ANAT 315
1/351
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
352 Terms
Pectoralis Major
Origin: Anterior surface of clavicle, anterior surface of sternum, external oblique aponeurosis
Insertion: lateral edge of the intertubercular groove, inferior to the greater tubercle.
Action: Adducts, flexes + medially rotates arm
Innervation: Medial + lateral pectoral nerves

Pectoralis Minor
Origin: Ribs 3-5
Insertion: Coracoid process of scapula
Action: Pulls scapula down and anteriorly
Innervation: Medial pectoral nerve

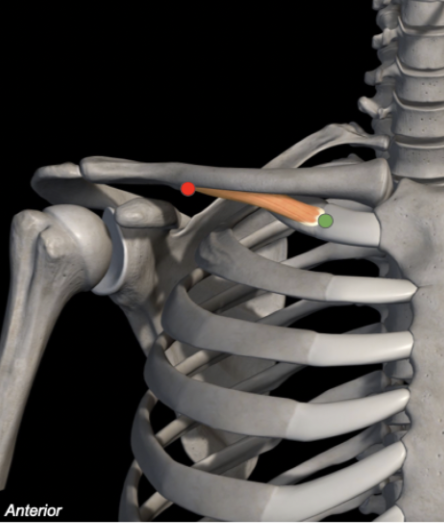
Subclavius
Origin: 1st Rib
Insertion: Inferior surface of clavicle
Action: Pulls down and stabilizes clavicle
Innervation: C5-C6
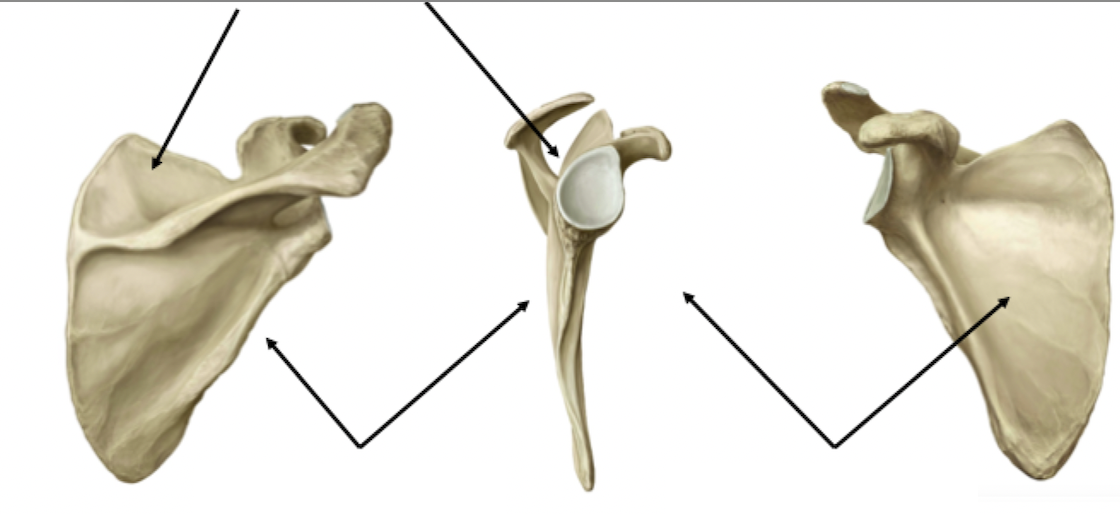
Serratus Anterior
Origin: Surface of ribs 1-8
Insertion: Medial surface of scapula on the costal surface
Action: Protracts scapula and elevates ribs
Innervation: Long thoracic nerve

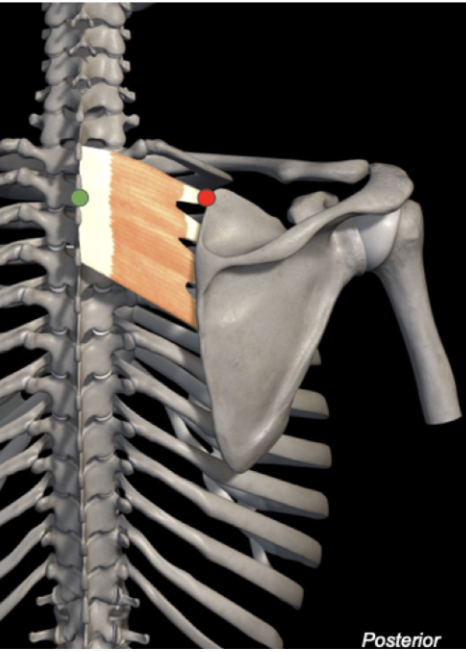
Serratus Posterior Superior
Origin: C7-T3 spinous processes
Insertion: Superior borders of ribs 2-4
Action: Elevates upper ribs
Innervation: T1-T4 ventral rami
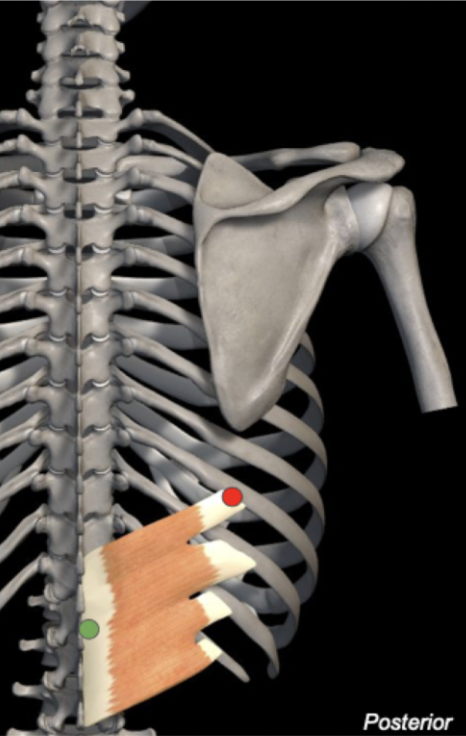
Serratus Posterior Inferior
Origin: T11-L2 spinous processes
Insertion: Inferior border of ribs 9-12
Action: Depresses lower ribs
Innervation: T9-T12 anterior rami
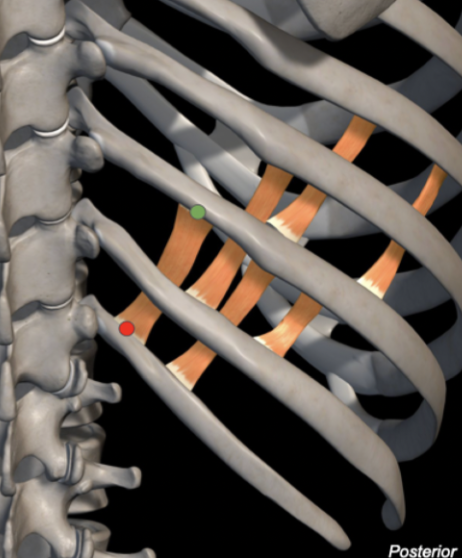
External Intercostals
Origin: Inferior border of ribs
Insertion: Superior border of rib below
Action: Elevates ribs
Breathing: Inspiration
Innervation: Intercostal nerves
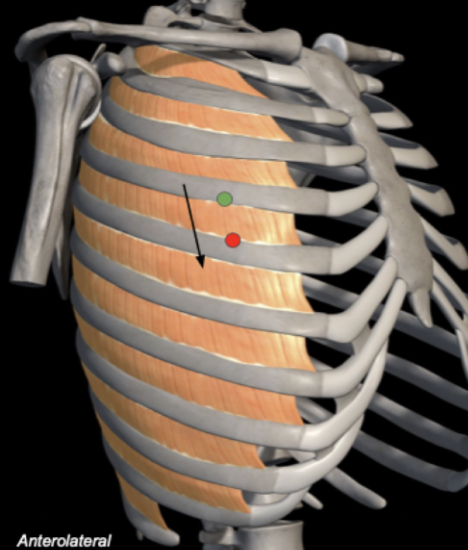
Internal Intercostals
Origin: Inferior border of ribs
Insertion: Superior border of rib below
Action: Lowers ribs
Breathing: Expiration
Innervation: Intercostal nerves
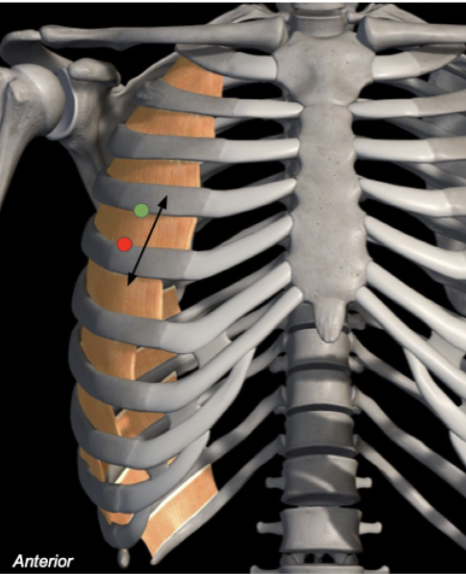
Innermost Intercostals
Origin: Inferior border of ribs
Insertion: Superior border of rib below
Action: Lowers ribs
Breathing: Expiration
Innervation: Intercostal nerves
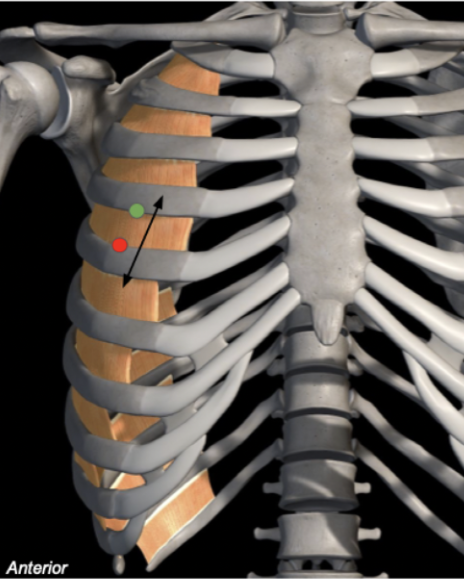
External - medial + inferior
Internal - medial + superior
hands in pockEt - external
hands in pIts - internal
Which way do the intercostal muscle fibres point?
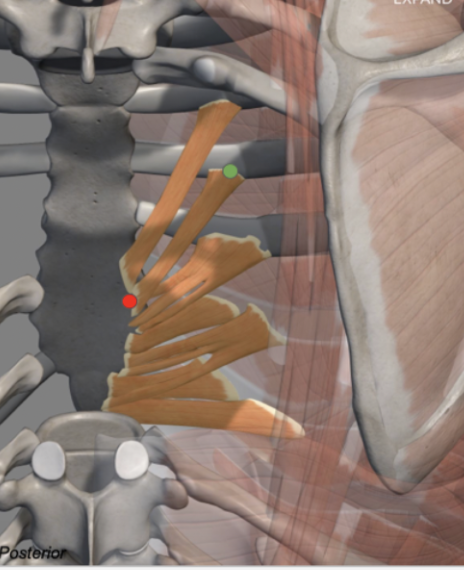
Transversus Thoracis
Origin: Pleural surface of ribs 2-6 (anteriorly)
Insertion: Posterior surface of sternum, xiphoid process
Action: Lowers ribs
Breathing: Expiration
Innervation: Intercostal nerves
Subcostales
Origin: Pleural surface of ribs 2-6 (posteriorly)
Insertion: Superior border of rib below
Action: Lowers ribs
Breathing: Expiration
Innervation: Intercostal nerves
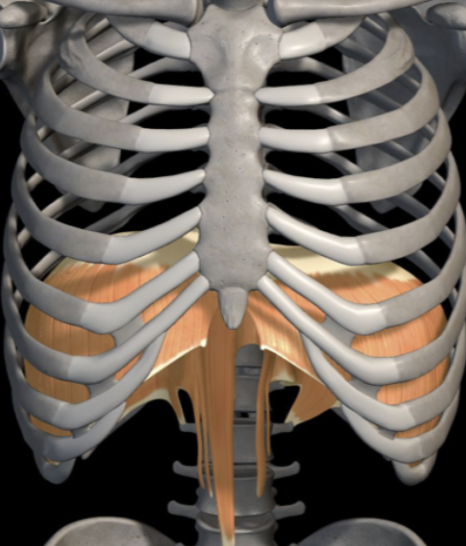
Diaphragm
Origin: Xiphoid process of sternum, L1-L4 vertebra, costal arch of ribs 7-12
Insertion: Central tendon of diaphragm
Action & Breathing: Contracts and compresses abdomen (inspiration); relaxes (expiration
Innervation: Phrenic nerve; C3, 4, 5 keeps diaphragm alive
Reference position for anatomical directional terms
Anatomical Position
Anterior/posterior (Front half/Back half)
Coronal/Frontal Plane

Right/left
Sagittal (Mid-Sagittal) Plane
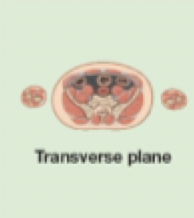
Superior/inferior (Upper half/Lower half)
Transverse/Horizontal Plane
Medial: toward the midline
Lateral: away from midline
Medial & Lateral
Proximal: toward an attached base
Distal: away from an attached base
Proximal & Distal
Posterior: toward the back, behind
Anterior: toward the front, in front of
Posterior & Anterior
Superficial: toward/closer to body surface
Deep: away from body surface/toward interior of body
Superficial & Deep
Superior: higher
Inferior: lower
Superior & Inferior
Axial & Appendicular
The skeleton can be divided into…
Bones of the skull
Accessory bones
Vertebral column
Thoracic cage (ribs, sternum, thoracic vertebrae)
AXIAL SKELETON
Upper limbs and pectoral girdle
Lower limbs and pelvic girdle
APPENDICULAR SKELETON
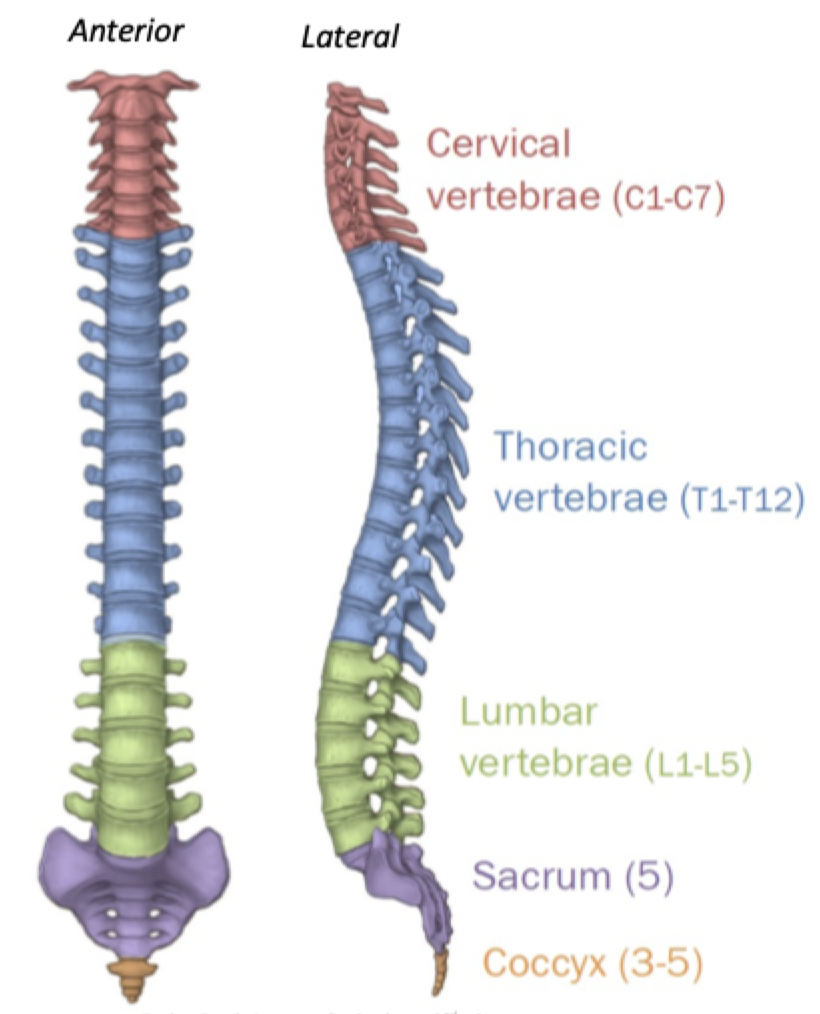
26 bones
24 vertebrae (7 Cervical 12 thoracic 5 lumbar)
Sacrum
Соссух
What makes up the vertebral column?
Column of support
Protection of spinal cord
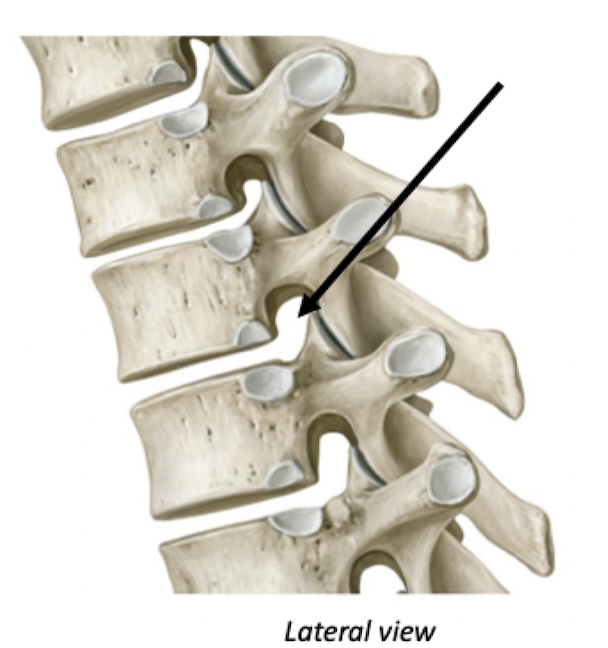
Passage for nerves
Attachment site for muscles
Functions of the vertebral column
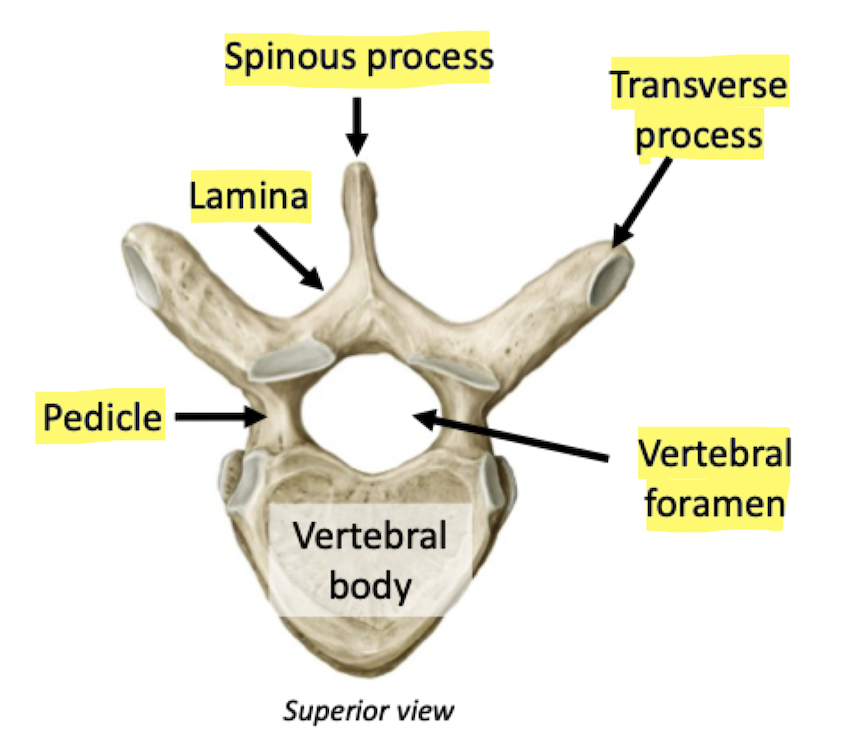
Label
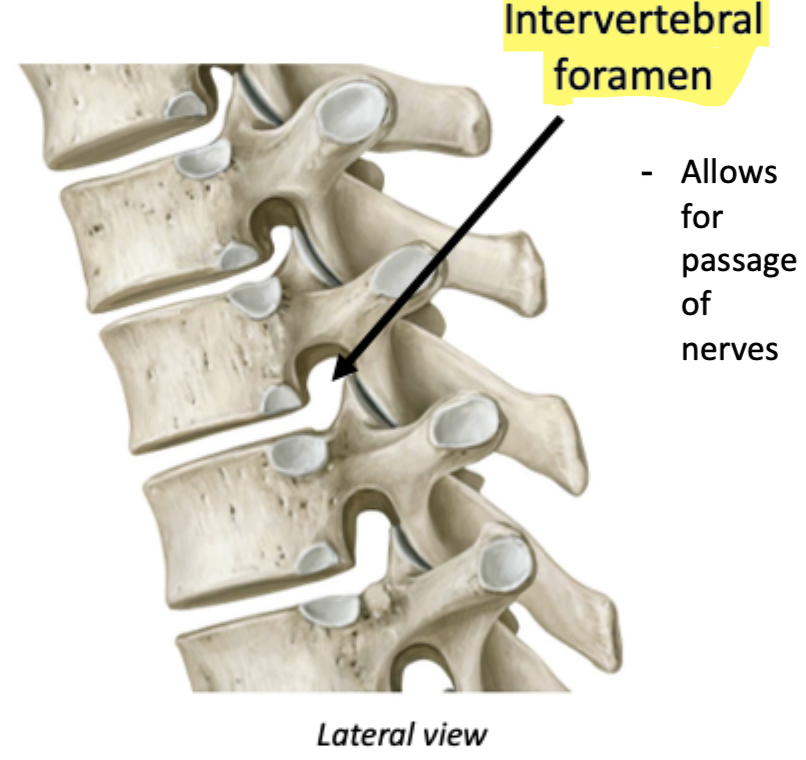
Label + Function
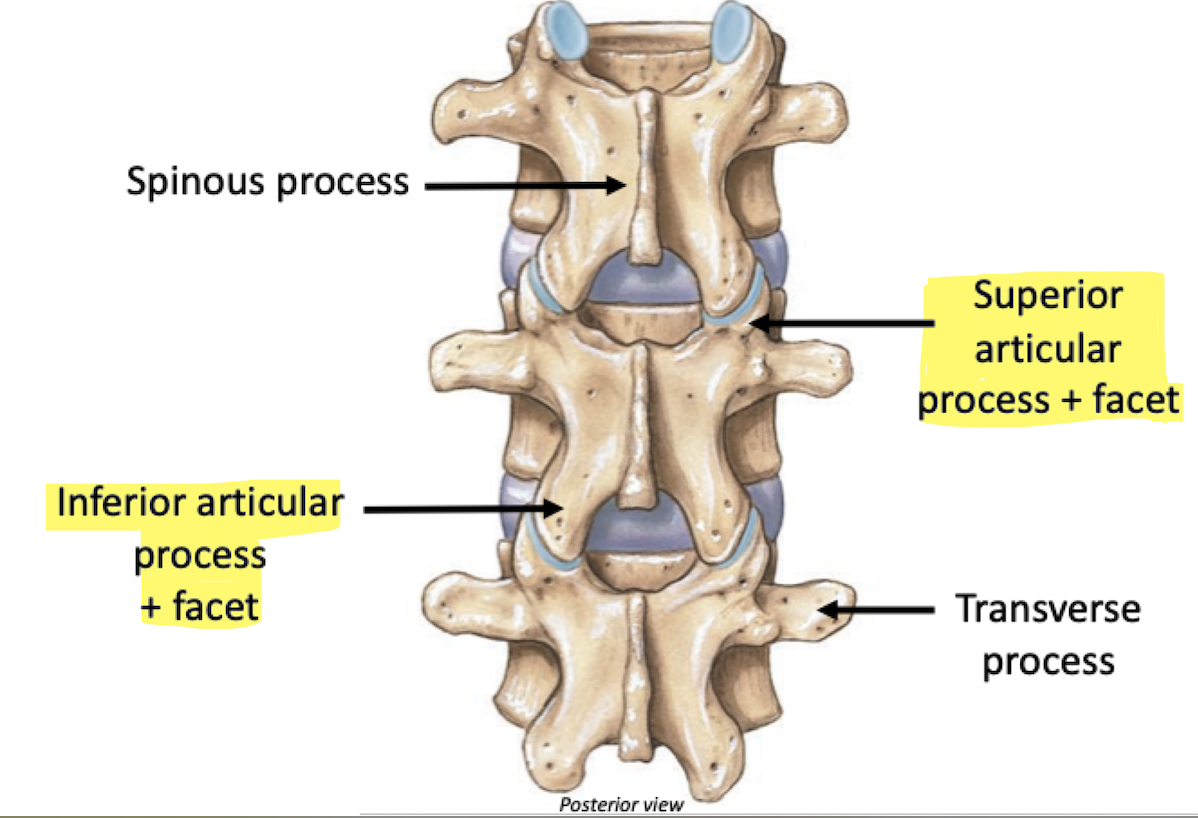
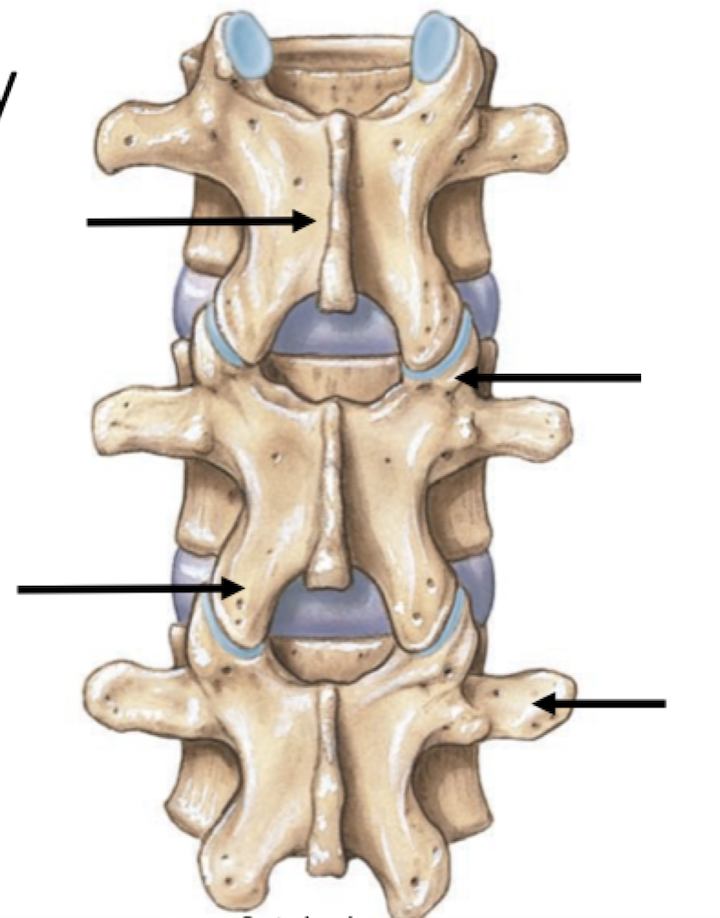
Label
Refers to a joint
Articular
Smooth, flat surface
Facet
Hole
Foramen
Projection
Process
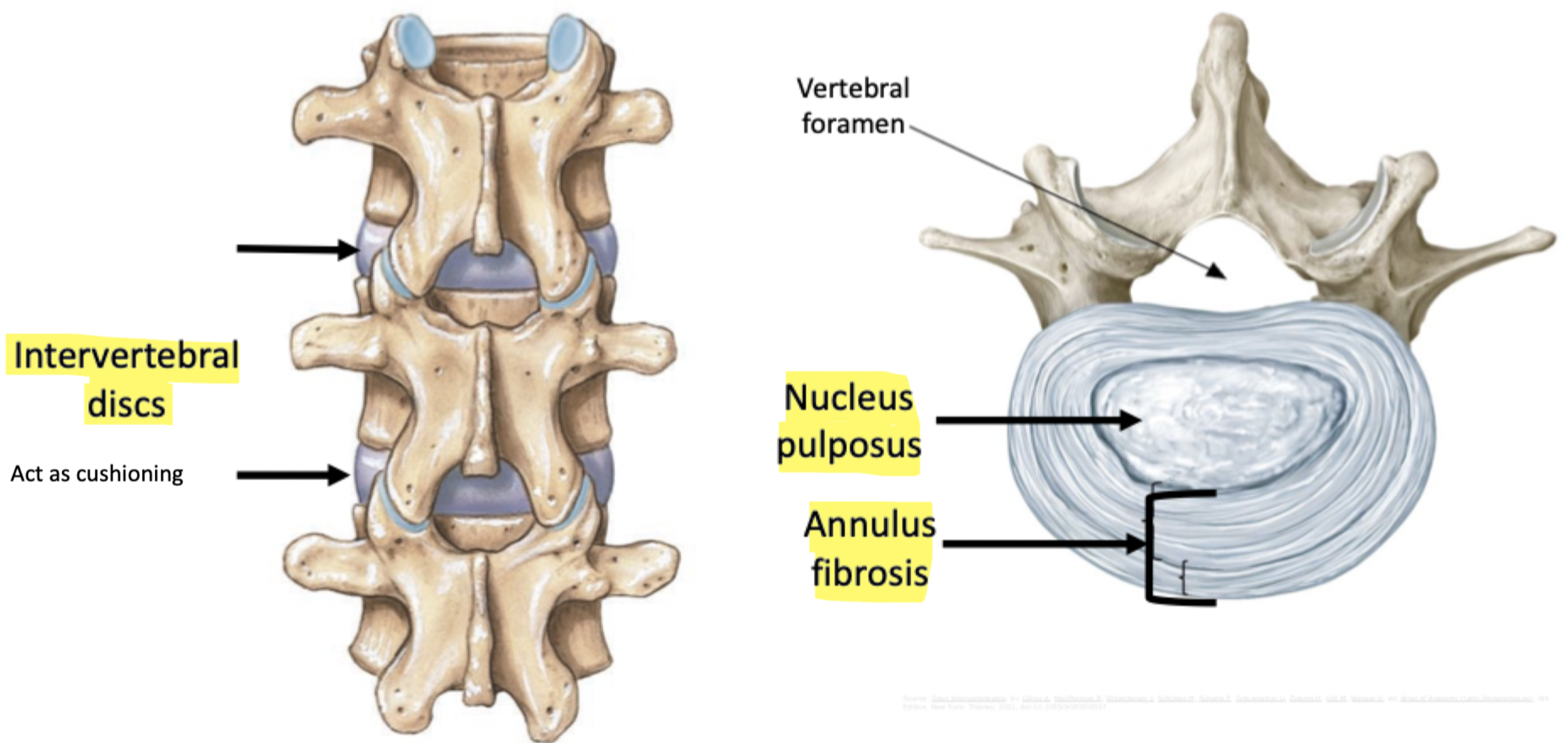
Label + Function
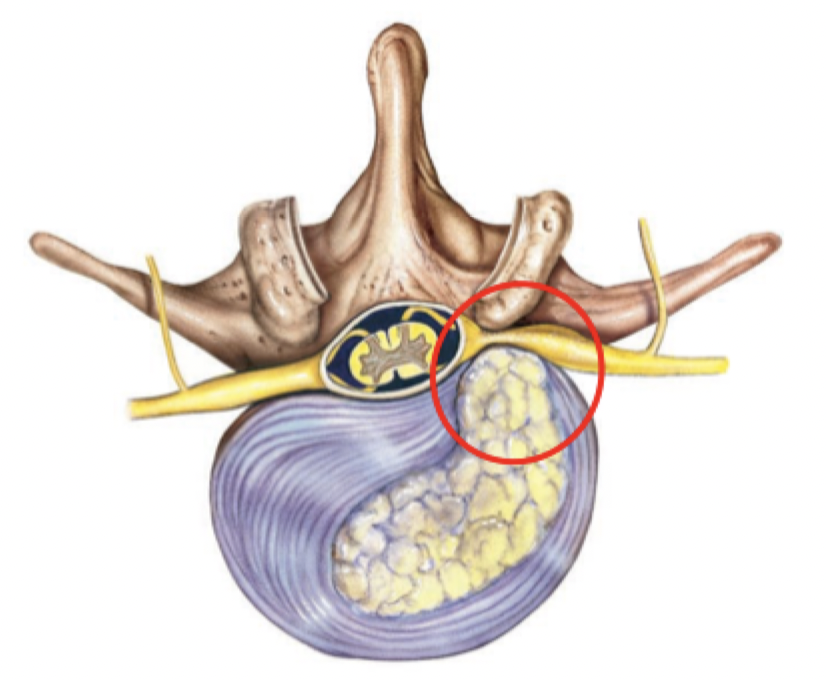
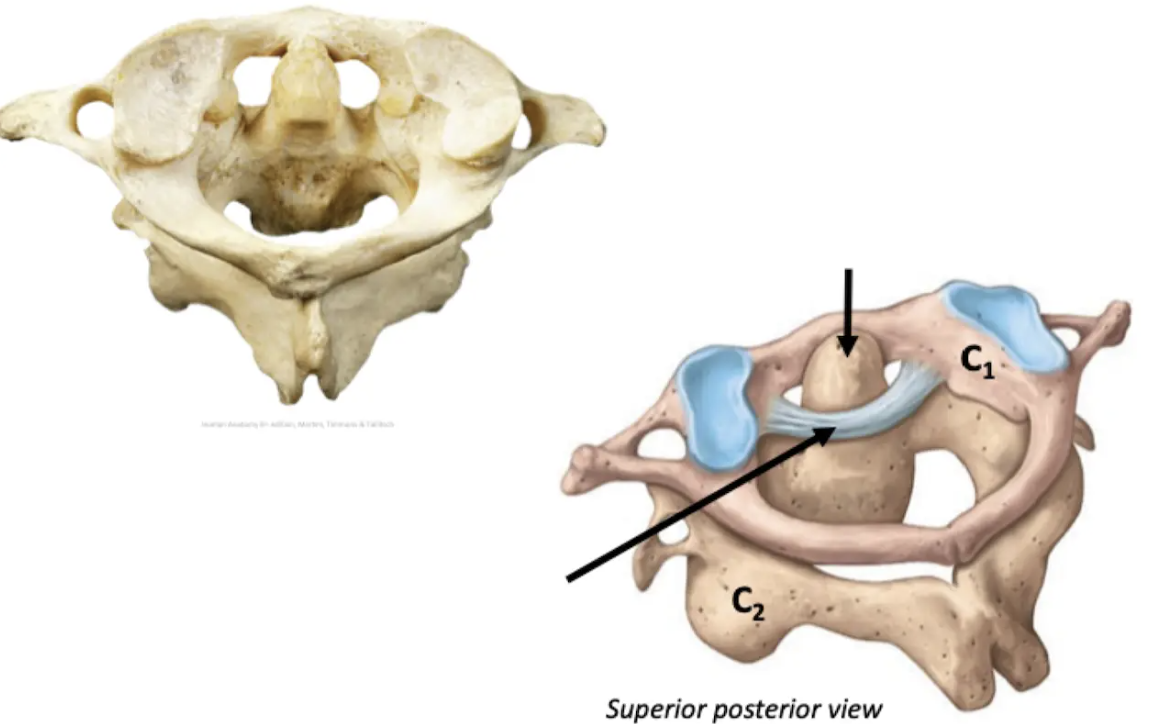
Nucleus pulposus herniates (protrudes) into vertebral canal due to tear or rupture in the annulus fibrosis
How does a Herniated Disc happen?

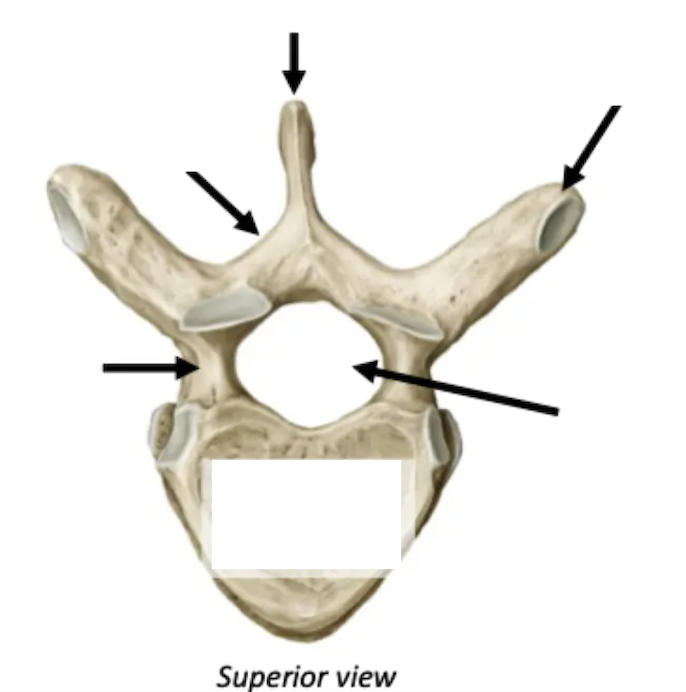
Label
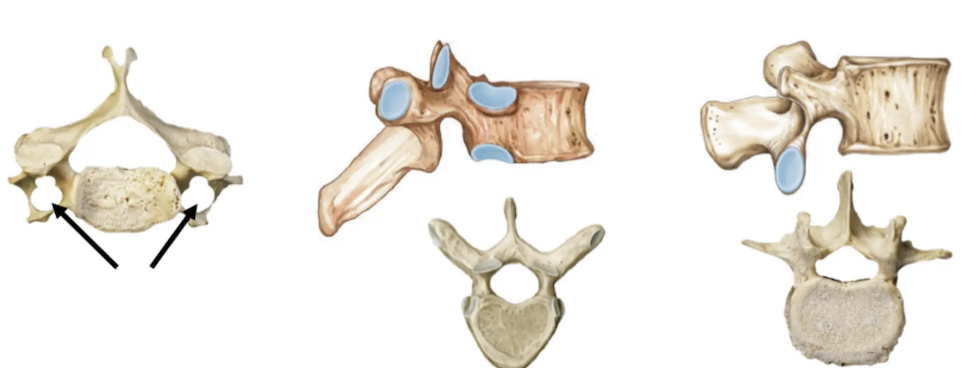
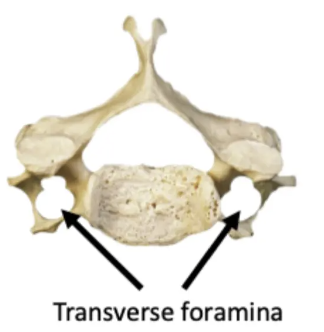
Size: Small - fine movements
Spinous process: Bifid
Vertebral body: Oval
Other features: Transverse foramen
Cervical Vertebrae
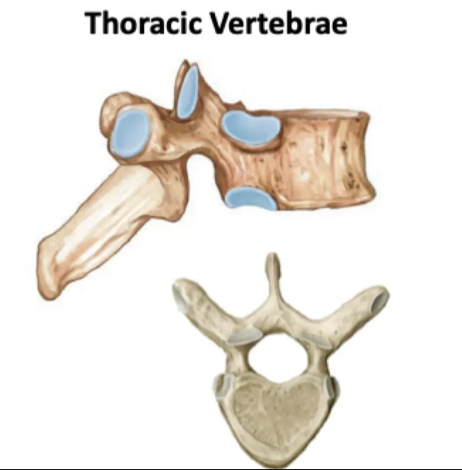
Size: Medium
Spinous process: Downward sloping
Vertebral body: Heart
Other features: Costal facets for ribs
Thoracic Vertebrae
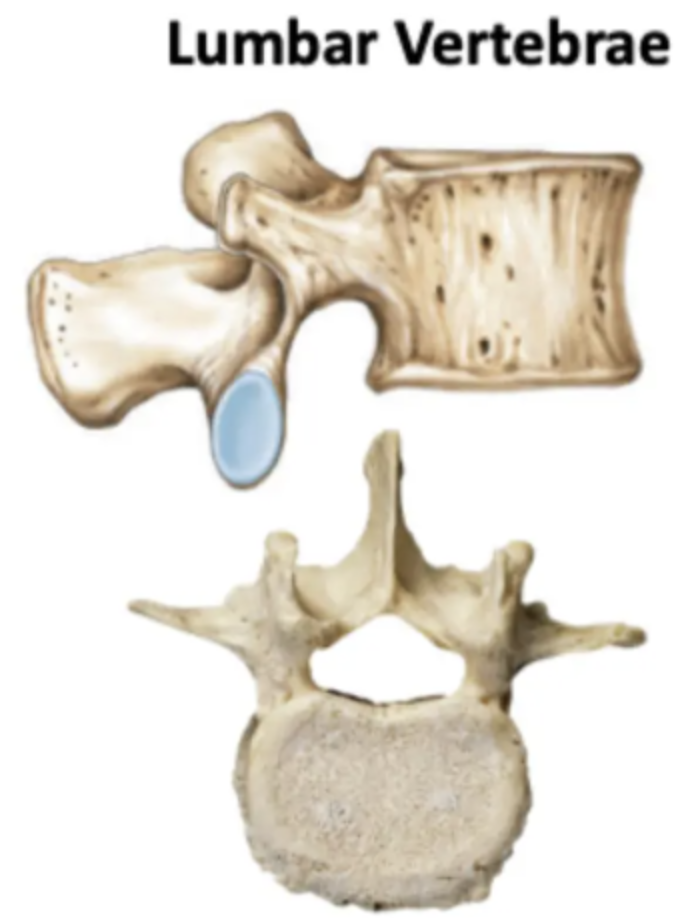
Size: Large - weight bearing
Spinous process: Short, stumpy
Vertebral body: Kidney
Other features: No articular facets for ribs
Lumbar Vertebrae
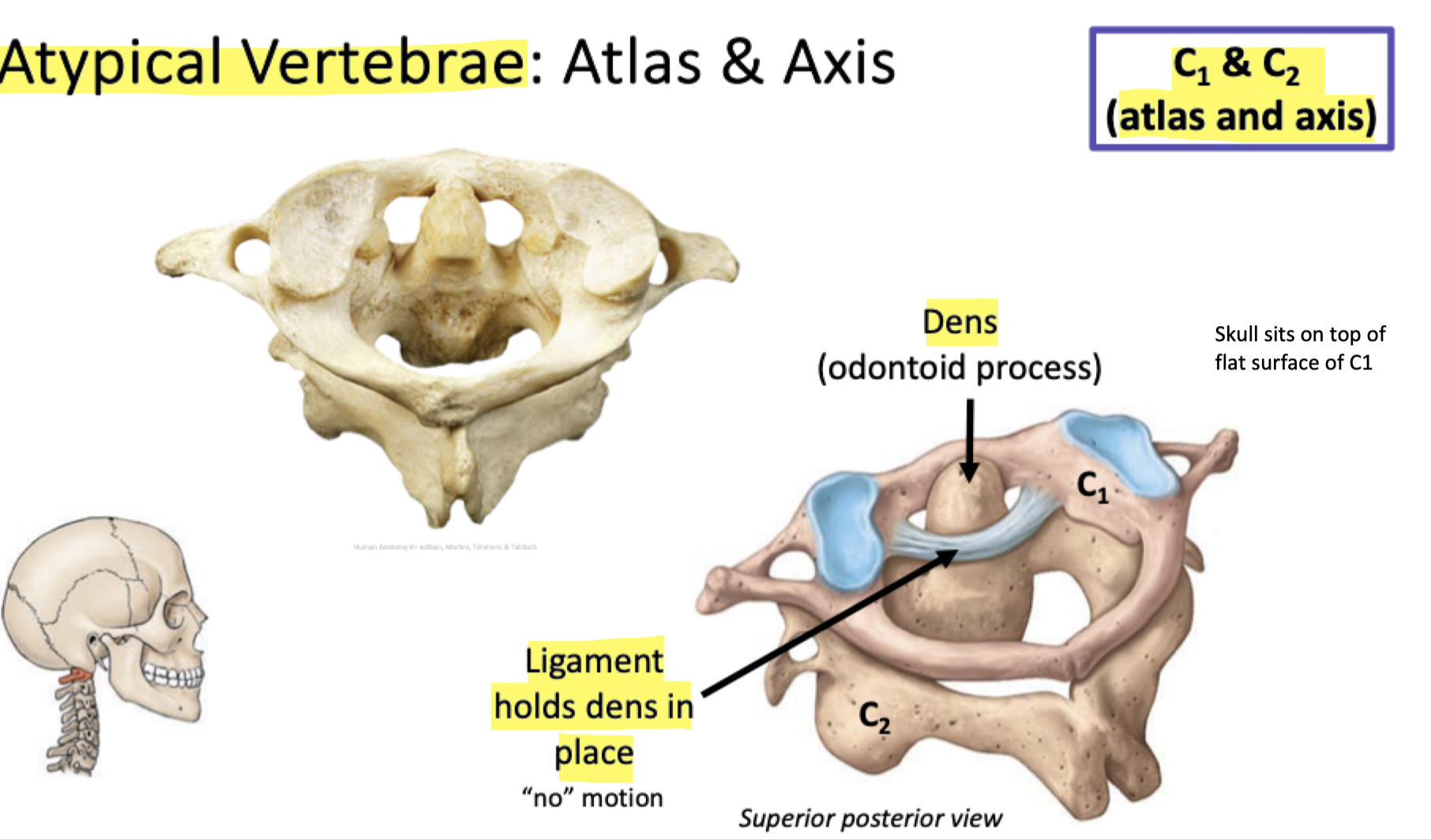
Label
Encloses and protects viscera of the thoracic cavity
Thoracic skeleton acts an anchor for muscles, including those for respiration
Attachment for muscles that move the upper limb, scapula
Functions of the Thoracic Cage

What makes up the Thoracic Cage?
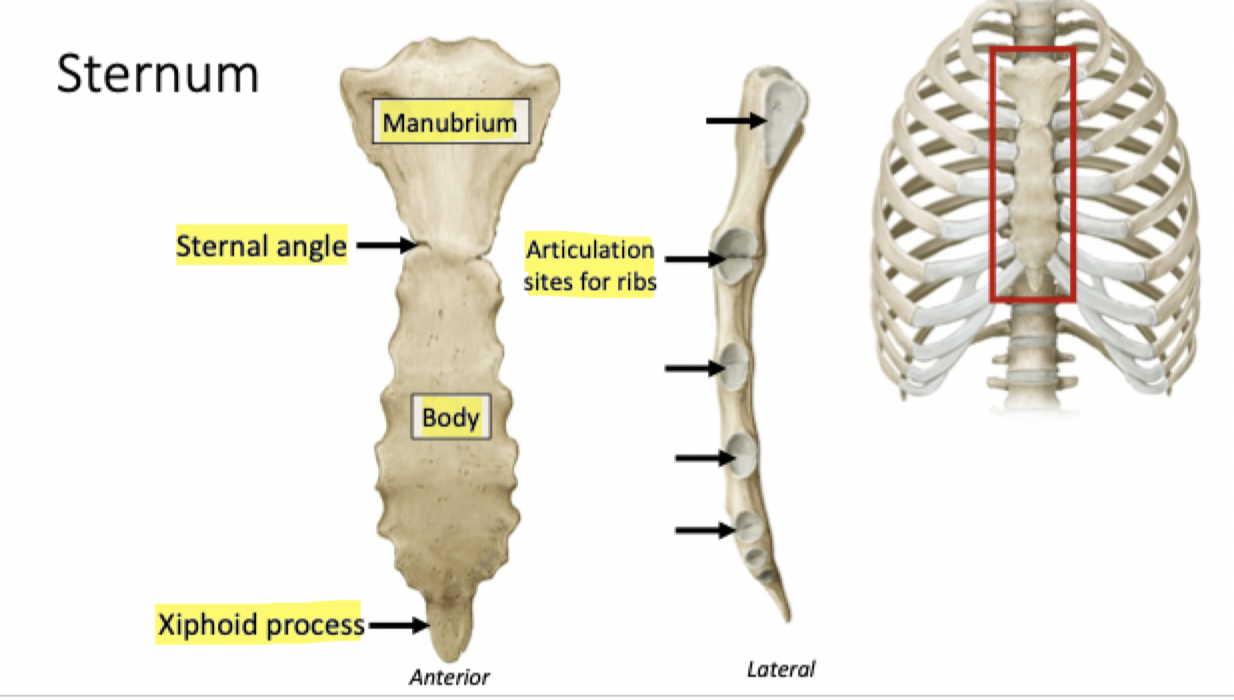
Label
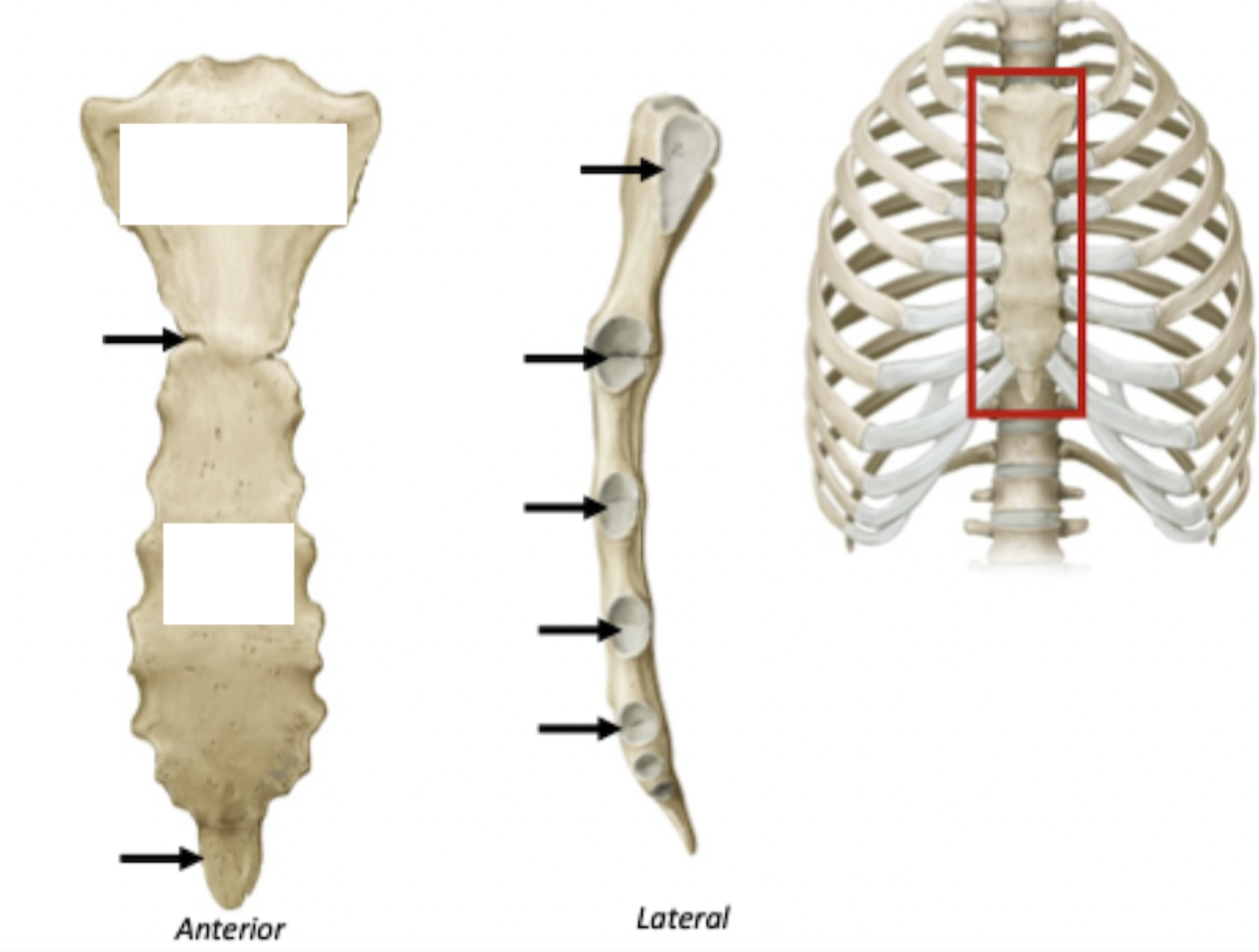
Label
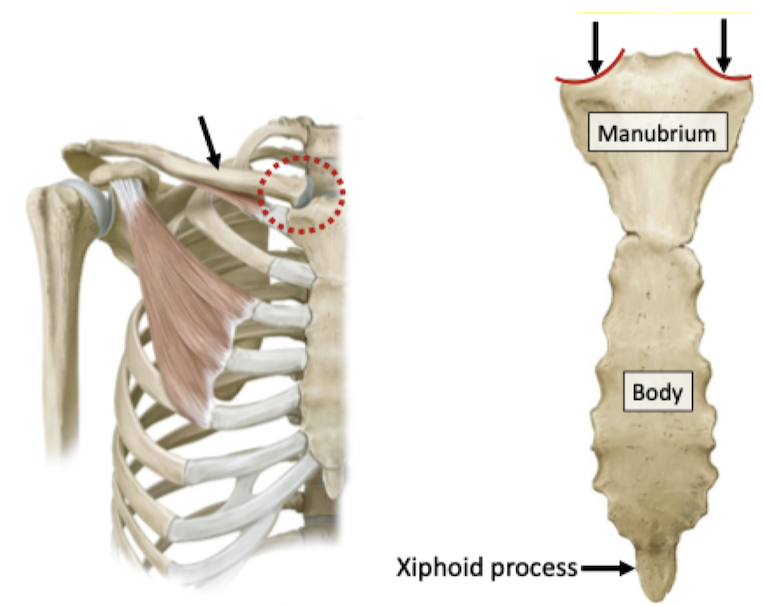
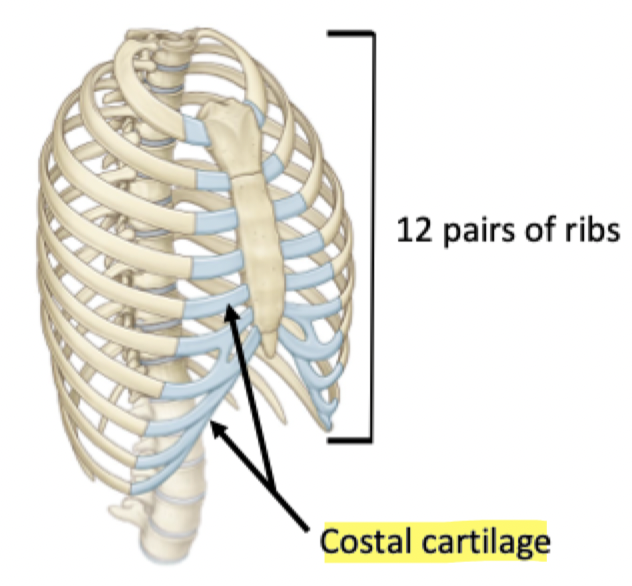
Most ribs articulate with sternum via costal cartilage
Contributes to the elasticity of the thoracic cage
Label + Function
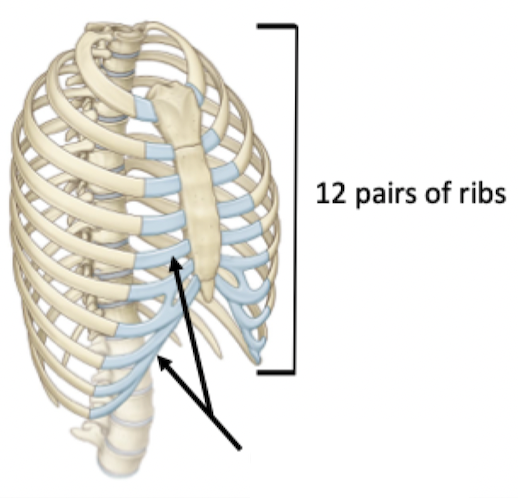
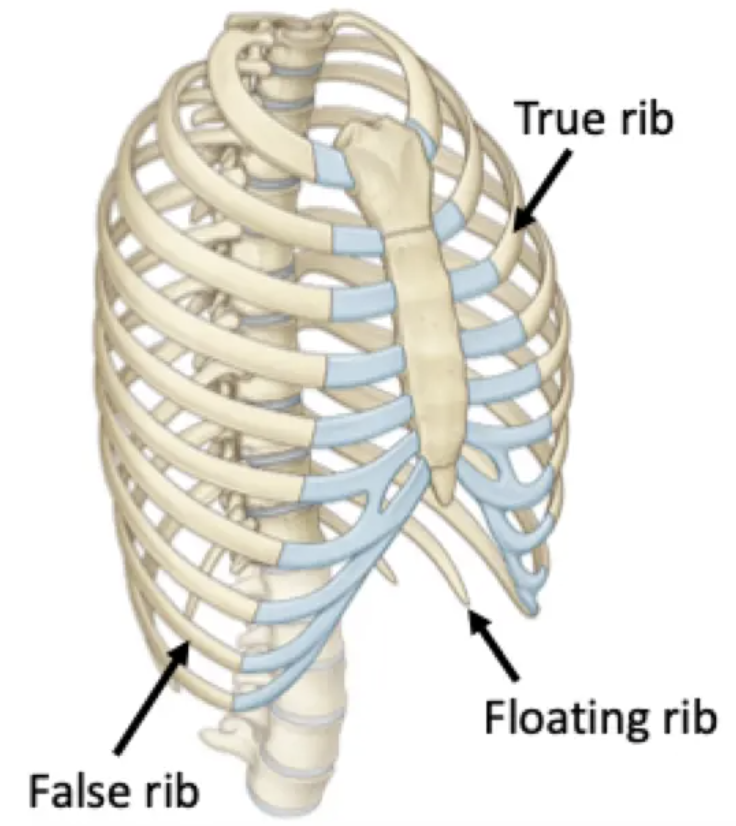
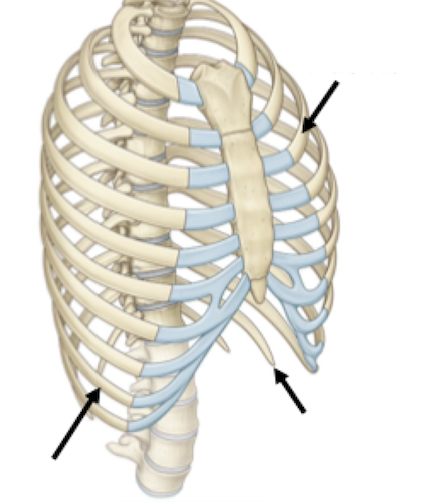
True ribs 1-7: articulate directly with the sternum via costal cartilage
False ribs 8-10: articulate indirectly via fused costal cartilage
Floating ribs 11 & 12: no anterior articulation. Don't wrap all the way around
Label + Explain
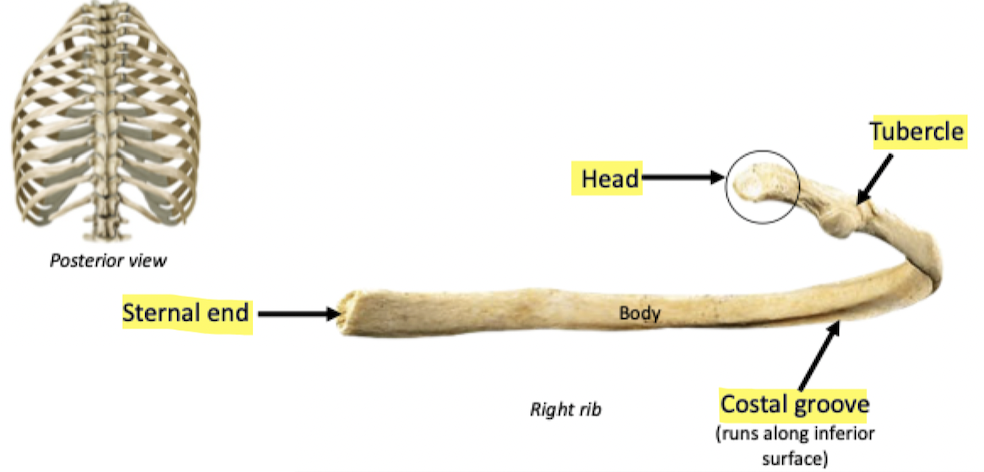
Tubercle: articulates with transverse process of thoracic vertebrae
Head: articulates with body of the thoracic vertebrae (via costal facet)
Label
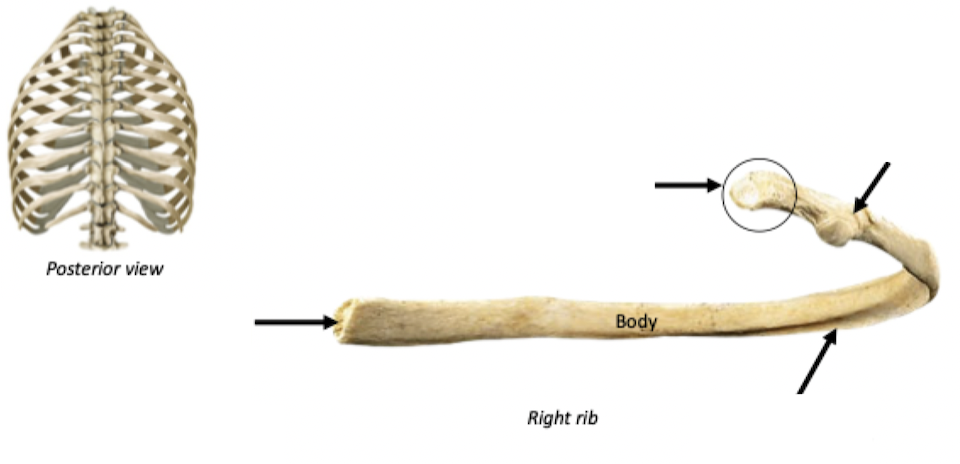
Bumb/Prominence
Tubercle
Relating to ribs
Costal
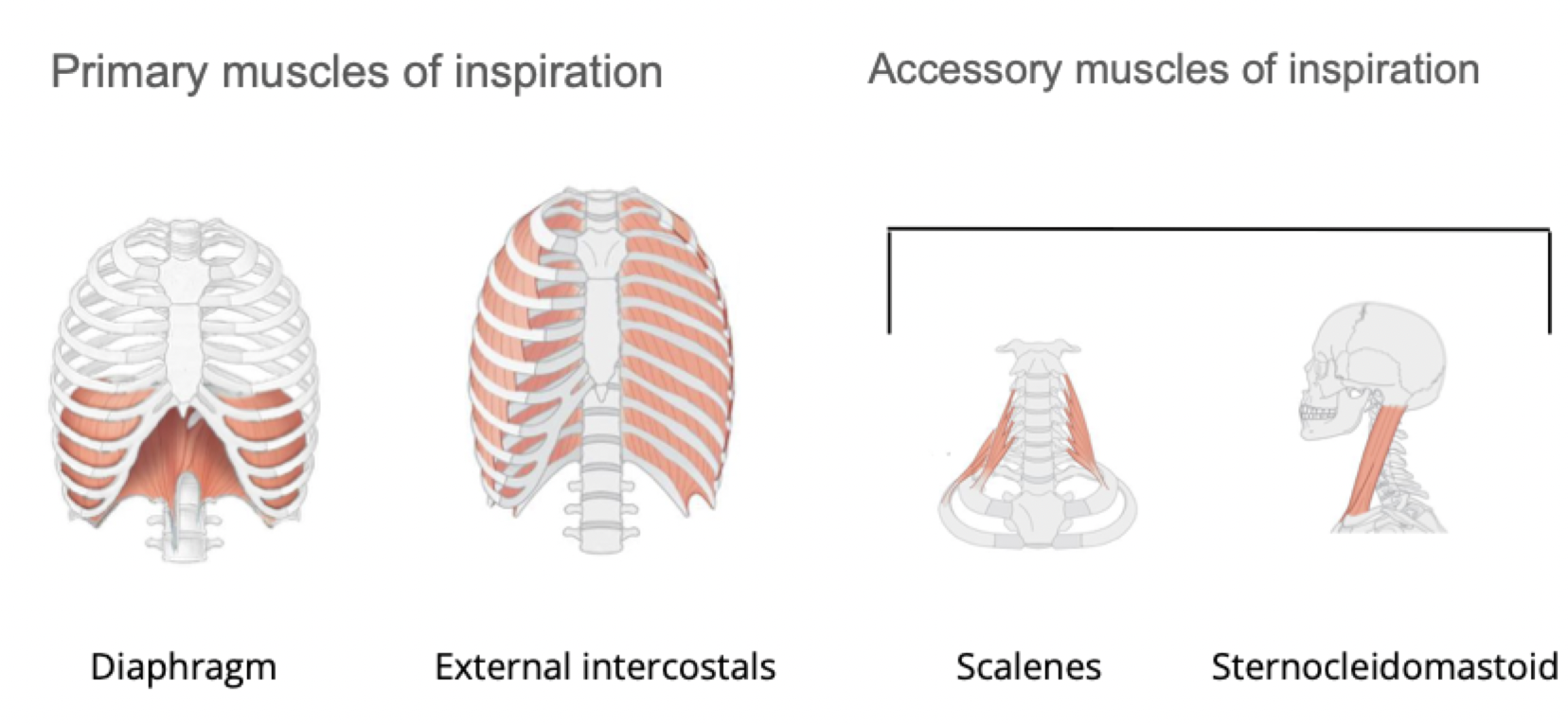
Primary muscles of inspiration: Diaphragm, External intercostals
Accessory muscles of inspiration: Scalenes, Sternocleidomastoid
Muscles of Inspiration
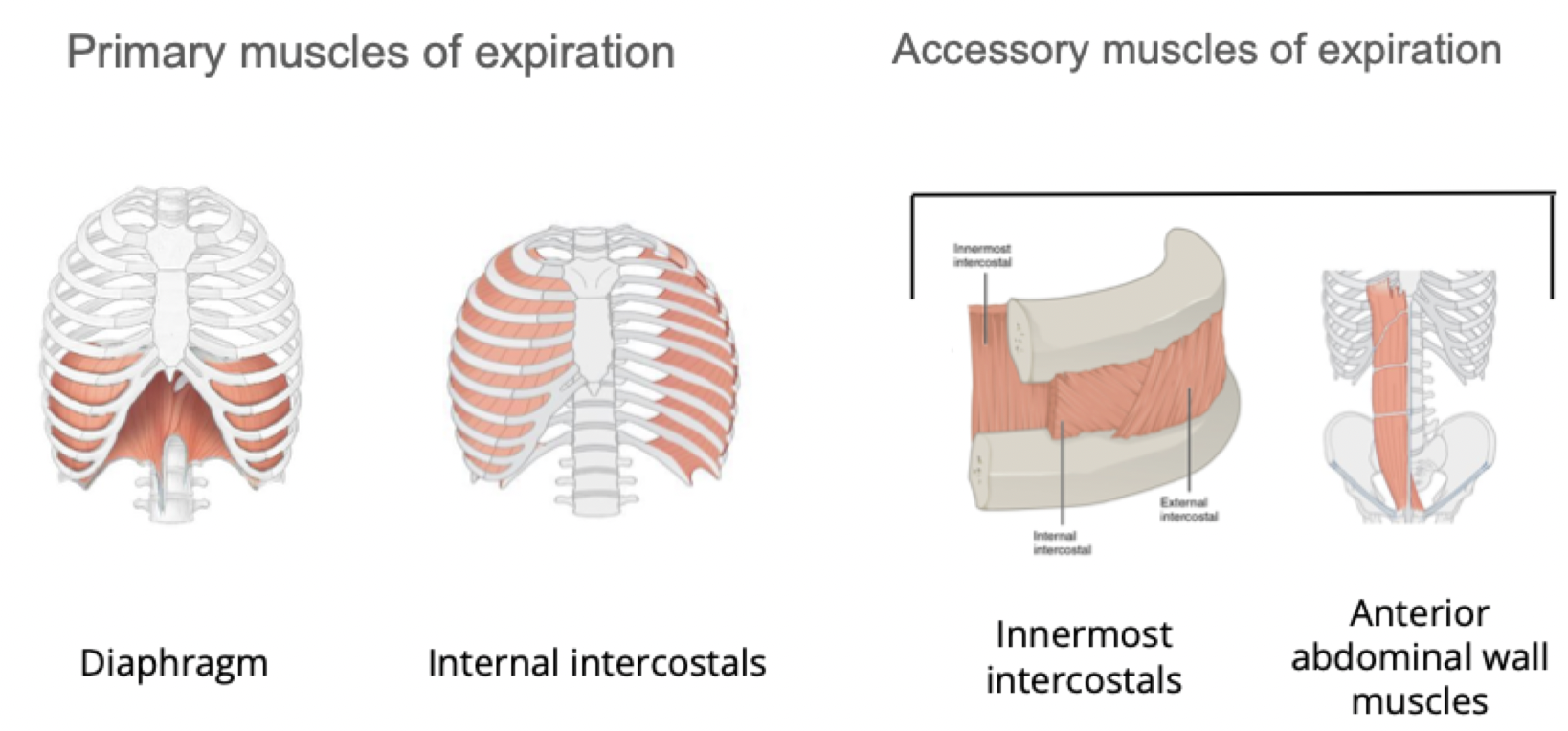
Primary muscles of expiration: Diaphragm, Internal intercostals Innermost intercostals
Accessory muscles of expiration: Innermost intercostals, Anterior abdominal wall muscles
Muscles of Expiration
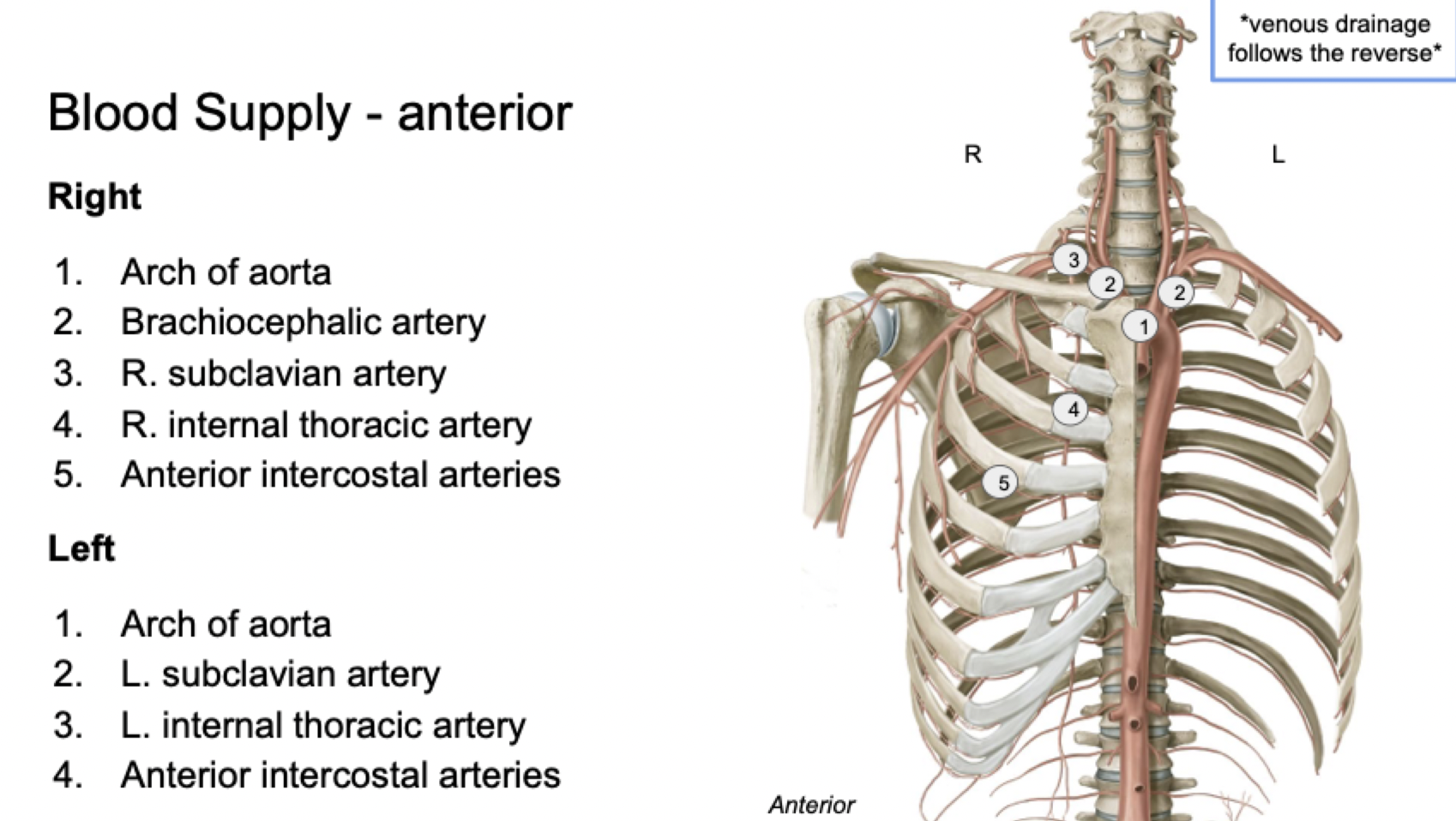
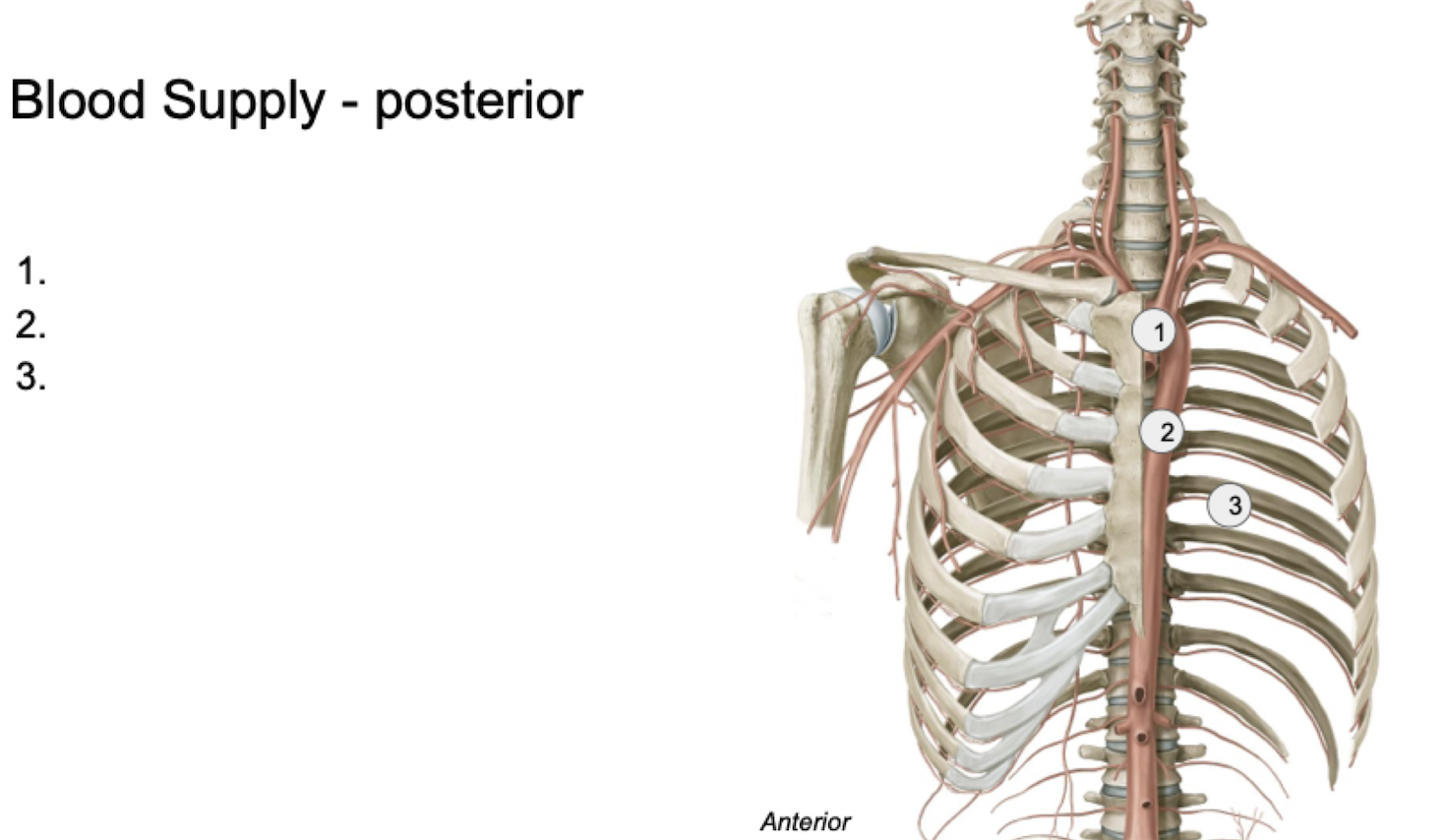
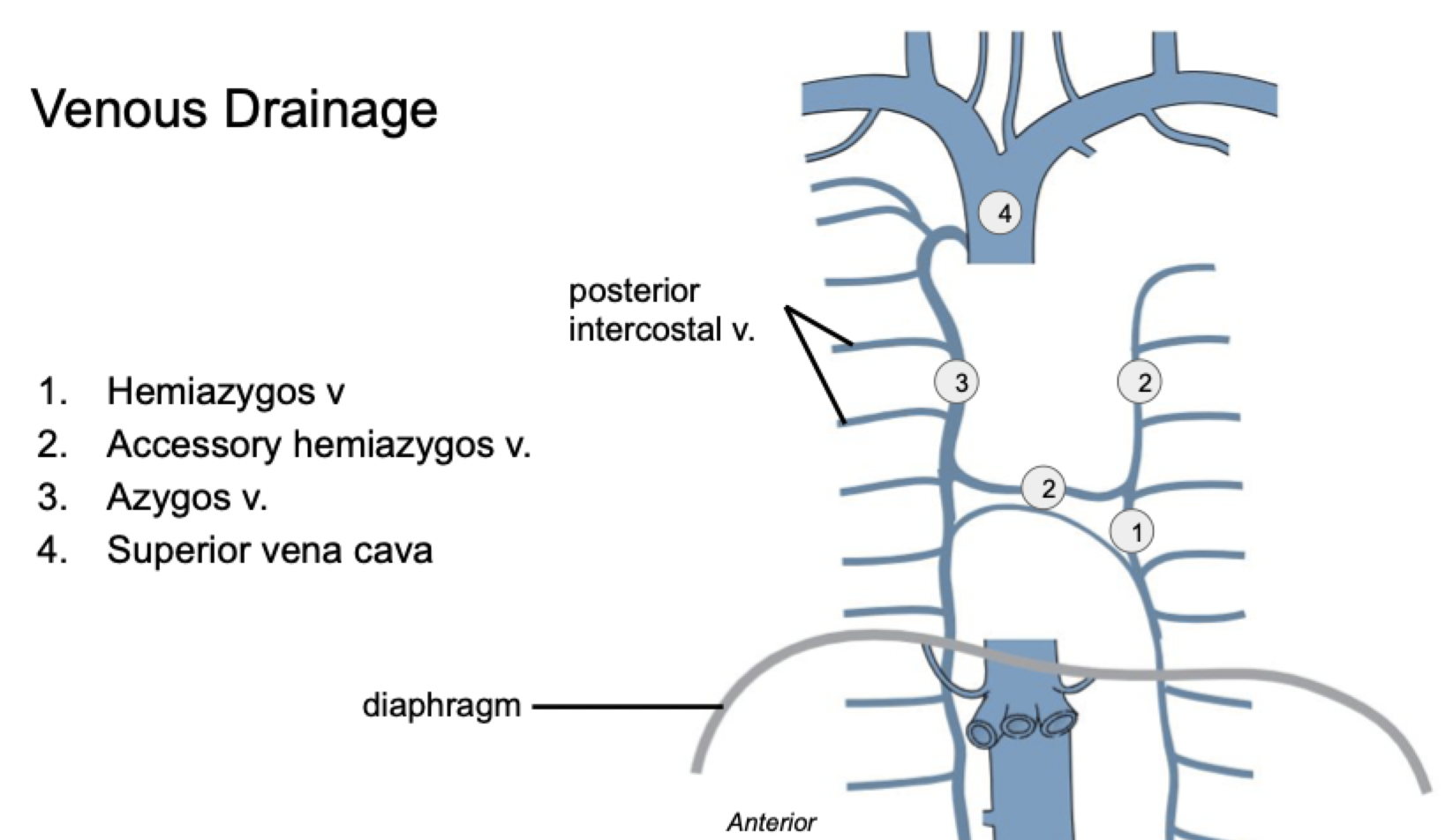
Label
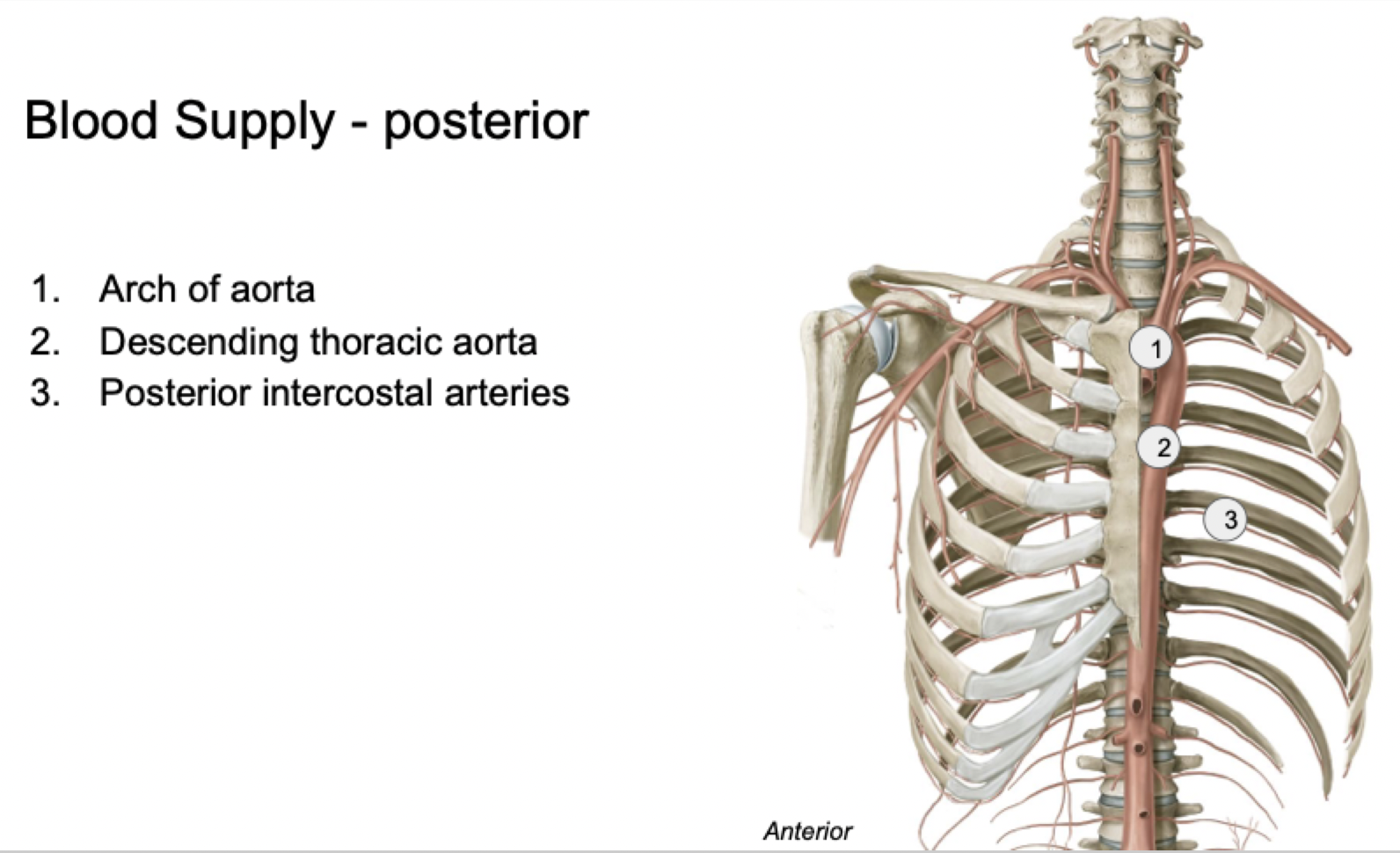
Label
Label
Also referred to as an articulation
The site where two (or more) bones connect
Link the skeletal system
Joints facilitate movement of the skeleton
What is a joint and why do we have them?
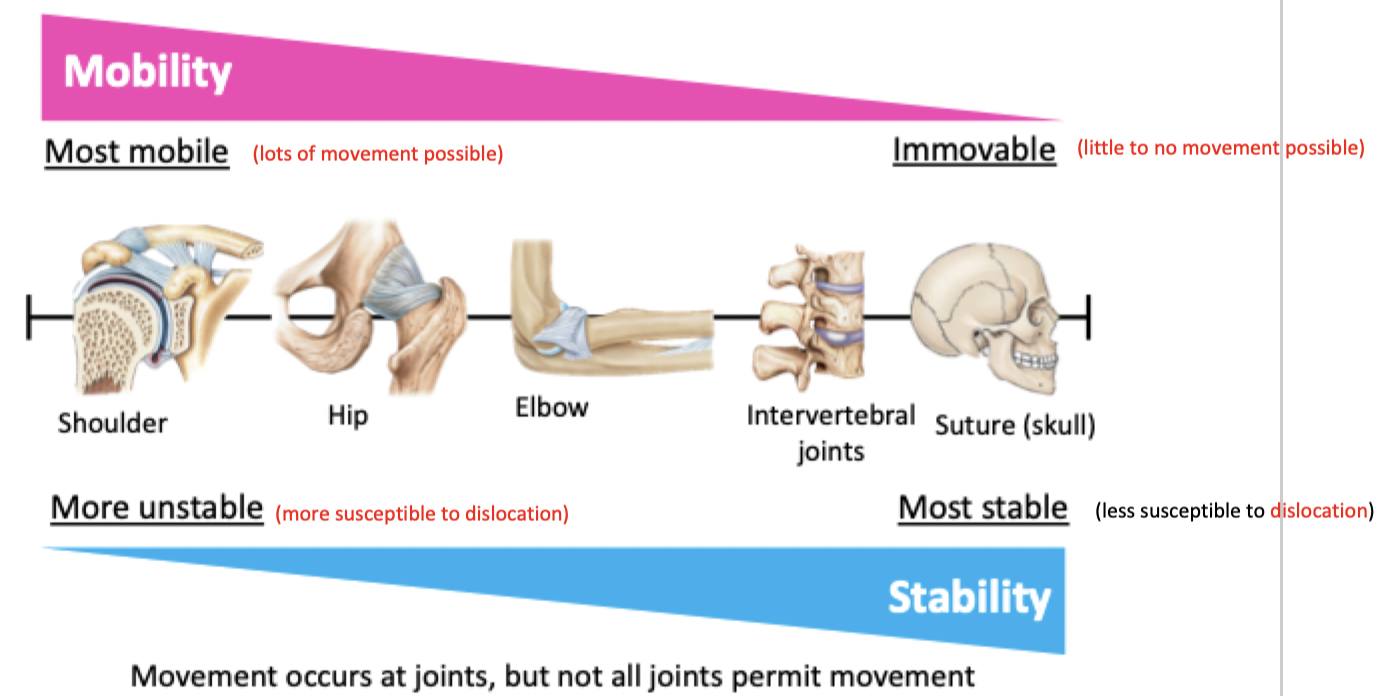
The more stable a joint, the less mobile & vice versa
Stability vs Mobility - Joints
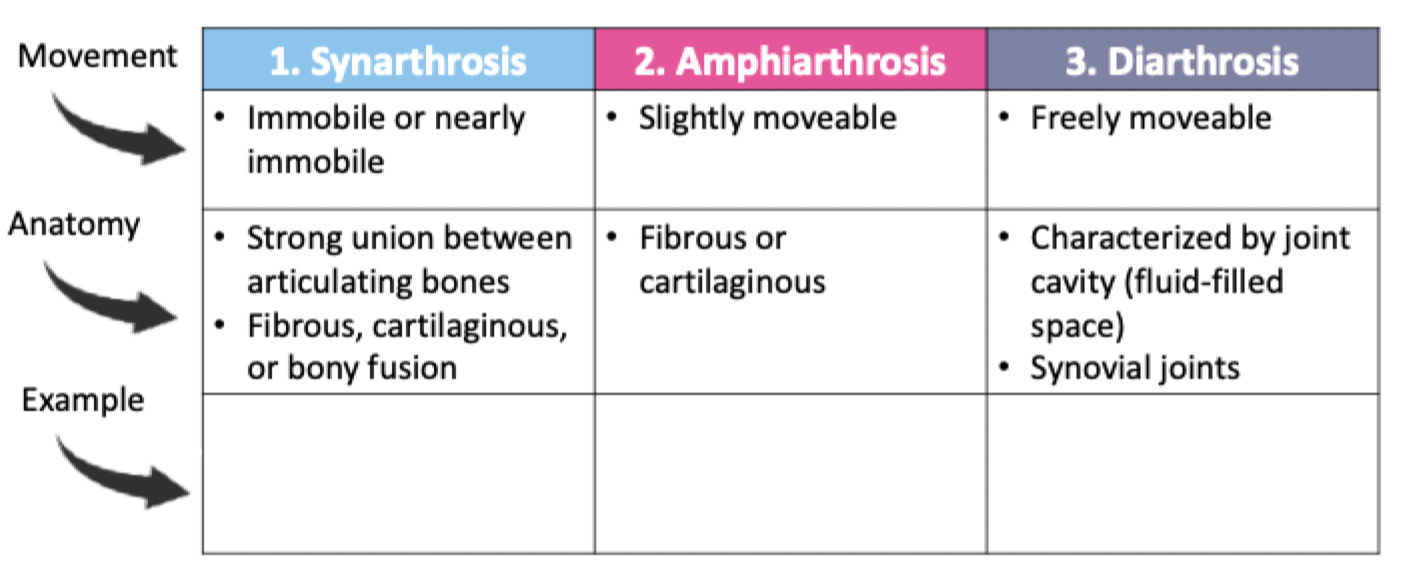
Classification of joints
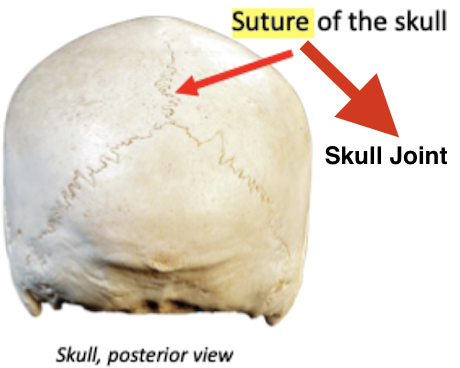
Joined by dense fibrous connective tissue
Fibrous synarthrosis
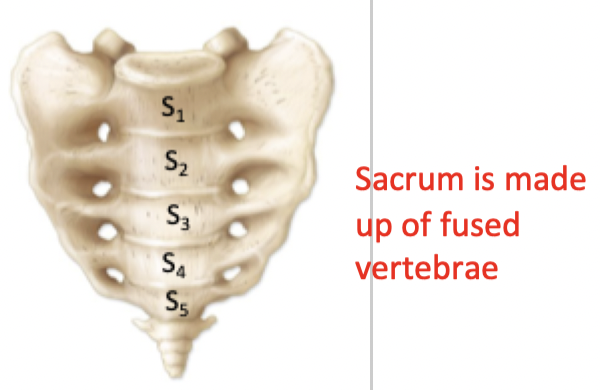
Created when bones fuse together
The boundaries separating the bones disappear upon fusion
Bony Fusion

Bones joined by a wedge of cartilage (allows for some degree of flexibility)
Cartilaginous amphiarthrosis
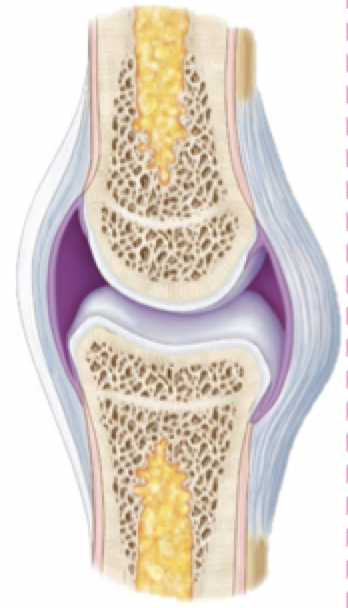
Specialized for movement: permit a wider range of motion than other joints
Typically found at the ends of long bones, such as those of the upper and lower limbs
All synovial joints have the same basic components:
Joint capsule
Articular cartilage
Joint cavity filled synovial fluid
Synovial membrane
Accessory structures
Synovial Joints
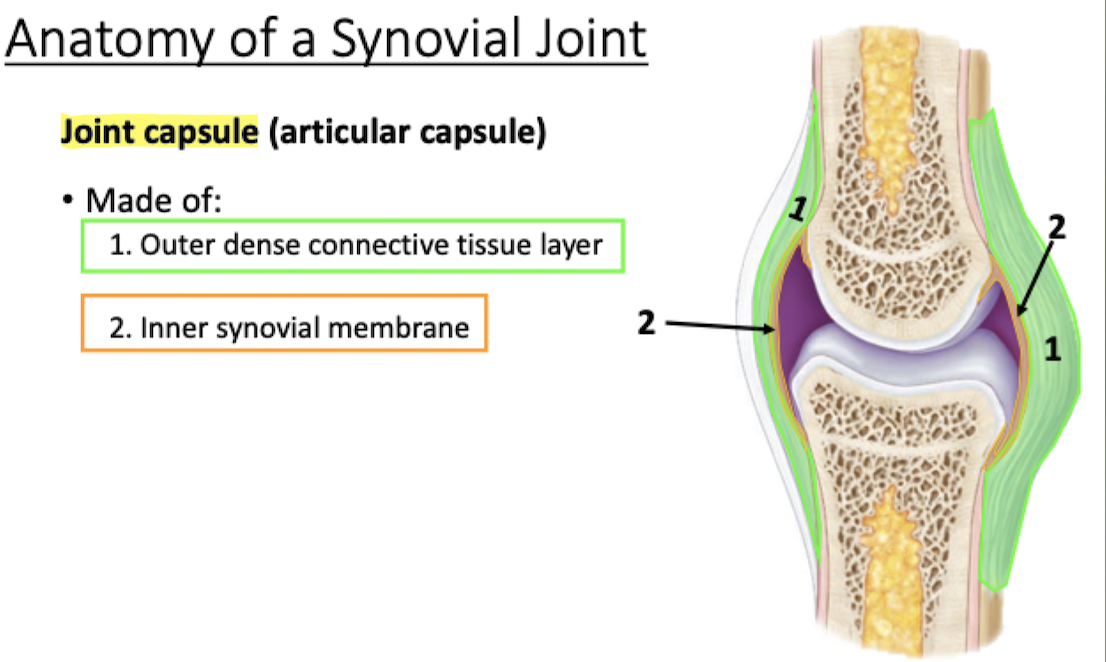
Surrounds synovial joint, encloses joint cavity
Made of outer dense connective tissue layer & inner synovial membrane
Joint Capsule
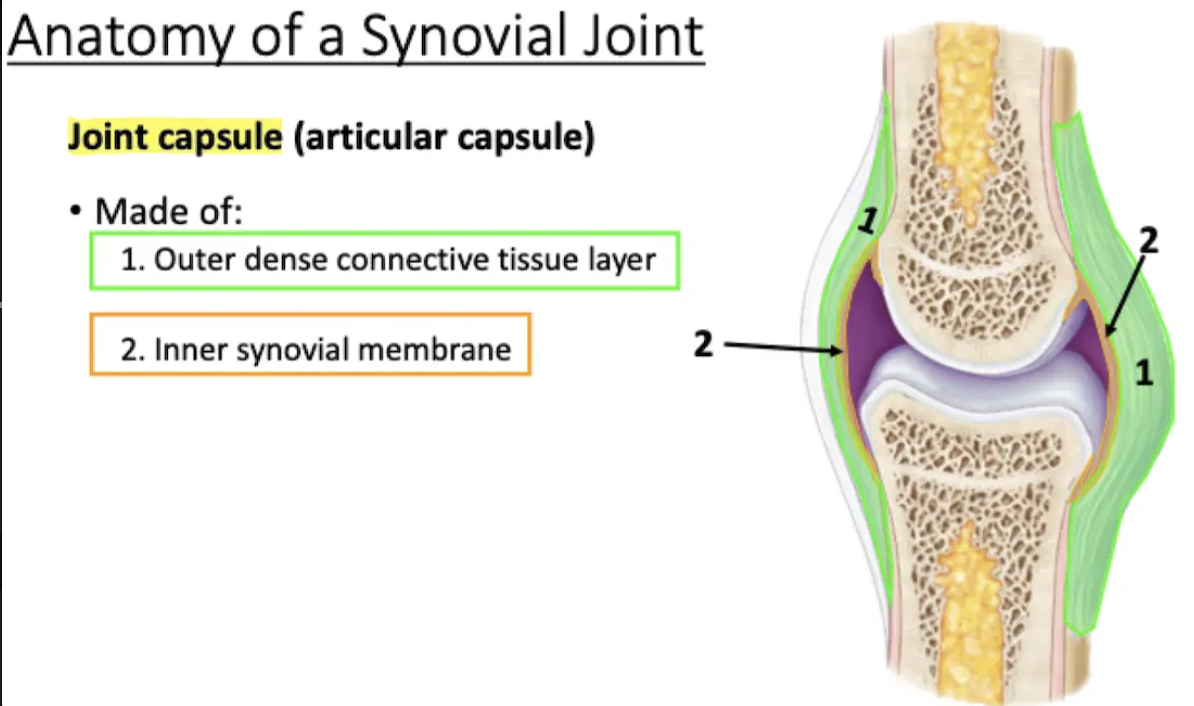
Lines inner surfaces of the joint (does not cover the articulating bone surfaces)
Produces synovial fluid
Synovial membrane
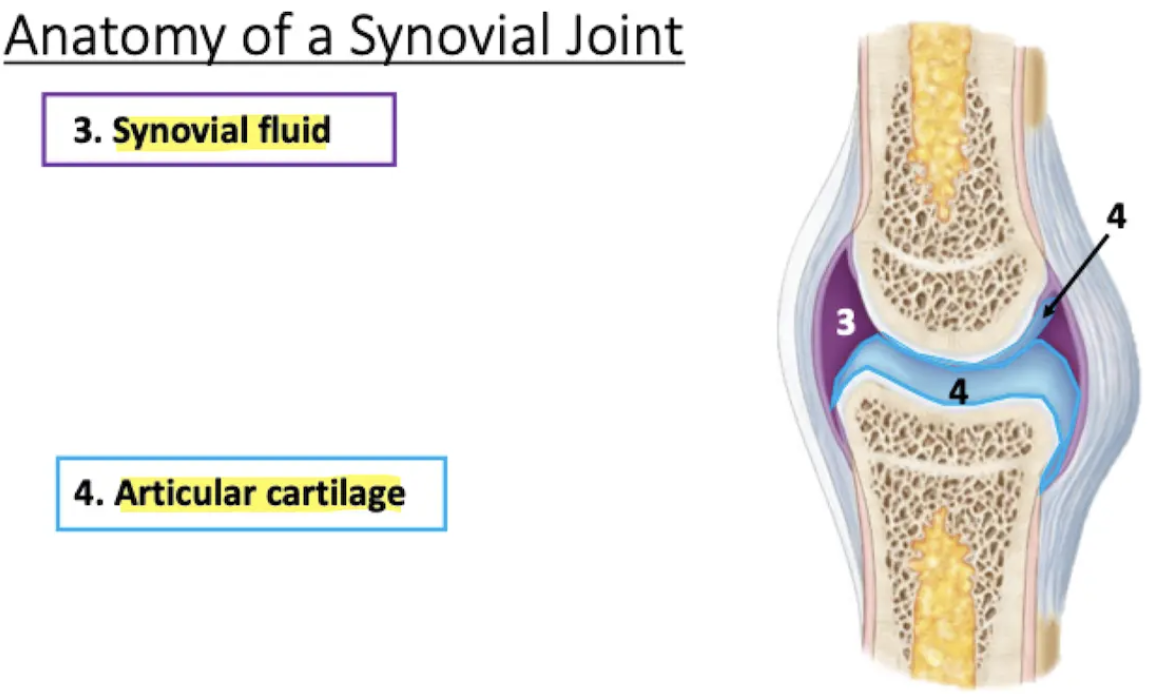
Fills the joint cavity
Lubricates (reduces friction)
Absorbs shock
Distributes nutrients to cells of the articular cartilage
Synovial fluid

Covers surfaces of articulating bones
Smooth surface helps reduce friction during movement
People with arthritis will have wearing away articular cartilage
Articular cartilage
Provide support and additional stability
1. Menisci
2. Ligaments
3. Bursae
4. Fat pads
Accessory Structures of Synovial Joints
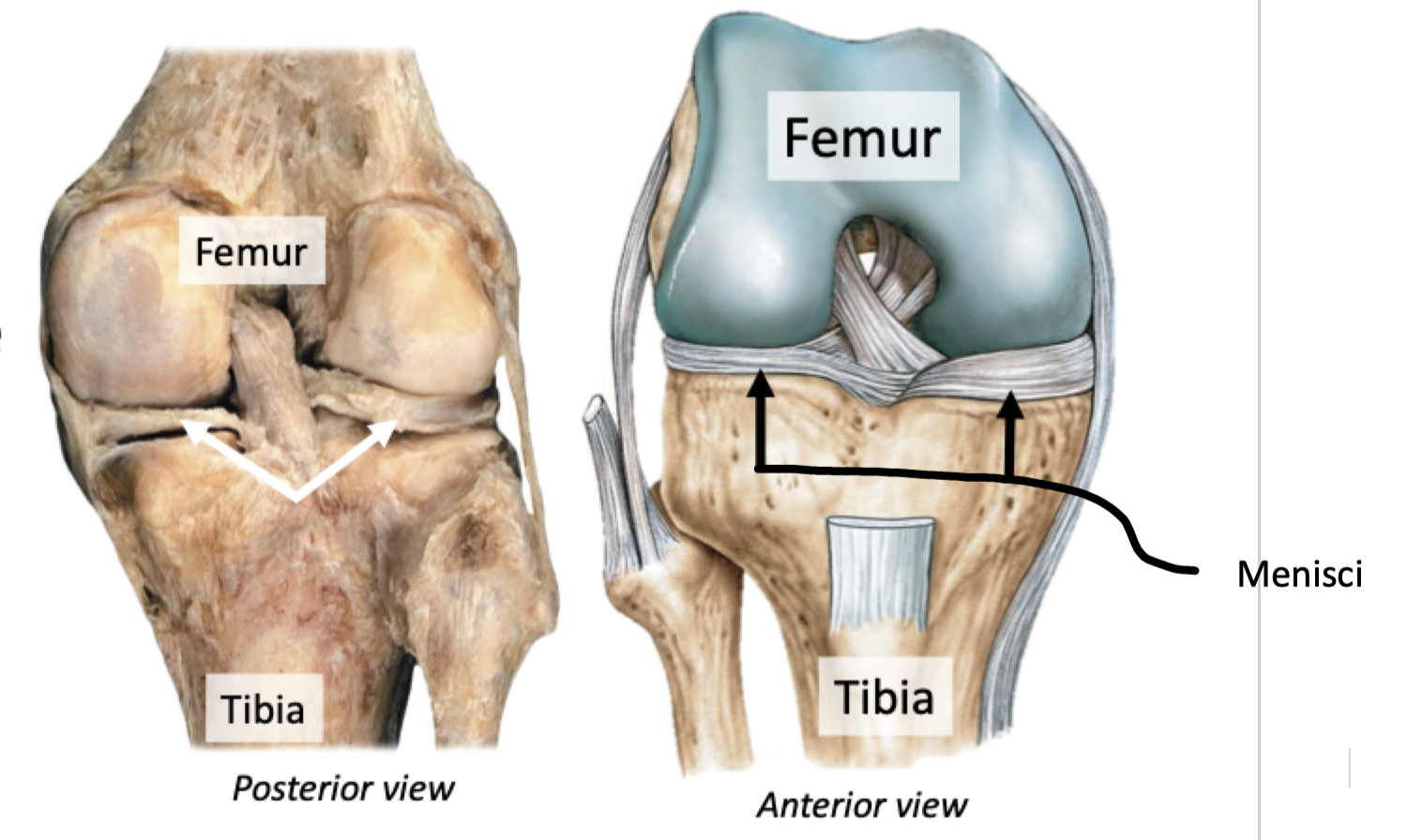
Menisci (meniscus)
Fibrocartilage pads between bone
Reduce friction, disperse weight, protect & cushion joint surface
Label + Explain
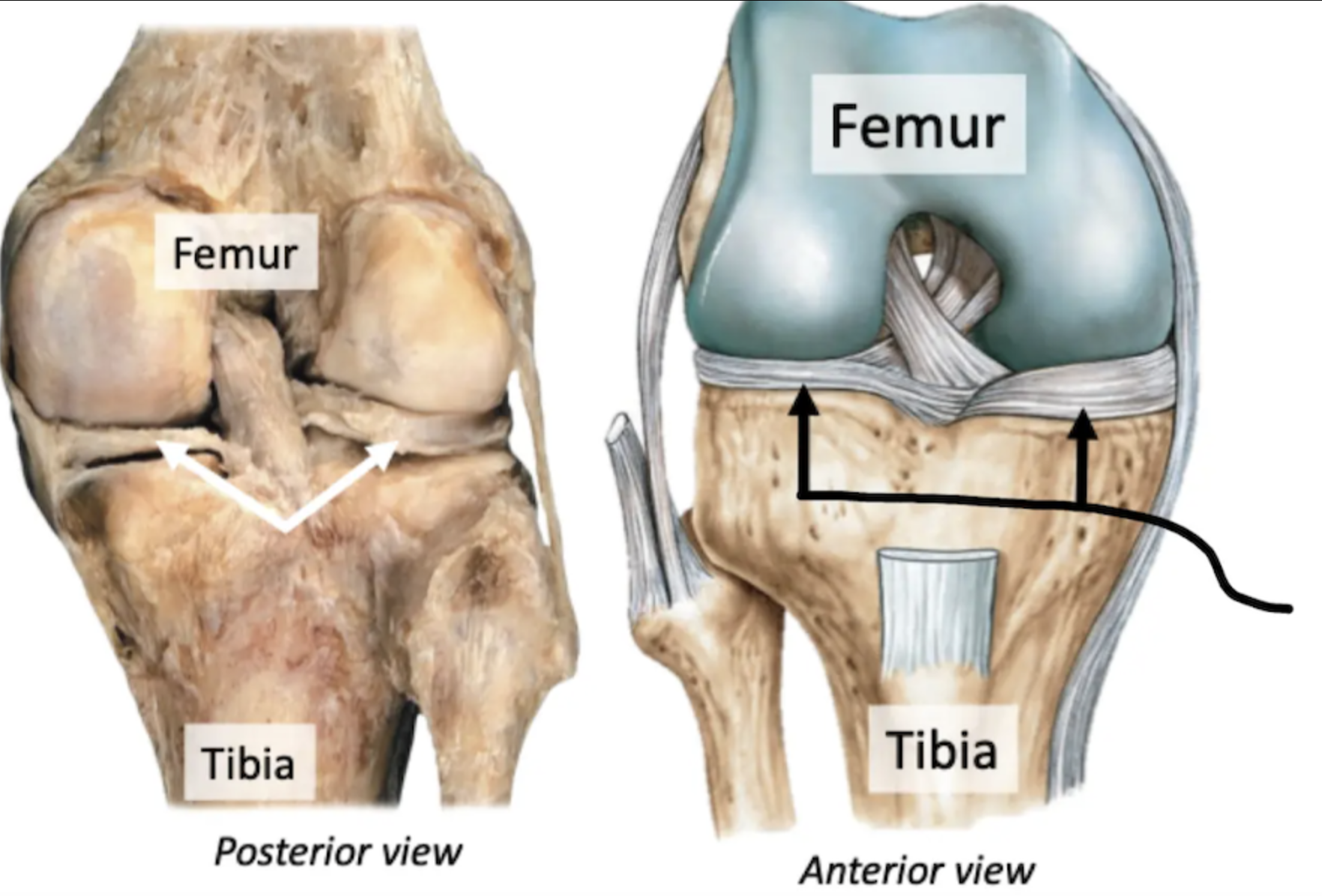

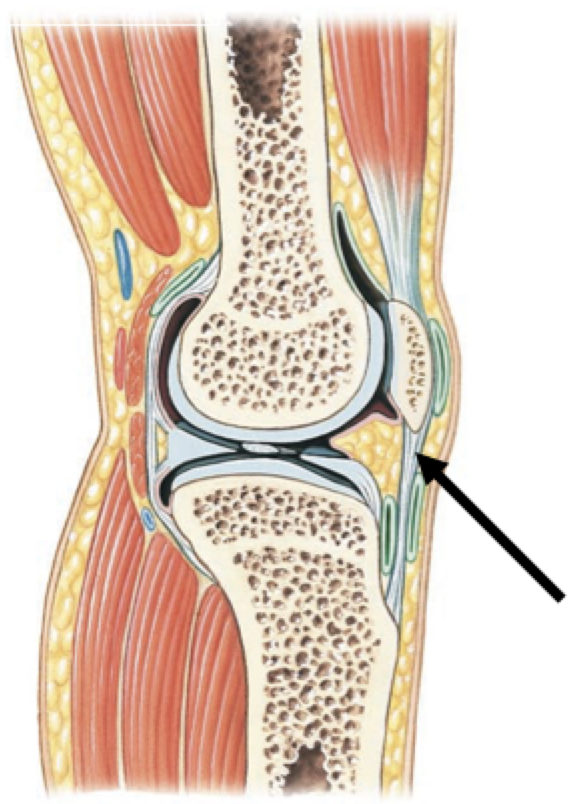
Ligaments
Fibrous connective tissue connecting bone to bone
Support and strengthen synovial joints
Label + Explain
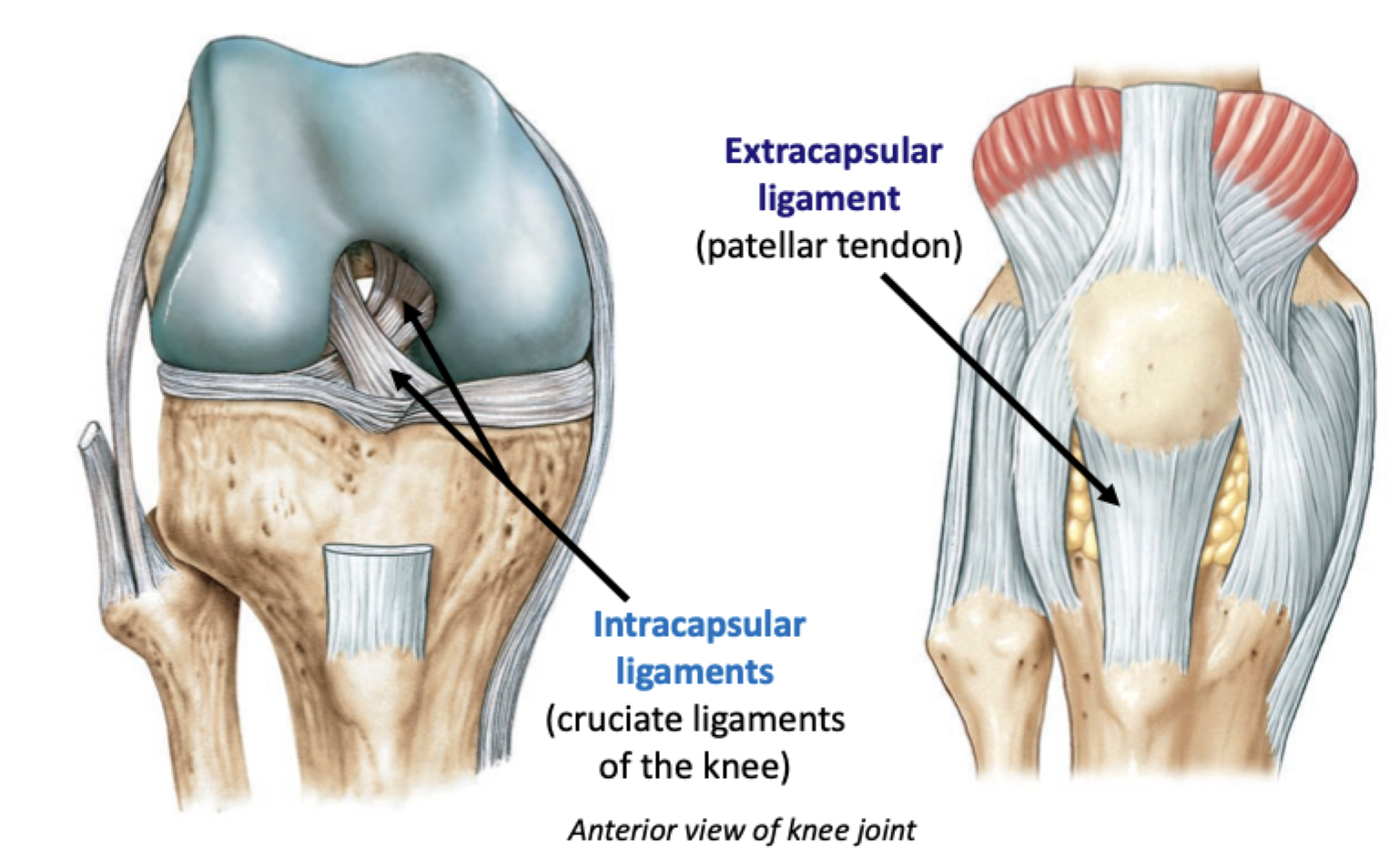
Outside (extracapsular)
Inside (intracapsular)
Relative to the joint capsule, can be located…
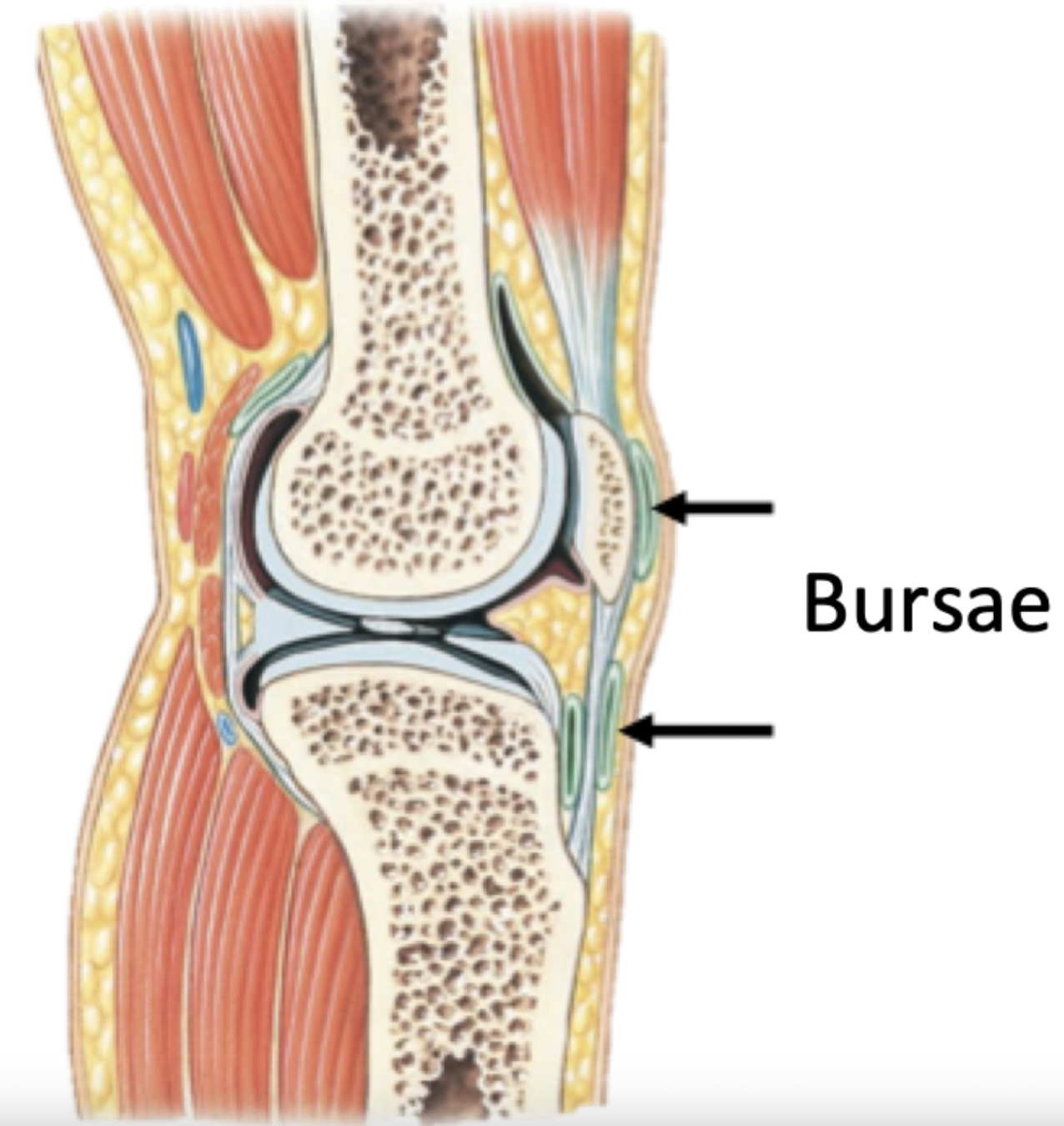
Bursa (bursae pl.)
Small fluid-filled pockets in connective tissue, occur around tendons and bones
Filled with synovial fluid, lined by a synovial membrane
Reduce friction
Act as shock absorbers
Label + Explain
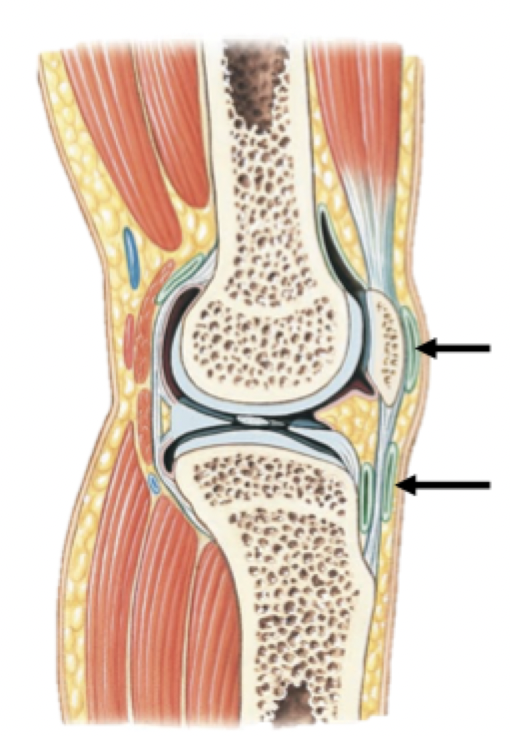
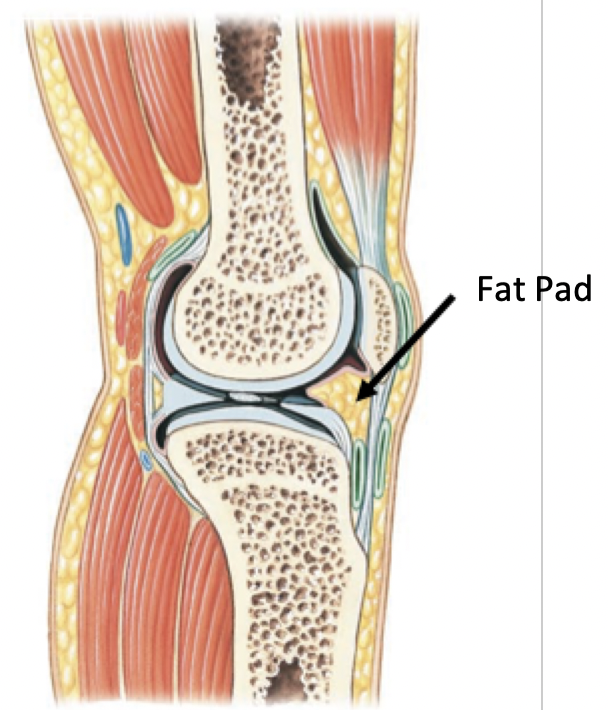
Fat Pads
Usually found around the periphery of the joint
Protect articular cartilages
Cushion joint as a whole
Label + Explain
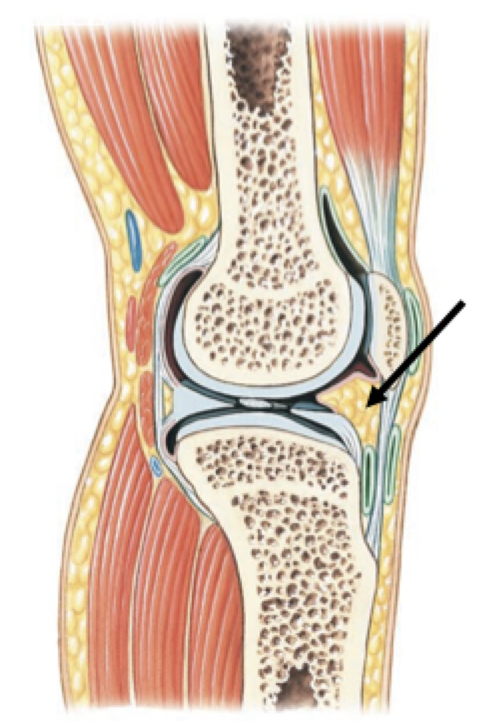
Gliding movements
Angular movements
Rotational movements
Special movements
Types of movement at synovial joints
Also referred to as: planar/linear movement
Two opposing (flat) surfaces slide past each other
Gliding movements
Movement that changes the angle between articulating bones
Flexion & Extension
Abduction & Adduction
Circumduction
Angular movements
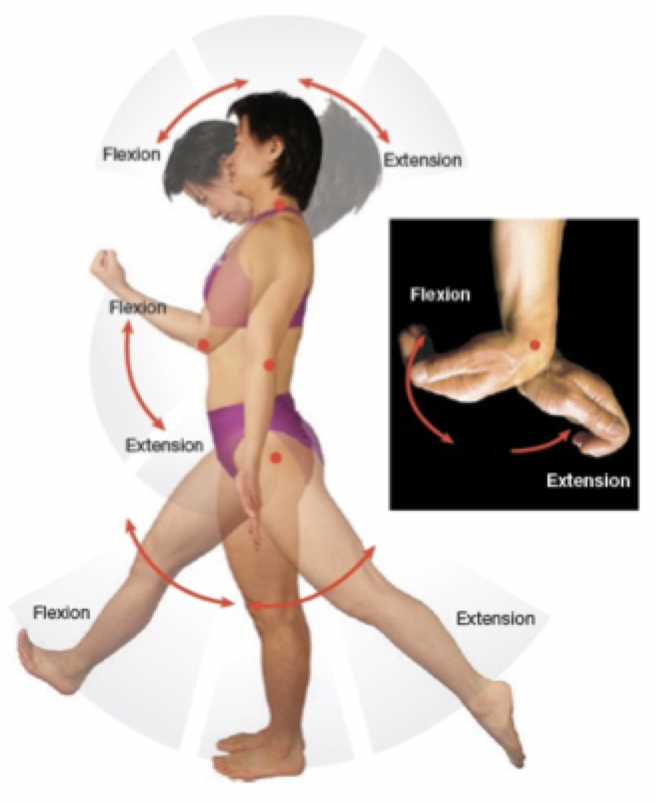
Flexion: Decrease in the angle between articulating bones
Extension: Increase in the angle between articulating bones
Flexion & Extension
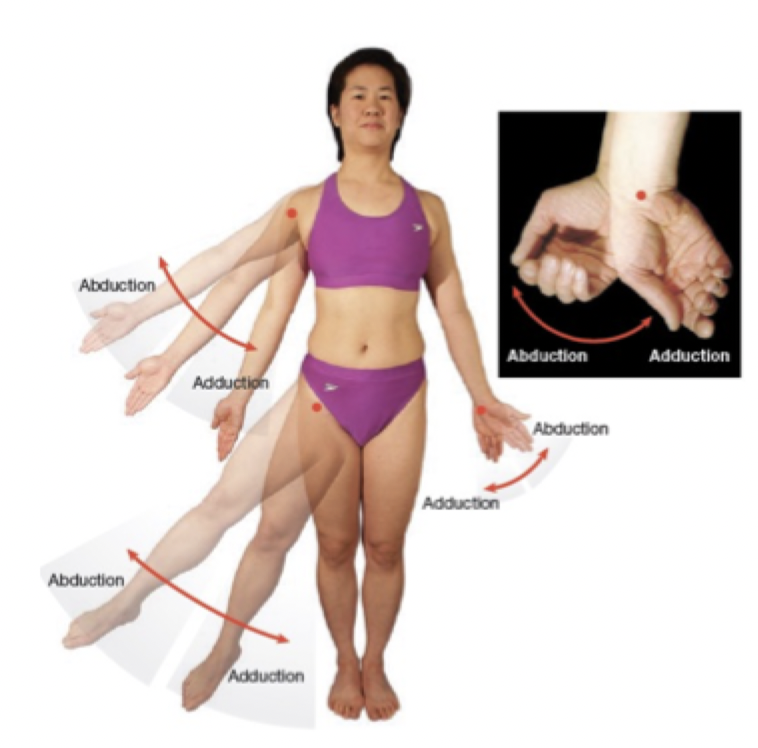
Adduction: Movement of a structure toward the midline
Abduction: Movement of a structure away from the midline
*Fingers (and toes) move away from or toward the middle finger (toe) (not the midline of the body)*
Abduction & Adduction
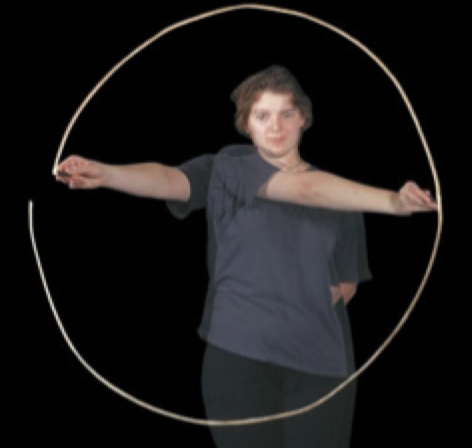

Combination of:
• Extension, Flexion, Adduction, Abduction
Best performed at ball and socket joints, such as hip and shoulder
Can also be performed by other body parts such as: fingers, wrist, and head
Circumduction
Rotations
Supination & Pronation
Rotational movements
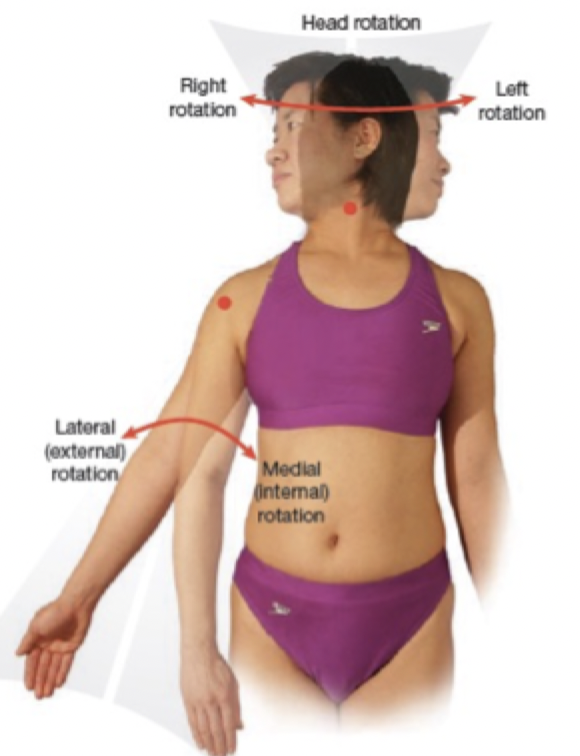
Right or left rotation
Medial (internal) rotation
Rotation towards the midline
Lateral (external) rotation
Rotation away from the midline
Rotations

Supination (think holding up soup)
Radius in anatomical position
Rotation of the forearm that makes the palm face anteriorly
Pronation (think pouring soup)
Radius rolls across anterior surface of ulna
Rotation of the forearm that makes the palm face posteriorly
Supination & Pronation
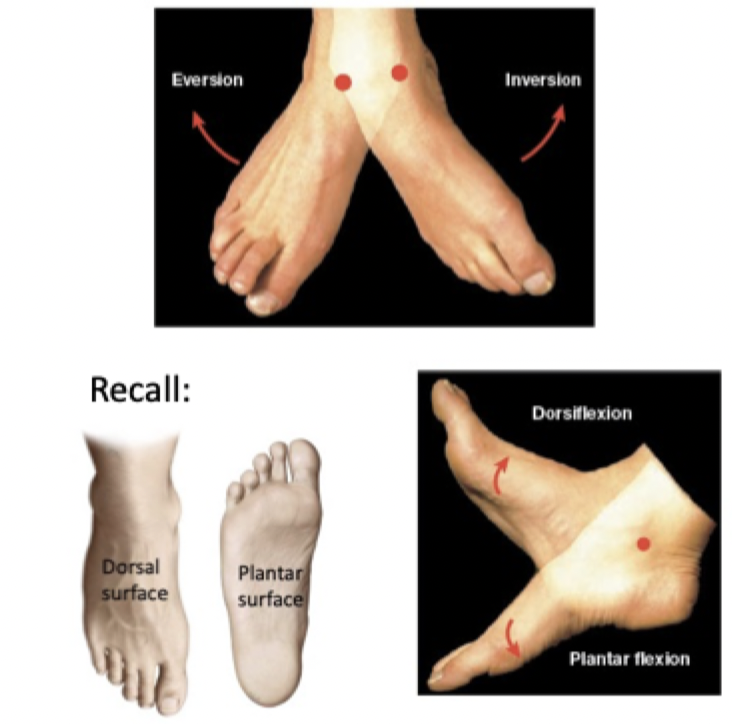
Inversion: Sole of foot twists inward
Eversion: Sole of foot twists outward
Dorsiflexion: Elevate sole of foot (decrease angle between dorsum of foot and anterior surface of leg)
Plantar flexion: Elevate heel of foot (decrease angle between plantar surface of foot and posterior surface of leg)
Special Movements: The Foot

Opposition: Thumb moves across palm to touch the tips of the fingers
Reposition: Thumb and fingers move from opposition back to anatomical position
Special Movements: The Thumb

Protraction: Moving part of the body anteriorly in the horizontal (transverse) plane
Retraction: Part of the body moves posteriorly in the horizontal plane
Ex. pulling back shoulder blades toward spine
Special Movements: Protraction & Retraction
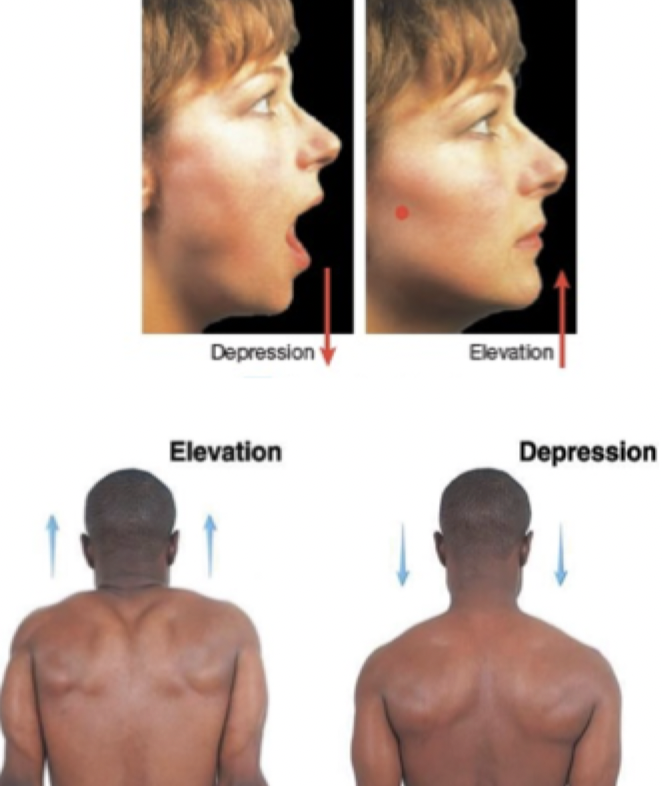
Elevation: Structure moves in a superior direction
Depression: Structure moves in an inferior direction
Special movements: Elevation & Depression
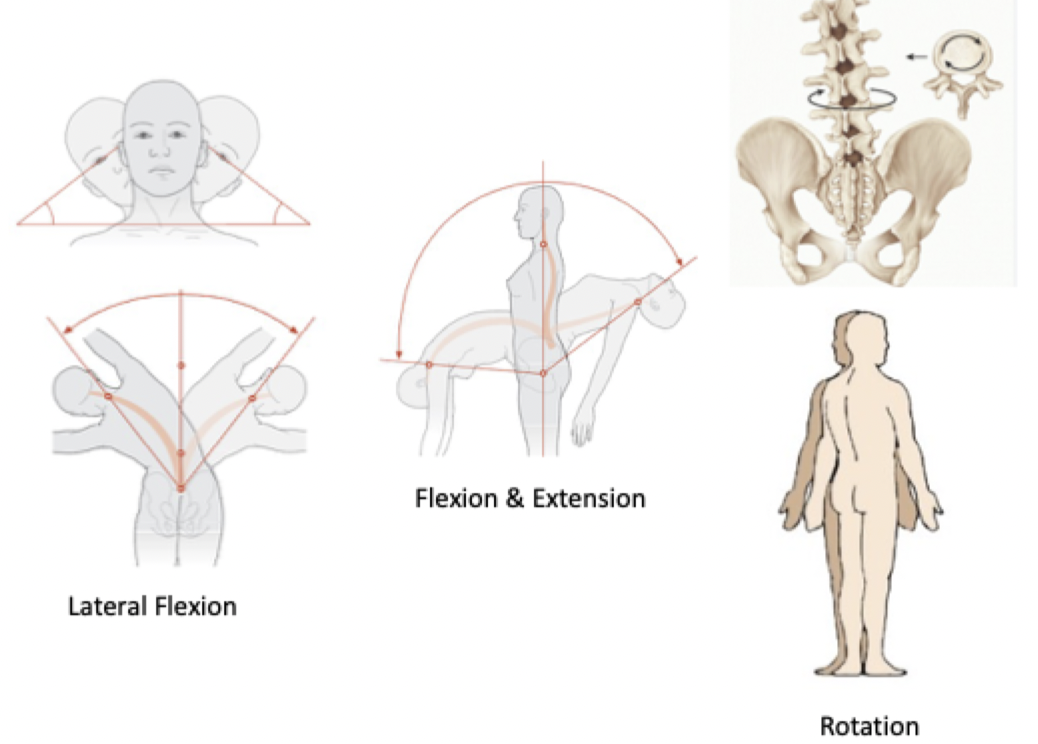
Lateral flexion: Vertebral column bends to the side
Flexion/Extension
Rotation (twisting)
Special Movements: Vertebral Column
Pivot joint
Hinge joint
Ellipsoid joint
Ball and socket joint
Saddle ioint
Gliding joint
Types of synovial joints
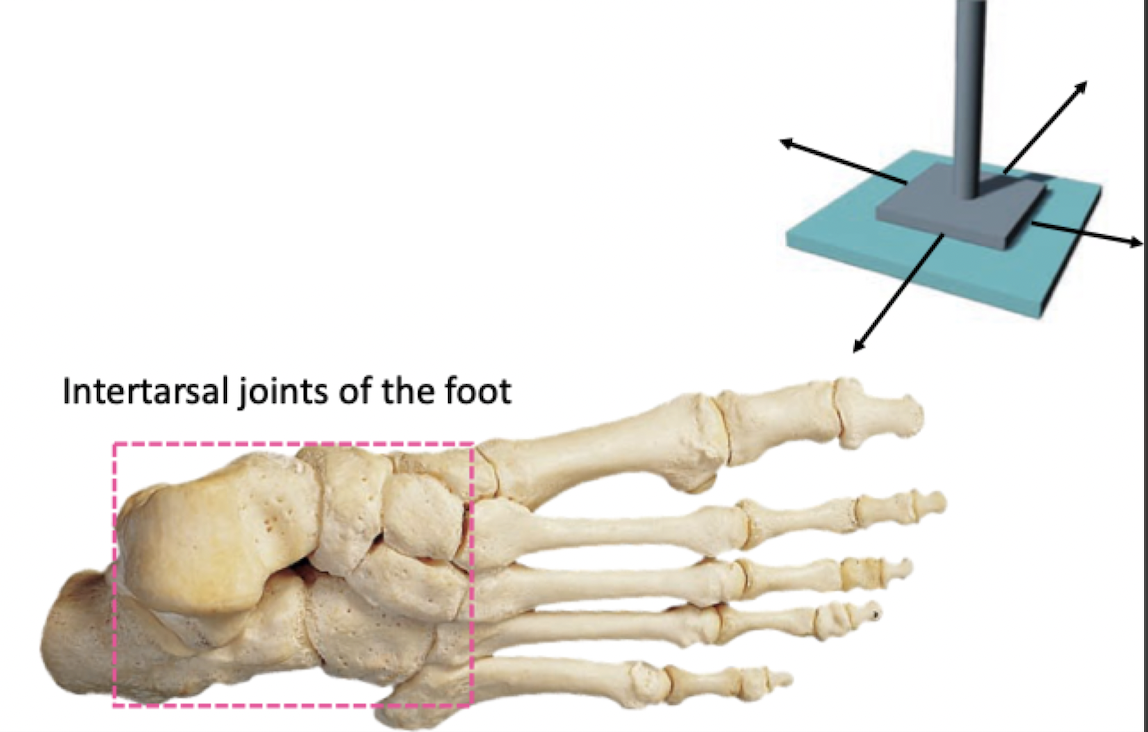
Flattened or slightly curved surfaces slide across one another
Gliding (plane) joint
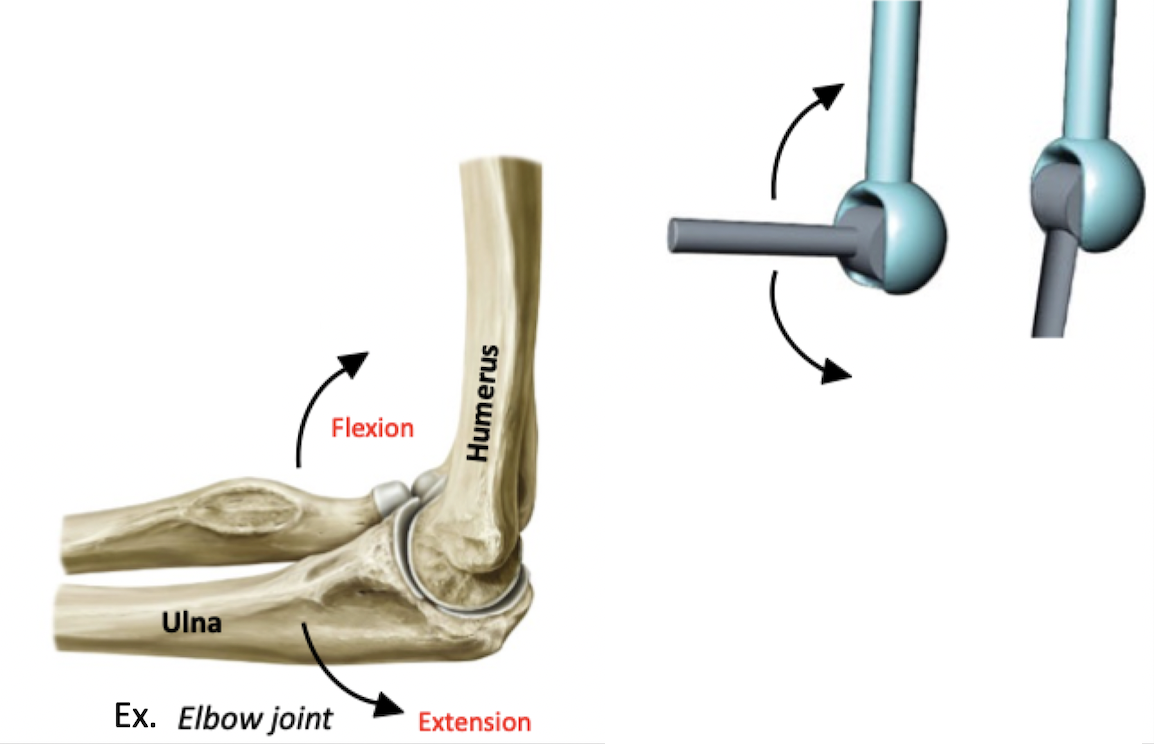
Monoaxial: angular movement across one axis (flexion/extension)
Convex surface of bone fits into a concave surface of a bone
Other hinge joints:
Ankle joint
Knee joint
Interphalangeal (finger) joints
*modified hinge joints, permit some other movements like slight gliding or rotation*
Hinge joint
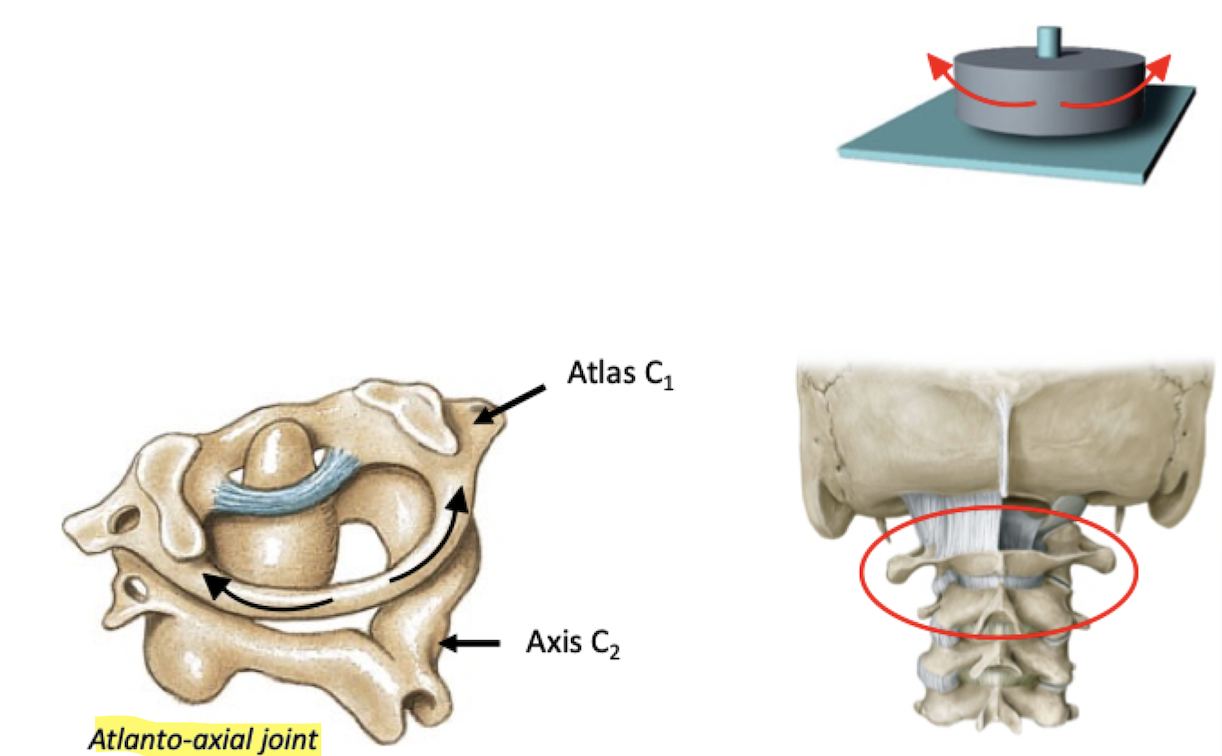
Monoaxial: permits only rotation
Pointed surface of bone articulates with a ring (made up of bone and ligament)
Other pivot joints: Proximal radioulnar joint
Pivot joint
Biaxial: permits motion across two axes
Oval articular face (condyle) sits within a depression on the opposing surface
Flexion, extension, abduction, adduction (and circumduction)
Ex. Metacarpophalangeal joints 1-5 of the hand
Ellipsoidal (condylar) joint
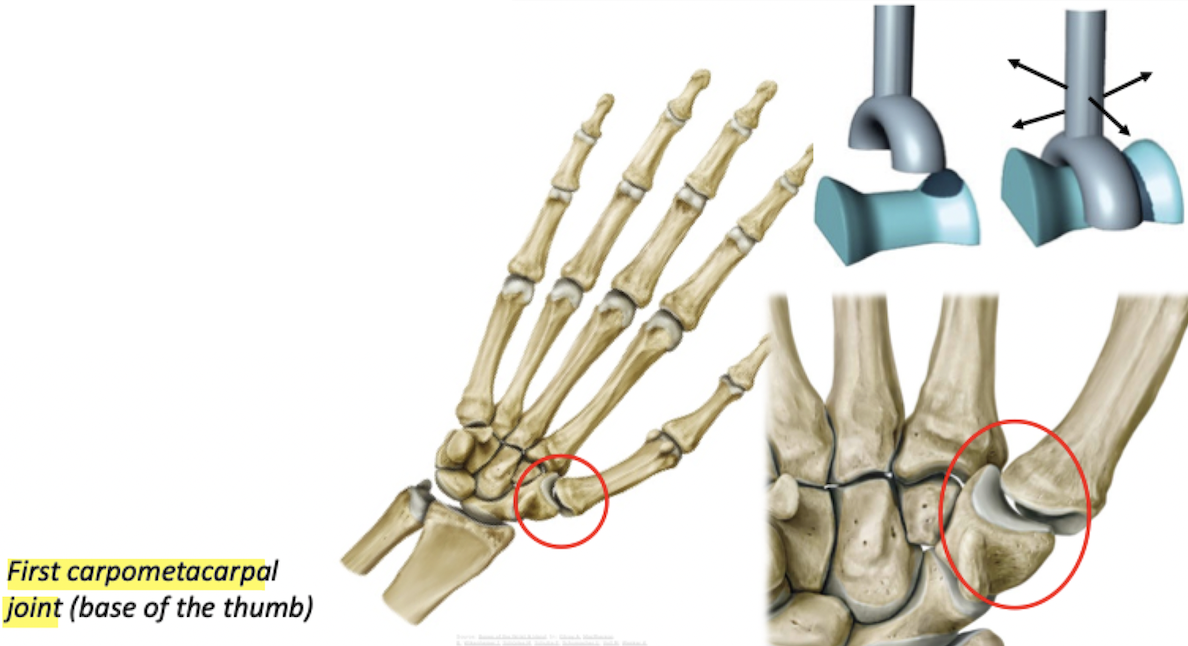
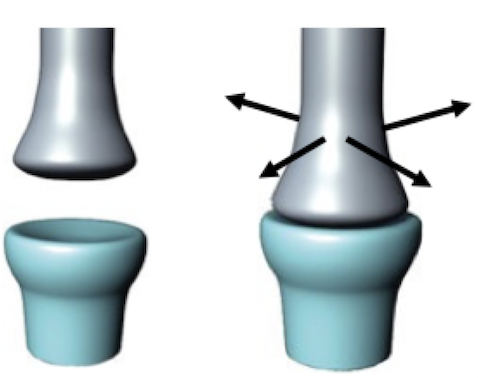
Biaxial: angular movement across two axes, opposition
Articular surface of a bone fits into a saddle-shaped bone
Saddle joint
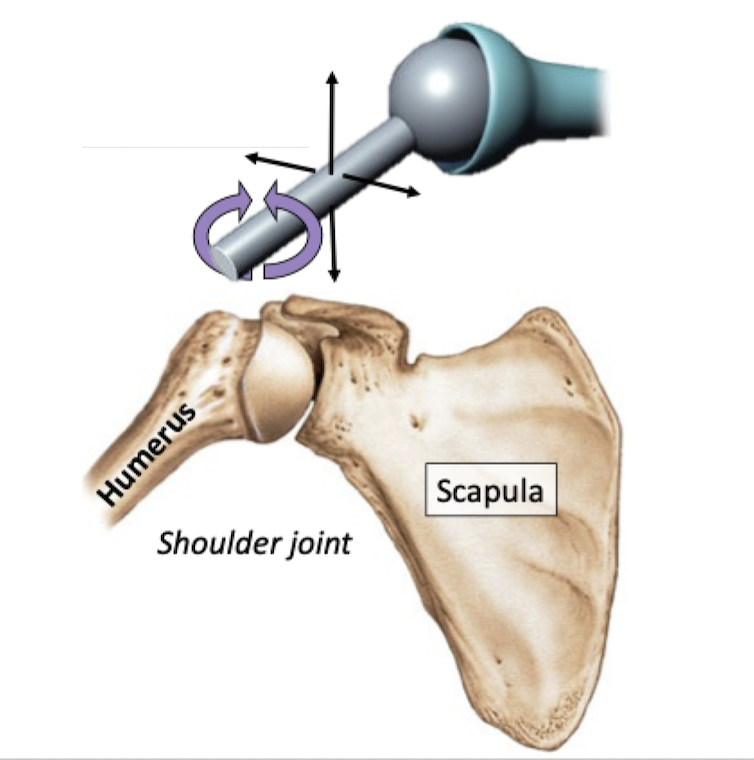
Most mobility
Triaxial: angular and rotational movement across three axes
Round head of a bone fits into a cup-shaped depression of a bone
Angular motion, circumduction, rotation
Other ball-and-socket joints: Hip joint
Ball-and-socket joint
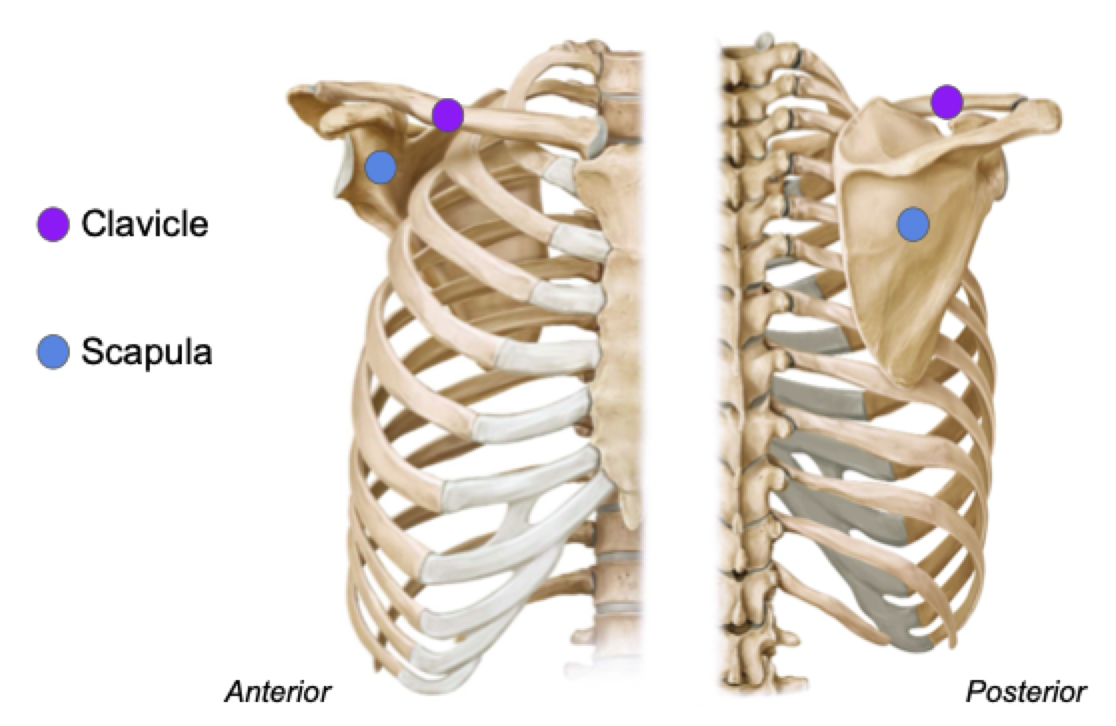
Pectoral Girdle
Label (What is the area called?)
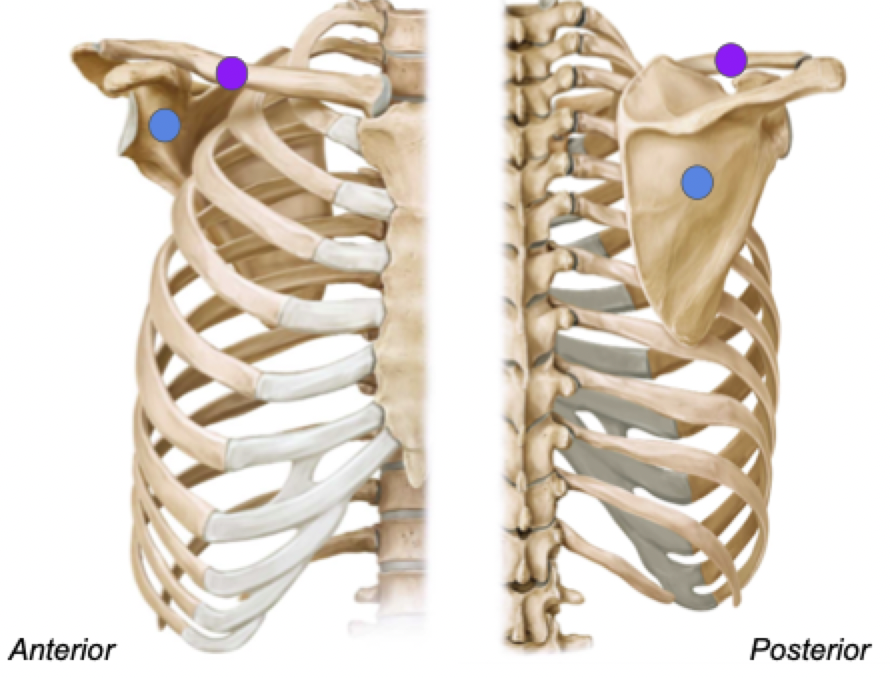
Orientation of pectoral girdle
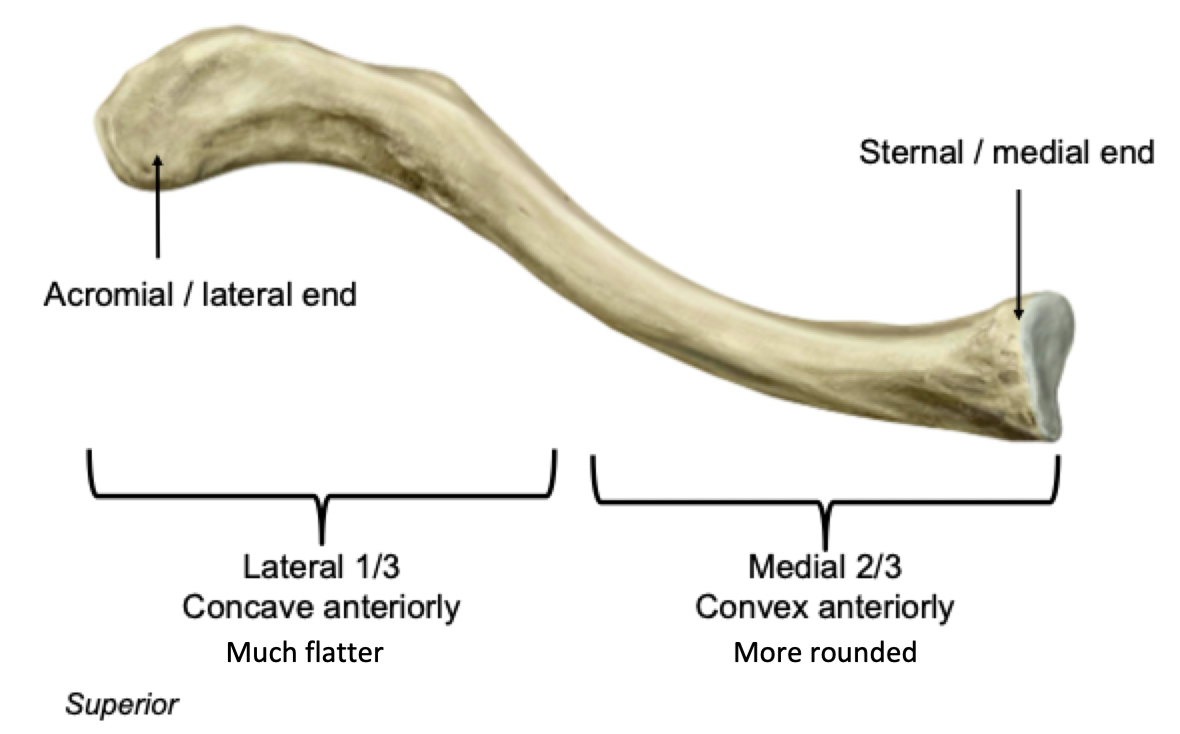
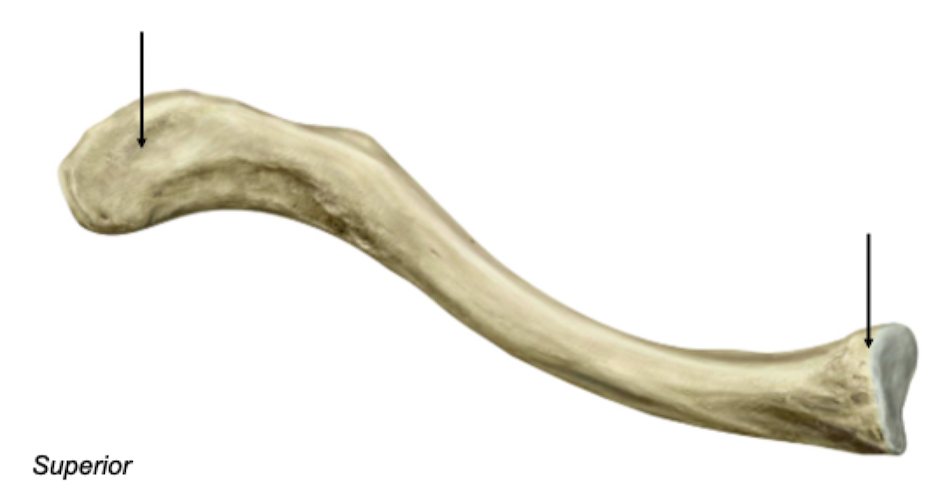
Clavicle - Superior view
Acromial / lateral end
Articulates with acromion of scapula
Sternal / medial end
Articulates with sternum
Label + Function
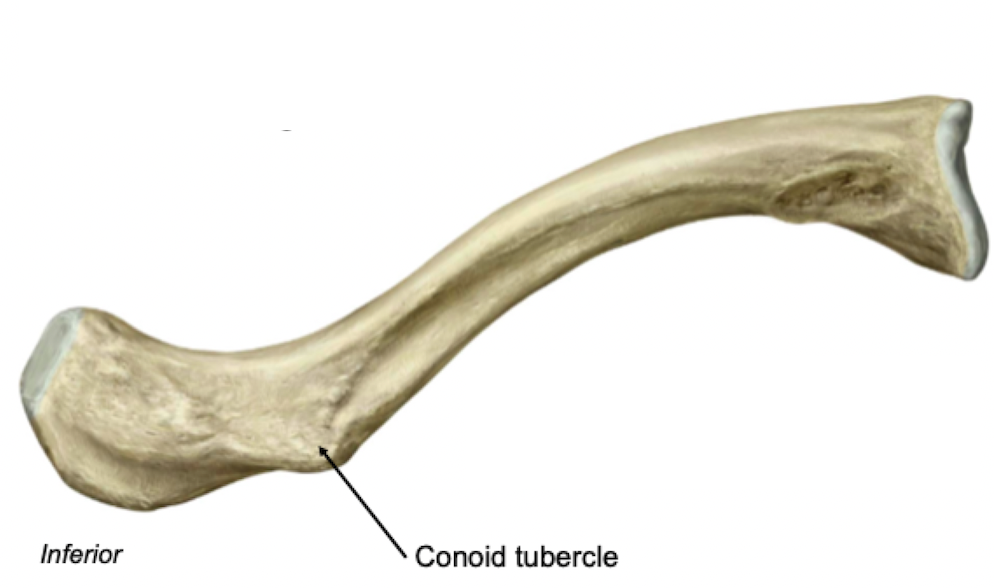
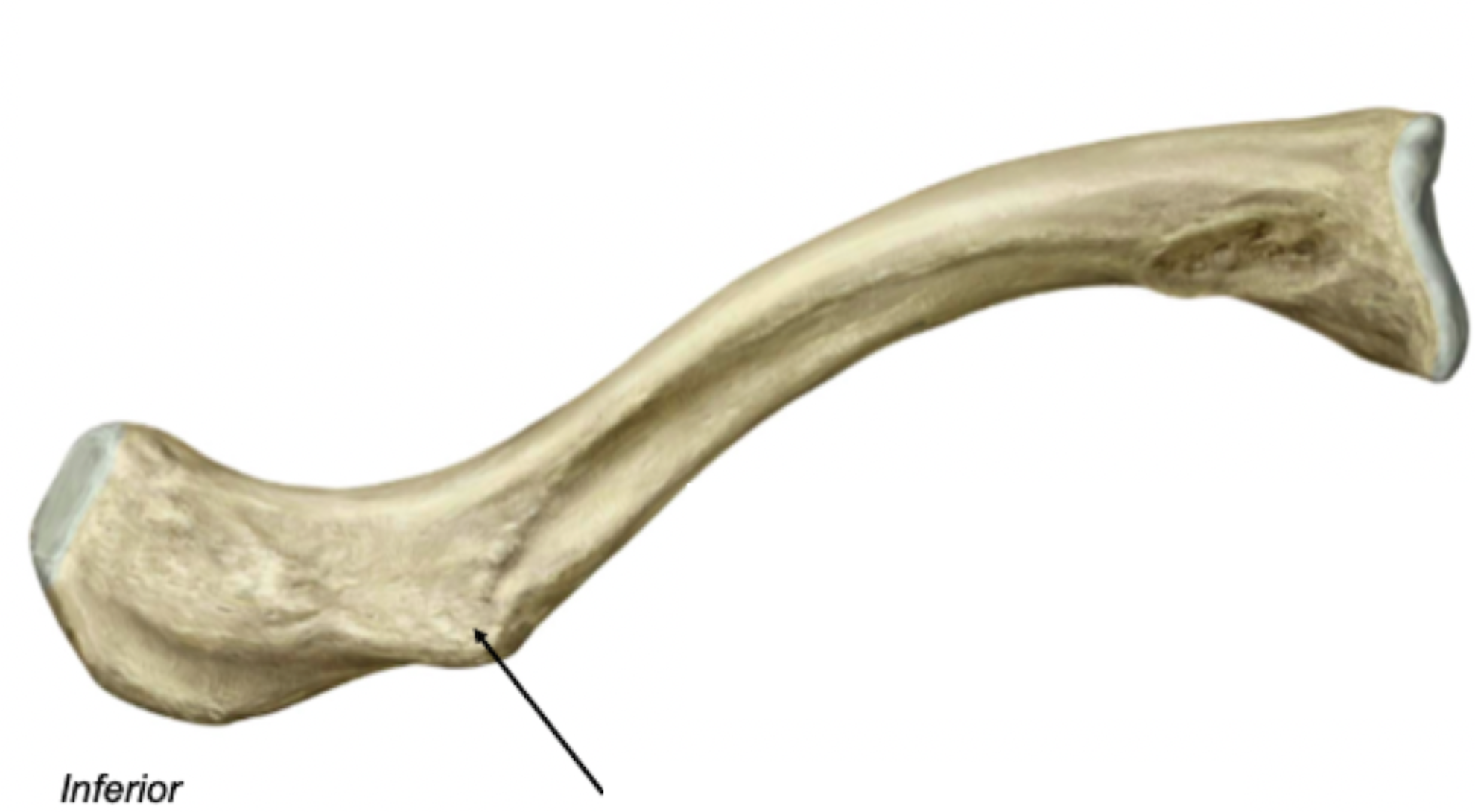
Clavicle - Inferior View
Rough inferior surface
Attachment sites for muscles and ligaments
Label + Describe
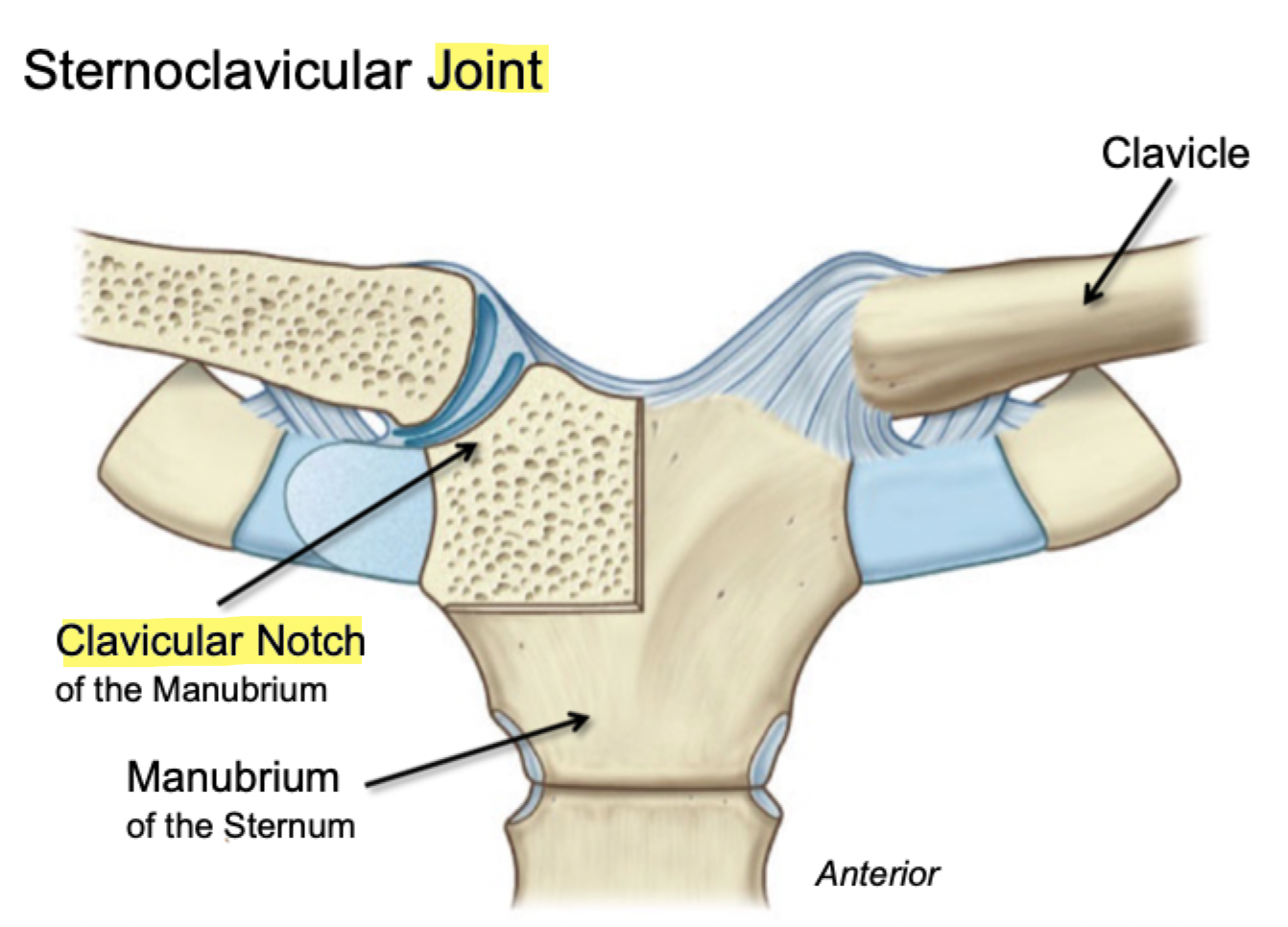
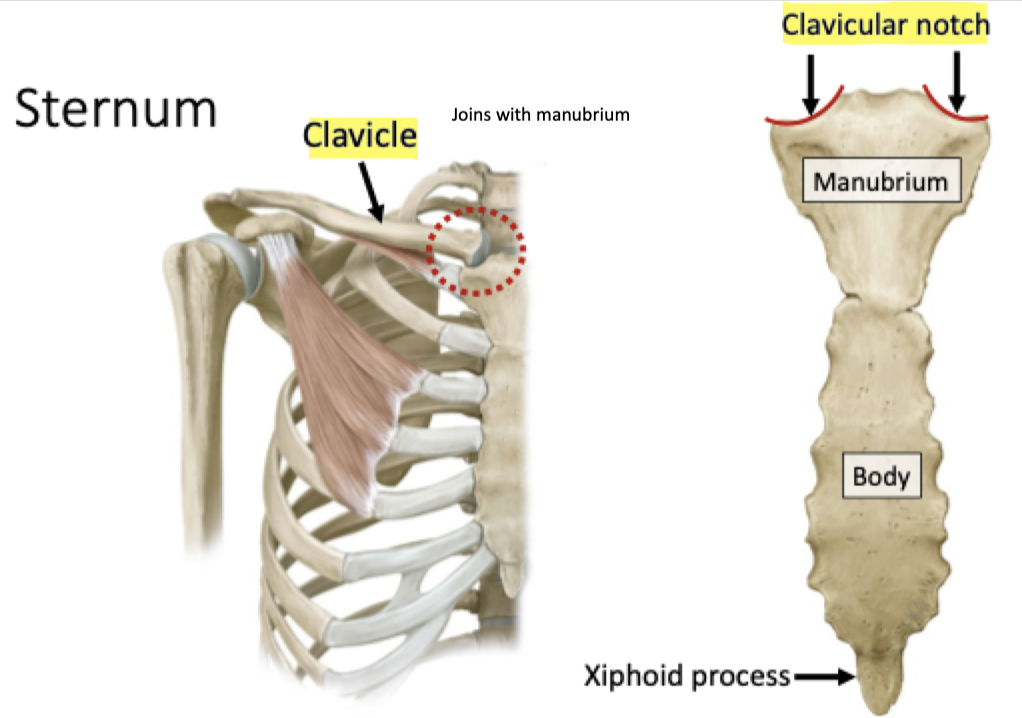
Sternoclaviular Joint
Label
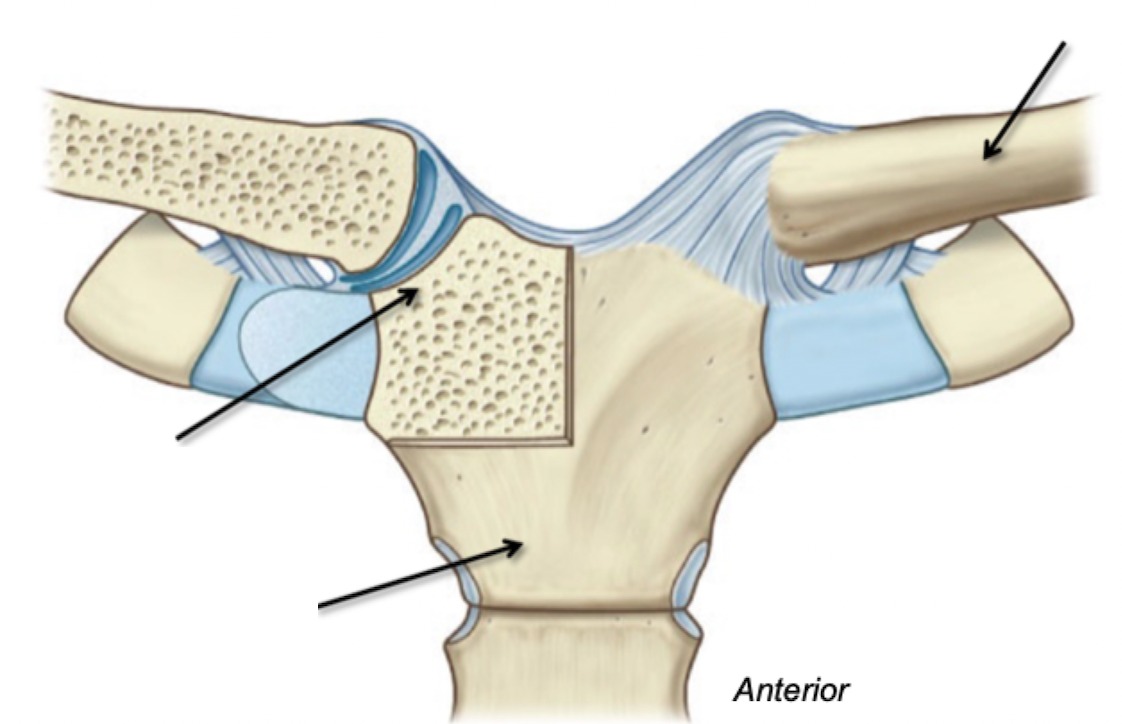
Depression in bone
Fossa
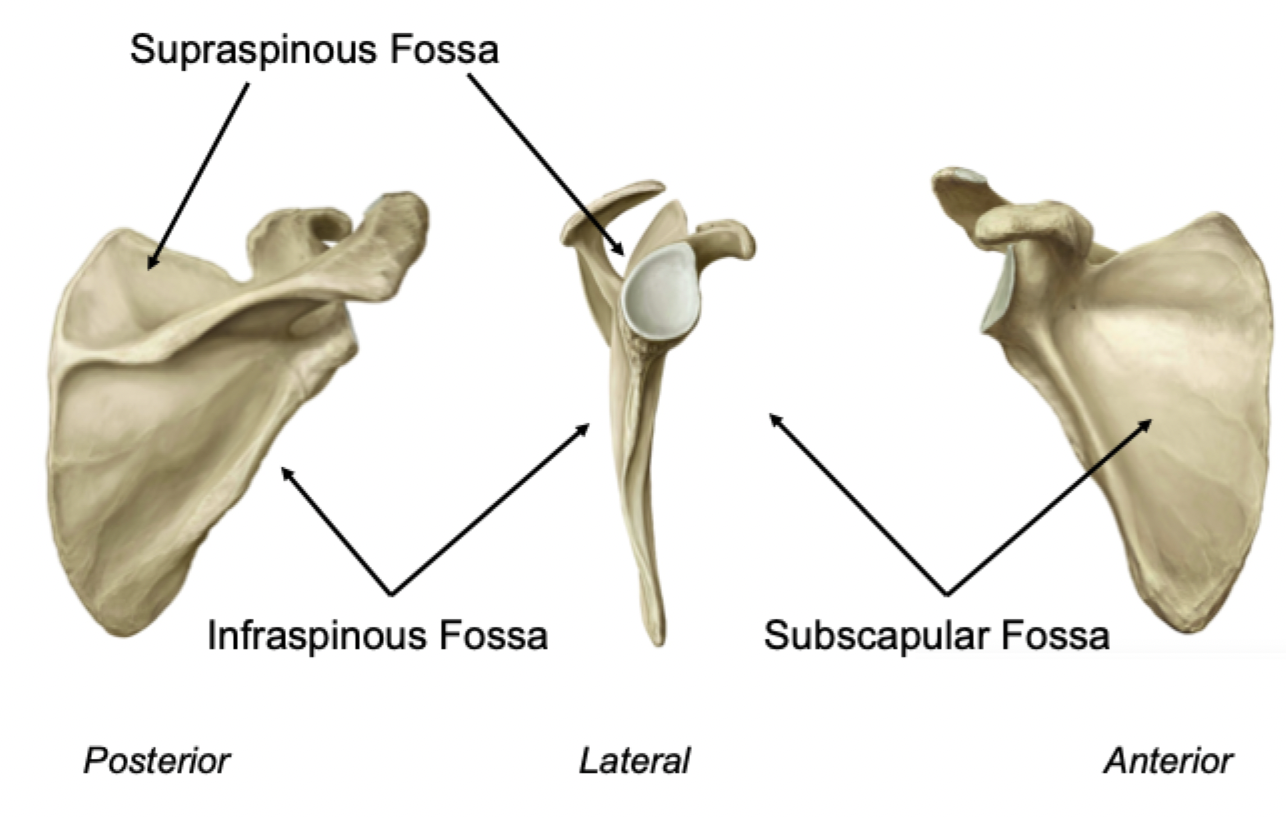
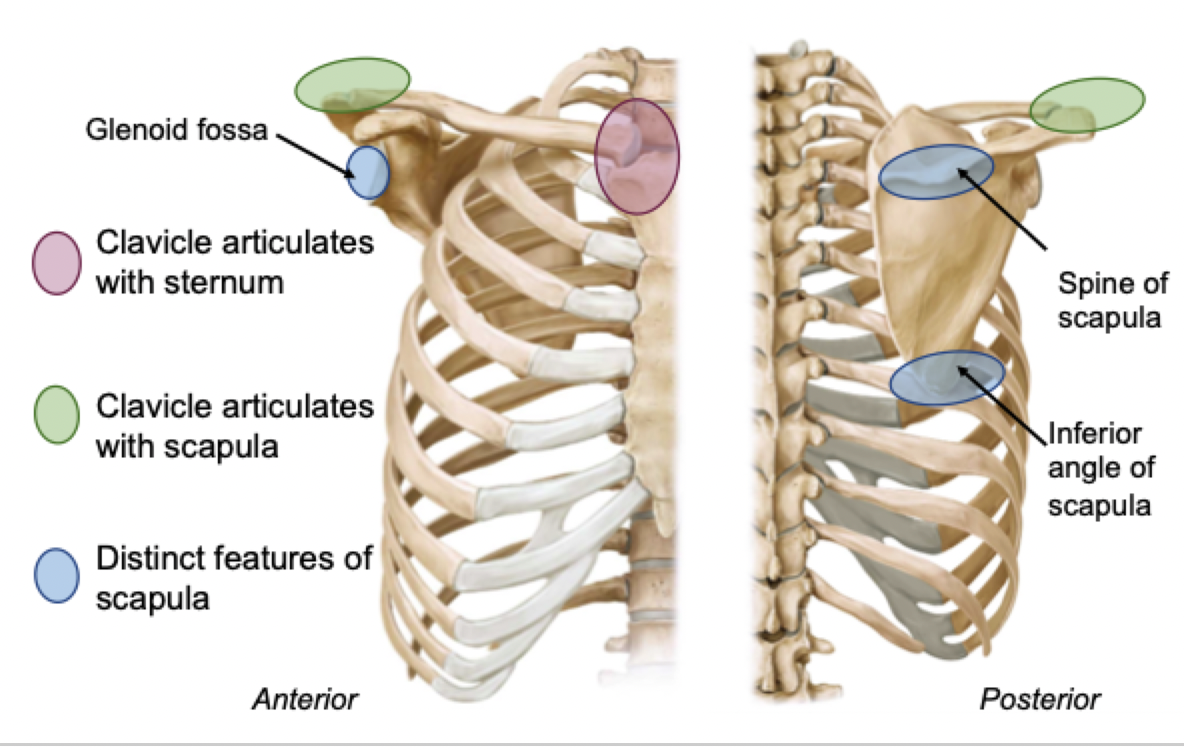
3 fossae of the scapula
Label