Lesson 10: Thermoregulation IV
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
Evaporation: sweating
Largely occurs only in mammals
Enhances cutaneous evaporation
Loosing water across skin through evaporation even when we don’t sweat
make thermoregulatory sweat through eccrine sweat glands
Apocrine sweat glands
type of sweat gland, primarily located in areas with hair follicles, like the armpits
Unlike eccrine sweat glands, apocrine glands secrete a thicker, more oily sweat that can be broken down by bacteria, causing body odor.
They are also more active during times of stress and sexual excitement to cause sexual attraction or repulsion
cutaneous evaporation
Evaporation of water related to skin
2 parts of eccrine sweat glands
Coil of gland: gland is coiled tube here where sweat first produced
Duct of gland: carries sweat thats been made all the way to surface of skin
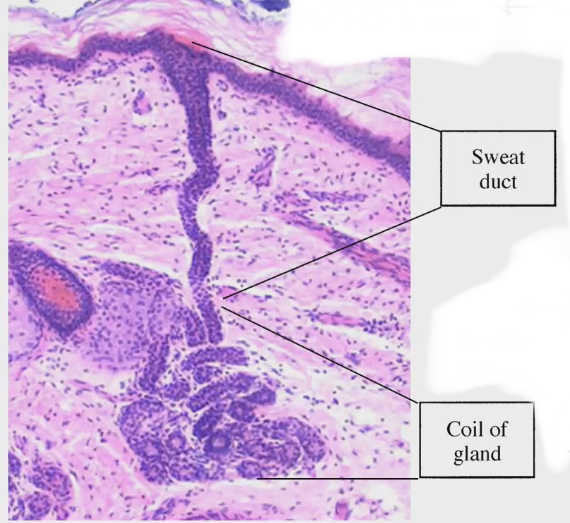
How is sweat made
Sweat gland needs to have water from blood plasma
To move water around the body, there are no pumps like there are for water. We need to establish osmotic gradients, and water molecules will follow through osmosis
Coiled part of gland lots of Na/K ATPase, gives energy to pump Na ions into coiled part of sweat gland. Cl ions will follow by electrostatic attraction.
Cost of making sweat= cost of pumping Na and Cl into coiled part of sweat gland. This is necessary to make water go into sweat gland through osmosis
Aquaporin is coiled part of sweat glands. Build of Na and Cl into coiled part of sweat gland, and water enters through osmosis, only because aquaporin is present
Push sweat up duct to body’s surface. As the sweat goes up, channels in duct part of sweat gland. Na and Cl diffuse back into blood plasma through these channels. This is because we don’t want to loose these salts from body.
ENaC: Na channel
CFTR: Cl channel
No aquaporins in the duct so that water doesn’t follow Na and Cl out of the sweat gland
Secrete mostly water on skin, with a little Na and Cl that didn’t leave duct
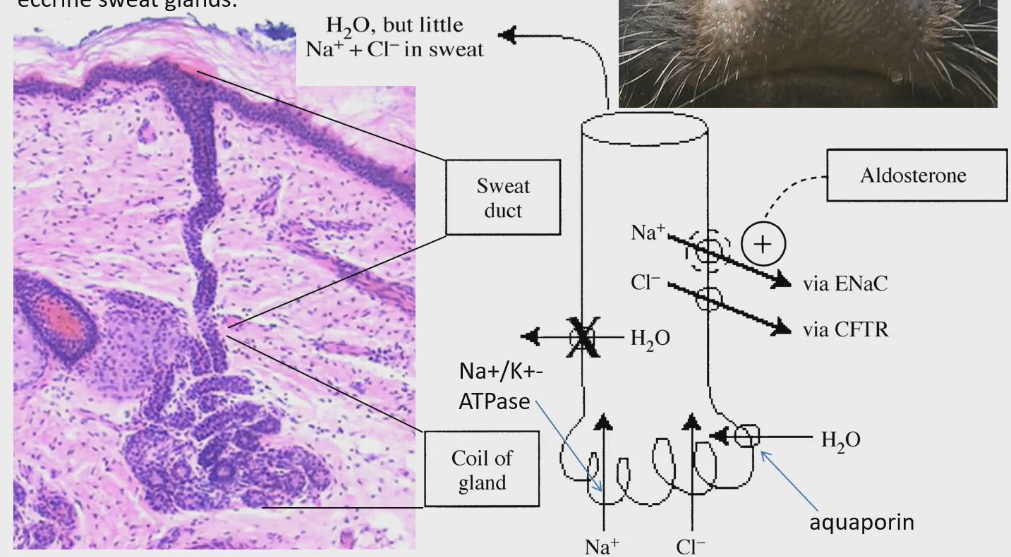
Water is polar and hydrophilic = can’t pass through cell membrane.
Can cross cell membrane only if there is a protein expressed called aquaporin
Aldosterone
Makes it easier for Na to be reabsorbed from sweat to blood plasma
In ENaC channel
Get rid of sodium through kidneys in urination. Sweat glands play an accessory role in that. Too much sodium in body = reduce expression of aldosterone = trap sodium in sweat and it also evaporates from surface of skin through sweat
Hormone produced by adrenal gland. Gets secreted by adrenal glands any time sodium concentration of blood plasma is too low. Increases expression of ENaC channel so Na can be reabsorbed into blood plasma
CFTR channel
Cystic fibrosis transport regulator
Protein that when mutated = cystic fibrosis
CFTR channel also found in lungs and digestive, not just in sweat glands.
Sweat test is part of cystic fibrosis diagnosis. If you have high levels of Na and Cl in sweat, suggests that CFTR channel isn’t working and Na is staying behind with the Cl thats not getting absorbed because they are attracted to each other = diagnosis of cystic fibrosis
Evaporation : panting
Entire respiratory system is lined with “water”
Every time we breathe we loose water by evaporation to air → respiratory evaporation
*** see breathe in cold day, fog is water Vapor, condensing as it hits cold air
Loose more water and heat as well
Not exclusive to mammals
Birds
Lizards don’t pant
they do mouth gaping → sit there with mouths open and take advantage of fact that oral cavity are lined with water. Evaporation only of oral cavity to get rid of heat
How is breathing regulation during panting
Respiratory system divided by
Alveoli : gas exchange occurs
Anatomical dead space: no gas exchange, transport air to alveoli then back to environment (nasal cavity, trachea, bronchi, bronchioles)
Entire respiratory system lined by water, both parts are lined with water
When we pant, regardless which part of respiratory system we bring air into, we will experience evaporative water loss
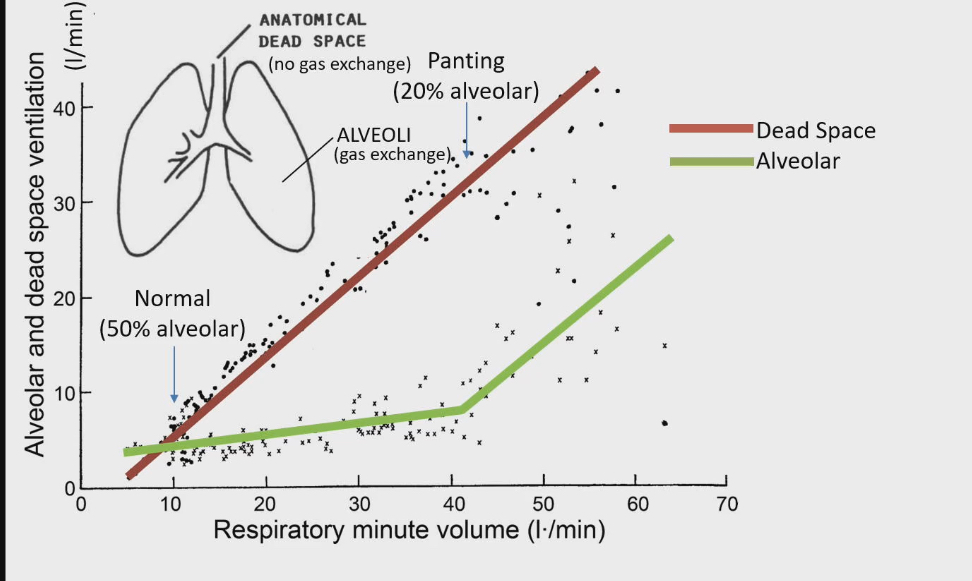
Breathing pattern of vertebrates changes at rest vs panting
X axis: total volume air breathing in and out/min
Y axis : volume air breathing in and out/min in alveoli vs dead space
At 10 l/value : 50 % alveolar
At 40 l/min only 20% of air in alveolar, the rest stays in anatomical dead space
At panting, majority of air in anatomical dead space=this is because they are taking short shallow breathes and not breathing deeply
Why is panting (short shallow breathes) most convenient
CO2 + H2O ↔ H2CO3 ↔ HCO2 + H+
CO2 in body functions like an acid
In order to maintain pH level in body, rate that we produce CO2 = rate we are loosing CO2
Balance ensures pH constant
Get more air into respiratory system, but don’t want accelerate CO2 loss through gas exchange in alveoli because that would cause respiratory alkalosis
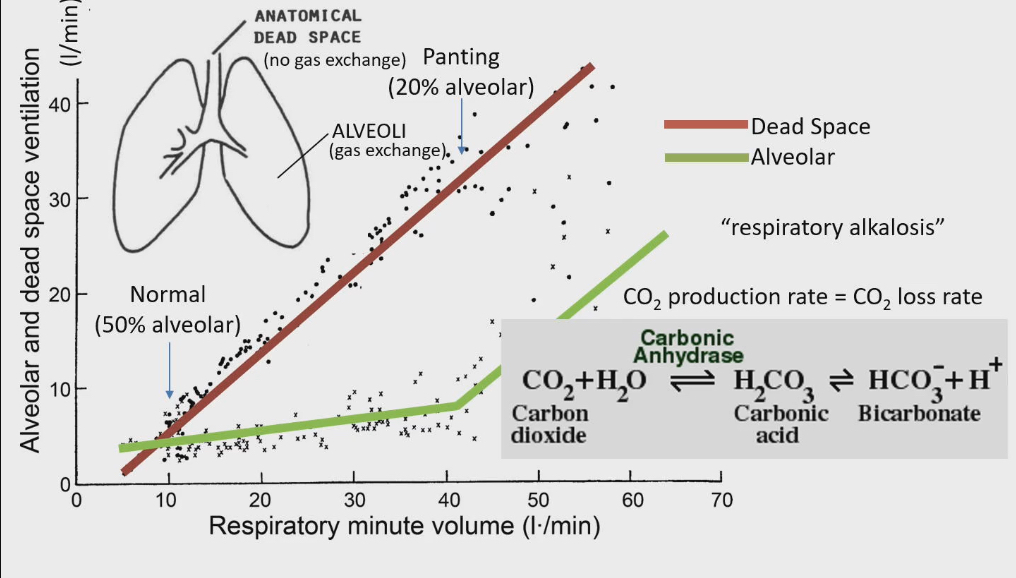
Respiratory alkalosis
a condition where the blood pH becomes too alkaline (basic) due to a decrease in carbon dioxide (CO2) levels
Panting is metabolically expensive
At normal breathing 10 l in respiratory system and 50% makes it to alveoli = 5 l in alveoli
At panting 40 l in respiratory system and 20% makes it to alveoli = 8 l in alveoli
Still have more air in alveoli while panting, more CO2 to pay for cost of panting, but keep CO2 production rate = CO2 loss rate balanced
change that air gets in and out off respiratory system during panting study
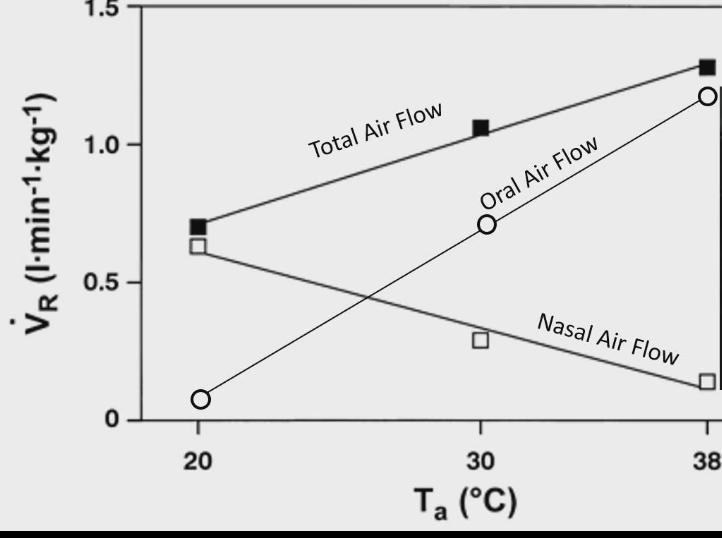
Reindeer study
Total airflow in respiratory system increases as temp gets hotter and we pant more
When reindeer not panting : barely any airflow in oral cavity, 90% of air flow through nasal cavity
When reindeer panting: barely any airflow in nasal cavity, 95% of air flow through oral cavity
Why?
Air that comes out of nose is cooler than air from mouth
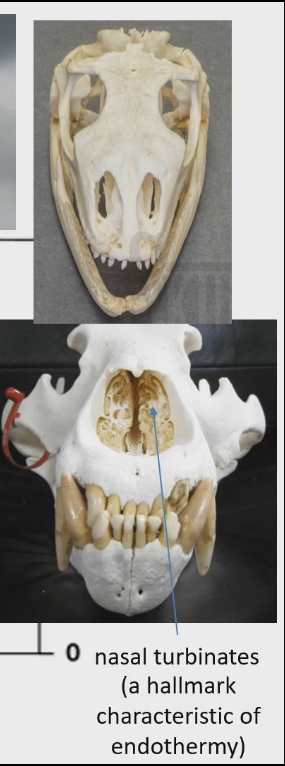
This is because in nasal cavity, we have structure called nasal turbinates. They reabsorb heat from nasal air back to body before it gets exhaled. More nasal turbinates = more heat reabsorbed and less heat lost when you breath out
Oral breathing bybysses the nasal turbinates and maximizes ability to get rid of heat from body
nasal turbinates
Structure in nasal cavity
They reabsorb heat from nasal air back to body before it gets exhaled.
More nasal turbinates = more heat reabsorbed and less heat lost when you breath out
Hallmark characteristic of Endotherms
Evaporation: saliva spreading
If you were to lick yourself, as it evaporates it will you down
Salivary glands of a rat
multiple salivary glands writhing the body that produce different saliva
Researchers took rats and put them at high temp.
Intact: all salivary glands intact. Body temp rises to 40.5ºC then levels off and survives 3 hrs of exposure
All removed: removed all salivary glands. Body temp rises to 43ºC → death
Removal of Parotid glands only: similar result to intact case → not that important of gland for cooling down, survive in heat without it
Removal of submaxillary/sublingual glands, results more liked all removed situation → important for cooling
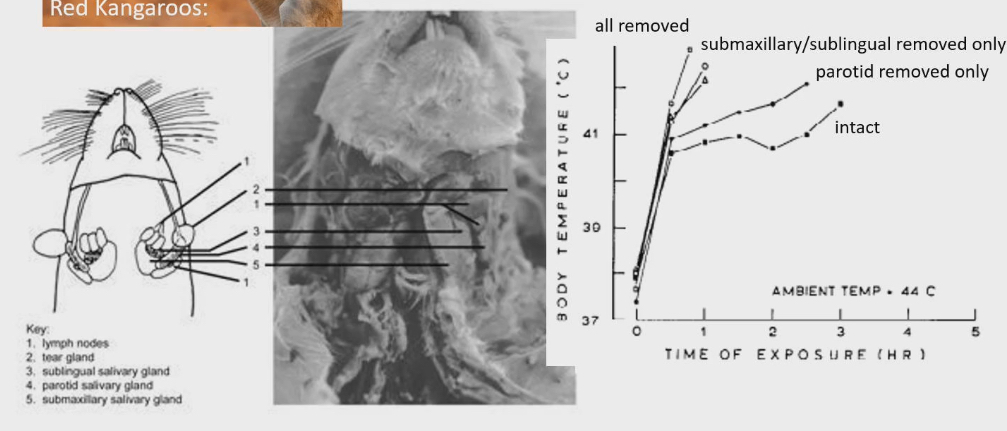
Why do different types of salivary glands make a difference
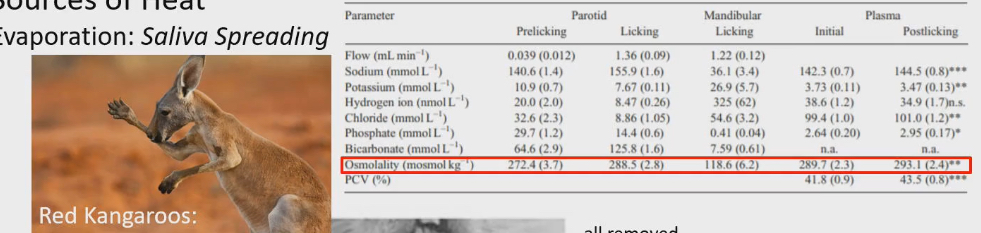
Study in kangaroo.
Parotid gland has more saltier saliva compared to mandibular gland.
Salty water doesn’t evaporate a quickly as fresh water.
Nutrient
Is a substance supplied by food that:
Serves as a source of free energy or (chemotrophic)
Serves as a raw material for growth, maintenance or gamete production (heterotrophic)
6 types of nutrients
Carbs
Proteins
Lipids
Vitamins
Minerals
Water
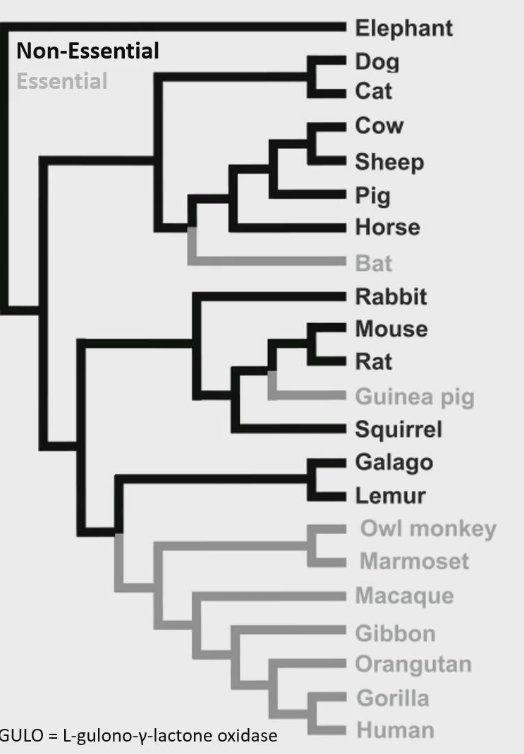
An essential nutrient
Is one that an animal cannot synthesize de novo (from other things) in adequate quantities to meet its nutritional requirements, therefore is must be obtained from its diet
What is an essential nutrients for one animal is not an essential nutrients for another animal
Squirrels make their own vitamin C, humans cannot
So for humans vitamin C is an essential nutrients but not for squirrels
Dark black: animals can make their own vitamin C
Light black : animal cannot make vitamin C on their own
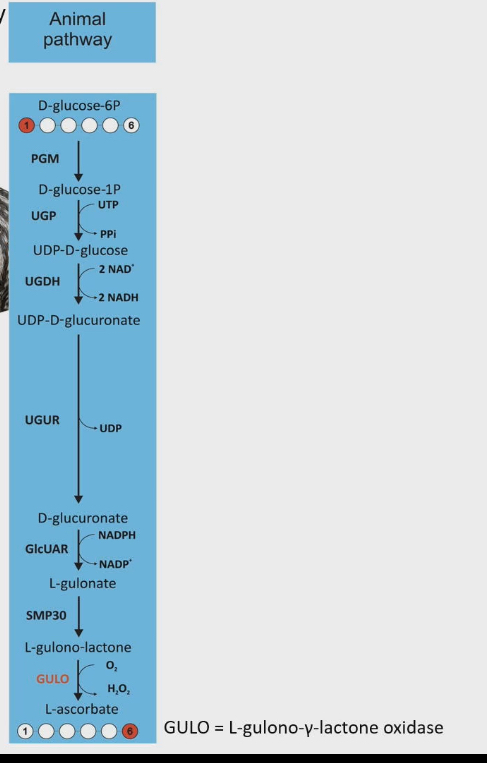
Vitamin C (asscorbate) pathway for animals that can make it on their own
Squirrels take glucose to produce vitamin C
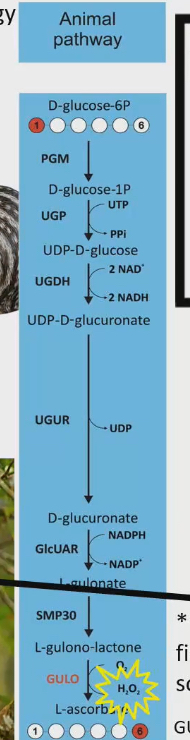
Only 3 groups of mammals where vitamin C is an essential nutrients
Humans and other primates
Guinea pig
Bat
Also teleost fishes and some songbirds
Evolutionary loss to make vitamin C because ancestors of all these animals had vitamin C as a nonessential vitamin
If the ability to make vitamin C was lost evolutionarily, there must be a reason for this
Gibbon eats figs that are most vitamin C rich food
One study showed that y 27% of gibbons diet was figs
Because they are eating huge quantities of food with vitamin C, biochemical ability to make vitamin C goes away because they are getting a steady source of it from diet already
Hydrogen peroxide
Byproduct of pathway to make vitamin C
Leads to aging and death
Certain groups of animals might have lost the ability to synthesize vitamin C because they were trying to minimize hydrogen peroxide exposure = contributes to longer lifespan
Amino acids
20 amino acids used to build proteins
Blue colour for animo acid = nonessential
Red colour for amino acid = essential
Most animals have of amino acids that are essential.
Lots variability in making or inability to make amino acids
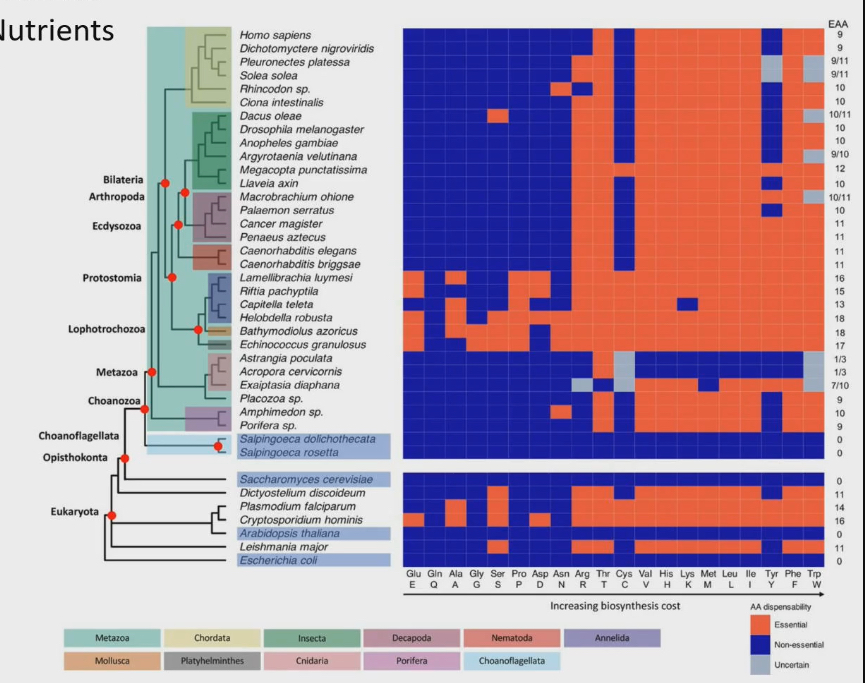
If things like yeast have the ability to make every amino acids, why would any species loose the ability to make their own
Organisms that loose ability to make amino acids, generally loose the ability to make the amino acids that are most expensive
genome size reduction
Every time animal looses ability to make a nutrients and that nutrients becomes an essential nutrients, it can get rid of any genes in genome that codes for enzymes necessary to make that nutrients
Therefore genome size gets reduced
By eliminating genes for biosynthetic pathways, animals can reduce their genome size and by extension their cell size
Benefit of reducing genome and cell size
As cells get bigger in size, relative rate they can use ATP gets lesser and lesser. Surface area to volume ratio get smaller = metabolic rate gets smaller
Smaller cell size = make and use ATP at faster rates = higher metabolic rates to digest food, reproduce, run faster
As cells get smaller, minimum time it takes to divide cells is faster
grow and repair tissues faster
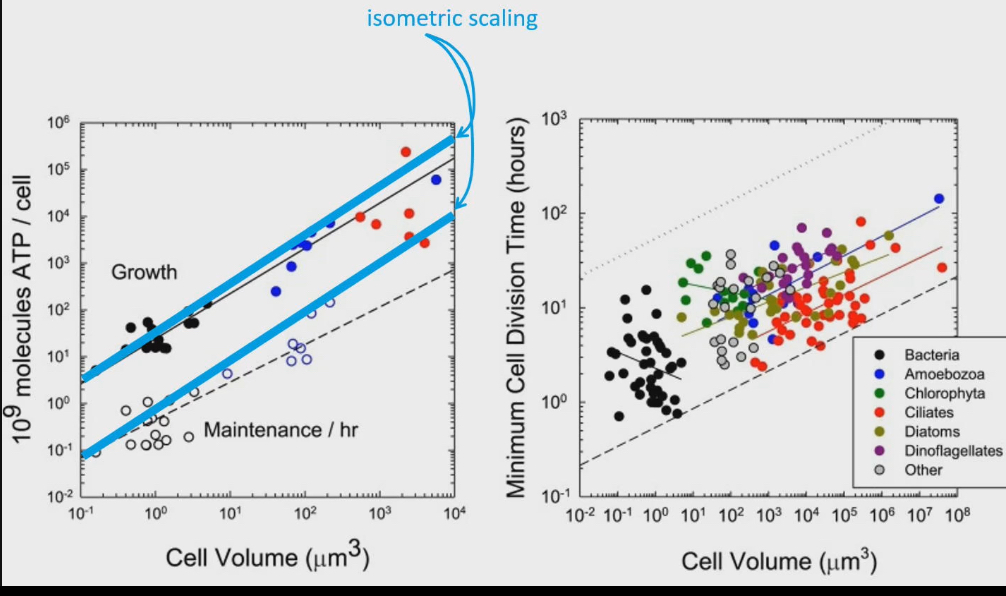
In summary an animal comprised of smaller cells will
Have. Higher metabolic capacity
Have a higher growth rate capacity
Feeding
The process of obtaining nutrients
Feeding behaviour
is modulated to meet the specific nutrient needs of the individual
Craving stems from this. Your body is encouraging you to eat food you are lacking. “Im really craving bag of salty chips” body is encouraging you to eat something salty because of a salt deficiency
That why we hear pregnant women with lots of cravings, nutrient demands are now higher
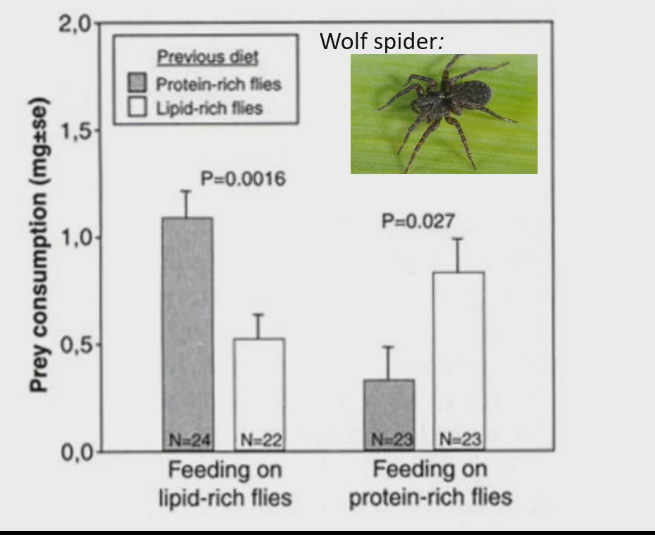
Wolf spider feeding behaviour
Feed spider flies that were earthier rich in lipids or rich in proteins
After a bit, we gave them option to each whichever fly they wanted
Turns out the spiders who previously ate the protein rich flies ate the lipid rich flies (because they were lipid deficient), and the spiders who previously ate the lipid rich flies ate the protein rich flies (because they were protein deficiant)
This means that spider has a way to tell which nutrients is in the food it is eating (which spider is lipid rich and which is protein rich so they can eat the nutrients they were originally starved of)
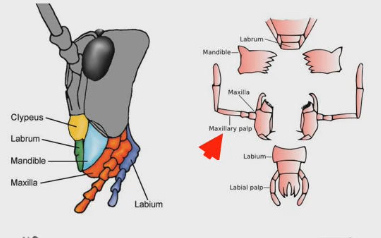
Maxillary palp
Maxillary palp
Structure in insect and spiders that can detect the nutrients in food
Like their version of our “tongue”
how responsive are neurons connected to maxillary pump to the detection of nutrients in food they are eating study
Fed insect protein rich diet or carbs rich diet and then expose them to both to see which they’d choose
Measure action potential = more action potential, the more the nutrient was exciting the palp and encouraging animal to each the nutrient
Insects that didn’t feed lots of carbs, got lots of action potential when sucrose (a type of carbs) was detected to encourage them to eat the nutrients they were deprived of
For insects that didn’t eat lots of protein, when exposed protein rich foods, palp became more sensitive got lots of action potential when amino acids was detected to encourage them to eat the nutrients they were deprived of
More leptin in circulation
More fat is present in the body
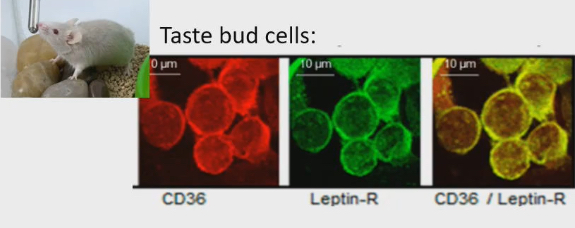
Taste bud cells and hormonal regulation
Leptin receptors in the taste bud cells (green colour)
Leptin can bind to taste bud cells to tell them how fat you are.
CD36 allows you to taste fat (red colour)
CD36 + leptin (yellow colour) they are communicating to each other
Leptin tells taste bud cells how fat we are are, taste bud cells will increase or decrease CD36 expression
If we are fat decrease CD36 expression, if we are lean increase CD36 so we can better taste fat
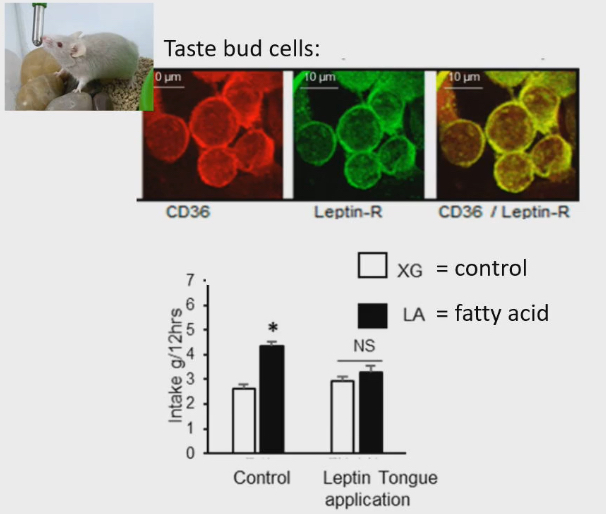
Taste bud cells and hormonal regulation
Measured how much food rats ate over 12 hrs.
Control mice
Ate food that had fat added to it
Mice they added leptin to tongue to bind to leptin receptors
Lost preference for fat consumption Because they are already a fat animal, so CD36 expression was decreased
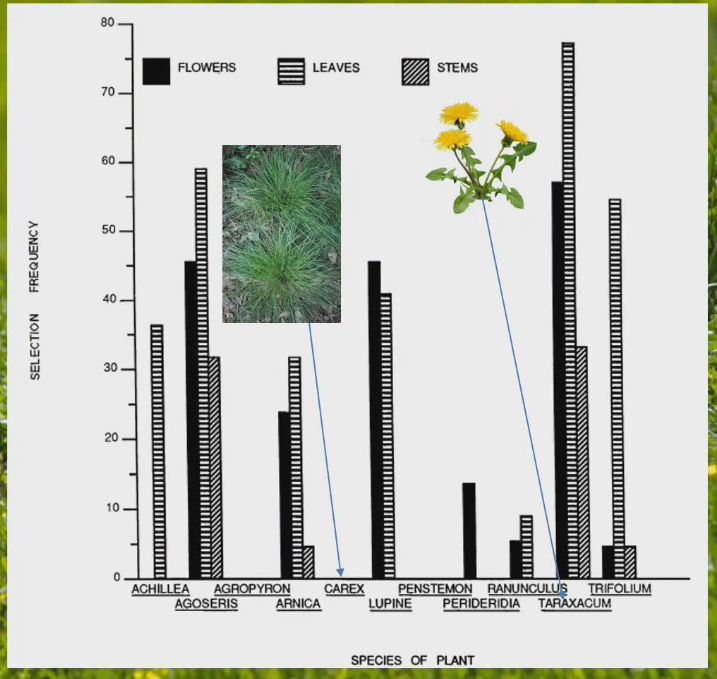
Study on selectiveness of ground squirrels choosing their food
What percentage of time do squirrels eat these foods when they come across flowers, leaves, stems
Selection frequency for dandelions was high, they ate it almost everytime they came across it
Selection frequency for carex was 0, they never ate it
Animals don’t just eat whatever they come across
Unsaturated fatty acids are important for hibernating animals
is vision important in selection of plants for squirrels
Put out dishes with food in ground squirrels environment
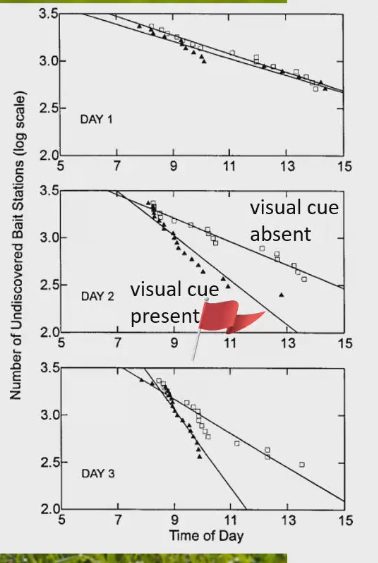
Next to half of the food dishes there would be a red flag
On first day, ground squirrels discover the food stations with and without the red flag at the same rate
On second and third day, stations with flags food disappears faster than food stations without flag
Clearly squirrels see the visual cue and remember that red flag = foods
feeding methods
Fluid feeder
Suspension feeder
Deposit feeder
Bulk feeder
Bulk feeder
Methods humans use
Animals identify foods they want to eat, grab it in some way and eat it
Ingestion of specific sizeable food items either whole or in large chunks
Ex. Most vertebrates
How is bulk feeding accomplished
Teeth are the most important structure
For something to be a tooth, it has to have a enamel (outer white covering) and dentin (softer white material in the middle)
Tooth like structure
Behave like teeth, but don’t contain enamel or dentin
Fish, amphibians and reptiles teeth
Homodont dentition, often swallow prey whole
All teeth are same shape

Mammals teeth
Heterodant dentition, bite, scrap, stab, chew
Different shape teeth between front and back teeth

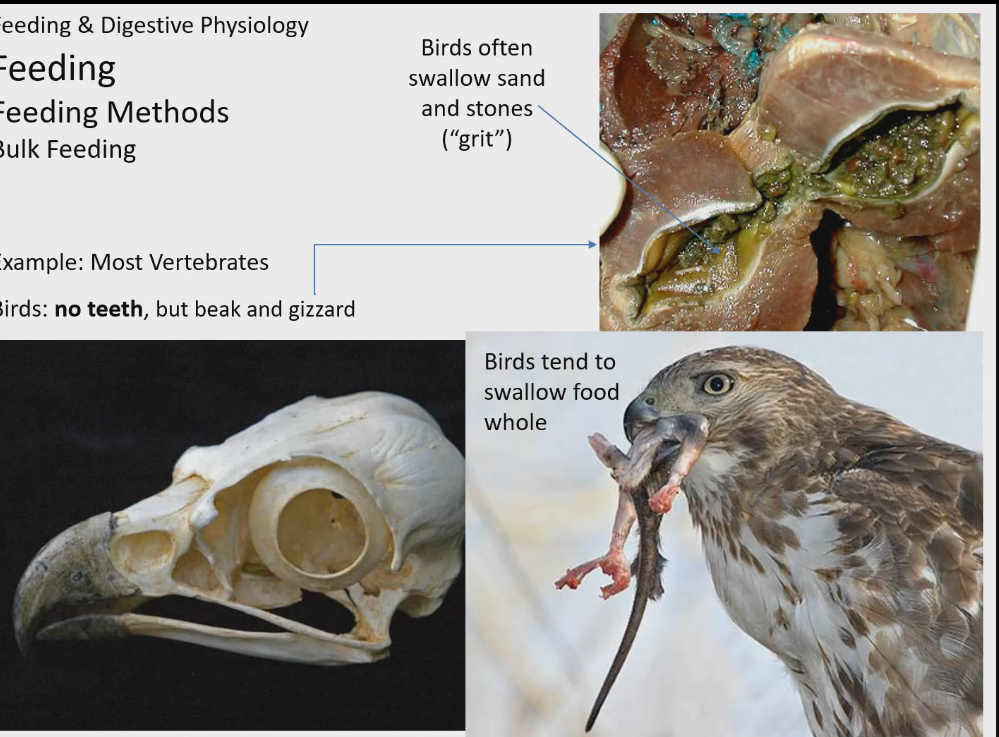
Birds teeth
Have no teeth but use beaks in a toothlike way
But they can’t chew food so it swallows it whole
Also has muscular structure in digestive system called a gizzard.
Very thick and muscular
Grinds down the food thats been swallowed whole to make it easier to digest
Muscular action helps to grind food
Birds will swallow sand and stones and store them in gizzard to act as a grit. As food you swallow is being grinded by gizzard, you aren’t just relying on muscular walls of gizzard but also on stones and sand to help

Why have birds abandoned teeth to have a gizzard
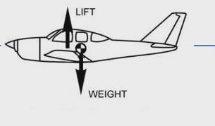
Hypothesis #1: Well if you have no teeth, jaw is lighter. Helps birds be lighter to fly
But gizzard is just as heavy
Hypothesis now: improving efficiency of bird flight. Just like planes, efficiency of flying objects is highest when centre of mass (gravity pulling on you the most) = centre of lift (whatever helps them fly, wings for bird)
This alignment means that you are pushing up at same spot gravity is pulling you down, maintain good level flight
Teeth located at front of body, but wings are at centre of body then centre of mass is not equal to centre of lift, and there would be no efficient flying
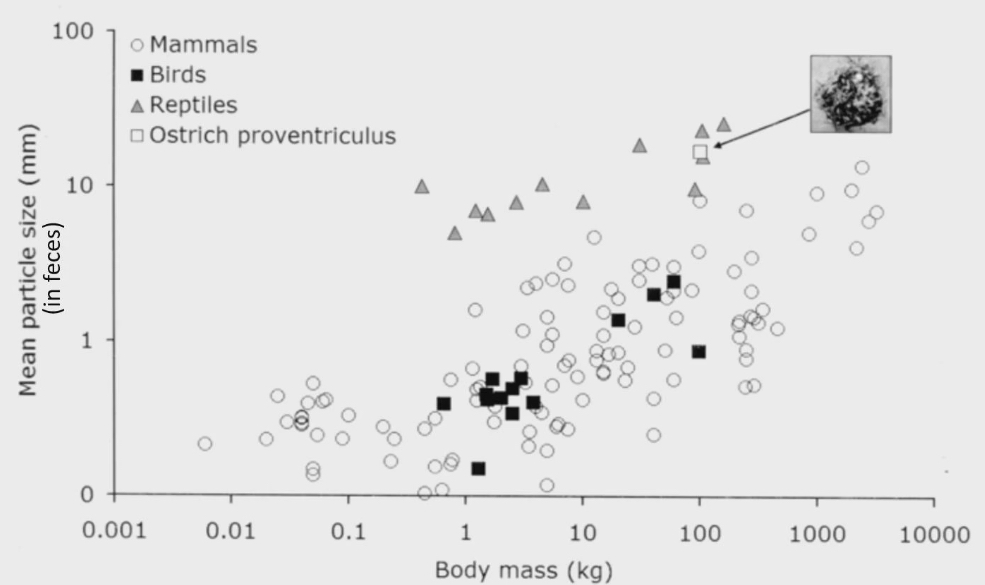
are teeth better than gizzard for digesting food study
Measured mammals, reptiles and birds, measured mean particle size in feces
Particle size in birds and mammals are almost the same. Turns out gizzard and teeth are equally as efficient in grinding food down to be digested
Mammals and birds are endothermic. They need to get as much energy out of food as possible so they grind particles they eat to be very small
Reptiles are above birds and mammals are not as good at breaking food down, because there was more particles in their poop. They are ectothermic = lower metabolic rate = don’t need to get as much nutrients from food they are eating
Deposit feeder
Eat substrate living on or in
Crabs live on mud, and they mud
Another ex. Earthworm, they live in dirt and they eat the dirt as they move
Fluid feeder
Consumes some kind of fluid with nutrients
Ex. Hummingbird hovers above flower and consumes all the nectar in it
Ex. Mosquitos feed on our blood
Suspension feeding
the capture and ingestion of food particles that are suspended in water.
Ex. Whales taking a big gulp of water and eating whatever organisms are suspended in that Ex. Krill, zooplankton
baleen whale Have baleens that act as a filter to get rid of the water after the big gulp, but trap all the organisms inside mouth