Microbio Lab Practical #2
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/29
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 1:42 AM on 3/15/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
1
New cards
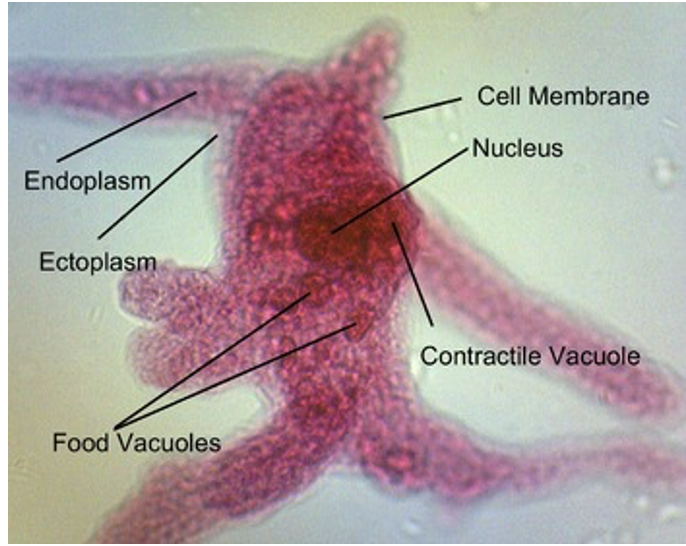
Amoeba
Supergroup: Unikonta
Subgroup: Gymnamoeba
Subgroup: Gymnamoeba
2
New cards
Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Supergroup: Unikonta
Subgroup: Fungus
Characteristics: budding yeast cells
Subgroup: Fungus
Characteristics: budding yeast cells
3
New cards
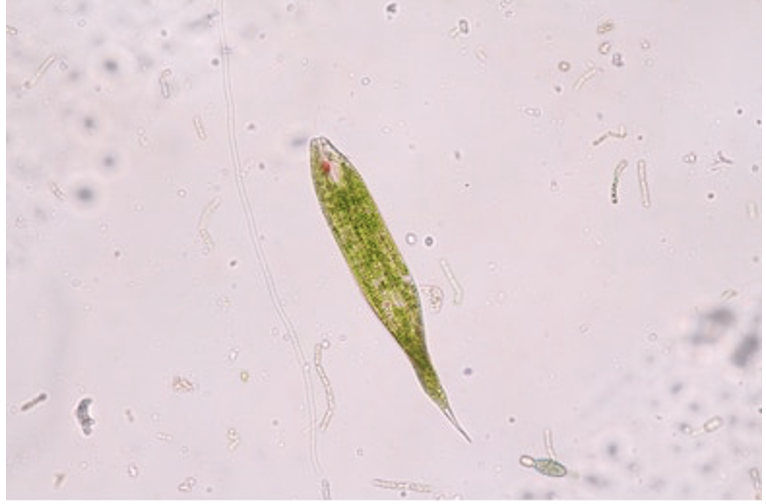
Euglena
Supergroup: Excavata
Subgroup: Euglenozoa
unicellular, green, autotrophs
Subgroup: Euglenozoa
unicellular, green, autotrophs
4
New cards
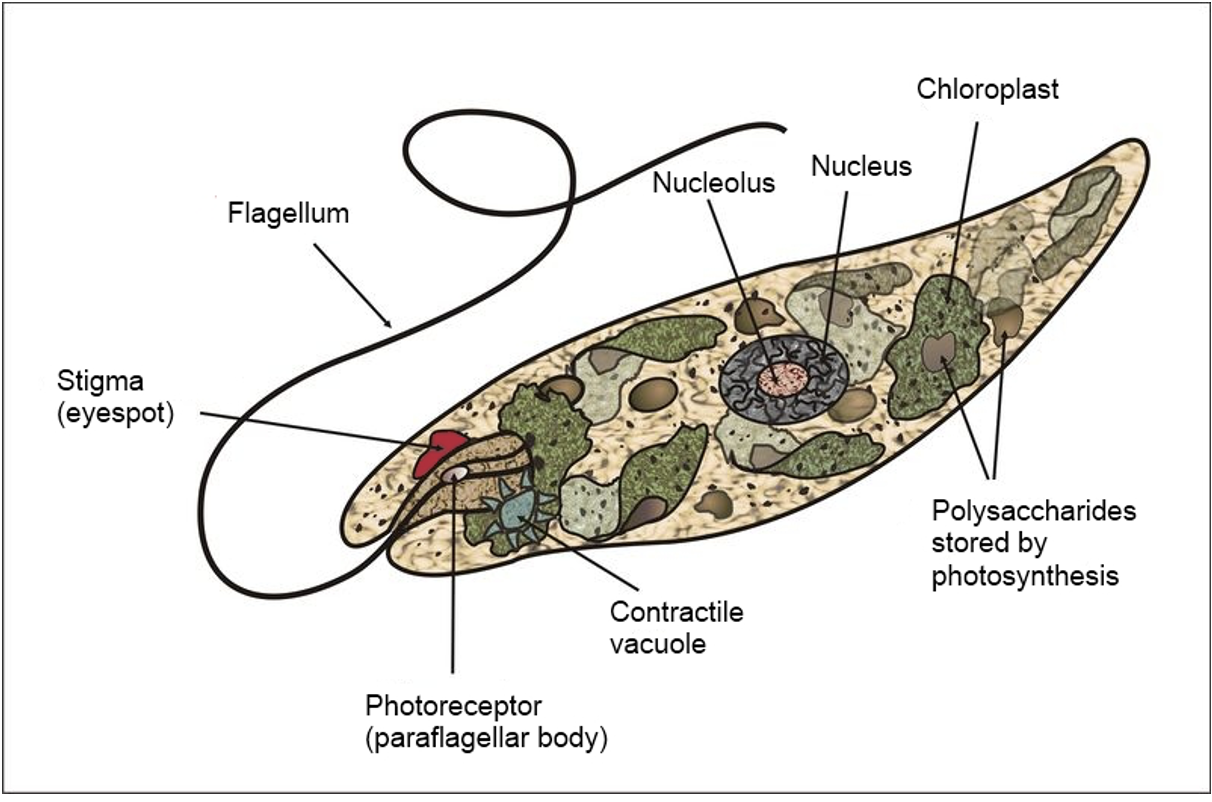
Euglena
Flagellum
Stigma: (eyespot) red
Chloroplast
Vacuole
Stigma: (eyespot) red
Chloroplast
Vacuole
5
New cards
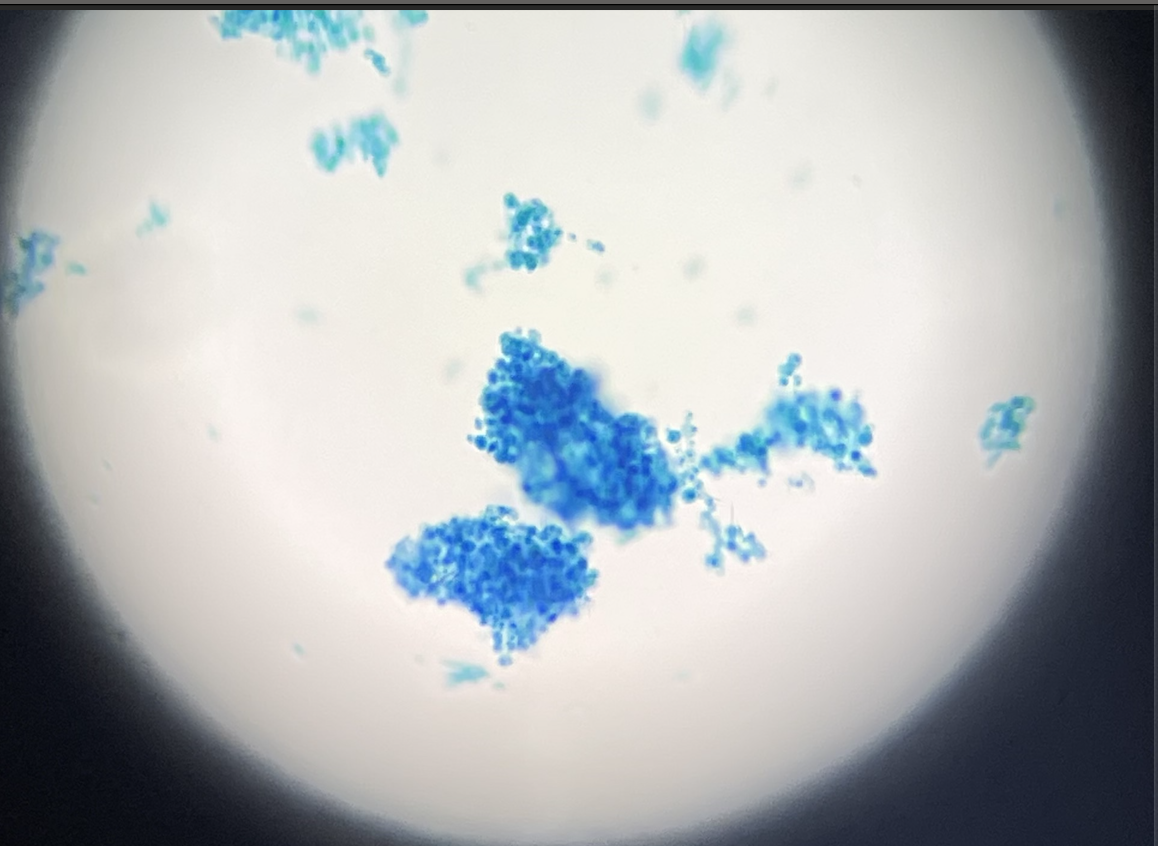
Chlamydomonas
Supergroup: Archaeplastida
Subgroup: Chlorophyte
Subgroup: Chlorophyte
6
New cards
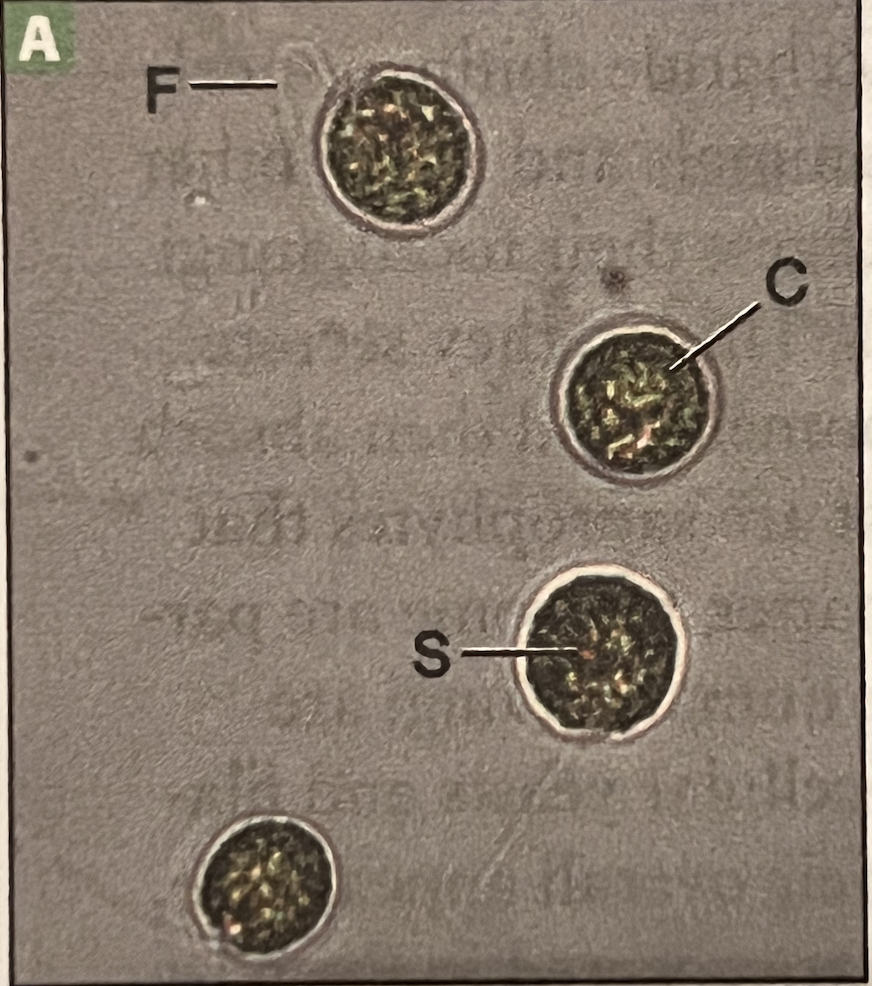
Chlamydomonas
F: Flagella
C: Chloroplast
S: stigma (red)
C: Chloroplast
S: stigma (red)
7
New cards
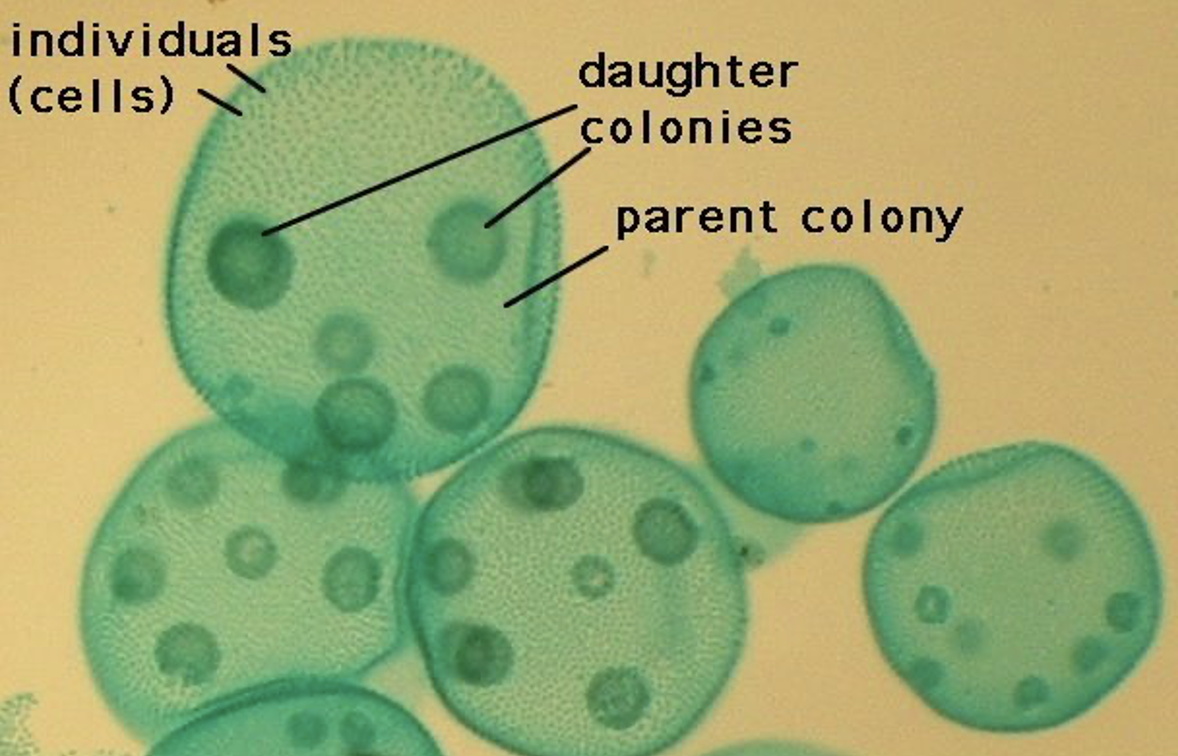
Volvox
Supergroup: Archaeplastida
Subgroup: chlorophyte
Subgroup: chlorophyte
8
New cards
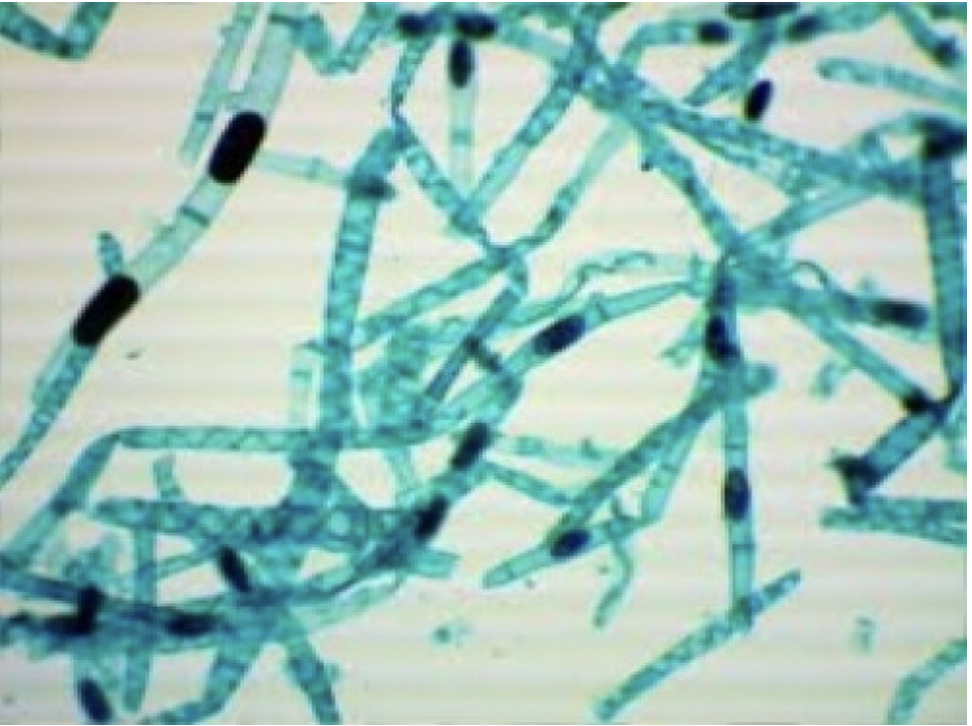
Spirogyra (vegetative)
Supergroup: Archaeplastida
Subgroup: Charophyte
filamentous alga that contains spiral chloroplasts and contains nucleus
Subgroup: Charophyte
filamentous alga that contains spiral chloroplasts and contains nucleus
9
New cards
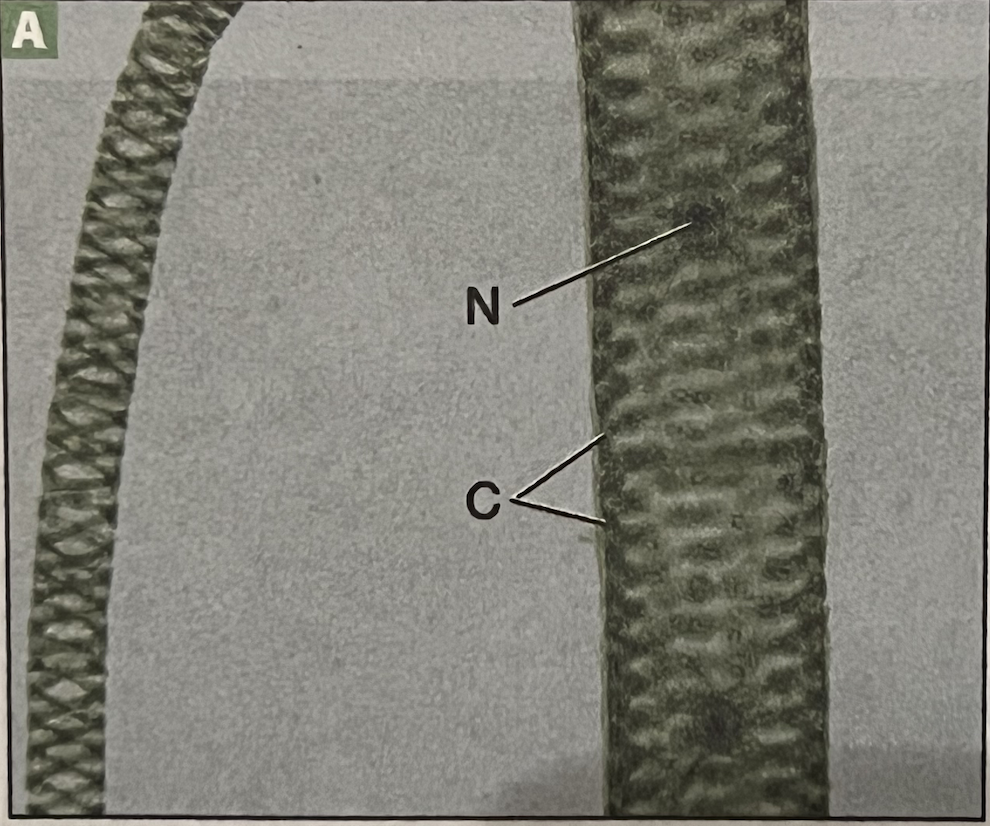
Spirogyra (vegetative)
N: Nucleus
C: Chloroplast (spiral)
C: Chloroplast (spiral)
10
New cards
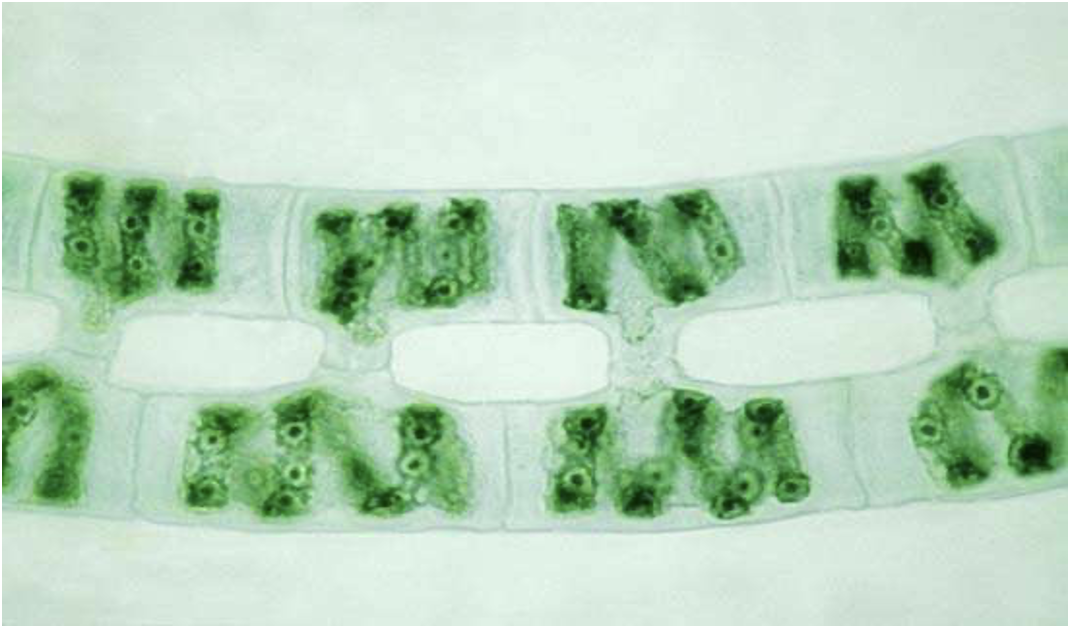
Spirogyra (conjugative)
Supergroup: Archaeplastida
Subgroup: Charophyte
two filaments beginning conjugation, they share cytoplasm and genetic material, contains zygospore
Subgroup: Charophyte
two filaments beginning conjugation, they share cytoplasm and genetic material, contains zygospore
11
New cards
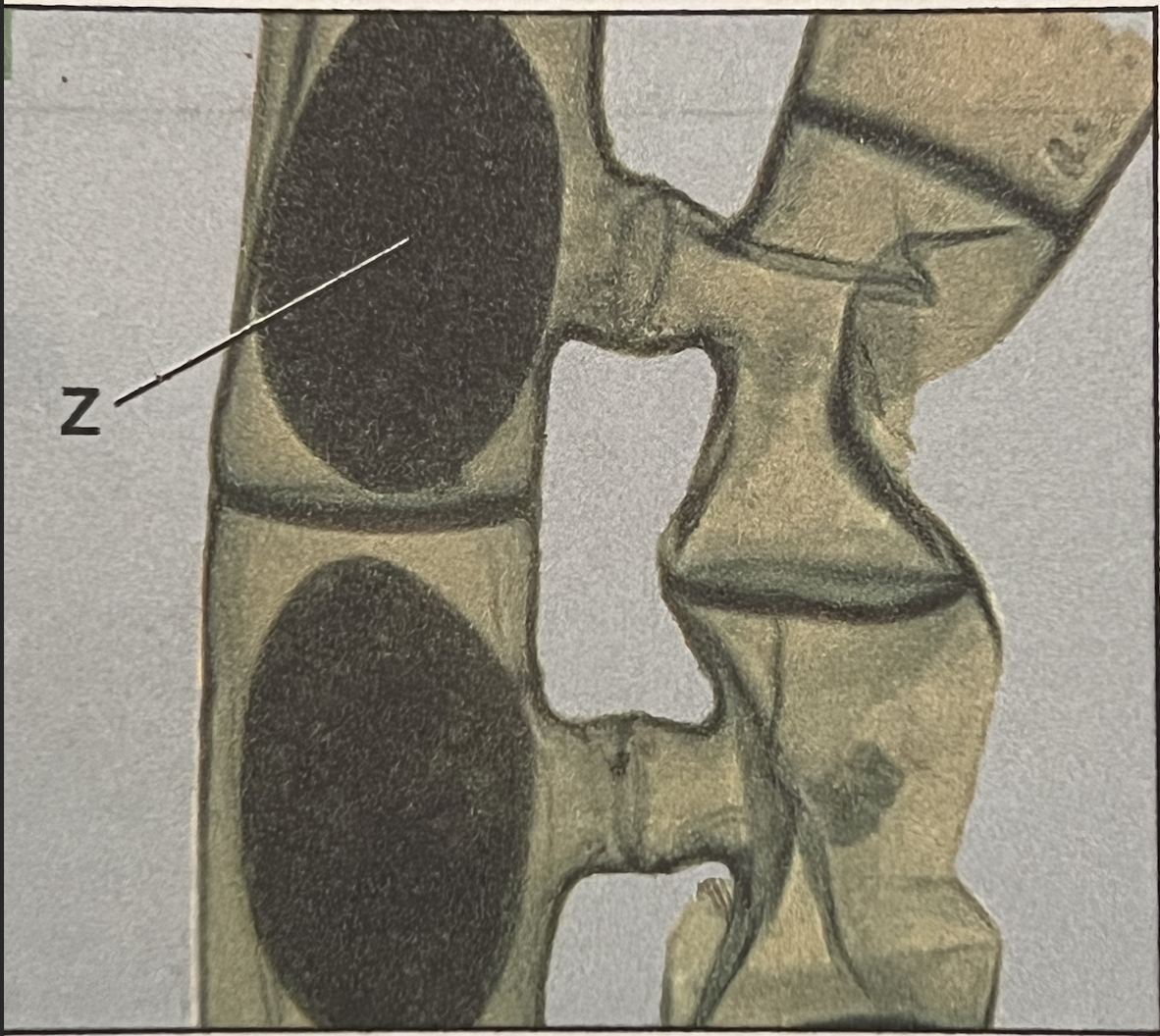
Spirogyra (conjugative)
Zygospore
12
New cards
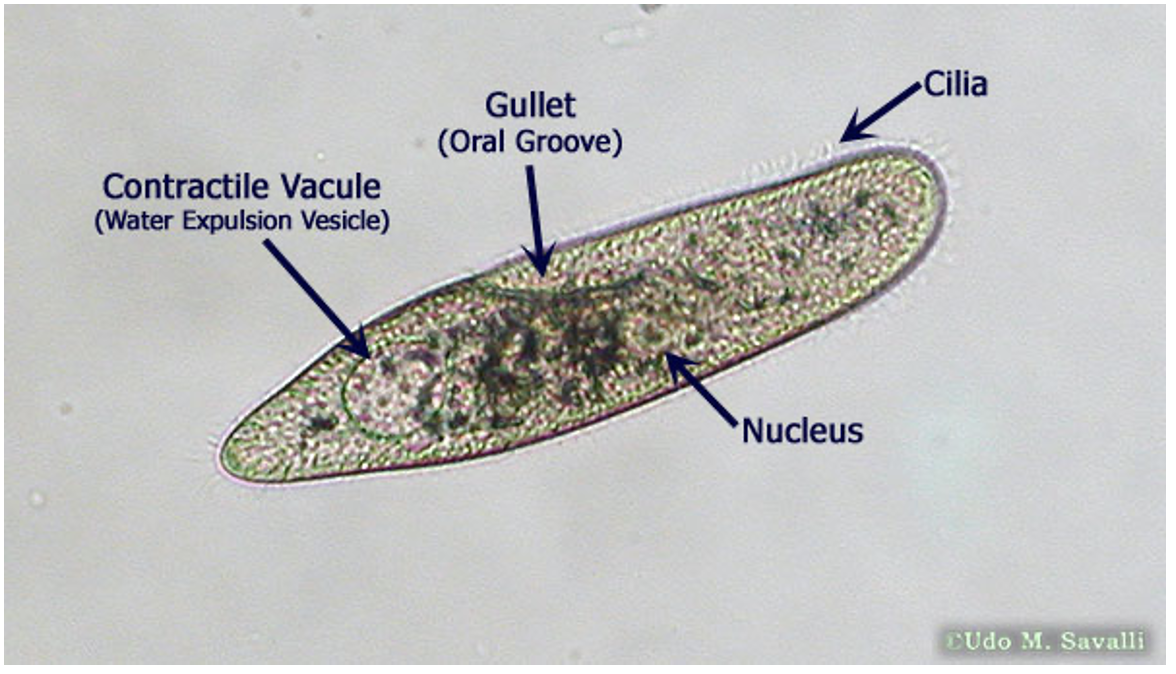
Paramecium
Supergroup: SAR
Subgroup: Alveolate
Subgroup: Alveolate
13
New cards
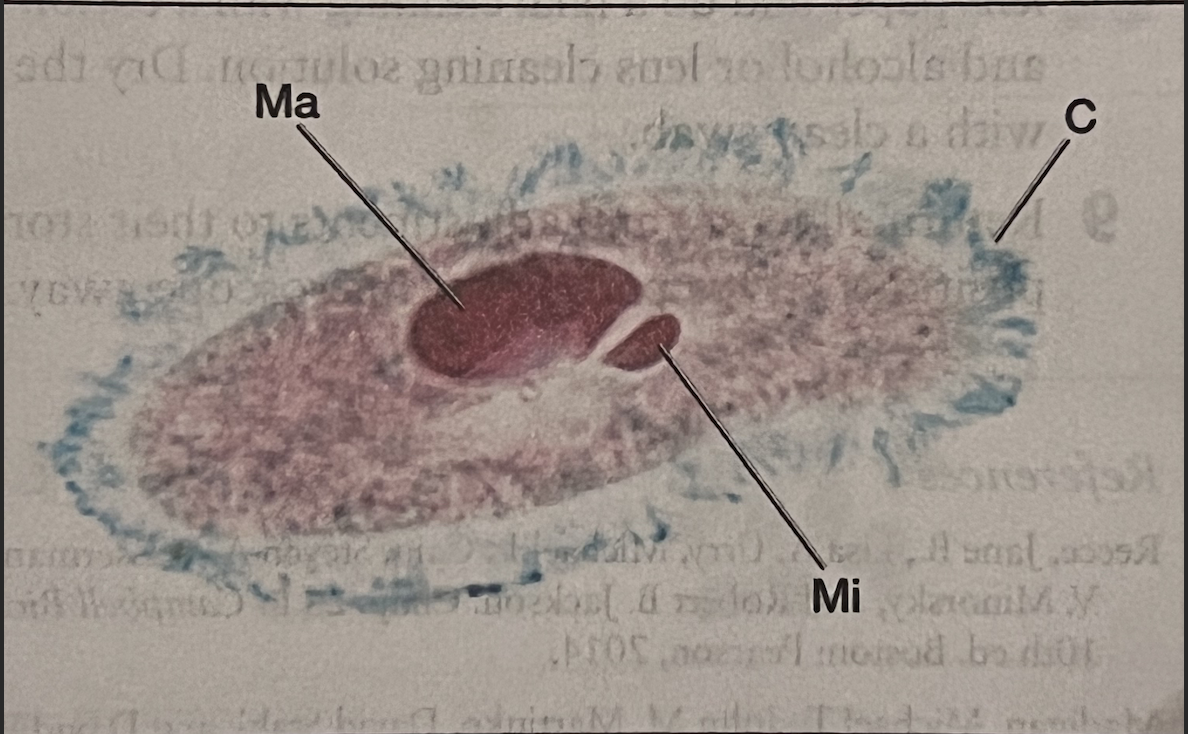
Paramecium
C: Cilia
Mi: Micronucleus
Ma: Macronucleus
Mi: Micronucleus
Ma: Macronucleus
14
New cards

Stentor
Supergroup: SAR
Subgroup: Alveolate
naturally green, trumpet shape, cilia, M: macronucleus
Subgroup: Alveolate
naturally green, trumpet shape, cilia, M: macronucleus
15
New cards
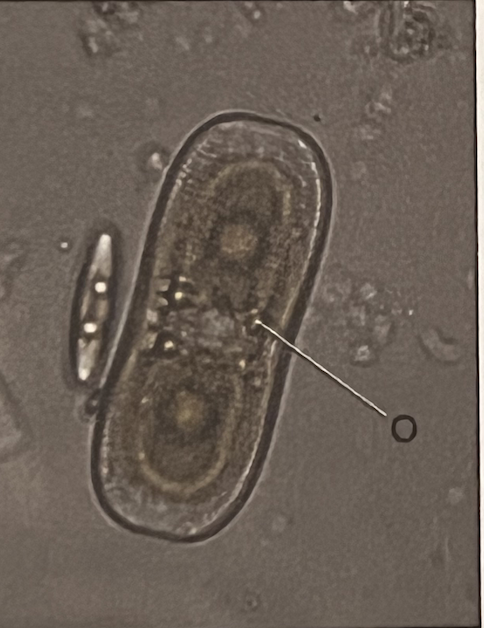
Diatom
Supergroup: SAR
Subgroup: Stramenopile
lack flagellum, can be pennate (bilateral symmetry), has a cell wall
Subgroup: Stramenopile
lack flagellum, can be pennate (bilateral symmetry), has a cell wall
16
New cards
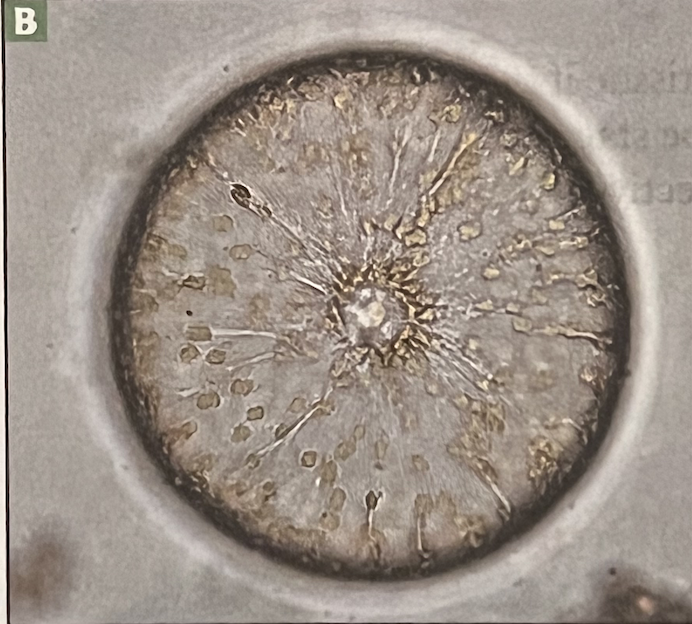
Diatom
centric shape (radical symmetry)
17
New cards
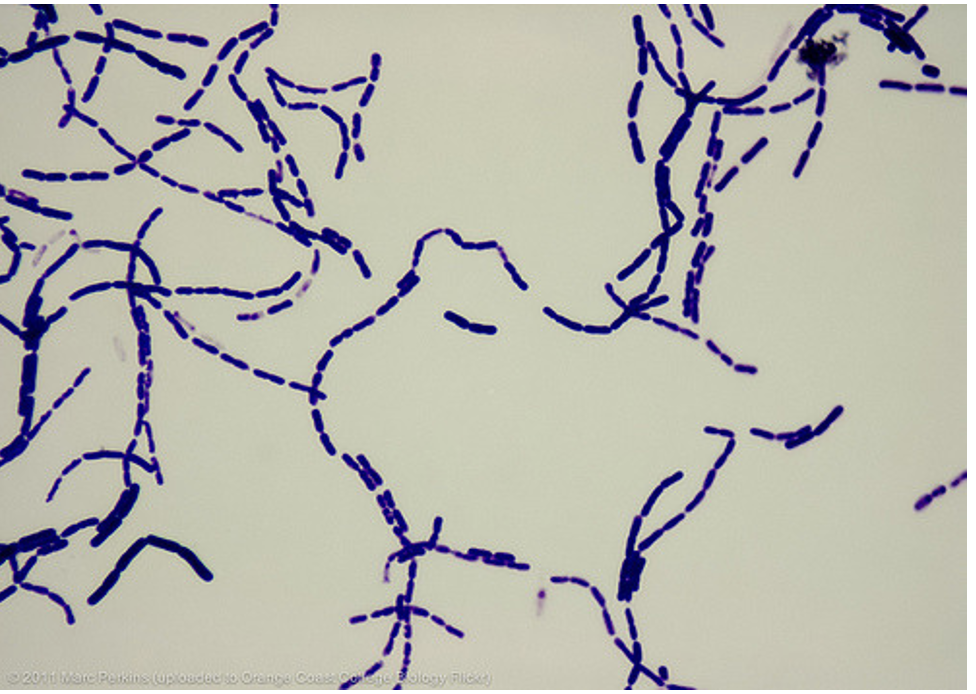
Bacillus cereus (simple stain)
Stain: Crystal Violet
Shape: Rod
Purpose of Stain: Cell morphology, size and arrangement can be determined
Arrangement: Streptobacilli
Why it stains: Stains have a positive charge that gets attracted to the negative charges on the bacteria making it stained.
Shape: Rod
Purpose of Stain: Cell morphology, size and arrangement can be determined
Arrangement: Streptobacilli
Why it stains: Stains have a positive charge that gets attracted to the negative charges on the bacteria making it stained.
18
New cards
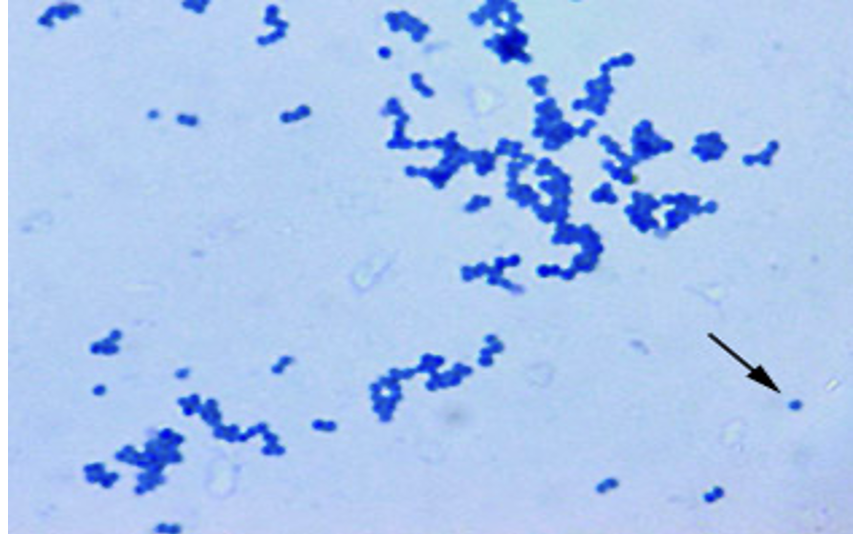
Micrococcus luteus (simple stain)
Stain: Methylene blue
Shape: coccus shape
Purpose of stain: Cell morphology, size and arrangement can be determined
Arrangement: Staphylococcus (irregular clusters)
Why it stains: Stains have a positive charge that gets attracted to the negative charges on the bacteria making it stained.
Shape: coccus shape
Purpose of stain: Cell morphology, size and arrangement can be determined
Arrangement: Staphylococcus (irregular clusters)
Why it stains: Stains have a positive charge that gets attracted to the negative charges on the bacteria making it stained.
19
New cards
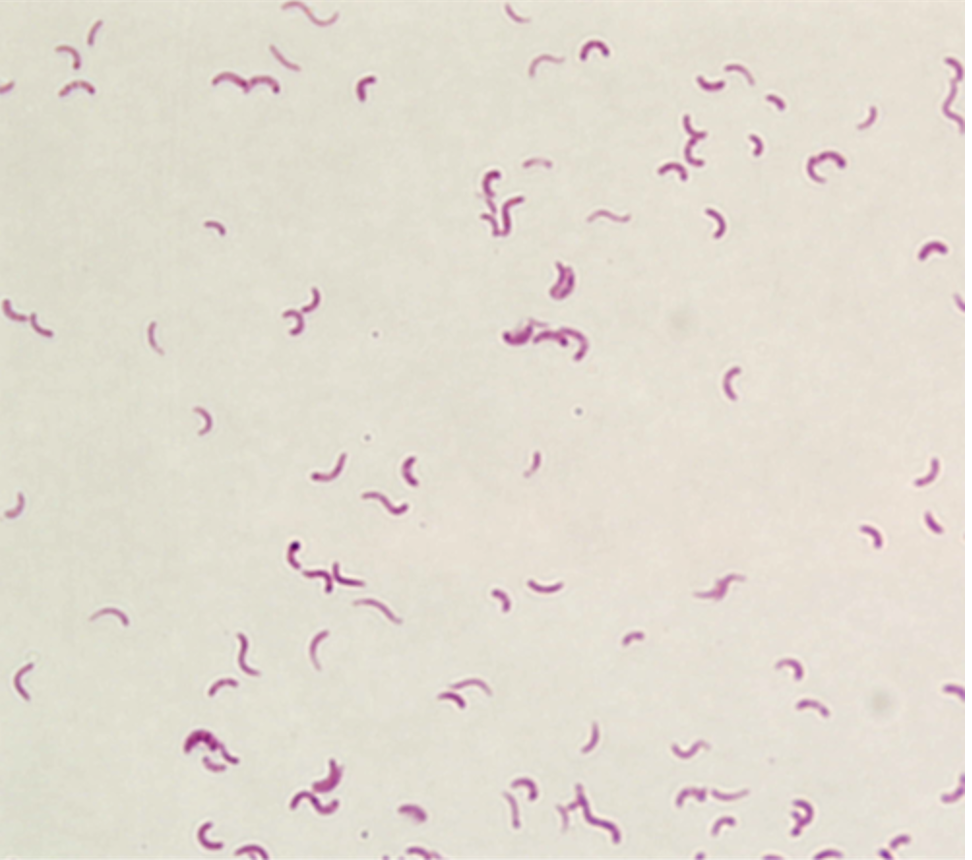
Rhodospirillum rubrum (simple stain)
Stain: Safranin
Shape: spiral
Purpose of stain: Cell morphology, size and arrangement can be determined
Arrangement: Spiral
Why it stains: Stains have a positive charge that gets attracted to the negative charges on the bacteria making it stained.
Shape: spiral
Purpose of stain: Cell morphology, size and arrangement can be determined
Arrangement: Spiral
Why it stains: Stains have a positive charge that gets attracted to the negative charges on the bacteria making it stained.
20
New cards
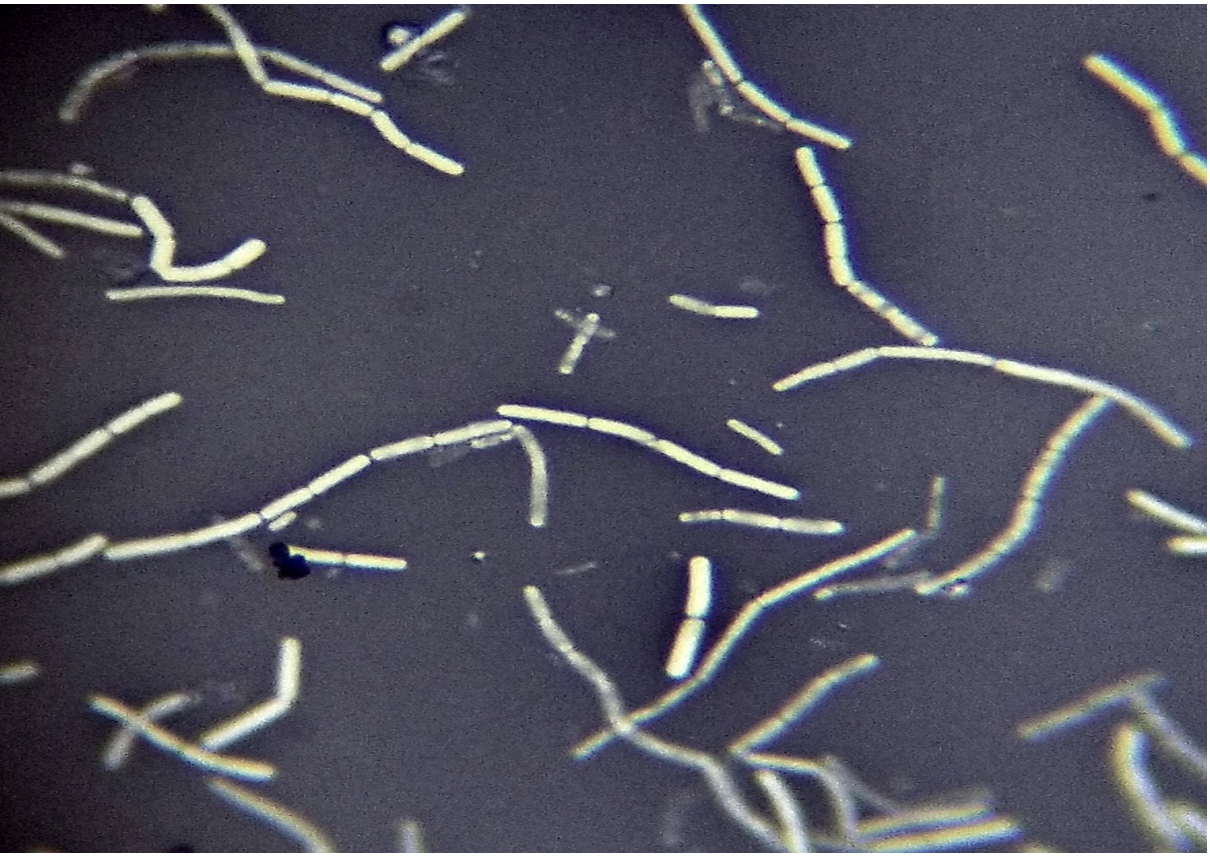
Bacillus cereus (negative stain)
Stain: nigrosin
Shape: rod
Purpose of stain: Cell morphology, size, and arrangement can be determined
Arrangement: Streptobacilli
Why it does not stain: The stain contains chromogen which is negative, and the bacteria are negative so it repels the stain making the background stained.
Shape: rod
Purpose of stain: Cell morphology, size, and arrangement can be determined
Arrangement: Streptobacilli
Why it does not stain: The stain contains chromogen which is negative, and the bacteria are negative so it repels the stain making the background stained.
21
New cards
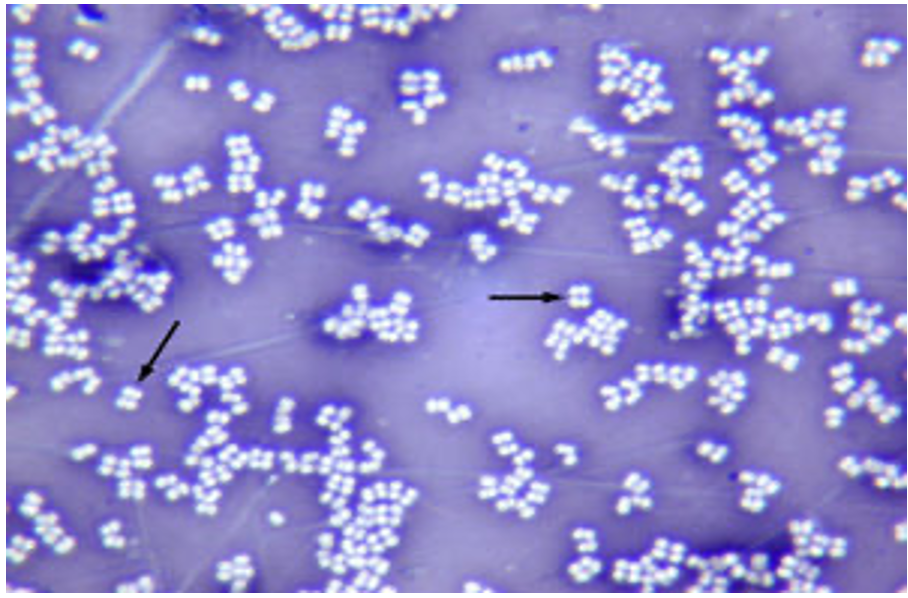
Micrococcus luteus (negative stain)
Stain: nigrosin
Shape: coccus
Purpose of stain: Cell morphology, size, and arrangement can be determined
Arrangement: Staphylcoccus (irregular clusters)
Why does it not stain: The stain contains chromogen which is negative, and the bacteria are negative so it repels the stain making the background stained.
Shape: coccus
Purpose of stain: Cell morphology, size, and arrangement can be determined
Arrangement: Staphylcoccus (irregular clusters)
Why does it not stain: The stain contains chromogen which is negative, and the bacteria are negative so it repels the stain making the background stained.
22
New cards
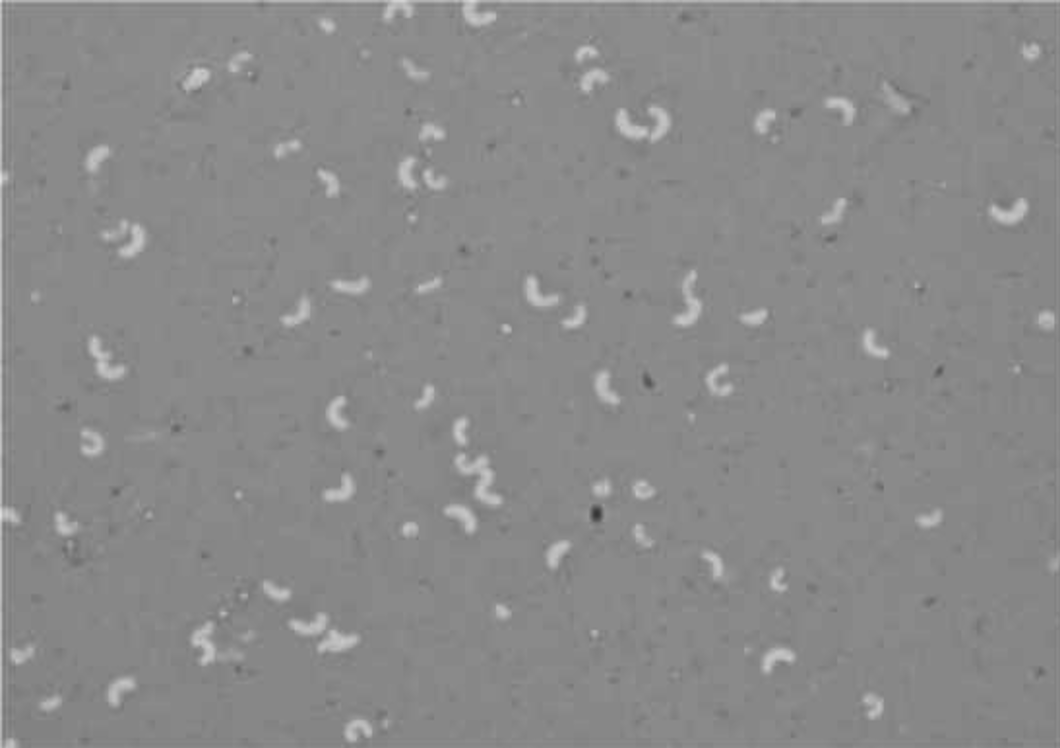
Rhodospirillum rubrum (negative stain)
Stain: nigrosin
Shape: spiral
Purpose of stain: Cell morphology, size, and arrangement can be determined
Arrangement: spiral
Why does it not stain: The stain contains chromogen which is negative, and the bacteria are negative so it repels the stain making the background stained.
Shape: spiral
Purpose of stain: Cell morphology, size, and arrangement can be determined
Arrangement: spiral
Why does it not stain: The stain contains chromogen which is negative, and the bacteria are negative so it repels the stain making the background stained.
23
New cards
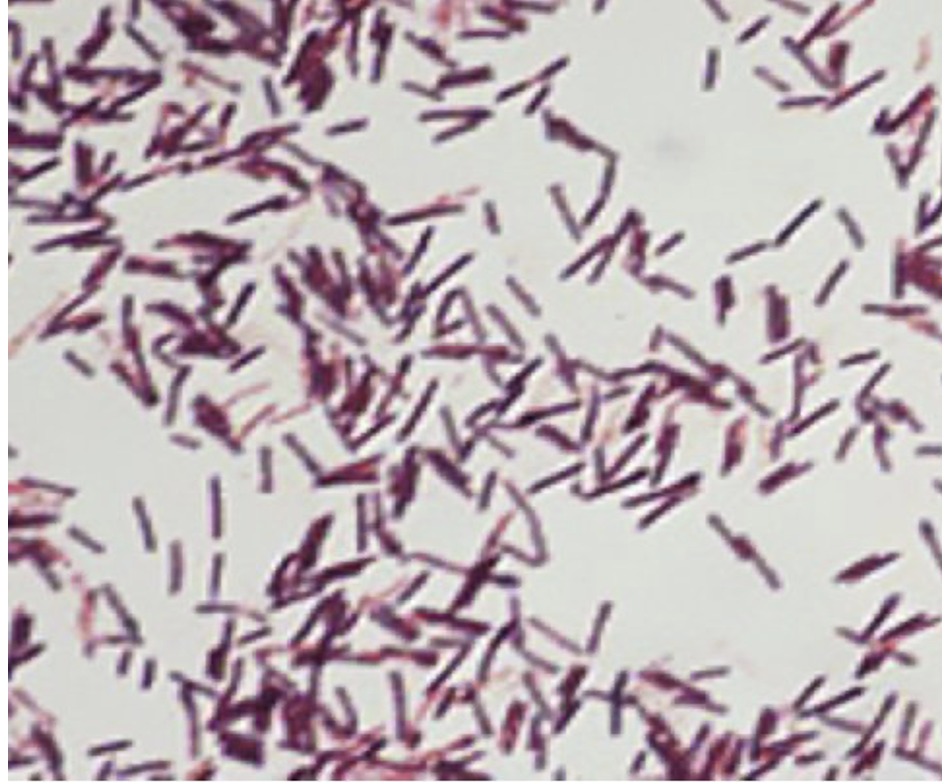
Bacillus cereus (gram stain)
Stains: Crystal violet and Safranin
Shape: rod
Purpose of stain: Cell morphology, size, and arrangement can be determined
Color: Purple
Reaction: Positive
Reagents used and purpose: It is called a differential stain because decolorization occurs between two stains. Crystal violet is the primary stain. Iodine is added (enhances crystal violet staining), then decolorization happens to gram negative cells with alcohol while gram positive stays purple. Safranin is added making gram negative cells red.
Shape: rod
Purpose of stain: Cell morphology, size, and arrangement can be determined
Color: Purple
Reaction: Positive
Reagents used and purpose: It is called a differential stain because decolorization occurs between two stains. Crystal violet is the primary stain. Iodine is added (enhances crystal violet staining), then decolorization happens to gram negative cells with alcohol while gram positive stays purple. Safranin is added making gram negative cells red.
24
New cards
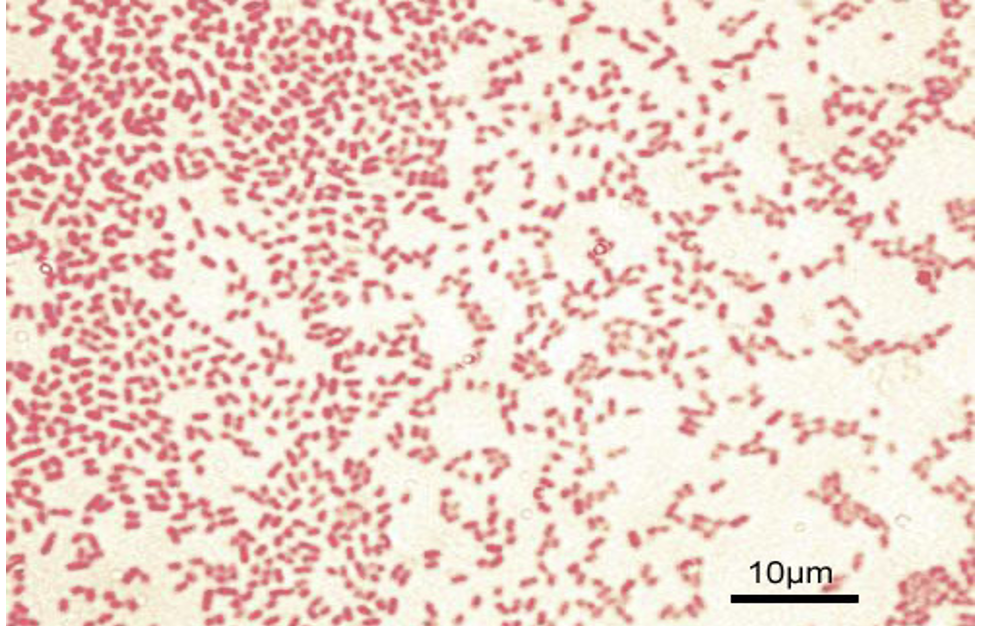
Escherichia coli (gram stain)
Stains: Crystal Violet and Safranin
Shape: bacillus
Purpose of stain: Cell morphology, size, and arrangement can be determined
Color: Reddish/pink
Reaction: Negative
Reagents used and purpose: It is called a differential stain because decolorization occurs between two stains. Crystal violet is the primary stain. Iodine is added (enhances crystal violet staining), then decolorization happens to gram negative cells with alcohol while gram positive stays purple. Safranin is added making gram negative cells red.
Shape: bacillus
Purpose of stain: Cell morphology, size, and arrangement can be determined
Color: Reddish/pink
Reaction: Negative
Reagents used and purpose: It is called a differential stain because decolorization occurs between two stains. Crystal violet is the primary stain. Iodine is added (enhances crystal violet staining), then decolorization happens to gram negative cells with alcohol while gram positive stays purple. Safranin is added making gram negative cells red.
25
New cards
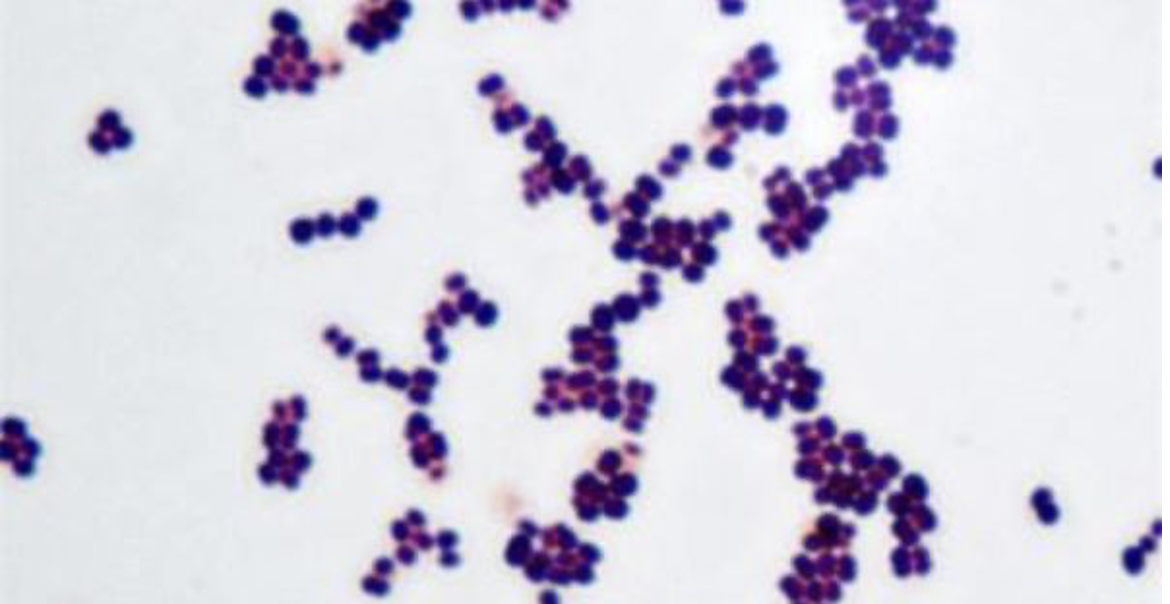
Micrococcus luteus (gram stain)
Stains: Crystal violet and safranin
Shape: coccus
Purpose of stain: Cell morphology, size, and arrangement can be determined
Color: Purple
Reaction: Positive
Reagents used and purpose: It is called a differential stain because decolorization occurs between two stains. Crystal violet is the primary stain. Iodine is added (enhances crystal violet staining), then decolorization happens to gram negative cells with alcohol while gram positive stays purple. Safranin is added making gram negative cells red.
Shape: coccus
Purpose of stain: Cell morphology, size, and arrangement can be determined
Color: Purple
Reaction: Positive
Reagents used and purpose: It is called a differential stain because decolorization occurs between two stains. Crystal violet is the primary stain. Iodine is added (enhances crystal violet staining), then decolorization happens to gram negative cells with alcohol while gram positive stays purple. Safranin is added making gram negative cells red.
26
New cards
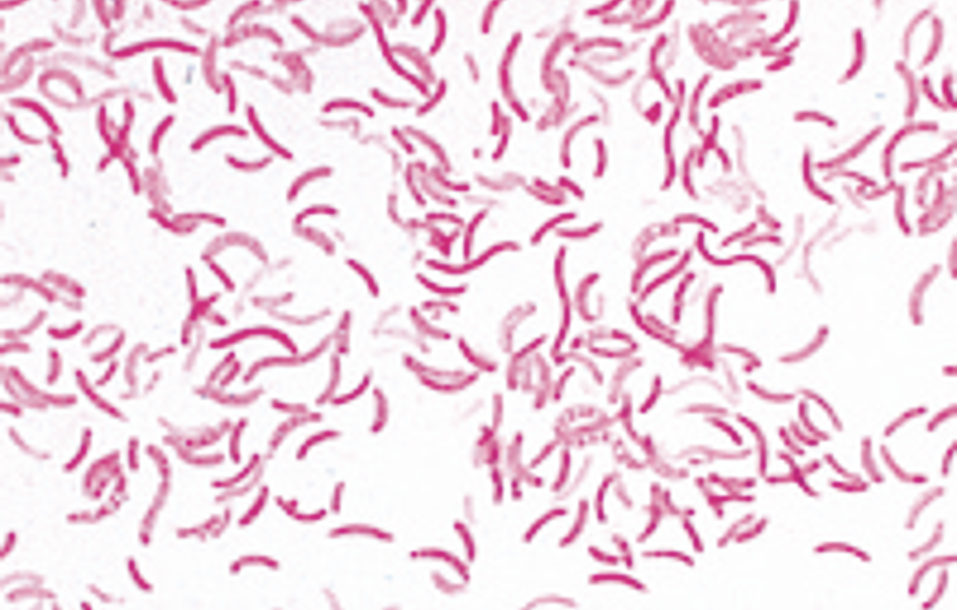

Rhodospirillum rubrum
Stains: Crystal violet and safranin
Shape: spiral
Purpose of stain: Cell morphology, size, and arrangement can be determined
Color: Reddish/pink
Reaction: Negative
Reagents used and purpose: It is called a differential stain because decolorization occurs between two stains. Crystal violet is the primary stain. Iodine is added (enhances crystal violet staining), then decolorization happens to gram negative cells with alcohol while gram positive stays purple. Safranin is added making gram negative cells red.
Shape: spiral
Purpose of stain: Cell morphology, size, and arrangement can be determined
Color: Reddish/pink
Reaction: Negative
Reagents used and purpose: It is called a differential stain because decolorization occurs between two stains. Crystal violet is the primary stain. Iodine is added (enhances crystal violet staining), then decolorization happens to gram negative cells with alcohol while gram positive stays purple. Safranin is added making gram negative cells red.
27
New cards
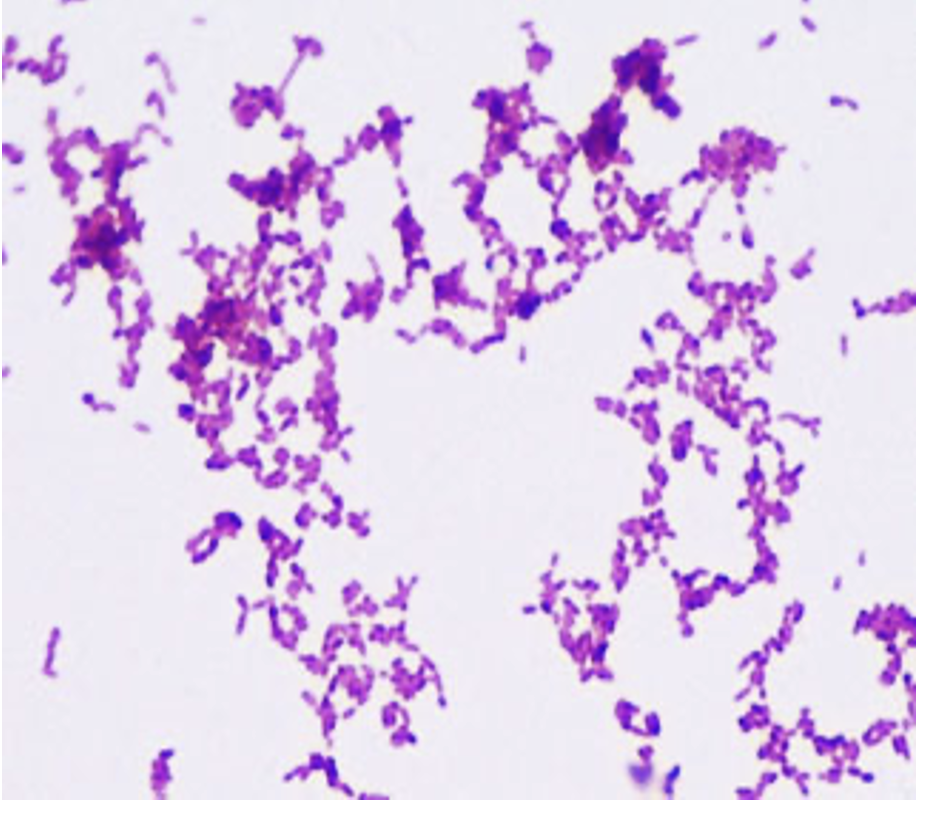
Mycobacterium smegmatics (acid fast stain)
Purpose of stain: To detect cells capable of retaining a primary stain when treated with alcohol.
Reagents used and purpose: Acid fast organisms contain mycolic acids (waxy substance) in cell wall which gives it a higher affinity for the primary stain and resistance to decolorization by acid alcohol. Carbolfuchsin is used as the primary stain because its lipid soluble and penetrates the cell wall making it red. After alcohol is applied methylene blue is the counterstain.
Why do we steam: helps melt the wax and allow the stain to move in
Reaction: Positive
Color: Reddish purple
Shape: bacillus
Reagents used and purpose: Acid fast organisms contain mycolic acids (waxy substance) in cell wall which gives it a higher affinity for the primary stain and resistance to decolorization by acid alcohol. Carbolfuchsin is used as the primary stain because its lipid soluble and penetrates the cell wall making it red. After alcohol is applied methylene blue is the counterstain.
Why do we steam: helps melt the wax and allow the stain to move in
Reaction: Positive
Color: Reddish purple
Shape: bacillus
28
New cards
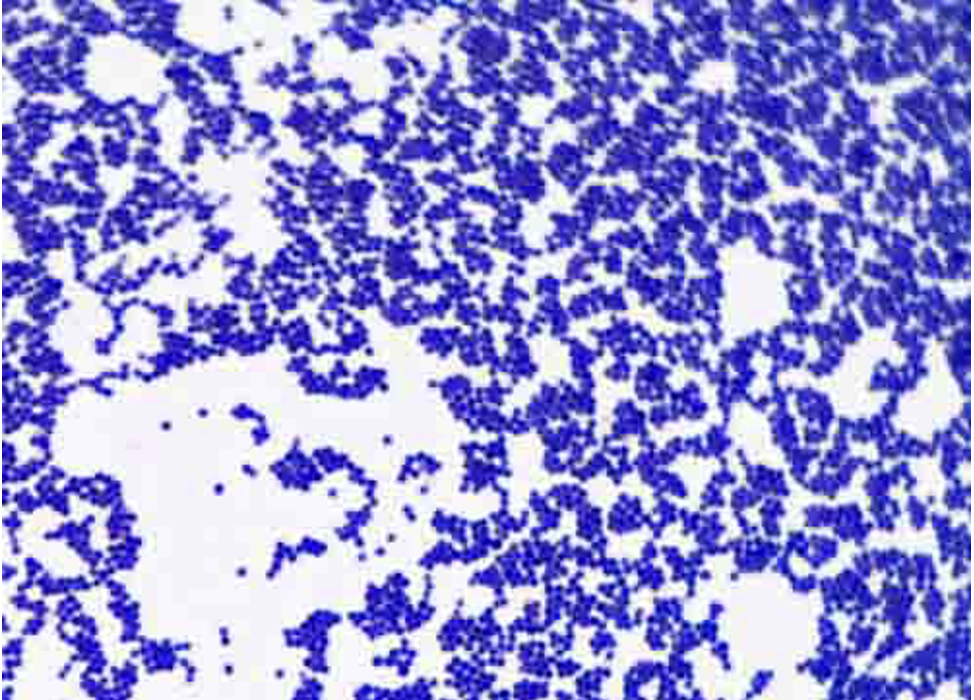
Staphylococcus epidermis (acid fast stain)
Purpose of stain: To detect cells capable of retaining a primary stain when treated with alcohol.
Reagents used and purpose: Acid fast organisms contain mycolic acids (waxy substance) in cell wall which gives it a higher affinity for the primary stain and resistance to decolorization by acid alcohol. Carbolfuchsin is used as the primary stain because its lipid soluble and penetrates the cell wall making it red. After alcohol is applied methylene blue is the counterstain.
Why do we steam: helps melt the wax and allow the stain to move in
Reaction: Negative
Color: Blue
Shape: coccus
Reagents used and purpose: Acid fast organisms contain mycolic acids (waxy substance) in cell wall which gives it a higher affinity for the primary stain and resistance to decolorization by acid alcohol. Carbolfuchsin is used as the primary stain because its lipid soluble and penetrates the cell wall making it red. After alcohol is applied methylene blue is the counterstain.
Why do we steam: helps melt the wax and allow the stain to move in
Reaction: Negative
Color: Blue
Shape: coccus
29
New cards
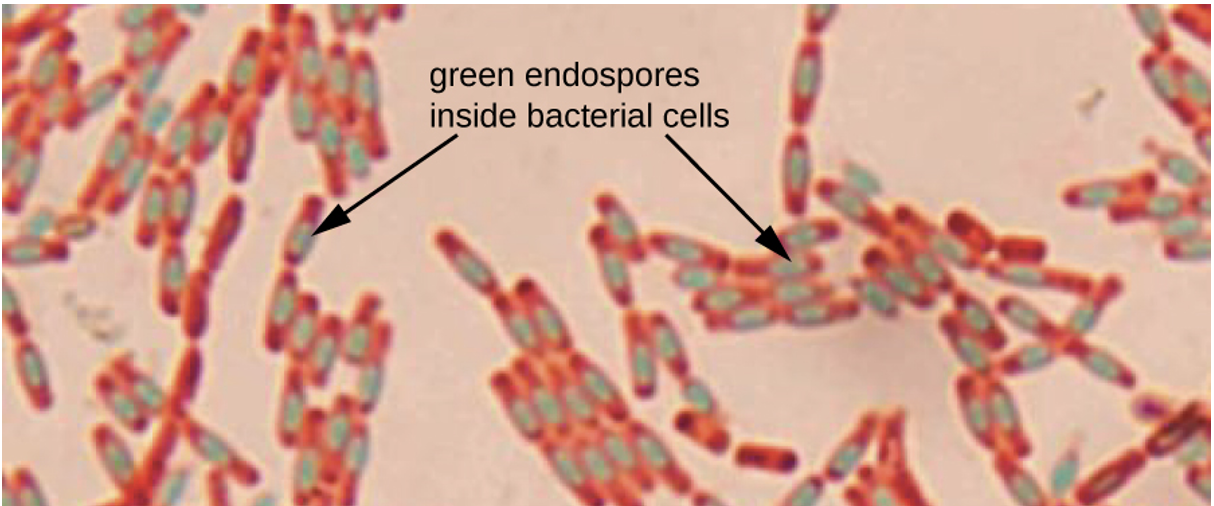
Bacillus cereus (endospore stain)
Purpose of stain: detect presence, shape, and location of endospores in cells
Reagents used and purpose: Malachite green is used as primary as it is water soluble and it is to go against the keratin on the spore. This allows the spore mother cell to be counterstained with safranin.
Why we use steam: It forces the malachite green into the spore
Color: Red with green endospore
Endospores: yes
Free spores: no
Reagents used and purpose: Malachite green is used as primary as it is water soluble and it is to go against the keratin on the spore. This allows the spore mother cell to be counterstained with safranin.
Why we use steam: It forces the malachite green into the spore
Color: Red with green endospore
Endospores: yes
Free spores: no
30
New cards
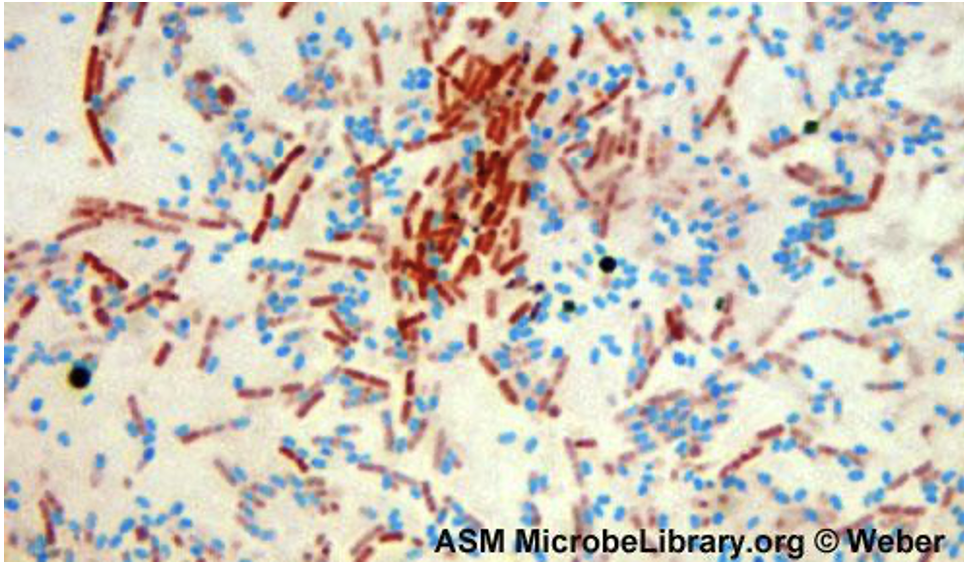
Bacillus cereus (endospore stain)
Purpose of stain: detect presence, shape, and location of endospores in cells
Reagents used and purpose: Malachite green is used as primary as it is water soluble and it is to go against the keratin on the spore. This allows the spore mother cell to be counterstained with safranin.
Why we use steam: It forces the malachite green into the spore
Color: Red
Endospores: no
Free spores: yes
Reagents used and purpose: Malachite green is used as primary as it is water soluble and it is to go against the keratin on the spore. This allows the spore mother cell to be counterstained with safranin.
Why we use steam: It forces the malachite green into the spore
Color: Red
Endospores: no
Free spores: yes