L8: Liquidity Risk
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
Liquidity Risk
Inability to meet short-term obligations as they become due and payable, or only being able to do so at unsustainable cost
Solvency risk
Inability to meet long-term obligations as they become due and payable, or only being able to do so at unsustainable cost
systemic, individual, technical/timing
3 sources of liquidity risk - SIT
Systemic Risk
Market-wide risks external to the company such as market disruptions, etc.
A company cannot influence these factors, but has to accept them and align its risk taking according to these risks
E.g. pandemic
Inflationary economy ->BSP -> price stablity
Higher interest rate = lower consumer spending
individual or idiosyncratic
Originates from something specific to the company
Event or crisis-driven, instead of market-wide
Ex. ABS-CBN shutdown
Technical/timing
The problem is the timing of cashflows
There is a mismatch in cashflow sources and needs
The balance sheet shows sufficient liquidity due to large expected inflows in distant time periods
first step
why manage LR?
Cash is king
The company needs to fulfill its short-term obligations
Choose suppliers that have different due dates
Liquidity is the ___ step to achieving long-term objectives
reduces
benefits of LRM
____ overall cost of borrowing or funding
Provides available funding for emergency needs
Enhances the overall ERM system
Funding, trading
2 types of LR
Funding LR
Refers to a company’s ability to raise the necessary cash to roll over its debt and meet short-term working capital requirements
trading LR
Risk that an institution will not be able to execute a transaction at the prevailing market price because there is temporarily no appetite for the deal on the other side of the market
sources of LR
LRM Process for FUNDING 1] Identify
Assess each type of asset or transaction and the liquidity risk embedded in them
Goal is to create the “____ of Liquidity Risk” report
Wholesale funding risk: uutang ka for a corporation
The risk that an institution cannot raise funds from large-scale external sources (like institutional investors) to meet its financial needs, especially during market stress.
Retail funding risk: uutang for an individual
The risk that an institution cannot secure funds from individual depositors or retail customers, often due to decreased confidence or market volatility.
Intraday liquidity risk: utang and pay the same day
The risk that a financial institution cannot meet its payment obligations during the day due to delays or insufficient liquidity, impacting its daily operations.
Intragroup liquidity risk
The risk related to transferring liquidity between entities within a group (e.g., subsidiaries), which may be restricted due to regulatory or operational barriers.
Cross-currency liquidity risk: difference in currency rates
The risk that an institution cannot convert liquidity across currencies when needed, potentially due to market disruptions or unfavorable exchange rates.
Off-balance sheet liquidity risk:if you have contingent liabilities that are not reflected in the books
The risk associated with commitments or guarantees not reflected on the balance sheet (e.g., credit lines), which may require cash outflows if unexpectedly drawn upon.
Funding concentration risk: look at the sources of your financing (cos yung iba mataas charges) ; short term vs long term risk
The risk of relying on a limited number of funding sources or counterparties, which could lead to liquidity issues if those sources become unavailable.
Funding cost risk: based on the interest rate (fixed vs variable – good if fixed)
The risk that an institution’s cost of obtaining funds increases, potentially due to market conditions or deteriorating creditworthiness.
Correlation risk - sumasabay ba yung assets and liabilities mo
The risk that multiple sources of risk become correlated, especially during market stress, amplifying liquidity shortages.
Asset risk: type of asset that you have (liquid vs illiquid assets)
The risk that assets held by an institution cannot be easily converted to cash or have lost value, limiting liquidity in times of need.
Liquid Assets
These assets can be quickly converted to cash with minimal impact on their value.
Cash and Bank Deposits
Stocks (especially large-cap stocks)
Government Bonds
Mutual Funds and ETFs
Money Market Funds
Treasury Bills
Foreign Currencies (major ones like USD, EUR, etc.)
Certificates of Deposit (CDs) (depending on maturity and penalties)
Precious Metals (like gold, but depends on market demand)
Illiquid Assets
These assets are harder to sell quickly without significantly affecting their price.
Real Estate
Private Equity Investments
Collectibles (art, antiques, etc.)
Venture Capital Investments
Small Business Interests
Hedge Fund Shares (often have lock-up periods)
Intellectual Property (patents, trademarks, etc.)
Long-term Loans and Bonds (especially if low credit quality)
Commodities in Specific Forms (e.g., certain types of agricultural goods)
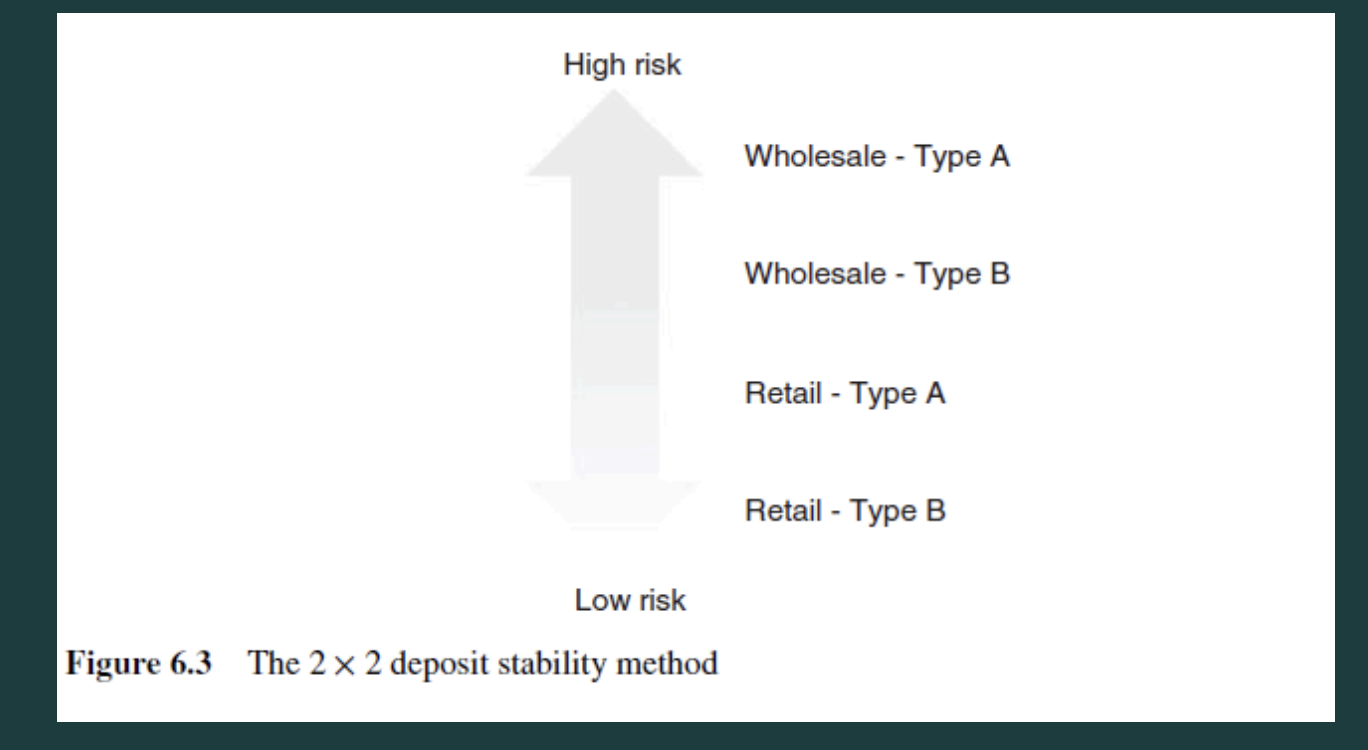
simple, scorecard
LRM Process for FUNDING 1] Identify
→ Categorize the liquidity risks identified
____ Categories
Perspective ng creditor because transactions are more complicated, mas matagal, and complex transactions
In terms of collection: mas mahirap individual
Amount of loan: mas mahirap loan
_____ Approach
![<p><strong><em>LRM Process for <u>FUNDING</u> 1] Identify</em></strong></p><p><strong><em>→ </em><u>Categorize</u> the liquidity risks identified</strong></p><ul><li><p>____ Categories</p><ul><li><p><span>Perspective ng <strong>creditor</strong> because transactions are more complicated, mas matagal, and complex transactions </span></p></li><li><p><span>In terms of <strong>collection</strong>: mas mahirap individual </span></p></li><li><p><span>Amount of loan: mas mahirap loan</span></p></li></ul></li><li><p>_____ Approach</p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/40647e81-758f-4f66-b571-0f958af079a5.png)
ok
LRM Process for FUNDING 1] Identify ok
→ Compute for liquidity and solvency ratios
![<p><strong><em>LRM Process for <u>FUNDING</u> 1] Identify ok</em></strong><br><strong><em>→ </em></strong>Compute for liquidity and solvency ratios</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/c106a874-92a9-42ff-a87a-f3ca4b5f77a3.png)
current, quick, cash
3 key liquidity ratios
CA/CL
current ratio formula
(Cash + MS + AR)/CL
quick ratio formula
(Cash + MS)/CL
cash ratio formula
debt to asset, to equity
2 key solvency/leverage ratios
TL/TA
debt to asset ratio formula
TL/TE
debt to equity ratio formula
risk heat map, trend analysis, industry benchmark
LRM Process for FUNDING 2] Analyze
The comprehensive list of sources of liquidity risk should be assessed for frequency and severity
Make sense of the liquidity and solvency ratios that you computed
Know the mismatches
From current to quick ratio dapat papaliit
Use these 3 guides
COMPARE ratios to legal and contractual obligations
The proposal is ethical and legal -> inventory is relevant in the business
external
LRM Process for FUNDING 3] Response
Seek ______ funding from banks or other lending institutions
Higher interest rate in bigger banks but problem if the smaller banks could accommodate the big funding needed
Take note of short term vs long term funding
Can be from banks, non-banks, even individuals
Ex. High-Net-Worth Individual (HNWI)
capitalization
LRM Process for FUNDING 3] Response
→ You can increase _____ through
Capital infusion of owners
Issuance of common shares
Issuance of preferred shares
Issuance of debt instruments
current assets
LRM Process for FUNDING 3] Response
→ you can liquidate ___ assets to convert to cash
Liquidity Reserve
LRM Process for FUNDING 3] Response
→ Set up a ____
Liquidity available to cover additional funding needs for a defined period of time under stressed conditions T
This is NOT for business-as-usual transactions
High Quality Liquid Assets
liquidity reserves are known as __ ___ Liquid Assets in BANKS
risk heat map
LRM Process for FUNDING 4] MOnitoring
Recheck your ______
Compute for the ratios at regular intervals
Set key performance indicators (KPIs) or trigger points
Trading LR
Arises when the company already has existing investment securities, whether debt or equity, and now needs to unwind it because the company needs cash
Applies to any type of asset
Contemplates a situation when forced liquidation of assets creates unfavorable price movements
ok
LRM Process for TRADING 1] Identify ok
Check existing investment portfolio, especially if substantial or concentrated in a certain issuer company or industry
Factors to consider:
- size and frequency of trade
Larger trades or infrequent trades can be harder to execute without affecting the asset's price. Smaller, frequent trades are generally easier to execute.
- trade completion time
The longer it takes to complete a trade, the more risk there is that market conditions will change, potentially impacting the price.
- asset type -
Some assets (like stocks of large companies) are more liquid and easier to trade than others (like niche or exotic assets), which may have fewer buyers and sellers.
trade customization
Customized trades (like options or derivatives) can be less liquid because they may not have a standard market. Standardized trades are usually more liquid.
- economic environment
In times of economic uncertainty or volatility, liquidity can dry up, making it harder to buy or sell assets without significant price changes.
- number of market trades
A higher number of trades in the market can indicate more liquidity. More trades mean more participants, which can make it easier to execute trades at desired prices.
harder
- size and frequency of trade
Larger trades or infrequent trades can be easier/harder to execute without affecting the asset's price.
longer-more
- trade completion time
The shorter/longer it takes to complete a trade, the less/more risk there is that market conditions will change, potentially impacting the price.
more-easier
- asset type -
Some assets (like stocks of large companies) are less/more liquid and harder/easier to trade than others (like niche or exotic assets), which may have fewer buyers and sellers.
less liquid
trade customization
Customized trades (like options or derivatives) can be more/less liquid because they may not have a standard market.
Standardized trades are usually more liquid.
higher-more
- number of market trades
A lower/higher number of trades in the market can indicate less/more liquidity.
More trades mean more participants, which can make it easier to execute trades at desired prices.
Spread
The difference between the highest price a buyer is willing to pay (bid) and the lowest price a seller is willing to accept (ask) for an asset.
low-more
A low/high bid-ask spread indicates a less/more liquid market, meaning there are many buyers and sellers, making it easier to buy or sell an asset without affecting its price significantly.
liquidity
Refers to how quickly and easily an asset can be bought or sold in the market without causing a significant change in its price.
Example: The USD is considered very liquid because it is widely traded, and transactions occur frequently, resulting in lower bid-ask spreads.
one go, staggered
LRM Process for TRADING 2] Analyze
When you consider unwinding (selling) an investment, you have two main options, either to unwind in ____ or _____
unwind all at once
Pros:
You eliminate future price uncertainty immediately, meaning you know exactly what you will receive right now for your investment.
Cons:
You may face a large bid-ask spread, meaning you might receive a worse price for your asset due to the difference between what buyers are willing to pay and what sellers are asking for. This can result in a significant loss.
staggered basis
Pros:
You face a more manageable bid-ask spread, meaning you might get better prices on individual transactions over time, as you can wait for more favorable market conditions.
Cons:
You remain exposed to price uncertainty until the full liquidation is complete, meaning the market price could fluctuate, and you may end up receiving less than expected for the remaining portions of your investment.
trading, market
LRM Process for TRADING 3] Response
Find the balance between ____ cost and ___ risk
Consider the level of need for cash in the short-term
Could depend on risk appetite
LRM Process for TRADING 4] Monistor
Monitor the same factors from Step 1
Factors to consider:
- size and frequency of trade -
trade completion time
- asset type -
trade customization
- economic environment
- number of market trades
EXPENSIVE!
Remember:
Liquidity is good, but it is _____
There is opportunity cost involved in maintaining a stable liquidity position
Remember the principle of “high risk, high return; low risk, low return”