Science : Physics - Second Grading
1/71
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
72 Terms
Momentum
A measure in one’s motion
p = mv : kg•m/s
Impulse
Changes in momentum
I = Ft : N•s || I = ▲p : kg•m/s || F = mvf-mvi / t
Impulse - Momentum Theorem
States that impulse is equal to the change in momentum
I = Ft : N•s || I = ▲p : kg•m/s || F = mvf-mvi / t
Conservation of Momentum
States that the total momentum of an isolated system remains constant if no external forces act on it.
pf = m1v1 + m2v2
Work
Where Force and Displacement are parallel to each other.
Expressed in Joules
W = Fd
Power
The rate at which work is done or the rate at which energy is transferred.
Expressed in Watts
P = Work / Time
Energy
The ability to do work
Expressed as Joules
Elastic Collision
A type of Collision wherein the colliding bodies DO NOT STICK TOGETHER.
m1v1 (I) + m2v2 (I) = m1v1 (F) +m2v2 (F)
Inelastic Collision
A type of Collision where in the colliding bodies DO STICK TOGETHER.
m1v1 + m2v2 = mv(F)
Potential Energy
A type of energy that is present in an object at rest
The potential of an object at work.
Gravitational Potential Energy = m•g•h
Kinetic Energy
The energy that an object possesses due to its motion.
Kinetic Energy = ½mv²
Fossil Fuels
A source of energy that is formed through ancient plants & animals
Wind Energy
A source of energy that uses the wind around us through wind turbines and more.
Converted into Kinetic Energy.
Solar Energy / Radiant
A source of energy that captures the sun’s energy and converts it to electricity.
Hydropower
A source of energy using the flow of water through machines called turbines, turning it into electricity.
Geothermal Energy
A source of energy using the heat from deep inside the earth.
Nuclear Energy
A source of energy created when tiny particles inside an atom are split apart in a process called nuclear fission
Biomass
A source of energy made from organic materials like wood, plants or waste.
Mechanical Energy
A combination of Potential Energy and Kinetic Energy
Mechanical Energy = (PE + KE)
Waves
A series of vibrations/oscillations traveling from one point to another.
Carries energy without transferring matter.
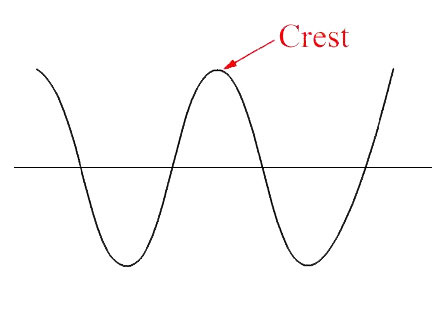
Crest
Highest point / peak of a wave
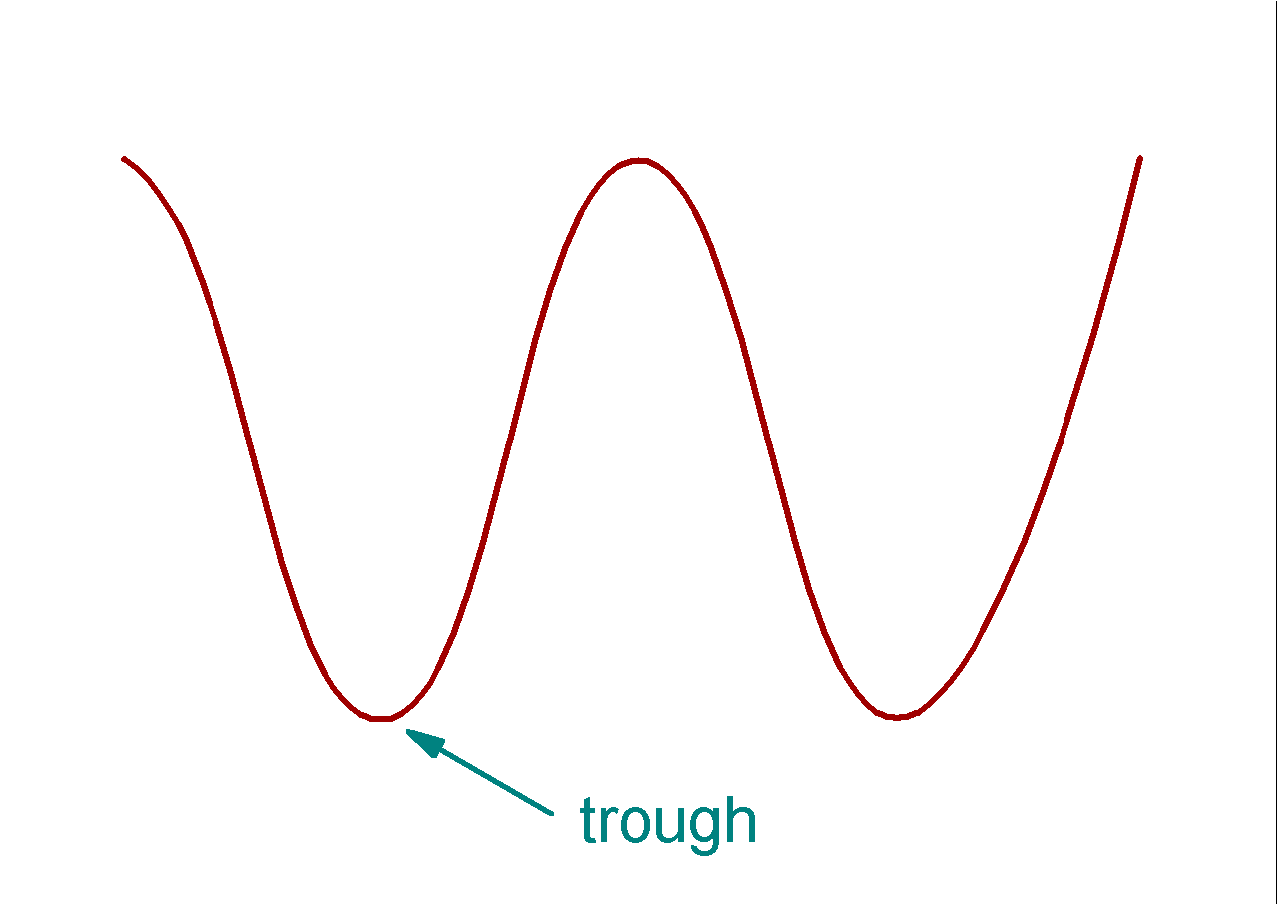
Trough
Lowest point / valley of the wave
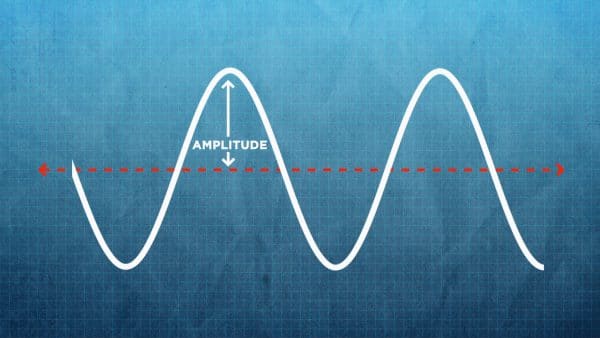
Amplitude
Height of the Wave
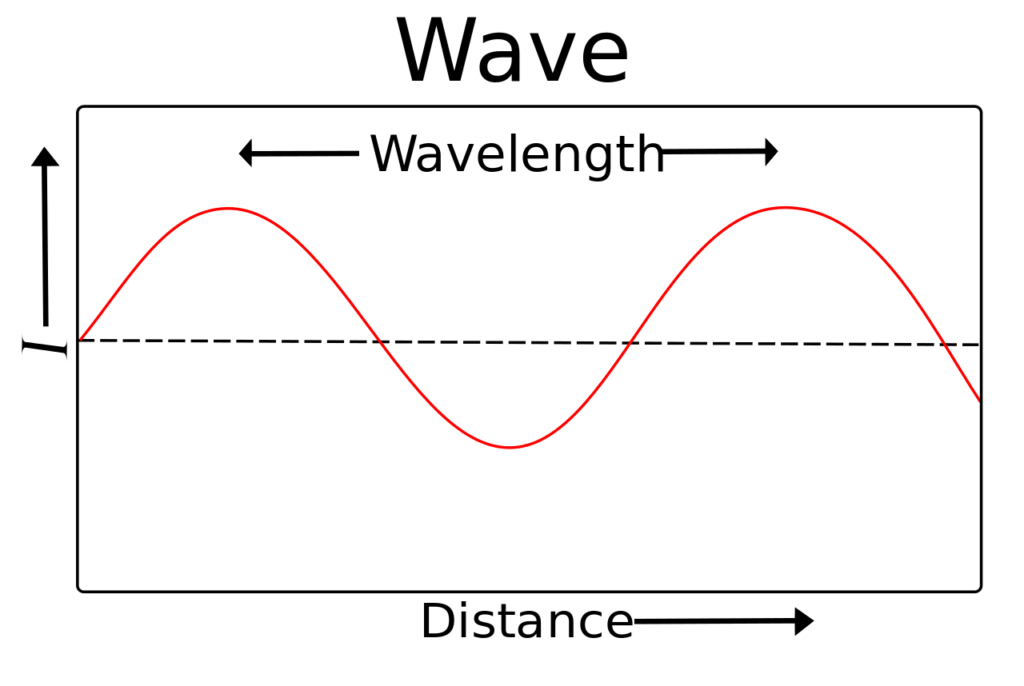
Wavelength
Distance between 2 successive points in a wave that are in phase
Origin
The beginning of the wave
Type of Wave : Nature
Mechanical and Electromagnetic
Type of Wave : Direction of Particle’s Vibration
Transverse & Longitude
Transverse
Vibrations of Particles are perpendicular
Mechanical
Requires medium to propagate
Electromagnetic
Travels in a vacuum
Longitudinal
Vibrations of particles are parallel
Characteristics of Waves : Frequency (f)
Number of waves it produces per second.
Unit : Hertz (Hz)
1Hz = 1 wave
Characteristics of Waves : Period (T)
Time it takes for a particle in a medium to make one complete vibrational cycle.
T = 1 / f
Characteristics of Waves : Wave Speed (v)
Distance traveled by wave per unit time.
V = λ / Period
Characteristics of Waves : Wavelength
Distance between 2 successive points in a wave that are in phase
λ = VT (Wave Speed x Period)
Compressions
Where vibrating particles are closed together.
Rarefractions
The area of a wave (or Slinky) that is spread out.
Soundwaves
Mechanical by Nature
A longitudinal wave
Type of Medium
Factor Affecting the Speed of Sound
Temperature
Factor Affecting the Speed of Sound
Optics
Study of Light
Ray
An electromagnetic radiation that can be detected by the human eye
Natural
Comes from sources that are naturally occurring such as the light from the sun, moon, and stars.
Artificial
Emitted by man-made devices that would not occur naturally in nature such as light bulbs, televisions or phone screens.
Luminous
Source of the Light
Non-Luminous
Reflection / Reflects the Light
Opaque
Lets no light pass through
Transparent
Allows most Light to pass through
Translucent
Lets some light pass through
Reflection
The turning back of light into the same medium after striking the sun.
Incident Ray
The ray that strikes the surface
Reflected Ray
The ray that rebounds from the surface
Normal Line
The perpendicular to the surface at the point of incidence.
Law of Reflection
States that the angle of incidence is equal to to the angle of reflection
Law of Reflection
Smooth shiny surfaces have regular reflections while Rough, Dull surfaces diffuse reflection.
Mirror
Object smooth enough to produce a reflection of light incident upon it.
Image
A copy of an object formed by light.
Type of Mirror : Plane
A mirror with a flat surface.
Type of Mirror : Spherical
Mirror w/ reflecting surface is taken from the surface of a sphere.
Has two types : Concave and Convex.
Electromagnetic Waves
Electromagnetic radiation that travel as waves
Transfers energy from one place to another.
At this speed, they can go around the world 8 times in one second.
Spectrum of Radiation : Radio
Have the longest wavelengths in the electromagnetic spectrum. They are used for various forms of communication, including radio and television broadcasting.
James Clerk Maxwell
Spectrum of Radiation : Microwave
Commonly used in technologies such as microwave ovens and certain communication devices.
Sir Jagadish Chandra Bose
Spectrum of Radiation : Infrared
Associated with heat and is used in applications such as thermal imaging.
William Herschel
Spectrum of Radiation : Visible Light
The range of electromagnetic waves that can be detected by the human eye, comprises different colors.
Isaac Newton
Spectrum of Radiation : UV
Beyond the violet end of the visible spectrum and is invisible to the human eye. It has applications in sterilization and is also a component of sunlight.
Johann Wilhelm Ritter
Spectrum of Radiation : X - Rays
Have high energy and short wavelengths, making them suitable for medical imaging and other applications.
Wilhelm Conrad Röntgen
Spectrum of Radiation : Gamma Rays
They have the shortest wavelengths and the highest energy in the electromagnetic spectrum. They are associated with certain nuclear processes.
Paul Villard
Non - Ionizing
Not mostly harmful
Ionizing
Technically Very Harmful
Concave Mirror
Shape: Curved inward, like the inside of a sphere.
Focal Point and Focal Length:
Focal Point: The point where parallel rays of light either converge (if they are incident on the mirror) or appear to diverge from (if they are extended backward through the mirror).
Focal Length: The distance from the mirror's center to its focal point.
Image Formation:
Concave mirrors can form both real and virtual images.
Real images are formed when the object is located beyond the focal point, and the image is formed on the opposite side of the mirror.
Virtual images are formed when the object is between the mirror and its focal point, and the image is formed on the same side as the object.
Examples:
Makeup mirrors, shaving mirrors, and some types of car rearview mirrors are examples of concave mirrors.
Convex Mirror
Shape: A convex mirror is curved outward, like the outside of a sphere.
Focal Point and Focal Length:
Focal Point: The point where parallel rays of light appear to diverge from when extended backward through the mirror.
Focal Length: The distance from the mirror's center to its focal point.
Image Formation:
Convex mirrors always form virtual images, regardless of the object's position.
The image formed is smaller than the actual object and appears upright.
Parallel rays of light are diverged by the convex mirror.
Examples:
Side mirrors on vehicles and security mirrors in stores or parking lots are examples of convex mirrors.
Speed of Sound Formula
V = 331 m/s + (0.6 m/s °C) T