Tissues part 1
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Types of epithelial, connective, muscle, and nervous tissue. With their description, function, and location.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
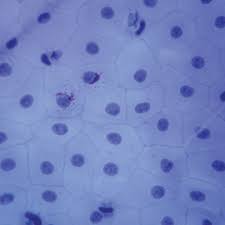
Simple Squamous (Epithelial)
- 1 layer of thin flat cells
- allows diffusion of molecules (movement)
-found in lungs or kidneys

Simple Cuboidal (Epithelial)
-1 layer of round cells
- secretes and absorbs
-found in ducts or kidneys
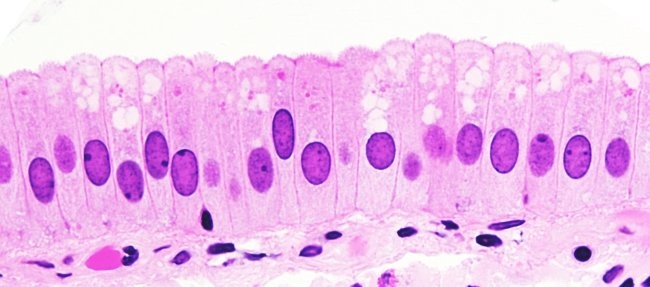
Simple Columnar (Epithelial)
-1 layer of rectangular cells
-absorbs and secretes
-found in the stomach and small/large intestines
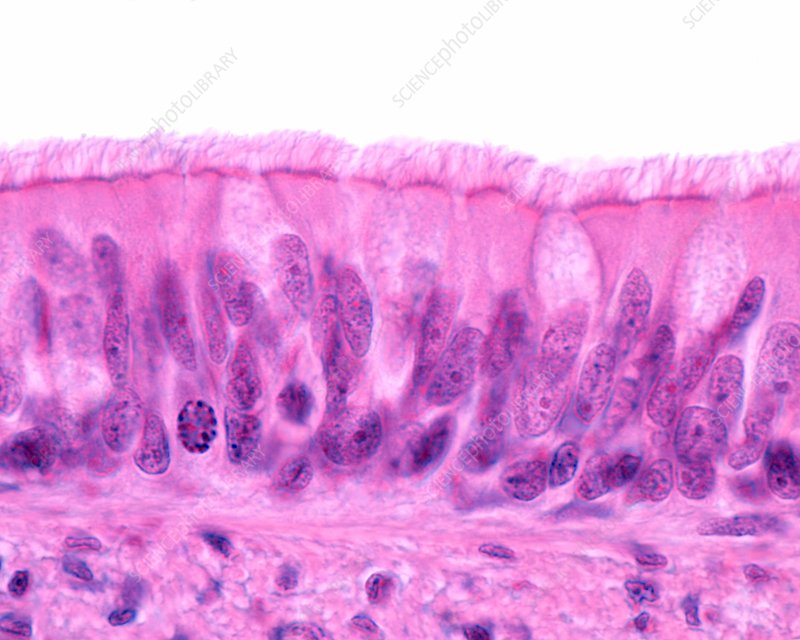
Pseudo-stratified Columnar (PCC)(Epithelial)
-has cilia and looks rectangular but isn’t
-acts as a filter
-found in nasal, larynx, trachea
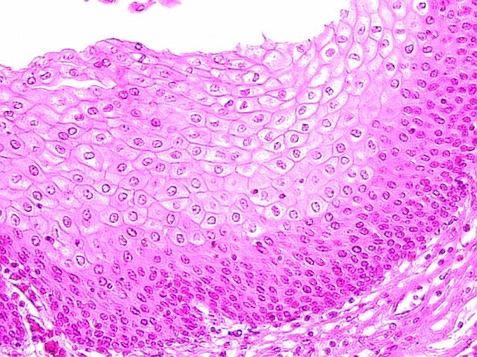
Stratified Squamous (Epithelial)
-many layers of flat cells
-protection
-found in different organs, skin, pharynx, and esophagus
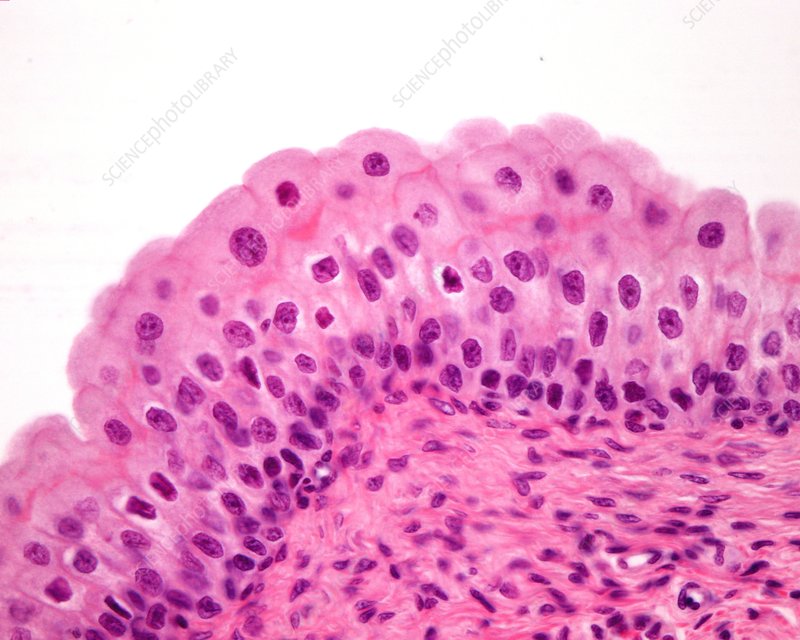
Transitional (Epithelial)
-2 to 5 cells thick, Cuboidal surface
- used for organs to stretch
-found ureters
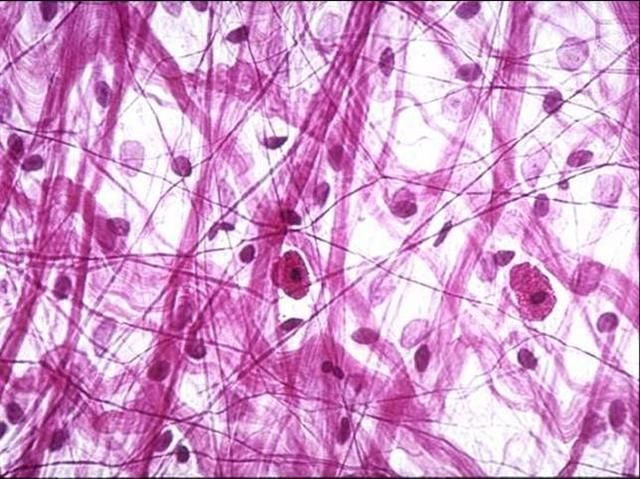
Areolar (Connective Loose)
-loose but can see thick (collagen) and thin (elastic) fibers
-is tough and has elasticity
-found in the dermis and wrapping organs
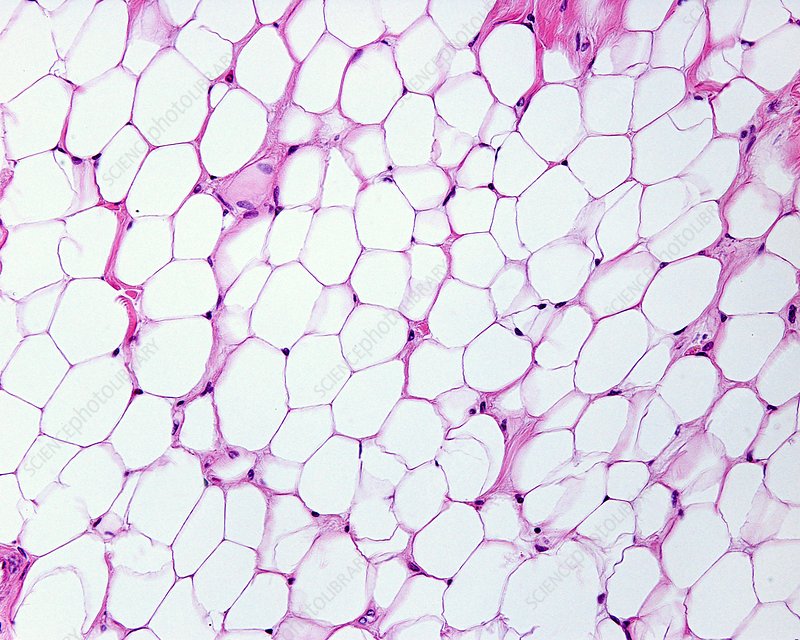
Adipose (Connective Loose)
-fat cells
-used to insulate and an energy reserve
-found under the skin
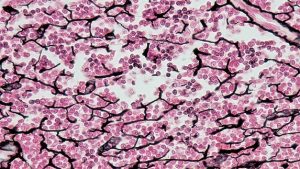
Reticular (Connective Loose)
-looks like cherry blossoms, short and black
-forms stroma and provides structural support
-found in the stroma, spleen, lymph nodes and bone marrow
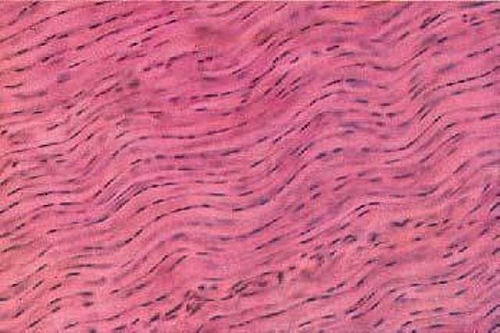
Dense Regular (Dense)
-parallel, organized, few nuclei
-it helps connect organs
-found in tendons
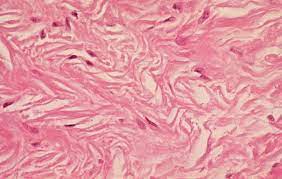
Dense irregular (Dense)
-collagen in many directions and few nuclei
-is for strength
-found in the dermis
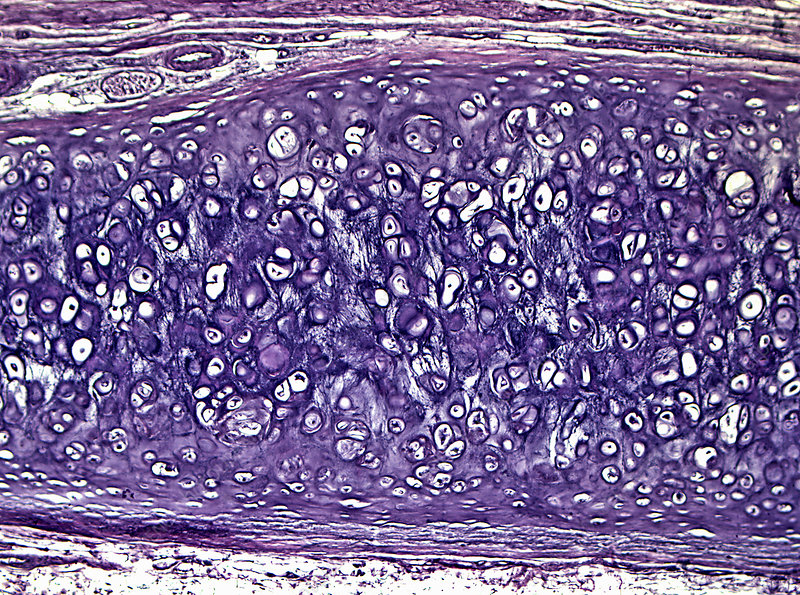
Hyaline (Cartilage)
-most abundant
-often paired chondrocytes, purple, amorphous
-is tough stuff and slick
-found in the shoulder joint trachea
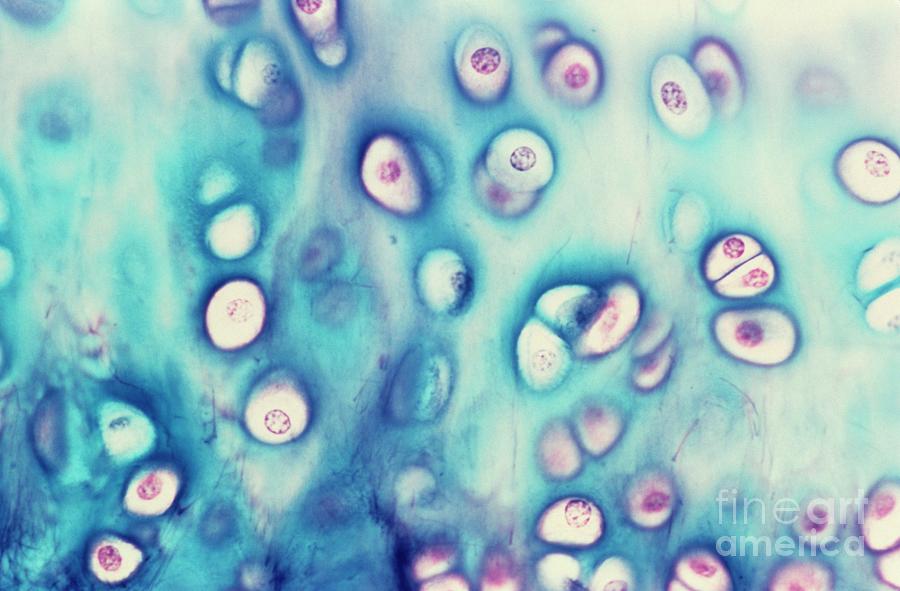
Elastic (Cartilage)
-black in color
-chondrocytes with lots of black in it
-is for flexibility
-found in external ear….
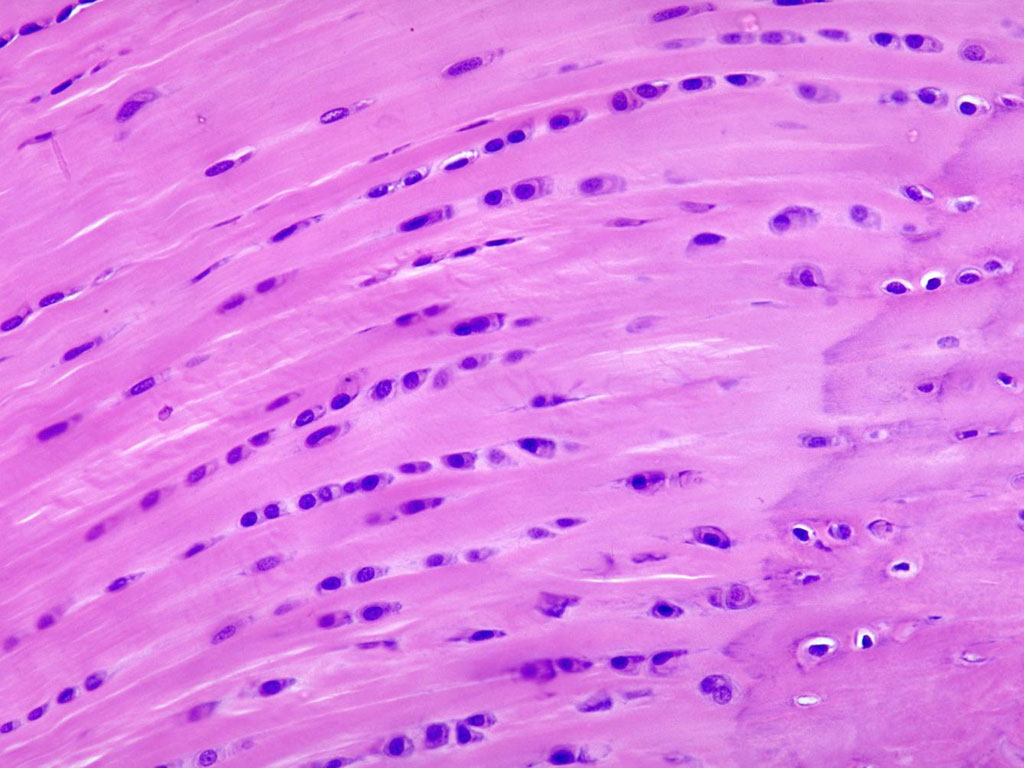
Fibrocartilage (Cartilage)
-is teal and has some collagen in it
-acts as the bodies shock absorber
-found in the knees and between vertebrae
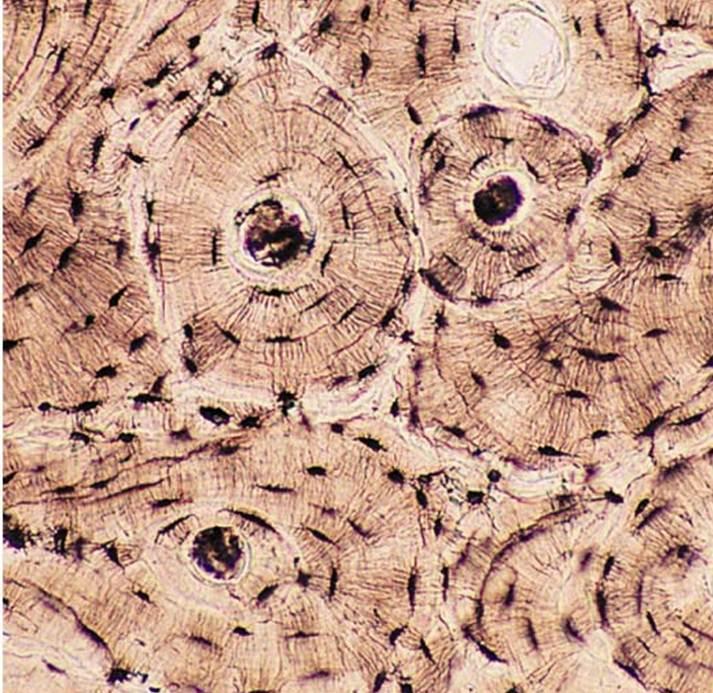
Bone (Other)
-looks like growth rings on a tree, made of osteocytes (brown and tan)
-it protects the structure and is a mineral reserve
-found in the skeleton
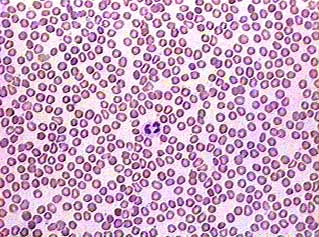
Blood (Other)
-Biconcave center (red with a thin center, RBC WBC)
-used to transport oxygen
-found in cardiovascular
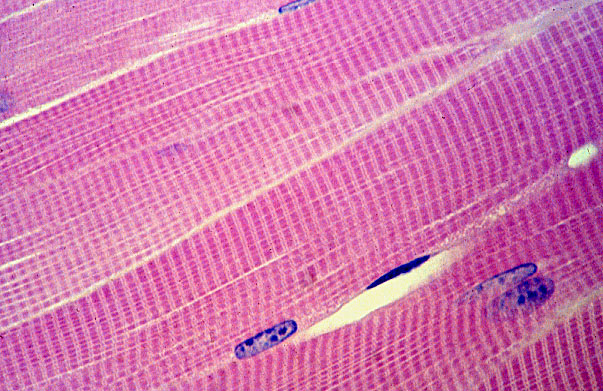
Skeletal (Muscle)
-striated
-long cylindrical cells that are multi nucleic
-is used for movement
-found in bones
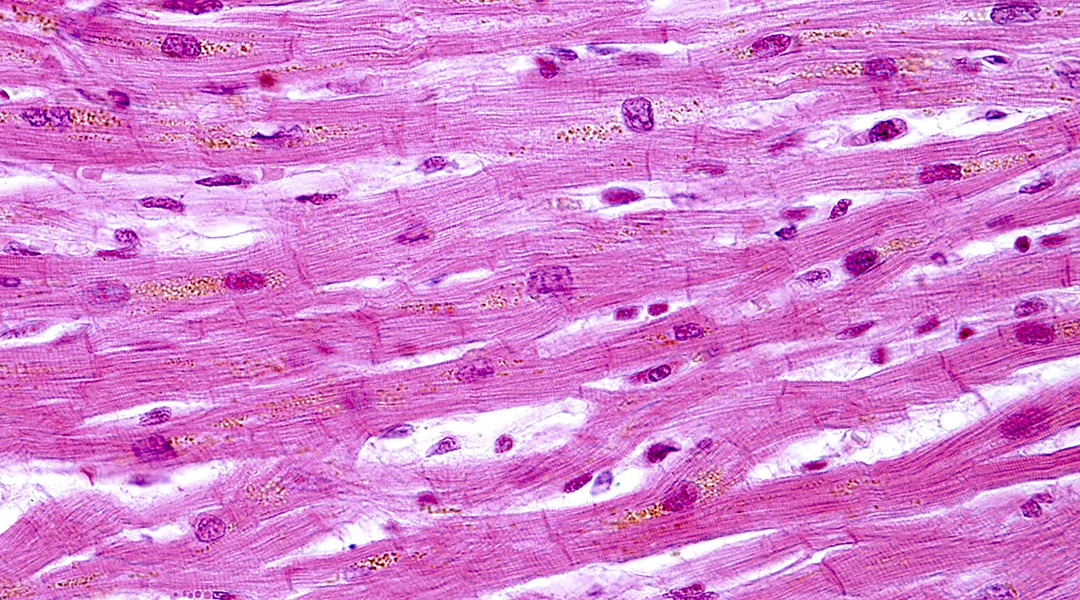
Cardiac (Muscle)
-striated, branched intercalated discs (gap)
-used for pumping for the heart
-found in the heart
Visceral/Smooth (Muscle)
-has no striations
-used for one-way movement (peristalsis)
-found in hollow organs
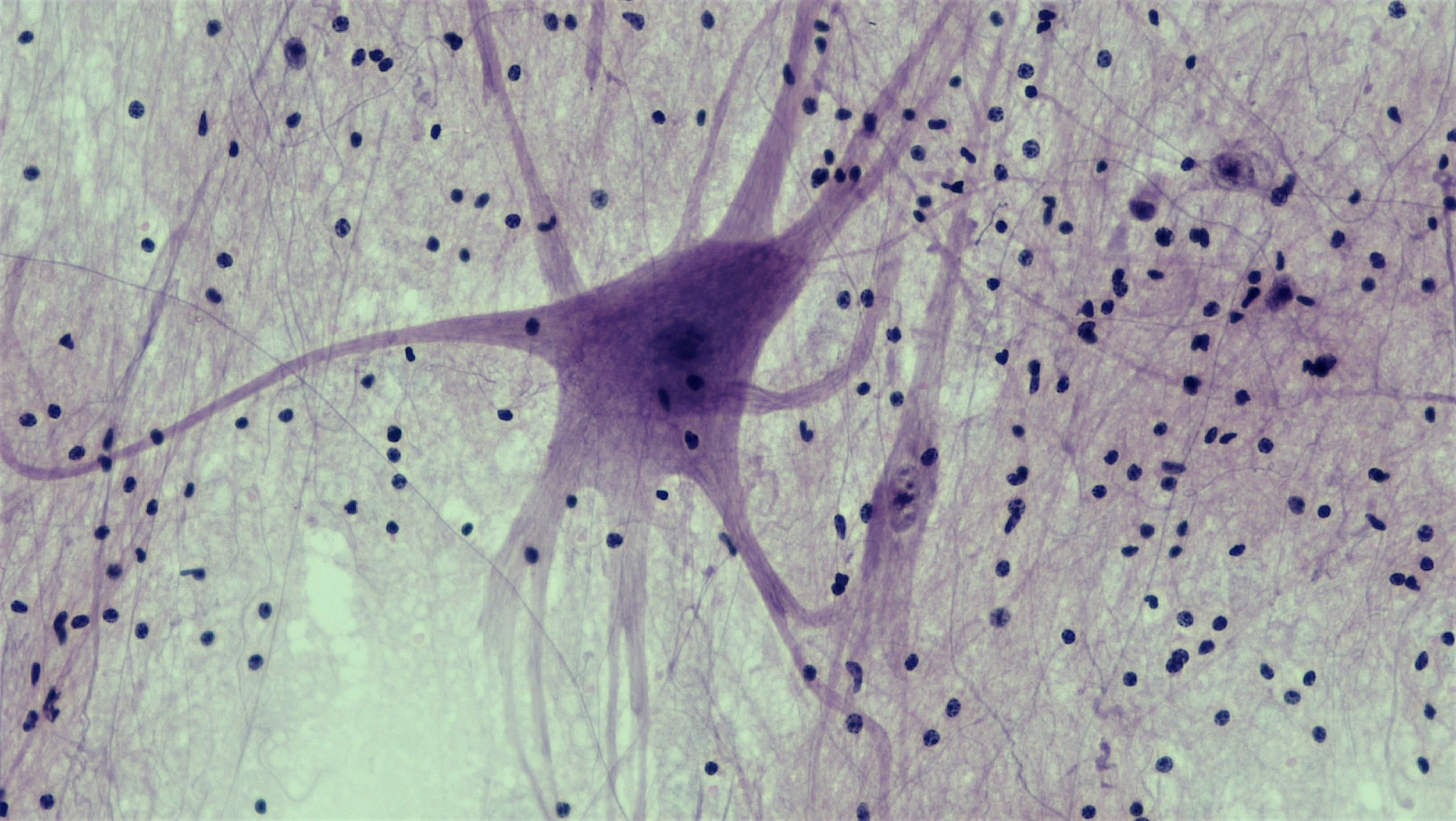
Nervous
-large neurons with tiny neuroglia
-used to respond to stimuli
-found in the brain and spinal cord