Psychological Treatments
5.0(1)Studied by 8 people
0%Unit 8: Clinical Psychology Mastery
0%Exam Mastery
Build your Mastery score
Supplemental Materials
Card Sorting
1/58
Last updated 11:39 PM on 4/15/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
1
New cards
Psychotherapy
= any type of therapy/treatment based on a psychological explanation (rather than physical) for the disorder
2
New cards
Psychiatrist
= a medical doctor with a specialty in mental health
* can prescribe medication (because they hold an M.D.)
* can prescribe medication (because they hold an M.D.)
3
New cards
Clinical Psychologist
= medical doctor
* CAN’T prescribe medication (because they hold a doctoral degree (PhD) instead of a medical degree (M.D.))
* have to refer to others to prescribe
* CAN’T prescribe medication (because they hold a doctoral degree (PhD) instead of a medical degree (M.D.))
* have to refer to others to prescribe
4
New cards
Psychoanalyst
= a certain kind of clinician whose techniques are based on the ideas of Freud or neo-Freudians
* known for talk therapy rather than prescribing medication
* known for talk therapy rather than prescribing medication
5
New cards
1) diagnose problem
* use objective or projective tests (MMPI-2, IQ, or TAT test)
* interview about patient’s life
* medical tests to rule out other problems
* ex. eye exam for supposed stress headaches
* collect symptoms and consult the DSM-5
\
2) Determine appropriate strategy for treatment
* (diff. schools of thought recommend diff. approaches)
* use objective or projective tests (MMPI-2, IQ, or TAT test)
* interview about patient’s life
* medical tests to rule out other problems
* ex. eye exam for supposed stress headaches
* collect symptoms and consult the DSM-5
\
2) Determine appropriate strategy for treatment
* (diff. schools of thought recommend diff. approaches)
Steps to diagnose a disorder?
6
New cards
**1) person who voluntarily starts therapy is someone who already recognizes a problem and seeks to improve**
**2) social contact**
(with therapist of other patients in group therapy)
→ helps reduce stress and isolation
**3) Opening up about emotions**
→ helps improve mood and lower blood pressure
**4) talking about a negative event/feeling**
→ helps make it less threatening
**5) Placebo effect + Novelty**
→ doing anything is better than doing nothing
**2) social contact**
(with therapist of other patients in group therapy)
→ helps reduce stress and isolation
**3) Opening up about emotions**
→ helps improve mood and lower blood pressure
**4) talking about a negative event/feeling**
→ helps make it less threatening
**5) Placebo effect + Novelty**
→ doing anything is better than doing nothing
Why does therapy work?
7
New cards
Individual Therapy
a treatment format
= one on one client to therapist
= one on one client to therapist
8
New cards
Group Therapy
a treatment format
\
benefits:
* decreases isolation
* connect with others who have had similar experiences
* less expensive than one-on-one therapy
* sharing advice from your experience provides a sense of purpose and deepens relationships
\
benefits:
* decreases isolation
* connect with others who have had similar experiences
* less expensive than one-on-one therapy
* sharing advice from your experience provides a sense of purpose and deepens relationships
9
New cards
Family/Couples therapy
a treatment format
= beings members of family together to __**explore dynamics within the complex group**__
* focuses on improving communication or analyzing power structures
= beings members of family together to __**explore dynamics within the complex group**__
* focuses on improving communication or analyzing power structures
10
New cards
Community Therapy
a treatment format
* focuses on prevention and early intervention rather than on therapy to prevent onset of mental health issues
* often in under served communities (socioeconomic issues, crime, etc.)
* focuses on prevention and early intervention rather than on therapy to prevent onset of mental health issues
* often in under served communities (socioeconomic issues, crime, etc.)
11
New cards
to gain insight into unconscious conflicts
to break down unhealthy defense mechanisms
to break down unhealthy defense mechanisms
Purpose of psychoanalytic and psychodynamic therapy?
12
New cards
Dream Analysis
a way to interpret client’s symptoms
= interpreting latent (hidden) content of dreams from manifest content (storyline
= interpreting latent (hidden) content of dreams from manifest content (storyline
13
New cards
Free Association
a way to interpret client’s symptoms
= clients let their minds roam freely to express whatever comes to mind without hesitation
= clients let their minds roam freely to express whatever comes to mind without hesitation
14
New cards
Resistance
= when patient is reluctant to say what they want to say
might be indication that therapist is getting closer to uncovering a meaningful conflict
might be indication that therapist is getting closer to uncovering a meaningful conflict
15
New cards
Word Association
= therapist presents stimulus word, client presents response word → shows subconscious associations
16
New cards
Transference
a way to interpret client’s symptoms
= over a lengthy analysis (many years), when patients express feelings for the analyst that actually represent feeling they have toward a significant person in their lives
= over a lengthy analysis (many years), when patients express feelings for the analyst that actually represent feeling they have toward a significant person in their lives
17
New cards
Counter-Transference
= when therapist projects own unresolved conflicts onto client
ex.
Therapist: “so basically you have a foot fetish”
but client is actually just shopping for shoes, and it’s __the therapist__ who has a foot fetish!
ex.
Therapist: “so basically you have a foot fetish”
but client is actually just shopping for shoes, and it’s __the therapist__ who has a foot fetish!
18
New cards
Psychodynamic Therapy
= more modern and condensed version of the traditional psychoanalytic approach (Freud)
* developed by neo-Freudians (Alfred Adler and Carl Jung)
* developed by neo-Freudians (Alfred Adler and Carl Jung)
19
New cards
Carl Rogers
“To my mind, ==empathy== is in itself a healing agent”
* one of the founders of humanistic psychology
* client-centered therapy
* one of the founders of humanistic psychology
* client-centered therapy
20
New cards
client-centered therapy
a type of therapy
= where therapist provides genuine, non-judgmental acceptance and empathy as the client works toward self-acceptance
\
* therapist doesn’t tell client what to do, only help their client gain insight into how they can improve
* ***client*** is the one in charge of their own progress
\
__**A**__cceptance
__**G**__enuineness
__**E**__mpathy
= where therapist provides genuine, non-judgmental acceptance and empathy as the client works toward self-acceptance
\
* therapist doesn’t tell client what to do, only help their client gain insight into how they can improve
* ***client*** is the one in charge of their own progress
\
__**A**__cceptance
__**G**__enuineness
__**E**__mpathy
21
New cards
Active Listening
psychotherapeutic technique
= therapist listens to a client closely, asking questions as needed,
→ in order to fully understand the content of the message and the depth of the client's emotion
= therapist listens to a client closely, asking questions as needed,
→ in order to fully understand the content of the message and the depth of the client's emotion
22
New cards
Unconditional Positive Regard
= showing complete support and acceptance of a person no matter what that person says or does
23
New cards
Gestalt Therapy
a humanistic approach
= help client become more WHOLE by pulling together the separate parts of one’s self
* using the whole person (their strengths) to help achieve their goals
= help client become more WHOLE by pulling together the separate parts of one’s self
* using the whole person (their strengths) to help achieve their goals
24
New cards
Existential Therapy
= a type of therapy that helps people finding meaning in their lives
\
\
25
New cards
Pros of Humanist Therapy
• Unconditional positive regard, active listening, and a more trusting, balanced relationship between individual and professional has spread to other fields
• It helps with milder forms of anxiety and depression
• It helps people build their strengths
• It helps with milder forms of anxiety and depression
• It helps people build their strengths
26
New cards
Cons of Humanist Therapy
• It’s not very useful to treat serious forms of many disorders
27
New cards
Behavioral Therapy
a type of therapy
* believes the symptoms were learned and that they ARE the disorder itself (AKA not any other underlying causes)
* believes the treatment is to use counter-conditioning (AKA extinction) to “unlearn” negative behaviors
\
there are 3 subcategories:
* classical conditioning methods
* operant conditioning methods
* and social learning methods
* believes the symptoms were learned and that they ARE the disorder itself (AKA not any other underlying causes)
* believes the treatment is to use counter-conditioning (AKA extinction) to “unlearn” negative behaviors
\
there are 3 subcategories:
* classical conditioning methods
* operant conditioning methods
* and social learning methods
28
New cards
Exposure Therapy
Behavioral Therapy > Classical Conditioning Methods > ________ Therapy
\
= a type of classical conditioning method
In this form of therapy, psychologists create a safe environment in which to “expose” individuals to the things they fear and avoid. The exposure to the feared objects, activities or situations in a safe environment helps reduce fear and decrease avoidance
\
= a type of classical conditioning method
In this form of therapy, psychologists create a safe environment in which to “expose” individuals to the things they fear and avoid. The exposure to the feared objects, activities or situations in a safe environment helps reduce fear and decrease avoidance
29
New cards
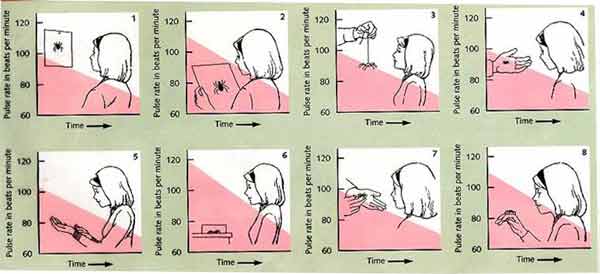
Systematic Desensitization
Behavioral Therapy > Classical Conditioning Methods > Exposure Therapy > ____ __ ____
\
= a type of exposure therapy where client works their way up through levels of fear, starting with the least fearful exposure
* used to normalize the body's response to particular sensations
\
= a type of exposure therapy where client works their way up through levels of fear, starting with the least fearful exposure
* used to normalize the body's response to particular sensations
30
New cards
Virtual Reality Exposure Therapy
Using virtual reality instead of the actual trigger of a phobia
Ex. People scared of flying go on virtual reality flights, not the real flight
Ex. People scared of flying go on virtual reality flights, not the real flight
31
New cards
Flooding
Behavioral Therapy > Classical Conditioning Methods > Exposure Therapy > ____ __ ____
= a type of exposure therapy
Instead of starting systematic desensitization at the least scary object, the patient is exposed to the **MOST SCARY** scenario. (That’s why it might be unethical.) It might happen in an emergency.
ex. a person who is very afraid of leaving the house might be forced to flee a fire or natural disaster
= a type of exposure therapy
Instead of starting systematic desensitization at the least scary object, the patient is exposed to the **MOST SCARY** scenario. (That’s why it might be unethical.) It might happen in an emergency.
ex. a person who is very afraid of leaving the house might be forced to flee a fire or natural disaster
32
New cards
Aversion Therapy
Behavioral Therapy > Classical Conditioning Methods > _____
= a type of classical conditioning method using an unpleasant stimulus to break an unwanted behavior.
\
• Ex. Hot sauce on your thumb or fingernails to stop thumb sucking or nail biting
= a type of classical conditioning method using an unpleasant stimulus to break an unwanted behavior.
\
• Ex. Hot sauce on your thumb or fingernails to stop thumb sucking or nail biting
33
New cards
Token Economy
Behavioral Therapy > Operant Conditioning Methods > _____
= authority figure gives out some stars or poker chips that kids, students, etc can later redeem for an actual prize.
* helps to reinforce good behaviors
* encourages delayed gratification.
= authority figure gives out some stars or poker chips that kids, students, etc can later redeem for an actual prize.
* helps to reinforce good behaviors
* encourages delayed gratification.
34
New cards
Social Learning
a type of behavioral therapy method
\
**• Model** – This is a person who actually performs the desired behaviors.
• **Verbal Instruction** – This occurs when a person describes the desired behaviors (in detail) and then instructs you to demonstrate those behaviors.
• **Symbolic** – This involves taking an in-depth look at how the media, movies, television, internet, books, plays and poems and music influence how you think, feel and behave.
\
**• Model** – This is a person who actually performs the desired behaviors.
• **Verbal Instruction** – This occurs when a person describes the desired behaviors (in detail) and then instructs you to demonstrate those behaviors.
• **Symbolic** – This involves taking an in-depth look at how the media, movies, television, internet, books, plays and poems and music influence how you think, feel and behave.
35
New cards
Pros of Behavioral Therapy
• Effective with phobias and some anxiety
• Works well when paired with cognitive therapy
• Works well when paired with cognitive therapy
36
New cards
Cons of Behavioral Therapy
• Because the treatments do not address the underlying problem, changing a behavior won’t work once the person returns to the environment(s) that trigger the behavior
37
New cards
Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy
= help a person become aware of automatic ways of thinking that are inaccurate or harmful (for example, having a low opinion of one’s abilities) and then finding ways to question those thoughts, understand how the thoughts affect their emotions and behavior, and change self-defeating patterns
\
* believes causes of disorder to be incorrect beliefs like:
* Negative filter (aka selective abstraction)
* over-generalization/globalization (from Seligman)
* learned helplessness (also from Seligman)
* magnification of small problems/minimization of successes
* Personalization (blame yourself when something bad happens to someone else)
* see only absolutes (ex. “if it’s not an A, it’s a failure”)
\
Treatments = help people form more rational conclusions about their experiences and interpretations of others’ actions,
\
* believes causes of disorder to be incorrect beliefs like:
* Negative filter (aka selective abstraction)
* over-generalization/globalization (from Seligman)
* learned helplessness (also from Seligman)
* magnification of small problems/minimization of successes
* Personalization (blame yourself when something bad happens to someone else)
* see only absolutes (ex. “if it’s not an A, it’s a failure”)
\
Treatments = help people form more rational conclusions about their experiences and interpretations of others’ actions,
38
New cards
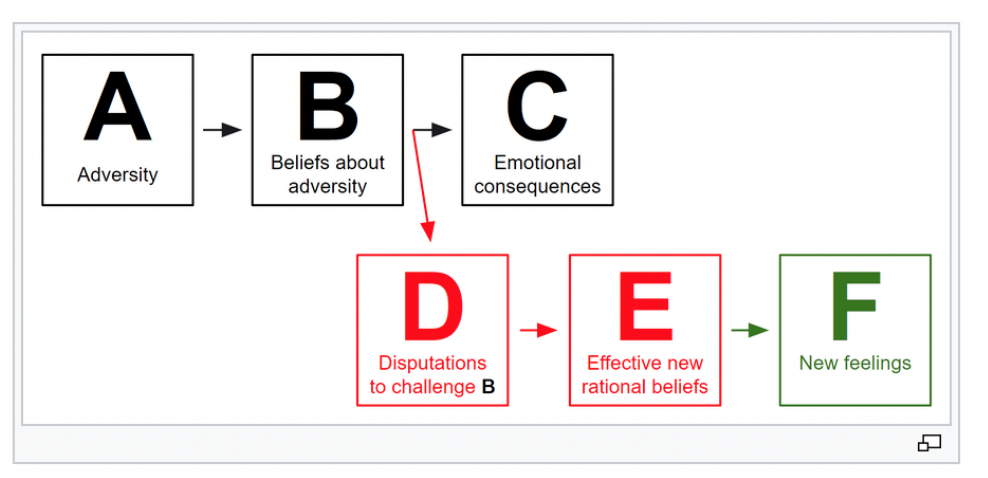
Rational Emotive Therapy
a type of Cognitive therapy by Albert Ellis
He proposed the ABC model
to depict how irrational responses can impact people’s thinking and feeling about themselves.
The DEF addition to the model = the therapy portion
\
He proposed the ABC model
to depict how irrational responses can impact people’s thinking and feeling about themselves.
The DEF addition to the model = the therapy portion
\
39
New cards
Beck’s cognitive therapy
a type of Cognitive therapy by Aaron Beck
* used for depression
\
* believed:
causes for maladaptive thoughts = cognitive triad
treatment = cognitive restructuring (changing the way you think)
* used for depression
\
* believed:
causes for maladaptive thoughts = cognitive triad
treatment = cognitive restructuring (changing the way you think)
40
New cards
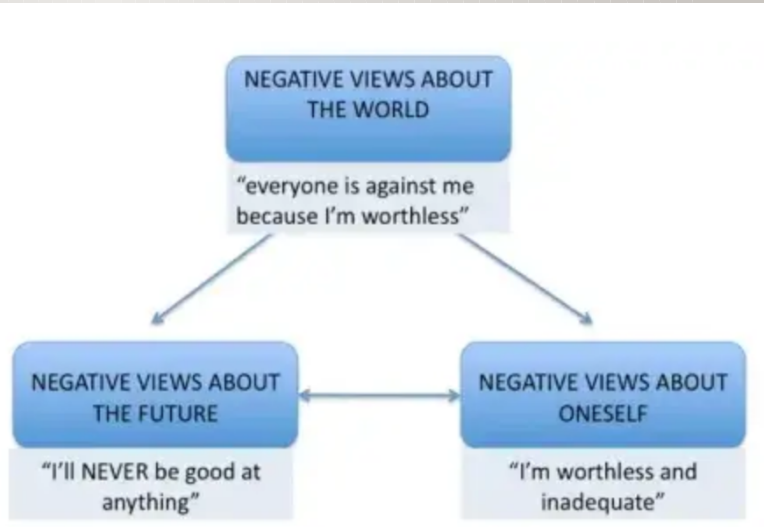
Cognitive Triad
a negative feedback loop where negative feelings about one’s current situation ”predicts” a negative future
41
New cards
cognitive restructuring
changing the way you think
42
New cards
Dialectical Behavioral Therapy
a type of talk therapy
* based on cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) ,
* but specially adapted for people who experience \[negative\] emotions very intensely
* helps __accept the__ __**reality**__ of their lives and their behaviors,
* helps them **change** their lives, including their unhelpful behaviors
\
helps people cope with the reality that their lives ==were/are harder than many other people’s.== but ALSO acknowledge that %%life can be better with the proper coping strategies%%.
\
DBT is based on the contrasting ideas: life can be both ==hard== and %%enjoyable%%
* based on cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) ,
* but specially adapted for people who experience \[negative\] emotions very intensely
* helps __accept the__ __**reality**__ of their lives and their behaviors,
* helps them **change** their lives, including their unhelpful behaviors
\
helps people cope with the reality that their lives ==were/are harder than many other people’s.== but ALSO acknowledge that %%life can be better with the proper coping strategies%%.
\
DBT is based on the contrasting ideas: life can be both ==hard== and %%enjoyable%%
43
New cards
Cognitive Therapy Pros
* has the most research supporting its efficacy and insurance companies only pay for evidence-based treatments
* helps with a wider variety of psychological disorders than the other treatment strategies
* Cognitive therapists often pair treatment with medications to address the biological aspects of many disorders. The medication helps improve a person’s depression, anxiety, etc enough that they can begin to focus on the underlying thoughts contributing to the disorder
* helps with a wider variety of psychological disorders than the other treatment strategies
* Cognitive therapists often pair treatment with medications to address the biological aspects of many disorders. The medication helps improve a person’s depression, anxiety, etc enough that they can begin to focus on the underlying thoughts contributing to the disorder
44
New cards
Cognitive Therapy Cons
* Humanists believe that Cognitive therapists focus only on a person’s weaknesses
45
New cards
Biomedical Therapy
a type of therapy
\
causes of disorder = brain structure or function problem; chemical imbalances
Treatment = brain surgery or brain stimulation or medication to bring the chemicals into a better balance or to try to reduce the problems caused by brain structure irregularities
* medications, brain surgery, or electromagnetic stimulation.
* lifestyle changes
* healthy food choices, physical activity, time in nature, social engagement, and adequate sleep → changes in hormones and/or neurotransmitters that lead to better mental health
\
causes of disorder = brain structure or function problem; chemical imbalances
Treatment = brain surgery or brain stimulation or medication to bring the chemicals into a better balance or to try to reduce the problems caused by brain structure irregularities
* medications, brain surgery, or electromagnetic stimulation.
* lifestyle changes
* healthy food choices, physical activity, time in nature, social engagement, and adequate sleep → changes in hormones and/or neurotransmitters that lead to better mental health
46
New cards
Psychopharmacology
using drugs (AKA psychotropic medications) to improve mental health
47
New cards
Anti-anxiety medications
a category are central nervous system depressants
* reduce heart-rate, breathing and other symptoms of an overly-active sympathetic nervous system
* most common:
* Benzodiazepines (sedation and hypnosis, relieve anxiety and muscle spasms, and reduce seizures)
* Barbiturates
* reduce heart-rate, breathing and other symptoms of an overly-active sympathetic nervous system
* most common:
* Benzodiazepines (sedation and hypnosis, relieve anxiety and muscle spasms, and reduce seizures)
* Barbiturates
48
New cards
\
Benzodiazepines
Benzodiazepines
a type of Anti-anxiety medication
= sedation and hypnosis, relieve anxiety and muscle spasms, and reduce seizures
\
how is it different than barbituates?
* ____ do not stimulate the GABA receptor directly, they simply make GABA receptors more efficient
* don't have as depressive an effect on the central nervous system as barbiturates do
= sedation and hypnosis, relieve anxiety and muscle spasms, and reduce seizures
\
how is it different than barbituates?
* ____ do not stimulate the GABA receptor directly, they simply make GABA receptors more efficient
* don't have as depressive an effect on the central nervous system as barbiturates do
49
New cards
Barbituates
a type of Anti-anxiety medication
= slow down the central nervous system and cause sleepiness
= slow down the central nervous system and cause sleepiness
50
New cards
Antidepressants
medications used to treat depression
* take time to work—usually 4 to 8 weeks—and symptoms such as problems with sleep, appetite, energy, or concentration sometimes improve before mood lifts
* take time to work—usually 4 to 8 weeks—and symptoms such as problems with sleep, appetite, energy, or concentration sometimes improve before mood lifts
51
New cards
selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs)
a type of Antidepressant medication
= AKA increase serotonin levels in the brain
* block the reabsorption (reuptake) of serotonin into neurons.
called “selective” because they mainly affect serotonin, not other neurotransmitters
= AKA increase serotonin levels in the brain
* block the reabsorption (reuptake) of serotonin into neurons.
called “selective” because they mainly affect serotonin, not other neurotransmitters
52
New cards
serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs)
a type of Antidepressant medication
= increase serotonin __and__ norepinephrine levels
* block the reabsorption (reuptake) of the neurotransmitters serotonin and norepinephrine in the brain
= increase serotonin __and__ norepinephrine levels
* block the reabsorption (reuptake) of the neurotransmitters serotonin and norepinephrine in the brain
53
New cards
norepinephrine-dopamine reuptake inhibitors (NDRIs)
a type of Antidepressant medication
= increase the levels of active **norepinephrine** and **dopamine** neurotransmitters throughout the brain
= increase the levels of active **norepinephrine** and **dopamine** neurotransmitters throughout the brain
54
New cards
Antipsychotics
medications used to treat psychosis
* AKA neuroleptics
* Most are dopamine antagonists – those drugs reduce the level of dopamine in the brain.
* AKA neuroleptics
* Most are dopamine antagonists – those drugs reduce the level of dopamine in the brain.
55
New cards
psychosis
a condition that involves some loss of contact with reality
* delusions (false beliefs)
* hallucinations (hearing or seeing things others do not see or hear)
* delusions (false beliefs)
* hallucinations (hearing or seeing things others do not see or hear)
56
New cards
Stimulants
medications used to treat ADHD and narcolepsy
* increase alertness, attention, and energy.
* elevate blood pressure, heart rate, and breathing.
* increase alertness, attention, and energy.
* elevate blood pressure, heart rate, and breathing.
57
New cards
Lobotomy
= a type of psychosurgery (procedures that involve the physical removal or alteration of part of the brain) that was used to treat mental health conditions such as mood disorders and schizophrenia
operating on the brain is a **LAST** resort for psychological disorders
operating on the brain is a **LAST** resort for psychological disorders
58
New cards
Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS)
a type of biomedical treatment
= magnetic fields to stimulate nerve cells in the brain to improve symptoms of major depression
= magnetic fields to stimulate nerve cells in the brain to improve symptoms of major depression
59
New cards
Deep Brain Stimulation
surgically implanting a “brain peacemaker” that sends out electrical impulses to specific parts of the brain