Stage 1 - Cell System
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/55
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
1
New cards
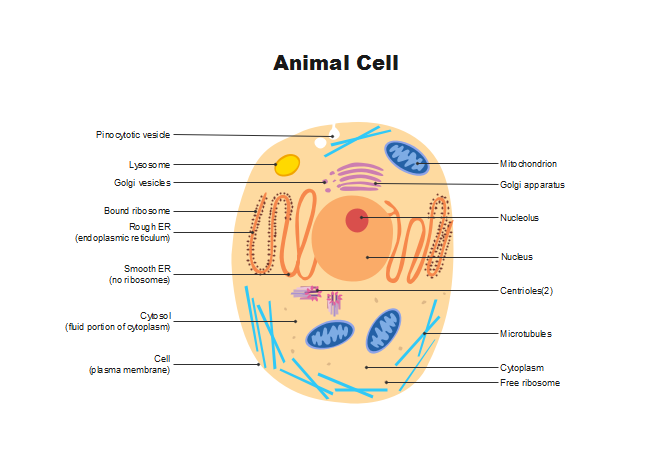
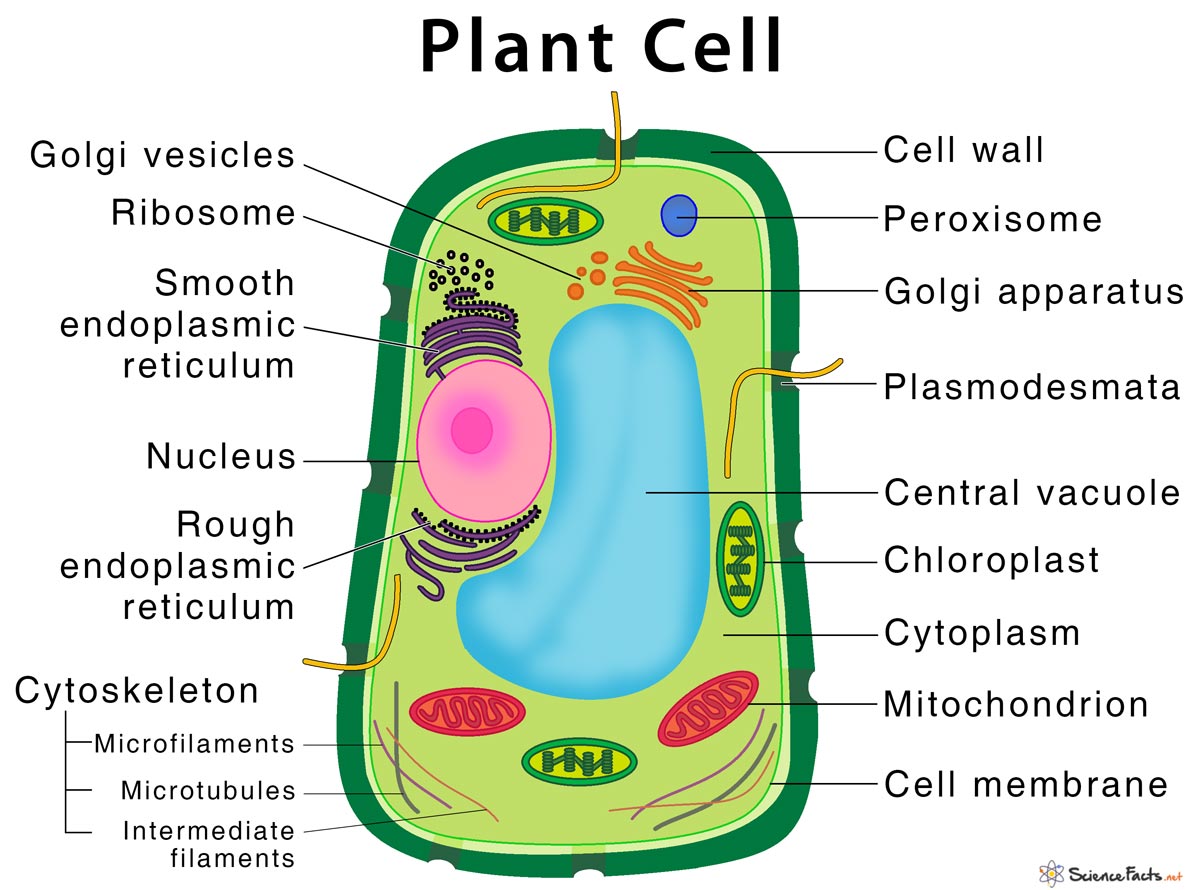
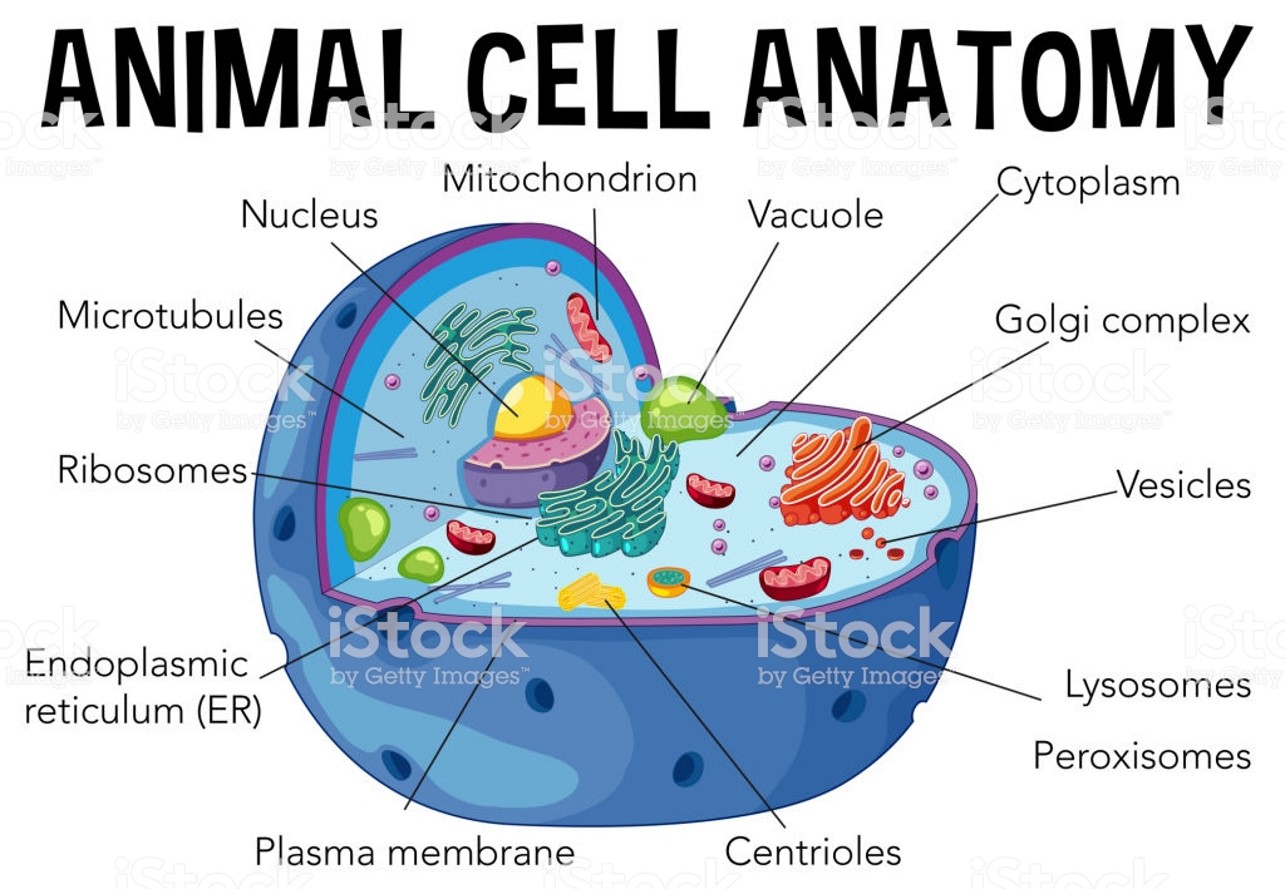
Cell
The smallest unit of life.
2
New cards
Unicellular Organism
An organism that consists of a single cell.
3
New cards
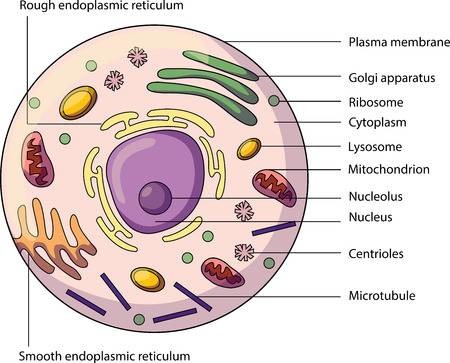
Multicellular Organism
An organism that consists of more than one cell.
4
New cards
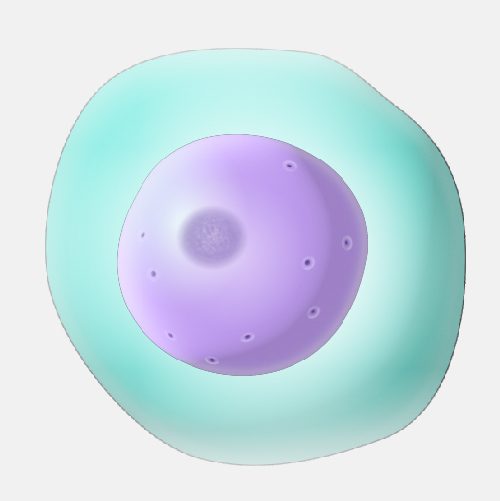
Nucleus
Contains genetic material which informs instructions for cells.
5
New cards
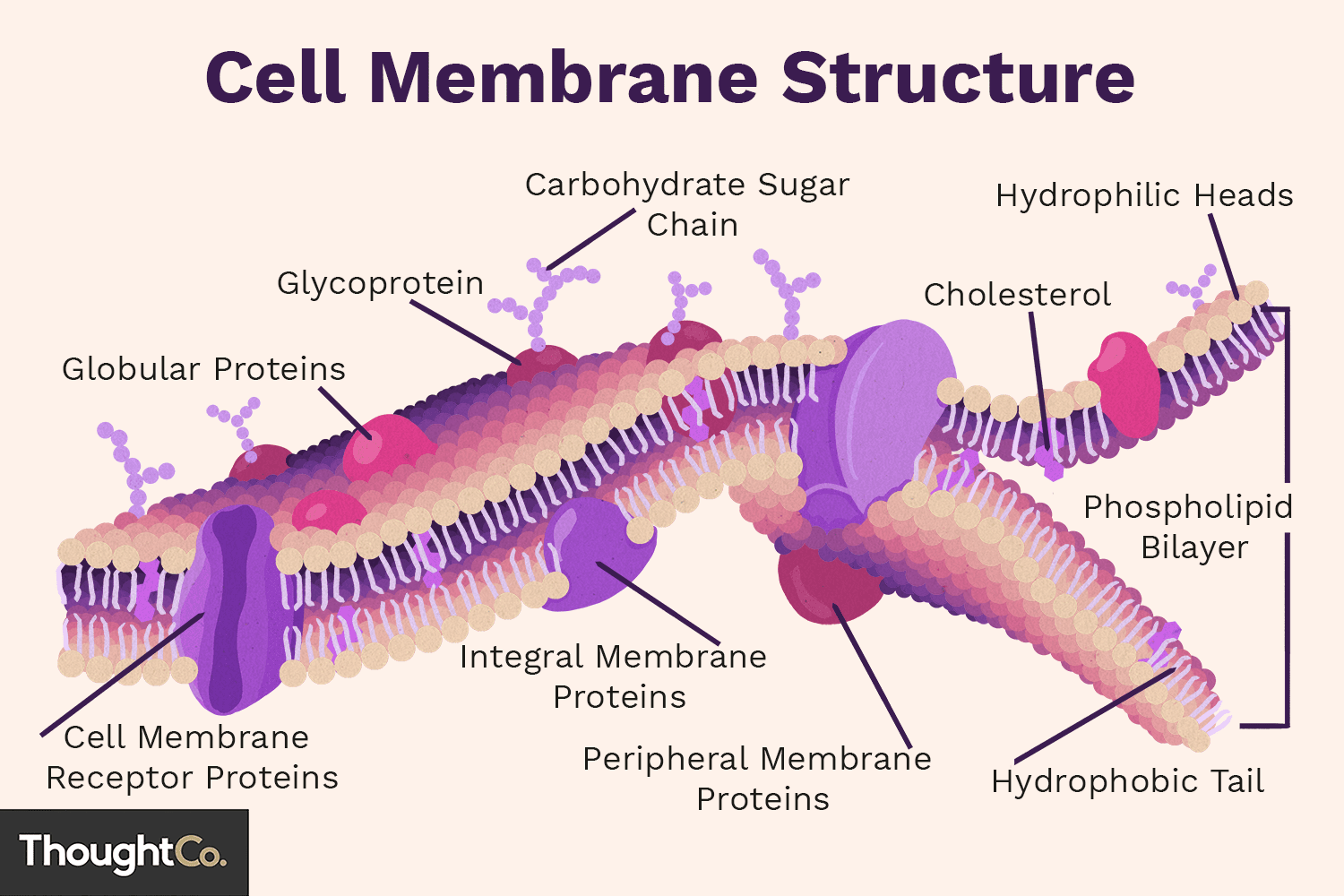
Cell Membrane
Barrier for managing movement in and out of cells.
6
New cards
Ribosomes
Produce protein from nucleus.
7
New cards
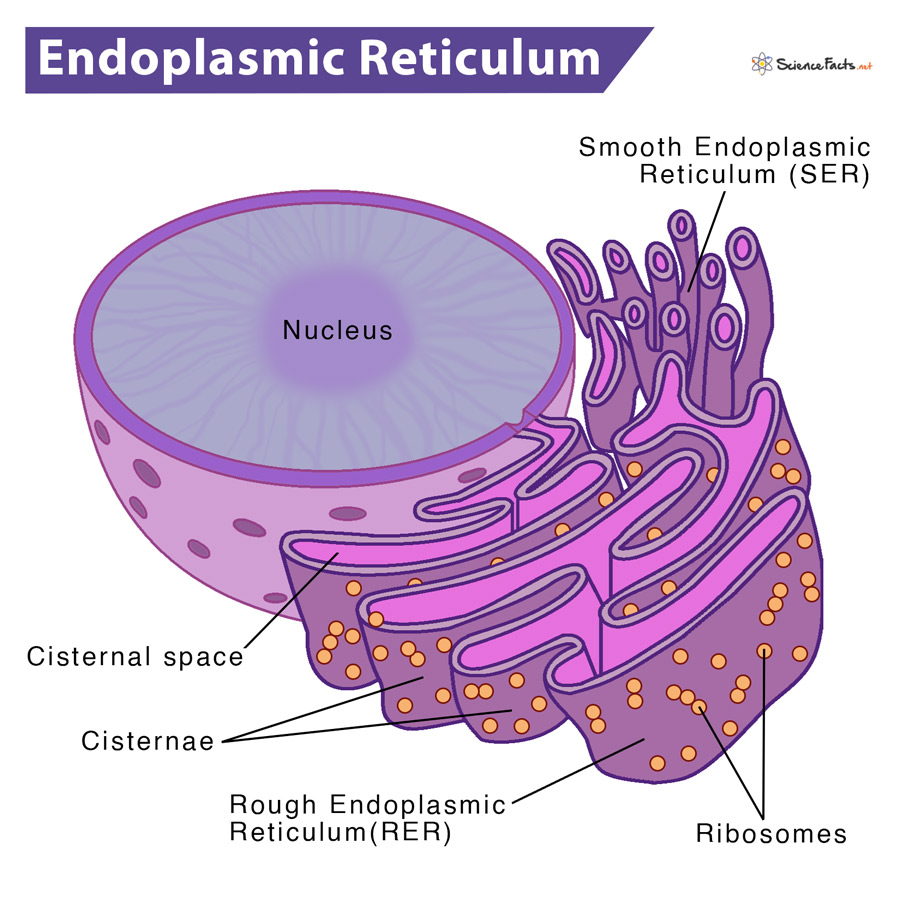
Endoplasmic Reticulum
Membrane layer that produces and process protein and lipids/fat.
8
New cards
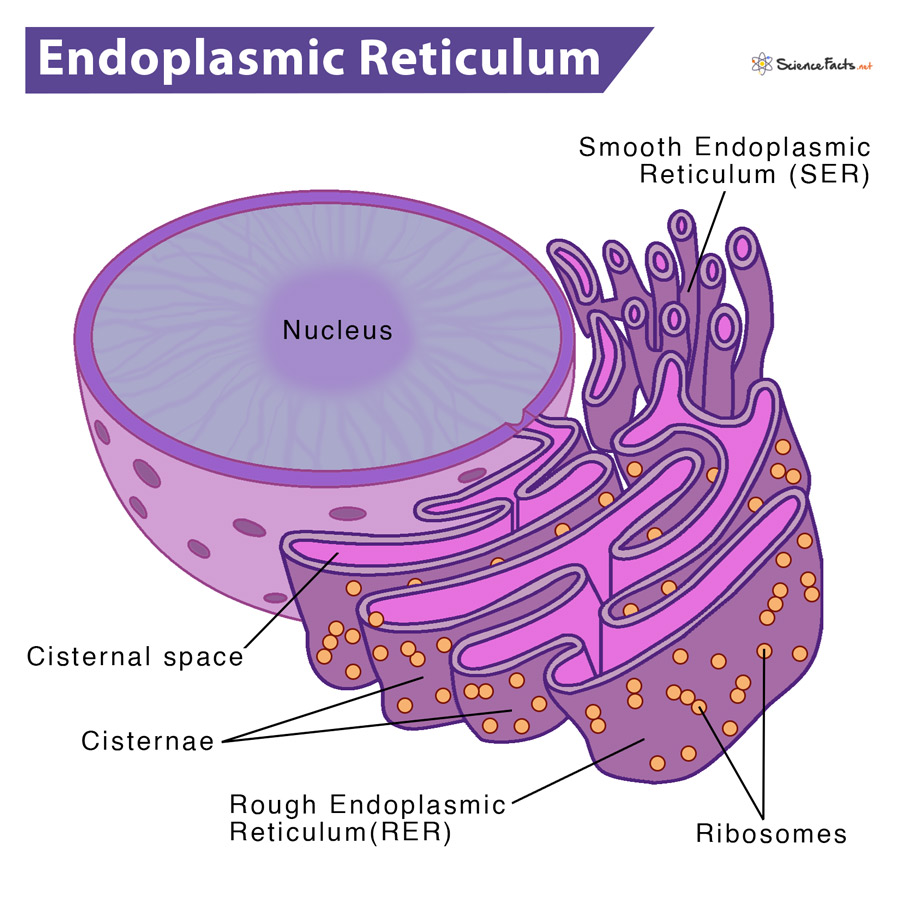
What does the Smooth ER and Rough ER do?
Smooth ER produces lipids/fats while Rough ER produces protein.
9
New cards
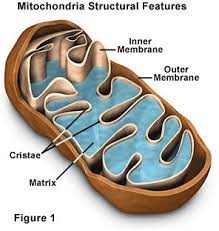
Mitochondria
The powerhouse of the cell that’s in-charge of cellular respiration.
10
New cards
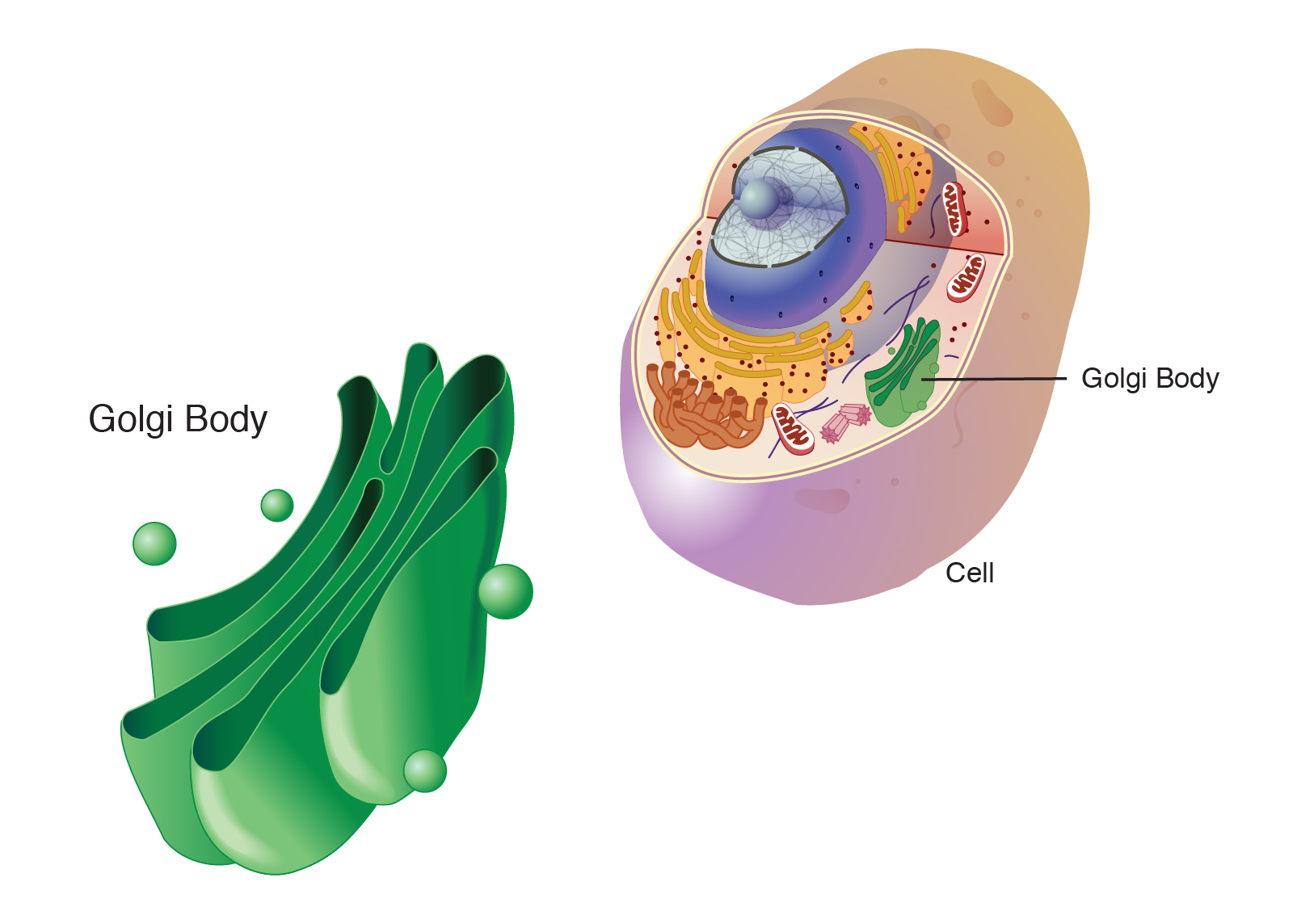
Golgi Apparatus
Packages and moves materials made in ER out of the cell.
11
New cards
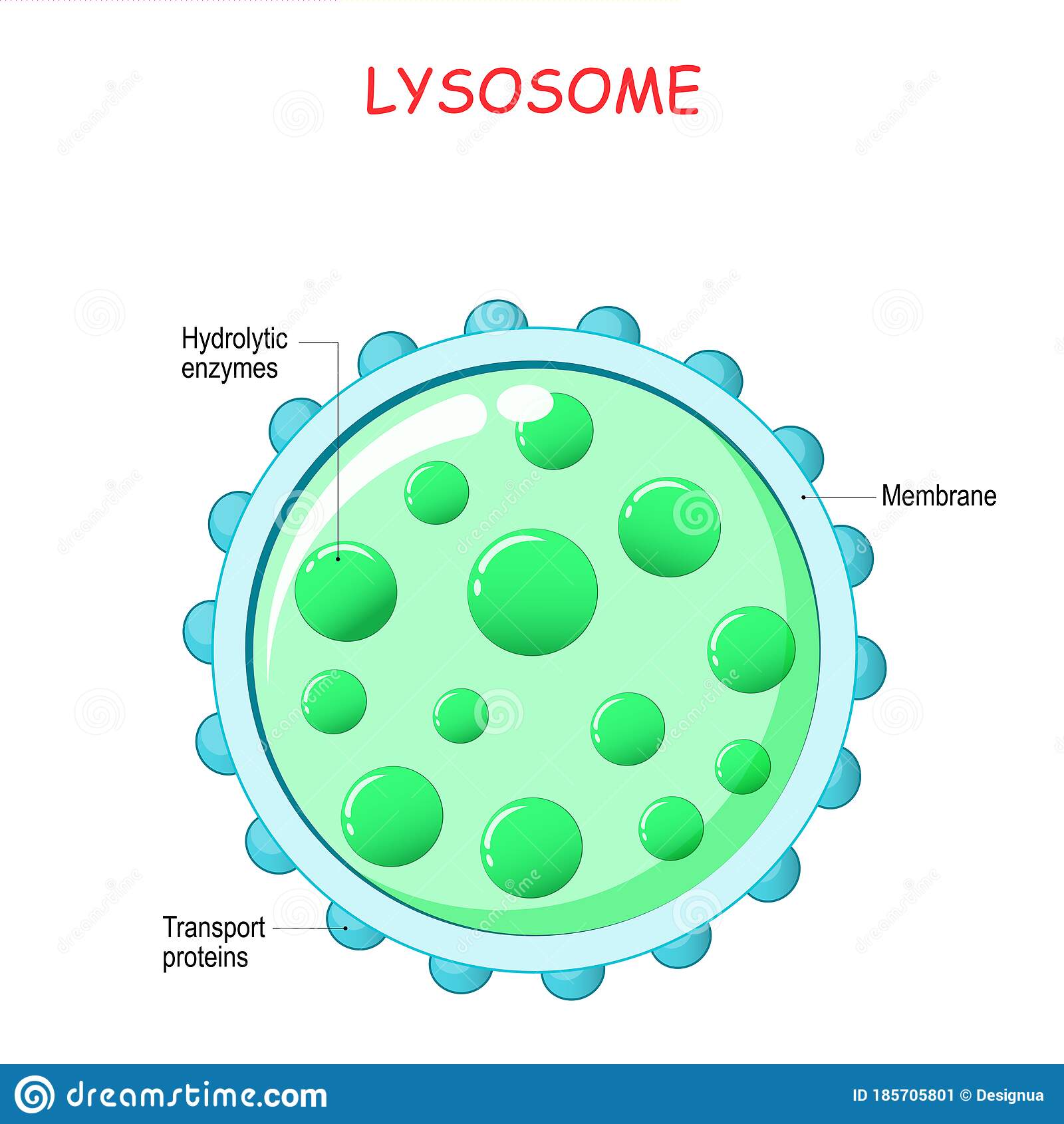
Lysosome
Found in animals’ cells that carries Lysozyme found in white blood cells to kill bacteria and remove unnecessary cells.
12
New cards
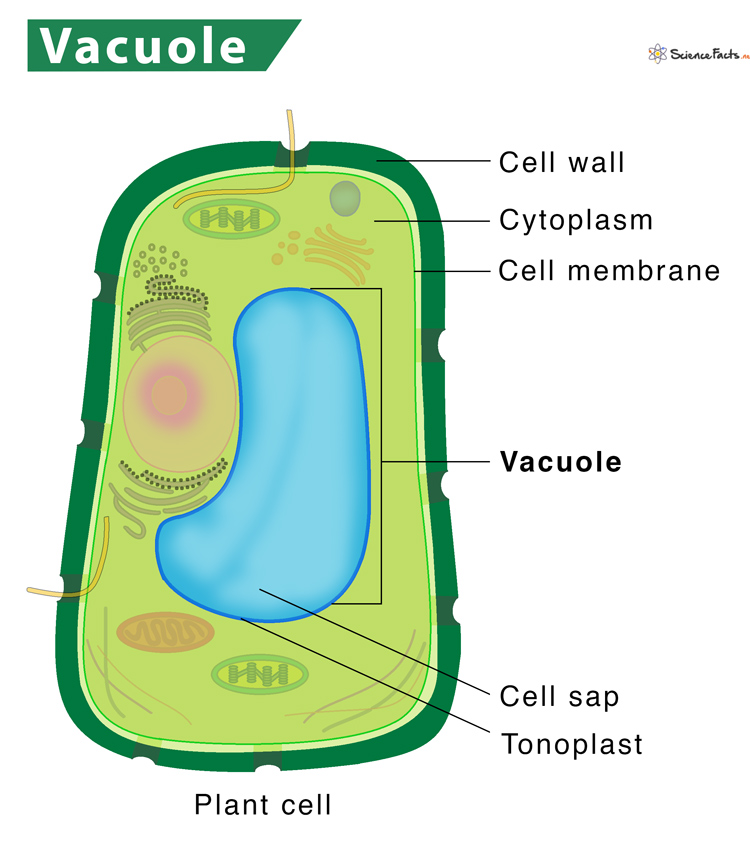
Vacuoles
Storage for various materials.
13
New cards
Chloroplast
Found in plant cells that contain chlorophyll that gathers sunlight for photosynthesis.
14
New cards
Cell Wall
Found in plant cells that protects the cell against hydrostatic/osmotic pressure changes to hold cell’s shape.
15
New cards
Cytoplasm
A thick solution that fills each cell.
16
New cards
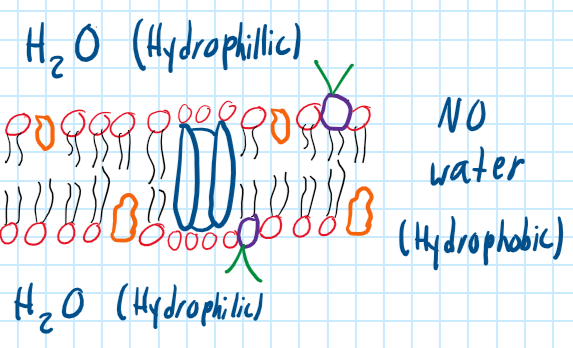
What is the membrane made of?
Phospholipid (Fat)
17
New cards
Carbohydrates
Short sugar chain pointing out of the cell that acts a recognition site for specific chemicals or antibodies.
18
New cards
Cholesterol
Lipid of membrane that protects from temperature changes and keep phospholipids from becoming too fluid.
19
New cards
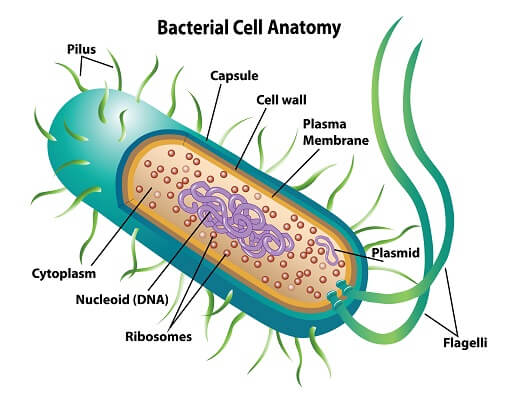
Prokaryotes
Unicellular organism without nucleus but has cell membrane.
20
New cards
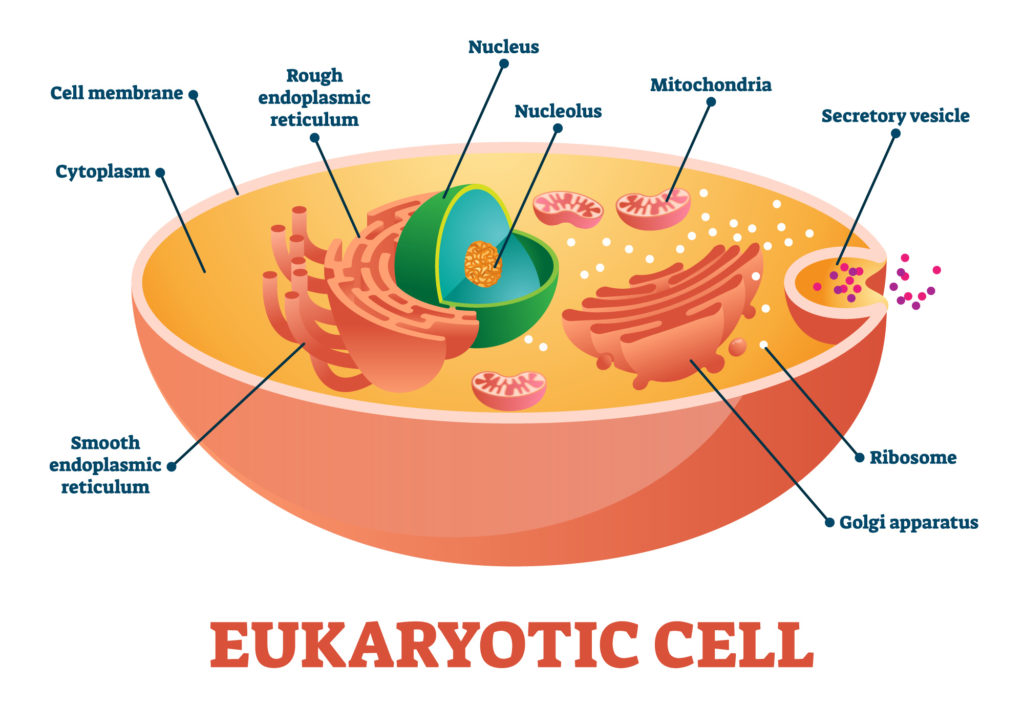
Eukaryotes
Multicellular organism with nucleus.
21
New cards
What organisms have Eukaryotic Cells?
Animals, Plants, Fungi, and Protista.
22
New cards
What organisms have Prokaryotic Cells?
Bacterium and Archaea.
23
New cards
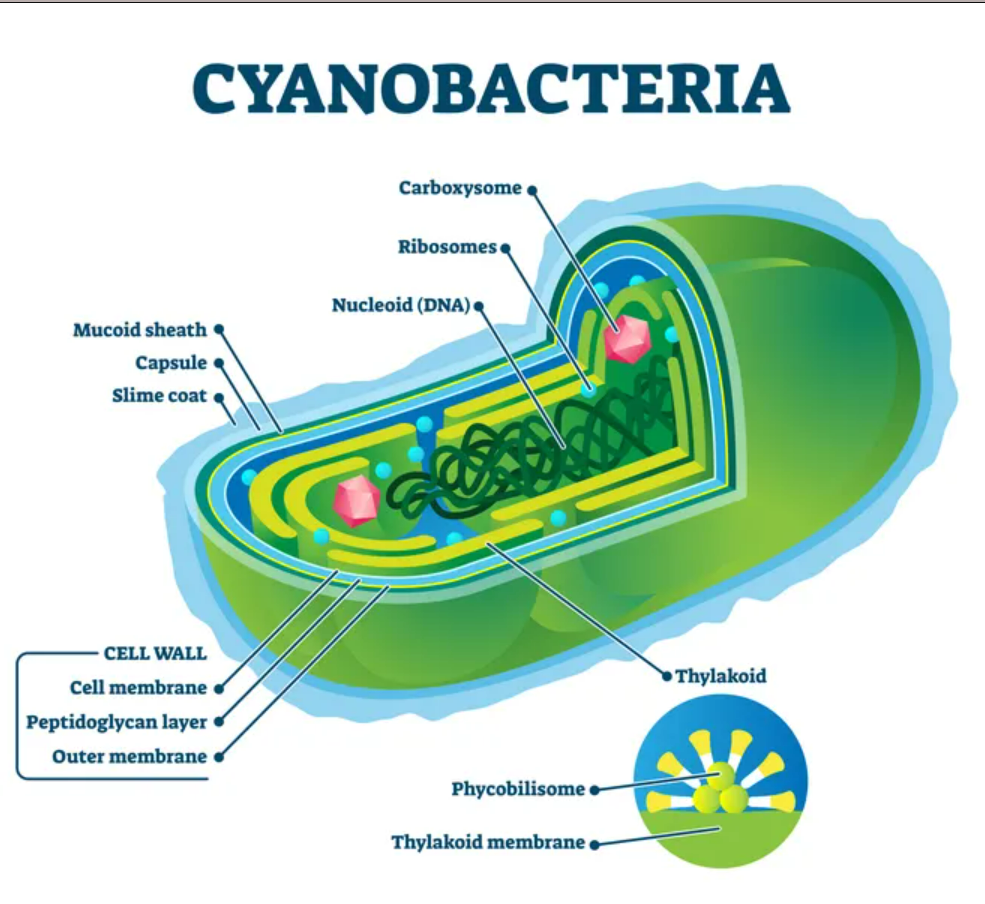
Cyanobacteria
Bacteria that perform photosynthesis.
24
New cards
Cell Differation
The process of immature cells to mature specialized cells.
25
New cards
Specialisation
Cells acquire special function.
26
New cards
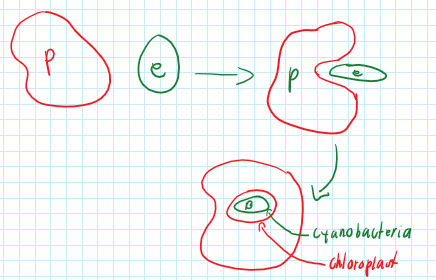
Endosymbiosis
The theory of evolution of the prokaryote to eukaryote.
27
New cards
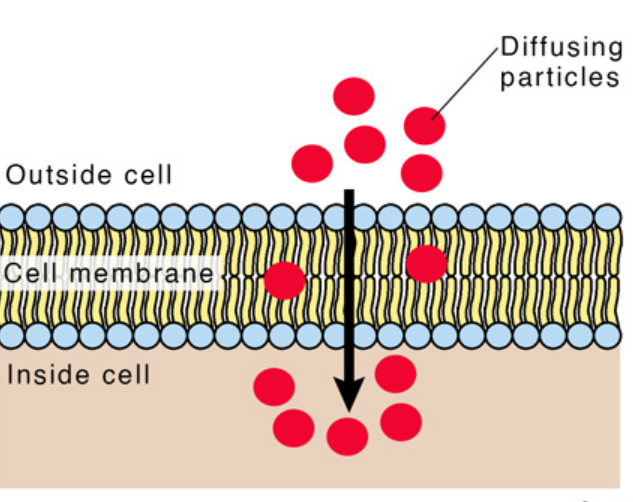
Simple Diffusion
Movement of particles from high concentration to low concentration through Bilayer.
28
New cards
Exocytosis
Particles removed from cell.
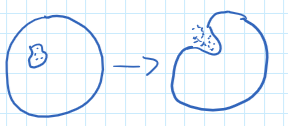
29
New cards
Endocytosis
Particles taken into cell.
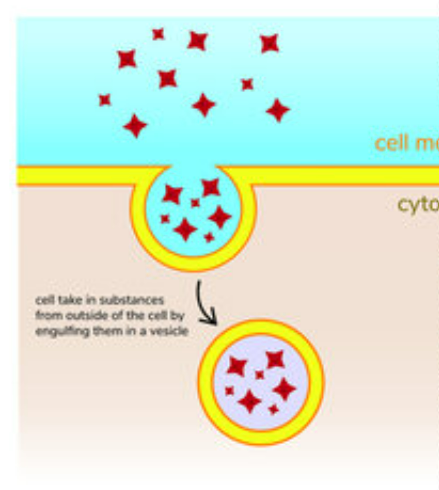
30
New cards
Osmosis
Water transport of molecules from high concentration to low concentration (passive).
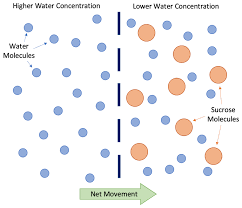
31
New cards
Active Transport
Moves substance from low concentration to high concentration.
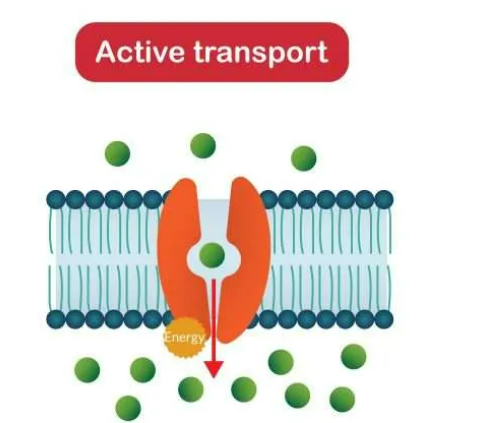
32
New cards
Passive Transport
Moves substance from high concentration to low concentration.
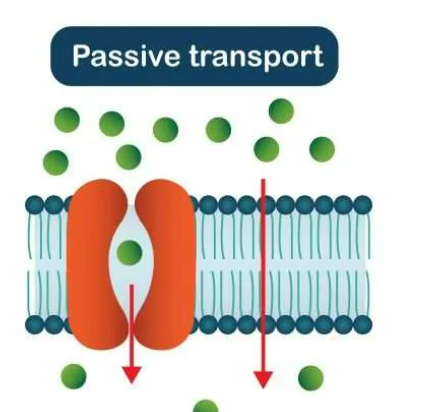
33
New cards
Facilitated Diffusion
The passive transport of the movement of molecules via an integral protein.
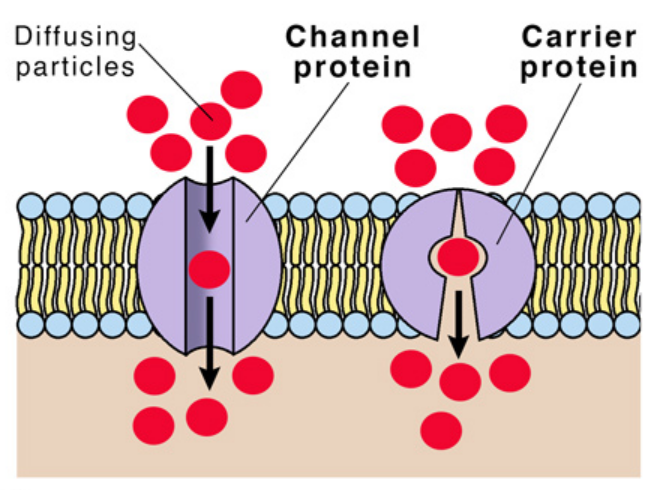
34
New cards
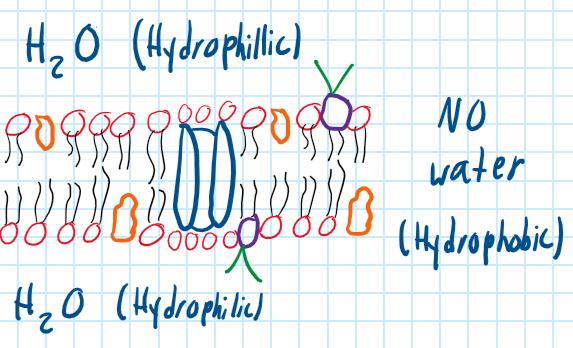
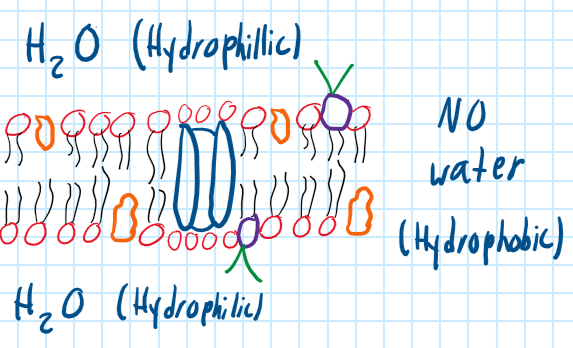
Phospholipid Bilayer
Main structure of the membrane with a hydrophilic head and hydrophobic tail.
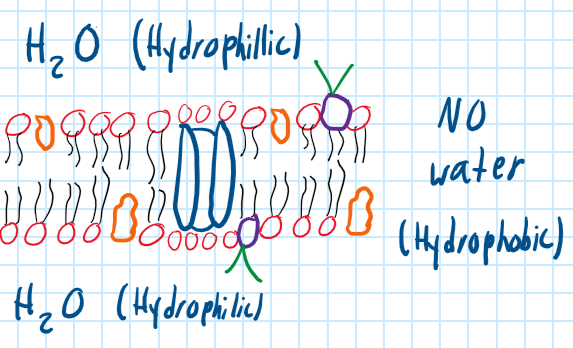
35
New cards
What does the Peripheral Protein do?
Speed up the chemical reaction and attached to the cytoskeleton to maintain cell’s shape.
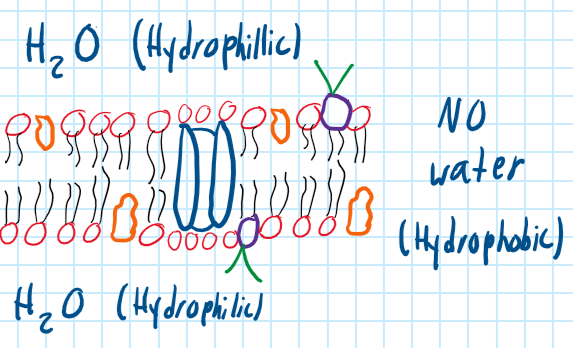
36
New cards
What does the Integral Protein do?
Acts as a channel to transport materials.
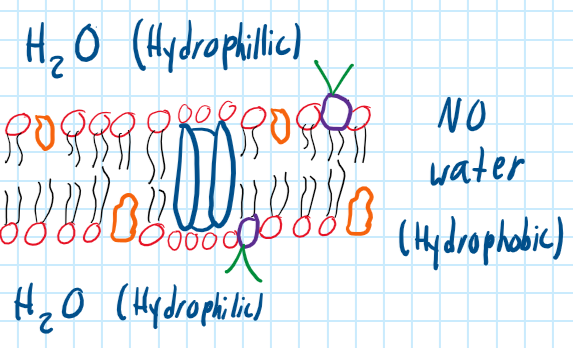
37
New cards
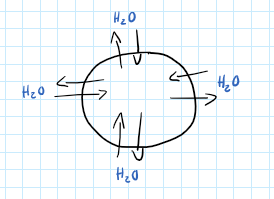
Isotonic
Same concentration of solute and water, in and out of cell.
38
New cards
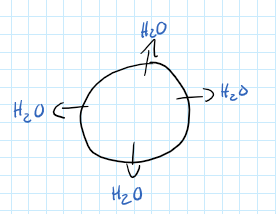
Hypertonic
Inside of cells is more concentrated with solute.
39
New cards
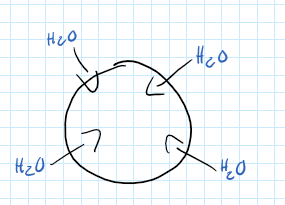
Hypotonic
Inside of cell is more diluted with water.
40
New cards
What is the difference between Chemoautotroph and Photoautotroph?
Chemoautotroph converts inorganic materials to organic molecules while Photoautotroph convert light for energy.
41
New cards
Heterotroph
Organisms that rely on autotrophs to provide for cells.
42
New cards
Photosynthesis
A process where carbon dioxide (CO2) and Water (H2O), covert to glucose (C6H12O6) and oxygen (O2) using light energy.
43
New cards
Aerobic Respiration
A process that uses the glucose and oxygen to make energy (ATP) for cells where carbon dioxide and water are formed.
44
New cards
Fermentation
An anaerobic process that makes acids or alcohol without oxygen to break down glucose.
45
New cards
Excretion
Removal of metabolic waste (toxic by-products).
46
New cards
Why is Chlorophyll essential for Photosynthesis?
It absorbs red and blue light but not green, which is why plants appear green and absorb light energy.
47
New cards
Name two fermentation processes
Alcohol and Lactic Acid fermentation
48
New cards
What substances can pass through the bilayer?
Smaller molecules that are non-polar (Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide)
49
New cards
What substances can pass through a channel?
Bigger molecules that are polar (Water)
50
New cards
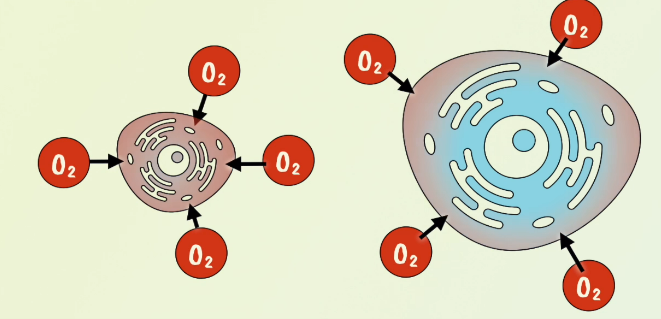
How does SA: V affect cell transport?
As the cell is growing, the volume increases faster than the surface area and causes slower exchange of resources.
51
New cards
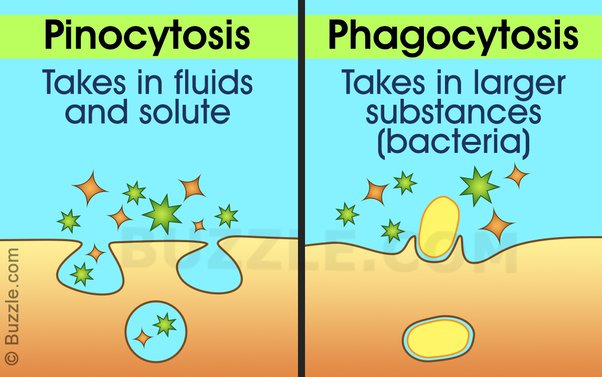
What is the difference between Pinocytosis and Phagocytosis?
Pinocytosis has a membrane indent that drinks nutrients and Phagocytosis engulfs towards the nutrients.
52
New cards
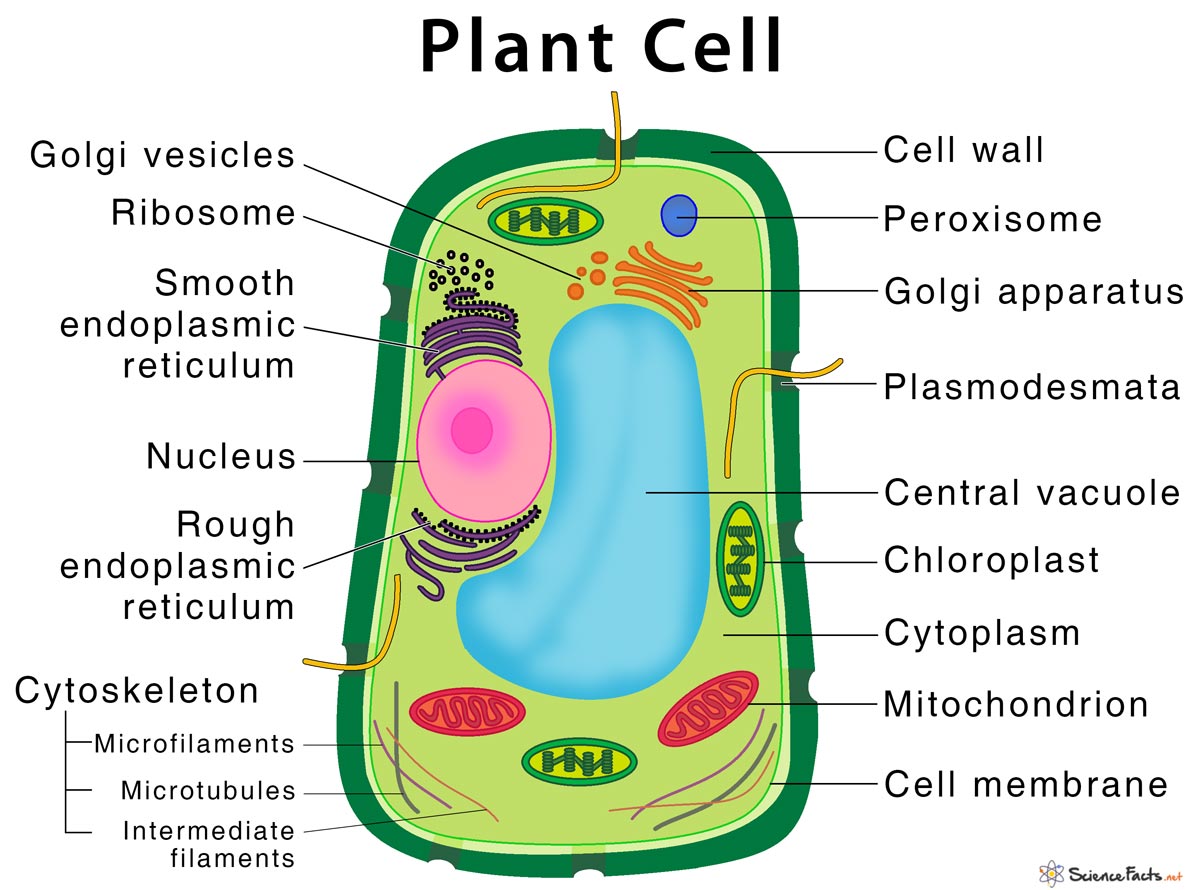
Peroxisome
Vesicle that carries peroxide to kill pathogens and break down nutrients.
53
New cards
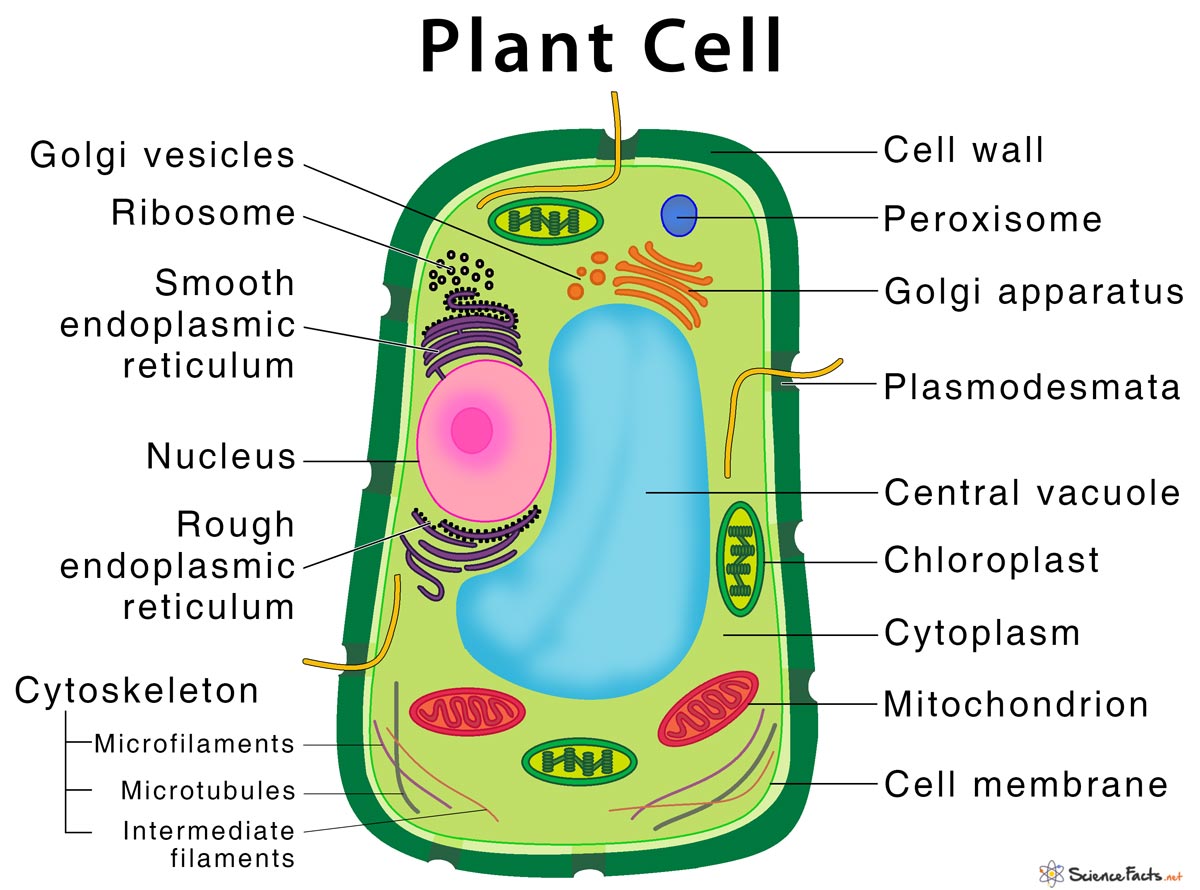
Plasmaderma
Openings in cell wall for cell communication and movement of resources.
54
New cards
What do prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells share in common?
* Cell membrane
* Nucleic acids
* Protein
* Ribosomes
* Nucleic acids
* Protein
* Ribosomes
55
New cards
What does the cell theory state?
* Are the structural and functional units of life.
* Come from pre-existing cells.
* Contain hereditary material.
* Come from pre-existing cells.
* Contain hereditary material.
56
New cards
What does MRS GRENC stand for?
Motion, Reproduction, Sensitivity, Growth, Respiration, Excretion, Nutrition, and Control.