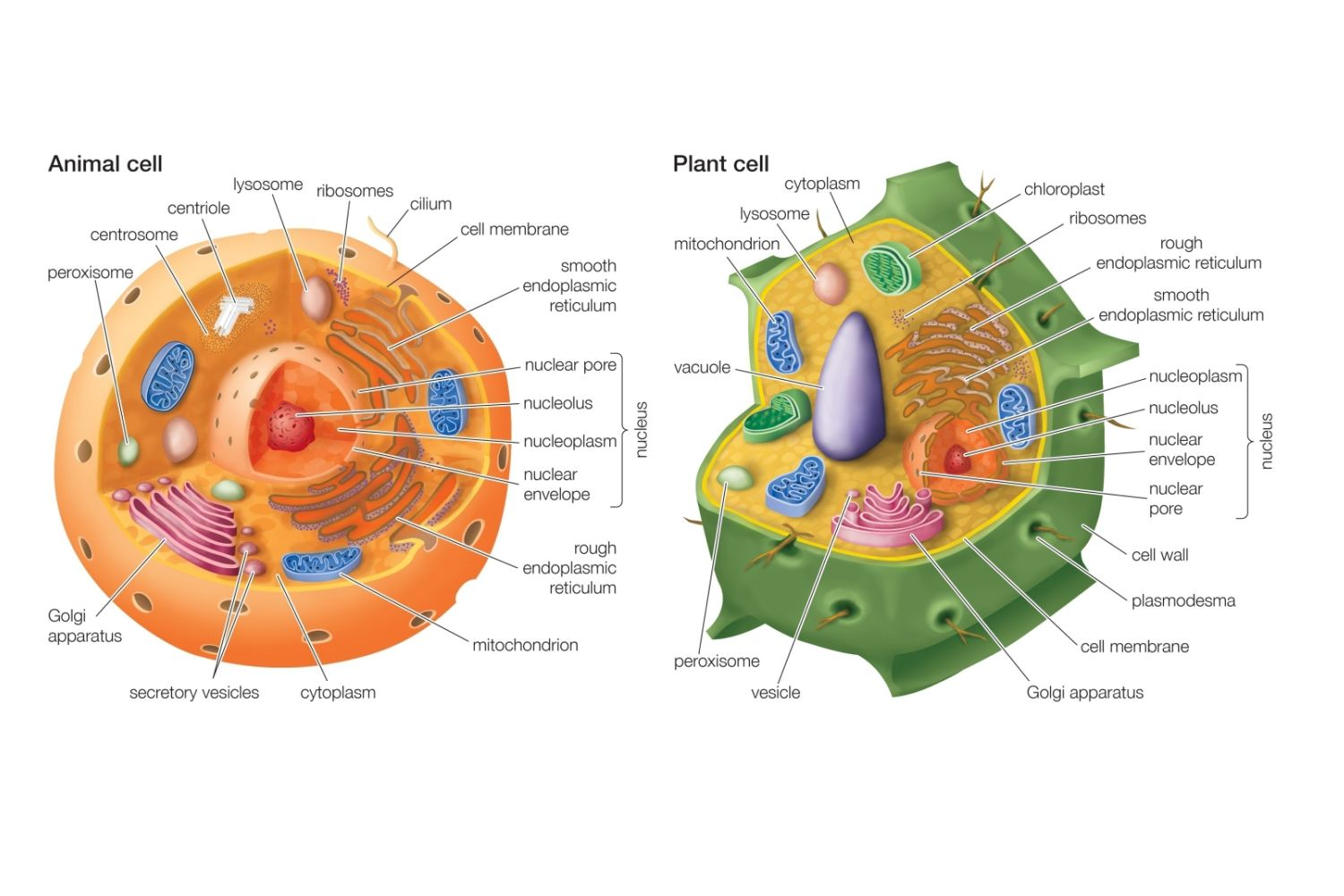
The Cell
Cell Theory
- Cells are fundamental units of life
- All organisms are composed of cells
- All cells come from preexisting cells
- same as studying life
- Life is continuous- we can trace back to cells
Cells like to keep a good surface area to volume ratio
- Volume determines metabolic activity per unit of time
- Surface area determines how many substances enter and leave
- Basically need a high ratio so that enough nutrients can enter and waste can exit for the processes to happen
- Cells increase surface area by folding
Cell Membrane
- made of lipids
- Selectively permeable barrier that helps maintain homeostasis
- Important in communication and receiving signals
- Has proteins for binding cells
- Plasmodesmata are membrane-lined channels found in plants that transport substances and connect them
- Extracellular matrices are found in animals
- Like a string of webs connected to the membrane that hangs outside
- Integrin connects the extracellular matrix to the membrane
- Connected to microfilaments in the cell membrane and the collagen outside
- for cell movement, the protein changes shape and detach
- Fibrous component is collagen, gel-like component is proteoglycans
- collagen is a protein, proteoglycans are proteins and polysaccharides
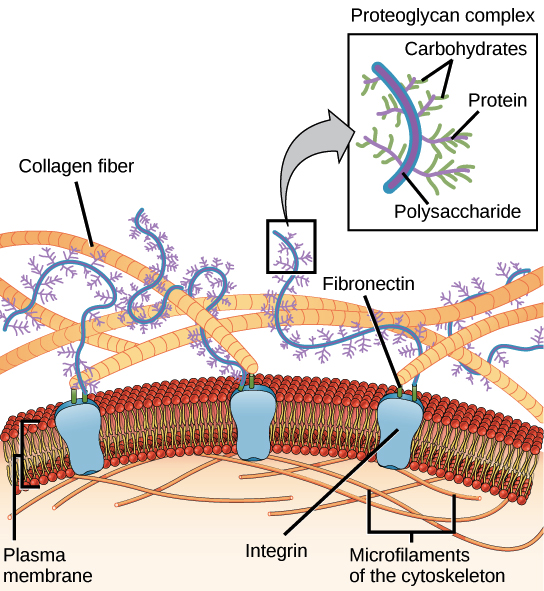
- contribute to physical properties of bone, cartilage, skin, bone, and other tissues
- help filter materials like in kidneys
- orient cell movement and repair
- collagen is a protein, proteoglycans are proteins and polysaccharides
- Cell junctions protrude through and between cells to bind them together
- Tight junction
- prevents substances moving in the space between the cells
- Desmosomes
- allows for substances to move in the matrix between cells
- Gap junction
- run between membrane pores, allows for substances to pass through them
- Cell Wall
- Bacteria
- have cell wall containing peptidoglycan (amino sugars and saccharides)
- some bacteria have a additional outer cell wall, very permeable
- some have slimy layer of polysaccharides called the capsule
- some bacteria, including cyanobacteria, contain molecules in membrane that can photosynthesize
- plants
- semi-rigid, provides support and limits its volume
- cellulose
- gel-like matrix contains proteins and polysaccharides
- act as barrier to infection
- contributes to form during growth
Organelles
- found in the cytoplasm along cytosol, which is water and dissolved particles
- Ribosomes
- sites of protein synthesis
- translates the nucleotide sequence of a messenger RNA into a polypeptide
- both types of cells, has a large and a small subunit
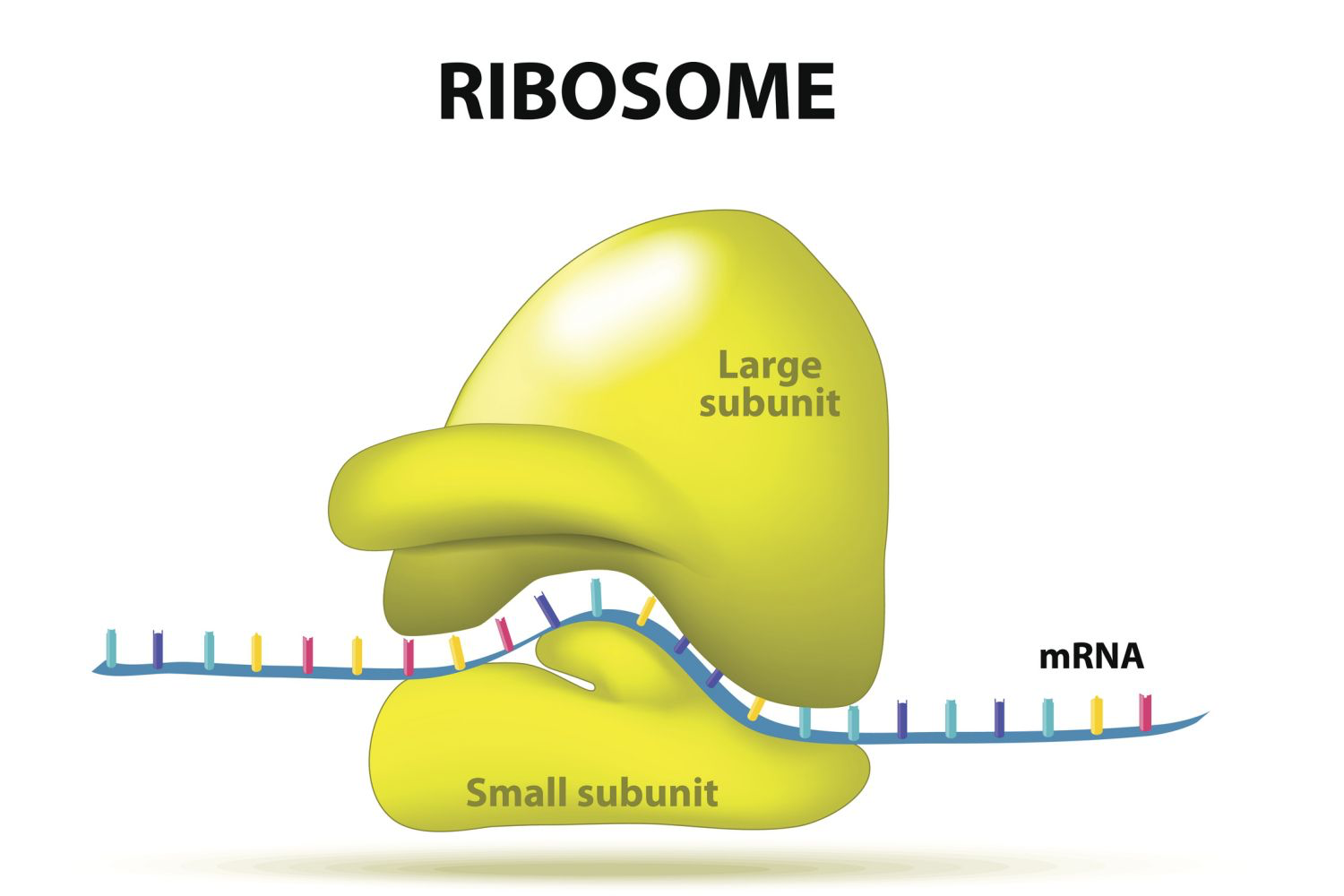
- each subunit consists of ribosomal RNA and protein
- not membrane bound organelles
- they are free in the cytoplasm, in the rough endoplasmic reticulum, or in mitochondria or chlorplast
- in prokaryotes they float freely in the cytoplasm
- Nucleus
- usually largest organelle
- where DNA is stored and replicated
- where DNA is transcribed to RNA
- contains nucleolus
- where ribosomes are made from RNA and proteins
- two membranes called the nuclear envelope
- has pores for substances to pass through
- In the nucleus, DNA combines with proteins called chromatin to make chromosomes
- strand of DNA encoded with genes
- outer membrane is continuous with the endoplasmic reticulum
- endomembrane system
- nuclear envelope, endoplasmic reticulum, golgi apparatus, and lysosomes
- vesicles
- membrane-bound shuttles that transport substances between components and the membrane
- Endoplasmic reticulum
- network of interconnected membranes in the cytoplasm, large surface area
- Rough endoplasmic reticulum
- ribosomes attached to surface
- newly made proteins enter the RER lumen, and are modified then tagged for delivery to specific locations
- transported in vesicles that pinch off of the ER
- all secreted proteins and most membrane proteins pass through RER
- Polypeptides also transported to RER while synthesizing
- folded into tertiary structure
- many combine with carbohydrate groups, becoming glycoproteins
- important in recognition and interaction between cells
- Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
- more tubular (like coral, RER is wall-y), no ribosomes
- chemically modifies small molecules like drugs and pesticides
- site of glycogen degradation
- synthesis of lipids and steroids
- stores calcium ions, important for cell responses
- Golgi Apparatus
- flattened sacs (cisternae) and small membrane enclosed vesicles
- further modifies proteins from the RER
- concentrates, packages, and sorts proteins
- adds carbs to proteins
- site of polysaccharide synthesis for plant cell walls
- three regions
- cis: recieves
- trans: exports in vesicles to the membrane or lysosomes
- medial: medial
- Lysosomes
- primary lysosomes originate from golgi apparatus
- contain hydrolases (digestive enzymes), macromolecules are hydrolyzed into monomers
- macromolecules enter the cell through phagocytosis
- part of the membrane encloses the material and a phagosome is formed
- phagosomes then fuse with primary lysosomes to make secondary lysosomes
- secondary lysosomes hydrolyze food molecules
- phagocytes are cells that specialize in taking in materials and breaking them down
- autophagy is the programmed destruction of cell components (materials and organelles) using lysosomes
- lysomal storage diseases happen when lysosomes fail to break cell components down
- Mitochondria
- energy-rich molecules begin breaking down in the cytosol
- then it enters the mitochondria where it gets turned into ATP
- need more energy=more mitochondria
- 2 membranes
- outer-very porous
- extensive folds called cristae increase surface area
- fluid filled matrix contains enzymes, DNA, and ribosomes
- peroxisomes
- collect and break down toxic by-products of metabolism (ex. H2O2) using special enzymes
- plant organelles
- plastids
- some are used for storage
- give plants their color
- chromoplasts
- leucoplasts (starch)
- chloroplast
- chlorophyll, photosynthesis, anabolic reaction
- two membranes
- internal membranes called thylakoids
- granum- stack of thylakoids, converts light energy into chemical energy
- stroma- aqueous matrix around grana
- contains ribosomes and DNA, synthesizes carbs
- glyoxysomes
- convert lipids into carbs for growth
- vacuoles
- mainly in plants and fungi
- storage of waste in toxins, deters herbavores
- structure for plants, water enters vacuole through osmosis, creates turgor pressure
- reproduction- colors attract pollinators
- catabolism- enzyme in seed vacuoles hydrolyze stored food for early growth
- contractile vacuoles can get rid of water by pumping it out and moving the cell
Cytoskeleton
some rod-shaped bacteria have network of actin-like, helical structures that help maintain shape
supports and maintains cell shape
holds organelles in position and can move them
involved in cytoplasmic streaming (things in cell move)
interacts with extracellular stuff to hold cell in place
dynamic instability
- filaments can lengthen or shorten with more assembly or detachment
- actin and myosin interact to contract muscles
motor protein
- any protein that causes movement
3 components
microfilaments
- helps a cell or its parts move
- determines shape
- made from actin monomers that attach in the plus end and detach at the minus
- actin is a protein, important in muscle contraction
intermediate filaments
- 50 kinds, 6 classes
- tough, ropelike, no dynamic instability
- anchor cells in place
microtubules
- thickest cytoskeleton component
- rigid internal skeleton for some cells or regions
- framework for motor proteins
- made from dimers of protein tubulin, chains of dimers surround a hollow core
- \
- and - ends, dynamic instability
- polymerization - rigidity, depolymerization- collapse
- form internal skeleton for cellular appendages
- cilia
- short, usually many
- stiffly moves cell
- can move fluid over a stationary cell
- flagella
- some prokaryotes use flagella to move
- one or two, longer, push or pull cell through water
- cilia and flagella microtubules are arranged in 9+2 pattern
- doublets- 9 fused pairs of tubules form a cylinder
- one unfused pair in center
- motion occurs when doublets slide past each other
- dynein
- motor protein that can change shape, causes sliding
- nexin
- crosslinks doublets and prevents sliding, so it bends
- kinesin
- combines with vesicles that walk along the microtubule