serotonin
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
what type of neurotransmitter is serotonin
indolamine
role of serotonin
controls mood, appetite, sleep
regulates cognitive functions including memory and learning
how is serotonin synthesised
from amino acid tryptophan in presynaptic serotonergic neurones
how is serotonin stored and released
stored in vesicles and released by exocytosis
what receptors do serotonin bind to
specific receptors serotonin or 5-HT receptors and produces either excitatory or inhibitory postsynaptic effects
how is serotonin removed from synaptic cleft
by specific serotonin transporters and degraded by enzyme monoamine oxidase
there are 7 different types of 5-HT receptors which serotonin binds once released. what does 5-HT1 receptors do
coupled to Gi/o heterotrimeric G proteins
Gi/o activation leads to inhibition in postsynaptic activity via inhibition of adenylyl cyclase
there are 7 different types of 5-HT receptors which serotonin binds once released. what does 5-HT2 receptors do
5-HT2 receptors are coupled to Gq/qq G proteins
their activation leads to excitation or increase in postsynaptic activity via activation of PLC and release of Ca2+ from intracellular stores
there are 7 different types of 5-HT receptors which serotonin binds once released. what does 5-HT3 receptors do
ligand-gated ion channels
activation leads to opening of ion channel permeable to Na+
leads to depolarisation and increase in postsynaptic activity
there are 7 different types of 5-HT receptors which serotonin binds once released. what does 5-HT4,6,7 receptors do
coupled to Gs G protein
activation of adenylyl cyclase
leads to excitation or increase in postsynaptic activity
there are 7 different types of 5-HT receptors which serotonin binds once released. what does 5-HT5 receptors do
coupled to Gi/o G protein
inhibits adenylyl cyclase
inhibition or decrease in postsynaptic activity
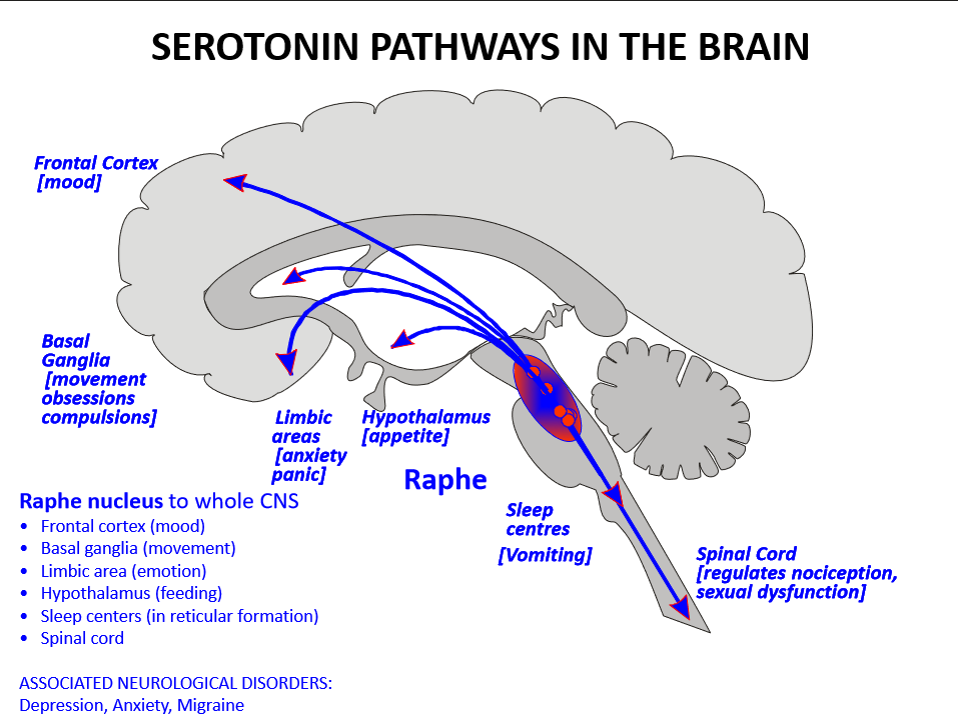
where is serotonin mainly produced and where does it project
raphe nuclei (midbrain/pons); projects to hypothalamus (appetite), basal ganglia (movement), limbic system (emotion), neocortex (cognition), and spinal cord (anti-nociceptive)
how is serotonin action terminated at the synapse
by the energy dependent process of serotonin transporters
Sodium/ potassium ATPases use energy from ATP hydrolysis to create a concentration gradient of ions across the pre-synaptic membrane. This gradient drives the opening of the transporter and co-transport of sodium and chloride ions and dopamine from the synaptic cleft. Potassium ions binding to the transporter enable it to return to the outward position. Release of the potassium ions into the synaptic cleft equilibrates the ionic gradient across the pre-synaptic membrane
drugs that affect serotonin
Reuptake inhibitors: fluoxetine (Prozac) → depression, anxiety, OCD
Hallucinogens: LSD → stimulate 5-HT2A → visual distortions