BCHM 218 Poll Everywhere and Weekly Quiz Qs
1/89
Earn XP
Description and Tags
BCHM 218 questions for modules 3 and 4 pulled from Poll Everywhere and the weekly quizzes!
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
90 Terms
You are studying the genome of a new virus and discover that it contains 19% Adenosine 32% Thymidine. What does that tell you about the virus?
a) Its genome is not composed of nucleic acids
b) Its genome is double stranded DNA
c) Its genome is single stranded DNA
d) Its genome is RNA
C
Which of the following chemical interactions is NOT involved in stabilizing the transition of single stranded DNA into a double helical structure?
a) Hydrogen bonding between paired bases
b) Hydrophobic interactions
c) Phosphodiester bonds
d) Van der Waals interactions
C
Which of the following would be a consequence of increasing the salt concentration of a solution of double stranded DNA?
a) It would melt at a lower temperature
b) It would melt at a higher temperature
c) Salt would not influence the melting temperature
B
Identify the correct relative order of UV absorption
a) Free dNTPs > dsDNA > ssDNA
b) Free dNTPs > ssDNA > dsDNA
c) ssDNA > dsDNA > Free dNTPs
d) dsDNA > ssDNA > Free dNTPs
e) None of the above
B

A 20bp DNA oligonucleotide binds two regions of the human genome with varying degrees of complementarity. As you cool a solution containing both the oligonucleotide and genomic DNA, how do you ensure binding at site A, but not site B?
a) Hold at a higher temperature and higher salt concentration
b) Hold at a lower temperature and higher salt concentration
c) Hold at a higher temperature and lower salt concentration
d) Hold at a lower temperature and lower salt concentration
C
You wish to PCR amplify a segment of DNA that is 1900bp in length. What is the minimum extension time required to ensure the successful amplification of this segment?
a) 30 seconds
b) 45 seconds
c) 1 minute
d) 2 minutes
e) 10 minutes
D
In vitro DNA amplification by PCR differs from in vivo DNA replication in that:
a) PCR uses RNA primers
b) PCR uses heat to separate the DNA double helix
c) PCR uses ddNTPs
d) PCR uses Mg2+ ions to coordinate reactants in the catalytic core of the polymerase
e) PCR uses a heat-sensitive yeast DNA polymerase
B
If treatment with Drug X increases the CT for Gene Y by 3 cycles, what is the effect of Drug X on the expression of Gene Y?
a) Decreased Expression by 3x
b) Increased Expression by 3x
c) Decreased Expression by 6x
d) Increased Expression by 6x
e) Decreased Expression by 8x
f) Increased Expression by 8x
E
If treatment with Drug X decreases the CT for Gene Y by 4 cycles, what is the effect of Drug X on the expression of Gene Y?
a) Decreased Expression by 4x
b) Increased Expression by 4x
c) Decreased Expression by 8x
d) Increased Expression by 8x
e) Decreased Expression by 16x
f) Increased Expression by 16x
F
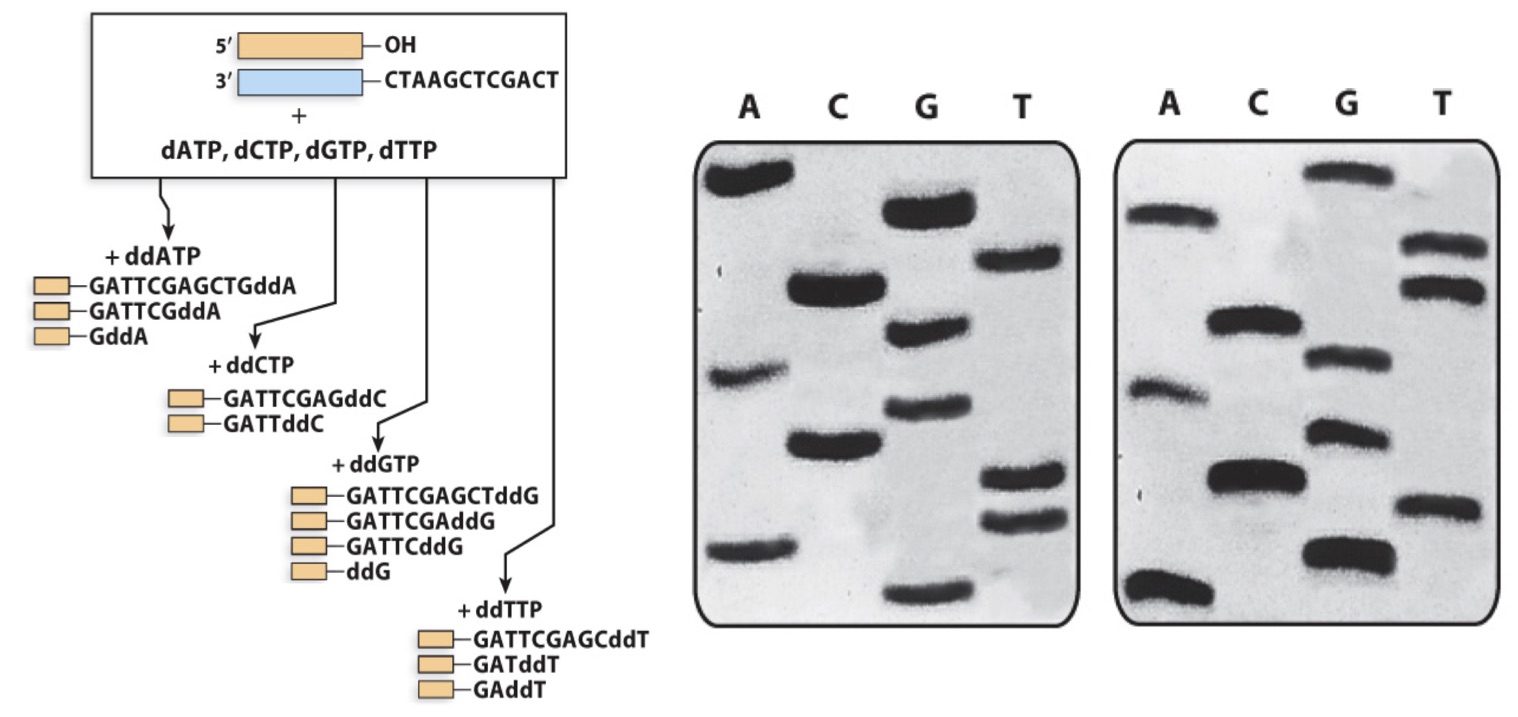
Which gel is the product of the Sanger sequencing shown here
a) left
b) right
A
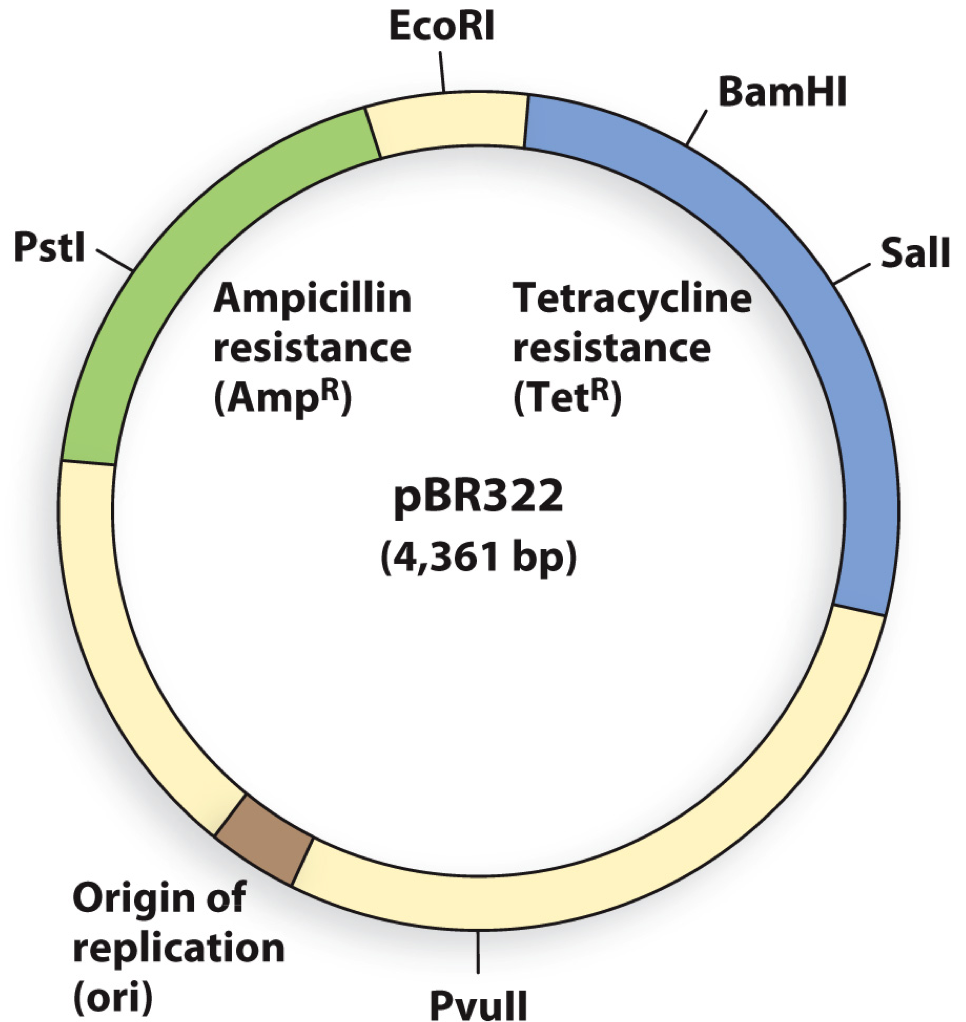
A DNA fragment was inserted into the plasmid. Transformed bacterium grows on both tetracycline and ampicillin. What restriction enzyme was used?
a) EcoRI
b) BamHI
c) PstI
d) SalI
A
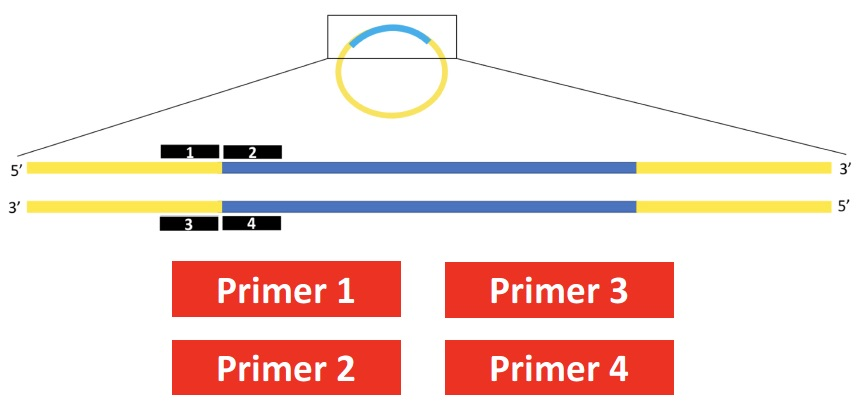
You are sequencing a DNA fragment that has been inserted into a plasmid of known sequence. Which primer would you use? Touch the red box to select.
a) primer 1
b) primer 2
c) primer 3
d) primer 4
C
Which component of Sanger sequencing is the functional equivalent of the adapters used during the Library Preparation step of Next Generation DNA Sequencing:
a) BAC
b) Taq polymerase
c) Radiolabeled primer
d) Plasmid vector
e) Labeled-ddNTPs
D
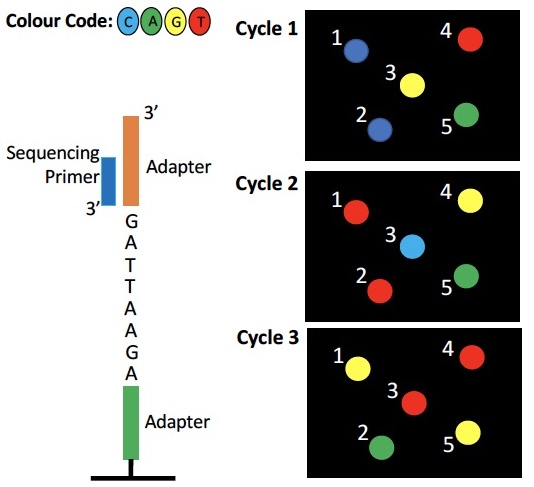
Which cluster represents the DNA fragment below?
a) 1
b) 2
c) 3
d) 4
e) 5
B
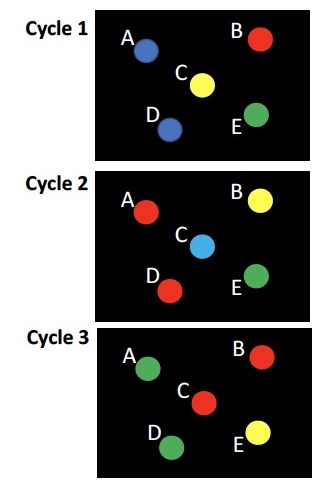
You are sequencing the genomes of 4 individuals in the same flow cell. The images below show a region of the flow cell during the first 3 cycles of Index Read 1. Which clusters represent DNA segments derived from the same individual?
a) A&B
b) A&C
c) A&D
d) B&C
e) B&D
f) B&E
C
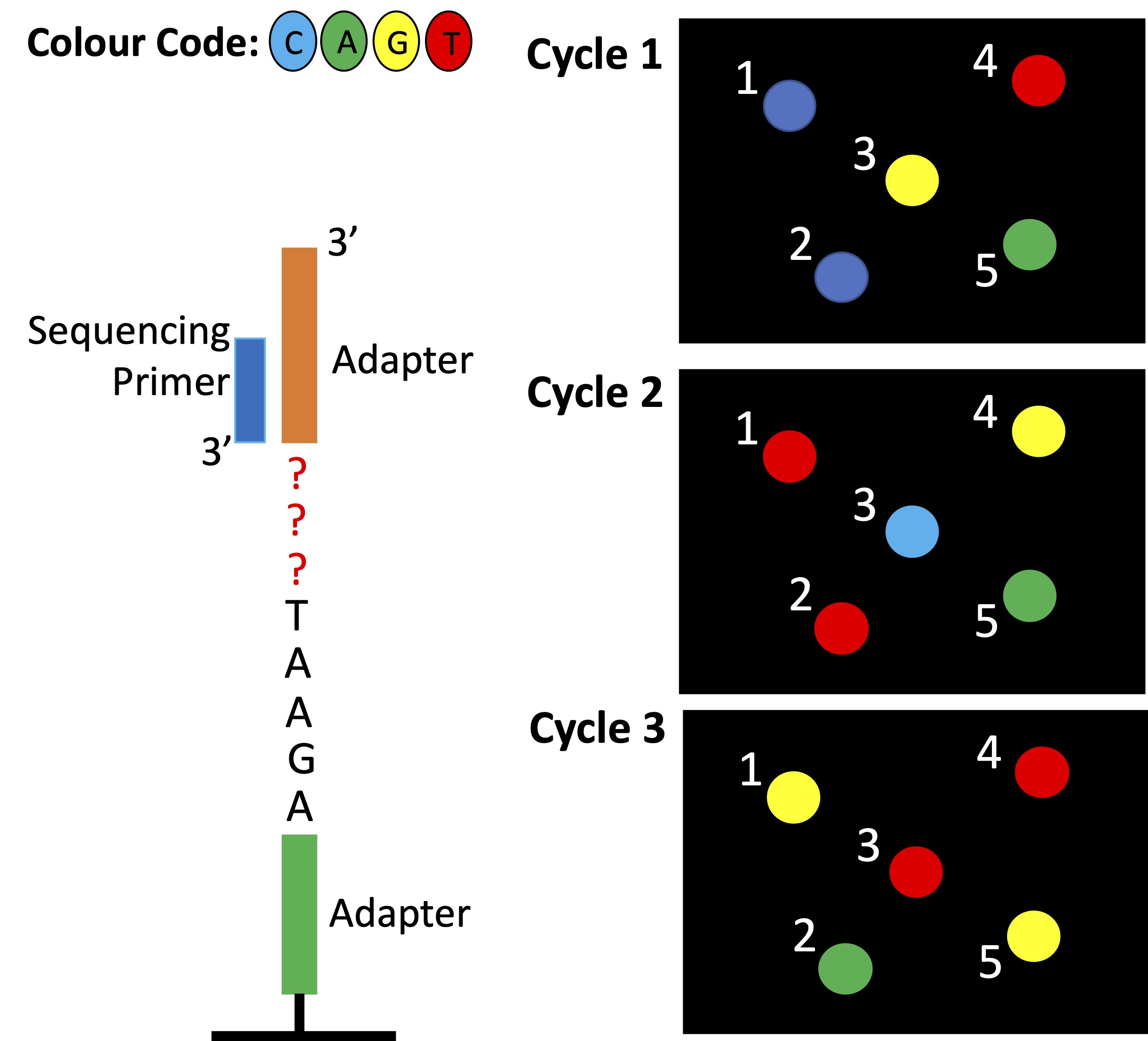
For the DNA segment below, what are the first 3 bases of sequencing read 1 and sequencing read 2?
a) CGA, AGA
b) CGA, TCT
c) GCT, AGA
d) GCT, TCT
B
The "Cluster Generation" step of next generation sequencing equivalent to which step of Sanger sequencing?
a) Growing up millions of clonal plasmid-bearing bacteria
b) Creating a radiolabeled sequencing primer
c) Inserting DNA fragments into a plasmid of known sequence
d) Determining the sequence of a DNA fragment by attaching a sequencing primer and synthesizing a complementary DNA strand
e) There is no equivalent step in Sanger sequencing
A
What are the first 3 nucleotides of the DNA fragment making up Cluster 4?
a) TGT
b) GAC
c) CTG
d) ACA
e) CGA
D
When considering all components of the gene unit, protein coding genes make up approximately what percentage of the human genome?
a) 1.5%
b) 33%
c) 66%
d) 100%
B
To study a disease caused by mutations in the BCHM2 gene, you create a knockout mouse that carries a mutated copy of Bchm2, the functional mouse equivalent of BCHM2 in humans. BCHM2 and Bchm2 are best described as:
a) Homologs
b) Orthologs
c) Paralogs
B
The histone octamer comprises:
a) One copy of H1, two H2A-H2B dimers and one H3-H4 tetramer
b) Two H2A-H2B dimers and two H3-H4 dimers
c) Two H2A-H2B dimers and one H3-H4 tetramer
d) Two H3-H4 dimers and one H2A-H2B tetramer
e) One copy of H1, two H2A-H2B dimers and two H3-H4 dimers
C
As a DNA packaging protein for the entire genome, it is important for histones to bind DNA via sequence-specific interactions with the major groove.
a) True
b) False
B (false)
For histone-DNA interactions, the regions of DNA where the minor groove comes in contact with the histone octamer experience significant compaction. This compaction would be facilitated by an abundance of:
a) A-T pairings
b) G-C pairings
c) The type of pairing doesn’t matter
A
The addition of H1 protein to a section of octomer-bound DNA will:
a) Enhance transcription
b) Repress transcription
c) Have no effect
B
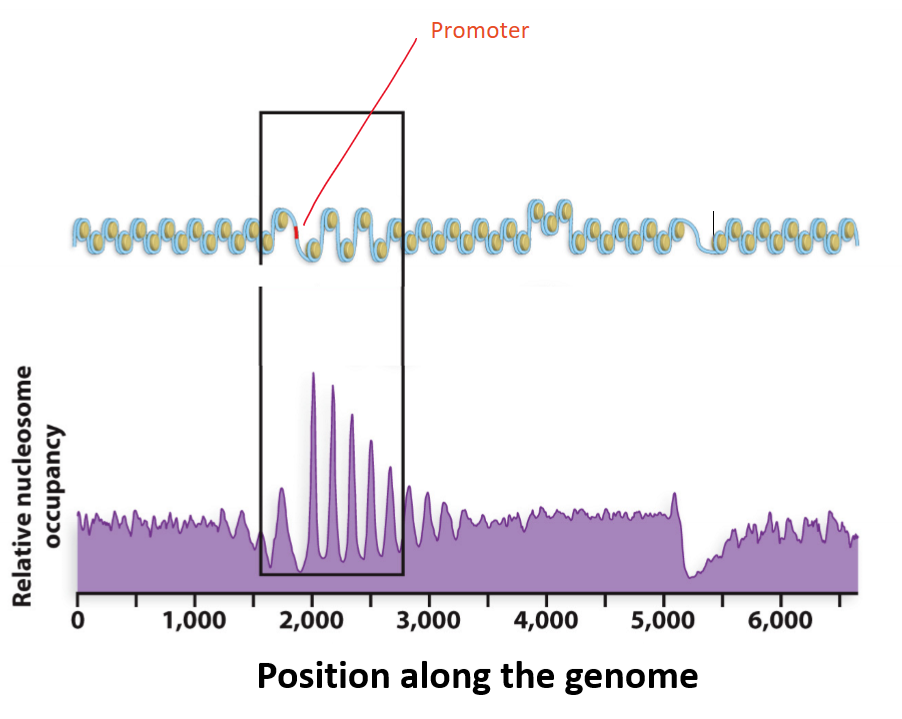
The promoter of the gene shown in the image is:
a) Open to transcription
b) Closed to transcription
A
You perform ChIP assays on DNA isolated from either heart or liver cells using an antibody for H3K9ac. You then perform qPCR on the resultant DNA products using primers directed towards the cardiac gene NKX2.5. Which sample will have the higher Ct value?
a) Heart cells
b) Liver cells
c) They will be the same
B

a) Embryonic stem cells
b) Differentiated Neurons
c) They will be the same
B
Panobinostat is an HDAC inhibitor that was recently approved for the treatment of multiple myeloma. One of its targets is an HDAC that acts on the Caspase3 promoter. True or false, you would expect Panobinostat to decrease Caspase3 gene expression.
a) True
b) False
B (false)
The N-terminus of an H3 subunit is acetylated at K9, resulting in a weakening of inter-nucleosome interactions and the recruitment of a protein complex that repositions the nucleosome, freeing up a nearby promoter. This is an example of:
a) A cis acting histone modification
b) A trans acting histone modification
c) Chromatin remodeling
d) B and C
e) A, B and C
E
Which one of the following is NOT an example of epigenetic inheritance?
a) A liver cell divides and the histone code around the alcohol dehydrogenase gene is such that the gene is actively transcribed in both the parent and the daughter cell
b) Expression levels of a neurotransmitter gene are passed from mother to offspring depending on the care the mother provides to that offspring
c) Some variants of the cystic fibrosis chloride channel result in more severe forms of the disease than others
d) Gene X is imprinted in mammals, such that only the parental gene is expressed
C
A protein complex containing a chromodomain and a histone methyltransferase (HMT) subunit would:
a) Bind acetylated histones and add acetyl groups
b) Bind methylated histones and add methyl groups
c) Bind methylated histones and remove methyl groups
d) Bind acetylated histones and remove acetyl groups
e) Bind unmodified histones and add methyl groups
B
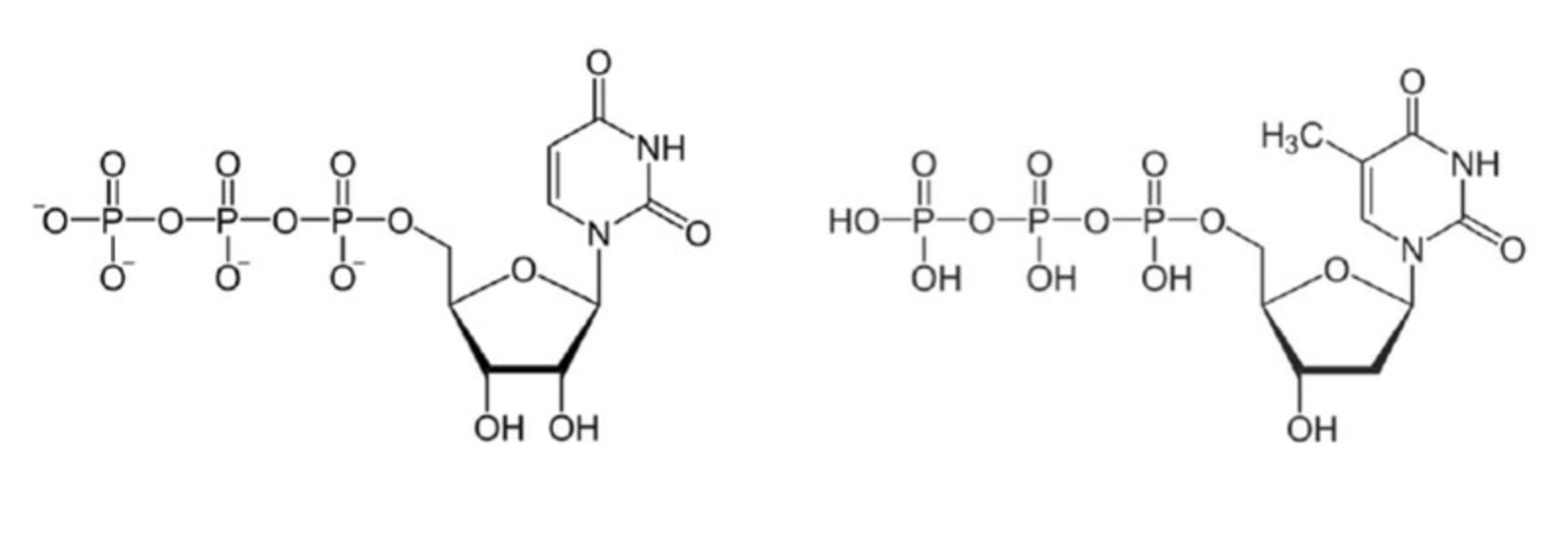
Which of the following is used as a building block for RNA synthesis?
a) Left
b) Right
A (left)
The sequence of the messenger RNA molecule (primary transcript) synthesized from a DNA molecule with a template strand having the sequence 5'- GTTA-3' is:
a) 5'-TAAC-3'
b) 5'-CAAT-3'
c) 5'-CAAU-3'
d) 5'-UAAC-3'
e) 5'-UAAG-3’
D
You treat cells with compound X and perform qPCR for GeneY. The Ct of GeneY decreases with treatment. You conclude that compound X:
a) Increases transcription of GeneY
b) Decreases transcription of GeneY
c) Enhances stability of GeneY mRNA
d) Reduces stability of GeneY mRNA
e) A & C are possible
f) B & D are possible
E
Drug X acts by enhancing the transcription of Gene Y. You would expect:
a) Cells treated with a-amanitin and Drug X to have a higher Ct than cells treated with a-amanitin alone
b) Cells treated with a-amanitin and Drug X to have a lower Ct than cells treated with a-amanitin alone
c) Cells treated with a-amanitin and Drug X to have the same Ct as cells treated with a-amanitin alone
C
You treat a human cell line with a-Amanitin and perform qPCR to quantify the expression of a tRNA for Leucine. You would expect the Ct to:
a) Increase with treatment
b) Decrease with treatment
c) Stay the same with treatment
C
A feature of the TATA Binding Protein is that:
a) It is only required for the transcription of 25% of genes
b) It makes up part of the ribosome
c) It binds the minor groove of DNA
d) It recognizes G-C rich DNA sequences
C
Which of the following statements regarding transcription only applies to eukaryotes and not to prokaryotes?
a) The promoter contains important regulatory sequences about 10 nucleotides and 35 nucleotides upstream of +1
b) The RNA transcriptional start site is designated +1
c) Regulatory sites are found within 100 base pairs of the start site of transcription
d) Regulatory sites can be found thousands of base pairs downstream of the start site of transcription
D
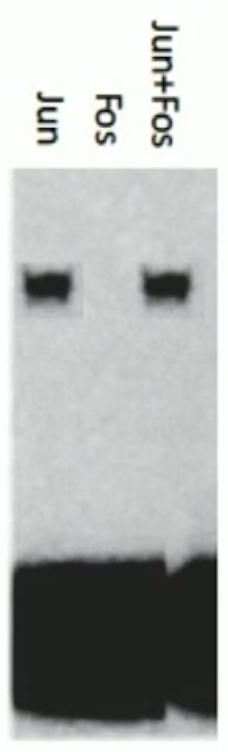
The promoter that you are studying contains a single AP-1 binding site. You incubate a radiolabeled segment of the promoter with either Jun monomers, Fos monomers or Jun and Fos monomers and perform an EMSA. The binding site in your segment recognizes:
a) Jun homodimers
b) Fos homodimers
c) Jun-Fos heterodimers
A

Which radiolabeled primer would be used to produce the DNA footprinting gel below? Click on the blue box to answer.
a) Option 1
b) Option 2
c) Option 3
d) Option 4
C
If eukaryotic pre-mRNAs were not post-transcriptionally modified, what would be the consequences?
a) enhanced enzymatic degradation
b) impaired ribosome binding
c) translation of non-coding DNA sequences
d) all of the above
D
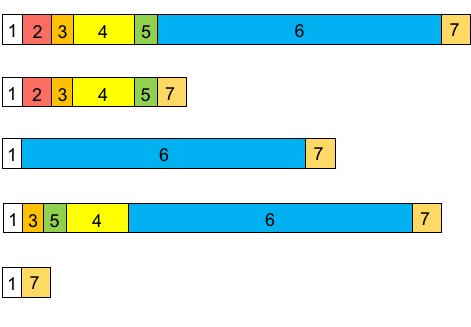
You are studying a gene with 7 exons. Which of the following is not a possible product of alternative splicing? Touch the transcript to select.
a) Option 1
b) Option 2
c) Option 3
d) Option 4
e) Option 5
D
Which of these substitution mutations is most likely to have a negative impact on protein structure and function?
a) CAU (His) to CGU (Arg)
b) UGC (Cys) to UAC (Tyr)
c) AUU (Ile) to GUU (Val)
d) UAA (Stop) to UAG (Stop)
B
A mutation in a tRNA for Leucine causes it to be mistakenly charged with Serine. The resultant charged tRNA would be:
a) Leu-tRNA^Ser
b) Ser-tRNA^Leu
c) Ser-tRNA^Ser
d) Leu-tRNA^Leu
B
Which of the following codons is capable of wobble base pairing?
a) 5'-CAC-3'
b) 5'-CAG-3'
c) 5'-CAA-3'
d) All of these codons are capable of wobble base pairing
e) None of these codons are capable of wobble base pairing
D
Which of the following anticodons is capable of wobble base pairing?
a) 5'-CAC-3'
b) 5'-CCI-3'
c) 5'-AAA-3'
d) 5'-GAC-3'
D
What is the minimum number of tRNAs required to translate the following codons: 5'-CCG-3', 5'-CCA-3', 5'-CCU-3'?
a) 1
b) 2
c) 3
B
The following codons encode Valine: 5'-GUU-3', 5'-GUC-3', 5'-GUA-3', 5'-GUG-3'. How many tRNA synthetases would be needed to charge all tRNAs for these codons?
a) 1
b) 2
c) 3
A
Which of these stages of translation is NOT a responsibility of the ribosome?
a) monitoring the fidelity of codon-anticodon interactions
b) initiation of translation at an AUG codon
c) termination of translation at a STOP codon
d) monitoring the fidelity of aminoacyl-tRNA charging
D
Which of the following translation-associated factors interacts with the A-site of the prokaryotic ribosome?
a) EF-TU
b) Initiation Factor 3 (IF3)
c) Initiation Factor 2 (IF2)
d) Release Factor 1 (RF1)
D
Which of the following compounds kill bacteria by interfering with codon-anticodon proofreading?
a) A-amanitin
b) Puromycin
c) Aminoglycosides
d) Ethidium Bromide
C
The initiation, synthesis and release of a polypeptide made up of 4 amino acids would consume how many molecules of GTP?
a) 2
b) 3
c) 4
d) 5
e) None, translation consumes ATP
D
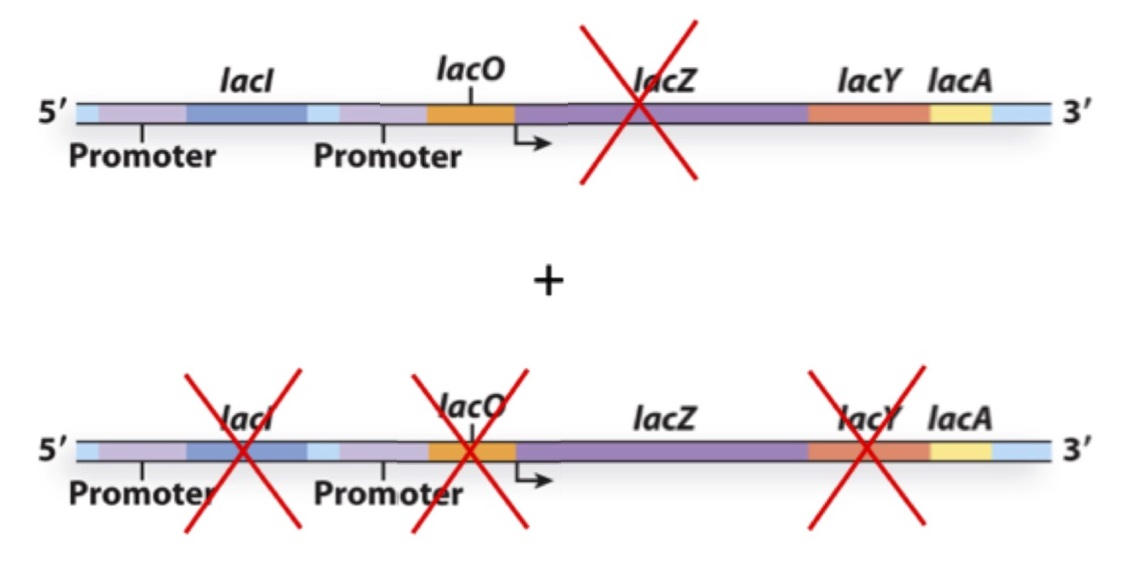
You create the following merodiploid bacterium and culture it in the presence of lactose. What gene(s) will be expressed?
a) LacZ, LacY and LacA
b) LacY and LacA
c) LacZ and LacA
d) LacX
e) None
A
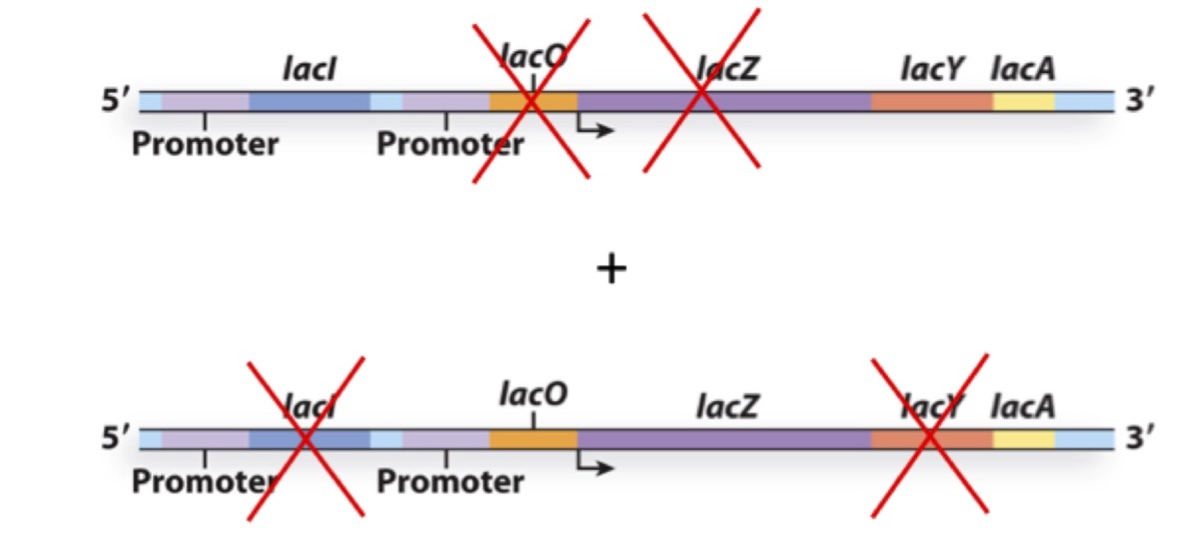
You create the following merodiploid bacterium and culture it in the absence of lactose. What gene(s) will be expressed?
a) LacZ, LacY and LacA
b) LacY and LacA
c) LacZ and LacA
d) LacZ
e) None
B
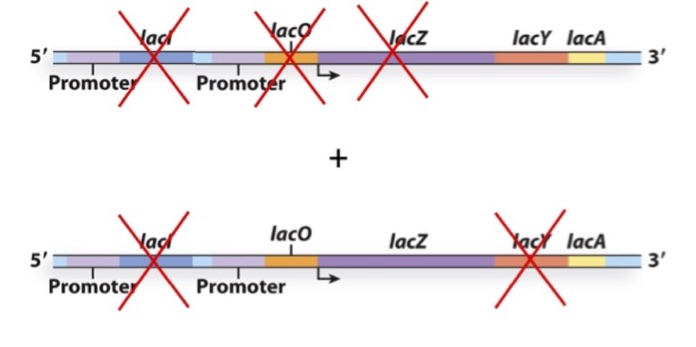
You create the following merodiploid bacterium and culture it in the absence of lactose. What gene(s) will be expressed?
a) LacZ, LacY and LacA
b) LacY and LacA
c) LacZ and LacA
d) LacZ
e) None
A
In the regulation of the Lac Operon, allolactose and cAMP are:
a) both activators
b) both repressors
c) an activator and a repressor, respectively
d) a repressor and an activator, respectively
e) both effectors
E
Introducing glucose into a bacterial culture containing lactose will cause:
a) Intracellular cAMP to go up
b) Increased binding of CRP to DNA
c) no change in Lac expression
d) reduced entry of lactose into bacteria
e) None of the above
D
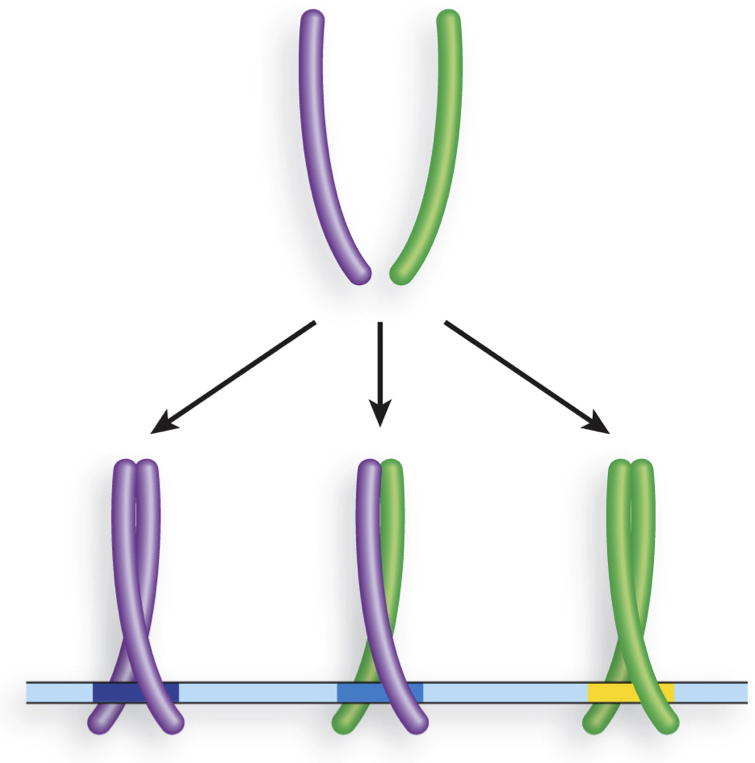
Which of the following dimeric transcription factors is UNLIKELY to bind an INVERTED REPEAT segment of DNA?
a) option 1
b) option 2
c) option 3
B
The repressor AraC binds DNA as a homodimer. Assuming each dimer binds a sequence of 4 nucleotides, each of which are separated by two nucleotides (NN), which of the following sequences is it most likely to bind?
a) ATGCNNCGTA
b) CAGTNNCAGT
c) ATGCNNGCAT
C
The protein Tam3 binds to a segment of DNA that is upstream of the TATA box and enhances the binding of RNA polymerase to the promoter. Tam3 needs to be bound by the small molecule, cGMP, to bind its DNA target sequence. Tam3 and cGMP are, respectively:
a) An activator and a co-activator
b) An activator and an effector
c) A repressor and an effector
B
You treat cells with a drug that causes increased expression of the circRNA ALPHA1, which contains a sequence that is complementary to miR-22. You would expect VEGF-A protein to:
a) Increase
b) Decrease
c) Stay the same
A
Which of the following does not describe an aspect of the three-dimensional structure of the DNA helix?
Question options:
A | Complementary strands are anti-parallel to each other in the double stranded form |
B | All of the above describe the structure of the DNA helix |
C | The hydrophilic backbone of the alternating sugar and phosphate groups is on the outside of the helix. |
D | The nearly planar and hydrophobic bases are stacked inside the helix relatively perpendicular to the backbone |
E | Additional stability is conferred by the hydrogen bonding between the complementary bases |
B
Which of the following will decrease the stringency of DNA-DNA hybridization:
A | Reducing temperature |
B | Increasing salt |
C | Adding organic solvents |
D | a & b |
E | b & c |
D
A major difference between quantitative PCR and end-point PCR is that in quantitative PCR:
A | The reaction involves the amplification of cDNA |
B | SYBR green added to the reaction mix emits fluorescence when bound to single stranded DNA |
C | Reaction products are quantified after every PCR cycle |
D | Amplification products are run on an agarose gel containing ethidium bromide |
E | The threshold cycle is used to indicate when the reaction plateaus after all reagents have been consumed |
C
If treatment of cells with Drug X increases the Ct of Gene Y by 3 qPCR cycles. Then Drug X is:
A | Decreasing the expression of Gene Y by 3x |
B | Increasing the expression of Gene Y by 8x |
C | Decreasing the expression of Gene Y by 8x |
D | Increasing the expression of Gene Y by 6x |
E | Increasing the expression of Gene Y by 3x |
F | Decreasing the expression of Gene Y by 6x |
C
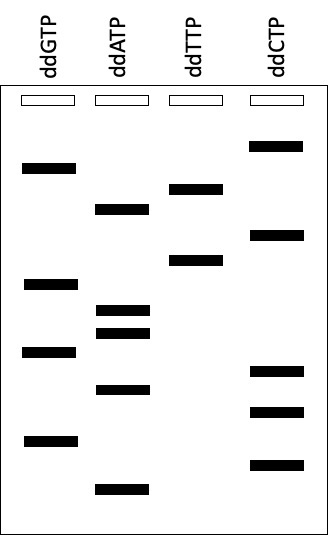
What is the sequence of the TEMPLATE DNA used to generate this Sanger sequencing gel?
A | 5'-cgtactgaagcacgca-3' |
B | 5'-acgcacgaagtcatgc-3' |
C | 3'-tgcgtgcttcagtacg-5' |
D | 3'-gcatgacttcgtgcgt-5' |
C
Inserting DNA into a plasmid for Sanger sequencing is equivalent to which step of next generation sequencing:
A | Index Read |
B | Genome Alignment |
C | Sequencing Read |
D | Cluster Generation |
E | Library preparation |
E
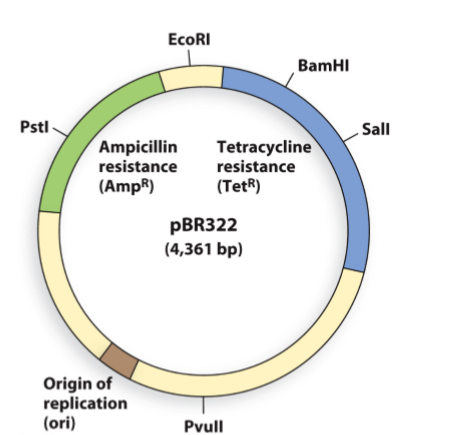
When cloning a DNA gene fragment into the PstI site of plasmid pBR322, which statement is correct?
A | bacterial colonies containing the gene fragment will grow on media plates containing ampicillin AND grow on plates containing tetracycline |
B | bacterial colonies containing the gene fragment will grow on media plates containing ampicillin BUT NOT grow on plates containing tetracycline |
C | bacterial colonies containing the gene fragment will NOT grow on media plates containing ampicillin BUT will grow on plates containing tetracycline |
D | bacterial colonies containing the gene fragment will NOT grow on media plates containing ampicillin AND ALSO NOT grow on plates containing tetracycline |
E | all of the above are incorrect |
C

You are performing next generation sequencing on a cluster that is made up of the clonal DNA segment shown in the diagram. The first three nucleotides of sequencing read 1 and sequencing read 2, respectively, would be:
A | CTG, ACT |
B | CTG, TGA |
C | GAC, TGA |
D | GAC, ACT |
C
Eukaryotic genomes are different from prokaryotic genomes in that:
A | none of the above |
B | eukaryotic genomes are not replicated every cell cycle |
C | eukaryotic genomes are always larger than prokaryotic genomes |
D | eukaryotic genomes do not have introns |
E | eukaryotic genomes have introns |
E
Two regions of genomic DNA which share sequence similarity both within and amongst species is called:
A | Homologous sequence |
B | Genetic sequence |
C | Heterologous sequence |
D | Paralogous sequence |
A
You want to compare genome packaging between cells isolated from the liver and the heart of the same individual. You perform a CHIP assay on genomic DNA from both cell types using an antibody directed towards H3K9me3. You then take the products of these CHIP assays and perform Next Generation Sequencing. The regions of the genome that accumulate read alignments in the samples from both cell types are most likely to represent:
A | Genes that are involved in fundamental cellular processes common to all cells |
B | Read alignments would accumulate over all parts of the genome |
C | Genes that are expressed in undifferentiated pluripotent stem cells |
D | Genes that are expressed in the heart but not in the liver |
E | Genes that are expressed in the liver but not in the heart |
C
Histone methylation in a particular region can be erased by a protein complex containing:
A | A bromodomain and an HDAC subunit |
B | A chromodomain and a HAT subunit |
C | A chromodomain and a Jumanji subunit |
D | A chromodomain and a HMT subunit |
E | A bromodomain motif and a HAT subunit |
C
Histone octamers bind DNA:
A | through histone DNA binding accessory proteins HX and HY |
B | through specific interactions within the DNA major groove |
C | through non-specific interactions with the phosphate backbone |
D | Histones only bind RNA |
E | through interactions with specific base residues GAATTC |
C
Which of the following is NOT a way chromatin remodeling complexes affect nucleosomes?
A | They can slide a nucleosome to a different location. |
B | They can replace the nucleosome with a new nucleosome that contains a variant histone. |
C | All of these answers represent mechanisms of chromatin remodeling complexes |
D | They can eject a nucleosome from the DNA. |
E | They can modify the N-terminal tails of histones. |
E
Which of the following statements regarding the H1 histone is FALSE?
A | H1 possesses 2 DNA binding sites and stabilizes linker DNA once bound. |
B | H1 supports gene repression by increasing DNA compaction. |
C | H1 is a key element of the histone octamer and is needed for nucleosome formation. |
D | Fully packaged DNA would possess one H1 unit for every 200 base pairs. |
E | all of the above |
C
Which of the following is true of the DNA footprinting assay, but not the electrophoretic mobility shift assay:
A | the technique involves the visualization of labeled DNA |
B | all answers apply to both techniques |
C | the technique can identify the precise location of protein binding to a sequence of DNA |
D | the technique involves the resolution of samples by nondenaturing gel electrophoresis |
E | the technique can be used to identify binding of a protein to a segment of DNA |
C
Which of the following is TRUE for transcription, but NOT DNA replication?
A | rNTPs are used as building blocks. |
B | It uses a template strand as a blueprint for a new polynucleotide. |
C | It has initiation, elongation, and termination steps. |
D | The process is initiated at specific sites by protein binding to the DNA. |
E | It requires primers for initiation. |
A
The majority of transcription in eukaryotic cells is accounted for by:
A | Synthesis of rRNA by RNA Pol I |
B | Synthesis of tRNA by RNA Pol I |
C | Synthesis of tRNA by RNA Pol III |
D | Synthesis of mRNA by RNA Pol II |
E | Synthesis of rRNA by RNA Pol III |
A
What is the sequence of the messenger RNA molecule (primary transcript) synthesized from a DNA molecule with a template strand having the sequence 5'-ATGACGTATGATGACGC-3':
A | 5' GCGUCAUCAUACGUCAU 3' |
B | 3' GCGUCAUCAUACGUCAU 5' |
C | 5' GCGTCATCATACGTCAT 3' |
D | 3' GCGTCATCATACGTCAT 5' |
A
Which of the following is true of transition mutations?
A | They involve the replacement of a purine by a pyrimidine |
B | They involve the insertion of a single nucleotide |
C | A mutation in the third position of a codon is often silent |
D | A mutation in the first position of a codon usually results in a nonsense mutation |
E | They only lead to missense mutations that have a minimal impact on protein structure and function |
C
Certain wobble interactions between tRNA and mRNA are enabled by:
A | Conversion of adenosine to inosine in the third position of the anticodon |
B | Conversion of adenosine to inosine in the first position of the codon |
C | Conversion of inosine to adenosine on tRNA |
D | Conversion of adenosine to inosine in the first position of the anticodon |
E | Conversion of adenosine to inosine in the third position of the codon |
D
A single nucleotide insertion mutation holds the potential to alter how many amino acids in the resultant protein:
A | One amino acid |
B | Two amino acids |
C | Three amino acids |
D | More than three amino acids |
E | No amino acids, the mutation would be silent |
D
The Shine–Dalgarno mRNA sequence is specifically recognized by:
A | The 16S rRNA of the 30S subunit |
B | N-formylmethionyl-tRNAfMet |
C | The 16S rRNA of the 50S subunit |
D | The 18S rRNA of the 40S subunit |
A
Which of the following compounds kill bacteria by interacting with the ribosomal peptidyl transferase center?
A | a-amanitin |
B | puromycin |
C | aminoglycosides |
D | ethidium bromide |
E | magnesium chloride |
B
Which of the following does NOT reflect the action of an effector molecule on the transcription of a gene?
A | An effector binds to an activator to increase the level of transcription |
B | An effector binds to a repressor to increase the level of transcription |
C | An effector binds to a polymerase to increase the level of transcription |
D | An effector binds to an activator to decrease the level of transcription |
E | An effector binds to a repressor to decrease the level of transcription |
C
In the context of regulation of the Lac operon, allolactose is:
A | an effector that increases DNA binding of its target protein |
B | an effector that decreases DNA binding of its target protein |
C | an effector of a positive regulator |
D | an effector of a transcriptional activator |
E | None of the above |
B
Which of the following would you expect to happen if you mutated the lac O (of the lac operon) to be non-functional? (assume there is only one gene copy)
A | constitutive expression of lac Z |
B | in the absence of lactose, beta-galactosidase would be produced |
C | in the presence of lactose, beta-galactosidase would be produced |
D | all of the above |
D
Which of the following DNA sequences represents an inverted repeat (where XXX represents any 3 nucleotides?
A | 5'-ATAGXXXTATC-3' |
B | 5'-ATAGXXXCTAT-3' |
C | 5'-ATAGXXXGATA-3' |
D | None of these answers is correct |
E | 5'-ATAGXXXATAG-3' |
B
You introduce a plasmid into mammalian cells that results in the increased expression of a specific non-coding RNA that you are studying. You then perform qPCR to quantify the expression of mRNA for the gene Tam2 and find that introduction of your plasmid causes the Ct for Tam2 to decrease from 27 to 23. The non-coding RNA encoded in your plasmid is most likely
A | A miRNA that is complementary to the coding sequence of Tam2 mRNA |
B | A miRNA that is complementary to the 3'UTR of Tam2 mRNA |
C | A long-non-coding RNA that shares sequence similarity with a segment of the 5'UTR of Tam2 mRNA |
D | A miRNA that is complementary to the 5'UTR of Tam2 mRNA |
E | A long-non-coding RNA that shares sequence similarity with a segment of the 3'UTR of Tam2 mRNA |
E