Micro Lecture 14 - Molecular Info Flow: Replication
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
84 Terms
Information is…
independent of the medium upon which it is stored or encoded
Meischer
1869
Nuclein
Griffith
1928
Transformation
Avery, Macleod, McCarty
1944
transformation
Hershey and Chase
1944
Blender experiment
Chargaff
1948
the “rules” - took things apart to discover A=T and G=C
What are monomers
Bases
Nucleosides
Nucleotides
What are bases
A C G T
What are nucleotides made of
base
sugar
phosphate
What are nucleosides made of
base
sugar
Know numbers on monomer slide (1,2,3..C)
…
What are purines and their structure
A and G
two ring structure
Larger
What are pyrimidines and their structure
C, U, and T
one ring structure
smaller
what did Franklin and Wilkins do
did X-ray diffraction pattern from a DNA smear
knew DNA was a helix but didnt recognize what they were looking at
Watson and Crick
figured out DNA structure from X-ray
Watson and Crick’s model
(how many nm per twist)
(how many base pairs per twist)
(how many H bonds between different base pairs)
postulated anti-parallel double stranded molecule
bases inside
3.4 nm per twist
10 bp per twist
C - G (3 H bonds)
A - T (2 H bonds)
explain Chargaff’s rules as they were understood
Purines match with pyrimidines
hydrogen bonds form between them
both DNA strands have the….
same amount of information
bases in one strand are___________ to those in the other strand
complementary
What is the modern central dogma (1950-today)
DNA —> RNA —> protein
write out todays chart
What did Meselson and Stahl observe
in 14N media, there was evidence of semiconservative DNA replication
What is the genome
complete cell DNA sequence
what is the genotype
specific DNA sequence
what is phenotype
appearance and/or behavior
genotype + environment = phenotype
the genome consist of ______ molecules (free-living cells range from _________ nucleotides)
Large
583,000 up to 150,000,000,000
Genomes of prokaryotes are _______ and ________ (mostly)
circular
haploid
DNA is ______ to fit in the cell
packed
the ______ of an E. coli cell is packed
nucleoid
Circle of ___________ is __________ the size of the cell
ds DNA
1500x
multiple loops held by…
each loop has _____________
anchoring proteins
supercoiled DNA…
What effect does supercoiling have on DNA
it compacts it
positive supercoils are
over winding
Unsupercoiled DNA has ____ wind(s) for _____ bases
1 wind for 10 bases
negative supercoils…
under winding
what do supercoils do to DNA
it twists DNA
What do topoisomerases do
they regulate supercoils
What does Type I Topoisomerases do
they relieve torsional stress caused by supercoils
what do Type II Topoisomerases do
they introduce negative supercoils
What do archaeal topoisomerases do
They introduce positive supercoils
DNA replication is ___________
semiconservative
Where does DNA replication begin
at oriC
DNA is opened at ______
oriC
What are the general steps of DNA replication
DNA opened at oriC
polymerization occurs bi-directionally around chromosome
Helicase unwinds DNA and recruits Primase
Primase begins replication
DNA polymerase III clamped to strand
DNAP III adds nucleotides in 5’ —> 3’ direction
RNase H removes primers
DNAP I fills gaps
Ligase seals in Okazaki fragments
What follows the opening of DNA at oriC
polymerization
DNA polymerization moves…
bi-directionally around the chromosome
____________ melts DNA
DNA Helicase
What places helicase and where is it placed
loader places helicase at each end of origin and each move in opposite directions
What does DNA helicase do
it unwinds DNA
Helicase recruits _____
primase
what does DNA polymerase need
a free 3’OH
What is primase’s function
to begin replication
builds an RNA primer forms 3’ OH for DNA to attach
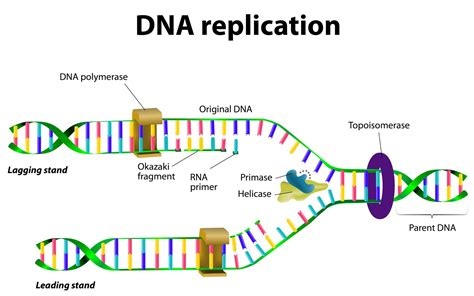
primer recruits…
clamp loader to each strand
What does the clamp (recruited by primer) bind to strand
clamp binds DNA Polymerase III to strand
Which way does Polymerase move down the strand
in the 5’ → 3’ direction on each strand (add bases to the 3’ end)
where does energy for polymerization come from
from phosphate groups on the recently added nucleotide
each fork has…
two strands
what is the leading strand
steady growth occurs here
the leading strand follows helicase
what is the lagging strand
polymerase continues to previous primer and the clamp loader places primase on new site (the primase adds a short RNA primer, which is continued by the polymerase to form an okazaki fragment)
it is built in pieces because it cannot continually add bases because it is in the 3’ —> 5’ direction
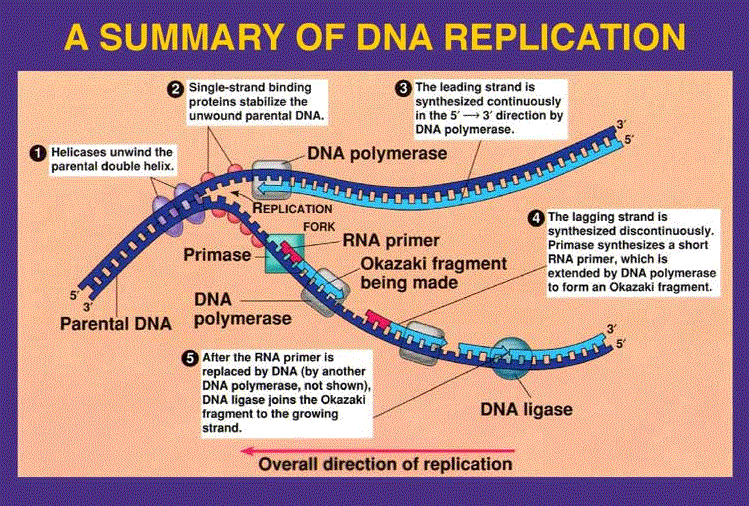
the lagging strand has ___________________
okazaki fragments
DNA present in _________ base pieces
1000
What does RNase H do
it removes primers
How many primers are there for each leading strand
One primer
How many primers are there for each lagging strand
many
how many primers are there per Okazaki fragment
one
Gaps (segments of Okazaki fragments) are created by _________________
DNA Polymerase I
what seals the nicks in DNA (the Okazaki fragments)
Ligase
Both forks move to _______ Sites
ter
Fork movement…
is simultaneous
move in opposite directions until both meet again at terminus
Replisomes are…
actually stationary
(enzymes involved in DNA replication for the replisome)
DNA is threaded through…
the replisomes
What are plasmids
extrachromosomal pieces of DNA
_______________________ plasmids
low-copy-number
How many plasmid copies are there per cell for Low-copy-number plasmids
one or two
_______________________ plasmids
High-copy-number
How many plasmid copies are there per cell for high-copy-number plasmids
up to 500 copies per cell
what do high-copy-number plasmids do
they divide continuously
they randomly segregate
What are the two types of plasmid replication
bidirectional and unidirectional
bidirectional replication of plasmids is…
similar to chromosomal replication
unidirectional replication of plasmids is also called
rolling circle replication
Unidirectional replication starts at…
nick bound by RepA protein
unidirectional replication…
provides 3’ OH for replication
Helicase moves around plasmid repeatedly
unidirectional replication is used by many _______________
bacteriophage viruses
plasmid genes are…
advantageous under special conditions
what are some advantages to plasmid genes
antibiotic resistant genes
genes encoding resistant to toxic metals
genes encoding proteins to metabolize rare food sources
virulence genes to allow pathogenesis
genes to allow symbiosis