Cellular Respiration
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Who does cellular respiration?
All cells
Why do cells do cellular respiration?
To produce ATP
To break down a large glucose molecule to a smaller and easier to use chemical energy for cellular work
Making proteins, active transport
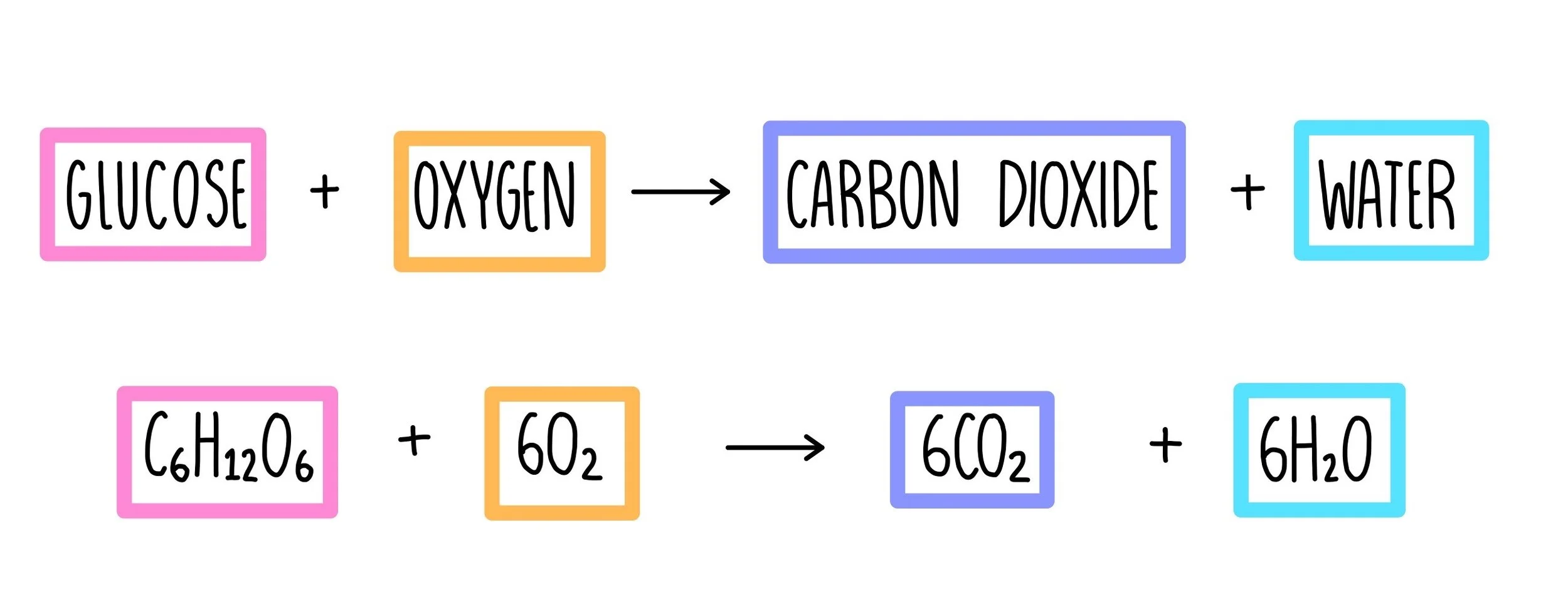
Aerobic Respiration
The process where cells use oxygen to break down glucose into ATP
Eukaryotes use mitochondria and prokaryotes use their cell membrane
Rxn is the oxidation of glucose - large amount of energy must be released in small steps
In the ETC, electrons are passed to successively more electronegative molecules with oxygen as the final electron acceptor
Releases little bursts of energy along the way
Redox Reactions
Used to carry energy throughout Cellular Respiration
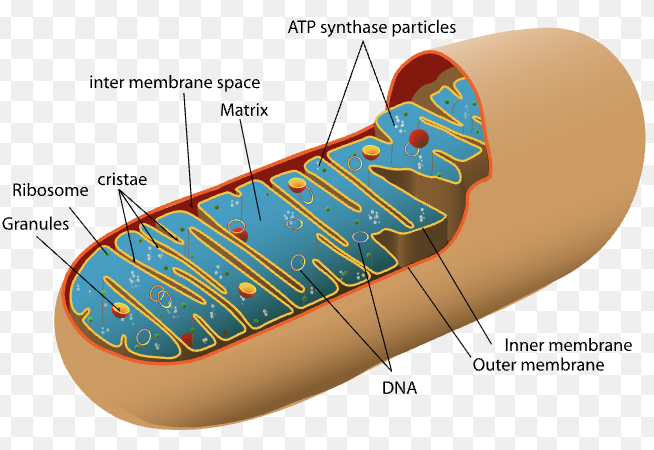
Mitochondria Structure
Outer membrane: Smooth boundary that encloses the mitochondrion
Inner membrane: Highly folded (to max out surface area!) membrane that contains the electron transport chain
Cristae: Folds of the inner membrane that increase surface area
Intermembrane space: Space between the outer and inner membranes where protons accumulate
Matrix: Inner compartment containing enzymes for respiration
Ribosomes: Found in the matrix; synthesize mitochondrial proteins
DNA: Circular mitochondrial DNA located in the matrix
ATP synthase: Enzyme embedded in the inner membrane that produces ATP
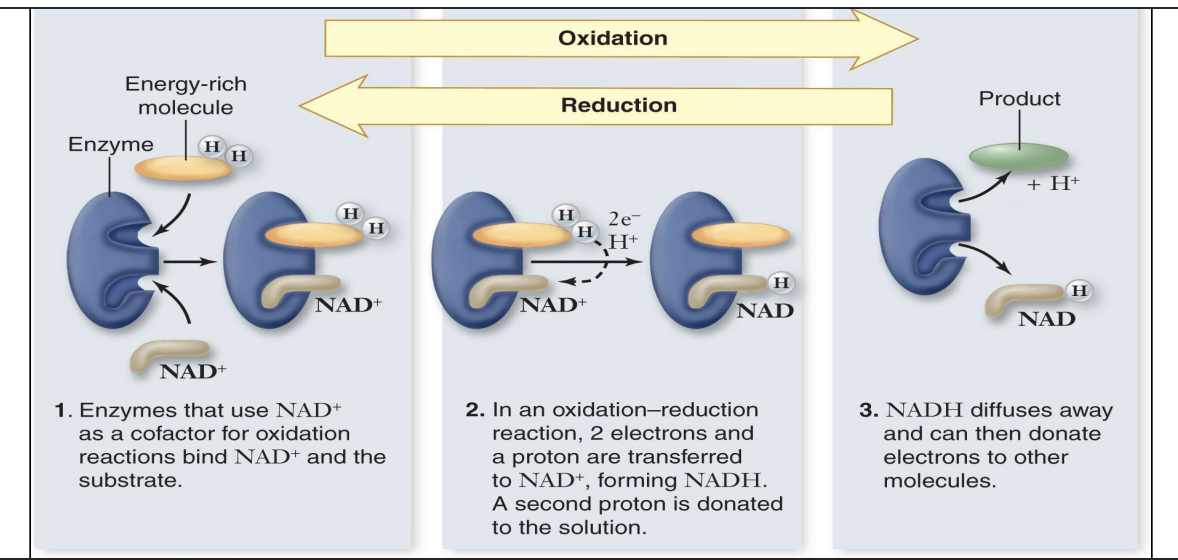
Electron Transport Molecules
Electrons are transferred from hydrogen to oxygen via NAD+
Dehydrogenase enzyme removes 2 H atoms, delivers 1H+ and 2e- (the other H+ is released)
NAD+ → NADH (NAD+ is reduced to NADH)
NADH then delivers electrons to ETC
Glycolysis
The splitting of sugar (glucose) into 2 pyruvate
Goes from 6C to 2 3C
Occurs in the cytoplasm of eukaryotes and prokaryotes
Can occur without oxygen
Produces a net (4 is made by 2 is used) of 2 ATP via substrate level phosphorylation
Reduces NAD+ to NADH (NADH now carries an electron and can move it to other steps; an electron carrier)
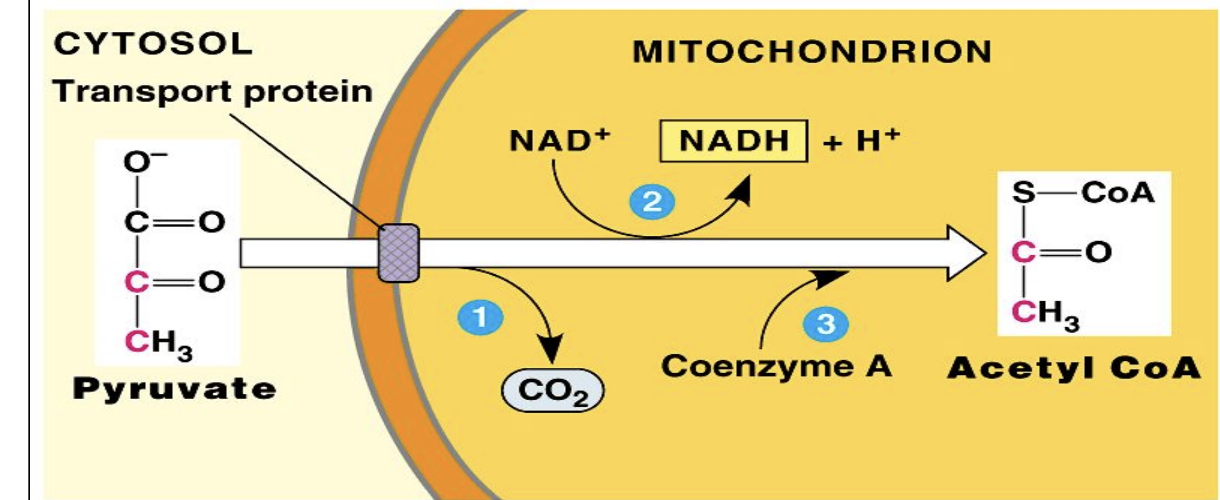
Pyruvate Conversion
Occurs before the Krebs Cycle if oxygen is available
Pyruvate (2 3C) enters the mitochondria and is converted to Acetyl CoA
Each gives off CO2 and reduces NAD+ to NADH
Krebs Cycle/Citric Acid Cycle
Occurs in the matrix of the mitochondria
Acetyl CoA enters the cycle
Gives off 2 CO2 as a waste product
Reduces NAD+ to NADH and FAD to FADH2
Produces 2 ATP
9 steps of chemical reactions and repeats twice; reduction
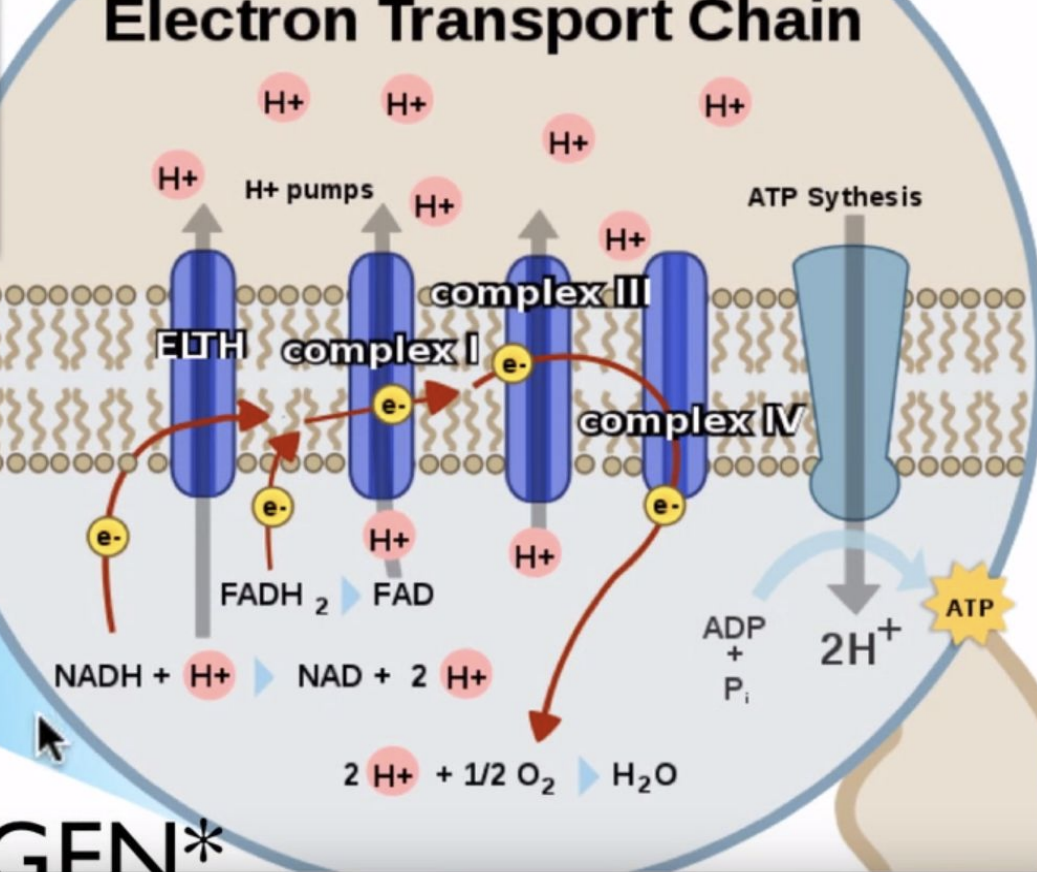
Electron Transport Chain
Electron carries (NADH and FADH2) release electrons into the chain
Electrons are carried by proteins down the chain
As they are passed along, the energy released fuels the pumping of protons across the membrane to create a gradient (active transport against the concentration gradient)
Oxygen is the final electron acceptor
Coupled with chemiosis at the end
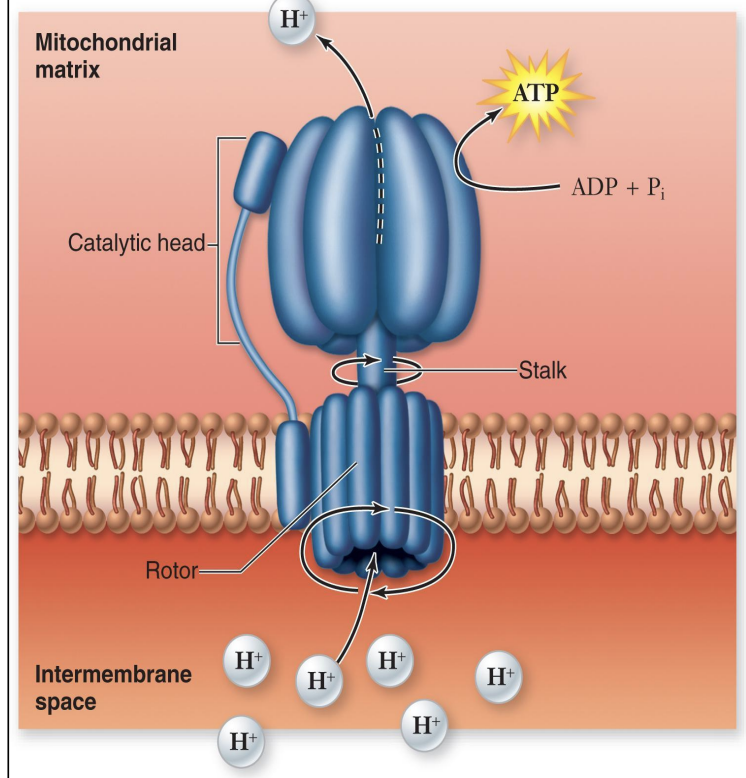
Chemiosmosis
Occurs in the inner mitochondrial membrane
ATP synthase converts ADP+P into ATP
Uses energy from the ion gradient to power the synthesis of ATP
ETC pumps H= INTO the intermembrane space
H+ leaks back through ATP synthase by facilitated diffusion and finally goes with the concentration gradient
Protons flowing through turn the rotor and catalyze ATP synthesis
Produces about 26-28 ATP per molecule glucose
Energy Yield of Respiration
Theoretical energy yield is 32 ATP per glucose for eukaryotes
The actual energy yield is somewhat less due to inefficiency and other needs of the cell
Catabolism of Proteins and Fats
Lipids and proteins can also feed into cellular respiration. Fats are broken into glycerol which enters glycolysis and fatty acids are converted to Acetyl CoA while proteins are broken into amino acids that enter glycolysis, pyruvate oxidation, or the citric acid cycle after the removal of their amino groups
Lactic Acid Fermentation
An anaerobic process that converts pyruvate into lactic acid, regenerating NAD⁺ so glycolysis can continue producing ATP when oxygen is absent.
Alcoholic Fermentation
An anaerobic process that converts pyruvate into ethanol and CO₂, regenerating NAD⁺ so glycolysis can continue producing ATP when oxygen is absent.
ATP Structure Reminders
ATP has more potential energy than ADP + P
Most energy lies between the 2nd and 3rd phosphate bonds
Substrate-Level Phosphorylation
Transfers phosphate group directly to ADP
Happens during glycolysis and the Krebs Cucle
Oxidative Phosphorylation
The rotation of ATP synthase squishes a free P onto ADP during ETC
Gluconeogenesis
Glycolytic and citric acid cycle intermediates can be reduced and used to form glucose through gluconeogenesis. The body keeps a constant supply of glucose by regulating digestion, storage, and release. Glucose from food enters the blood, excess is stored as glycogen in the liver, and when blood glucose is low, glycogen is broken down or glucose is made from other molecules through gluconeogenesis, keeping blood glucose levels stable.