance.
BOUND TO HEMOGLOBIN…
-different sites
-it will lower the affinity of O2 to hemoglobin, as more CO2 bind
-Bohr effect; Haldane effect
-Bohr effect causes a right shift, where more H+ and CO2 push the curve to the right, making O2 have less affinity for hemoglobin, so O2 is offloaded onto tissues that need it. Haldane effect causes a left shift, where a lot of O2 in the area makes the hemoglobin have a higher affinity, so it keeps the O2 until it gets to tissues that need it
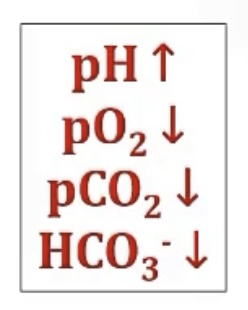
High altitude
-list out its affect on pH, pO2, pCO2, HCO3-, and tell whether it’s alkalosis or acidosis?
Exercise
-describe the changes in each…
•ventilation
•blood flow
•PaO2
•PaCO2
•O2 and CO2 in veins
•O2 and CO2 in arteries
-increases
-increases
-stays balanced
-stays balanced
-O2 falls, CO2 rises
-O2 and CO2 stay balanced
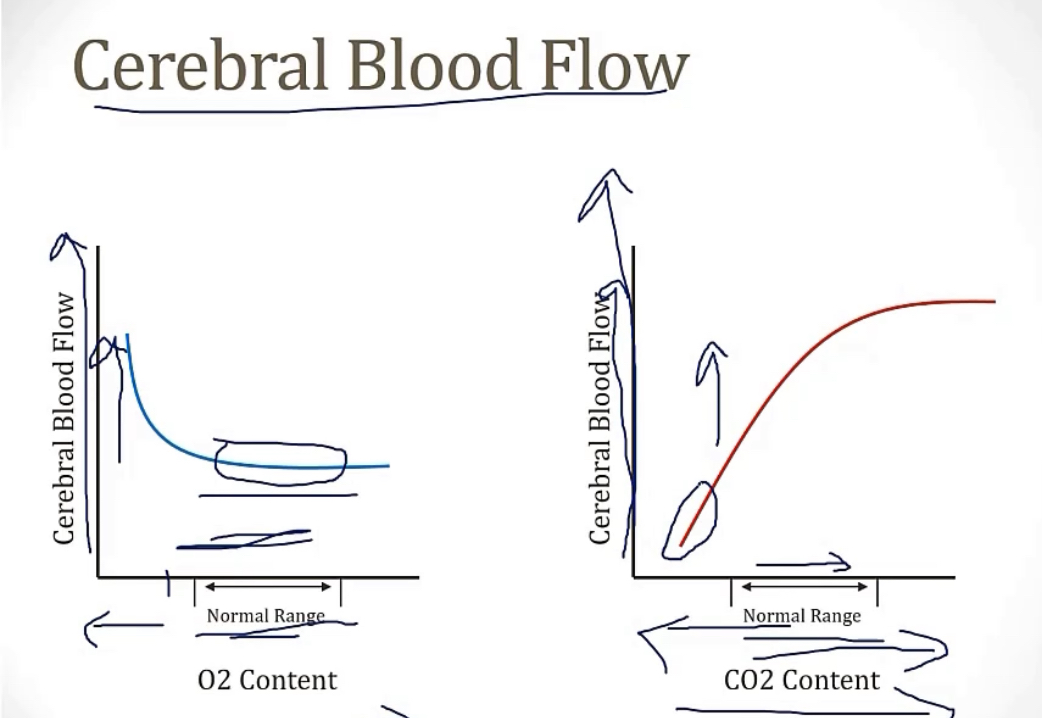
Cerebral blood flow
-primarily determined by CO2 or O2?
-how could this be helpful in clinic, if someone comes in with high intracranial pressure?
-by CO2
-If someone in a trauma has high intracranial pressure, you hyperventilate them, which will crash the CO2, and decrease cerebral blood flow, which decreases the amount going into their brain, where they may have intracerebral bleeding
Panic attacks
-hyper/hypo ventilation?
-lead to high/low CO2? Also called?
-this causes cerebral vaso-constriction or dilation?
-this will causes what kinds of symptoms?
-hyperventilation
-low CO2; hypocapnia
-cerebral vasoconstriction
-CNS symptoms(dizziness, blurred vision)
CO2 breathing control is mainly set by what receptors? Where are they located?
-central chemoreceptors; medulla
Oxygen
-transported by 2 main mechanisms, which are __ and __
DISSOLVED…
-this is determined by what law?
-based on PaO2 and __
BOUND TO HEMOGLOBIN…
-on the oxygen-dissociation curve, the line forms an __ shape; this is due to the __ of oxygen to hemoglobin, which means __
-hemoglobin has 2 forms, depending on if oxygen is bound, which are the __ form, and the __ form
-the __ form means that oxygen has been released, and delivered to tissues(this is the preferred form in tissues)
-the __ form means that there is oxygen bound, and is the preferred form in lungs
-dissolved; bound to hemoglobin
DISSOLVED…
-Henry’s law
-solubility
BOUND TO HEMOGLOBIN…
-S; positive cooperativity; the more oxygen that binds, the higher the affinity for the next oxygen to bind
-taut; relaxed
-taut
-relaxed
Hemoglobin
3 main types of hemoglobin, which are __, comprised of __; then __, comprised of __; and finally __, which is comprised of __
-hemoglobin __ does have the highest affinity among the 3, and this is because the __ chains have altered binding to __
-hemoglobin A; alpha2beta2; hemoglobin A2; alpha2delta2; hemoglobin F; alpha2gamma2
-F; gamma; 2,3-BPG
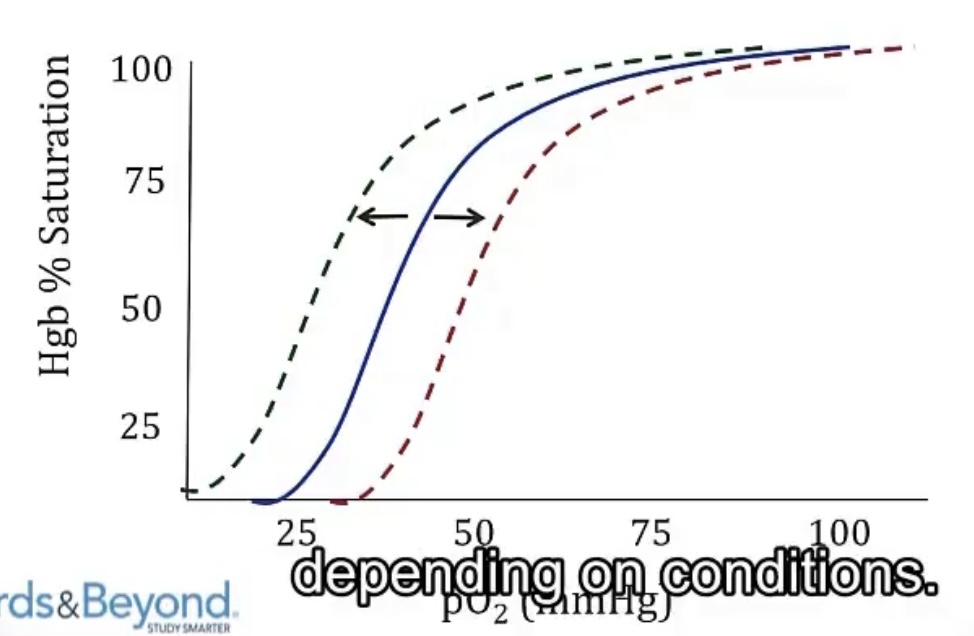
Oxygen-Dissociation Curve
-right shift curve means __ of oxygen
-right shifts are primarily caused by __, since this means an increase in __
-another important cause of right shifts are a product of glycolysis, using an extra molecule of __, which is an increase in __; this will increase in states of __
-left shift curve means __ of oxygen
-left shifts are primarily caused by __, since this means a decrease in __
-release/lower affinity of oxygen
-increased metabolic activity; CO2
-ATP; 2,3-BPG; hypoxia
-holding onto/higher affinity of oxygen
-decreased metabolic activity; CO2
Myoglobin
-basically, the hemoglobin of __
-compared to hemoglobin, these are made of __ chain, and therefore can only bind __ molecule of oxygen
-muscle tissue(skeletal and heart)
-1; 1
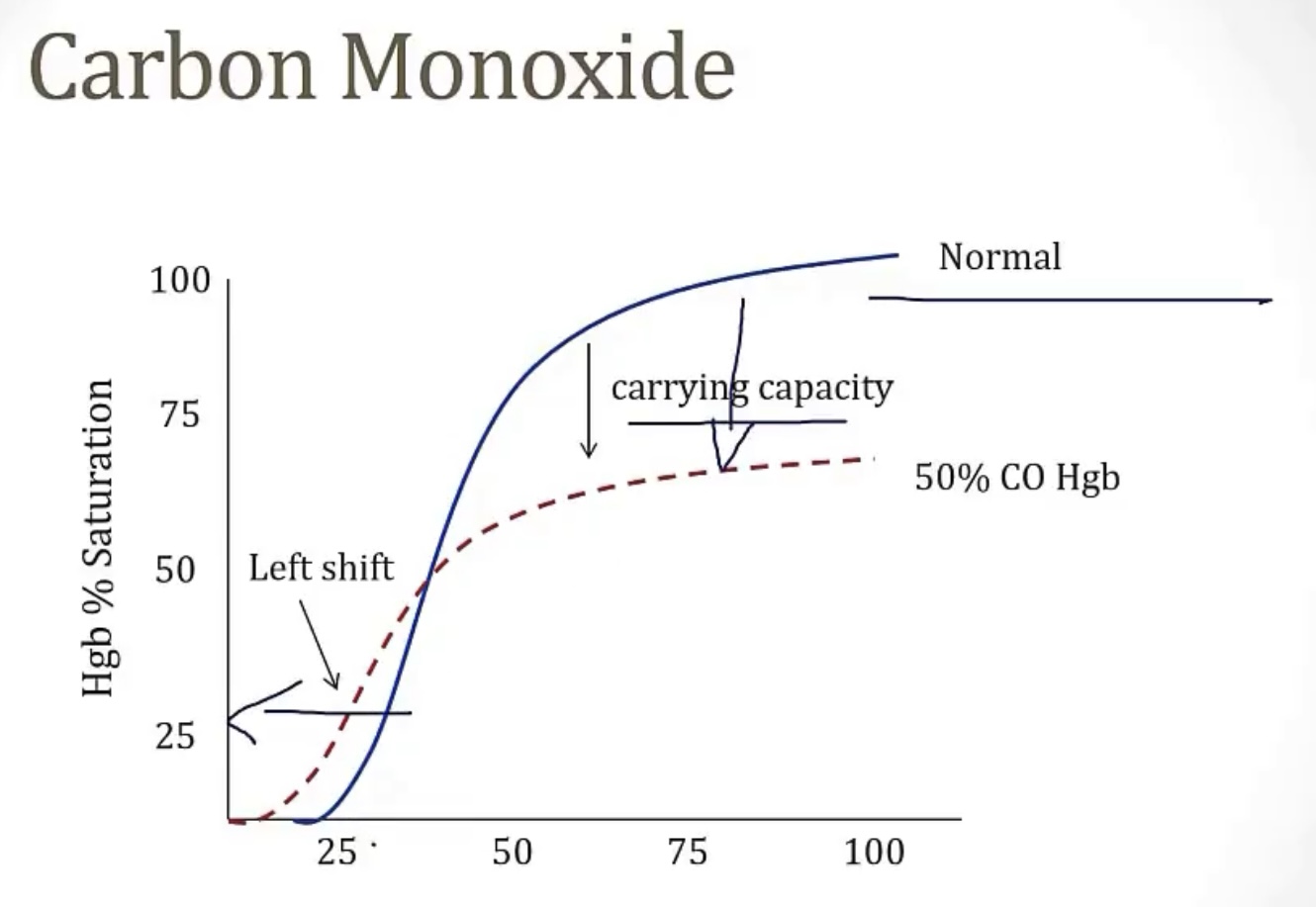
Carbon monoxide
-will bind to hemoglobin and form __, which will __ other binding sites, causing a __
-this leads to a __ shift curve
-classic sign of someone with carbon monoxide poisoning is __, because the carboxyhemoglobin is red
-it’s important to note that pulse oximetry will be __ for carbon monoxide poisoning, because the device can’t differentiate __ from __. For this reason, you must check the __ level
-treatment from carbon monoxide poisoning is __
-carboxyhemoglobin
-block; functional anemia
-left
-cherry red lips
-unreliable; carboxyhemoglobin; oxyhemoglobin; carboxyhemoglobin
-oxygen
Methemoglobinemia
-occurs when the iron in hemoglobin that binds the __, does not become reduced, leaving it as __, and unable to bind more __. This state of Fe3+ is called __
-this primarily occurs from some __, certain ones being __ or __
-will make the blood have a textbook __
-treatment is __
-oxygen; Fe3+; oxygen; methemoglobin
-drugs; benzocaine; NO
-chocolate brown blood
-methylene blue
-Delivery of oxygen to tissues depends on 2 main things, __ and __
-O2 content depends on 3 factors, __, __, and __
-Dissolved O2, which is your __, can be found using an __
-hemoglobin saturation can be found using __
-cardiac output; O2 content of blood
-O2 binding capacity, hemoglobin saturation, and dissolved O2
-PaO2; ABG
-pulse oximetry
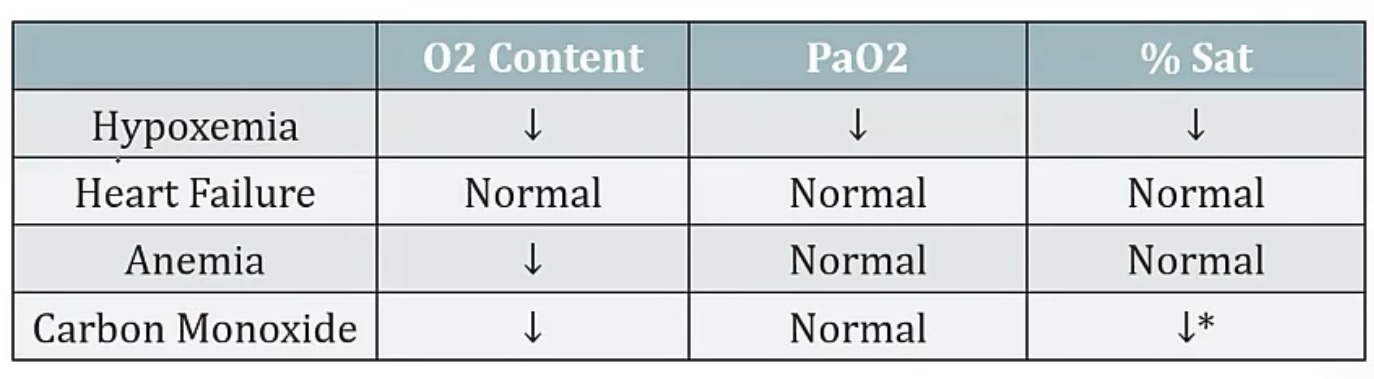
Hypoxia
-describe
-can you have hypoxia without hypoxemia?
-what are some examples that would cause this?
-how would heart failure lead to hypoxia?
-how would anemia lead you to hypoxia?
-how would carbon monoxide lead you to hypoxia?
-lack of O2 delivery to tissues
-yes!
-heart failure, anemia, carbon monoxide
-heart failure has decreased cardiac output, so less flow to tissues
-anemia has decreased oxygen carrying capacity, due to less RBCs
-carbon monoxide causes a functional anemia, so less RBCs to carry oxygen, means less O2 delivery to tissues
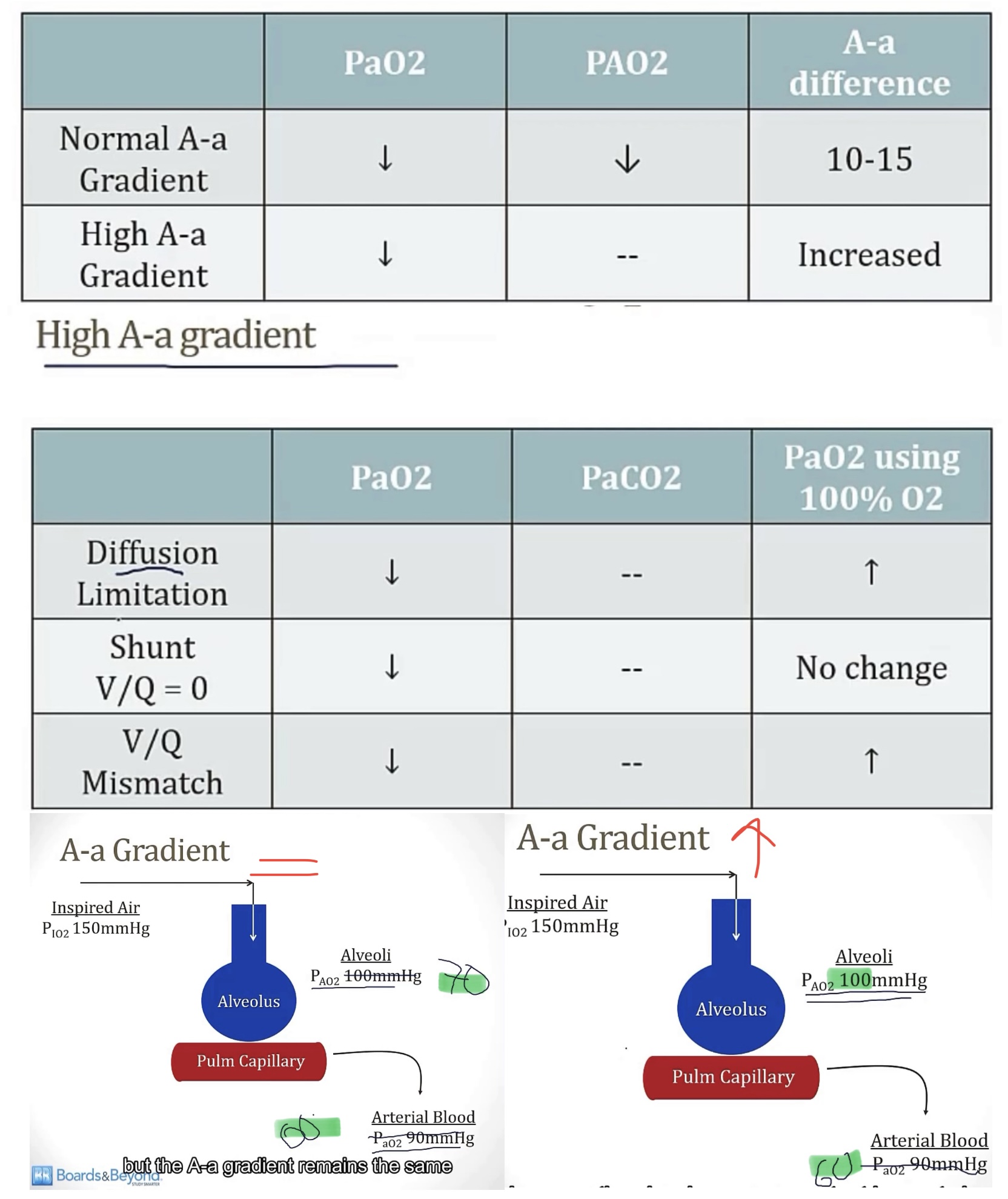
Hypoxemia:
-describe
-the causes of this can be grouped, based on the __
-a normal value of the above is __
HYPOXEMIA WITH A NORMAL A-a GRADIENT…
-discuss PAO2 and PaO2, causes, and treatment
HYPOXEMIA WITH AN INCREASED A-a GRADIENT…
-discuss PAO2 and PaO2, causes, and treatment
EXAMPLES WORTH KNOWING…
-intra-cardiac shunt is __
-inhalation of an item into your airway is __
-pulmonary embolism is __
-lack of O2 in the blood/defect oxygenating the blood
-A-a gradient(alveolar O2-arterial O2)
-10-15
Hypoxemia with a normal A-a gradient:
•Pa02 decreases, and PA02 also decreases(keeping A-a gradient normal)
•2 causes…
1)decreased oxygen content of air, like high altitude
2)hypoventilation
•This problem always resolves with oxygen!
Hypoxemia with an increased A-a gradient:
•only Pa02 decreases(causing increased A-a gradient)
•3 causes…
1)diffusion defect(consider area, wall thickness, and density; such as emphysema, pulm fibrosis, and pulm edema)
2)shunt(damaged portion of lung has blood move from vein to artery without becoming oxygenated, giving a V/Q of zero, ie, hypoxemia)
3)V/Q mismatch(reduced ventilation causing low V/Q, but not zero)
•shunts will NOT resolve with oxygen, because the problem isn’t with oxygen, it’s movement from alveoli to artery
•V/Q mismatch WILL resolve with oxygen
EXAMPLES WORTH KNOWING…
-a pure shunt
-a pure shunt
-a V/Q mismatch with increased dead space
Ischemia
-describe
-lack of blood flow
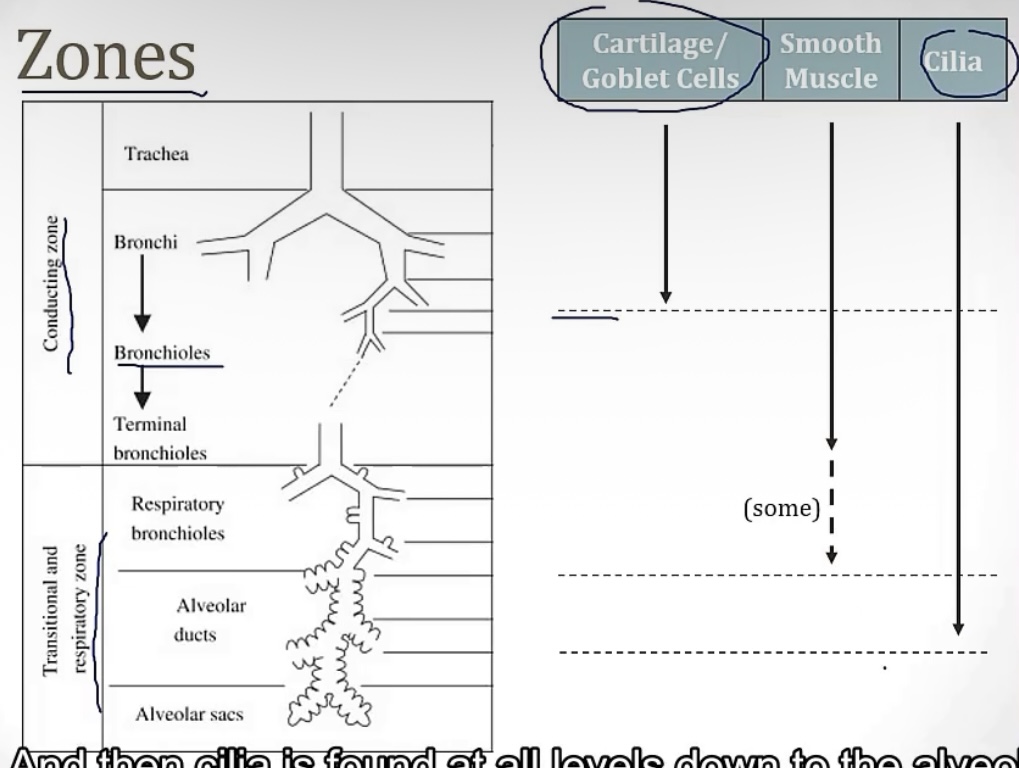
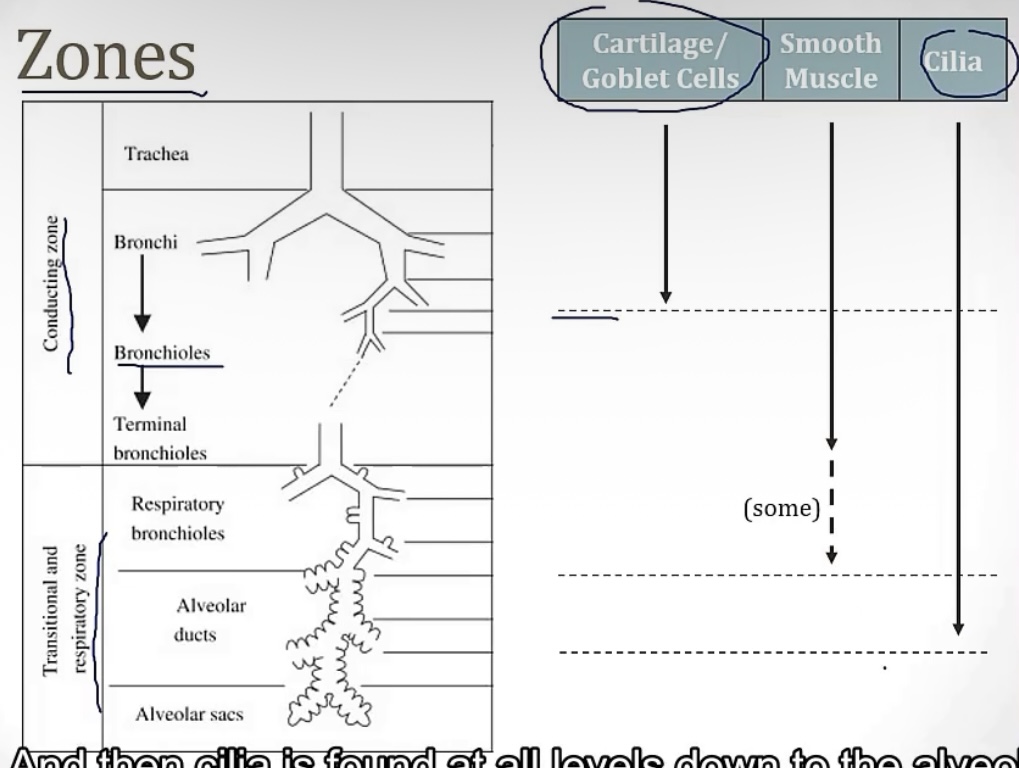
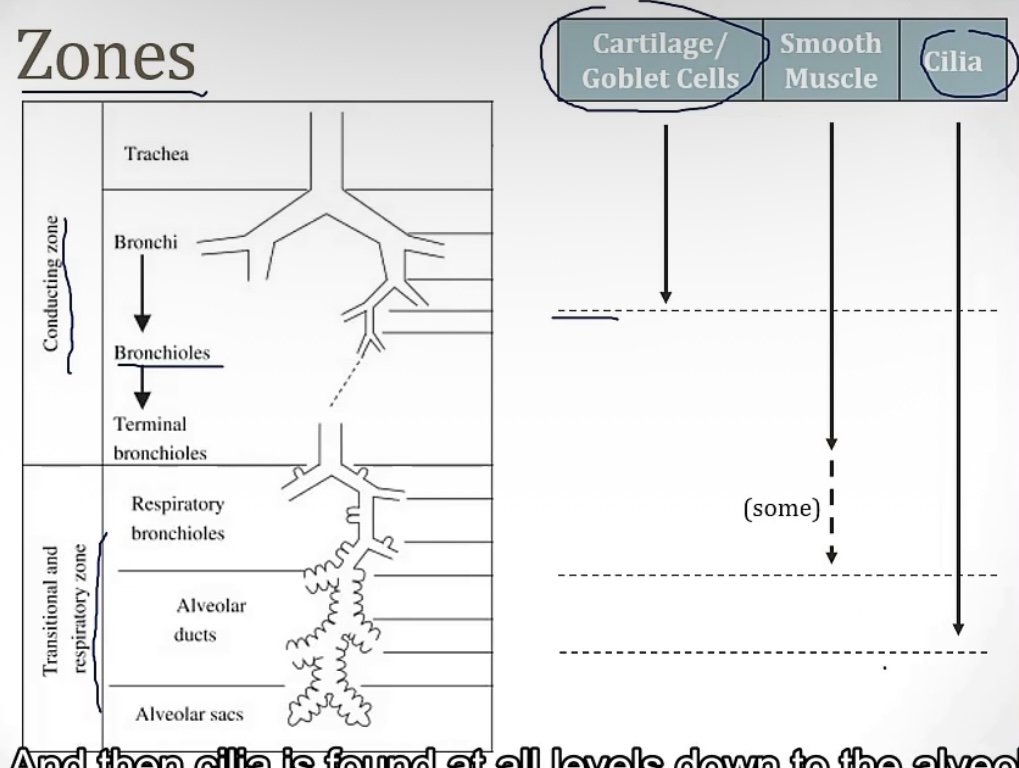
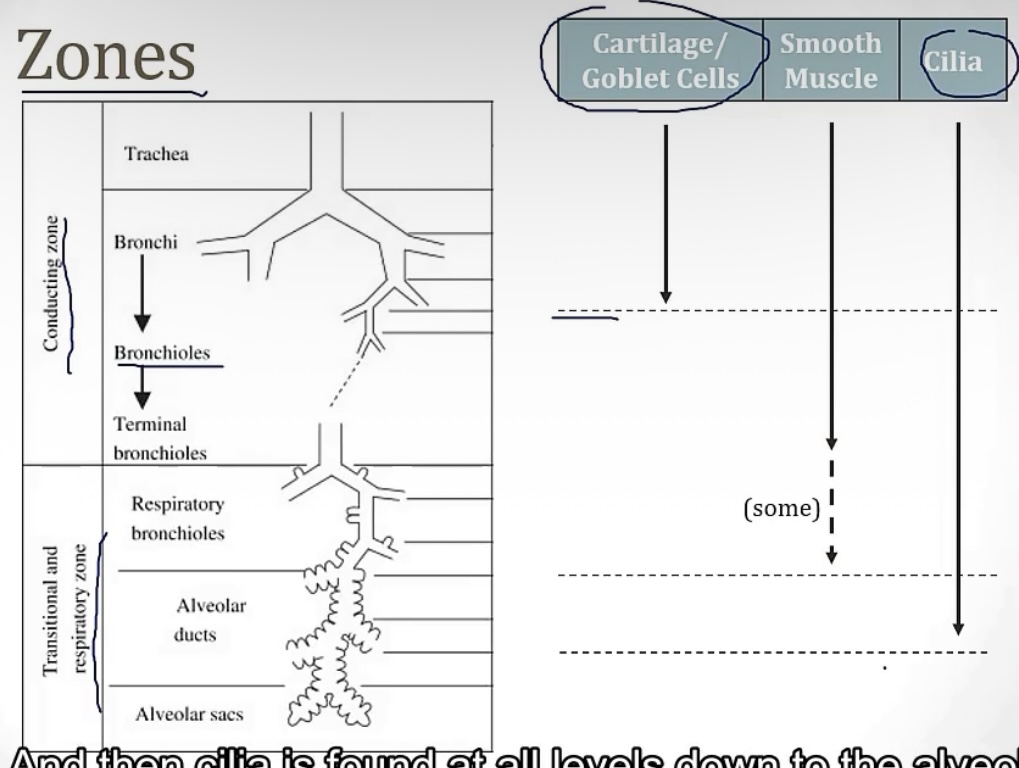
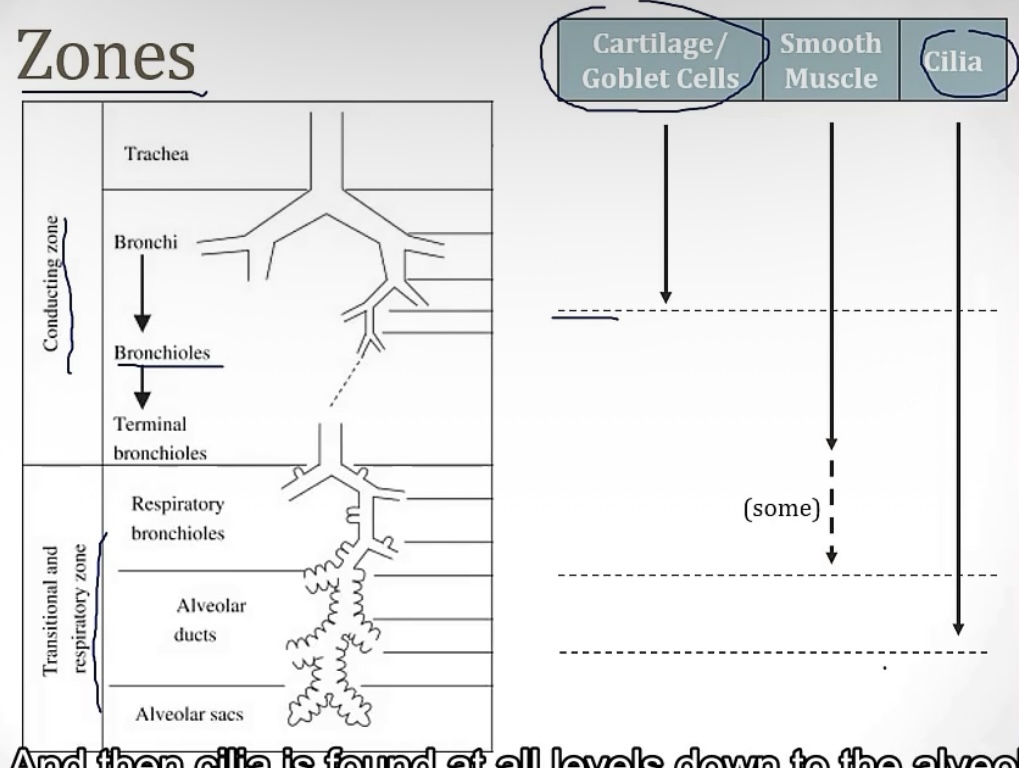
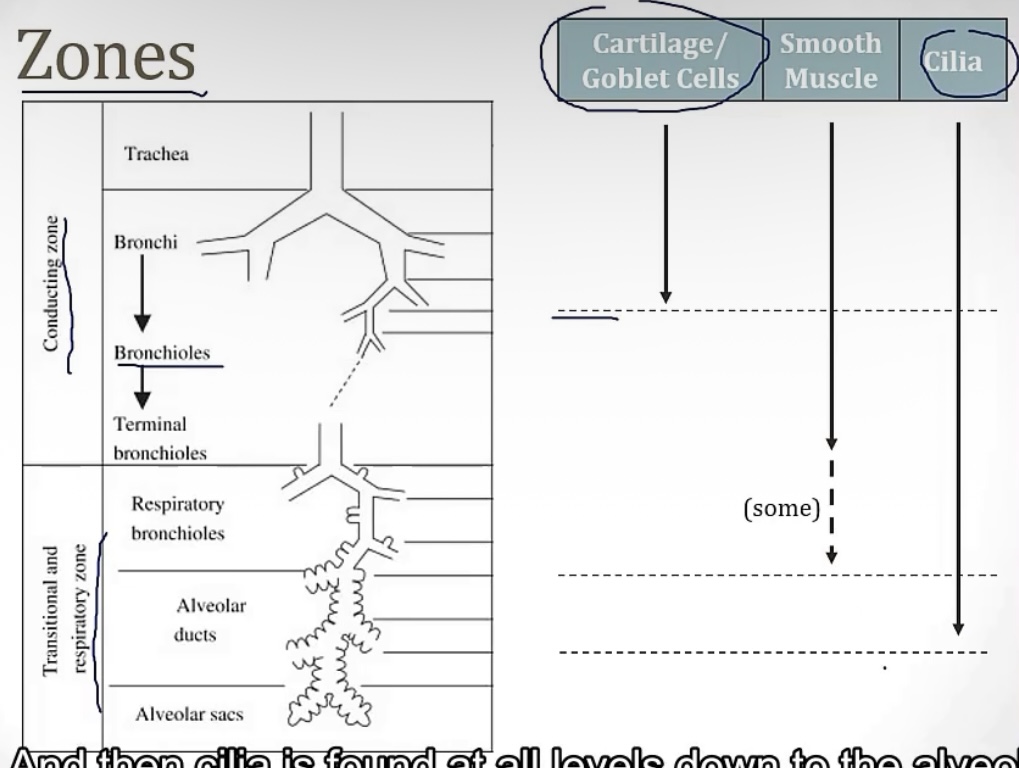
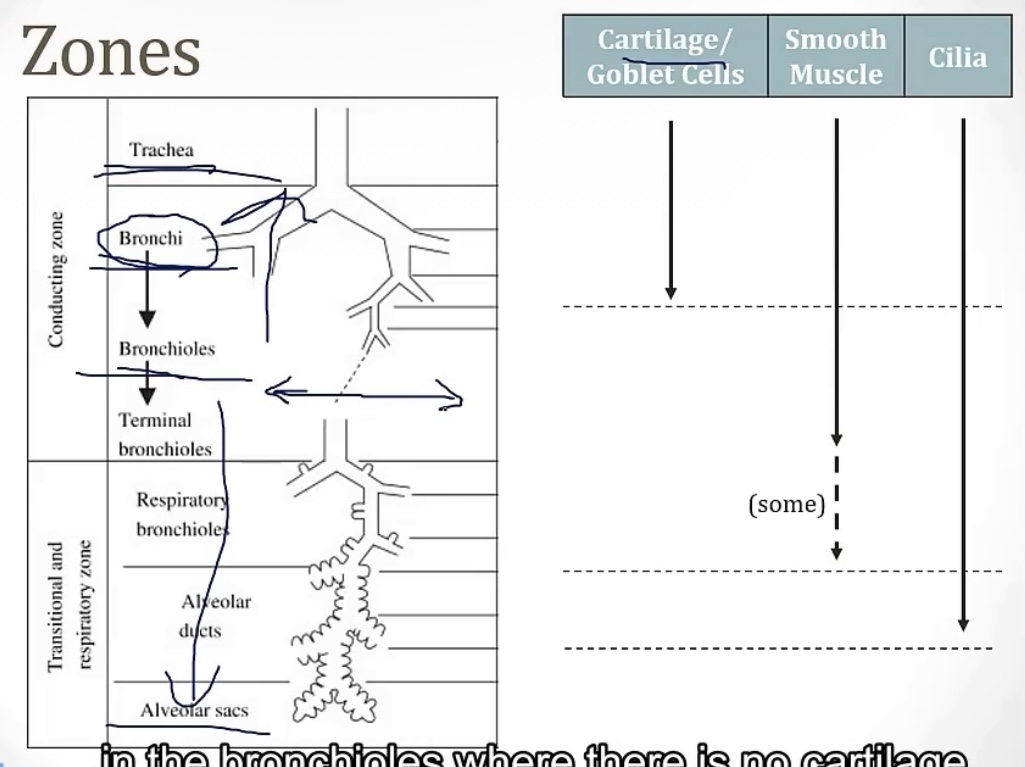
Conducting zone vs Respiratory zone
-2 portions of the airway
-which one has gas exchange?
-which one filters, warms, and humidifies air?
-which one is made up of large airways, nose, pharynx, trachea, and bronchi?
-which one is made up of bronchioles, alveolar ducts, and alveoli
-which one has atomic dead space?
-more on the conducting zone…it is made up of what kind of muscle? And sympathetic activation causes bronchodilation or bronchoconstriction? Therefore, parasympathetic activation causes __?
-respiratory zone
-conducting zone
-conducting zone
-respiratory zone
-conducting zone
-smooth muscle; bronchidilation(to breathe better while running!); bronchocontriction
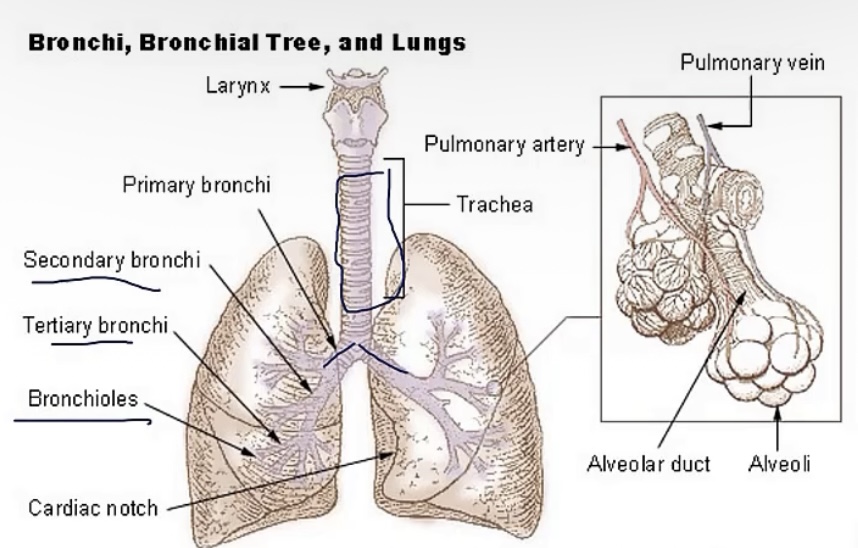
Bronchi
-is there cartilage?
-what are the names of the sections these are divided into?
-yes
-primary(left/right)—>secondary(lobar) —>tertiary(segmental)
Bronchioles
-is there cartilage?
-what are the names of the sections these are divided into?
-no
-lobular—>terminal—>respiratory(feeds alveoli)
Across the airway, the structures with the least resistance are the __; the structures with the most resistance are the__
-terminal bronchioles; medium bronchi
Pneumocytes
TYPE 1…
-thick or thin? And this allows for __
TYPE 2…
-produces __
-these are key for __; due to their ability to __
TYPE 1…
-thin; gas exchange
TYPE 2…
-surfactant
-regeneration; proliferate to form other cell types
Goblet cells
-they secrete __
-made up of mostly __ and __
-protects against __, and therefore __
-mucus
-glycoproteins; water
-particulates; infection
Ciliated epithelial cells
-the cilia function to __ to the __
-the mucus is eventually __
-move mucus; epiglottis
-swallowed
Club cells(bronchioles)
-are they ciliated?
-what do they secrete?
-these help with __, using the enzymes __
-no
-protective proteins
-detoxification; P450
Describe what portions of airway have what cell types…
1.) Trachea and bronchi
2.) Bronchioles
1.) ciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelial cells; goblet cells
2.) ciliated simple cuboidal epithelium; club cells
Surfactant
-helps the alveoli to not __
-produced by __
-it is a mix of __, especially __
-collapse
-type 2 pneumocytes
-lecithins(lipids); dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine(DPPC)
Know that surface tension = __, which shrinks the surface area into __
-liquid-liquid forces; spheres
Law of LaPlace
-determines the __, which tells the force required to collapse an __
-low collapsing pressure= __
-high collapsing pressure= __
-when alveoli are large, there’s a low/high collapsing pressure?
-when alveoli are small, there’s a low/high collapsing pressure?
-when there is small alveoli surfactant, there’s a low/high collapsing pressure?
-collapsing force; alveoli
-easy to remain open
-difficult to remain open
-low collapsing pressure
-high collapsing pressure
-low collapsing pressure

Fetal lung maturity
-lungs will mature around __ weeks, when there’s an adequate level of __
-35; surfactant
Neonatal RDS
-a deficiency of __
-presents with __
-will respond poorly to __
-risk factors from the mother include __ and __
-the biggest complication that could arise is that __, leading to __
-if a baby is delivered prematurely, good prevention would include __
-if a baby presents with neonatal RDS, treatment is __
-surfactant
-atelectasis, decreased lung compliance, hypoxemia, increased pCO2
-O2
-maternal diabetes; C-section delivery
-alveolarization does not progress normally; bronchopulmonary dysplasia
-betamethasone
-surfactant
Lung lobe anatomy(picture)
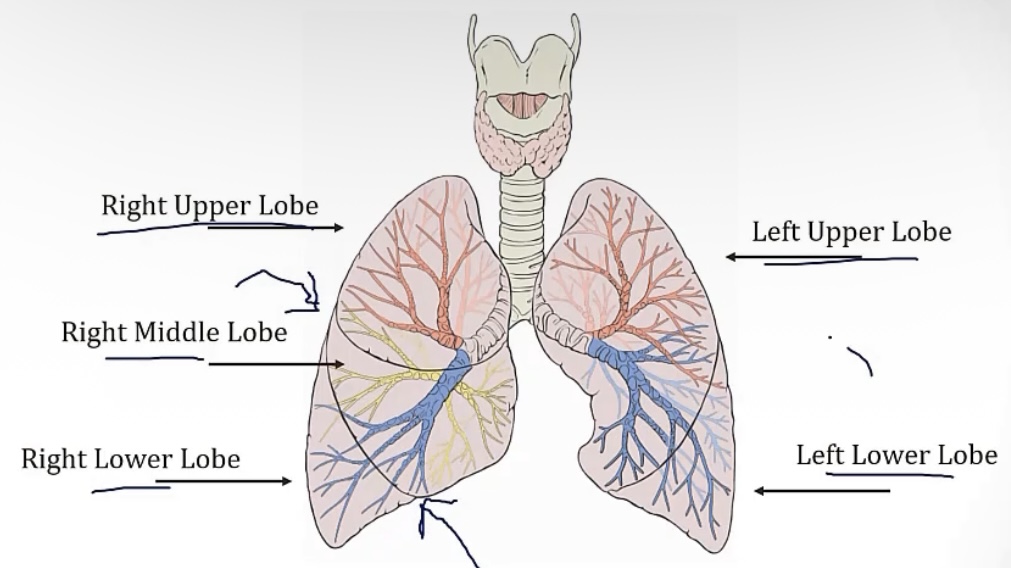
Foreign aspiration
-what lung is most likely to aspirate? Why?
-note mediastinal anatomy in the picture
-right lung; it’s larger/wider
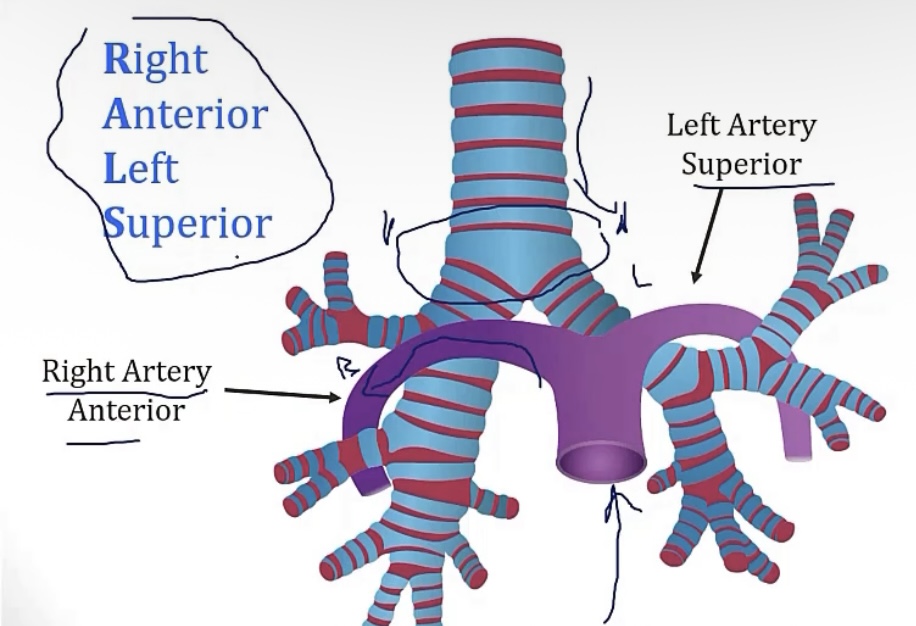
Mediastinum
-describe
-divided into 3 segments, __, __, and __
-trick for anterior mediastinum: __
-the space between the lungs
-anterior, middle, and posterior
-the terrible Ts(thymic masses, teratoma/germ cell tumor, thyroid growths, terrible lymphomas)
Muscles of breathing in normal/quiet vs intense/exercise breathing
QUIET…
-inspiration is due to __
-expiration is due to __
EXERCISE…
-__ raises the ribs for inhalation
-__ raises the sternum for inhalation
-for exhalation, there’s muscles such as the __, __, __, and __
RESPIRATORY DISTRESS…
-this is evident when the __ muscles are used
QUIET…
-diaphragm
-passive movement
EXERCISE…
-scalenes
-SCM
-Rectus, obliques, abdominals, and intercostals
RESPIRATORY DISTRESS..
-accessory
Diaphragm
-innervated by nerves __
-esophageal hiatus is at spinal level __
-aortic hiatus is at spinal level __
C3-C5(phrenic)
-T10
-T12
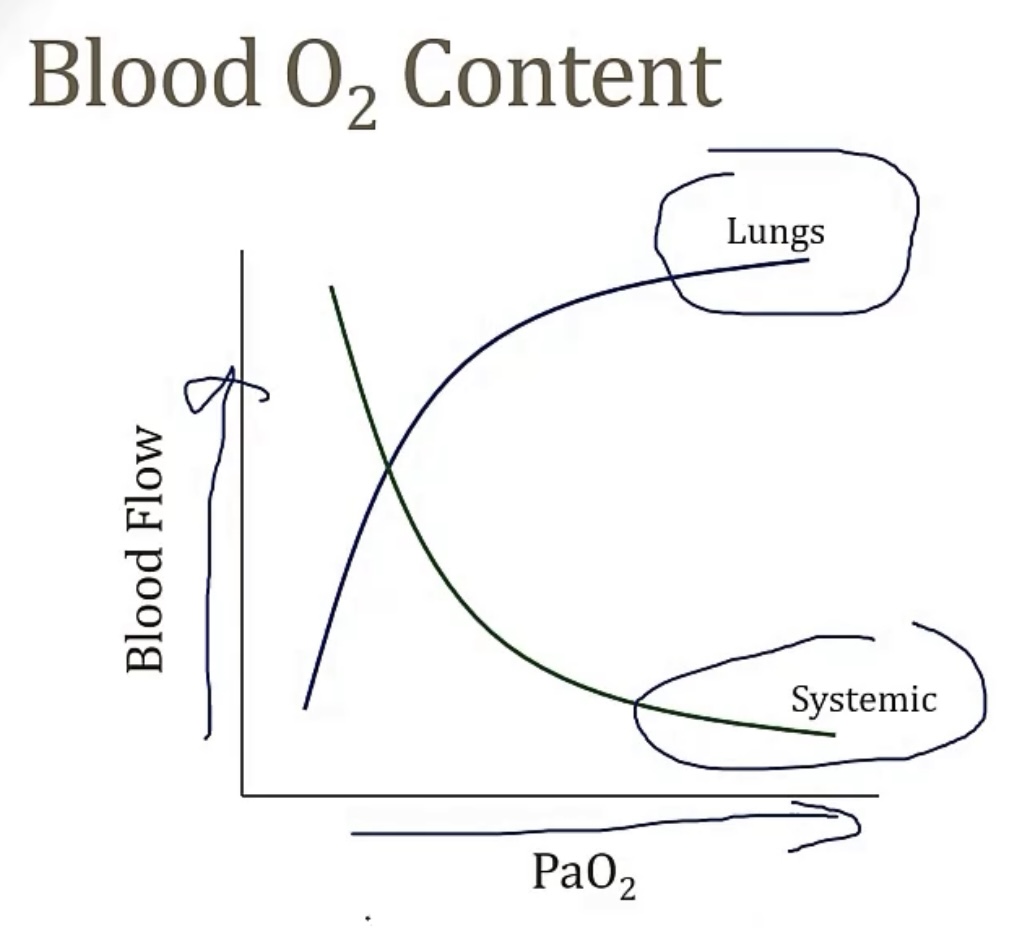
Pulmonary circulation
-pulmonary pathway is a high/low pressure system?
-walls of pulmonary arteries are thin/thick? High/low resistance?
-during hypoxic states, vessels will vasoconstrict/vasodilate?(view picture to see how this relates to systemic vessels) This increases/decreases blood flow? This shunts blood where?
-now discuss the above concept for fetal circulation…
-low pressure system
-thin; low
-vasoconstrict; decreases; to more ventilated areas
-low O2 states in the fetus create vasoconstriction, so when the baby is born, and it enters the world, with a high O2 content, then the lung arteries automatically dilate
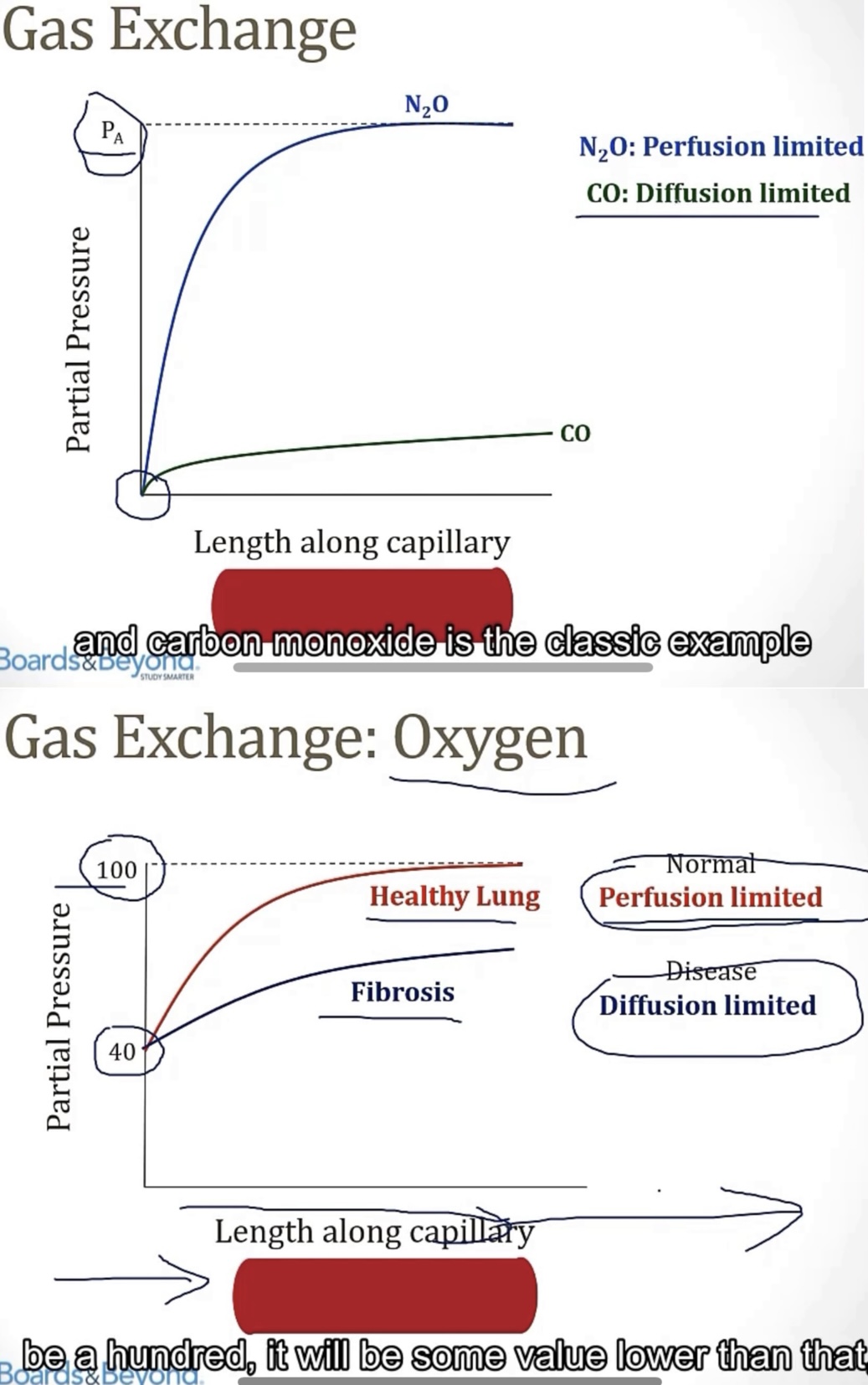
Perfusion limited gas exchange is determined based on __. Observing the picture, the best example is with __, and you can see capillary content quickly reaches equilibrium with the content in the __, causing the plateau.
Diffusion limited gas exchange is determined based on __. Observing the picture, the best example is with __, and you can see capillary content __, which is a hallmark of diffusion limited gas exchange, because it’s based on diffusion capability, not blood flow.
This can also be demonstrated when looking at healthy lungs, versus those in someone with __
Knowing that CO is diffusion limited allows for its use, in small levels, to run a test called __, where the patient __(describe the DLCO test). Many pulmonary conditions present with a decreased DLCO, such as __ or __
-blood flow/perfusion; NO; alveoli
-ability to diffuse across a barrier/wall; CO; never reaches equilibrium
-fibrosis
-DLCO(diffusing capacity of carbon monoxide); inhales CO, then they exhale, the breath is measured, to see how much CO diffused from the alveoli into the arteries; emphysema; fibrosis
Two vessel types(alveolar & extra-alveolar)
Capillaries are alveolar/extra-alveolar?
Arteries & veins are alveolar/extra-alveolar?
An increased lung volume __ the alveolar vessels; causing the resistance to __, this forces the extra-alveolar vessels to __
-Alveolar
-Extra-alveolar
-crushes; increase; open
Pulmonary hypertension:
-presents with a loud __, or __, heard in the __(where on the chest)
-histology-wise, this can present with thickening of the arterial walls, also called __, due to __ and __
-if untreated, this can develop into __
-gold standard diagnostic test for this is __. Due to this being invasive, a more non-invasive option is an __
-most common cause of pulmonary hypertension is from increased pressure in the __, which directly connects to the __, which is why it’s called __. Things that cause this are all related to the heart, such as __, or __
-when pulmonary hypertension is due to an increase in the pulmonary vascular resistance, it’s called __
-P2, second heart sound; left upper sternal border
-arteriosclerosis; thickened smooth muscle walls and narrowed lumen
-cor pulmonale
-right heart catheterization; echocardiography
-left atrium; pulmonary veins; pulmonary venous HTN; heart failure; valve disease
-pulmonary arterial HTN
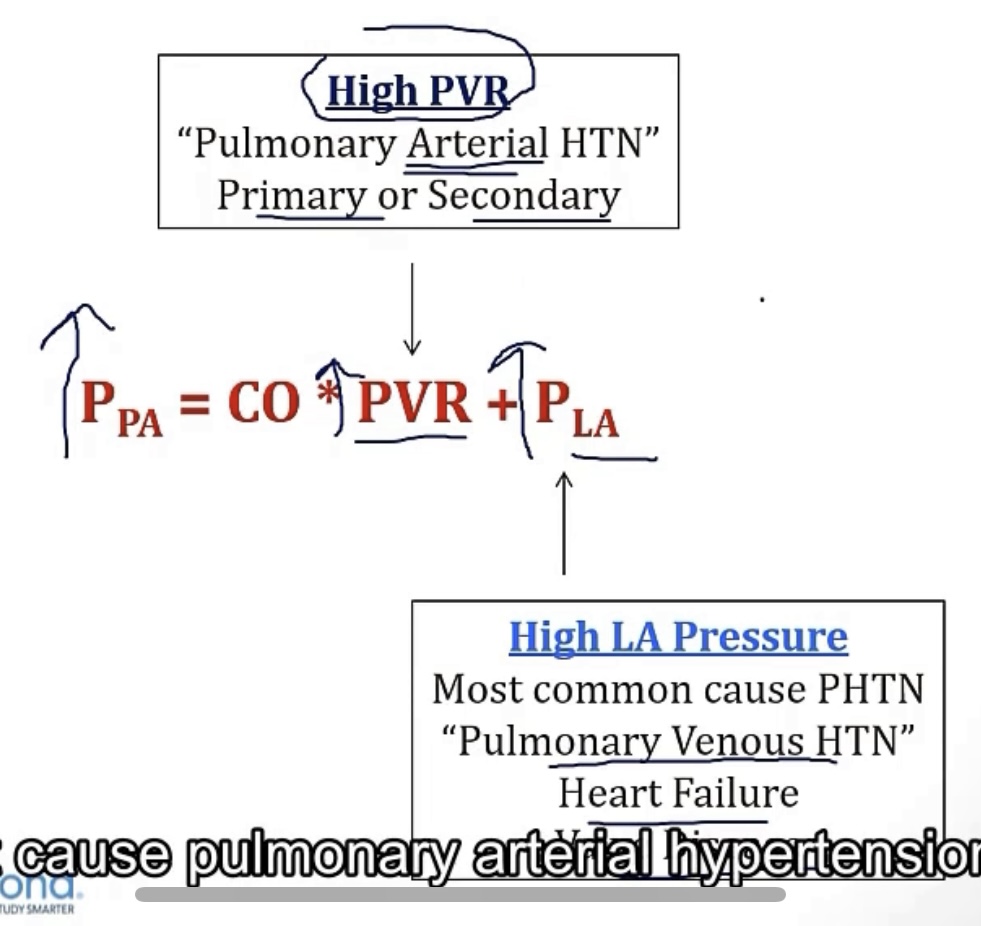
Pulmonary venous hypertension
-caused by issues of the __, or just simply __
-this can be any cause of high __, such as __, __, or __
-left side of the heart; left heart disease
-left atrial pressure; heart failure; mitral stenosis; mitral regurgitation
Pulmonary arterial hypertension
-due by a high __
-this can be caused by __(such as in __, __, or __)
-another cause of pulmonary arterial HTN is __, which creates decreased __, and therefore increased __
-if the above 2 reasons are not the cause, certain connective tissue diseases may cause pulmonary arterial hypertension, such as __
-treatment will consist of a few options, including __, __, or __
-pulmonary vascular resistance
-chronic hypoxemia; high altitude; sleep apneas; COPD)
-chronic pulmonary emboli; area for blood flow; pulmonary vascular resistance
-scleroderma
-epoprostenol(prostacyclin/vasodilator); bosentan(endothelin antagonist); sildenafil(PDE-5 inhibitor)
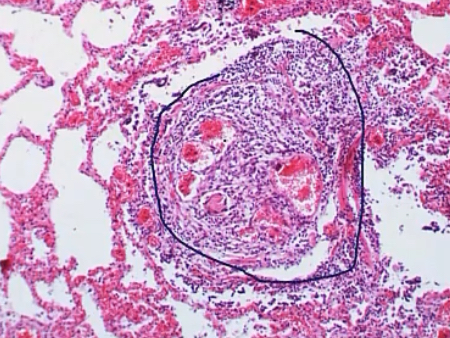
Idiopathic PAH
-traditionally presents in the age/sex of __
-the key symptom being a high __
-you will see high concentrations in the vasoconstrictor __, and low concentrations in the vasodilator __
-histology-wise, a diagnostic hallmark is __, which is caused by __, leading to branch points and __
-can sometimes be associated with the gene mutation __, which __, and is primarily __
-young women
-PVR
-endothelin; NO
-plexiform lesions; endothelial proliferation; multiple lumens
-BMPR2; inhibits smooth muscle proliferation; familial
Lung embryology
-the lung bud is an outgrowth from the __, which forms around the __ week of development
-foregut; 4th
Tracheoesophageal fistula
-most commonly seen alongside __
-where the esophagus does not __, which causes a buildup of __, as well as __, __, and __
-doctors will be unable to insert an __
-with the fistula between the trachea and the esophagus, there will be __, causing __; this can be seen on __
-esophageal atresia
-connect with the stomach; secretions; drooling, choking, and vomiting
-NG tube
-air in the stomach; gastric distention; x-ray
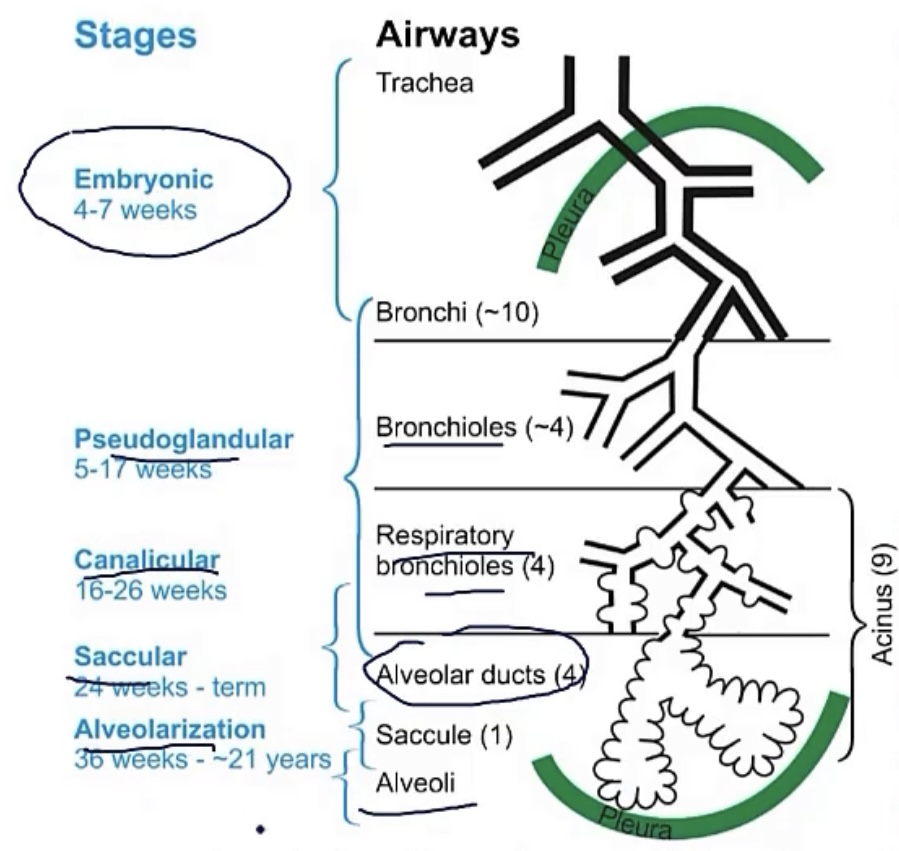
4 stages/periods of lung maturation
1.) __(between weeks __-__)
2.) __(between weeks __-__)
3.) __(between weeks __-__)
4.) __(__)
-pseudoglandular; 5-16
-canalicular; 16-26
-saccular; 26-birth
-alveolar; after birth
Pseudoglandular period
-stage __ in fetal lung maturation, during weeks __-__
-at this stage, the lungs will resemble a __
-there is branching to the level of __, and there will be no __ or __
-1; 5-16
-gland
-terminal bronchioles; respiratory bronchioles; alveoli
Fetal respirations
-fetal breathing will/will not occur in utero
-during this, the baby __ on __
-this is okay, though, as it __
-understanding this, for mothers born with decreased amniotic fluid, also called __, this can lead to __. This is an element of __, caused by __
-will
-aspirated; amniotic fluid
-stimulates lung development
-oligohydramnios; pulmonary hypoplasia; potter’s sequence; fetal kidney abnormalities
Canalicular period
-stage __ in fetal lung maturation, during weeks __-__
-there is now division of the __, as they go on to form __, which further divide into __
-this period is when __ cells form, which function to produce __
-the end of this period officially marks the potential of __
-2; 16-26
-terminal bronchioles; respiratory bronchioles; alveolar ducts
-type II pneumocytes; surfactant
-survival after birth
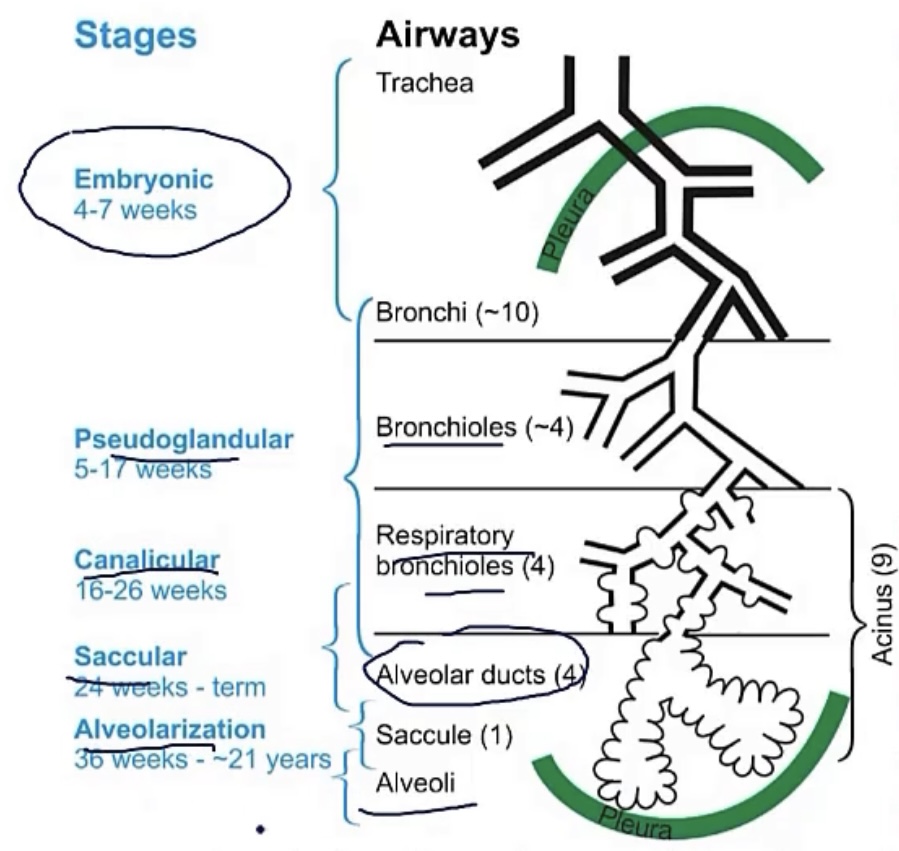
Saccular period
-stage __ in fetal lung maturation, during weeks __-__
-at this point, the __ have now formed
-there is also multiplication of __, as they come into contact with __
-3; 26-birth
-terminal sacs
-capillaries; alveoli
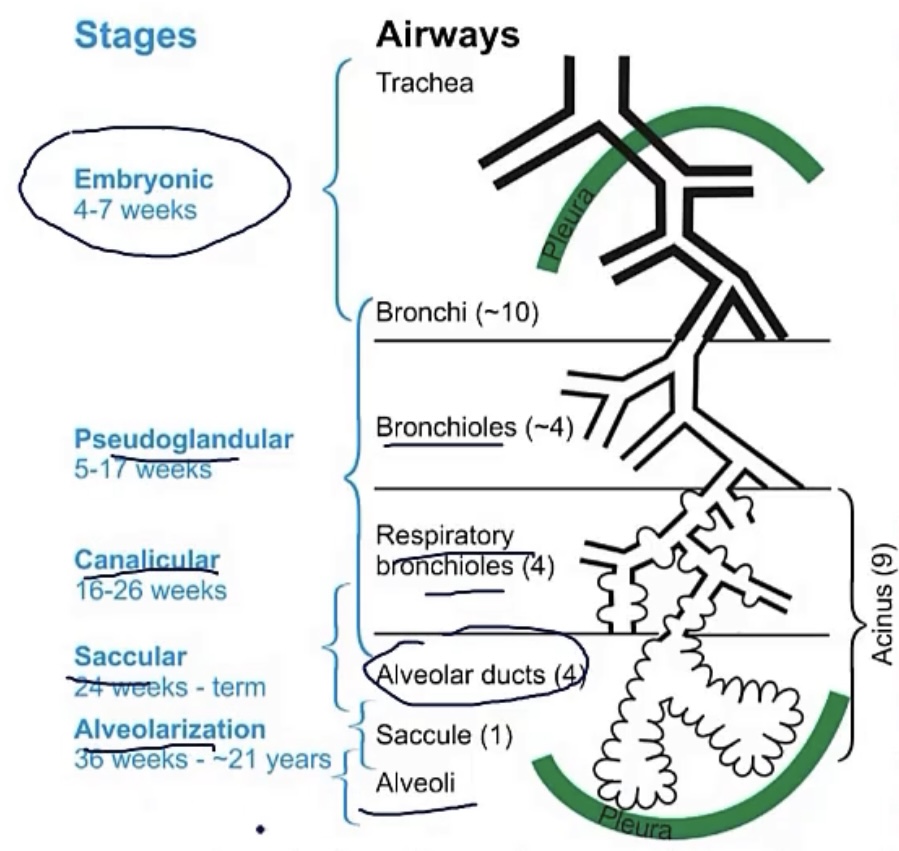
Alveolar period
-stage __ in fetal lung maturation, which occurs __
-from this stage, the number of __ and __ begin to increase
-lung development will continue until age __
-4; after birth
-respiratory bronchioles and alveoli
-10
Pulmonary hypoplasia
-this is __
-2 main causes…
1.) __, covered in ‘fetal respirations’ flashcard
2.) __, which is when a hole in the __ leads to __; this is often __
-underdevelopment of the fetal lungs
-oligohydramnios
-congenital diaphragmatic hernia; diaphragm; herniation of the GI into the chest, which causes underdevelopment of the fetal lungs; fatal
Bronchogenic cysts
-normally, the future lung buds off of the __/__ in development
-sometimes, abnormal buddings occur around the same area, usually found in the __
-these will have fluid that is __
-they will be lined with __, but will have no communication with __. Also, they will contain __
-they may lead to __ or __
-foregut/future esophagus
-mediastinum
-clear
-respiratory epithelium; lungs; cartilage
-pneumonia; compression of airway
PVR in utero vs at birth
In utero, PVR is __, but upon birth, it __
-this is mostly accompanied with __ going from only about __, to __
-high; falls significantly
-cardiac output; 10%; 100%
Proper lung physical exam should include __, __, and __(such as __ or __)
-percussion; auscultation; special tests; pectoriloquy; fremitus
Percussion on a physical exam of the lungs
-describe it
-the normal sounds you hear are __, and abnormal would be __
-dull could indicate __ or__(such as in __)
-hyperresonant indicates that __, such as in __ or __
-finger tapping against the thorax
-resonant; dull or hyperresonant
-pleural effusion; consolidation; pneumonia
-air is trapped; pneumothorax; emphysema
Lung auscultation on a physical exam of the lungs
-normal sounds heard should be __
-there are a few different adventitious(or abnormal) lung sounds that could be heard…
RALES/CRACKLES…
-this is when small airways __
-can be heard at what point in breathing?
-could point to __, __, or __
WHEEZES…
-from air flowing through __
-can be heard at what point in breathing?
-classic cause is __
-could point to __, __, or __(in which case the wheezing would be __)
RHONCHI…
-heard when there’s __
-due to the size of airways involved, the breath sounds will be __
-classic cause is __
BRONCHIAL BREATH SOUNDS…
-sounds like __, like flow through a __
-this will be accompanied with a __ than normal
-commonly seen in __, such as in __
STRIDOR…
-can be heard at what point in breathing?
-it will be most loudly heard over __, indicating partial obstruction of the __ or __
-classic causes include __, __, __, __
-vesicular
RALES/CRACKLES…
-pop open after collapse
-any point of inspiration or expiration
-pulmonary edema, pneumonia, or interstitial fibrosis
WHEEZES…
-narrowed bronchi
-any point of inspiration or expiration
-asthma
-heart failure, chronic bronchitis, obstruction(cancer); unilateral
RHONCHI…
-secretions in the large airways
-coarse
-COPD
BRONCHIAL BREATH SOUNDS…
-high-pitched lung sounds; tube
-longer expiratory phase
-consolidation; pneumonia
STRIDOR…
-entirely inspiratory
-the neck; trachea or larynx
-diphtheria, croup, epiglottitis
Special tests on a physical exam of the lungs
PECTORILOQUY
-this will include a few different tests, which are __, __, and __
-with bronchophony, voice sounds may appear __
-with whispered pectoriloquy, patient will whisper __, which should sound __, but will be __
-with egophony, the patient will say __, which will sound to the physician as __
-all 3 of these indicate __ or __
FREMITUS
-place your hands on the patient’s back as they say __
-it will vary with density of the lung tissue, but the classic condition with increased fremitus is __
-common cases with decreased fremitus are __, __, or __
PECTORILOQUY…
-bronchophony; whispered pectoriloquy; egophony
-louder and clearer
-99; muffled; abnormally clear
-‘E’; ‘A’
-effusion or consolidation
FREMITUS…
-‘99’
-lobar pneumonia
-pleural effusion; pneumothorax; atelectasis
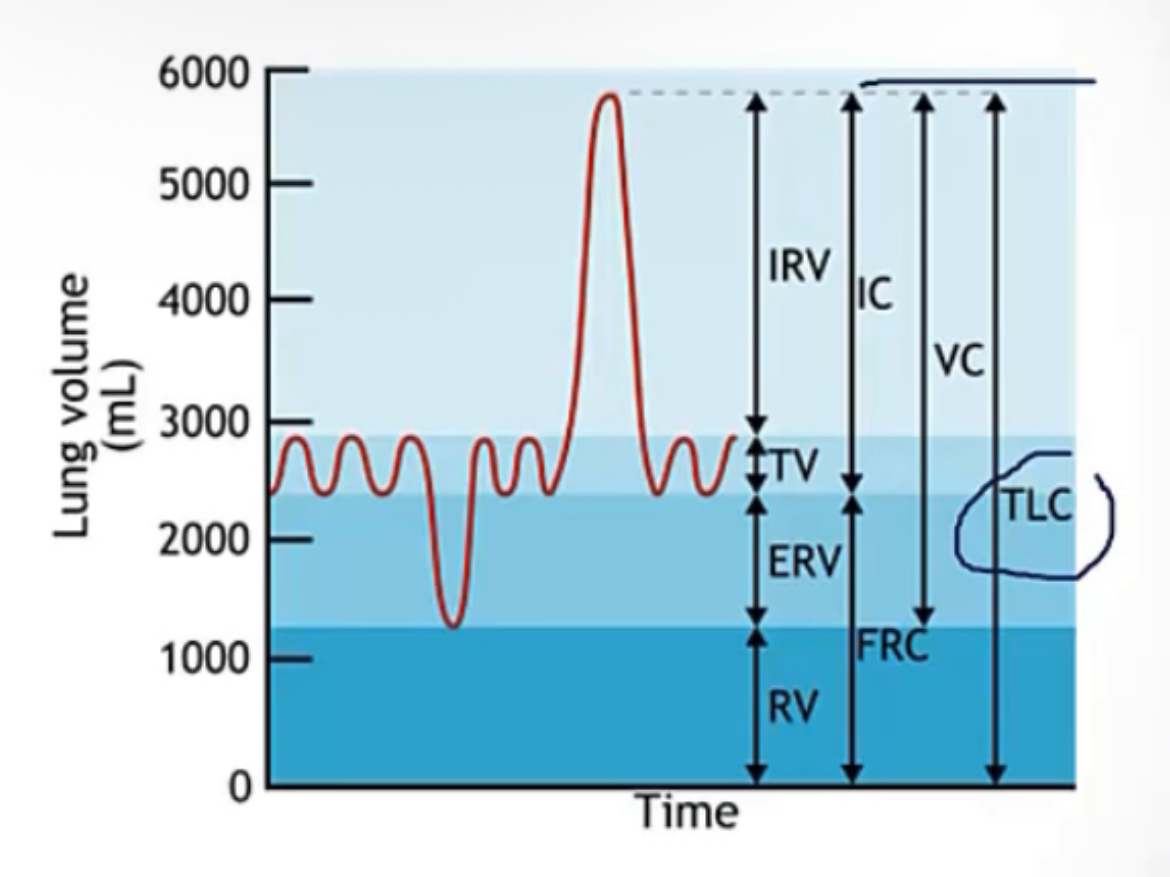
Lung volumes
Tidal volume(TV)
-describe
Expiratory reserve volume(ERV)
-describe
Inspiratory reserve volume(IRV)
-describe
Residual volume(RV)
-describe
Total lung capacity(TLC)
-describe
Inspiratory capacity
-describe
Vital capacity
-describe
Functional residual capacity
-describe
-here the pressure inside the system is __, because the pressure equals the atmospheric pressure
Tidal volume(TV)
-air in/out with each quiet breath
Expiratory reserve volume(ERV)
-extra air pushed out with force, beyond the tidal volume(the residual volume will remain in the lungs)
Inspiratory reserve volume(IRV)
-extra air drawn in with force, beyond the tidal volume(lungs filled to capacity)
Residual volume(RV)
-air that cannot be blown out of the lungs, no matter what
Total lung capacity(TLC)
-sum of all volumes(RV + ERV + IRV + TV)
Inspiratory capacity
-the most air that you can inspire(TV + IRV)
Vital capacity
-the most air that you can exhale(TV + IRV + ERV)
Functional residual capacity
-residual volume after a quiet expiration(RV + ERV); volume when the system is relaxed
-zero
Lung pressures
Alveolar pressure- describe
Intrapleural pressure- describe
Transpulmonary pressure- describe and give formula
Alveolar pressure(pressure within the alveoli)
Intrapleural pressure(pressure in the pleural space)
Transpulmonary pressure/TPP(pressure across the walls of the alveoli, required to keep them open, or they’ll collapse)
(Alveolar pressure - Intrapleural pressure = Transpulmonary pressure)
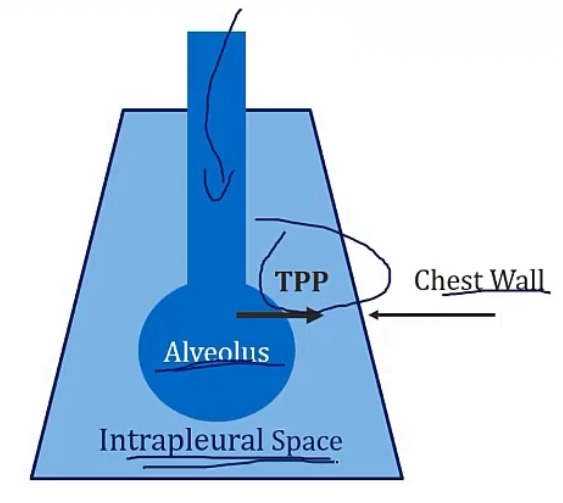
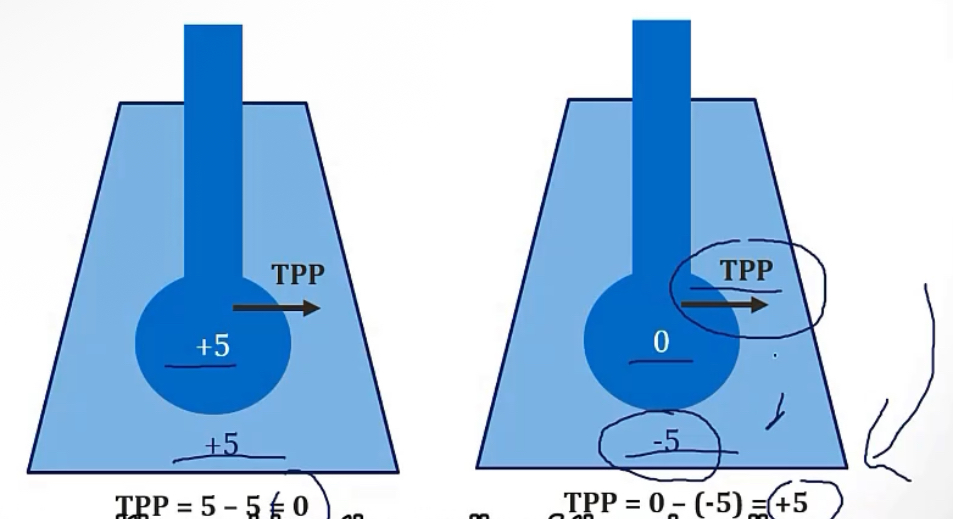
More of Transpulmonary pressure/TPP…
-describe
-equation
-examples in picture
-pressure across the walls of the alveoli, required to keep them open, or they’ll collapse
-(Alveolar pressure - Intrapleural pressure = Transpulmonary pressure)
-if you have a TPP of 0, from alveolar and intrapleural being equal, this will collapse the lungs. If you have a situation where the TPP comes out to be a positive number, this is what required for proper respiration
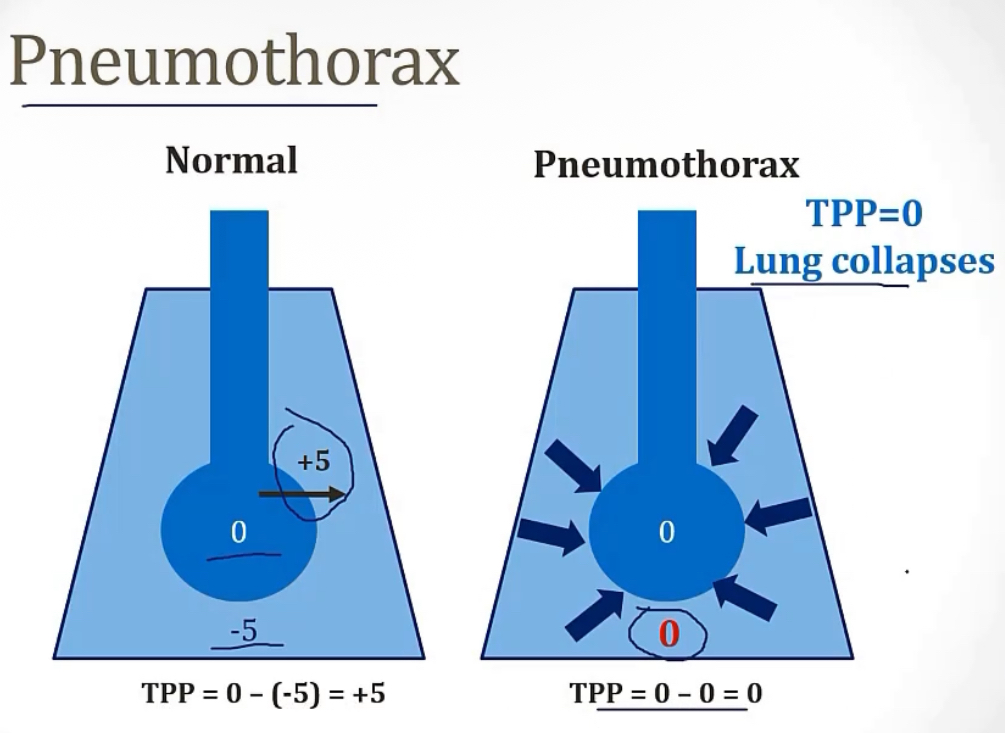
More on Intrapleural pressure…
-describe
-negative/positive during normal quiet breathing?
-the reason for the above answer is because while the alveoli want to __, the chest wall wants to __, creating the __ pressure
-the picture shows an example with a pneumothorax
-pressure in the pleural space
-negative
-collapse; expand; negative
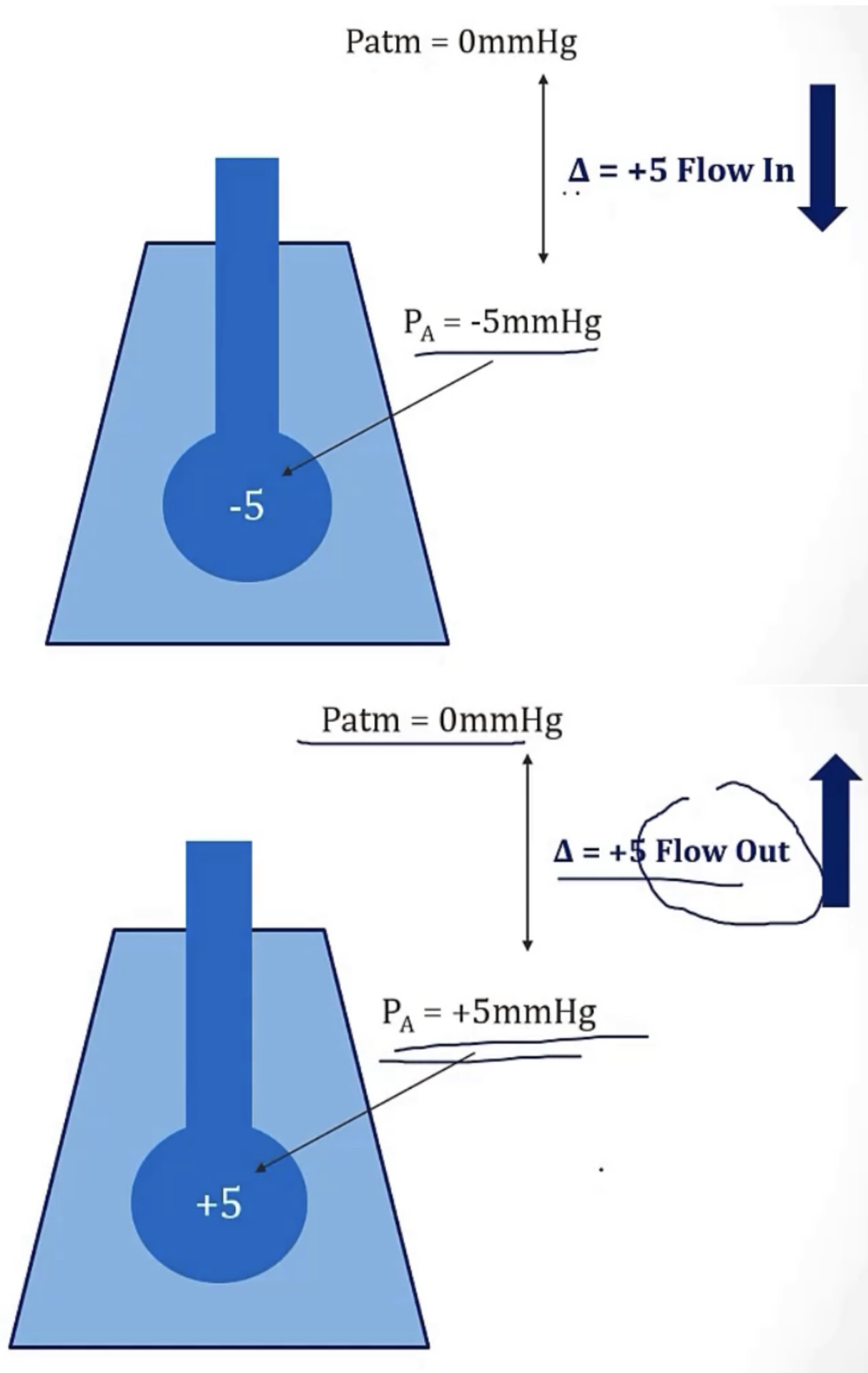
What are the 2 main reasons that there needs to be a difference in pressure between the alveoli, and the atmosphere?
-air flow moves in a gradient of __ to __, so a positive alveolar pressure will have air moving __, and a negative alveolar pressure will have air moving __
-air flow, in general, is decided based on changes in the __ pressure, due to movement of the __
1) to keep the alveoli from collapsing
2) to force air to flow into the lungs
-high; low; out of it; into it
-Intrapleural; diaphragm
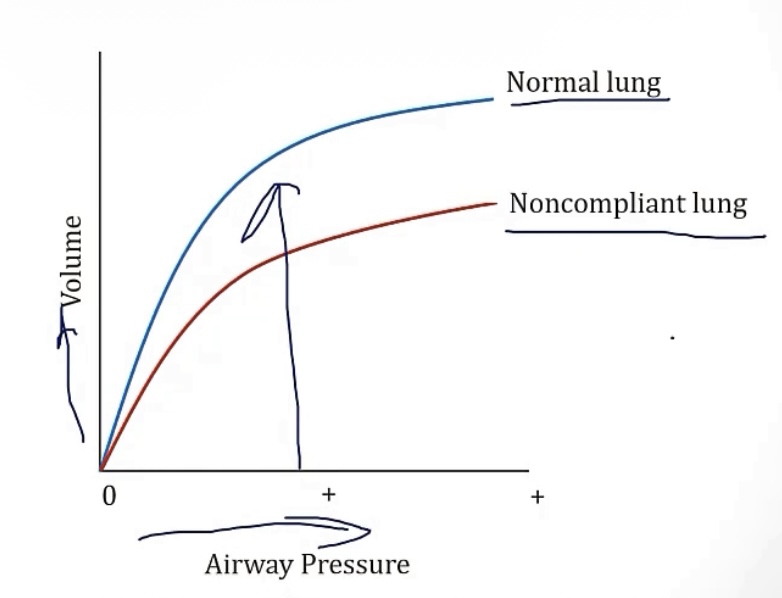
Compliant lung vs noncompliant lung
-Compliant lungs need __ amount of effort from diaphragm
-Compliant lungs generate __ pressure change across lungs, which generates a __ volume change
**noncompliant lungs are the opposite**
-less lung compliance means a __ FRC(air leftover after quiet exhalation), which is seen in cases of __, __, and __
-greater lung compliance means a __ FRC, which is seen in cases of __
-small
-small; large
-lower
-lesser; pneumonia, pulmonary edema pulmonary fibrosis
-greater; emphysema, aging, surfactant
Forced exhalation
-this is same/different as normal quiet breathing exhalation?
-think of if you breathed in, held it, then pushed it out like you’re firing a nerf bullet with your lungs, the charge up and the forced push-off…
-the pleural pressure will be __, which __ the airway, putting pressure on the __, pushing air out, forcing it to flow through the airways
-different
-positive; compresses; alveoli
Equal pressure point
-during a case of force expiration, when you force air out and the pleural pressure is __, you’d think this would collapse the alveoli
-BUT, this doesn’t happen because there’s a point tracing back up the airway called the __(where __ pressure and __ pressure are equal), where lowering the alveolar pressure anymore will was to __. Thankfully, in healthy people, this point is so much higher up in the airway, that the area is __, which protects it from collapsing
-this idea can be concerning for those with unhealthy lungs, because for these individuals, the equal pressure points shifts closer to the alveoli, making it easier for alveolar collapse
-positive
-equal pressure point; pleural and airway; collapse; cartilaginous
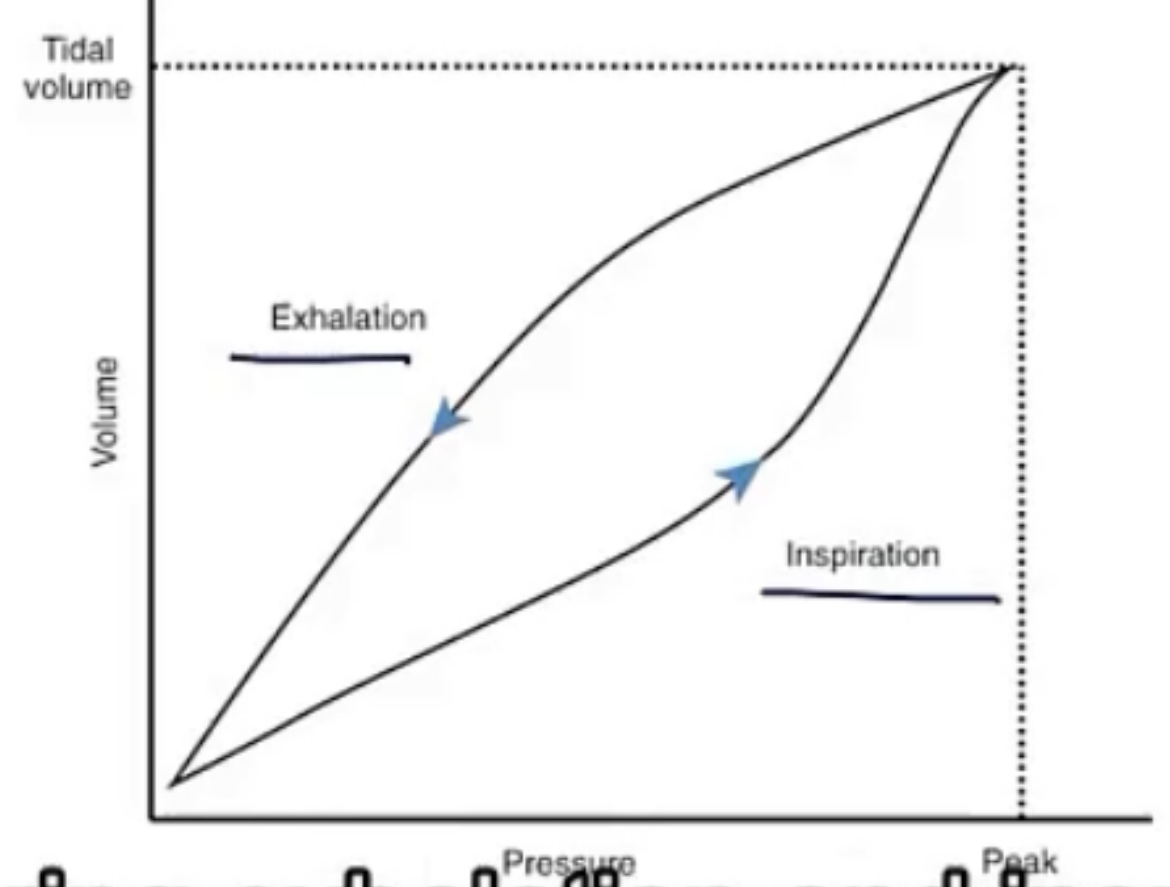
Hysteresis
-when pressure volume curves are taken, they can be different depending on if the patient is __ or __
-the slope of a pressure volume curve equals the __, so it is said that the same lung can have difference compliance levels, based on what stage of respiration it’s in, and this is called __
-the difference in these curves is caused by __
-when starting to inhale, the lung volume is very __, so the molecules are __, causing a high __(meaning you must exert a __ force to break the tension, creating a different curve). Inversely, at the start of expiration, the lung volume is very __, so the molecules have plenty of room, therefore there’s __ surface tension
-inhaling or exhaling
-compliance; hysteresis
-surface tension
-small; very close and bouncing around; surface tension; large; large; lower
Ventilation = __ x __(aka __)
Alveolar ventilation:
-used for __
Dead space ventilation:
-considered __ ventilation
-volume; frequency or RR
-gas exchange
-wasted
Dead space
-this space is filled with __, but no __ occurs here
2 types…
1.) anatomic dead space
-describe
-this can include the __ and __
2.) physiologic dead space
-describe
-this includes functional dead space, and the __ of the lung is the greatest contributor
-air; gas exchange
1.) anatomic dead space
-volume of conducting portions of the respiratory tract
-nose; trachea
2.) physiologic dead space
-anatomic PLUS volume of alveoli that doesn’t exchange gas
-apex
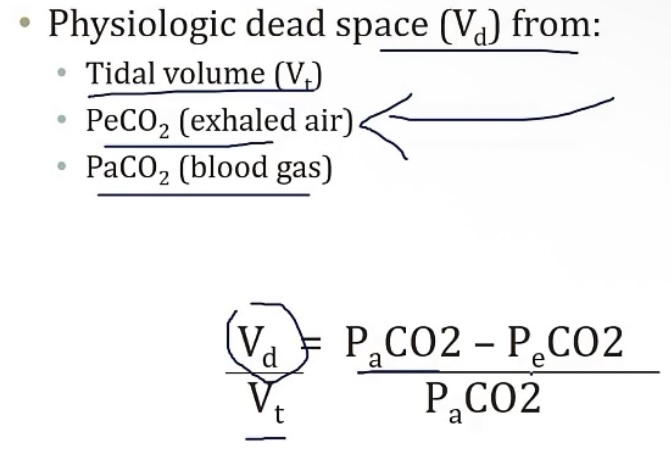
Measuring dead space
-Can be calculated using __
-equation is in the picture
IF THE DEAD SPACE WERE ZERO…
-the left side of equation would be zero, and this means there would be complete __ occurring across all __
-as dead space decreases, the expiratory CO2 will start to be equal to the __, and as there’s more __, there’s less retained __
IF THE DEAD SPACE WERE 100%…
-the left side of equation would be one, and this means there would be no __ occurring across all __
-as the dead space increases, the expiratory CO2 would be __, since no CO2 is diffusing across the alveoli
-and with less __, there’s more __
-Bohr’s method
IF THE DEAD SPACE WERE ZERO…
-gas exchange; alveoli
-arterial CO2; gas exchange; CO2
IF THE DEAD SPACE WERE 100%…
-gas exchange; alveoli
-decreasing
-gas exchange; CO2 retention
Alveolar ventilation equation
-use this to predict the __
-the equation is __(volume/minute) - __
-example in picture
-alveolar CO2 level
-total ventilation; dead space

PAO2 is __
PACO2 is __
PaO2 is __
PaCO2 is __
PV is __
Pe is __
-alveolar O2
-alveolar CO2
-arterial O2
-arterial CO2
-venous pressure
-expired pressure
Elevated CO2 is called __/__(same thing)
-it will drive you towards alkalosis/acidosis?
-this will cause your respirations to __
-3 major causes of high CO2 are __, __, and __
-hypercapnia/hypercarbia
-acidosis
-increase
-increased CO2 production; hypoventilation; increased dead space
Alveolar gas equation
-used to predict the __
-equation is in the picture
-alveolar O2 level
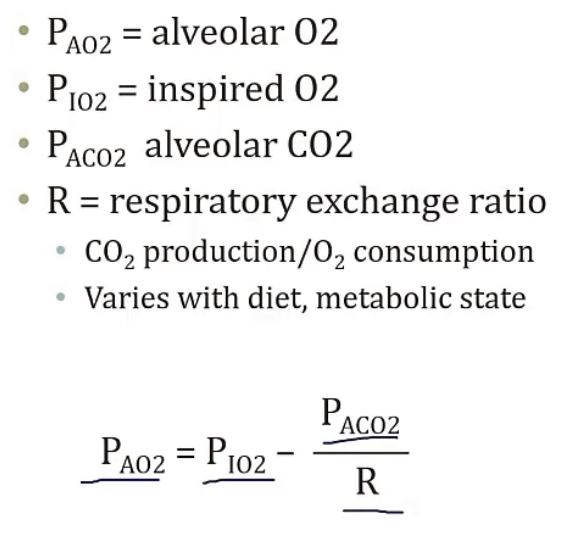
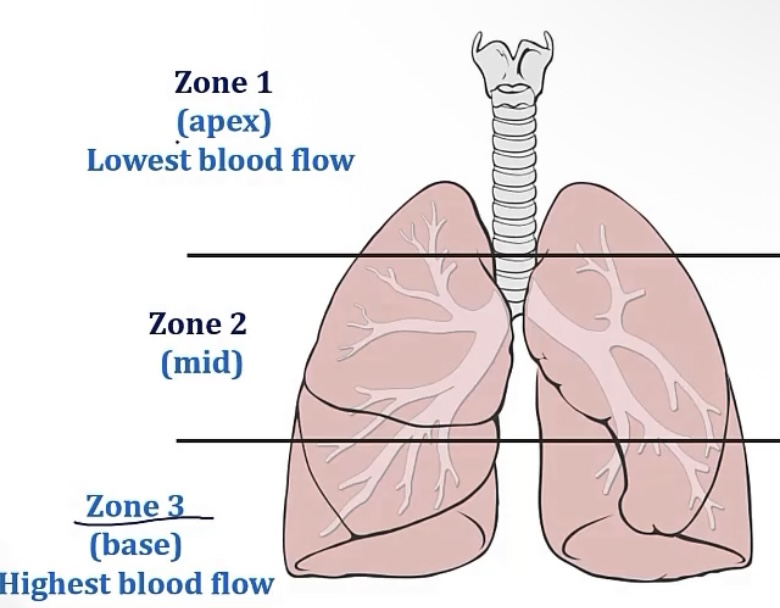
Lung perfusion
-when standing up, perfusion of the lungs is __(as opposed to when you’re __), due to __
-for this reason, the lungs are divided into __ zones
-the zone with the greatest blood flow is the __
-the zone with the least blood flow is the __
-zone 2 is just the __
-similarly, ventilation is greatest in __, also due to __, but it’s because __
-zone 1 will have the greatest PaO2, which is why __ is most likely to develop here, such as in __
-uneven; laying down; gravity
-zones
-base
-apex
-middle
-zone 3/the base; gravity, the above zones push down on zone 3, forcing the air out
-bacteria; tuberculosis
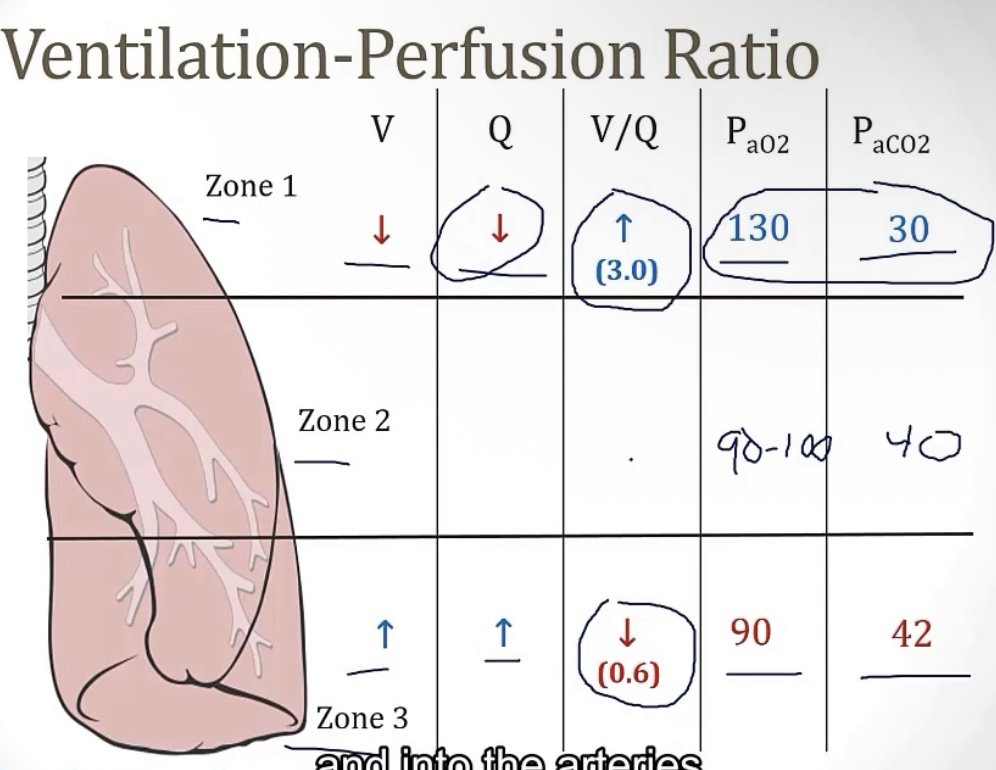
Ventilation-Perfusion Ratio:
-also called the __, it is the __/__
-a normal V/Q ratio is __
-following with change in perfusion and ventilation in the 3 zones of the lungs, the V/Q ratio in the base will be the __, while the V/Q ratio in the apex will be the __. This is because while both values will decrease from bottom to top, the __ will decrease more
-V/Q ratio; alveolar ventilation/pulmonary blood flow
-0.8
-lowest; greatest; blood flow
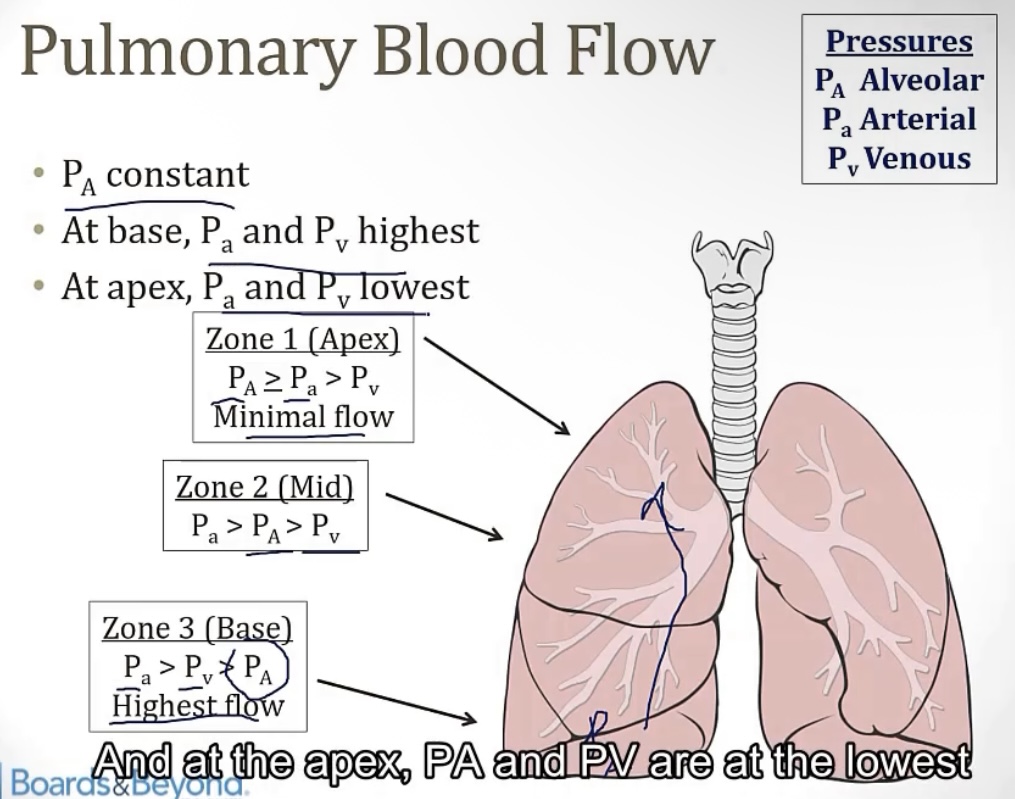
Pulmonary blood flow
-the flow is generally determined by the __; this compares to normal vessels wheee the blood flow is determined by the difference between __ and __
-so in the lungs, high alveolar pressure means __ blood flow, which means the formation of __
-alveolar pressure; arterial and venous pressure
-little; dead spaces
Effects of exercise on the V/Q ratio
-during exercise, the blood flow __, and the perfusion __
-remember, perfusion will crease more quickly than blood flow, so the V/Q ration will __, getting closer to 1
-exercise will also make tissues use more __, causing an increase in __ and a decrease in __
-increases; increases
-increase
-O2; venous CO2; venous O2
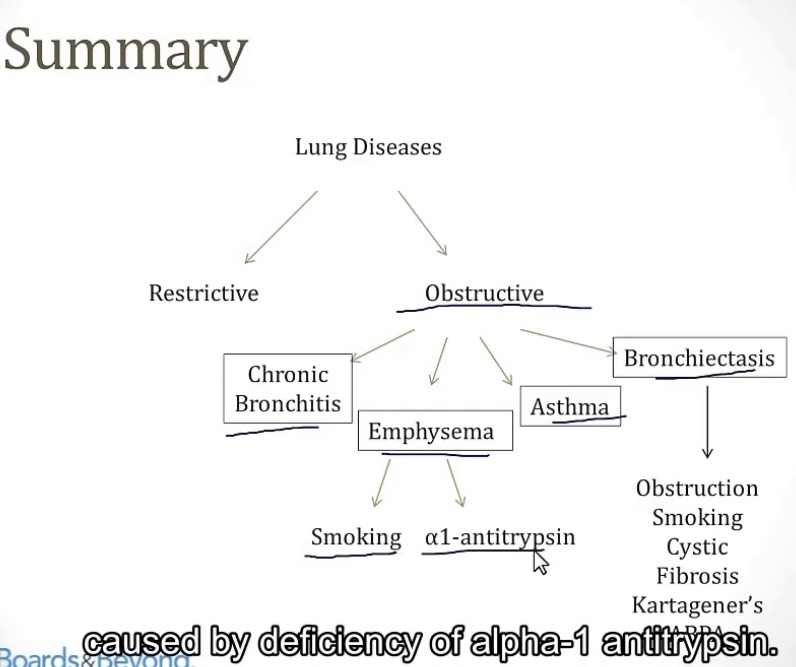
Obstructive lung diseases
-The FVC is raised/reduced?
-The FEV1 is raised/reduced?
-The FEV1/FVC is raised/reduced?
-Both the residual lung volume, and total lung volume, will increase/decrease?
-examples of obstructive disease are __, __, __, and __
-of these conditions, __ is the only one that will show improvement from administration of a bronchodilator
-reduced
-reduced
-reduced(hallmark)
-increase
-chronic bronchitis, emphysema, asthma, bronchiectasis
-asthma
Chronic Bronchitis
-obstructive/restrictive?
-presents as a __, with __
-strongly associated with __(bad!)
-the productive sputum comes from hypertrophy of the __, which can cause the lungs to become __
-the __ will be high, which indicates thickness of gland walls
-there will also be an increased risk of __
-the CO2 will be __, and the O2 will be __
-there will normally be pulmonary __, and __-sided heart failure
-general patient presentation will include __, __, __, and __
-obstructive
-chronic cough; productive sputum
-smoking
-mucus glands/cells; plugged
-Reid index
-infections
-high; low
-hypertension; right
-wheezing, cough, crackles, cyanosis(shunting)

Emphysema
-obstructive/restrictive?
-commonly associated with __(bad!)
-the pathology of this disease is that smoking will create too many __, which will overwhelm the __. This leads to a deficiency of __, due to ineffective __, causing damage to the __ lobes.
Side note, in addition to the release of proteases, smoking also recruits __ and __
Hallmark of this disease is loss of __, so the smaller airways will __, leading to air getting __
-general presentation is __(which doesn’t have sputum like __), __, __, __
-2 general types of emphysema, based on which portion of the airway is damaged…
1.) centriacinar emphysema(this is the form commonly associated with __)
2.) panacinar emphysema(this is the form commonly associated with __)
-obstructive
-smoking
-proteases; anti-proteases; alpha1 anti-trypsin, anti-proteases; lower
-neutrophils and macrophages
-elastic recoil; collapse in exhalation; trapped
-cough; chronic bronchitis; hyperventilation; weight loss; barrel chest
-smoking
-alpha1 anti-trypsin deficiency

COPD
-the overarching term that includes __, __, and __
-chronic bronchitis; emphysema; asthma
Alpha1 Anti-Trypsin Deficiency
-cause of __, more specifically the subtype __
-deficiency is __
-causes a decrease in __, which keeps __ in balance, including __
-this deficiency can also cause polymerization of the AAT in __(cell), causing alpha1 buildup in the __(organ), leading to __
-patients with this condition should NEVER __, as this can stimulate __ production, which is bad since they don’t have the __ to inhibit it
-emphysema; panacinar emphysema
-inherited
-AAT(elastase inhibitor); proteases; elastase
-hepatocytes; liver; liver cirrhosis
-smoke; elastase; alpa1 anti-trypsin
Asthma
-obstructive/restrictive?
-reversible/irreversible?
-airways are hyper-responsive; usually due to __, which is a __ hypersensitivity(other asthma triggers can be __)
-general presentation is __
-if severe and untreated, asthma can cause __, which is fatal
-diagnosis is based using __, which is a __ that causes __. This is given incrementally, and the doctor waits for the FEV1 to drop significantly. If this occurs using only a small dose, then that’s a positive test for asthma
-pathology for asthma includes __ and __
-aspirin causes a special subtype, called __. These individuals have the classic triad of __, __, and __. It is caused by a dysregulation in the metabolism of __, which leads to overproduction of __. For this reason, treatment is with a __, such as __ or __
-obstructive
-reversible
-allergens; type I; exercise, stress, aspirin
-dyspnea, wheezing, cough, hypoxia
-status asthmaticus
-metacholine; muscarinic; bronchoconstriction
-curschmann’s spirals and Charcot-Leyden crystals
-AERD(aspirin exacerbated respiratory disease); asthma, chronic rhinosinusitis; nasal polyps; arachidonic acid; leukotrienes; leukotriene receptor antagonist; montelukast or zafirlukast
Bronchiectasis
-obstructive/restrictive
-general presentation is __
-the hypoxia can lead to __
-can be caused by different things, such as tumors, smoking, __, __, and __
KARTAGENER’S SYNDROME…
-a condition that’s part of __
-the cilia are unable to properly __ due to a mutation in the protein __
-other elements of this condition include __, __, __, and __
ALLERGIC BRONCHOPULMONARY ASPERGILLOSIS…
-Aspergillus exposure causes a __ reaction
-Aspergillus only targets those that are __
-primarily in patients with __ and __
-on labs, you will see high __ and __, as well as __ and __
-diagnosis is by an __
-treatment is with __
-obstructive
-recurrent infections, cough with excessive foul-smelling sputum
-cor pulmonale
-cystic fibrosis, kartagener’s syndrome, allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis
KARTAGENER’S SYNDROME…
-primary ciliary dyskinesia
-beat; dynein
-chronic sinusitis(recurrent infections); bronchiectasis; male infertility; and situs inversus
ALLERGIC BRONCHOPULMONARY ASPERGILLOSIS…
-hypersensitivity
-immunocompromised
-asthma; CF
-CD4 and interleukins; eosinophilia; IgE
-Aspergillus skin test
-steroids

Spirometry
-method used to assess __
-produces a graph that measures __ over __
-the graph SHOULD produce a __, and expiration should last more than __
-the 2 volume values in respiration that normal spirometry CANNOT measure are __ and __
SPIROMETRY WITH VOLUMES…
-this form of spirometry can calculate __, and the curve will appear __ in comparison to a normal spirometry curve
-this can make it easy to determine an obstructive or restrictive disease, based on the starting volume value(obstructive diseases will have a __ starting point, and restrictive diseases will have a __ starting point)
-pulmonary function
-volume; time
-sharp peak; 6 seconds
-residual volume; forced residual capacity
SPIROMETRY WITH VOLUMES…
-residual volume; upside down
-greater; lesser
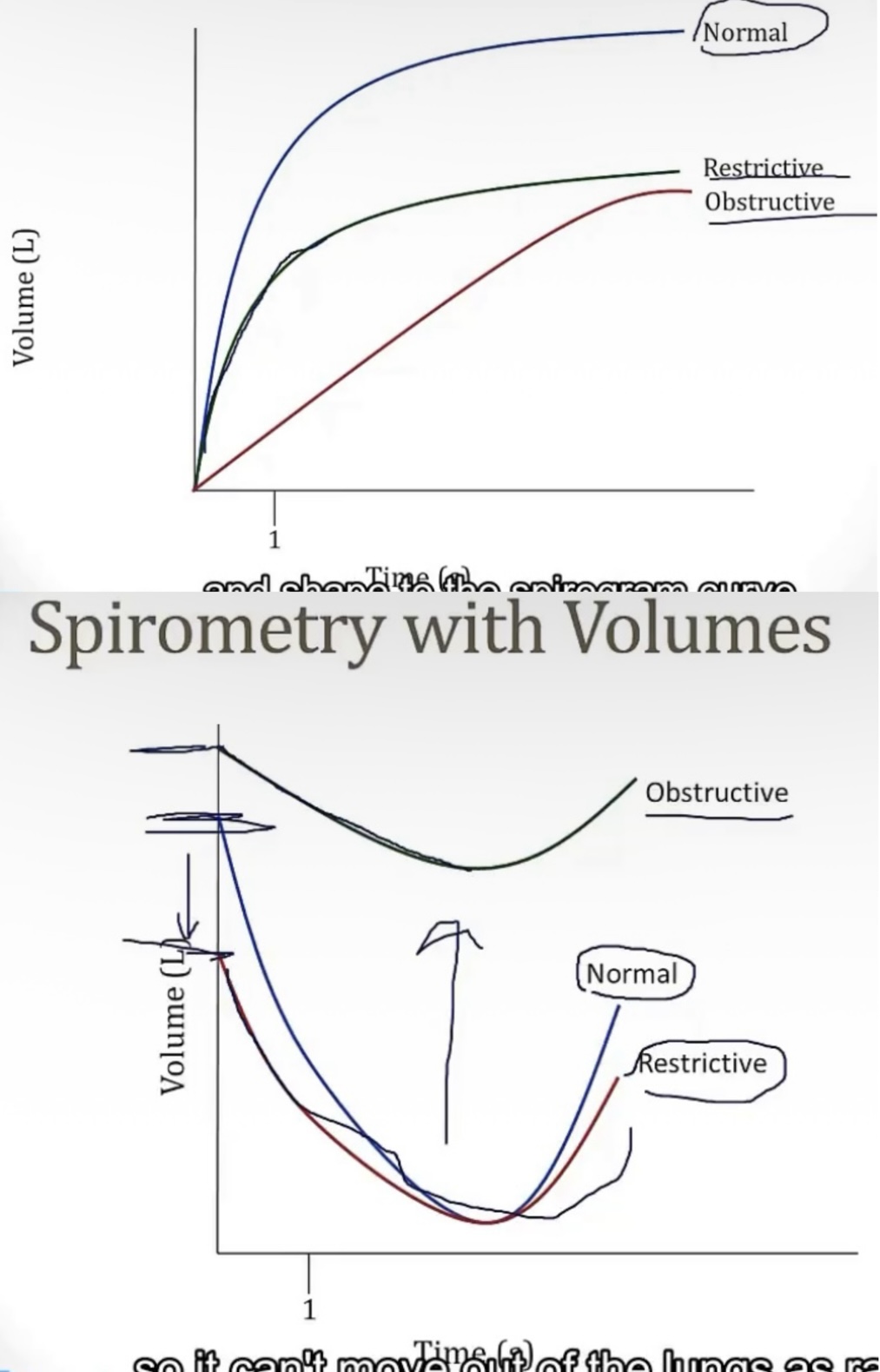
Obstructive and restrictive diseases on spirometry:
-an restrictive disease will have an FEV1 that is __, and an FVC that is __, leading to an FEV1/FVC ratio that is __
-an obstructive disease will have an FEV1 that is __, and an FVC that is __, leading to an FEV1/FVC ratio that is __
-decreased; decreased; normal
-very decreased; decreased; decreased
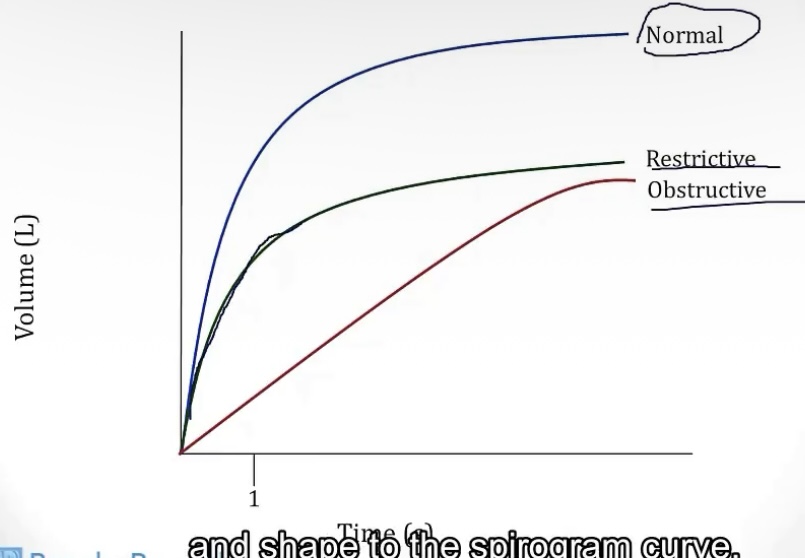
Flow volume loop
-charted with data from a __, that plots __ over __
-this chart will not provide an FEV1, but will give you a __. This is helpful for __ lung diseases, as the PEF will __ as obstruction gets worse.
-spirometry; volume flow; volume
-PEF(peak expiratory flow); obstructive; drop significantly
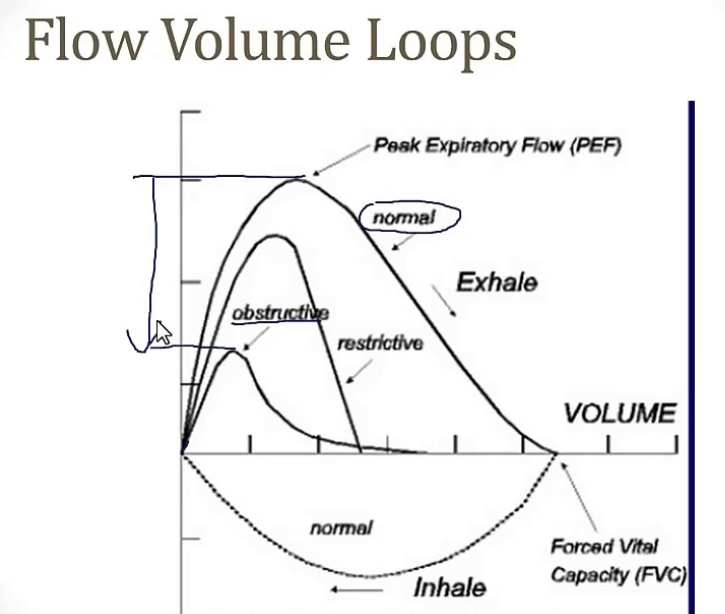
Work of breathing is proportional to __
-there are 2 forms of resistance the body must overcome to breathe, __ and __
AIRFLOW RESISTANCE…
-the slower you breathe, the __ resistance
-due to faster breathing causing a __ flow, while slow breathing allows a more __ flow
ELASTIC RESISTANCE…
-the faster you breathe, the __ resistance
-explain
-picture includes both a normal work of breathing, and examples of those with obstructive and restrictive diseases
-resistance
-airflow resistance; elastic resistance
AIRFLOW RESISTANCE…
-lower
-turbulent; laminar
ELASTIC RESISTANCE…
-lower
-this is because with a faster respiratory rate, the alveoli don’t have as much time to deflate as if you were breathing slowly, so there’s less elastic resistance to overcome, since they’re not as inflated
Restrictive lung diseases
-FEV1/FVC ratio is __(compared to obstructive)
-caused by 2 main mechanisms, __ and __
POOR BREATHING MECHANICS…
-this is a __ pulmonary issue(not primary), therefore A-a gradient is __
-this mechanism can be caused by __ issues(examples being __), or by __ issues(examples being __)
INTERSTITIAL LUNG DISEASE…
-characterized by __, with a hallmark __ appearance on X-ray
IN GENERAL…
-once you are aware that the problem is restrictive, the difference between interstitial lung disease and something extra-pulmonary can be determined using a __. This will be normal for __ complications, and decreased for __ complications
-normal
-poor breathing mechanics; interstitial lung diseases
POOR BREATHING MECHANICS…
-secondary; normal
-neuromuscular; ALS, polio, myasthenia gravis; structural; obesity and scoliosis
INTERSTITIAL LUNG DISEASE…
-bilateral diffuse patterning; honeycomb
IN GENERAL…
-DLCO
-extra-pulmonary; interstitial lung disease
DLCO(diffusing lung capacity of carbon monoxide)
-measures the ability of the lungs to __
-the patient will inhale a small amount of __
-since CO is __-limited, its uptake will be dependent on __
-the machine will observe the __(state of respiration), measuring the amount of __
-a normal value is
-exchange gasses
-carbon monoxide
-diffusion; the ability to diffuse across a barrier
-exhale; CO
-75%-140%
Interstitial lung disease
-obstructive/restrictive?
-all include the hallmark __ pattern on the lungs
-a group that can include __(unknown cause), __(think plagues around the eyes and nose), __(think particulates in the lungs), __(think hypersensitivities), and __(think exogenous)
IDIOPATHIC PULMONARY FIBROSIS…
-onset is __
-slow onset __
-typically affects people over the age of __
PNEUMOCONIOSIS…
-3 types…
1.) coal miner’s lung
-inhalation of __, either from work in __, or from __(bad!)
-X-ray concern is focused in the __ of the lungs, which shows __
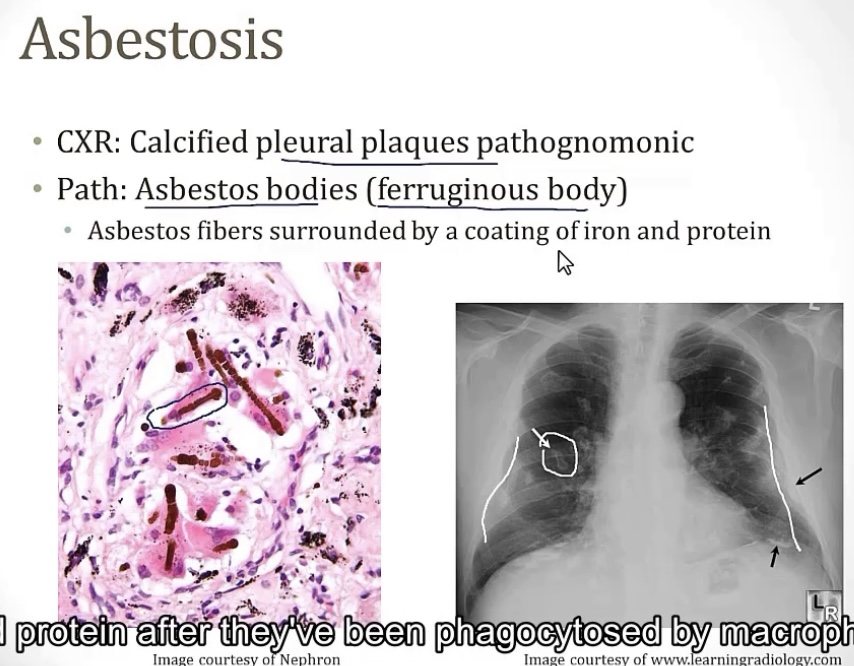
2.) asbestosis
-inhalation of __, either from work in __, __, or __
-X-ray concern is focused in the __ of the lungs
-can lead to __, __, or __
-2 major types of lung cancers being __(less common) and __(more common)
-the less common type will occur __ after exposure, and will have __ and __
-histology will see the presence of __(aka __), which are described as __
3.) silicosis
-inhalation of silica, from __, __, __, either from work in __, __, or __
-increases risk for __ and __(more specifically __)
MEDICATIONS…
-most common meds to cause this issue are __, __, __, and __
HYPERSENSITIVITY PNEUMONITIS…
-mixed type of hypersensitivity including types __ and __
-commonly from exposure to __
-a couple common types are __(from __), __(from __)
-these patients will have __
-treatment will be __(action), and pharmacologically __
-restrictive
-honeycomb
-idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis; sarcoidosis; pneumoconiosis; hypersensitivity pneumonitis; medications
IDIOPATHIC PULMONARY FIBROSIS…
-idiopathic
-dyspnea
-40
PNEUMOCONIOSIS…
-coal dust; mines; smoking
-upper portion; small, rounded nodular opacities
-asbestos fibers; shipyards, roofing/insulation, or plumbing
-lower portion
-asbestosis; pleural plaques; lung cancer
-mesothelioma(less common); bronchogenic carcinoma(more common)
-decades; pleural effusion; pleural thickening
-asbestos bodies; ferruginous bodies; asbestos fibers coating iron and protein
-stone, sand, or glass; mines, sandblasting, or metal production foundries
-TB; lung cancer; bronchogenic carcinoma
MEDICATIONS…
-bleomycin; busulfan; amiodarone; methotrexate
HYPERSENSITIVITY PNEUMONITIS…
-3 and 4
-environmental antigens
-farmer’s lung; moldy hay or grain; poultry lung; waste from birds
-bronchoalveolar lavage
-reducing exposure; steroids