Lecture 1: Function and Structure of Renal System
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
The renal system act as __, removing metabolic products and toxins from the __ and excreting them through the __.
filters; blood; urine
What does the renal system regulate? (3)
body’s fluid status
electrolyte balance
acid-base balance
The renal system maintains body stores and concentrations of Na+, K+, H+, H2O, etc in such a way that the __ and __ of intra- & extracellular compartments are regulated.
volumes; compositions
ex: controls plasma blood volume → blood pressure regulation
The renal system produces or activates __ that are involved in erythrogenesis, Ca2+ metabolism, and the regulation of blood pressure and blood flow.
hormones
What makes up the kidneys and urinary system?
kidney
ureter
bladder
urethra
The kidneys __ 18L of fluid/day.
filter
The kidneys __ 1-3L of fluid/day.
excrete
The kidney make up <0.5% of __
body weight
The kidneys receive 20% of __
cardiac output
Once filtrate reaches the ureter, it will not __ contents as it will travel through bladder and urethra.
change
How is the aorta connected to the kidney?
aorta → renal artery → kidney → renal vein → IVC
The __ is 180L/day, 60 times/day compared to __, which has a filter rate of 4L/day and 1.3 times/day.
GFR (glomerular filtration rate); capillaries
demonstrates importance of reabsorption and filtration in renal system
measures amount of plasma that filters from glomerulus
There are millions of __ sitting in the cortical section of the kidney.
nephrons (functional unit of kidney, responsible for filtering blood and producing urine)
The cortical section of the kidney is __, and the renal medulla is __.
isoosmotic; hyperosmotic
cortex has proximal tubule
medulla has loop of henle
The glomerulus is a network of capillaries within the __
renal corpuscle
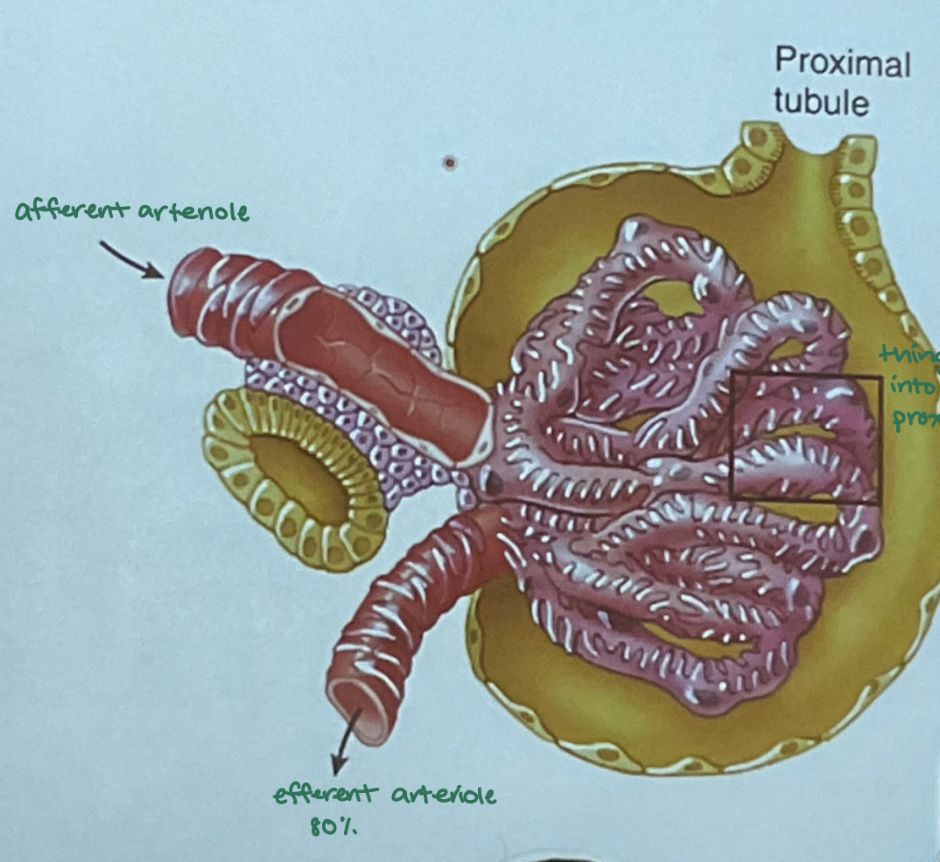
20% of volume is pushed out in the __, and 80% return and are picked up by __ to re-enter circulation.
glomerulus; renal capillaries
2/3 of reabsorption occurs in the __
proximal tubule
There is no loop of Henle in the __
cortical nephron (located in cortex/outer layer of kidney)

How does osmosis change in the loop of henle?
hyperosmotic in descending limb, hypoosmotic in ascending limb
meaning: water reabsorption in descending limb, and solute reabsorption in ascending limb
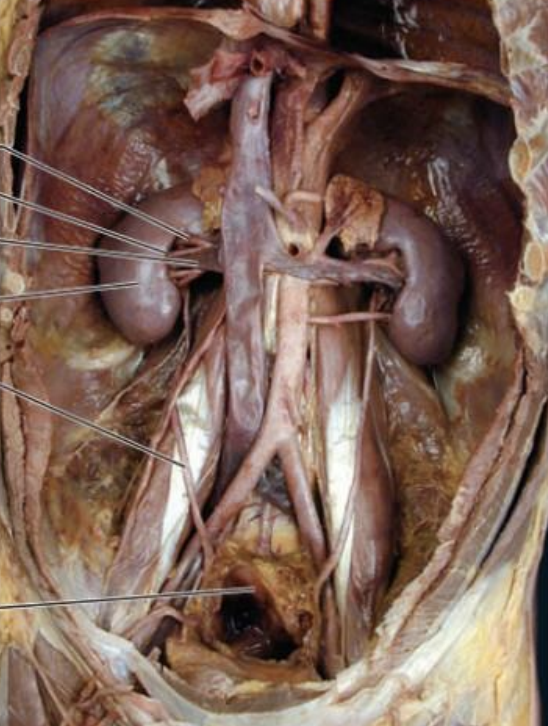
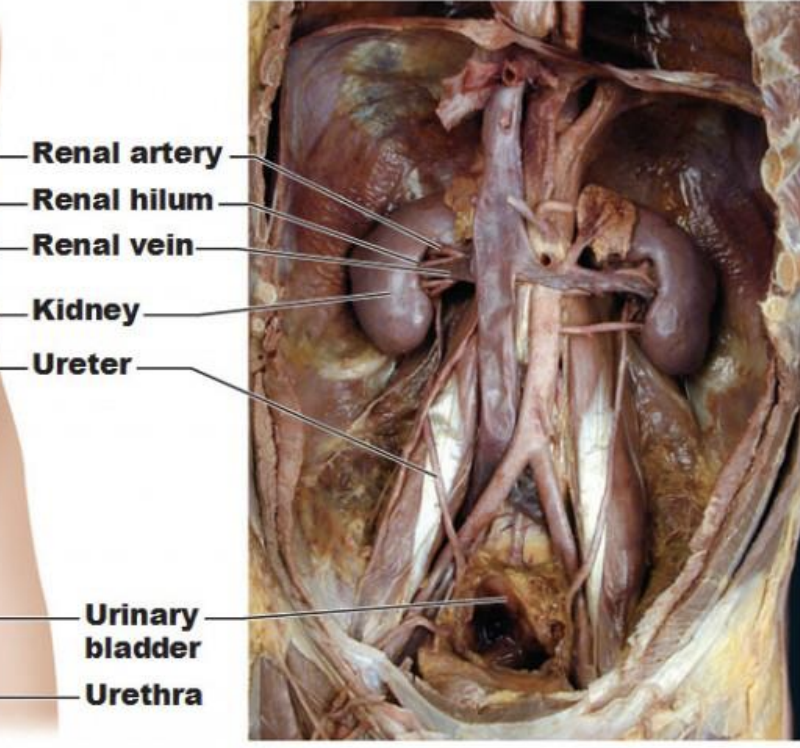
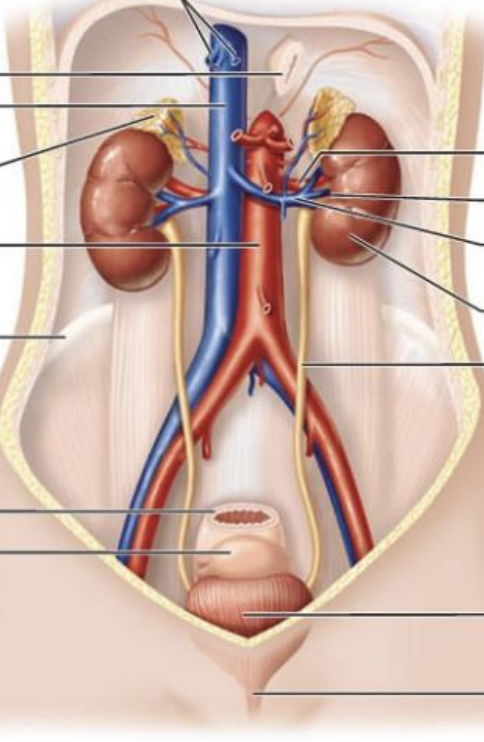
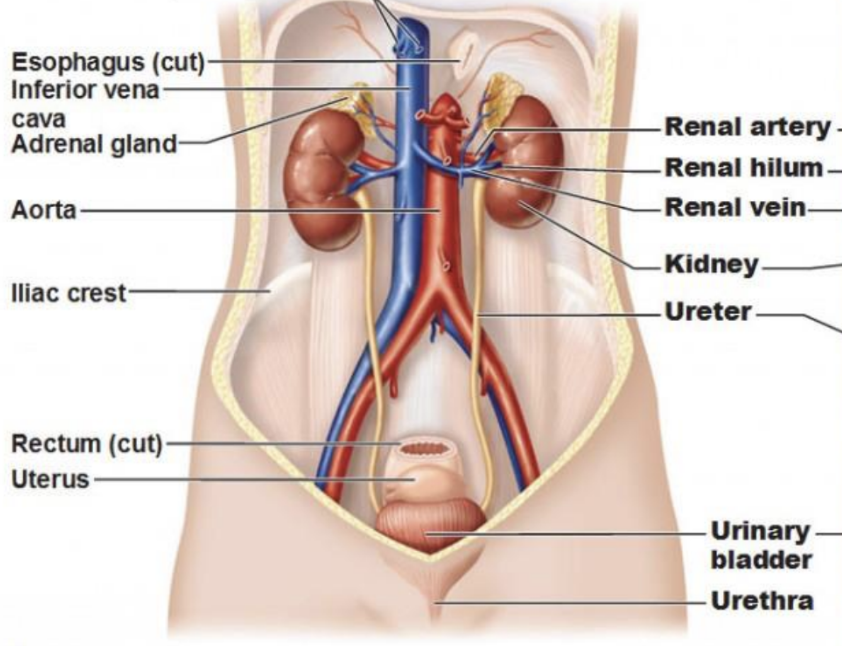
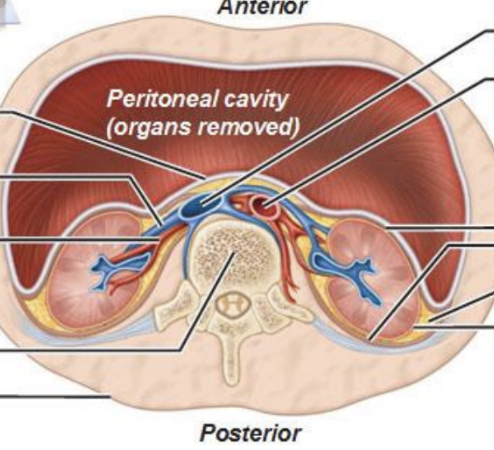
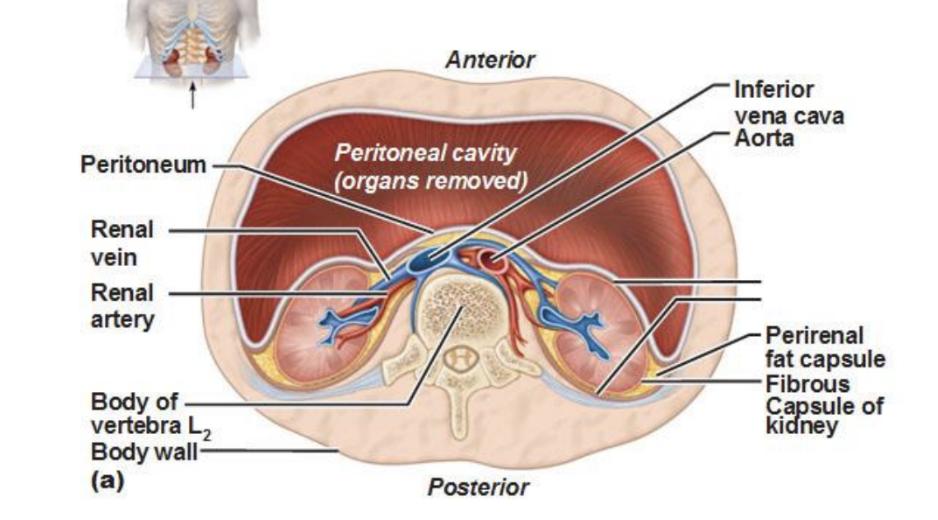
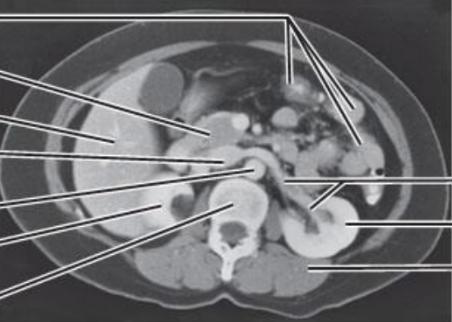

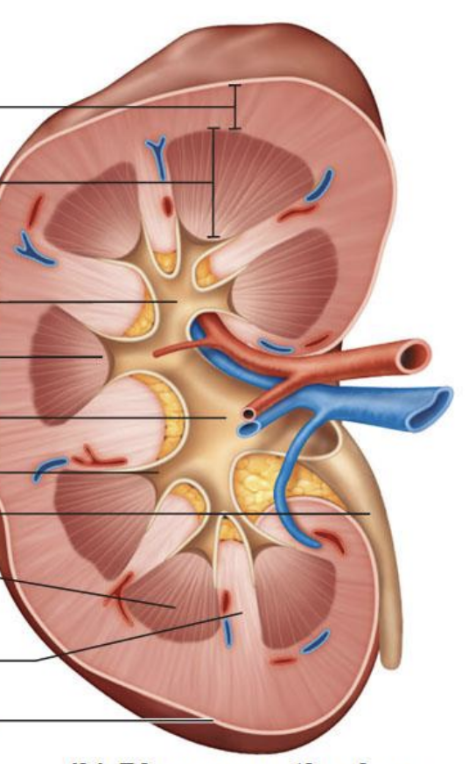
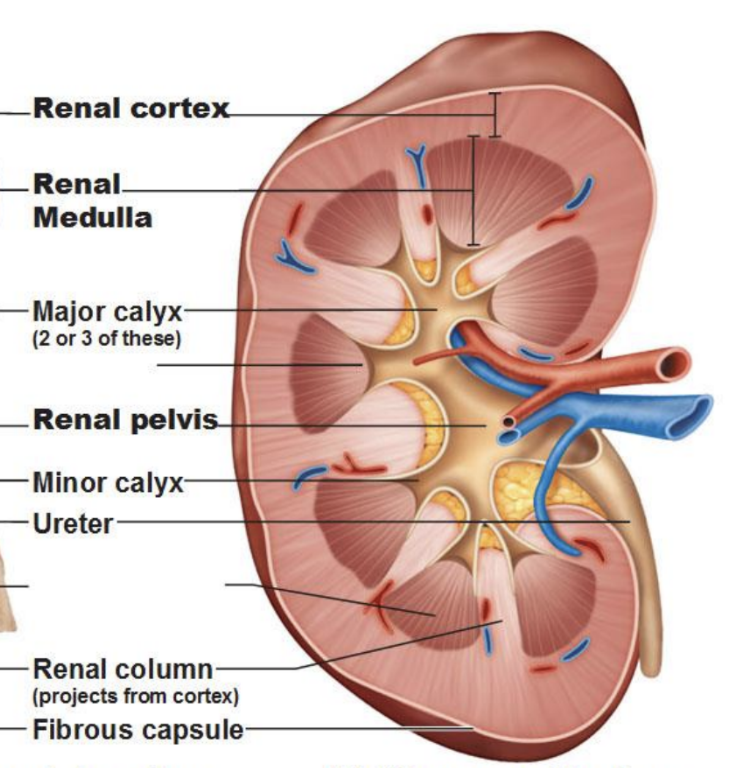
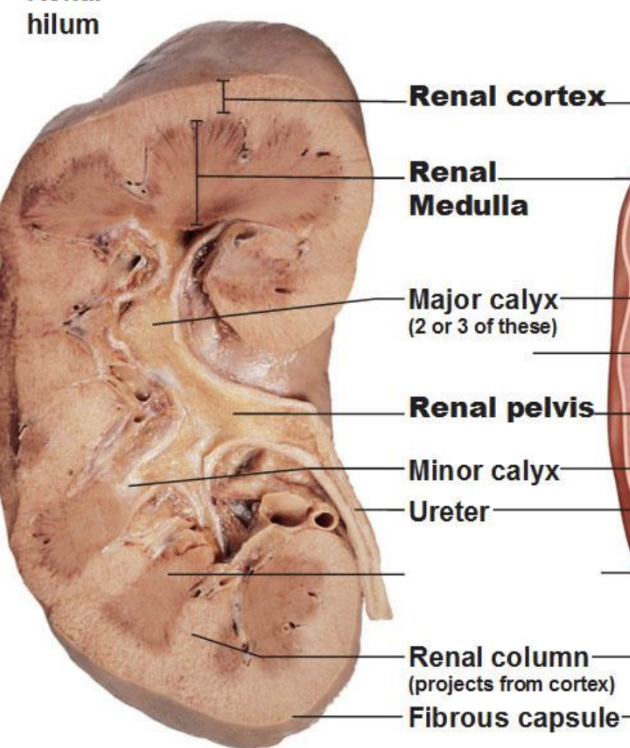
Describe the route from the glomerulus to the renal pelvis.
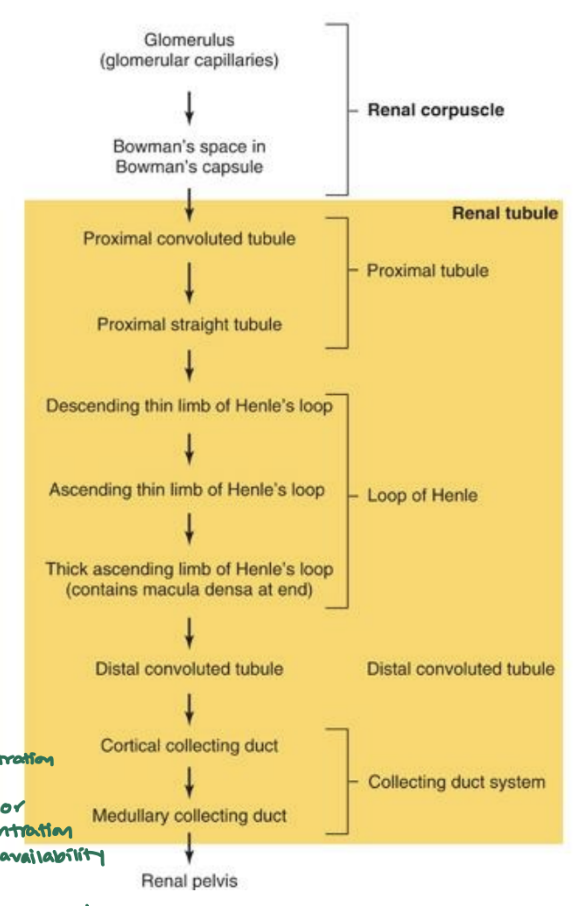
100% of __ are reabsorbed in the proximal tube.
amino acids
Different cells have different __ controls for different __.
regulatory; ions
Filtrate comes through the __ with high [Na+]. [Na+] and other ions are transported into the __ and pushed back into the __ to return into circulation.
tubular lumen; tubular epithelial cell; peritubular capillary
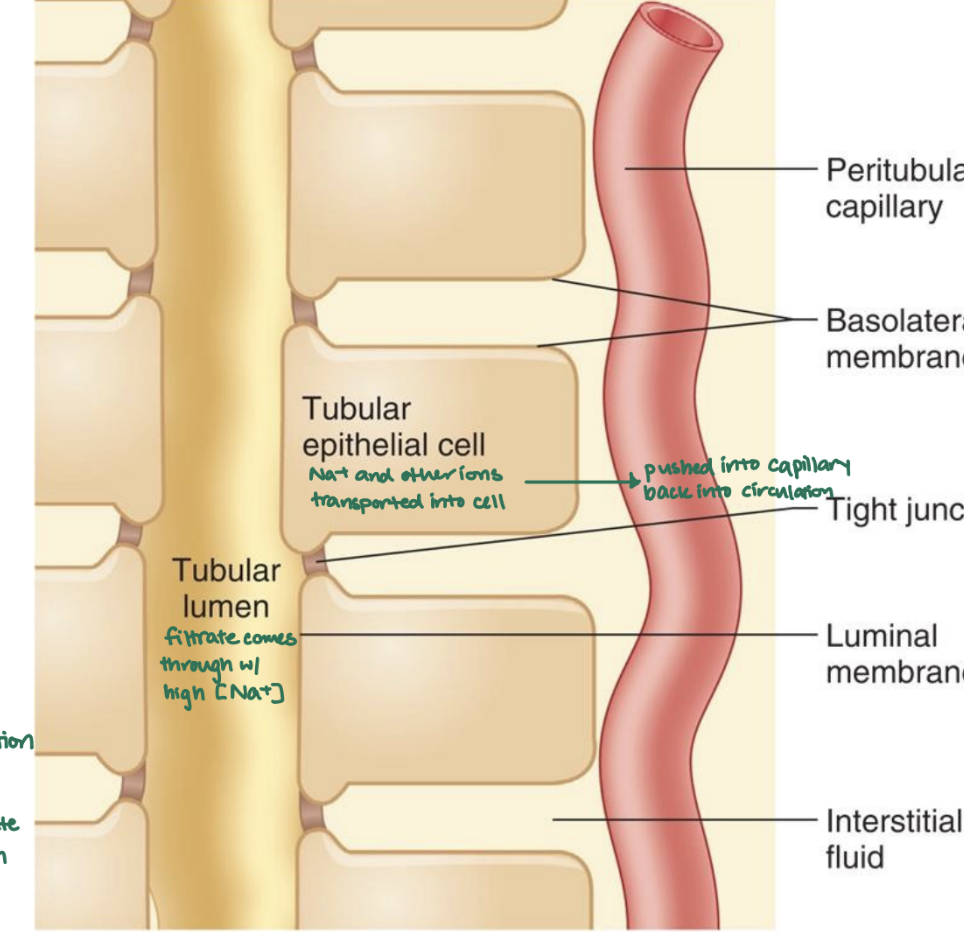
Filtrate → capillaries = __
capillaries → filtrate = __
reabsorption; secretion
What 4 things does the kidney regulate?
water
acid-base balance
electrolytes (Na+)
nitrogenous waste excretion
How does the glomerulus work?
plasma enters afferent arteriole → glomerulus capillaries, where filtrate passes into the Bowman’s capsule
→ filtrate channels to proximal tubule
→ remaining blood leaves through efferent arteriole
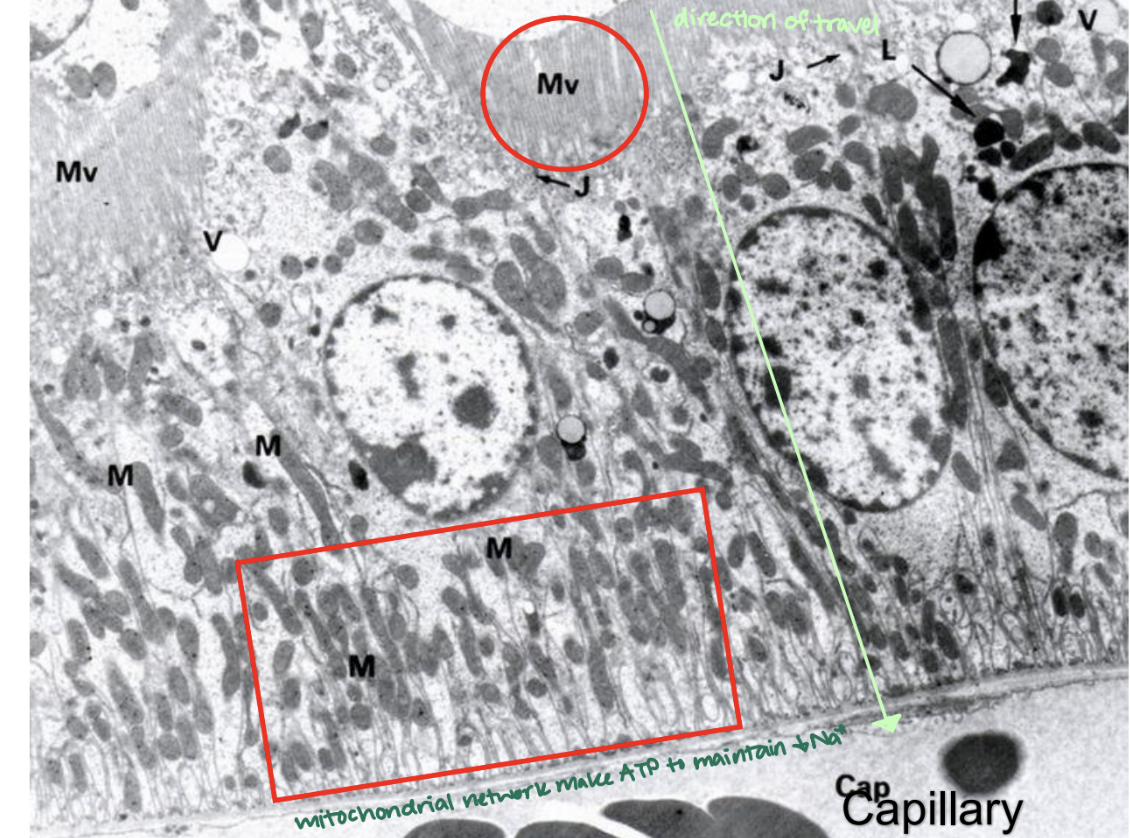
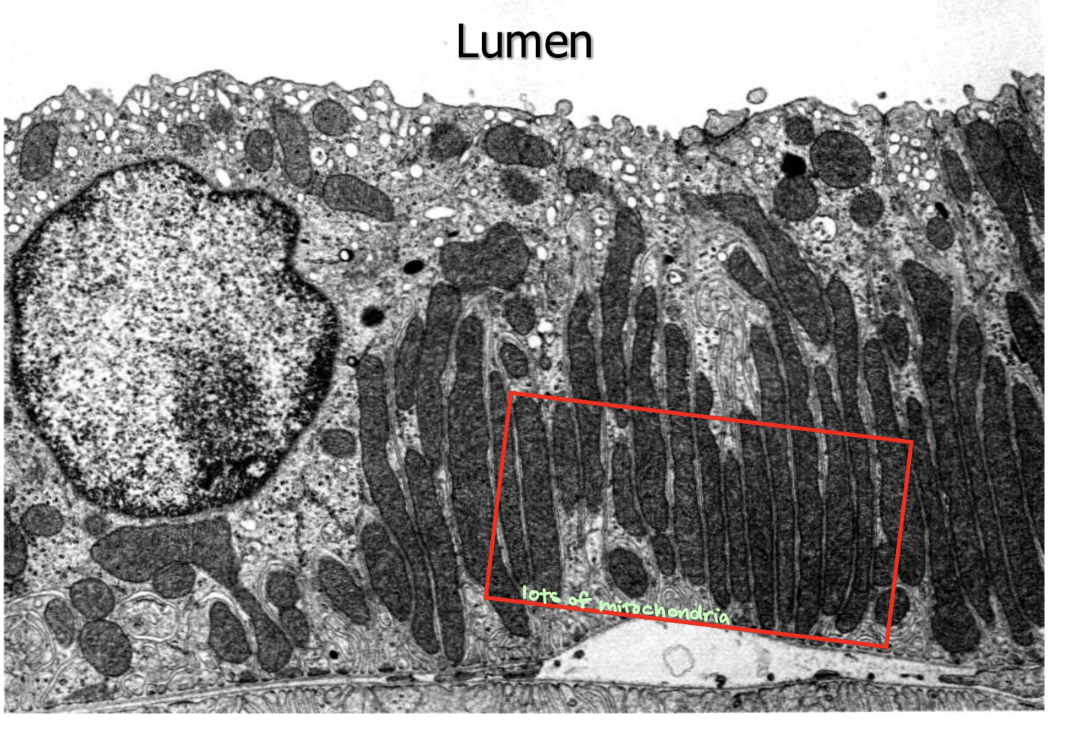
The proximal tubule has a low intracellular __ concentration due to:
Na; Na/K pump
In the proximal tubule, there is a __ to make ATP to maintain a low Na concentration.
mitochondrial network

The __ reabsorbs 65% of glomerular filtrate.
proximal tubule
Fluid reabsorbed in the proximal tubule has the same __ as filtrate.
osmolality
isoosmotic since ion flow causes fluid to follow
What is reabsorbed exclusively in the proximal tubule? (3)
glucose, amino acids, certain organic acids (usually completely reabsorbed)
body wants to maintain these in blood
What is exclusively secreted in the proximal tubule?
other classes of organic acids and bases
What is the goal of the descending limb of the loop of henle?
generate higher osmolarity (absorb more water)
The descending limb has no regulatory control. It is __
passive
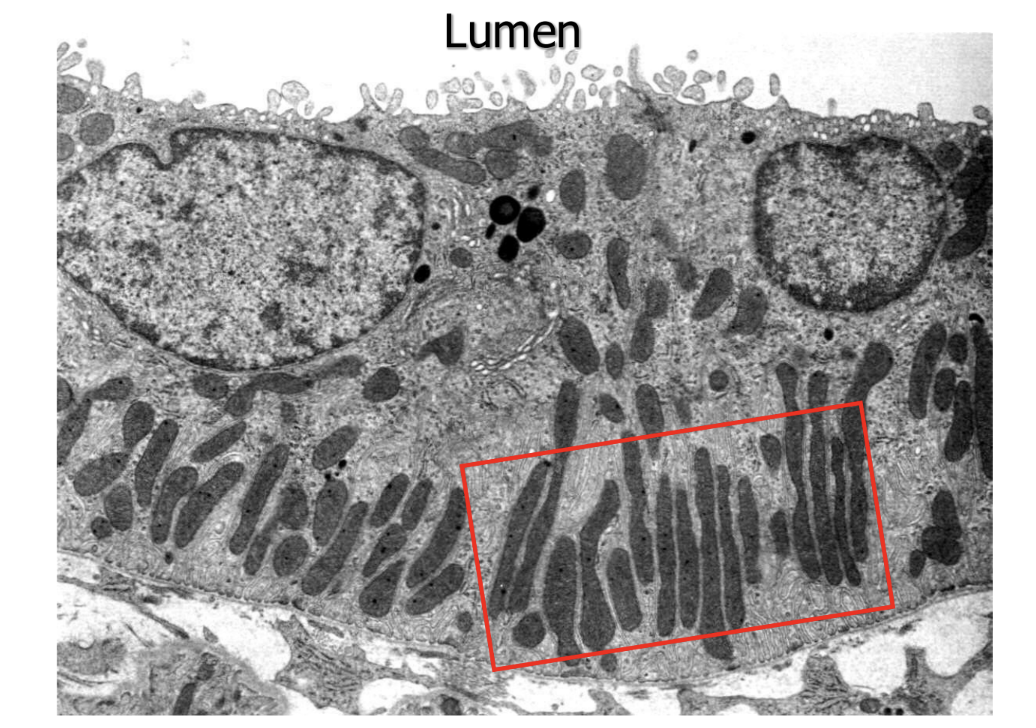
The thin limbs of the loop of henle are __ and __ epithelia without __.
thin; flat; mitochondria

What does this image show?
thin limbs of loop of henle
How do the thin limbs maintain the environment of the interstitium? How does this contribute to the counter-current multiplier
descending limb = permeable to water but not solutes → water reabsorbed passively by high osmolarity of interstitial fluid & water passively leaves filtrate, making it more concentrated
hyperosmotic
ascending limb = impermeable to water but permeable to solutes → sodium and chloride passively transported out of filtrate into interstitial space
hypoosmotic
→ maintains osmotic gradient in kidneys interstitium
crucial for countercurrent multiplier system → enables kidney to produce concentrated urine when needed (during dehydration)
collecting ducts can efficiently function by allowing water to move out of collecting duct and into interstitium
What vasoconstrictors are found in the glomeurulus and JGA (juxtaglomerular apparatus)?
sympathetic nerves (catecholamines)
angiotensin II
endothelin
What vasodilators are in the glomerulus and JGA? (6)
PGE2
PGI2
nitric oxide
bradykinin
dopamine
ANP (atrial natriuretic peptide)
There are a lot of __ in the thick ascending limb.
mitochondria
The thick ascending limb reabsorbs 25% of __
salt (sodium escapes but not water)
The thick ascending limb reabsorbs little __, so fluid remaining is __. Why?
H2O; dilute
sets stage for regulatory control in collecting duct
The thick ascending limb provides __ to glomerulus at __.
regulatory feedback; macula densa (T-G feedback)
The thick ascending limb sets up the __
counter-current multiplier
The early distule tubule has __
mitochondria
The __ reabsorbs 5% of filtered salt.
distal tubule
Like the thick ascending limb, the __reabsorbs little H2O, so fluid remaning is diluted even more.
distal tubule
no aquaporins
The early distal tubule is similar to the thick ascending limb except they have different __.
transporters
The early distal tubule regulates hormonal __
Ca2+
In the collecting tubule, there are 2 __ with different regulatory controls. What are they?
cell types (principal cell, a-intercalated cell)
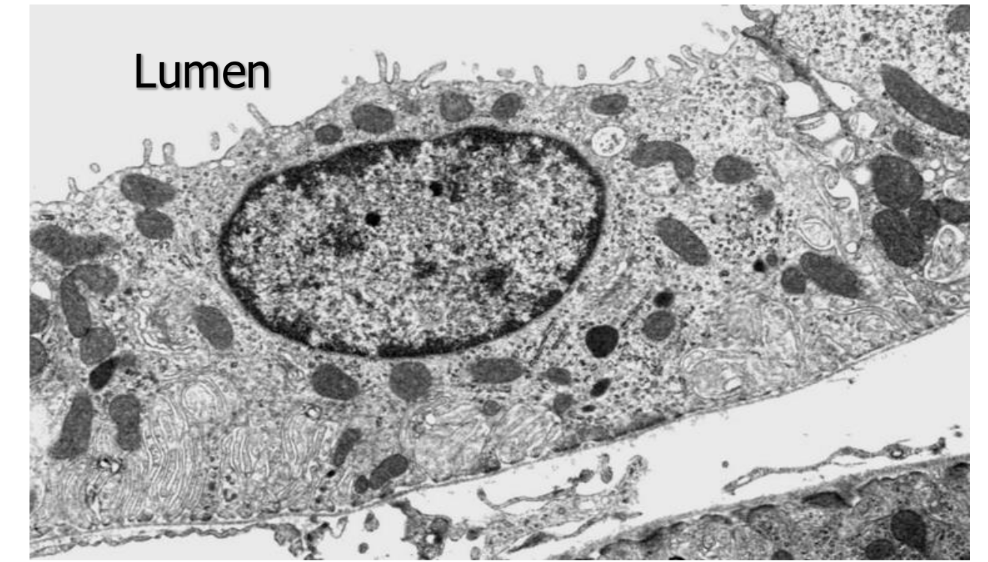
What is the function of principal cells? (3)
adjust amounts of Na+ and H2O reabsorbed into body
adjusts amount of K+ secreted
hormonal control: aldosterone & ADH
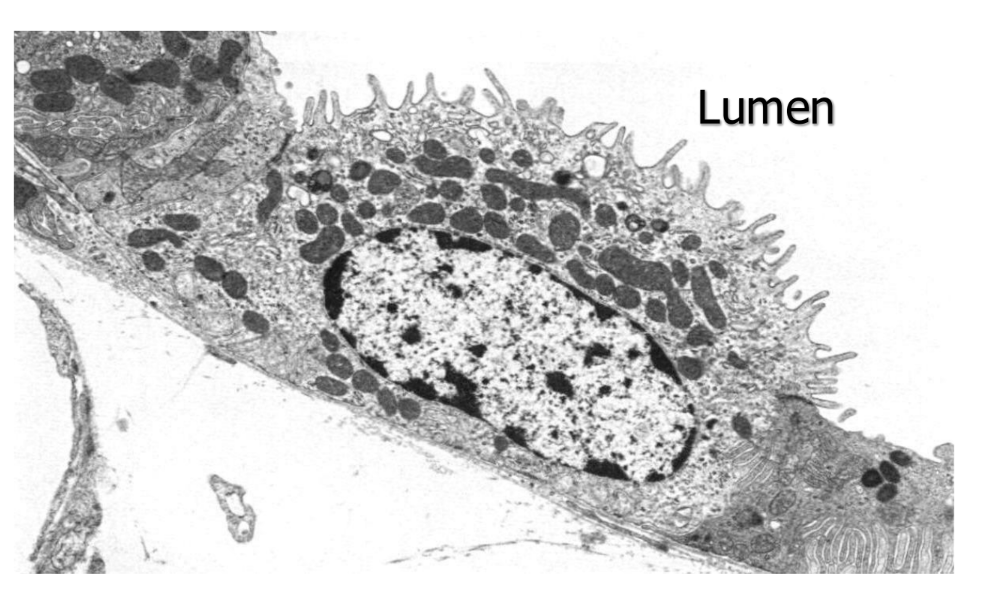
What is the function of a-intercalated cells?
adjust amounts of K+ reabsorbed
acid-base regulation: H+ secretion