Chapter 4: Covalent Compounds, Formulas, and Structure
Covalent Molecules
- Covalent bonds are another form of bonding used to achieve noble gas configuration and create molecules. Electrons are shared between atoms rather than transferred. Covalent compounds are physically attracted to each other rather than electrically attracted.
- Covalent molecule electron sharing is shown using Lewis electron-dot structures. The valence electrons are represented as dots around the atomic symbol
- A covalent bond occurs when one atom donates one electron and another atom donates a second electron, the two atoms then share the electron pair. Two shared pairs creates a double bond. Three shared pairs creates a triple bond
- Each element wants to obtain noble gas configuration—a full valence shell. The octet rule states noble gas configuration is achieved if there are eight electrons around each atom.
- Hydrogen is an exception with an “octet” of two.
- Magnetic properties are caused by unpaired electrons created small magnetic fields. When paired, the magnetic fields cancel out. More unpaired electrons created stronger magnetic properties.
- Substances with unpaired electrons are paramagnetic.
- Substances with all paired electrons and a small magnetic field are diamagnetic.
Lewis Structure of Molecules
- Drawing polyatomic molecules need to be organized in certain ways to bond
- Carbon is usually the central atom. Multiple carbons are usually in a chain
- Hydrogen is never the central atom because it can only form one covalent bond
- Halogens, without oxygen, can only form one covalent bond, therefore usually aren’t central
- Oxygen forms only two covalent bonds and not typically the central atom. May link two carbons in a carbon change
- The atom that only appears once will often be central
- All valence electrons must be organized around each atom in certain steps
- Valence electrons of all atoms are added together
- Subtract an electron if the polyatomic is positively charged. Add an electron if its negatively charge
- Create a bonding pair of electrons between two atoms
- Place eight nonbonding pairs on each outer atom of the structure to complete the octet (also called lone pairs)
- Add pairs to central atom if electrons left over
- If the central atom has an octet, the structure is complete
- If it has fewer, and not boron, a double bond must be created to the central atom from a nonbonding pair until an octet is formed
- The central may have more than 8, unless it is from Period 2, then it cannot have more than 8.
- Electron-deficient molecules include boron.
Multiple Covalent Bonds
Some molecules require double bonds to complete octets.
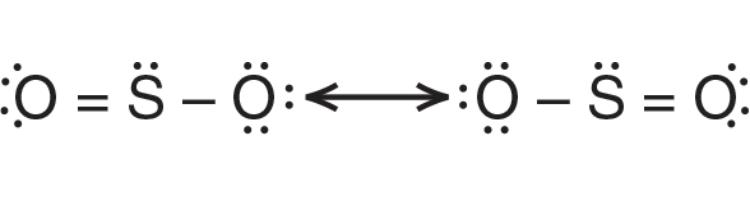
Molecules that have equally probable structures are called resonance structures
In SO2, the rightmost oxygen can be double bonded to the sulfur or the leftmost oxygen. Both are equally likely to form
Lewis Structures of Ions
- If a polyatomic has a charge, simply add electrons if it is negatively charged (add one electron if charge is -1 for the molecule).
- If positively charged, subtract electrons (subtract one electron if the charge is +1)
Lewis Structures of Odd Electron Compounds
- Some compounds cannot have an octet around each atom.
- For NO2, both oxygens are double bonded to the nitrogen with two lone pairs each, giving each atom an octet. However, one electron still remains. Add the electron to the central atom.
- Unpaired electrons, or free radicals, make molecules unusually reactive and cancerous. They can also cause the molecule to form dimers, or pairs of molecules.
- NO2 dimerizes to N2O4
Formal Charge
- Formal charge can be calculated to determine which version of a Lewis structure is more likely to form
- It is calculated by subtracting the amount of electrons an atom has in a Lewis structure by its valence electrons
- The molecule with the smallest formal charge is the preferred structure
- If a molecule has a charge, the formal charge should be equal to that
Resonance Structures
- Structures that are equivalent, including the formal charge, are resonance structures.
- Benzene, a structure with resonance structures, is known as an aromatic molecule and cancerous. Aromatic molecules have a smell, but are defined as containing a benzene ring.
Covalent Bond Polarity and Electronegativity
- Electrons are only shared equally in a covalent bond if they are diatomic. If they are not shared equally, the electrons will spend more time around the atom that is more electronegative, or attracts the electrons more.
- Unequal electron sharing in covalent bonds are called polar bonds. Polar bonds have a positive and negative end.
- polarity is shown by δ+ and δ− for partial positive and partial negative atoms.
- Electronegativity is the ability of an atom to attract electrons. It is considered a diagonal trend because it increases going left to right and down to up.
- Fluorine is the most electronegative and francium is the least.
Dipole Moments
- Atoms that attract electrons will be partially negative (δ−). The other atom in the bond will be partially positive (δ+).
- Dipole moments is the difference in charge between two covalently bonded atoms and the distance between the nuclei.
- Dipole moment = (q)(r)
- q = difference in charge
- r = distance between two nuclei
- units for dipole moment = coulombic-meters (Cm)
- debye is another unit = 3.34x10^-30 Cm
- Dipole moments can become nonpolar if opposing dipole moments cancel each other out
Electronegativity and Ionic Character
- Diatomic elements are considered nonpolar because they share electrons equally.
- ∆EN of 1.7 or greater is considered ionic
- ∆EN of lower than 1.7 are considered polar covalent
- ∆EN of zero is nonpolar
Bond Order /h3
- Bond order is the average amount of bonds that an atom makes
- Chlorine and fluorine have a bond order of one
- Oxygen has a bond order of two
- Nitrogen has a bond order of three
- Calculate bond order by dividing how many bonds there are by how many atoms there are in those bonds
- For SO3, there are four total bonds: two single and one double, bonded to three oxygens. The bond order for sulfur in this molecule is 4/3.
Bond Strength, Bond Energy, and Bond Length
- A double bond is twice as strong as a single bond, the strength is called bond energy
- Atoms vibrate when covalently bonded and the vibration frequency can be calculated
- E = hv
- energy equals Planck’s constant time the frequency of the vibration
- Bond energy can also be measured by measuring the amount of energy released when organic molecules are burned
- Bond length can be measured by x-ray crystallography or by using the frequency of vibration and the length of the vibrating medium.
Nomenclature
- covalent molecules are named using numerical prefixes
- N2O4 is dinitrogen tetroxide
- SO3 is sulfur trioxide
Molecular Geometry
- The Lewis structure of a molecule can help establish the molecular geometry
Valence-Shell Electron-Pair Repulsion Theory
- The valence-shell electron-pair repulsion theory (VSEPR theory) is a way to determine the 3D shape of covalently bonded molecules if given certain information
- Theory is that electron pairs repel each other because of the negative charge and will arrange themselves to be as far apart as possible.
- Region that a bonding pair occupies is the bonding domain
- Region for lone/nonbonding pairs is the nonbonding domain
Basic Structures
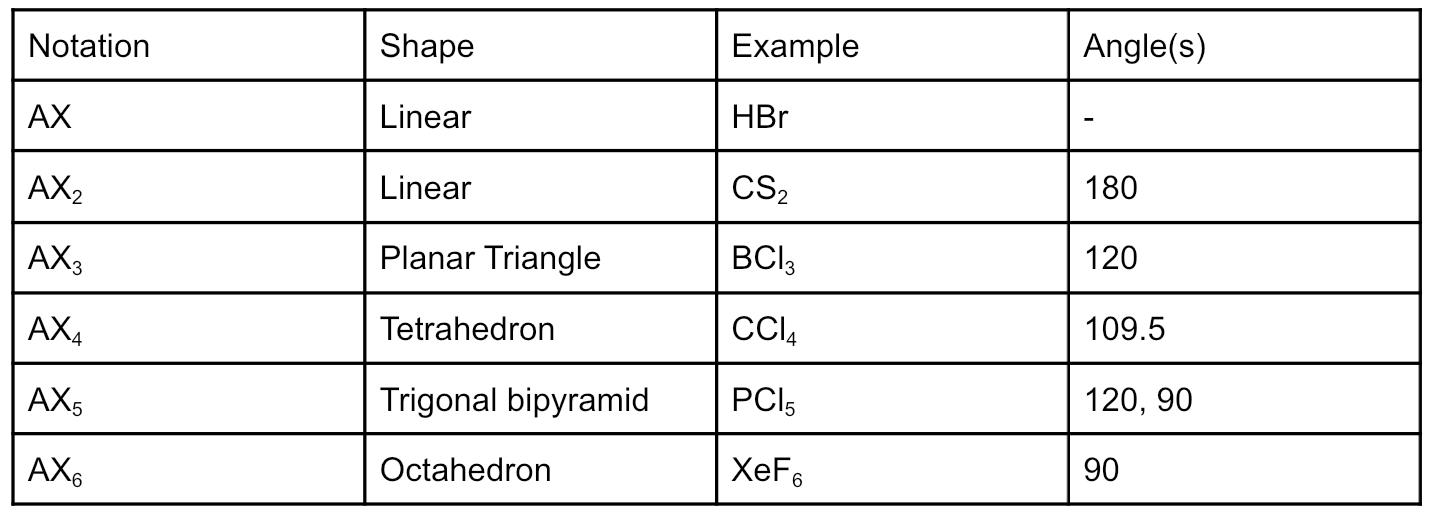
AXE system: A is the central atom, X and E represent the number of bonding and nonbonding electron domains associated to A.
For molecules with NO nonbonding domains
AX to AX4 have all equidistant bonds.
For, AX5 the 120 is for the angle between the three equatorial bonds. is the angle between the axial and equatorial atoms
For AX6 the 90 is angle between all of the bonds
Finding the geometry of a central atom with no nonbonding regions is done by counting the atoms bonded to it.
- Five bonds to the central atom are trigonal bipyramidal.
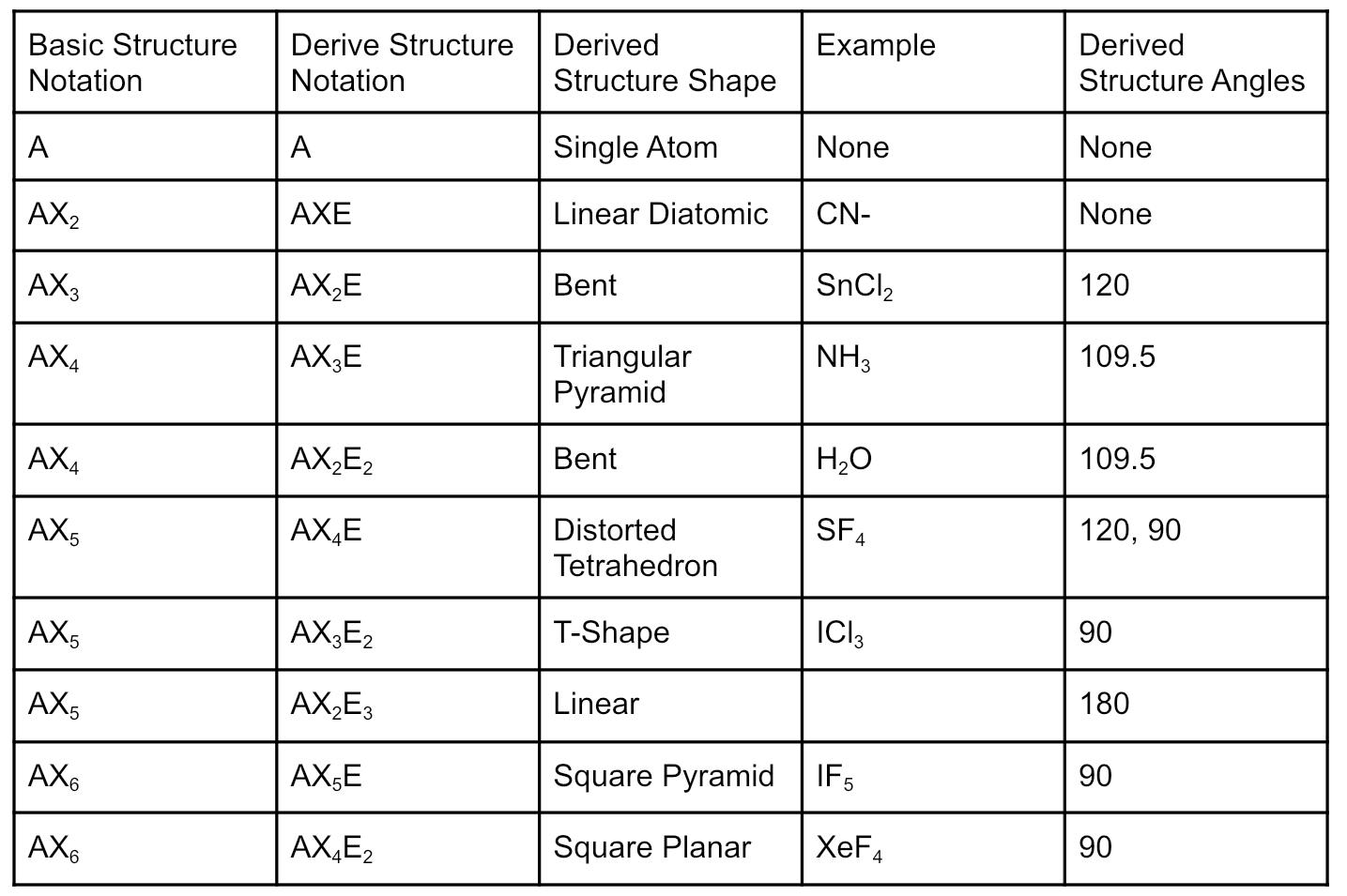
Derived Structures
Derived structures have nonbonding domains where a bonding domain would usually be. The result is the same basic structure.
Complex Structures
- Complex molecule geometry is determined by finding the geometry around each atom and then combining the structures.
- Organic molecules have complex, important structures that define chemical, physical, and biological properties and traits.
- Carbon never has a nonbonding pair because it makes triple, double, and single bonds, with a total of four possible bonds.
- Oxygen in organic compounds always has two nonbonding domains.
- Nitrogen in organic compounds has one nonbonding domain
Molecular Polarity
- Bond polarities depend on the individual EN values of the bonding atoms. Depending on the structure of the molecule, the molecule may have polar bonds but be overall nonpolar.
- Four general molecule polarity rules
- No matter what, symmetrical molecules are nonpolar
- Asymmetrical molecules with polar bonds are polar
- A molecule with more than one type of atom bonding to the central atom is often nonsymmetrical, therefore polar
- A central atom with nonbonding electron pairs often asymmetrical and polar
- CH3Cl is polar because is not symmetrical
- CBr4 is nonpolar because it is symmetrical.
- Four equal dipole moment will add up to zero because of tetrahedral geometry
Covalent Bond Formation
Wave Mechanics and Covalent Bond Formation
- The valence bond theory (VB theory) states covalent bonds are the overlapping of two electron orbitals when the electron spins are paired
- The molecular orbital theory (MB theory) says molecule are similar to atoms in the way that they have distinct charges and energy levels that can be populated by electrons
Valence Bond Theory
- VB theory states that if two hydrogen atoms approach each other, the atomic orbitals will overlap with electrons of opposing spin. The paired electrons spread out over the molecule to form the final electron cloud.
- MO and VB theory have the same results with a high electron density along the internuclear axis
- H2 and other compounds with overlapping two s orbitals form a sigma bond (σ).
- Can also be formed by overlapping s and p orbital (HF)
- Overlap two p orbitals (F2)
Orbital Overlap Model (Pi Bonds)
- Every covalent bond has only one sigma bond, AKA a single bond
- If the bond is double or triple, more orbital overlap is needed, and a pi bond (π) is formed.
- Pi bond is a sideways overlap of two p orbitals
- A double bond is one sigma and one pi bond
- Triple bond is two pi, one sigma
- Bond and orbitals arrange themselves to not interfere with each other
Hybrid Orbital Model
- p orbitals orient themselves 90 degrees from each other.
- s orbitals are spherical with no directionality
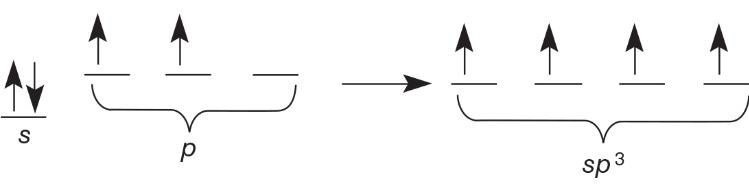
sp^3 Hybrid Orbitals
Hybrid orbitals are a set of orbitals with identical properties formed from the combination of two or more different orbitals with different energies
Hybrid orbital models are used to show sigma bond formation
Above is the orbital diagram of carbon and the conversion of the s and p orbitals to the hybrid orbital sp^3.
sp^3 means on s and three p orbitals have been combined to a hybrid. p electrons are shown as being higher energy by the p being placed higher than the s.
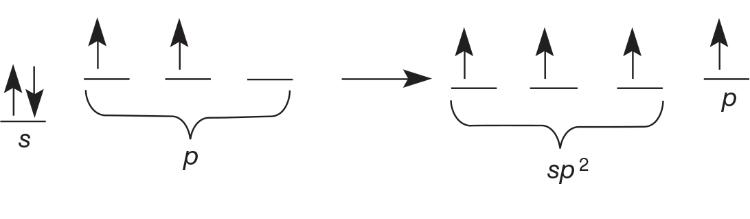
sp^2 Hybrid Orbitals
CH2O has single bonds to hydrogen and a double bond to oxygen
- 3 sigma bonds and 1 pi bond
- sp^2 hybrid
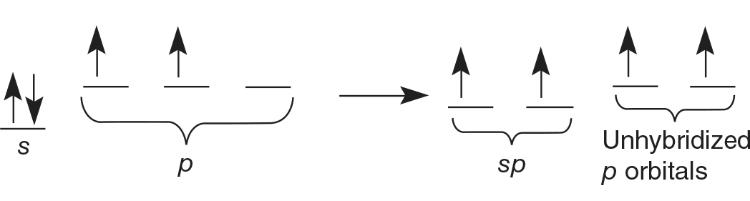
sp Hybrid Orbitals
Carbon dioxide has a double bond to each oxygen.
- 2 sigma bonds and 2 pi bonds
- sp hybrid