Endocrine System and Blood: Hormones, Glands, and Functions
1/149
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
150 Terms
Endocrine system
The function is to coordinate the body system and maintain homeostasis. Works with the nervous system, is a more leisurely system of communication than the nervous system (longer for reaction).
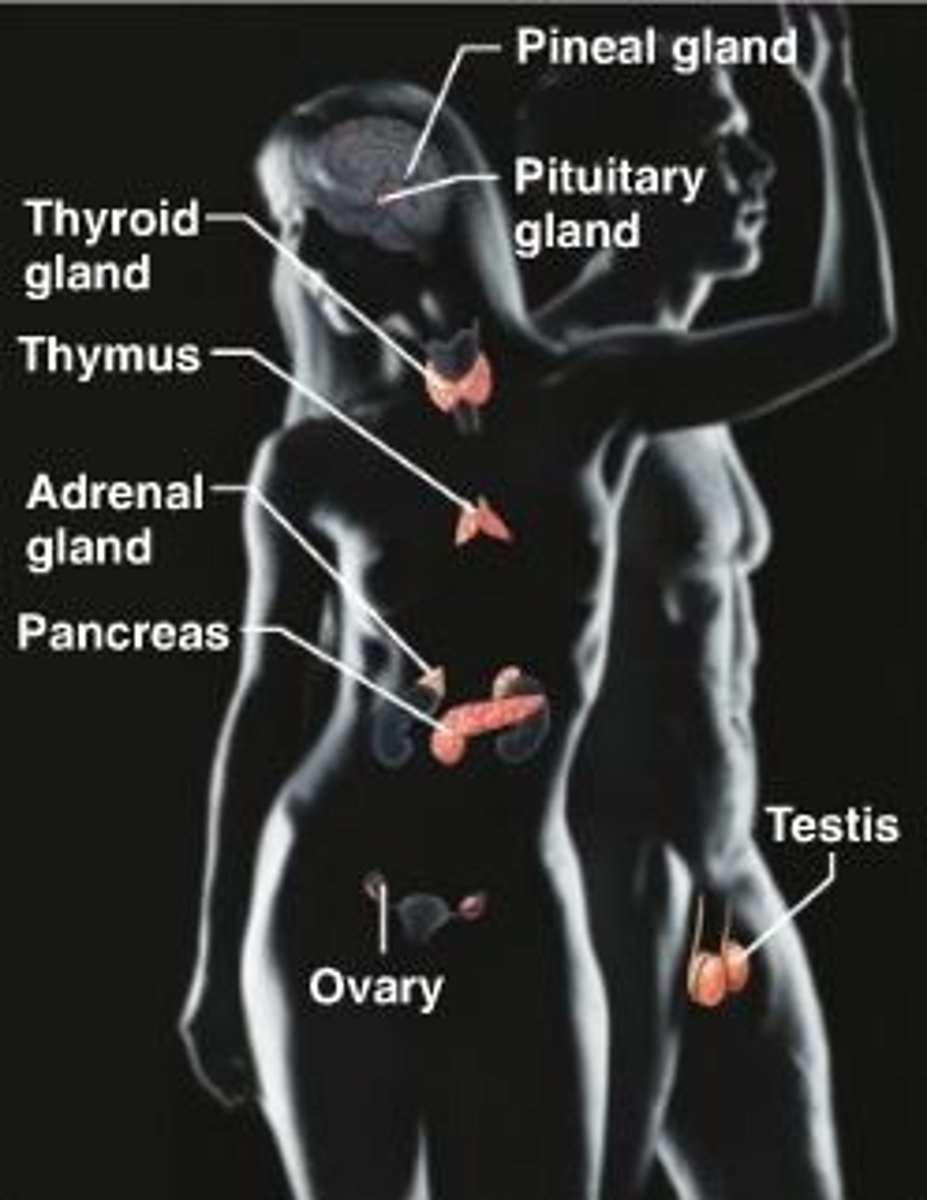
Organs with some endocrine system
Hypothalamus, thymus, pancreas, ovaries, testes, heart, placenta, stomach, intestines, kidneyGlands: pituitary, thyroid, parathyroids, adrenal, pineal
Function of hormones
Endocrine glands contain secretory cells that release hormones into extracellular fluid to diffuse into the bloodstream. Hormones are one type of chemical messenger of the body. Affect only target cells.
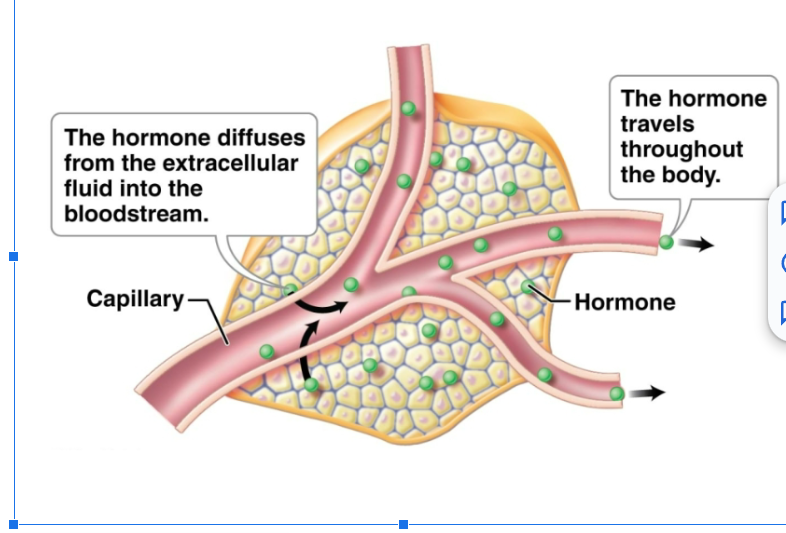
Mechanism of hormones
Target cells have receptors, which are protein molecules that recognize and bind specific hormones. Cells other than target cells lack correct receptors and are unaffected. The mechanism by which a hormone influences target cells depends on the chemical makeup of the hormone
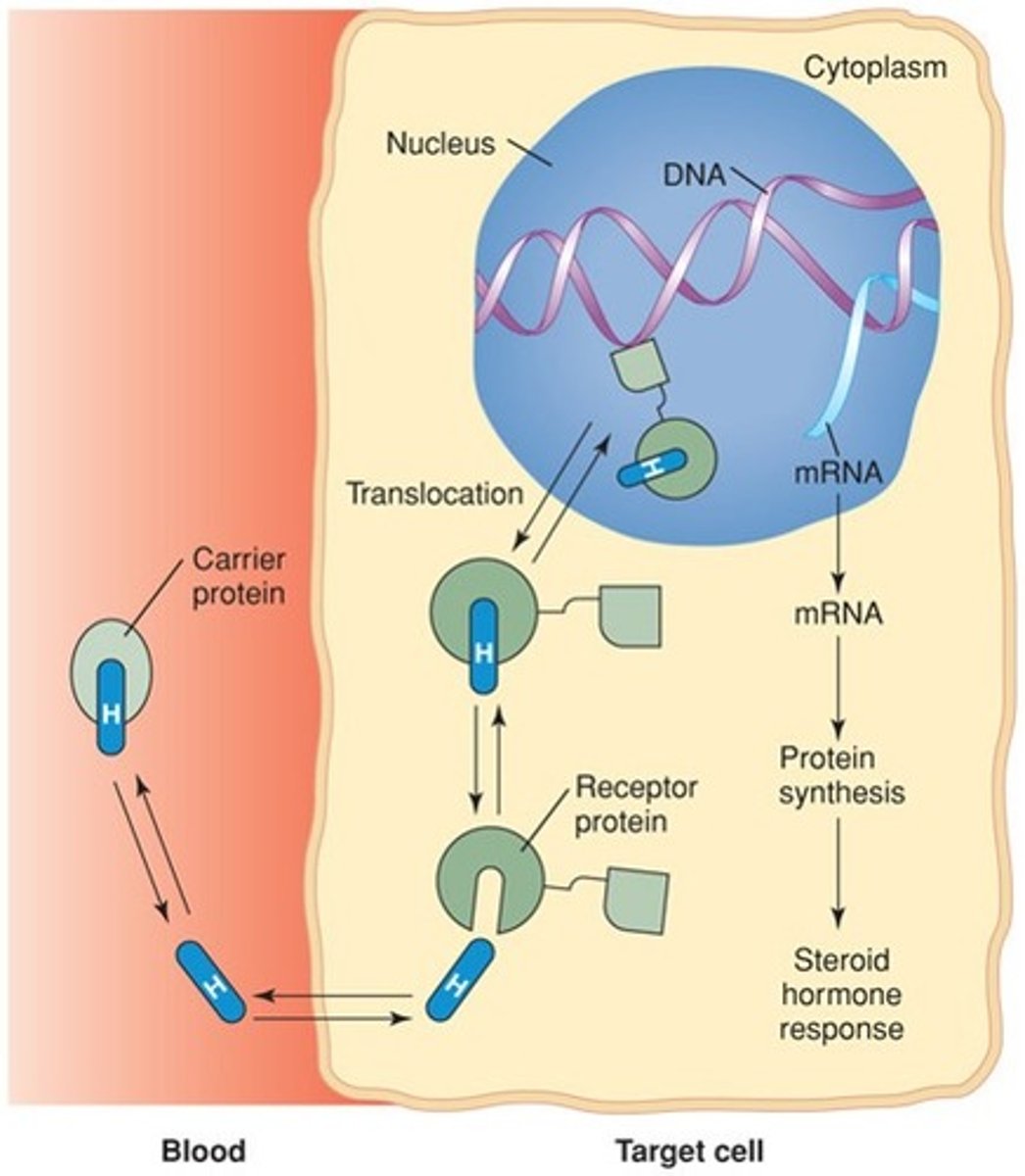
two types of hormone
Lipid soluble and water soluble
lipid soluble hormones
Derived from cholesterol. Include steroid hormones (ovaries, testes, adrenal glands). -Move into a cell and stimulate synthesis of proteins- Move easily through the target cell's plasma membrane. Once inside the target cell, the hormone combines with receptor molecules. In nucleus, the hormone-receptor complex attaches to DNA and activates certain genes to synthesize specific proteins
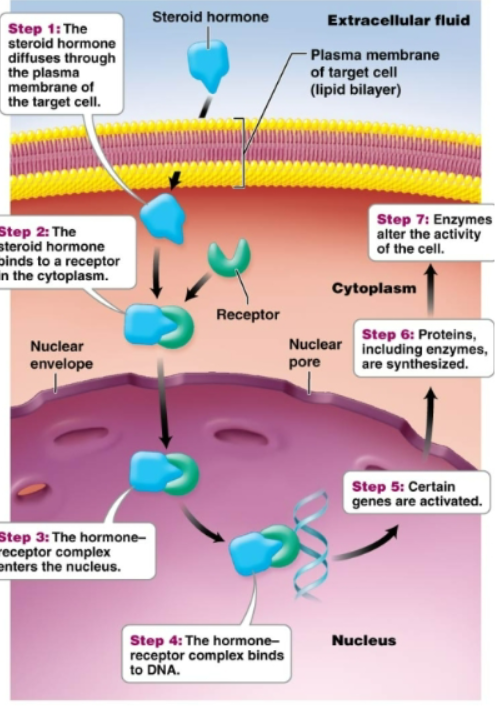
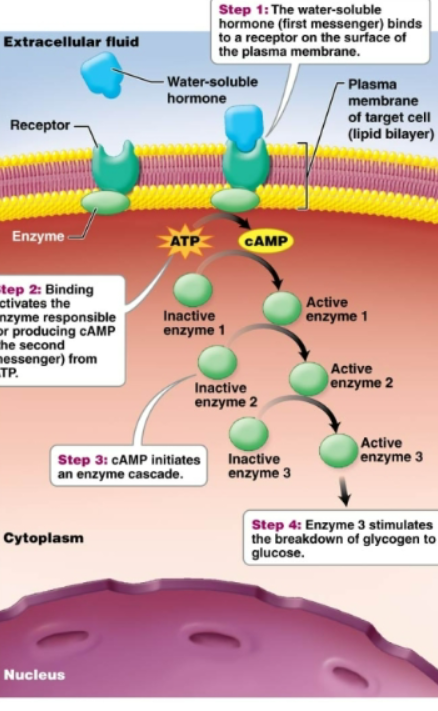
water soluble hormones
Made of amino acids. Can not pass through the lipid bilayer of the plasma membrane. Considered first messenger (knocks on door, relay messages to receptor, who then starts process within target cell). Exert their effects indirectly by binding to the receptors on the surface of the target cell. This stimulates second messengers within the cell that carry out the effect of the hormone (cAMP) -Activate proteins already present in cell without ever entering the cell-
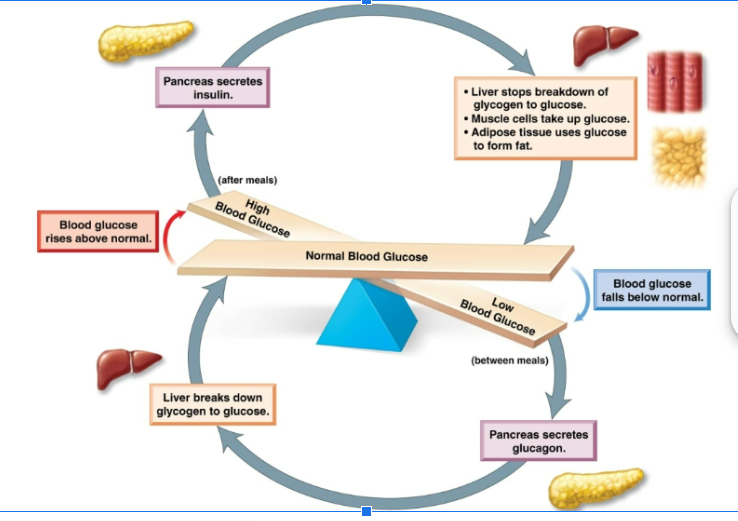
negative feedback mechanism
Increased blood level of the hormone inhibits its further release. Alternatively, some endocrine glands are sensitive to the particular condition they regulate rather than the level of hormone they produce. Ex: pancreas stops secreting insulin when levels of blood glucose decline
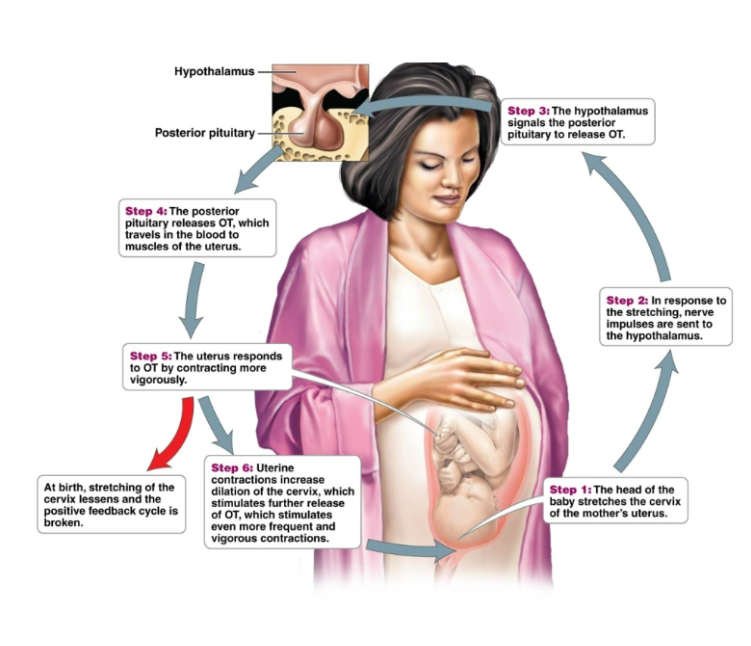
positive feedback mechanism
Outcome of a process that further stimulates the process. Ex: oxytocin and uterine contractions of childbirth. Less common than negative feedback mechanism
antagonist
The effect of one hormone that opposes of another hormone
synergist
the response of a tissue to a combination of hormones is much greater than its response to either individual hormone
permissive
One hormone must be present (ask permission) for another hormone to exert its effects
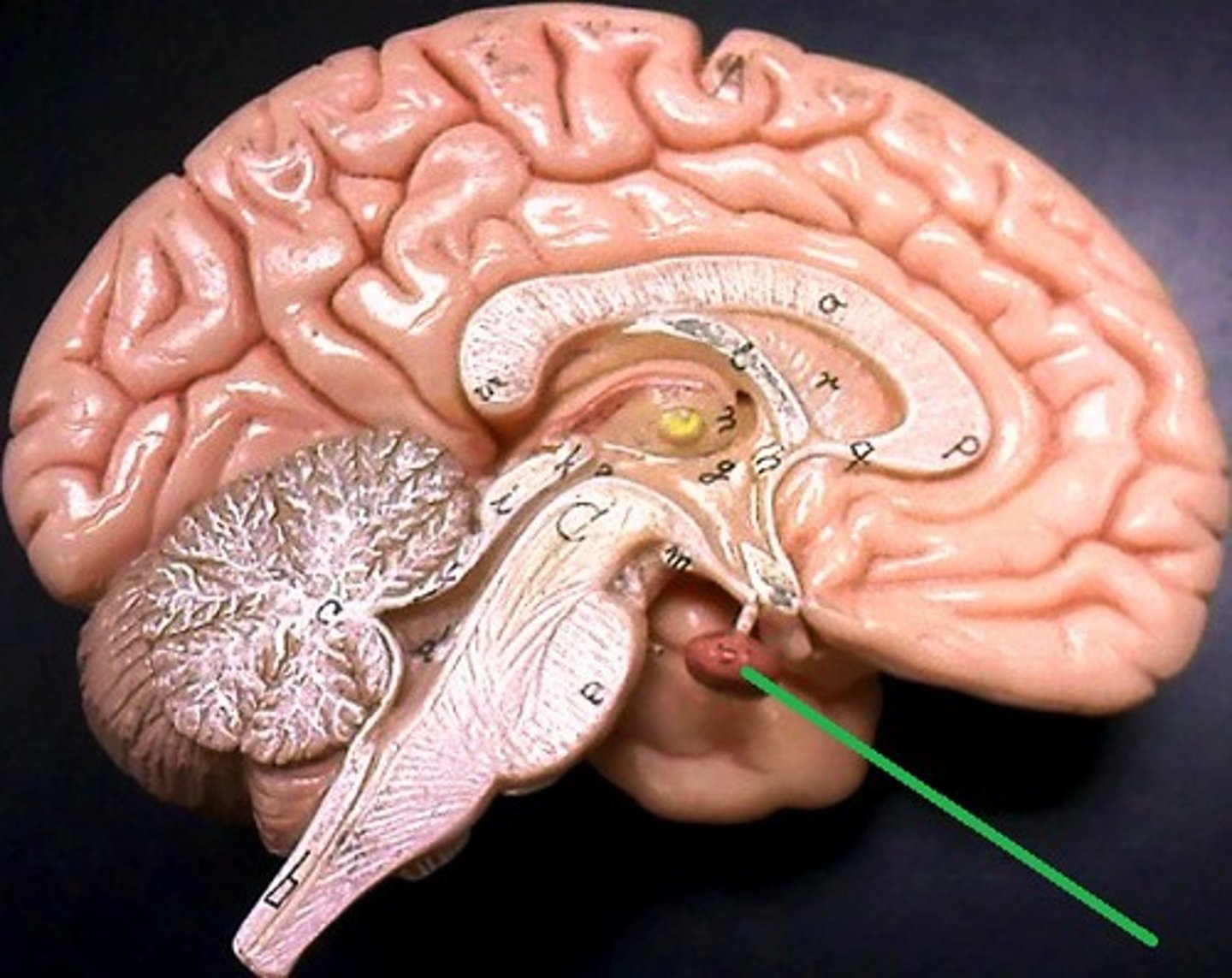
pituitary gland
Located at the base of the brain. Consists of 2 lobes, anterior and posterior
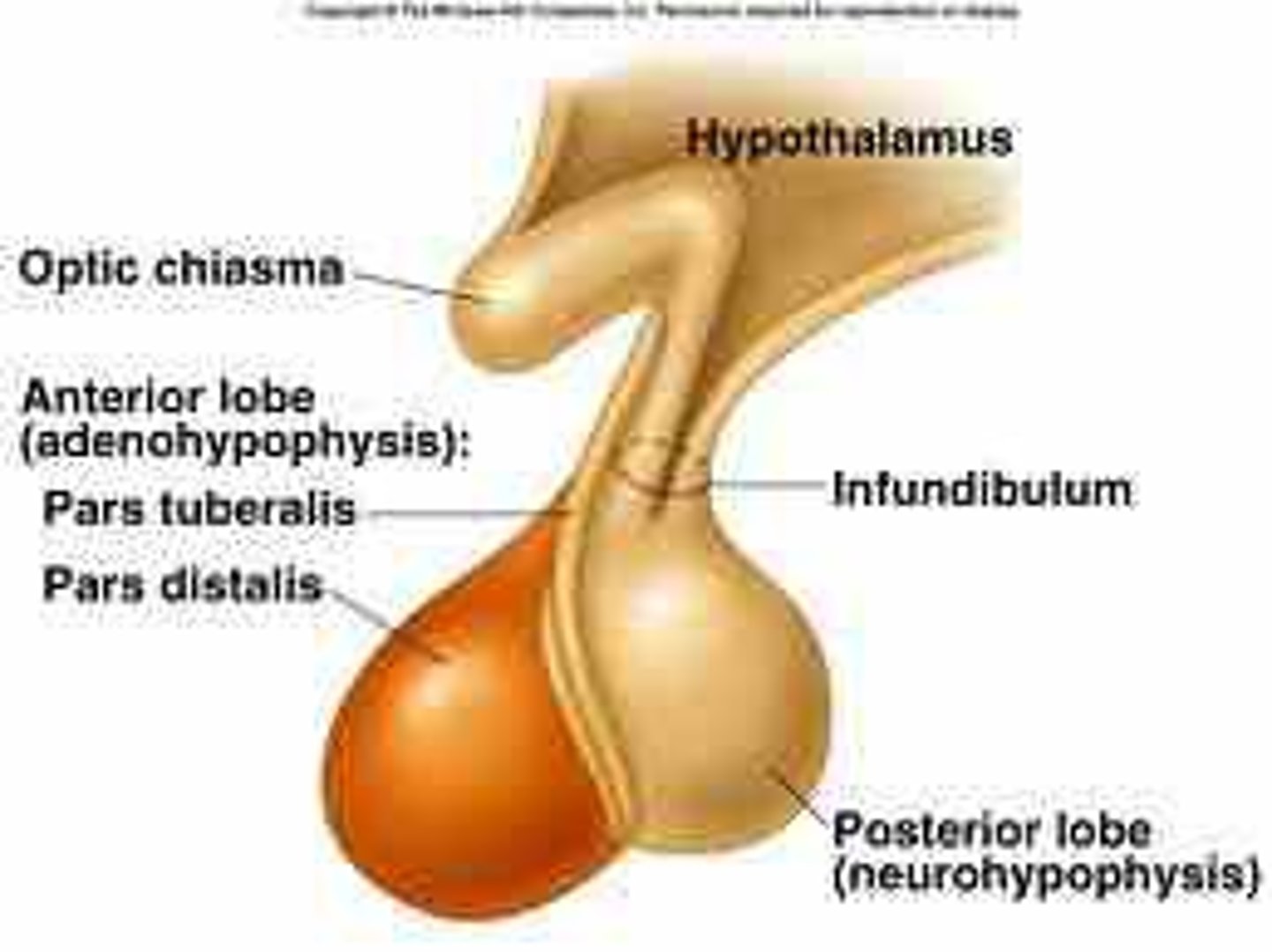
anterior pituitary
Circulatory connection to hypothalamus, which synthesizes and secretes releasing and inhibiting hormones. Releasing hormones stimulate hormone secretion by this and inhibiting hormones inhibit hormone secretion by this
anterior lobe
The two hormones of hypothalamus regulate the synthesis and release of growth hormone GH. Growth hormone releasing hormone stimulates release of GH, growth hormone inhibiting hormone inhibits release of GH
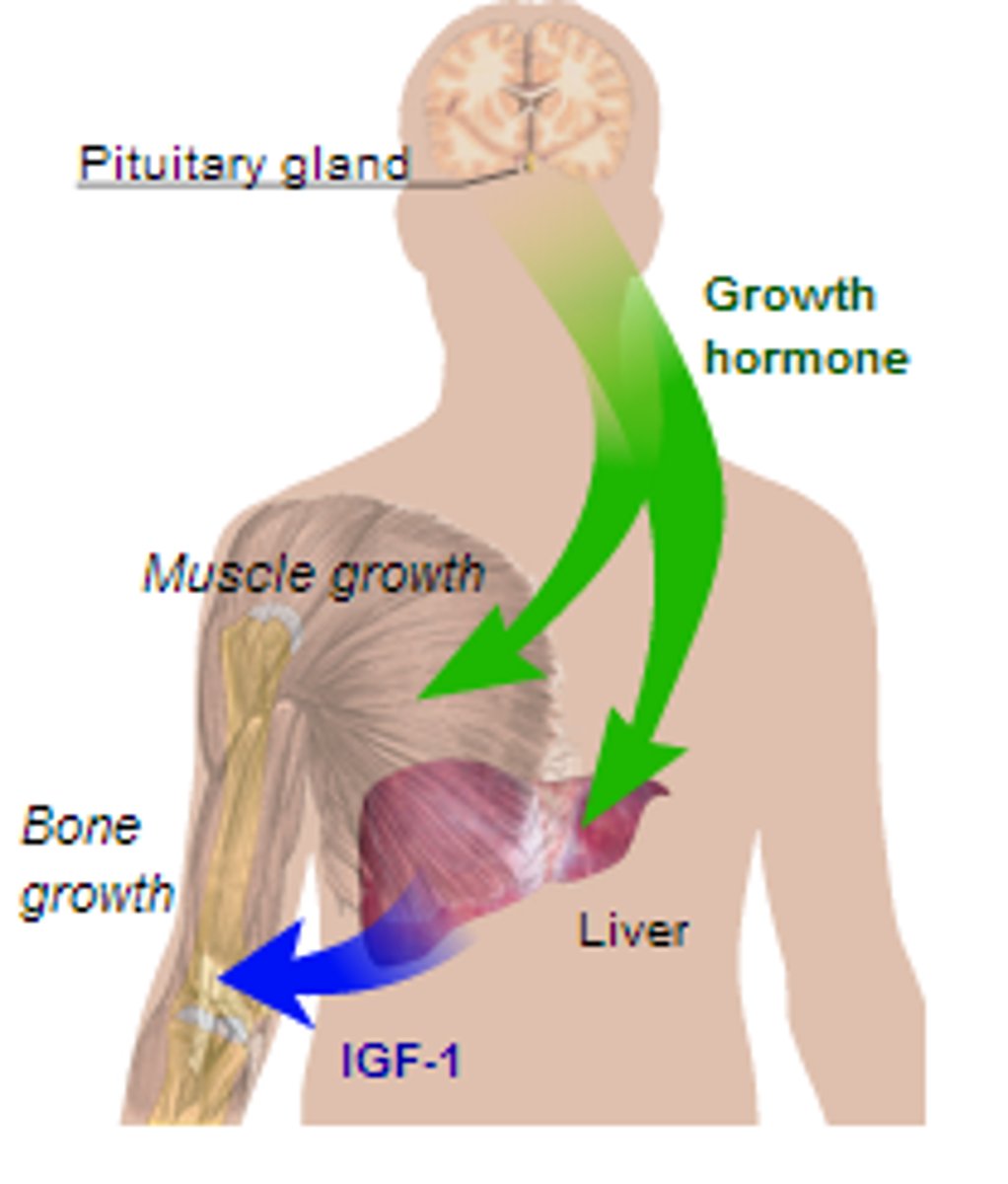
growth hormone
Stimulates rate of cell division and an increase in cell size. Ex: bone, muscle, cartilage
tropic hormones
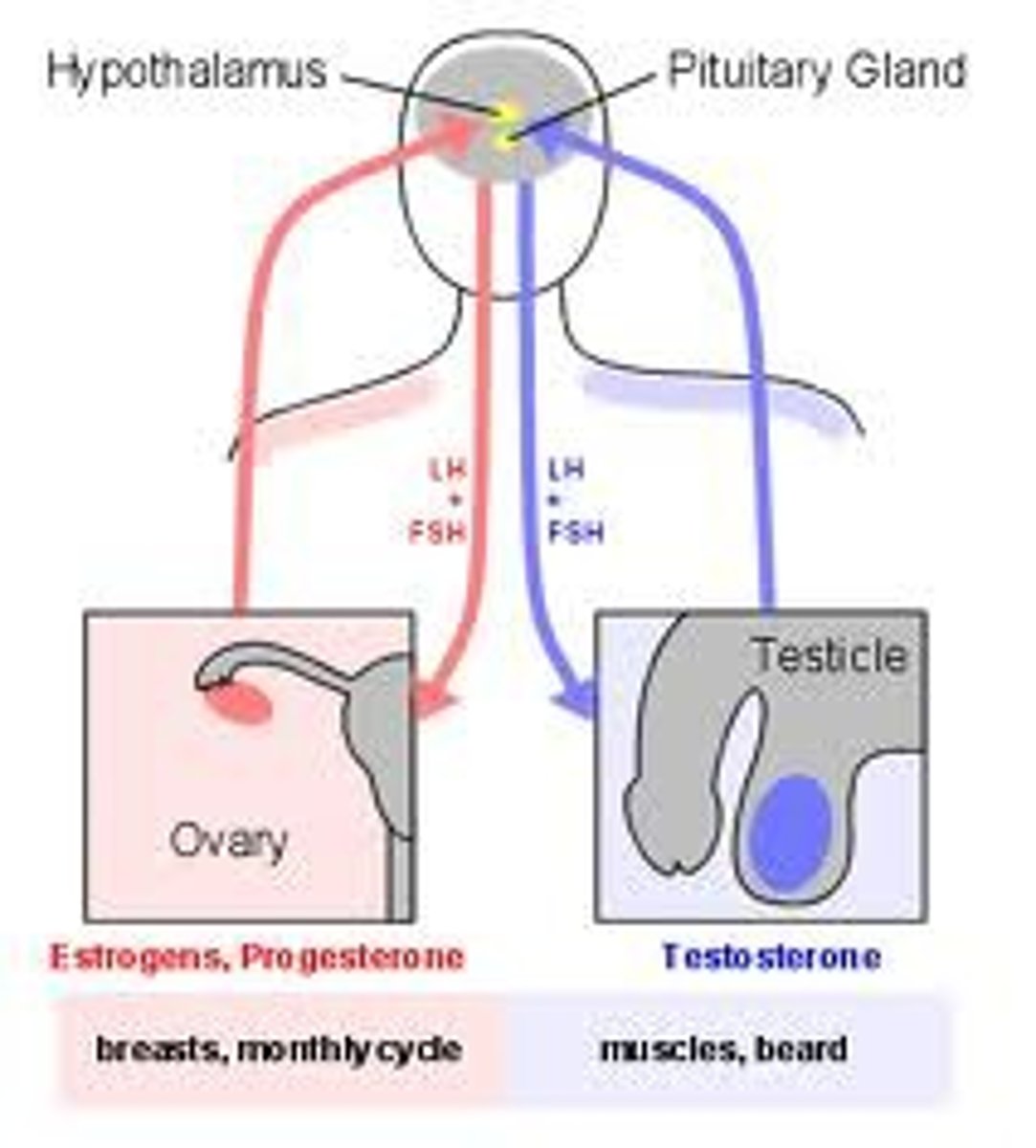
Hormones that influence the secretion of hormones by other glands. Include the following hormones of the anterior pituitary: Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), Adrenocorticotropic (ACTH), Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), Luteinizing hormone (LH)
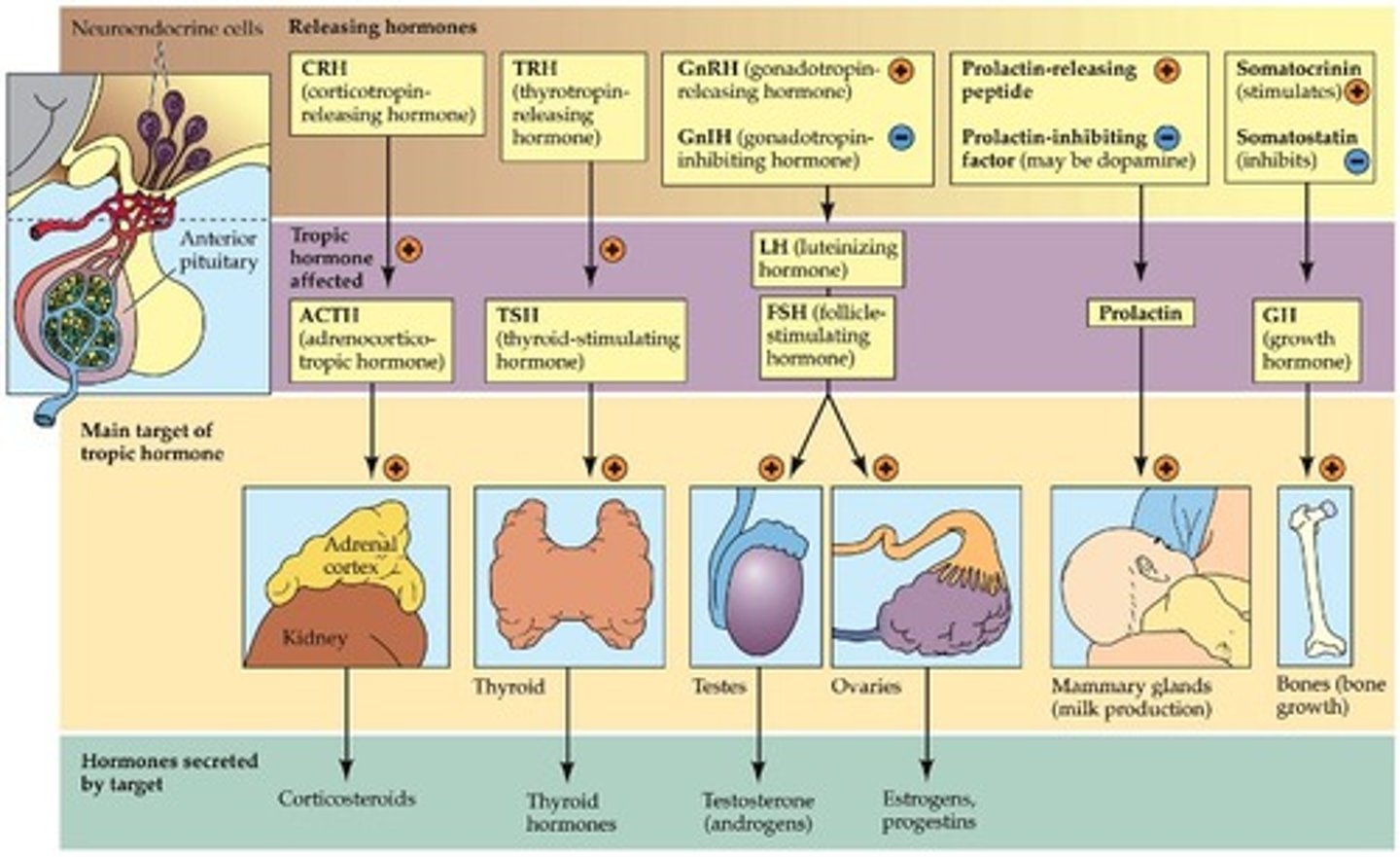
thyroid stimulating hormone
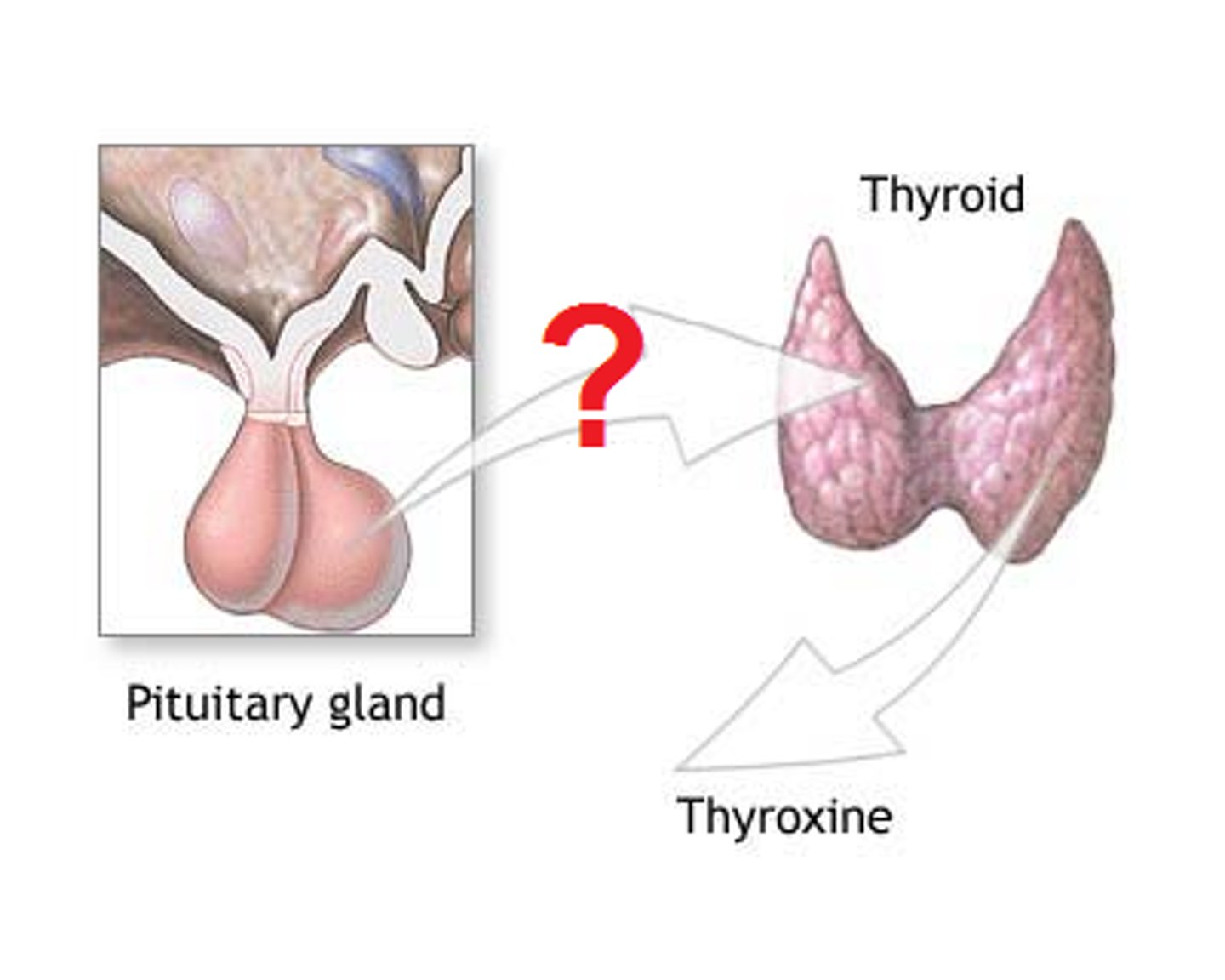
Tropic hormone that acts on thyroid gland to stimulate the synthesis and release of other thyroid hormones
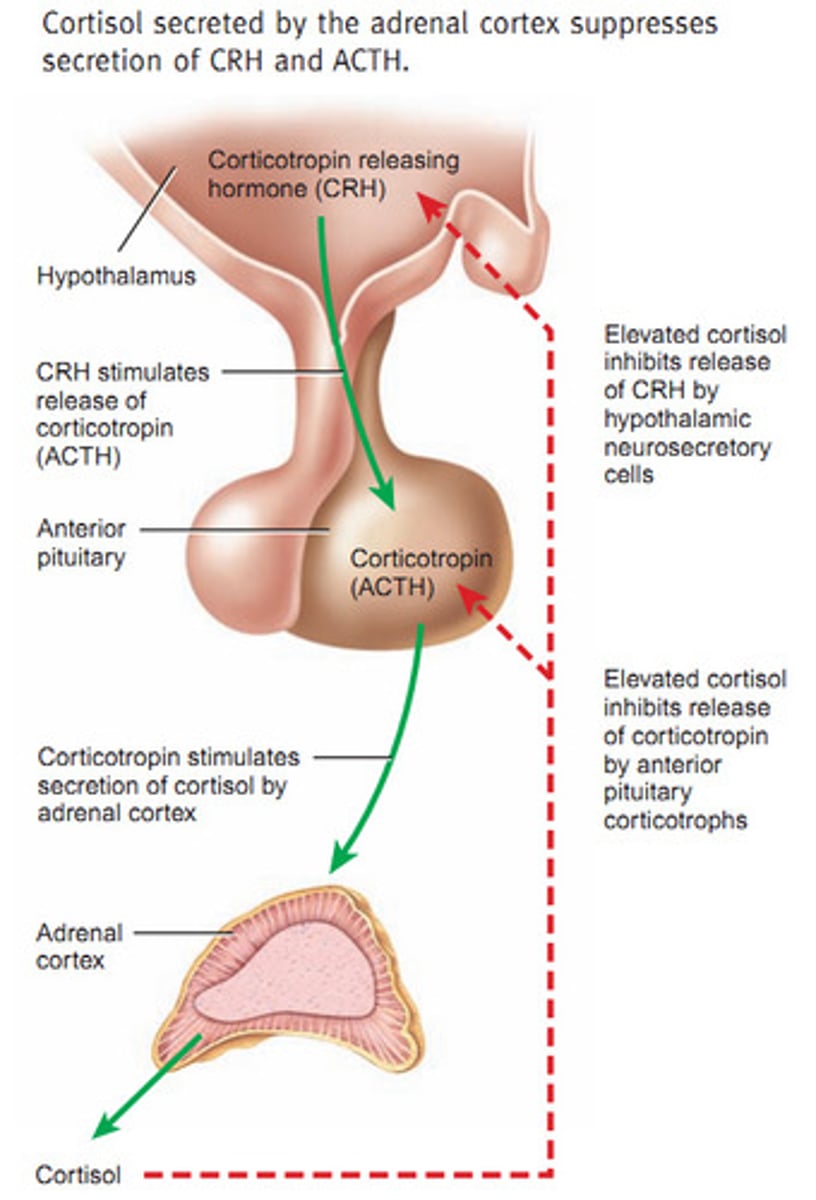
adrenocorticotropic hormone
Tropic hormone that controls the synthesis and secretion of glucocorticoid hormones from the cortex of the adrenal glands
follice stimulating hormone
Tropic hormone that in females, promotes development of egg cells and secretion of estrogen. In males, promotes production of sperm
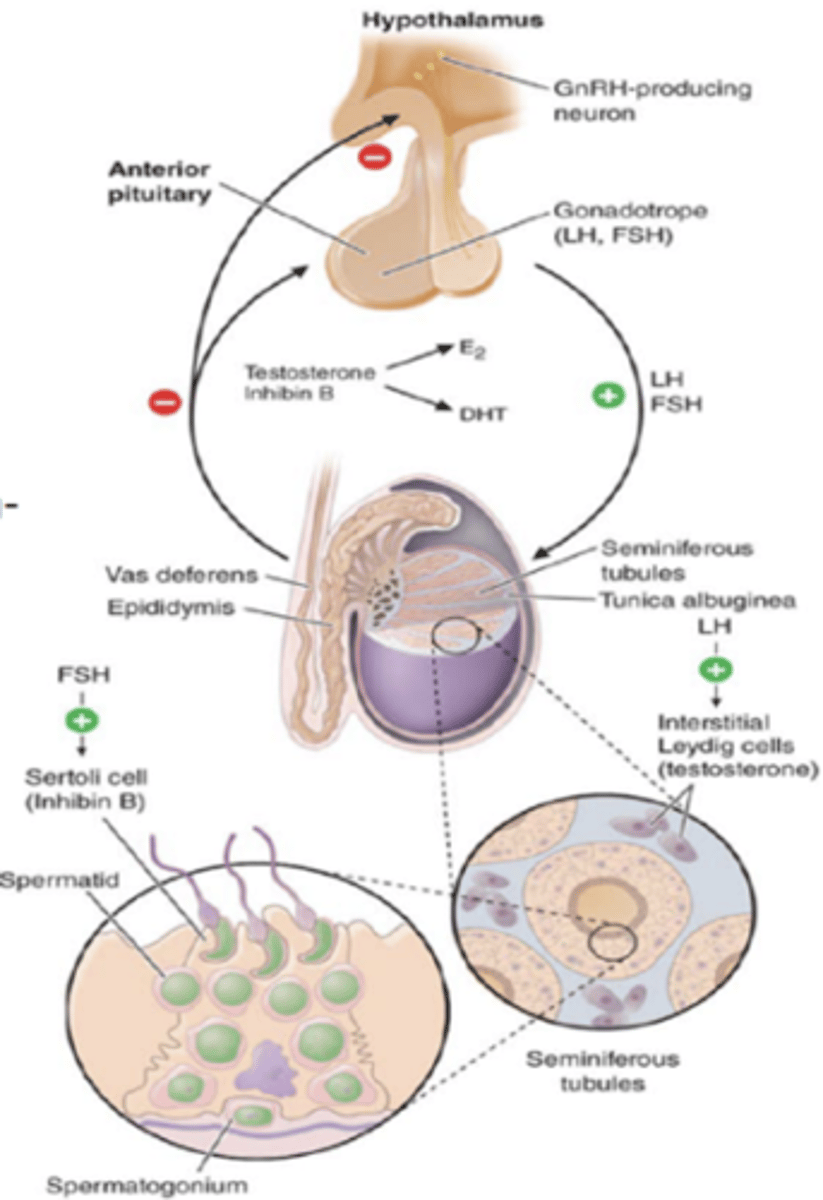
lutenizing hormone
Tropic hormone that in females causes ovulation and secretion of estrogen and progesterone. In males, stimulates production and secretion of testosterone
posterior lobe
Cells within this lobe of the pituitary gland do not produce any hormones. Neurons of the hypothalamus manufacture antidiuretic hormone ADH and oxytocin OT. ADH and OT travel down nerve cells (neurosecretory cells) into the posterior pituitary, where they are stored and released
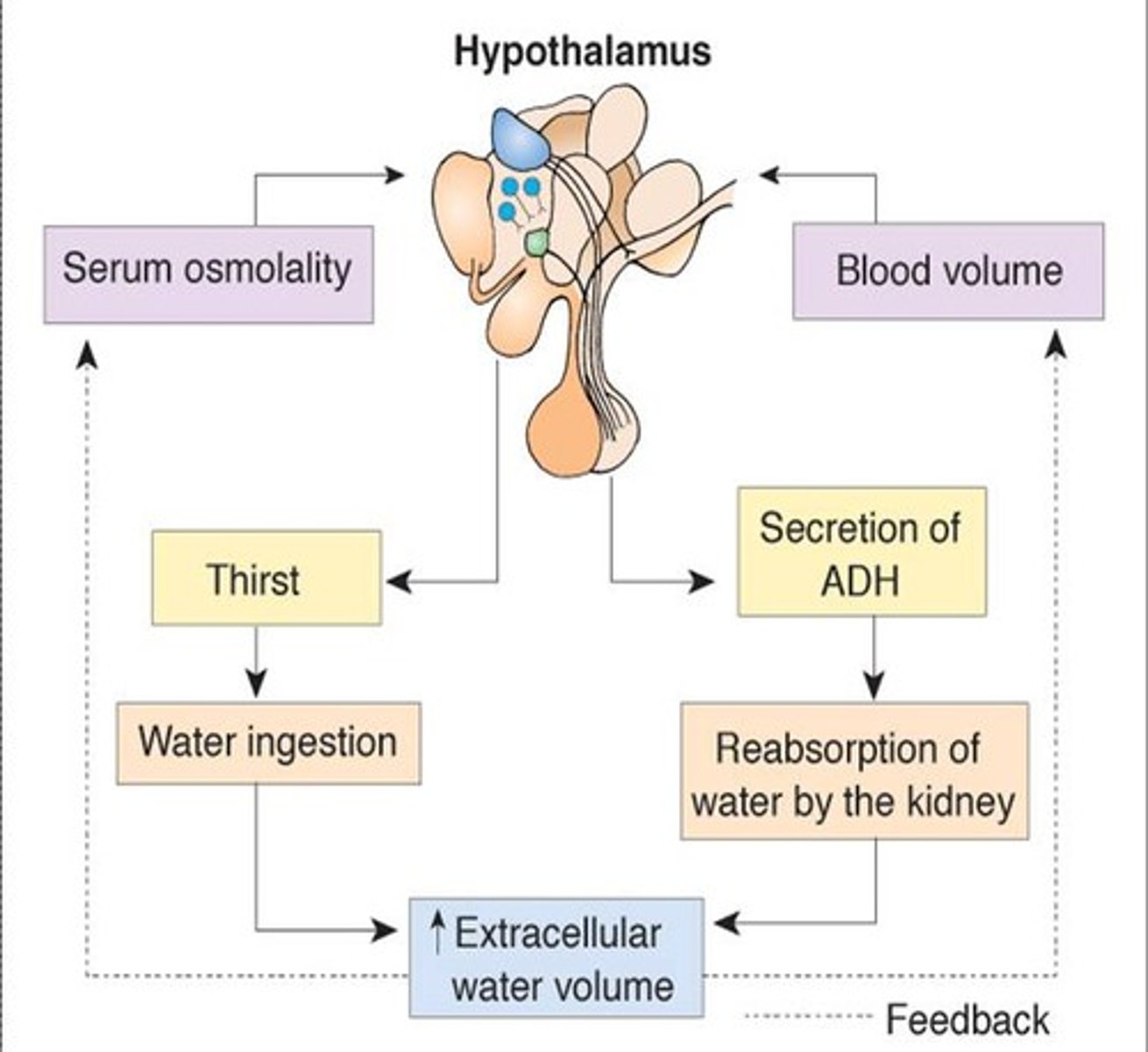
antidiuretic hormone ADH
Causes kidneys to remove water from fluid destined to become urine. A deficiency of this results in: diabetes insipidus and excessive urine production and dehydration. Can also be treated in administering this in a nasal spray
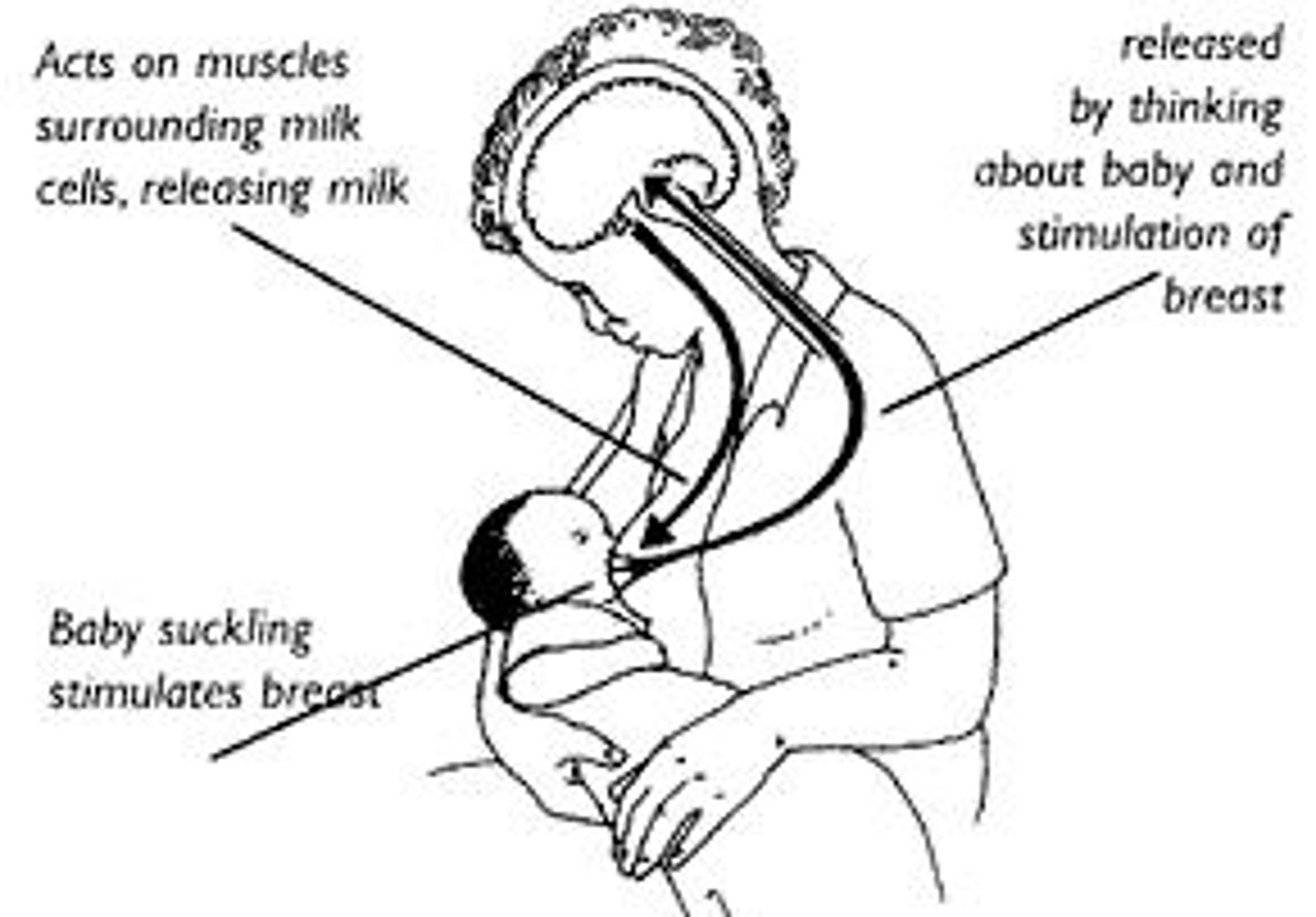
Oxytocin
In females, it stimulates uterine contractions of childbirth and mild ejection from the mammary glands. In males, it may facilitate sexual behavior and transport of sperm.
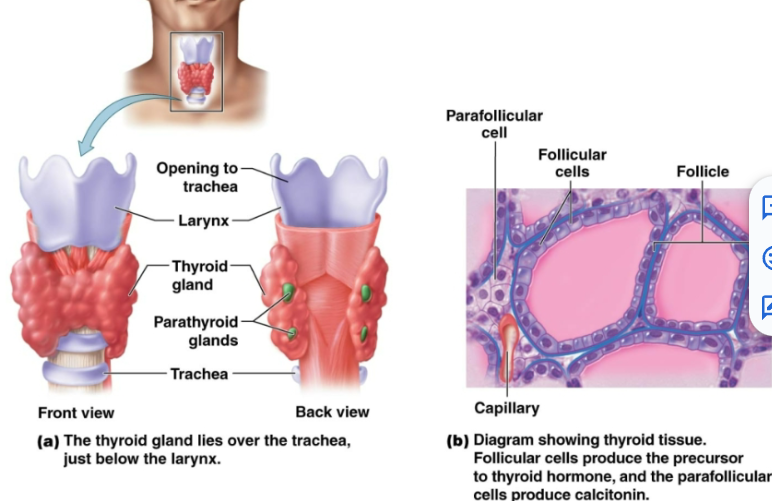
thyroid hormone
Includes thyroxine and triiodothyronine. Produced in follicular cells. -Regulates metabolic rate and production of heat -Maintains BP -Promotes normal functioning of several organ systems. Goiter is enlarged
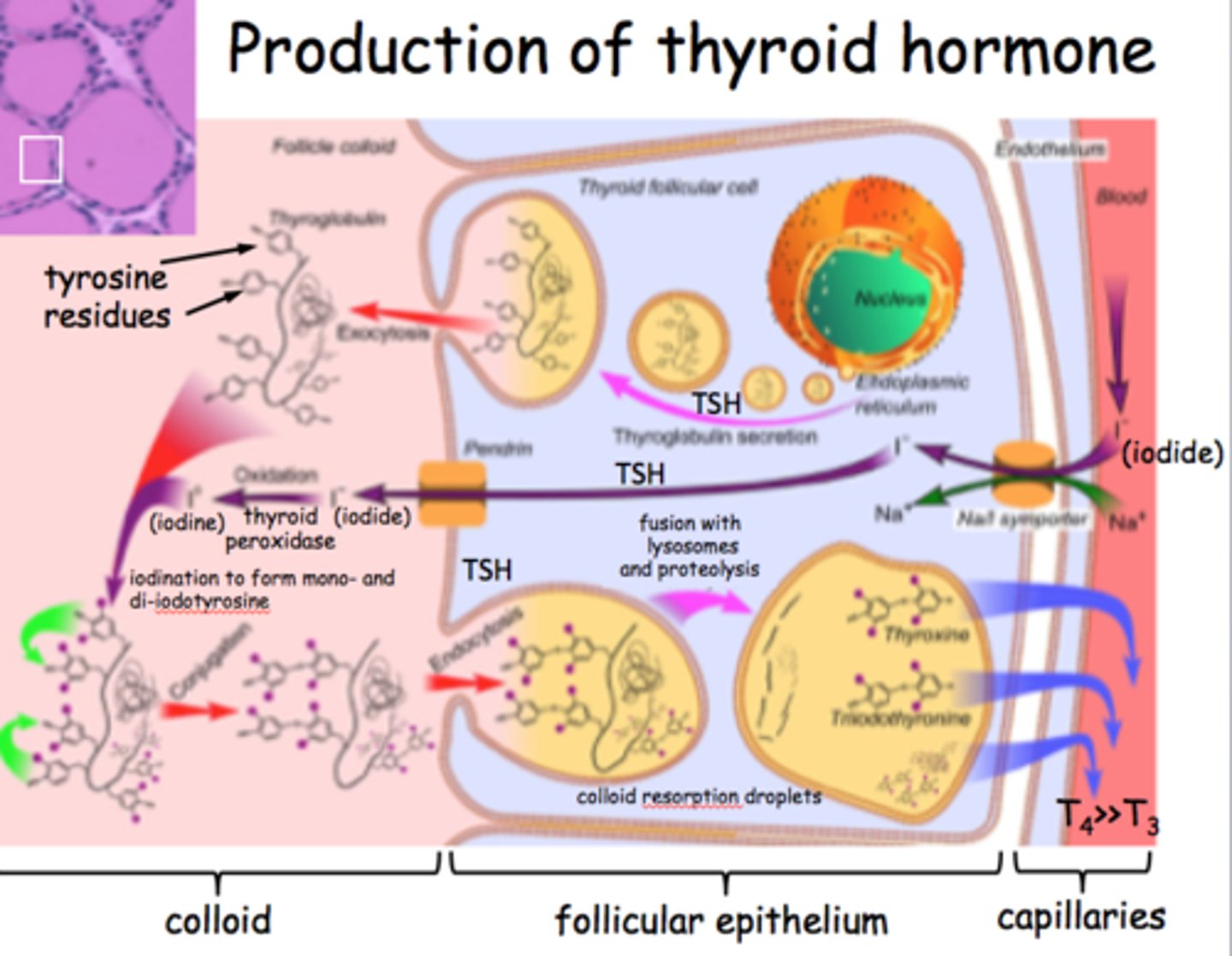
calcitonin
Produced by parafollicular cells. Lowers the levels of calcium in blood. -Stimulates absorption of calcium by bone -Inhibits breakdown of bone -Increase excretion of calcium in urine
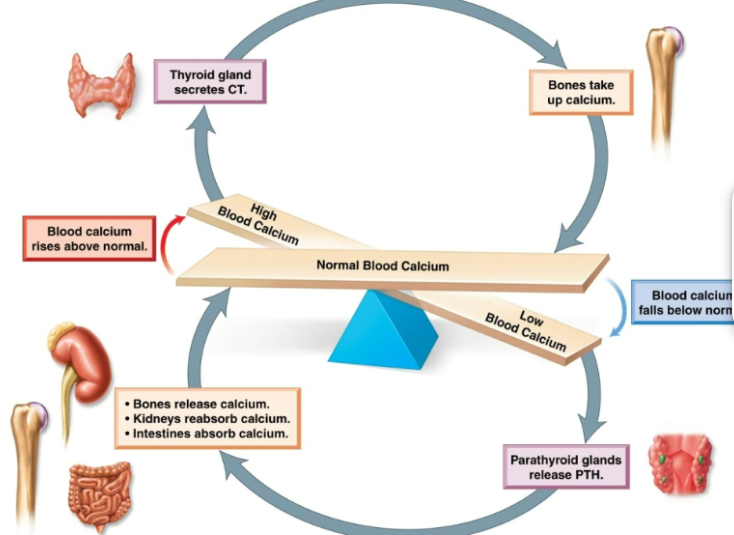
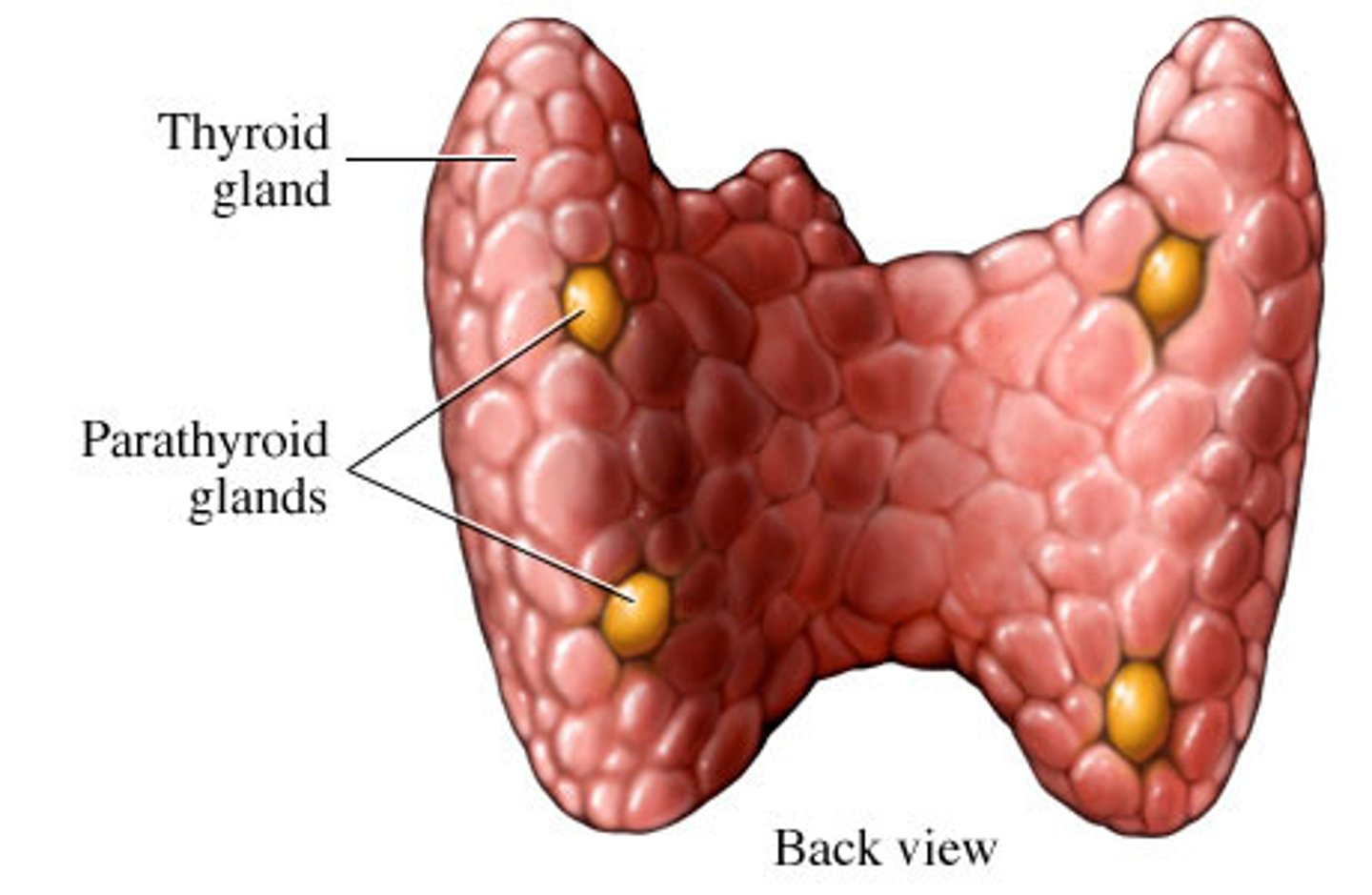
parathyroid glands
Four small round masses at the back of the thyroid gland.
paraythyroid hormone
Increase level of calcium in blood. Stimulates osteoclasts to break down bone, releasing calcium into blood. Stimulates kidneys to remove calcium from fluid destined to become urine, returning it back to blood. Stimulates the rate at which calcium is absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Inhibits osteoblasts
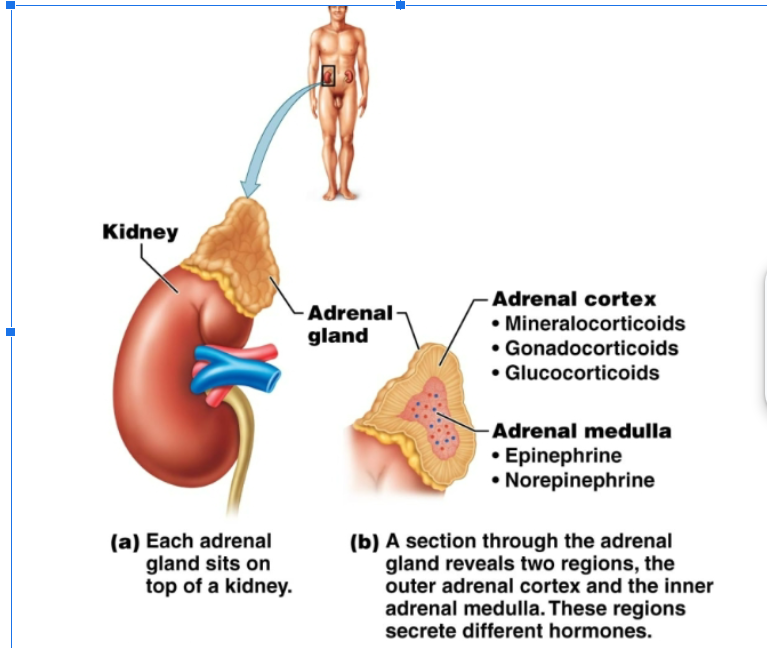
adrenal gland
Located at the top of the kidneys. The adrenal cortex (outer region) secretes gonadorcoricoids, glucocorticoids, and mineralocorticoids. Adrenal medulla (inner region): secretes epinephrine (adrenaline), norepinephrine (noradrenaline)
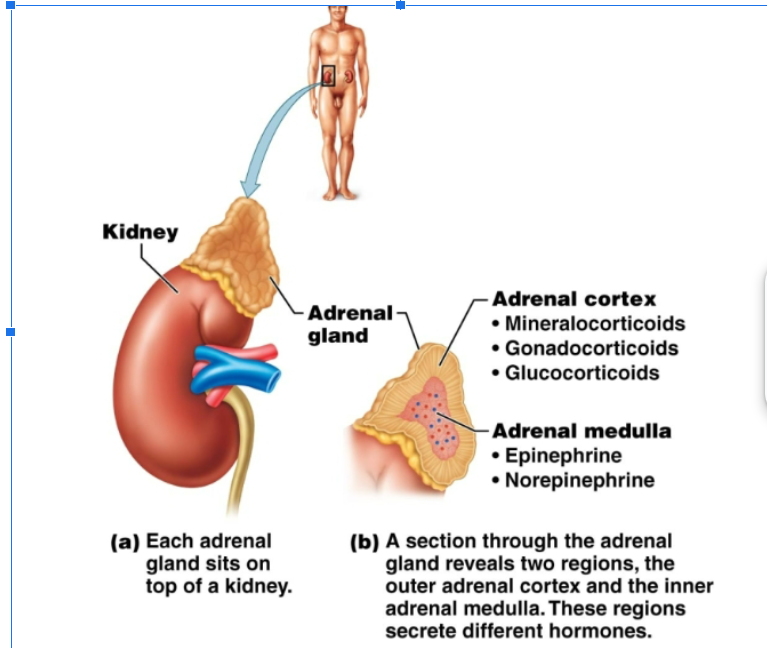
gonadocorticoids
Androgens and estrogens secreted by the adrenal cortex in both males and females.
mineralcorticoid
Mineral homeostasis and water balance
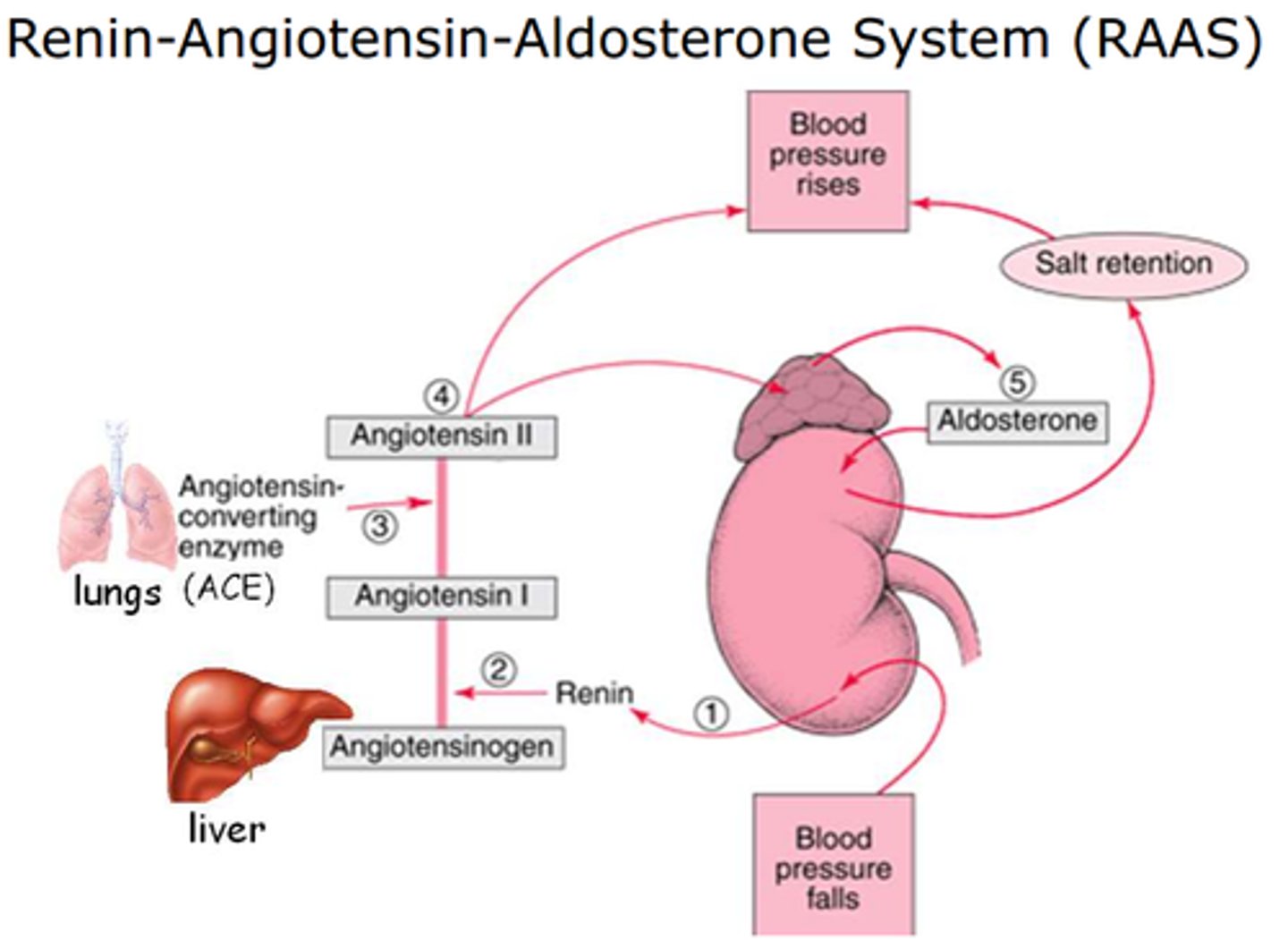
aldosterone
Acts on cells of kidneys to increase reabsorption of sodium ions into the blood, promote excretion of potassium ions in the urine
glucocorticoid
Acts on cells of kidneys to increase reabsorption of sodium ions into the blood, promote excretion of potassium ions in the urine
adrenal medulla
Produces epinephrine (adrenaline) and norepinephrine (noradrenaline). Both of these are used in our fight and flight response to danger
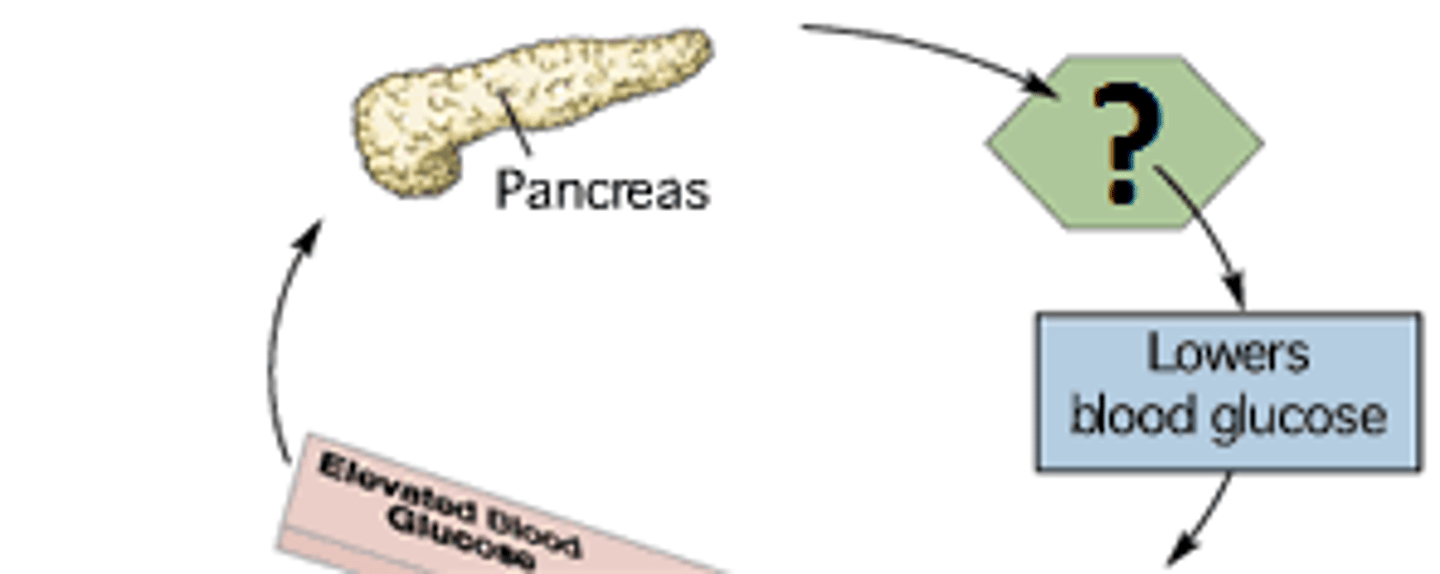
pancreas
Located behind the stomach. Endocrine cells occur in —— islets. Produces glucagon and insulin hormones.
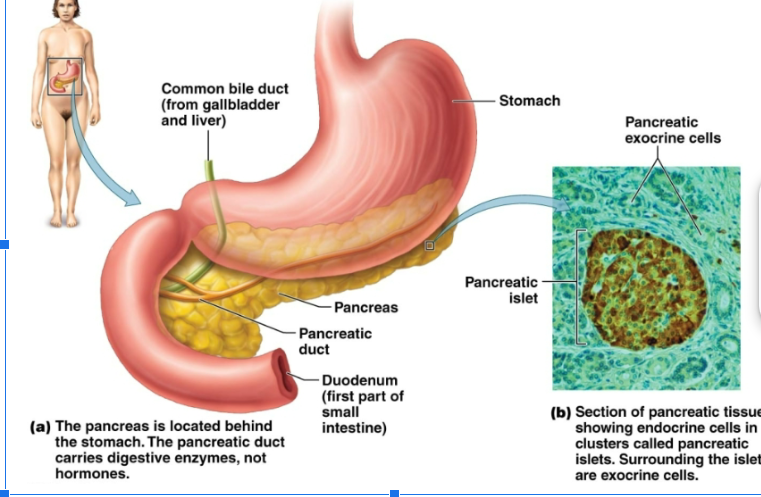
glucagen
Increase glucose in blood. Prompts liver to convert glycogen to glucose and to form glucose from lactic acid and amino acids
insulin
Decrease glucose in blood. Stimulates transport of glucose into muscle cells, white blood cells, and connective tissue cells. Inhibits the breakdown of glycogen to glucose. Prevents the conversion of amino acids and fatty acids to glucose
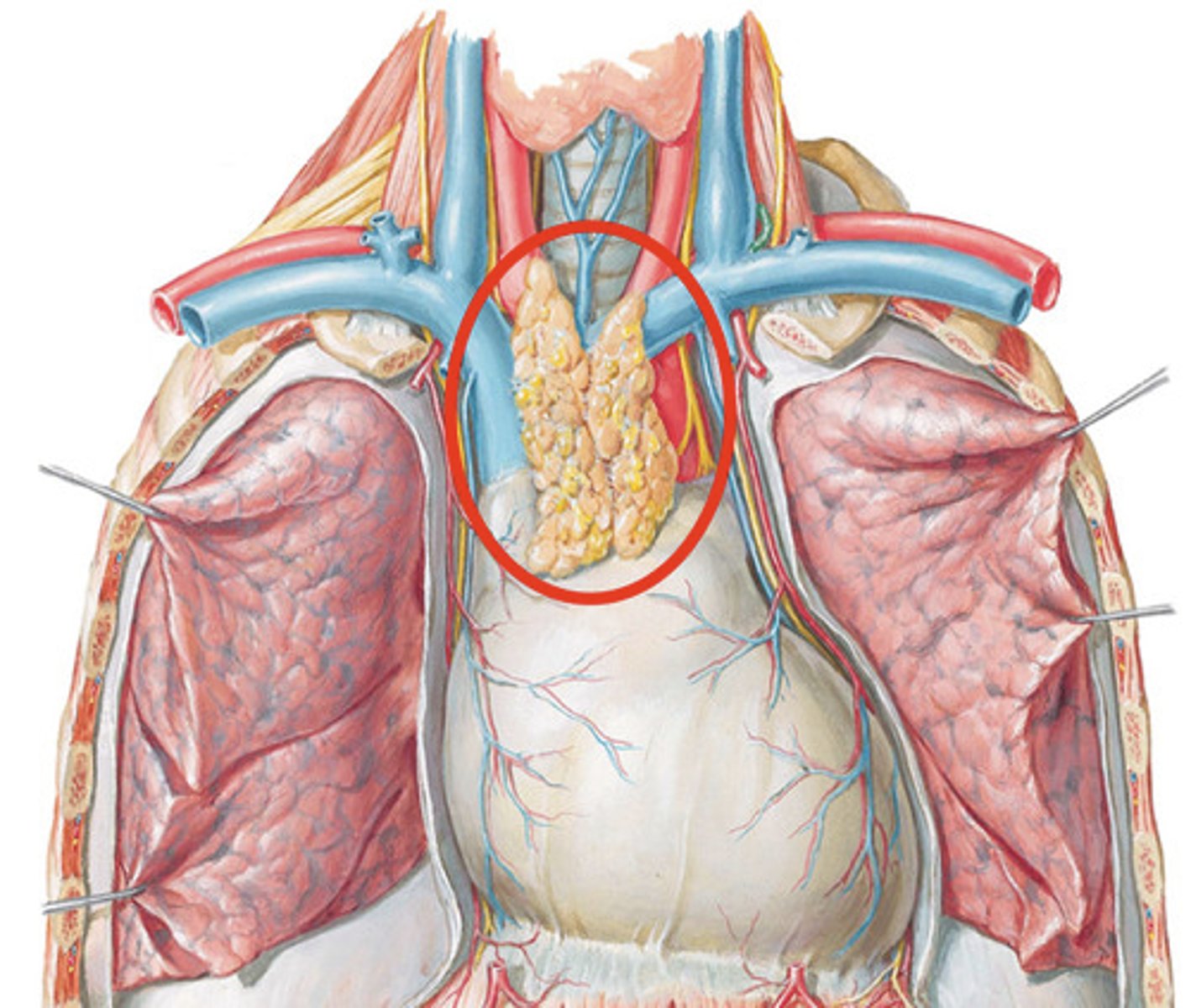
thymus gland
Lies on top of heart. Secretes hormones that promote the maturation of: T lymphocytes, Thymopoietin, Thymosin
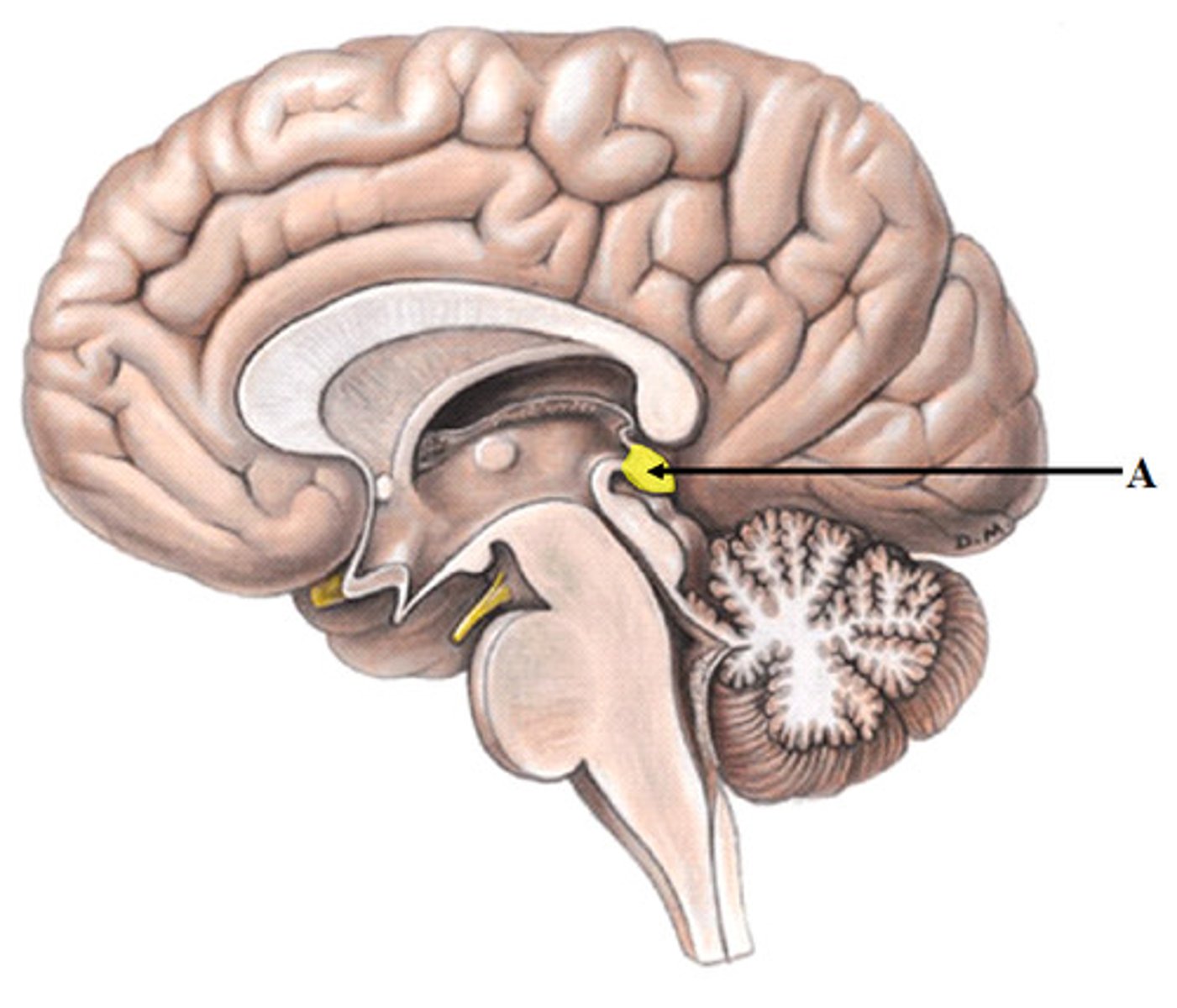
pineal gland
Located at the center of the brain. Produces melatonin. Levels of circulating melatonin are greater at night during daylight hours.Recieves input for visual pathways. Light inhibits secretion of melatonin. Promotes sleep, reduces jet lag, and may slow aging.
functions of blood
Transportation, protection, regulation of PH and body temp
plasma
Liquid that makes up 55% of blood. 93% water, 7% of dissolved substances such as ions, dissolved gases, hormones, plasma proteins, and water products. Formed elements: cellular components of blood - make up 45% of blood
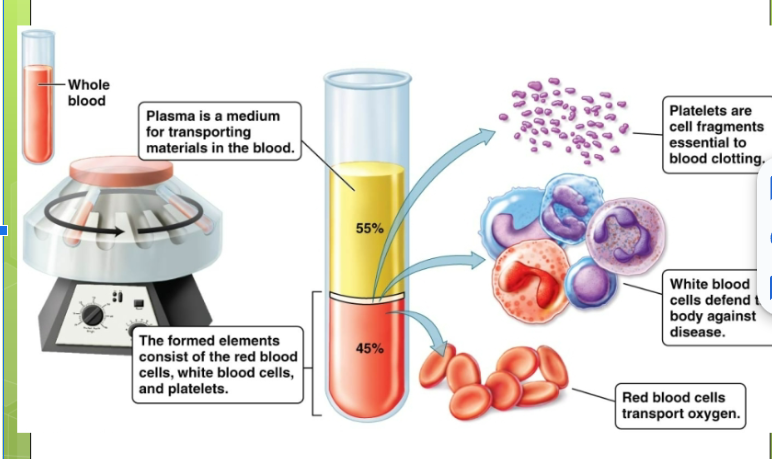
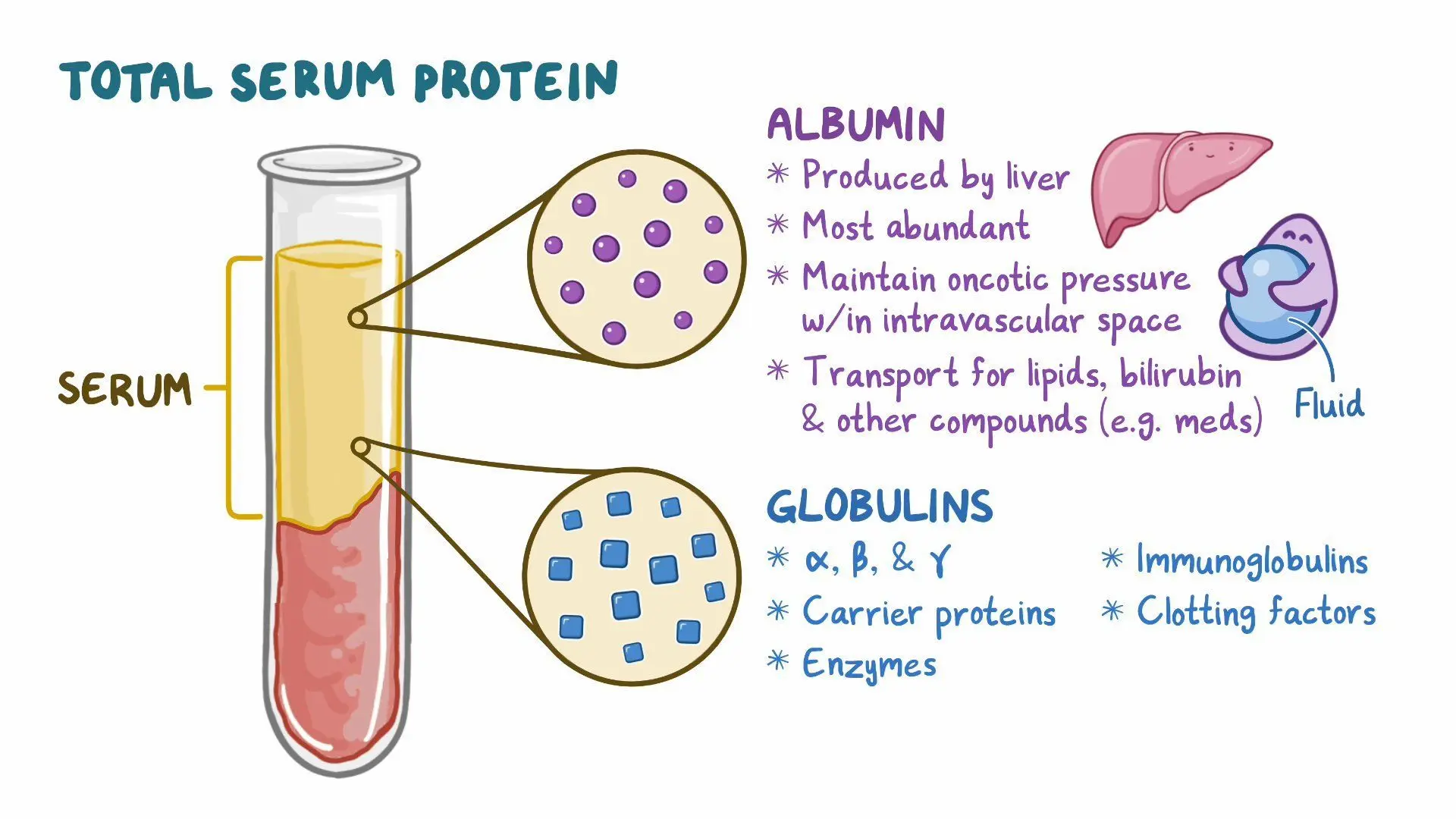
plasma protein
Helps balance water flow between blood and cells
albumins
Important for blood water balancing ability
globulins
To transport liquids and fat soluble vitamins, some are antibodies.
platelets
White and red blood cells. Sometimes called thrombocytes. Fragments of larger precursor cells called megakaryocytes. Essential to blood clotting.
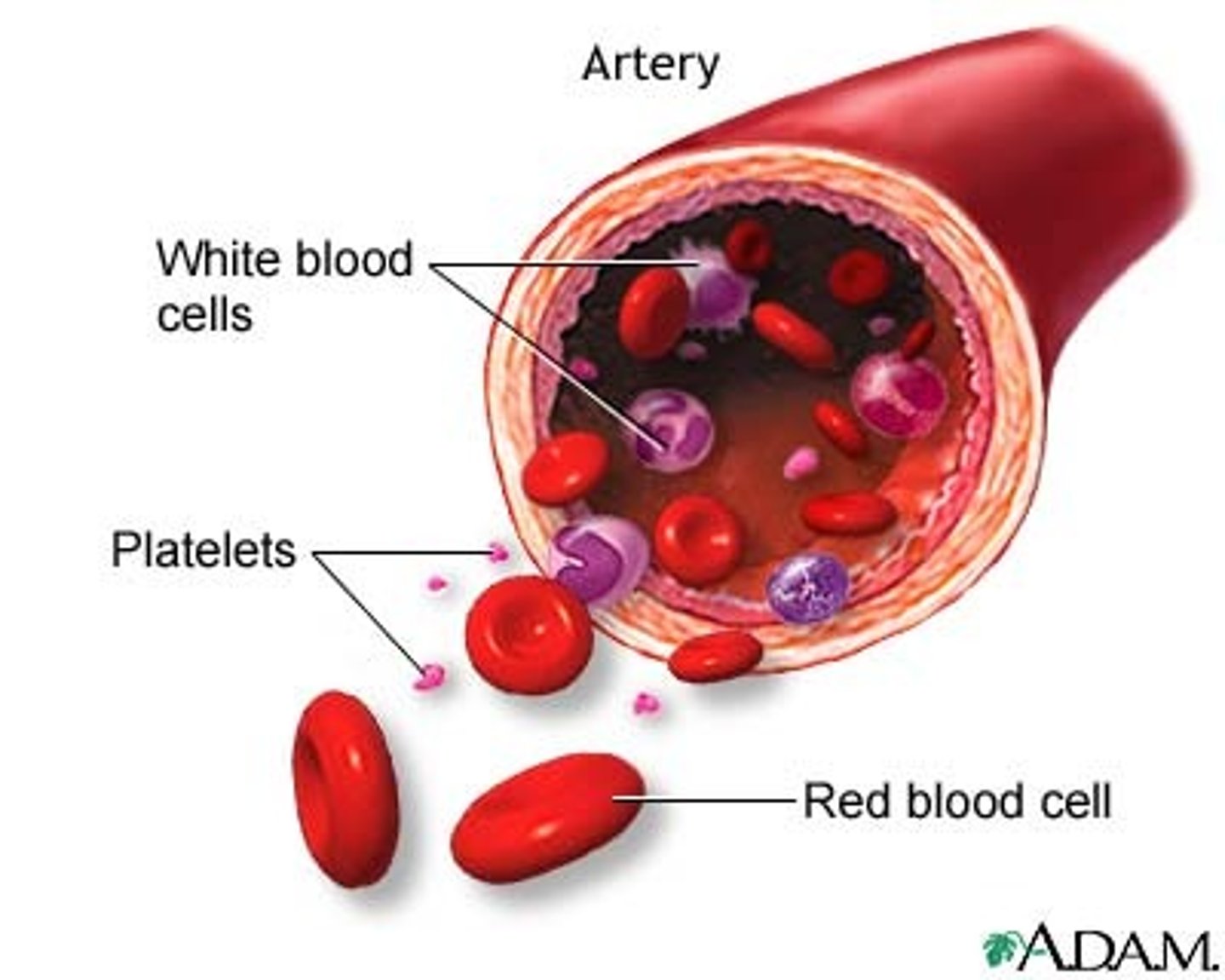
leukocytes
(White blood cells) have a nucleus. One type is produced in the lymph nodes and the other is lymphoid tissue
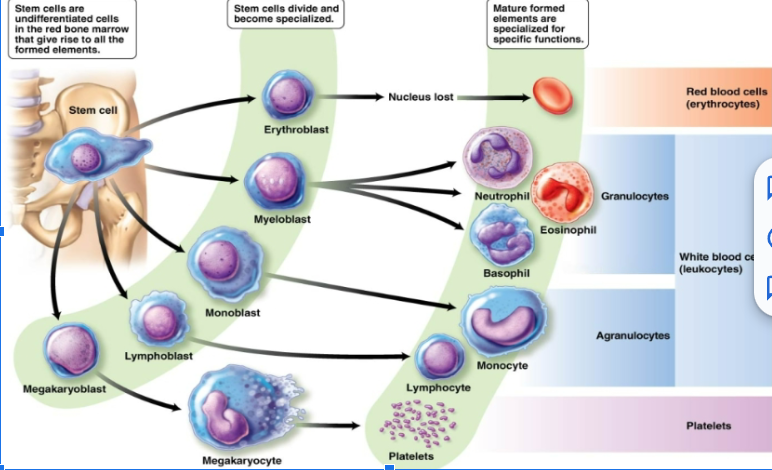
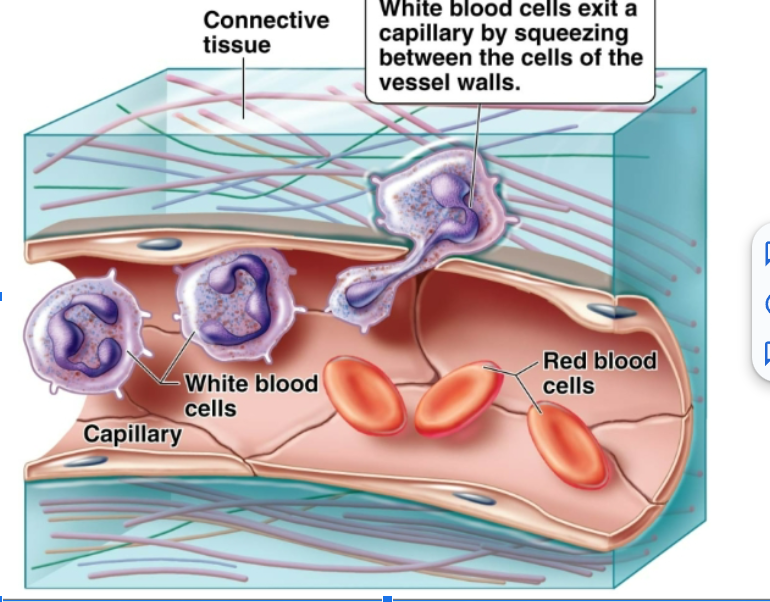
function of white blood cells
Remove waste, toxins, damaged and abnormal cells. Help defend the body against disease. Can leave the circulatory system and move to the site of infection or tissue damage. Some are capable of phagocytosis.
neutrophils
Do not stain. Most abundant of white blood cells. Engulf microbes through phagocytosis, to stop spread of infection. Component of pus: liquid associated with infection. (Dead neutrophil, bacteria, and cellular debris)
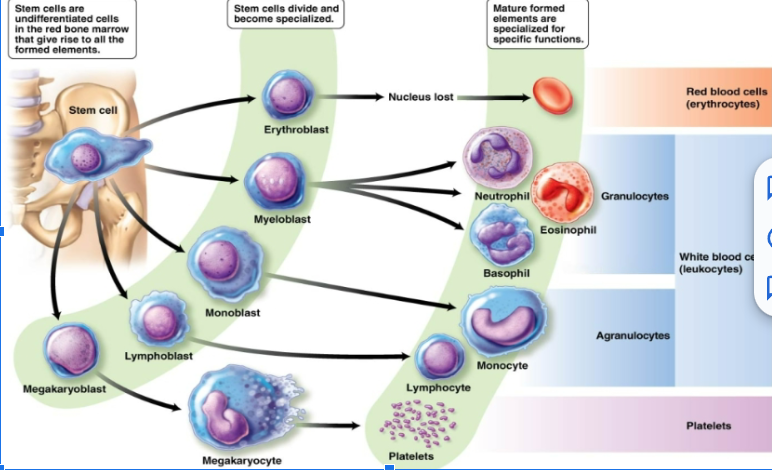
eosinophils
Defend against parasitic worms. Lessen the severity of allergies
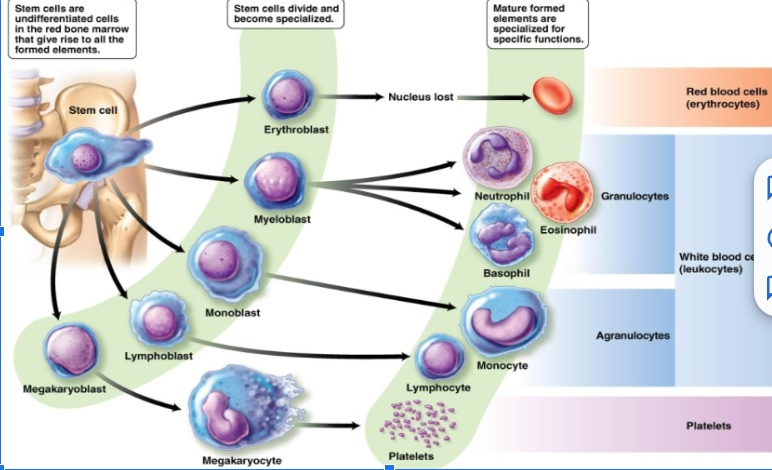
basophils
Release histamine that attracts other white blood cells and causes blood vessels to dilate. Also play a role in some allergic reactions
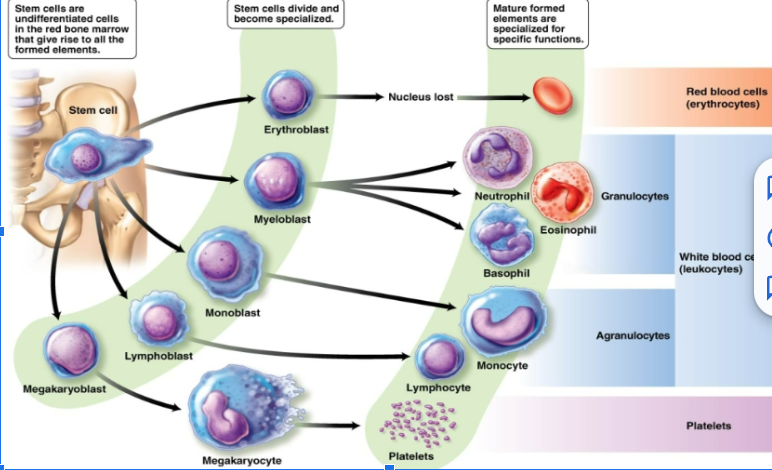
monocytes
Larges of formed elements. Develop into macrophages: phagocytic cells that engulf invading microbes, dead cells, and cellular debris
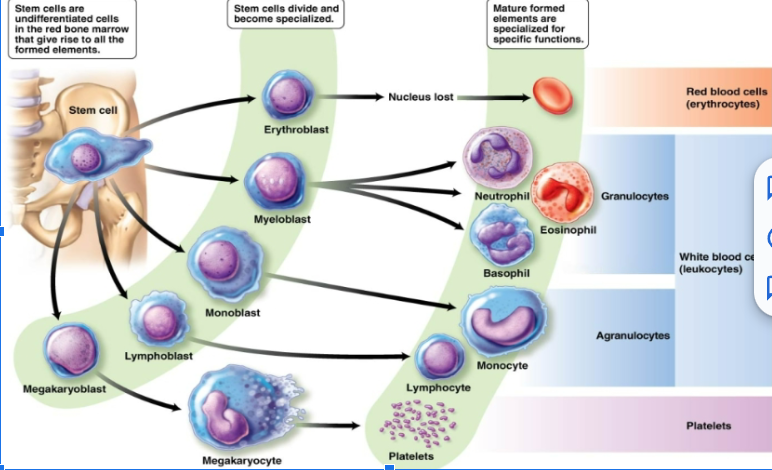
B lymphocytes
Give rise to plasma cells, which produce antibodies. Antibodies are proteins that recognize specific molecules (antigens) on the surface of invading microbes or other foreign cells.
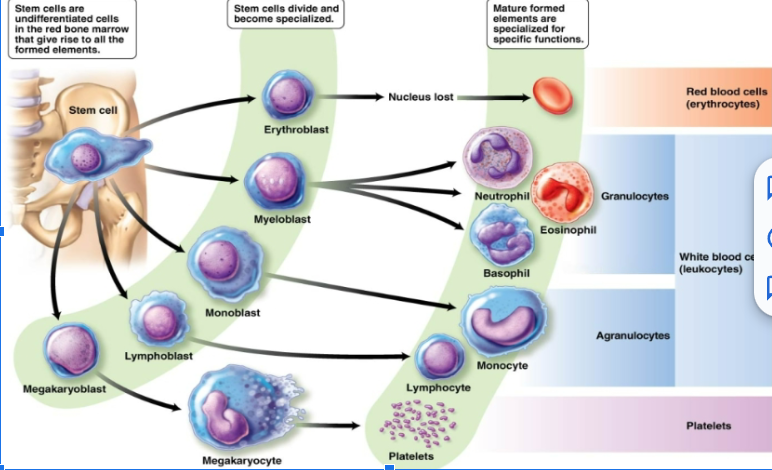
T lymphocytes
Specialized white blood cells. Kills cells not recognized as coming from the body, or cells that are cancerous
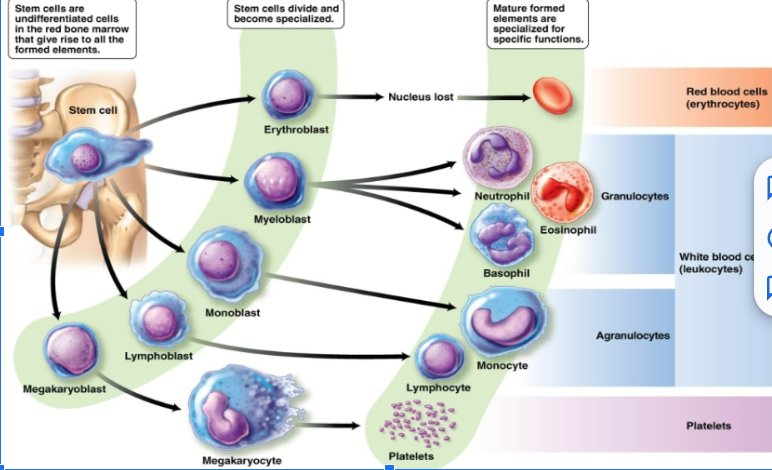
function of red blood cells
Erythrocytes that transport oxygen to cells. Carry about 25% of the blood's total carbon dioxide. Shaped like biconcave disks are very flexible. No nucleus when mature. Contains hemoglobin
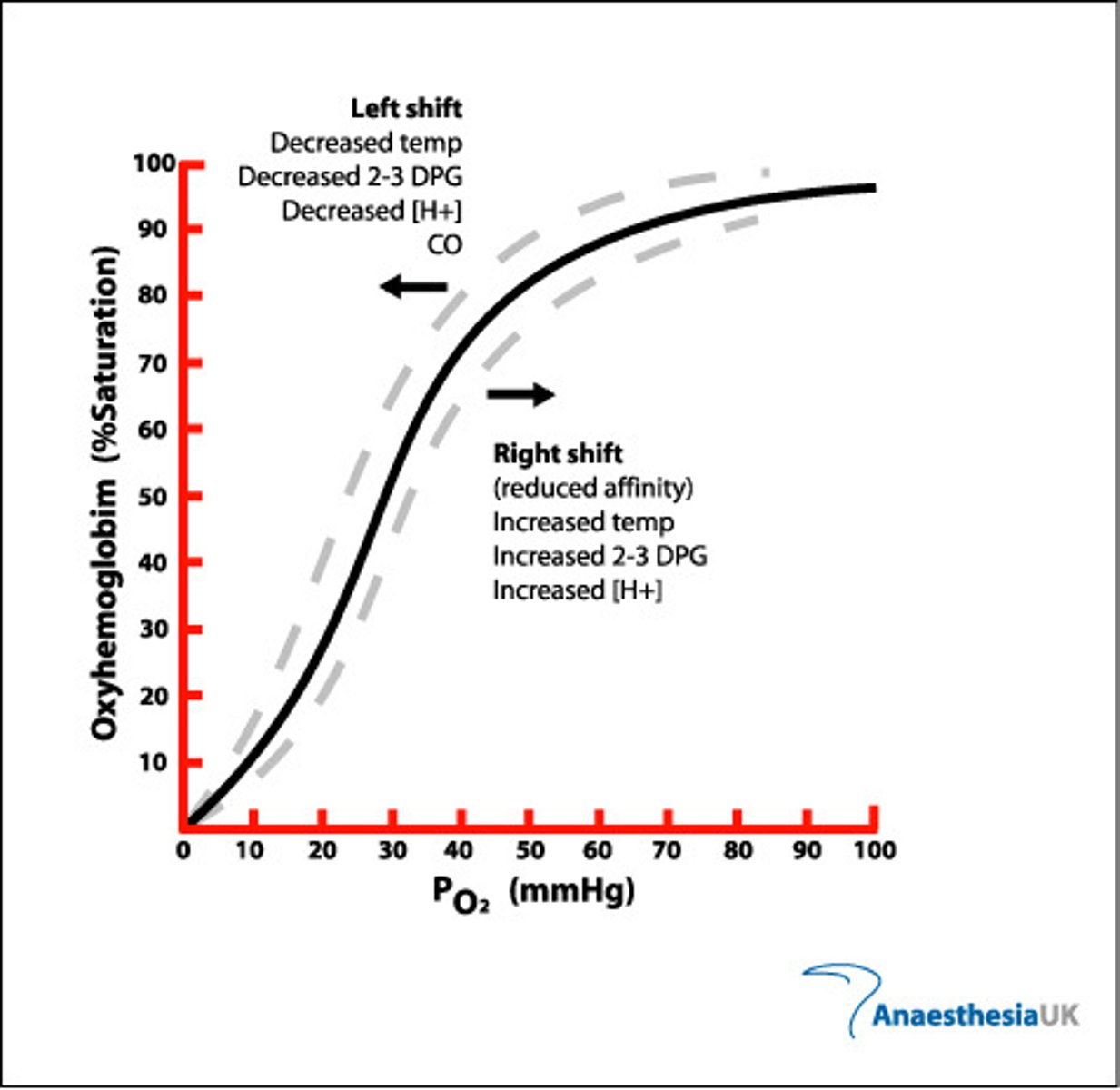
oxyhemoglobin
Hemoglobin bound with oxygen. Has a much greater affinity for carbon monoxide than for oxygen. Odorless and tasteless, an insidious poison
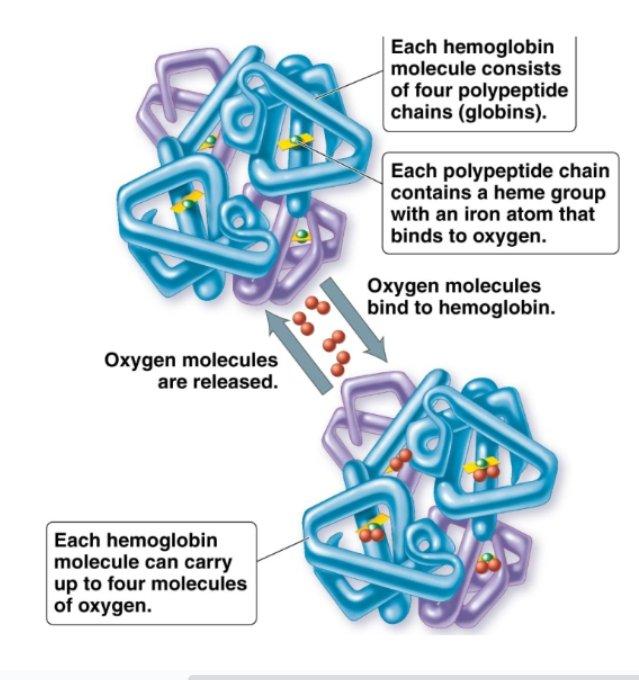
hemoglobin
Oxygen binding pigment in red blood cells. Each molecule has 4 subunits. Then each subunit has a polypeptide chain and a heme group. The iron ion of heme group binds to oxygen
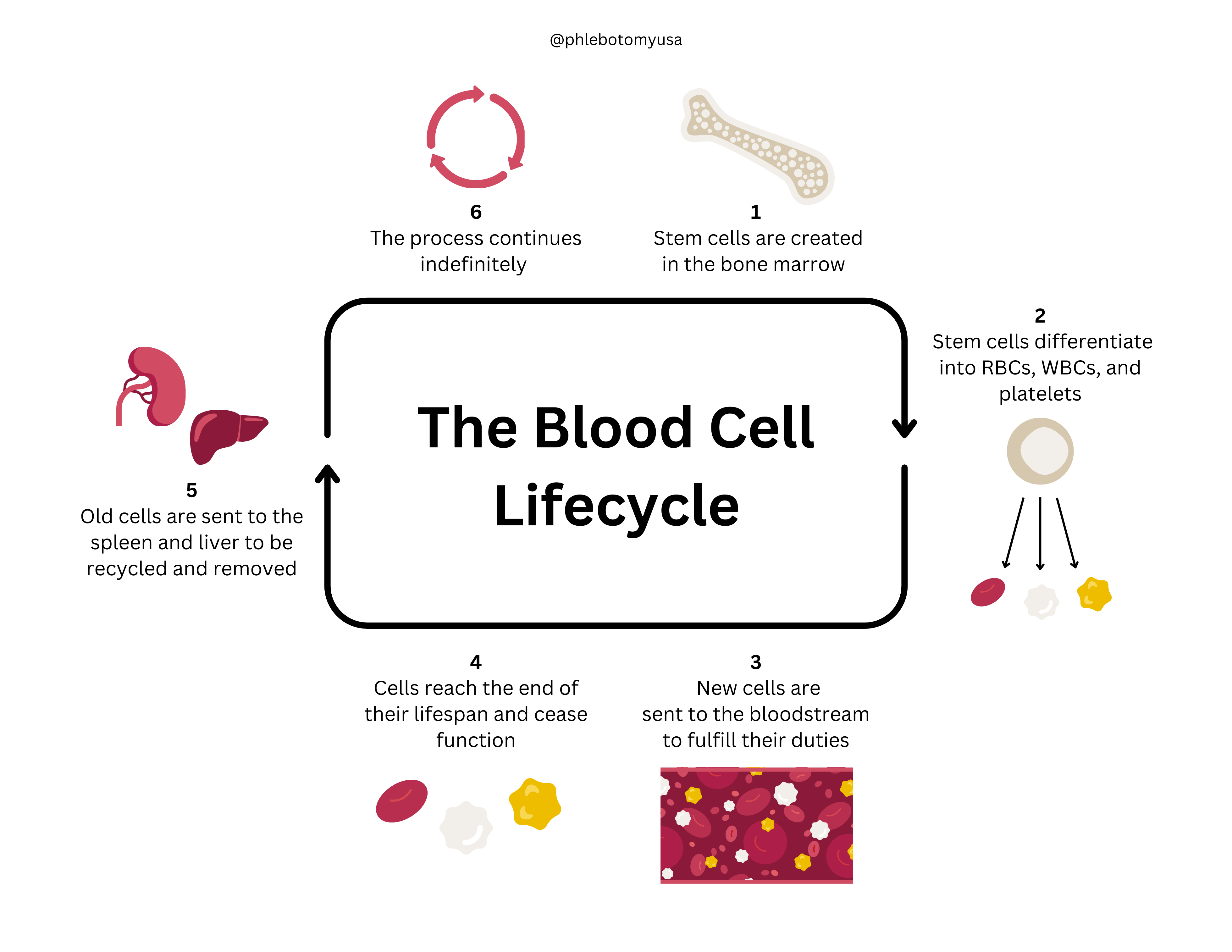
lifecycle of red blood cells
120 days. Produced in red bone marrow. Undergo phagocytosis in the liver and spleen. Hemoglobin is degraded into its protein component (globin) and heme component. The iron from the heme is sent to the bone marrow for recycling. The remaining portions of the heme are degraded to bilirubin, which the liver releases into bile.
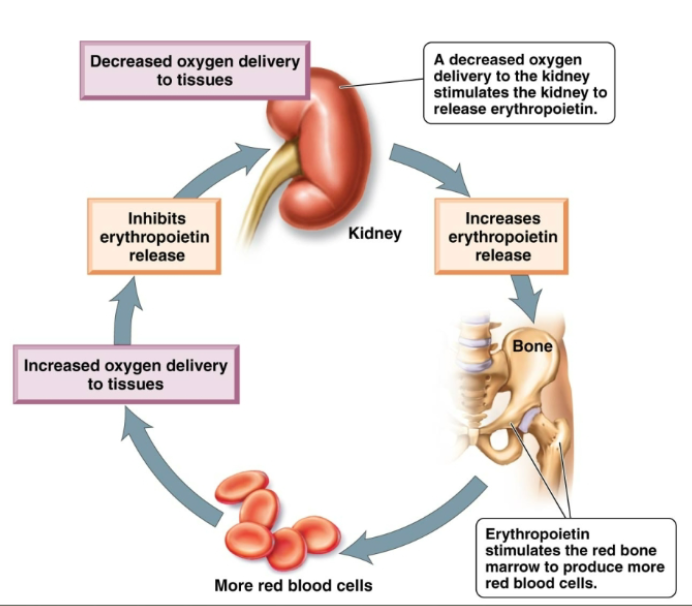
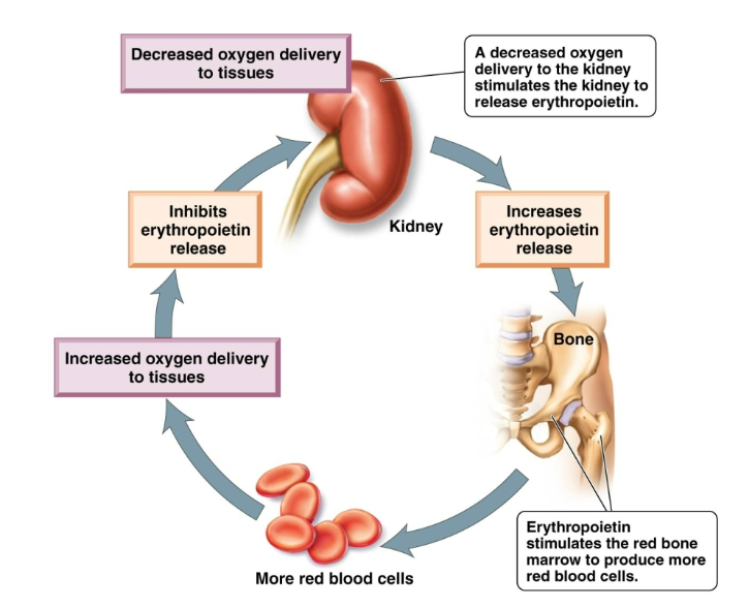
how are red blood cells produced
Regulated by negative feedback mechanism: production matches destruction. In case of blood loss, the rate of RBC is increased. Kidney cells sense reduced oxygen and produce the hormone erythropoietin. Erythropoietin stimulates the red bone marrow to produce more RBCs. The increased oxygen-carrying capacity of the blood inhibits production of erythropoietin.
anemia
The blood's ability to carry oxygen is reduced. Can result from too little hemoglobin, too little red blood cells, or both. Fatigue, headache, dizziness, paleness, breathlessness, and heart palpitations. Iron deficiency, hemolytic, sickle cell and pernicious
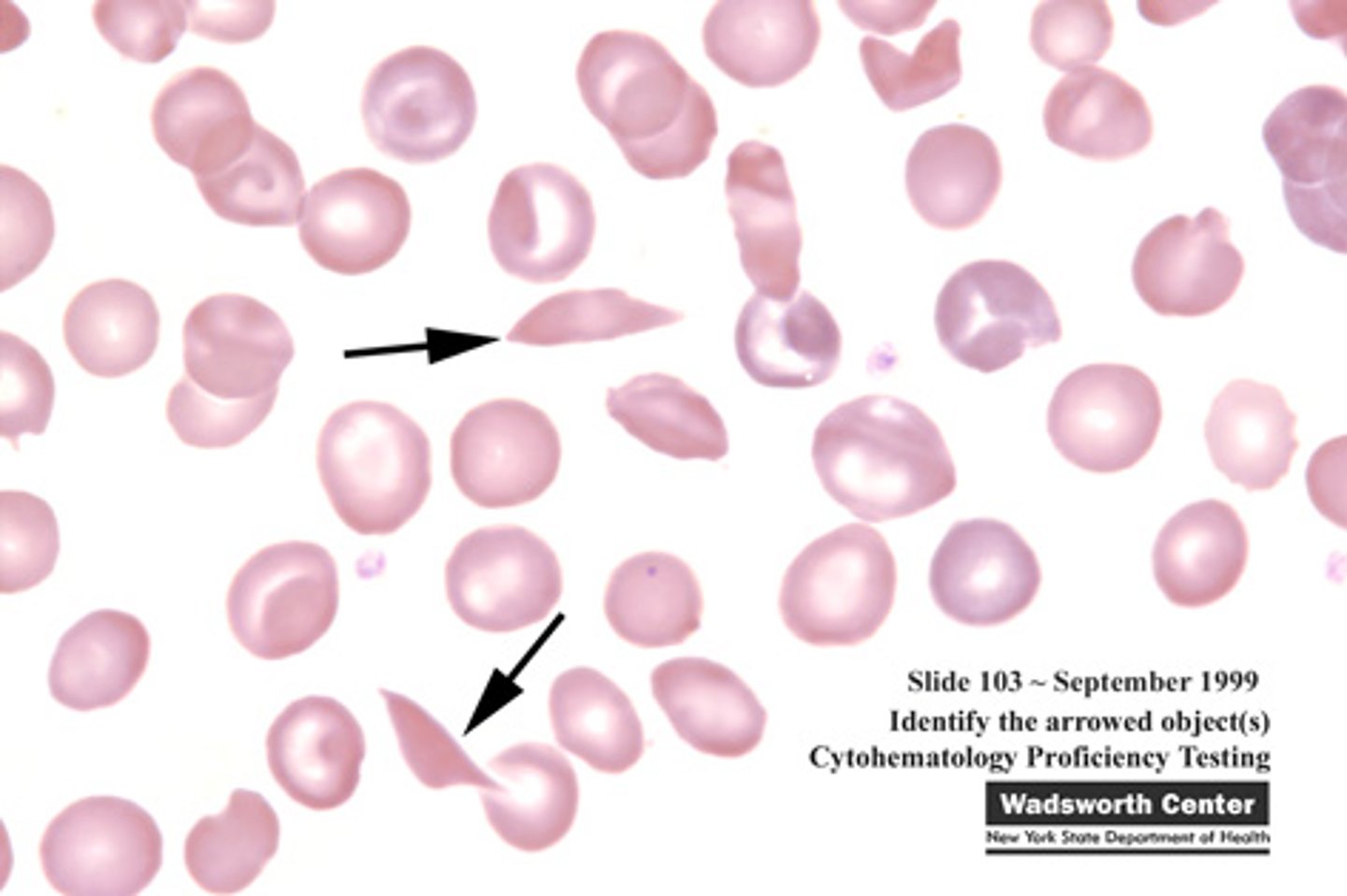
blood types
Type A only has A antigen. Type B only has B antigen. Type AB has both A and B antigens. Type O has neither A or B antigens (Universal donor)
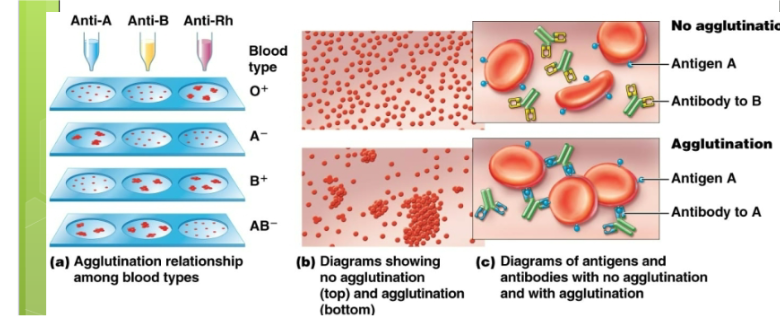
Rh factor
First discovered on the resus monkey. Another important antigen. Individuals who lack these antigens are RH negative, individuals who have those on their RBCS are RH positive. RH negative people will not form Anti RH antibodies unless exposed through transfusion or given birth to RH positive babies. Also hemolytic disease of newborns.
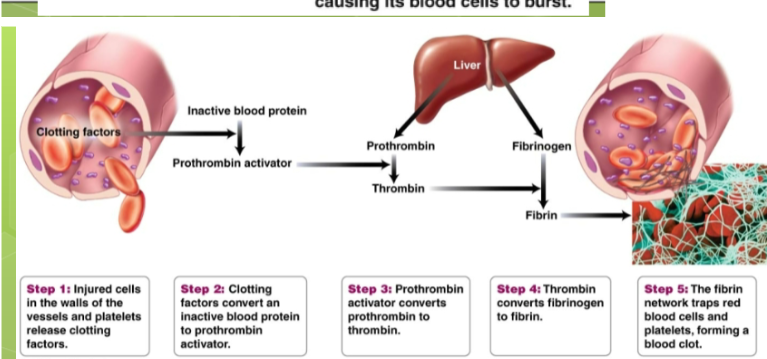
Steps of blood clotting
Acuteness occurs. The vessel constricts. Platelets form a plug that seals the leak. Platelets cling to collagen and produce a chemical that attracts more platelets. Aspirin prevents the formation of this and thereby inhibits clot formation.
cardiovascular system
Blood vessels and heart. Distributes blood, delivers nutrients, and removes waste
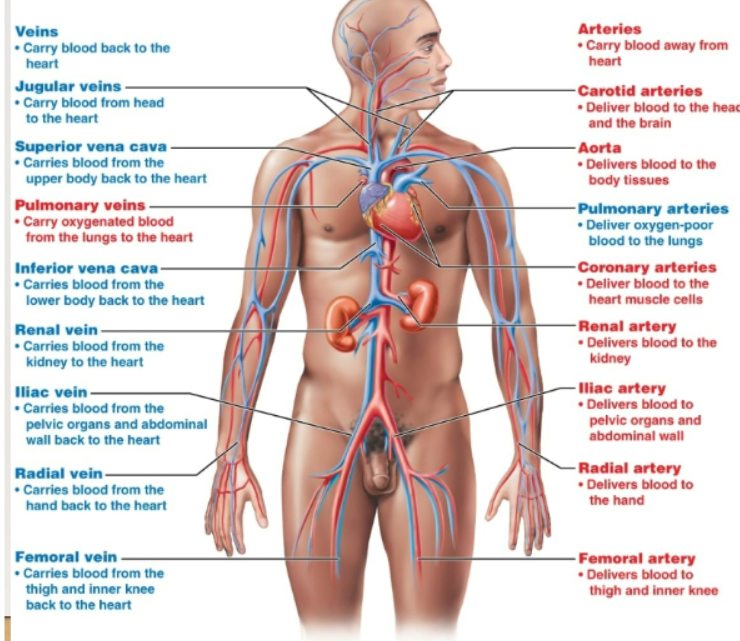
Arteries, arterioles, capillaries, venules, veins
How does blood travel through the body?
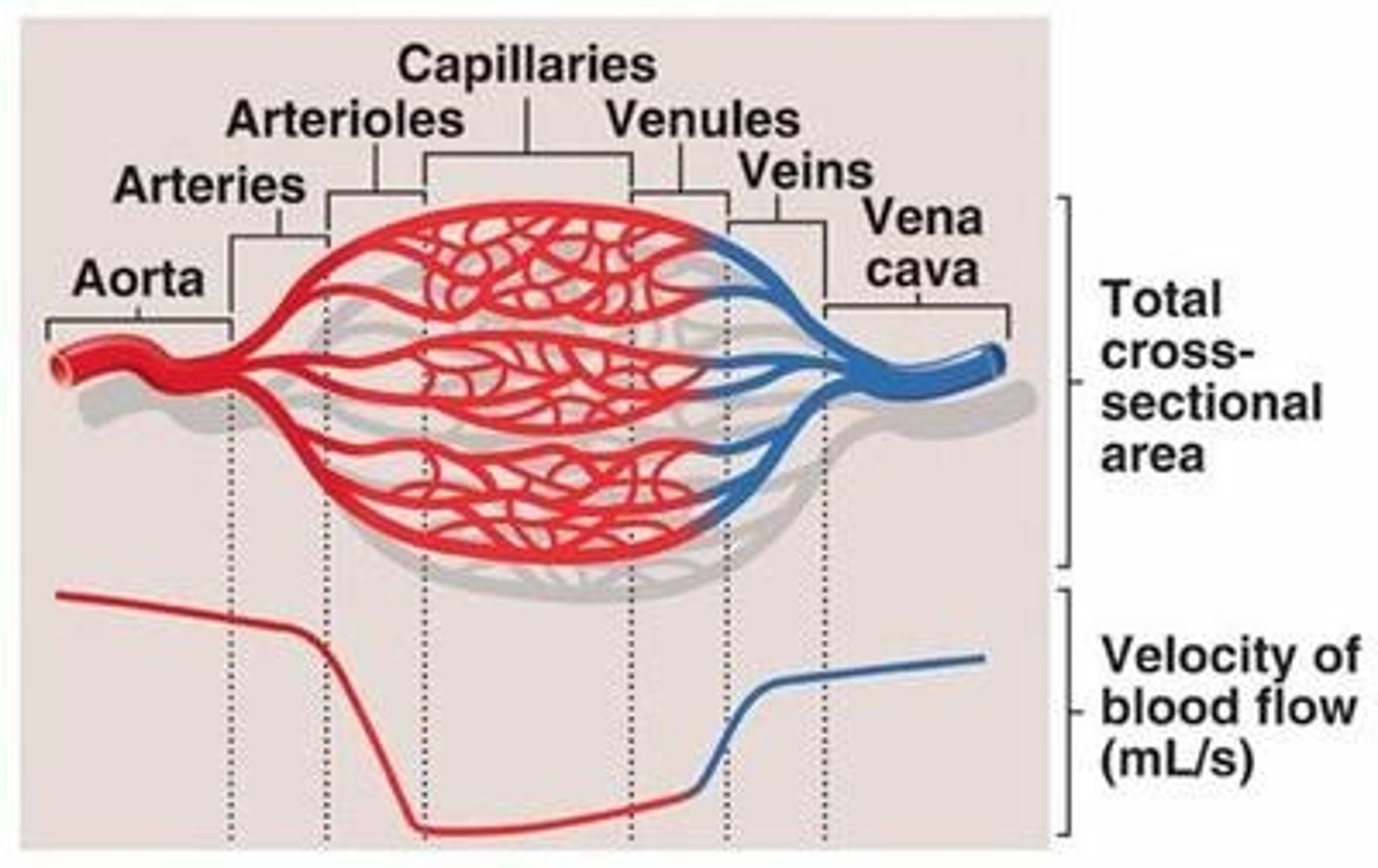
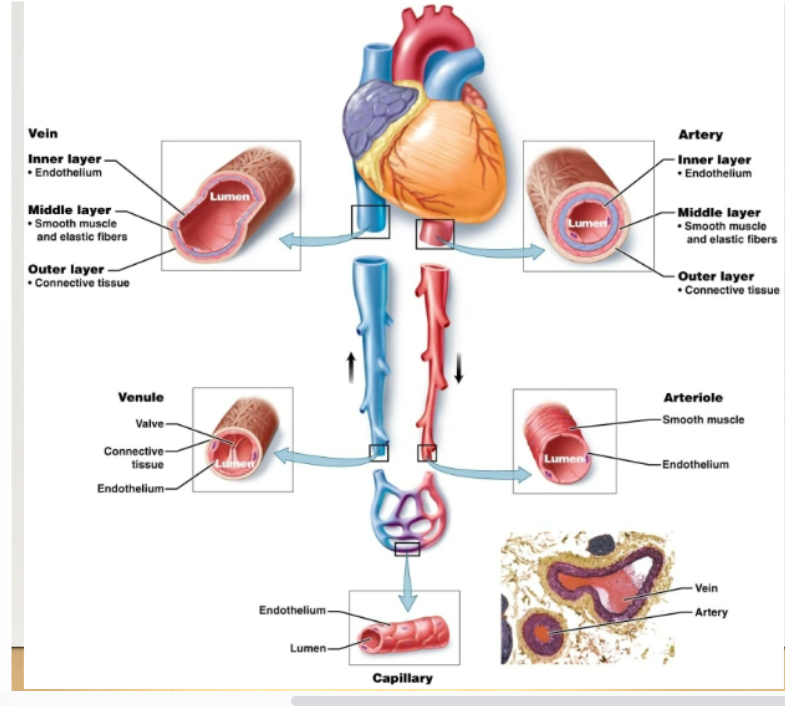
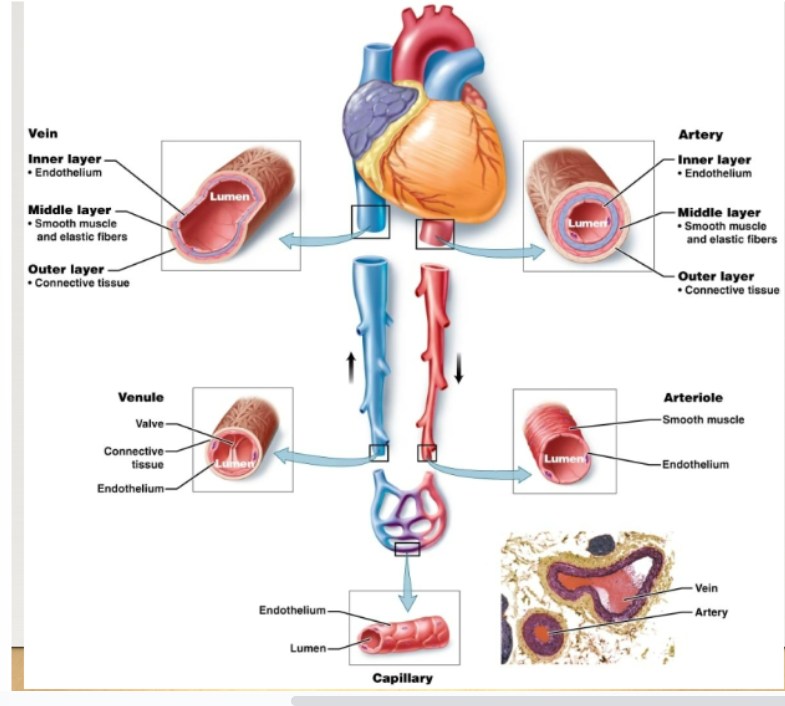
blood vessels
Lumen: hollow interior which blood flowsEndothelium: inner layer lining consisting of simple squamous epitheliumEach type of blood vessel has traits that reflect its particular function
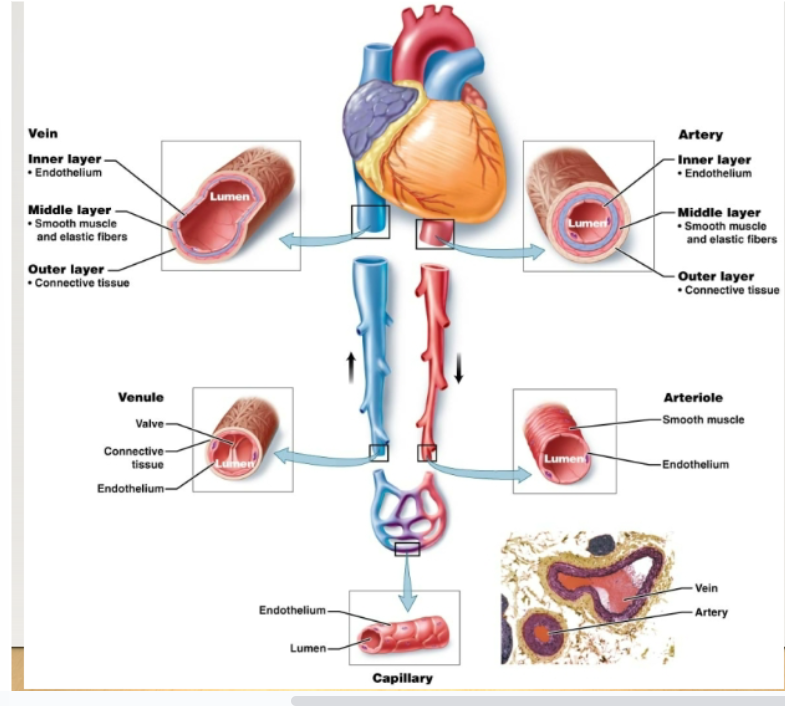
arteries
Thick, muscular vessels that carry blood away from the heart to body tissues
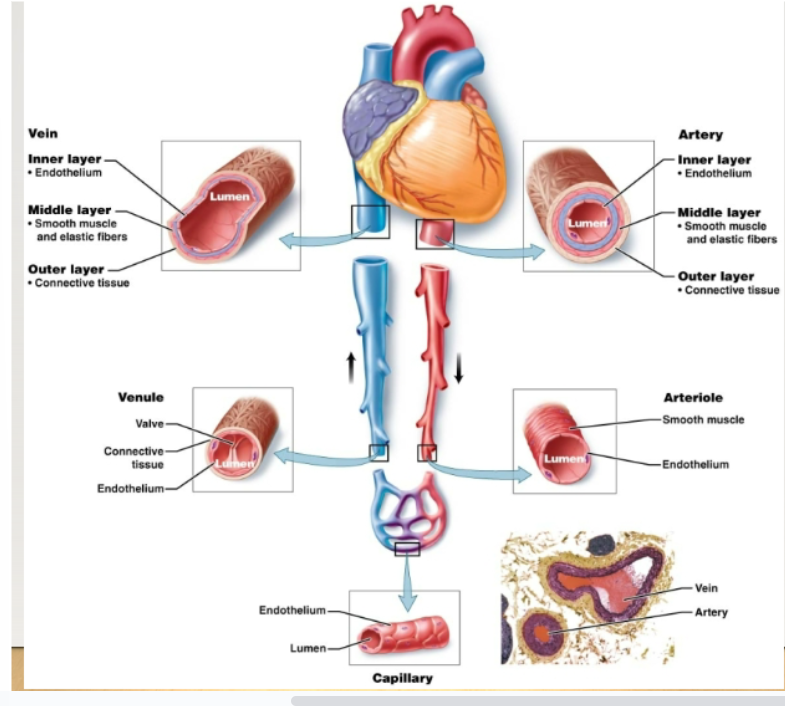
artery layers
Inner: endothelium Middle: elastic fibers- allow the artery to stretch and return to log shape Smooth muscle- allows the artery to contract Outer: connective tissue
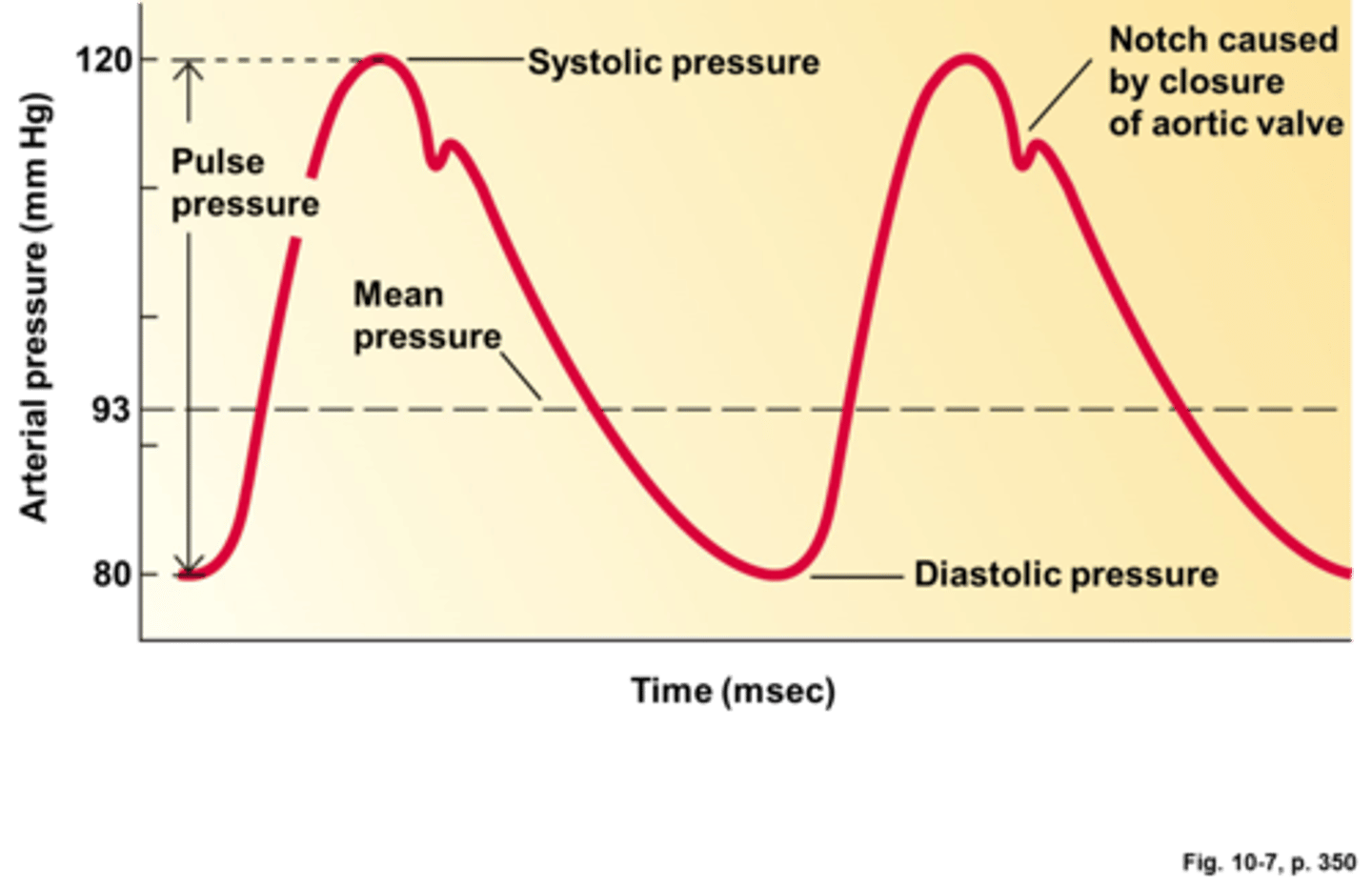
Pulse
Pressure wave created by the alternate expansion and contraction of the arteries. Moves along the arteries with each heart beat. …. rate is the same as heart rate
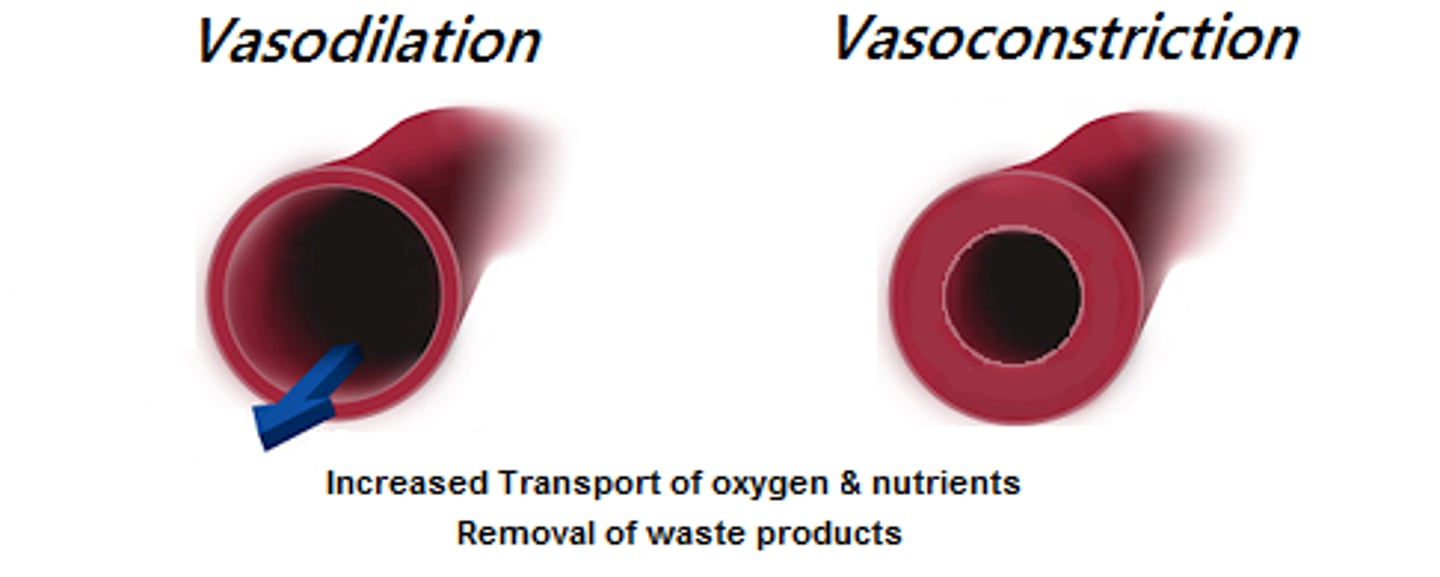
vasoconstriction
Smooth muscle of the middle layer contracts and the diameter of the lumen narrows, reducing blood flow
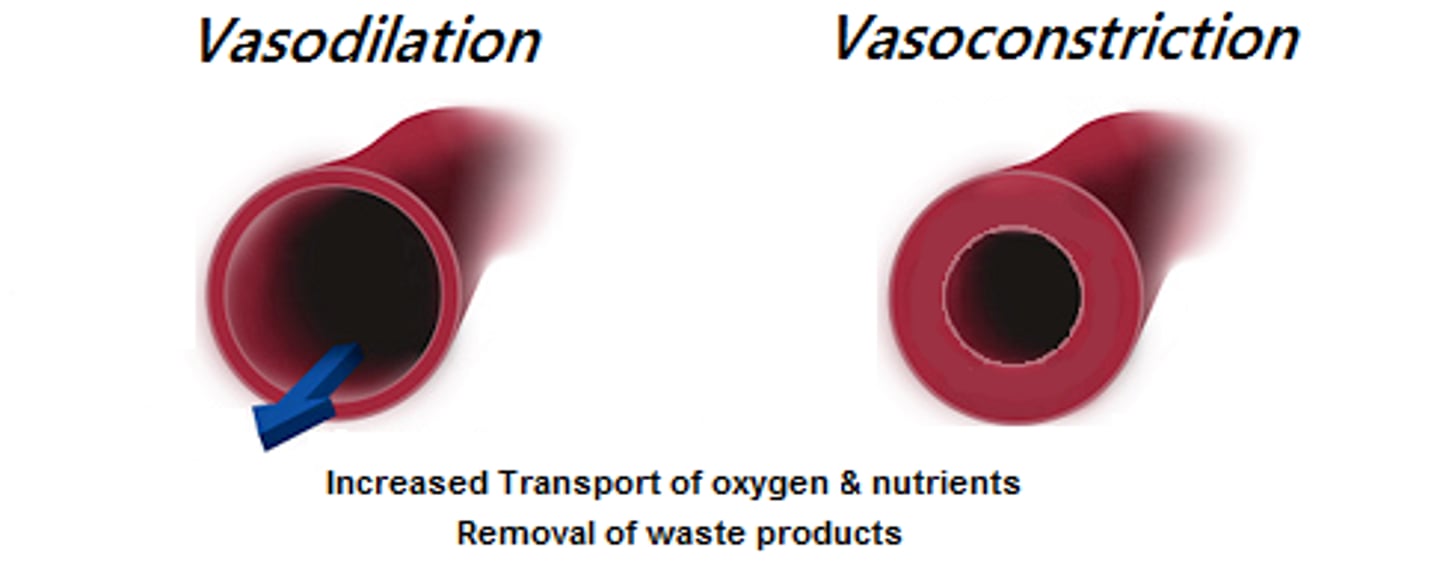
vasodilation
Smooth muscle of the middle layer relaxes and the diameter of lumen increase, increasing blood flow
arterioles
Smallest arteries. Prime controllers of blood pressure (pressure of blood against vessel walls). Serve as gatekeepers to the capillary networks, keeping them open or closed
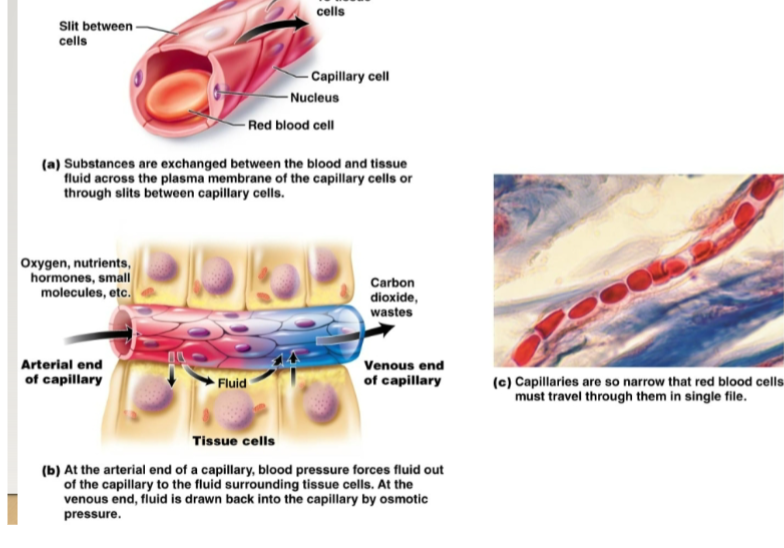
capillaries
Microscopic blood vessels containing arterioles and venules. Site of exchange of materials between blood and body cells.-Walls are one cell thick -Enormous surface area for exchange, exchange occurs through endothelial cells (Across plasma membrane) or through slits between cells. -Blood flows very slowly, allowing more time for exchange of materials. Capillary bed is a network of capillaries serving a particular area. Precapillary sphincter regulates blood flow into it
veins
Carry blood back to heart. Walls have the same three layers as arteries, but are thinner. Also have large lumens. Serve as reservoirs for blood volume. Three mechanisms to move blood against gravity from lower parts of body back to heart: contraction of skeletal muscles, pressure differences caused by breathing, valves in veins
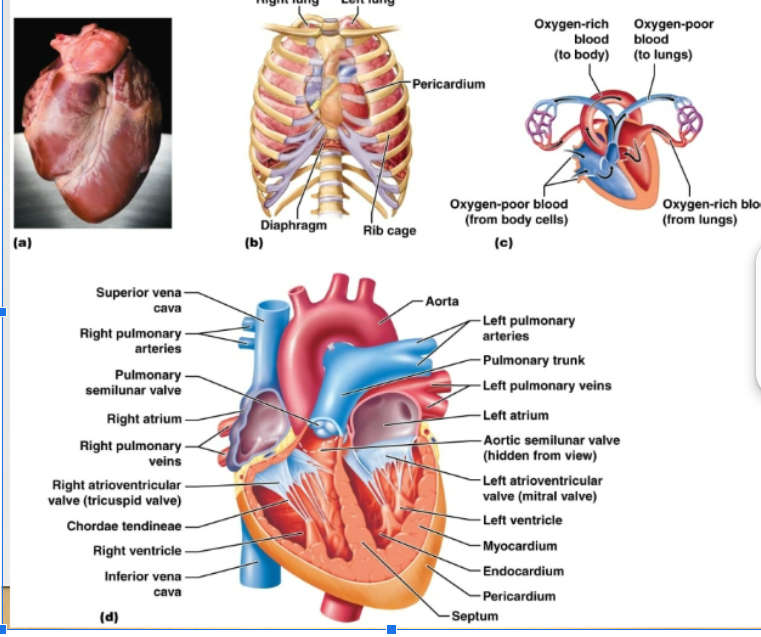
Myocardium, Endocardium, Pericardium
Three layers of heart:
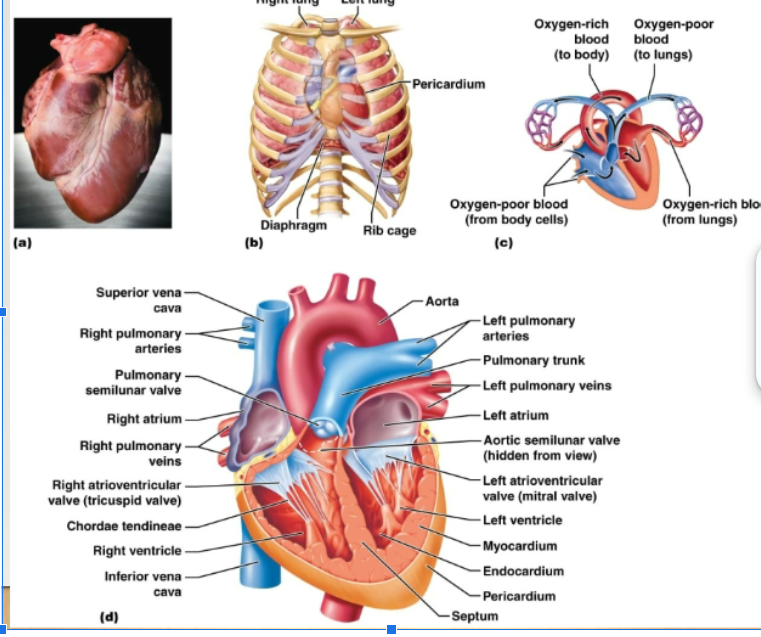
myocardium
Wall of heart, mostly cardiac muscle tissue
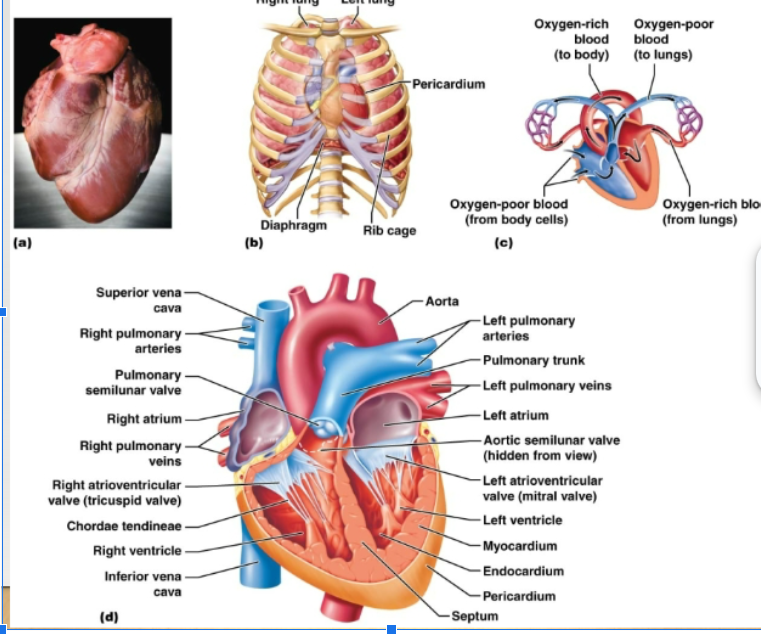
endocardium
Thin lining of the cavities of the heart. Reduces resistance to blood flow through the heart
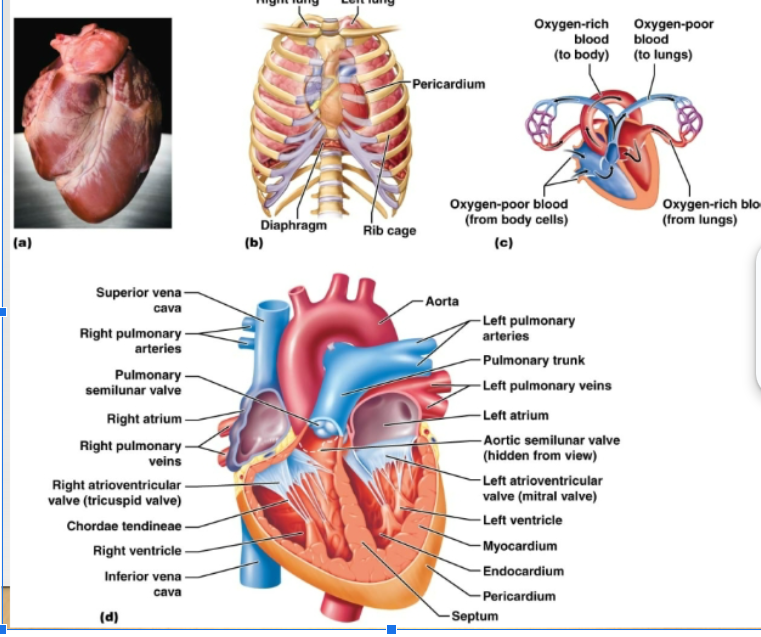
pericardium
Thick fibrous sac that holds the heart
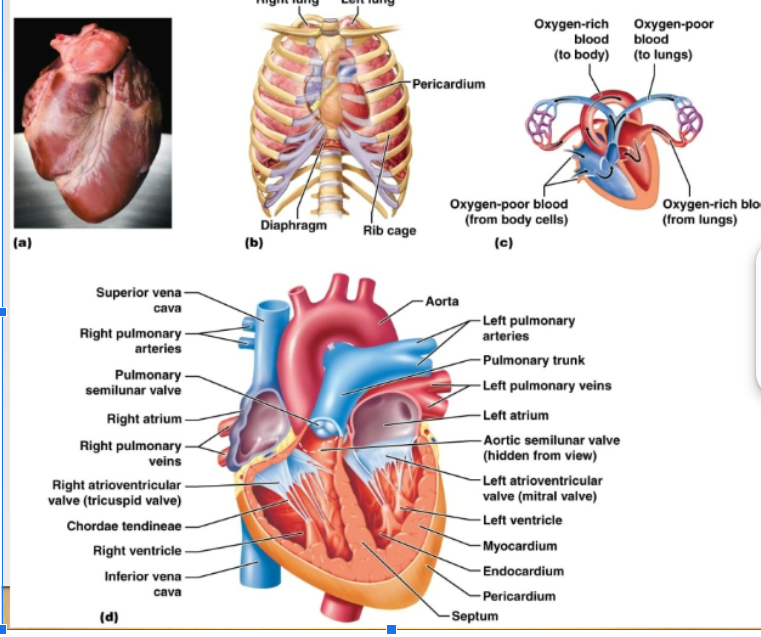
atrioventricular valves
Valves, separate the atria from the ventricles
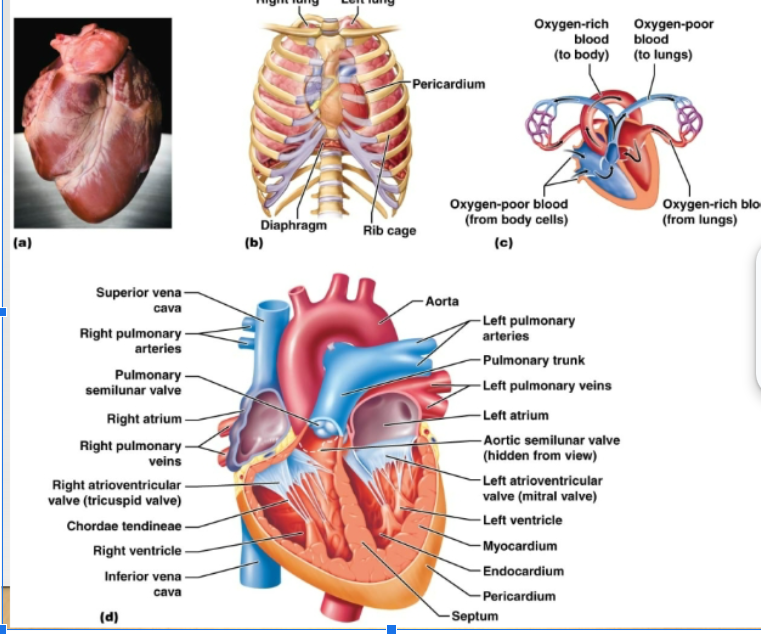
semilunar valves
Separate the ventricles from the exit vessels. Prevent backflow of blood into ventricles. Aortic semilunar valve: between L ventricle and aorta Pulmonary semilunar valve: between the R ventricle and pulmonary artery
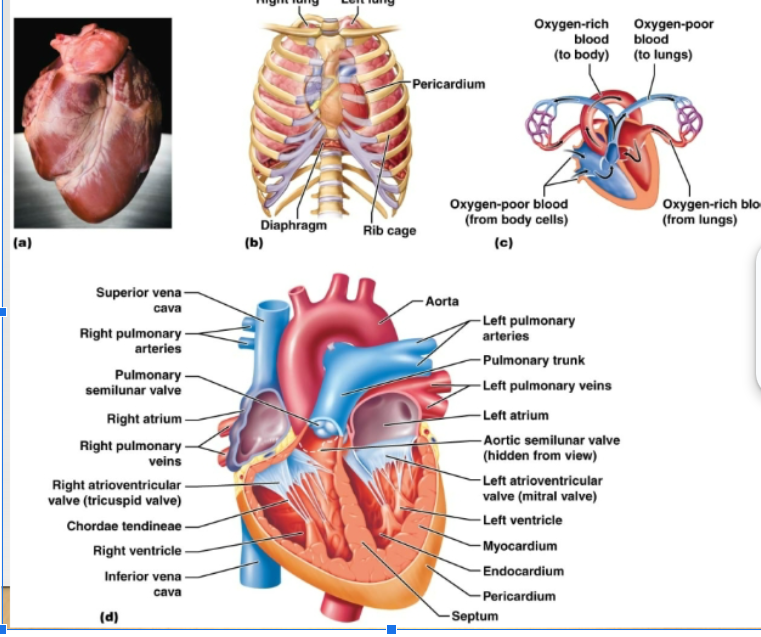
tricuspid valve
On the right side of the heart, has 3 flaps
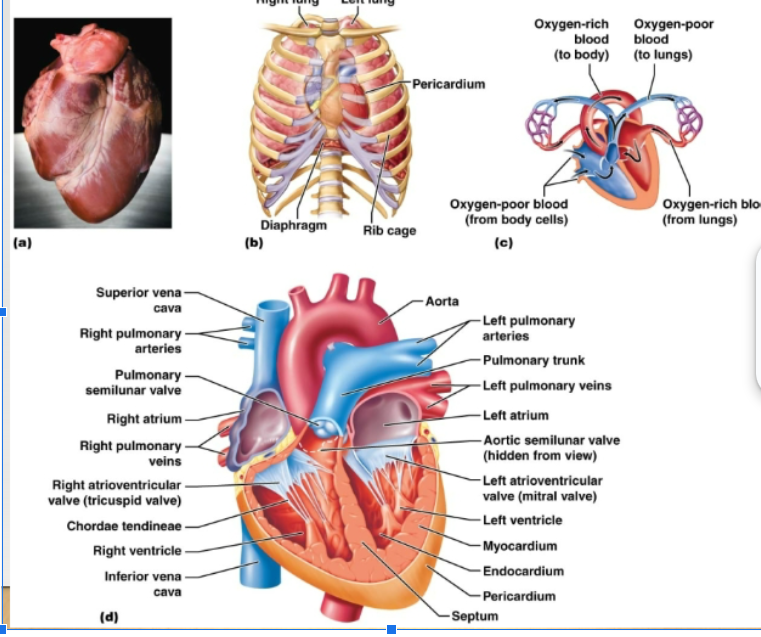
bicuspid valve
Left side of the heat, has 2 flaps
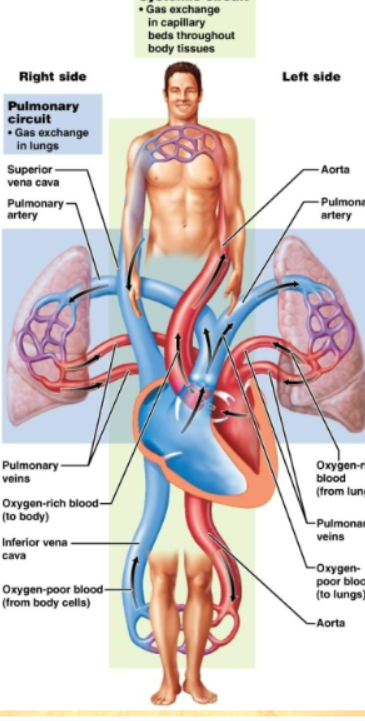
how does the blood flow through the heart?
Right side of heart: contains blood low in oxygen, pumps blood thru pulmonary circuit, transports blood to and from the lungs Left side of heart: contains blood rich in oxygen, pumps blood thru systemic circuit, blood to and from body tissues
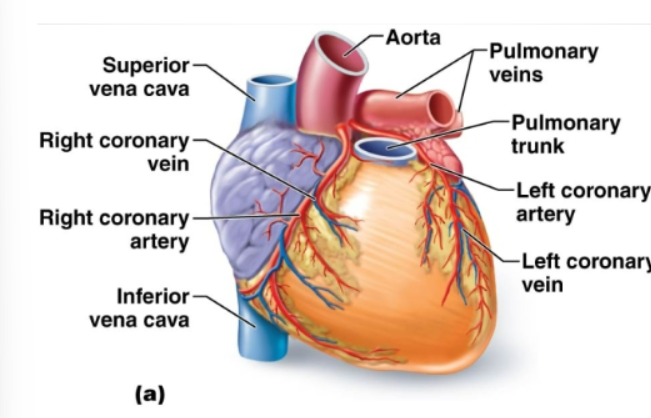
Coronary arteries
The first 2 arteries that branch off the aorta and branch extensively. Bring oxygen and nutrients to heart muscles
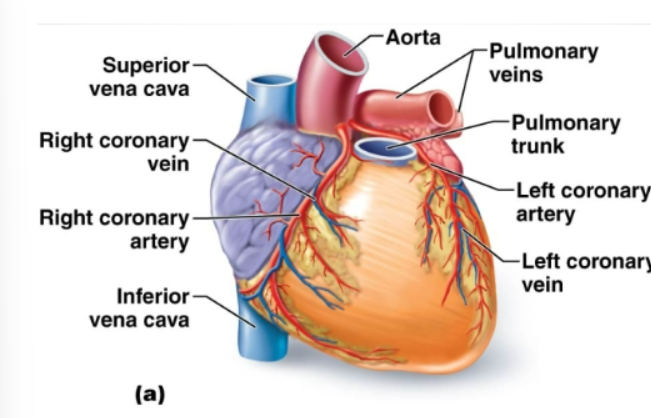
Coronary veins
Blood passes thru capillary beds, enter ….., and flows into right atrium
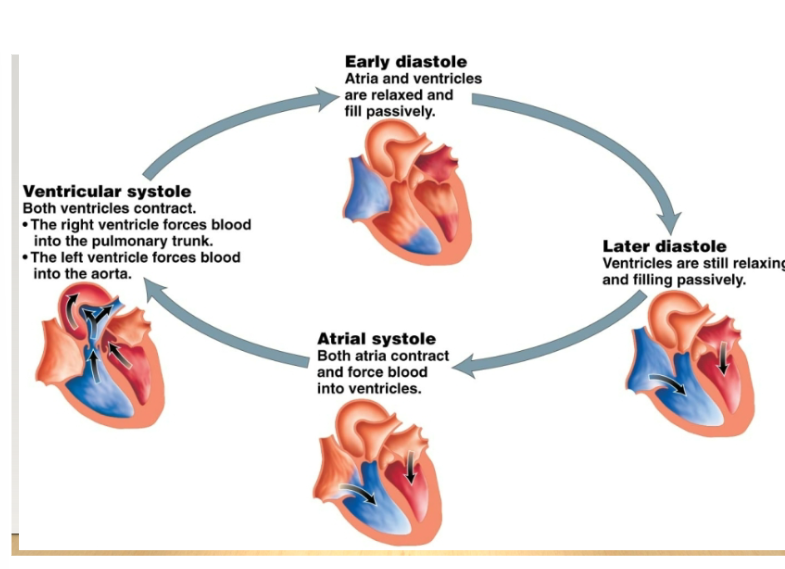
Steps into the cardiac cycle
All chambers relax and blood passes through the atria into ventricles. -Atria contrax -Ventricles contract -Heart relaxes, and cycle begins
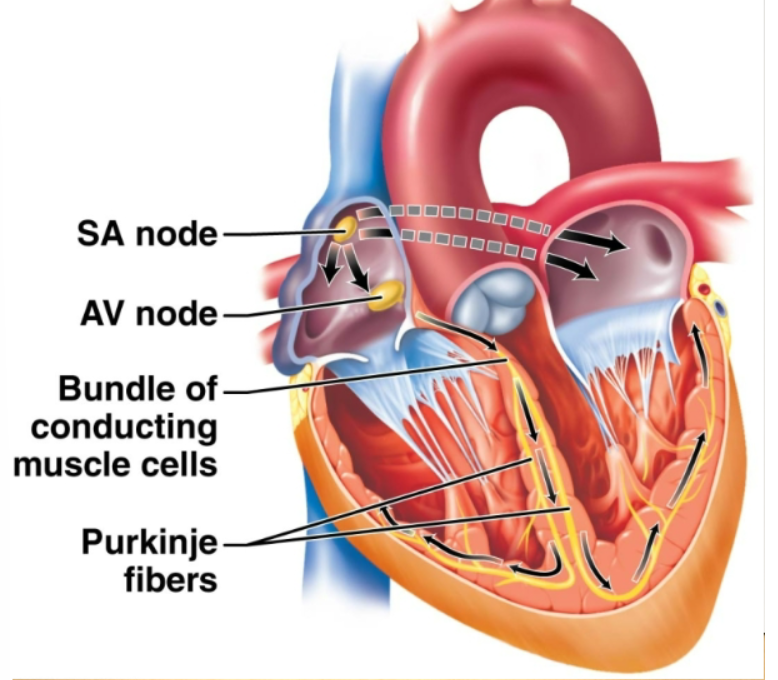
sinoatrial node
Pacemaker. Located in the right atrium, causes atria to contract. Generates an electrical signal that sets the tempo of the heartbeat.
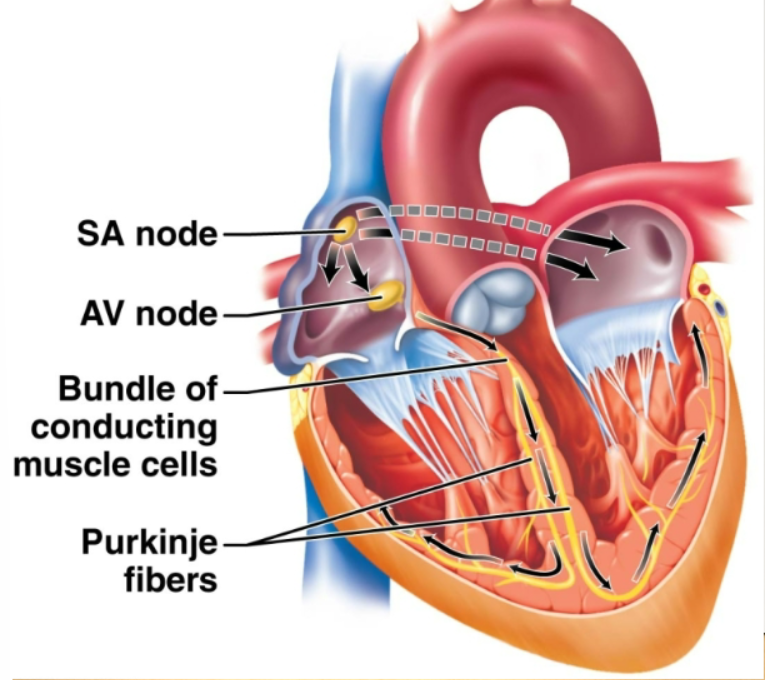
atrioventricular node
Located between the two atria. Receives the signal from the SA node. Transmits the signal by the way of atrioventricular bundle (located along the wall between the two ventricles) to the Purkinje fibers that penetrate the walls of the ventricle, causing the ventricles to contract.
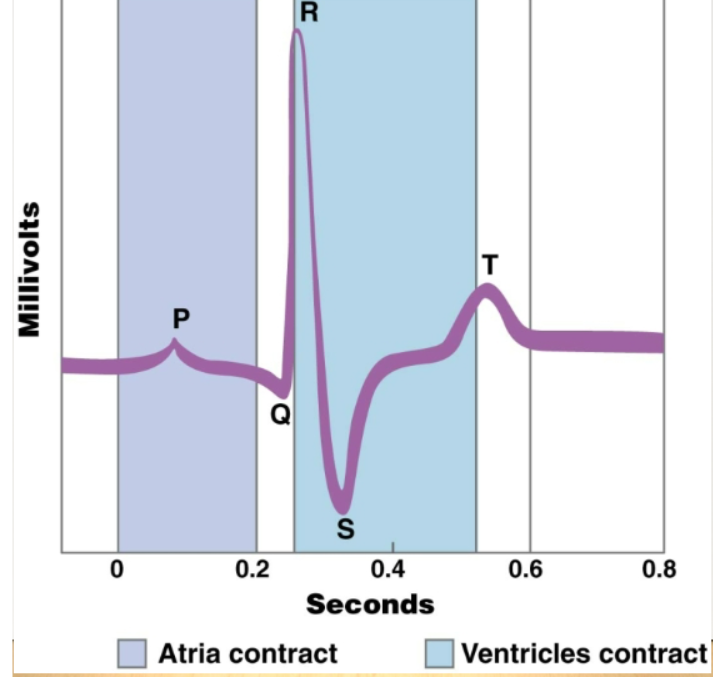
electrocardiogram
A powerful tool recording the electrical events associated with the heartbeat. Abnormal patterns can indicate heart patterns. P wave: signals from SA nodes across atria and cause them to contract. QRS wave: spread of signals through ventricles and ventricular contraction. T wave: return of the ventricles to the electrical state before contraction
blood pressure
The force exerted by the blood against the walls of blood vessels. (120/80). It can be measured using a sphygmomanometer. Measures pressure in the brachial artery of the arm.
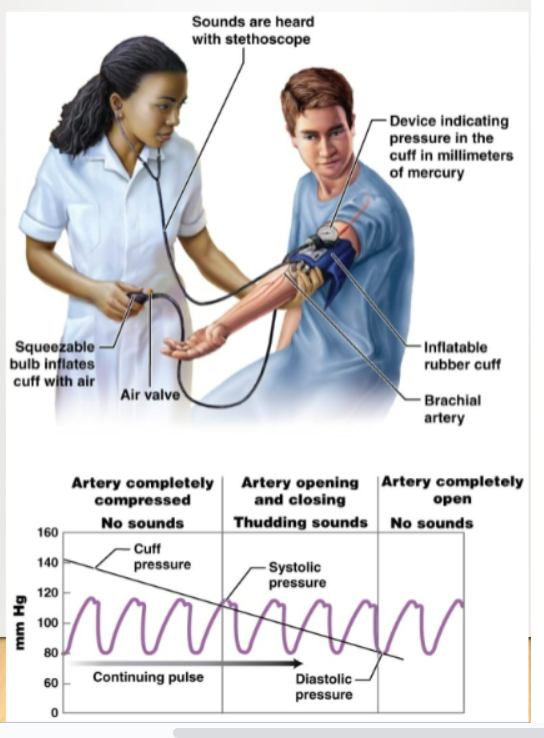
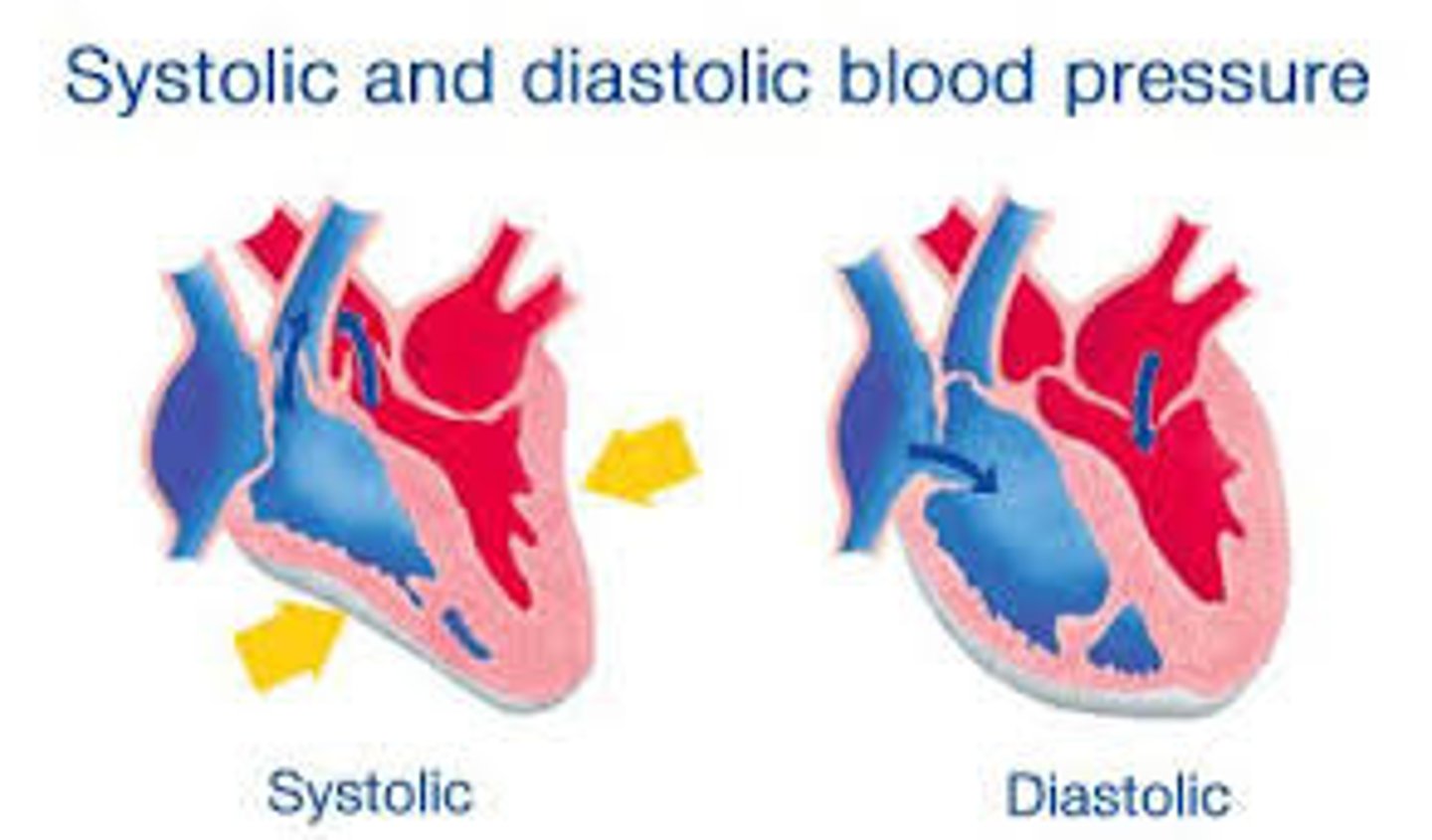
systolic pressure
Highest pressure in the artery during each heartbeat (ventricles contracting). About 120 mm Hg in a healthy adult.
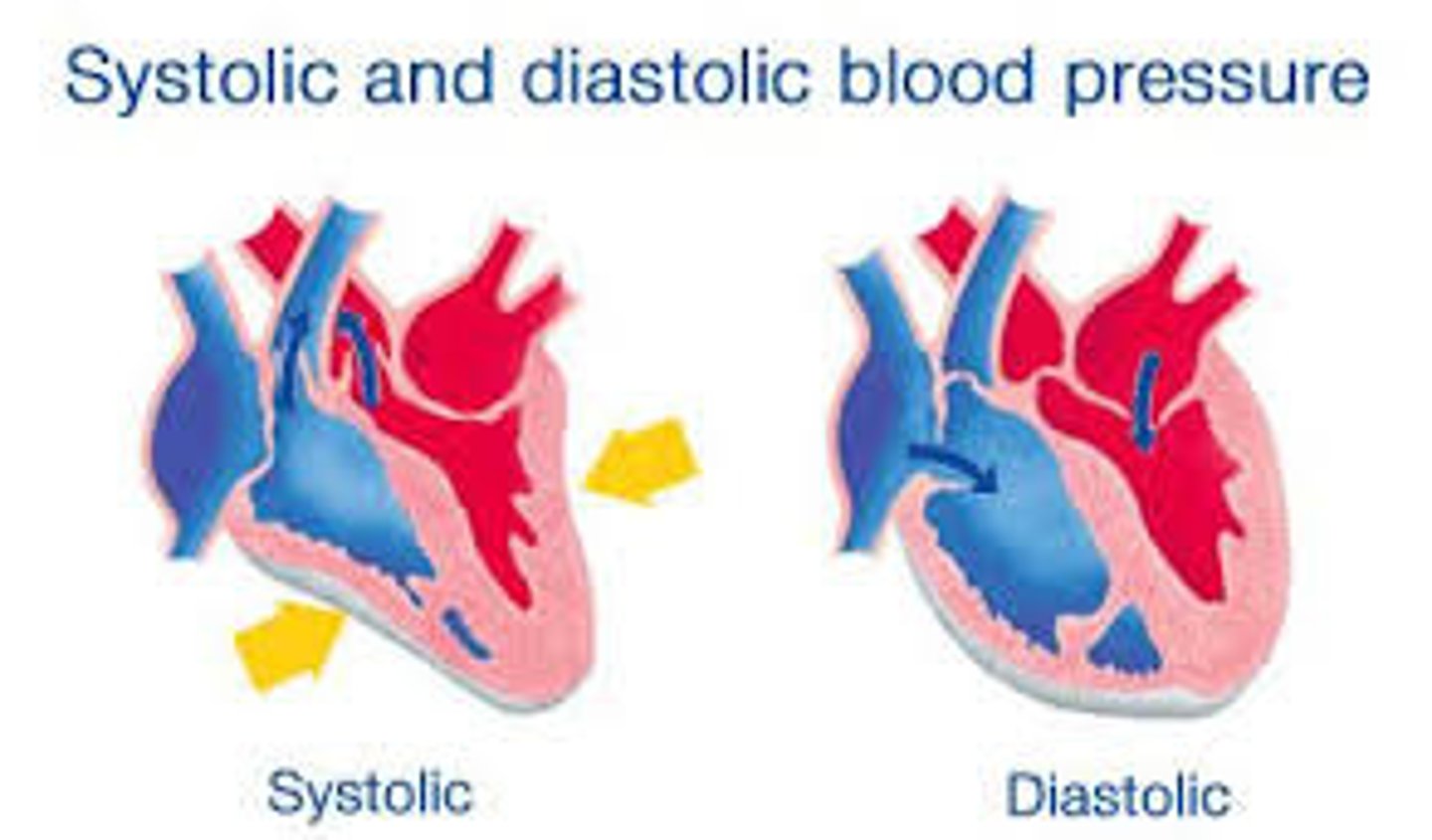
diastolic pressure
Lowest pressure in the artery during each heartbeat (ventricles are relaxing). About 80 mm HG in a healthy adult
lymph
Fluid identical to the interstitial fluid
lymphatic vessels
Cells which lymph nodes through, have one way valves to protect backflow
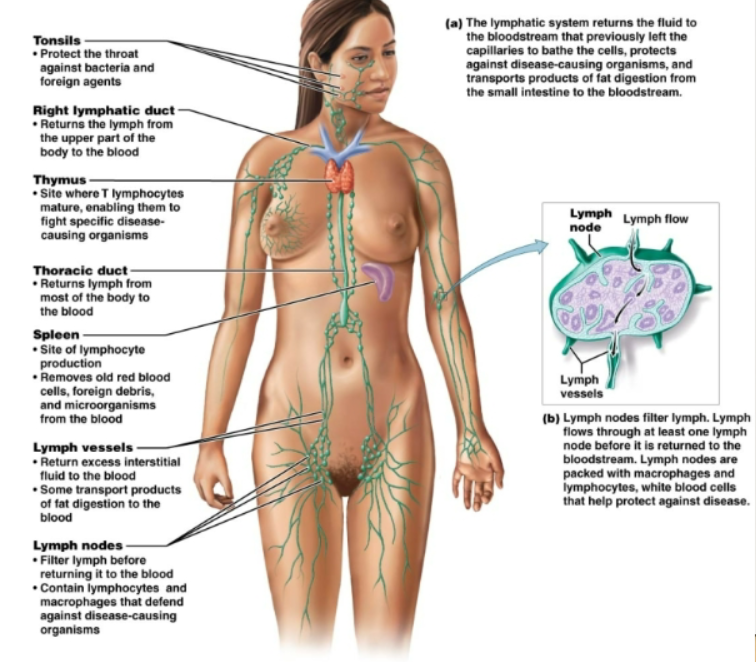
functions of the lymphatic system
Return excess interstitial fluid to the bloodstream. Transport products of fat digestion from the small intestine to the blood stream. Defend body against disease causing organisms and abnormal cells
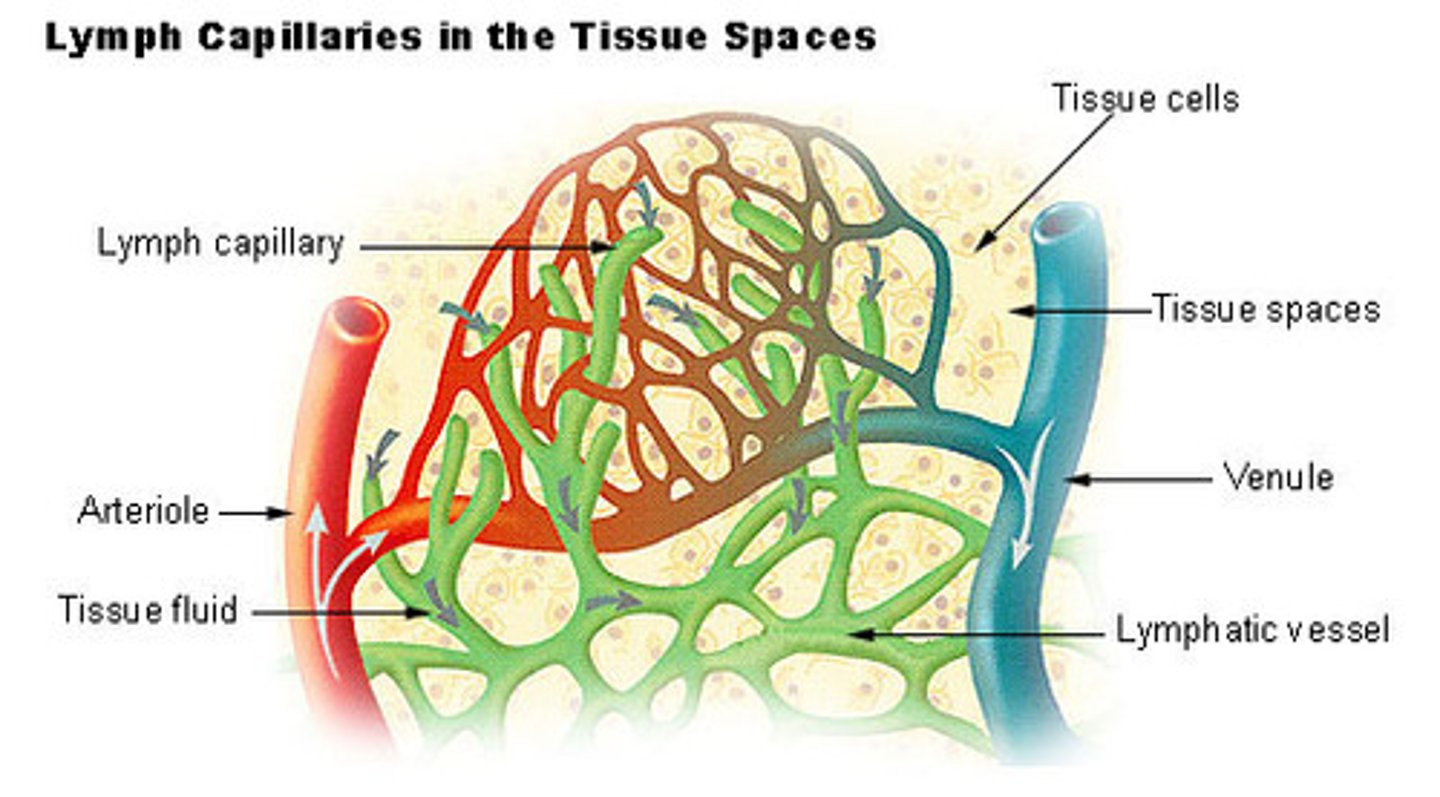
lymphatic capillaries
Extra fluid enters these microscopic tubules. It differs from blood capillaries because they end blindly and are more permeable. Drain into larger lymphatic vessels. Lymph eventually enters ducts that join with large veins at the base of the neck.
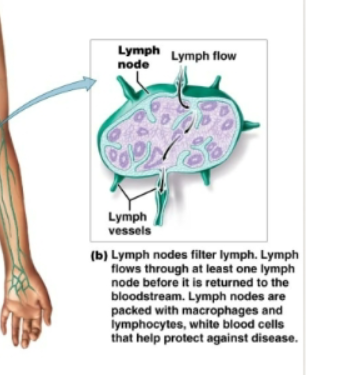
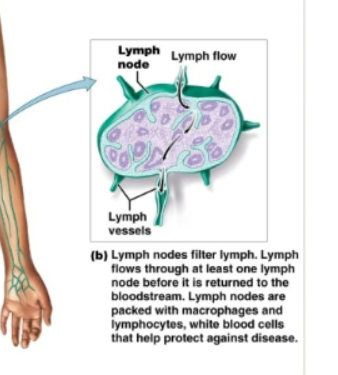
lymph nodes
Bean shaped structures. Filter lymph as it flows through them. Contain macrophages and lymphocytes to defend against disease causing organisms.
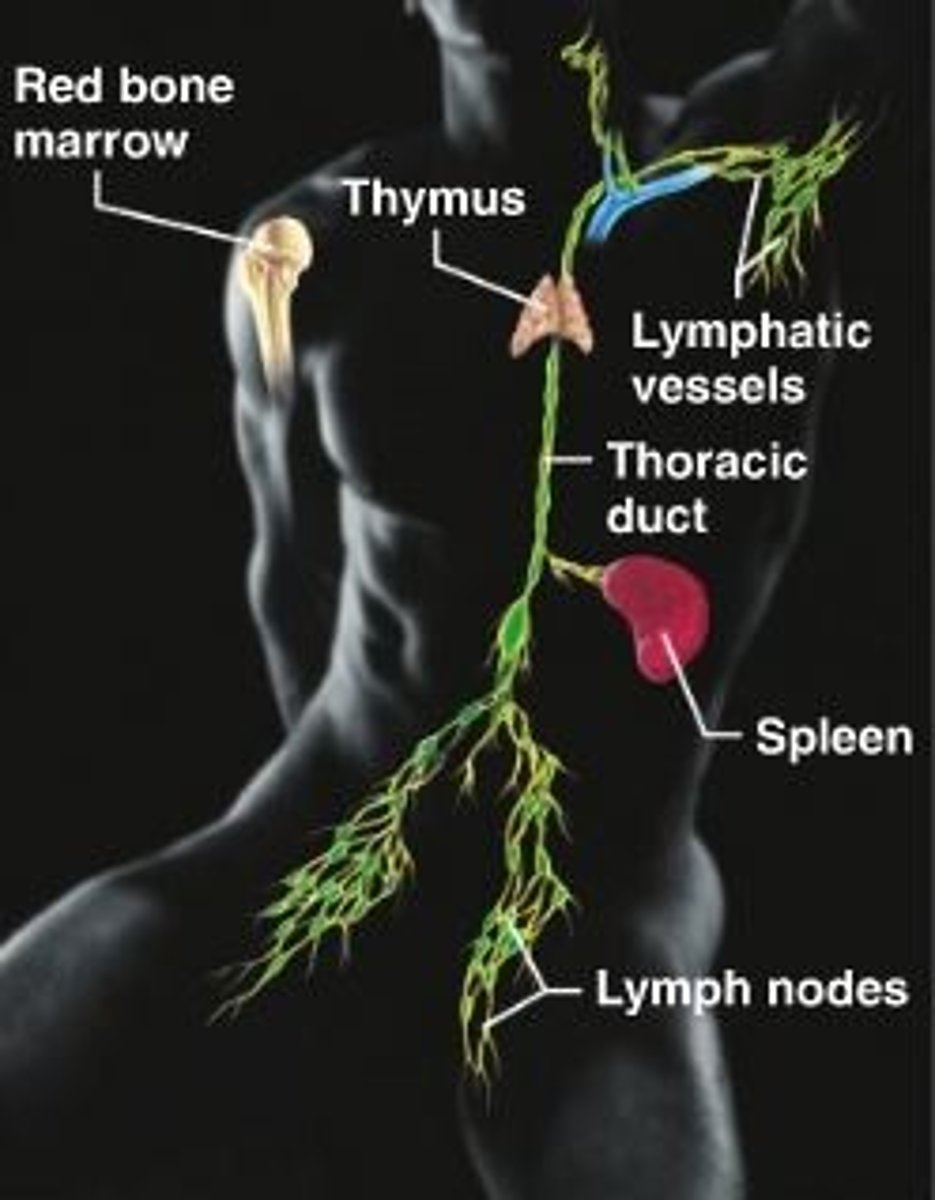
list of lymphoid organs
Tonsils, thymus gland, spleen, Peyer's patches on small intestine, red bone marrow
pathogen
Disease-causing bacteria, viruses, prions, protozoans, fungi, parasitic worms
cancer cells
Once normal body cells whose genetic changes caused unregulated cell division
3 strategies for defending against foriegn organisms, molecules, or cancer cells
Physical and chemical surface barriers: nonspecific, keep foreign organisms or molecules out Internal cellular and chemical defenses: nonspecific, attack any foreign organism or molecule that has gotten past surface barriers Immune response: specific, destroy specific targets and remember them