Shoulder
1/188
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
189 Terms
traps, delts, pecs
the prime movers of the shoulder are _____, ______, and _____
dynamic stability
the function of the Rotator Cuff is ___________
stability
For scap ________, the traps, rhomboids, levator scap, and serratus anterior all work together
supraspinatus, infraspinatus
______ and _____ insert on the greater tuberosity
subscapularis
_______ inserts on the lesser tuberosity
long head of biceps
the groove on the proximal humerus houses what tendon
short head of biceps, coracobrachialis, coracoclavicular lig., pec minor
Coracoid process is the insertion point for:
(supraspinatus/short head of biceps)
(infraspinatus/coracobrachialis)
(coracoclavicular lig./costoclavicular lig.)
(pec minor/pec major)
are not
the posterior cuff muscles (are/are not) distinct bands of insertion on the proximal humerus
long
the (long/lateral/medial) head of the triceps attaches on the infraglenoid tubercle
lateral
the (long/lateral/medial) head of the triceps attaches on the posterior humerus
olecranon process
the triceps insert on the __________ of ulna
lower traps, serratus anterior
when shoulder pain is present, the ______ and ______ will be inhibited
lats
the ______ help the shoulder extend and internally rotate → flexion and end range elevation can stretch this muscle
upward rotation, posterior tilt
the function of the serratus anterior is _________ and _________ and ER of the scap → it is to help protract the scap around the thoracic wall and to prevent winging
70 deg, inactive
Below ~ _______ SA is (inactive/active)
pec minor
If the ________ is restricted, the medial border and inferior border of the scap will begin winging → poor posture plays a role
Glenohumeral Joint
________ is characterized by:
ball and socket jt
convex head on concave fossa
1/3 - ½ of head fits into fossa
ABD, horiz. FL, flexion
the resting position for the GH jt is 60 deg of _____, 30 deg of ______, 60 deg of elbow _____ with forearm 30 deg from horizontal plane
ABD, ER, FL, EX, ADD, IR
the close-packed position for the GH jt is 90 deg of _____, full _____ with elbow ______ 90 deg OR full _______, _______, _______
instability
the close-packed position of the GH jt is a position of ligament ________ where the joint is in a position for dislocation
Rotations
_____ of the GH joint include elevation, IR/ER, and horiz. add/abd
Translations/Glides
_____ of GH jt include sup/inf, medial/lateral, ant/post
do not
IR/Hor. ADD and ER/Hor. ABD (do/do not) follow the normal convex concave rules because of the size of the ball in the socket
Scapular Rotations
______ include IR/ER, Upward Rotation/Downward rotation, Ant/Post tilt or tip
Scapular Translations/Glides
______ include sup/inf (shrug) and ant/post (protraction/retraction)
Scapulohumeral Rhythm
_____ is the ratio of motion b/w humerus and scapula (upward rotation) during arm elevation (2:1 - humerus:scapula)
below, does not
(below/above) 30 deg of abd the scapula (does/does not) move a lot
concave, convex; convex, concave
SC jt is _____ on _____ in the sagittal plane and _____ on ______ in the frontal plane
full elevation
SC joint is in closed packed position with _______
inferiorly, retracts
During active elevation, clavicle glides ______ and ______ 20 deg
Hor. ADD, Full elevation, IR
______ and ______ and ______ will close down the AC joint
full shoulder elevation
Things that can cause issues with _______:
Gh jt
scapular mov’t
SC jt
AC jt
Spine
shoulder elevation
For bilateral __________ these things are necessary:
cervical side bend same
thoracic opposite side bend and rotation to same side
thoracic EX
Lumbar EX
DASH
Disabilities of Arm, Shoulder, and Hand is shortened to ______ with an error with a single score of 8 and a MDC of 13
FOOSH
______ is falling on an outstretched hand and is a common MOI of shoulder/wrist/hand injuries
facets
If symptoms are in scapula, there might be an issue with the ______ in the C spine
neck
If symptoms are below the elbow, look at the _____ for issues
alleviated, abnormal
Symptoms that are ________ while sleeping on involved side are considered ______
C4-C7
________ dermatomes cover shoulder, arm, and scapula
inferior angle, neck
If pain is above _______ of scapula, look at the _____
C5 & C6, C5
______ myotomes and ______ dermatome are areas of pain referral in the AC jt and Subacromial Space
scapula, posterior
Pain in _____ and _______ shoulder is more likely due to cervical issue
cervical
Numbness and tingling (even more so with extending the hand) are usually from ______ region
forearm, hand
Referral of infraspinatus can be to distal ______ while supraspinatus can refer to the _____
heart
the _____ can refer to the L shoulder/chest/clavicle region
s/sx: SOB, incr. HR, sweating, chest tightness, arm p!/paresthesias
spleen, emergency, shock
If the _____ is injured, it is an ______ as the injury will not cause death but the _____ of the injury will
Kehr’s Sign
____ is pain referred to the left shoulder from a spleen injury usually post trauma → hypotension is usually associated
cholecystitis, gallstones
______ is pain referred from _______ to r scapula after eating
risk factors: >40 yo., obese, female, fertile
lungs, diaphragm, ulnar
the ____ or _____ (Pancoast tumor) can refer pain to the shoulder or lateral scapula → pain can extend down medial aspect of arm/4th/5th digits mimicking _______ nerve
s/sx: forearm/hand weakness and tingling/numbness
Horner’s syndrome (can affect facial muscles)
Thoracic Outlet Syndrome, ulnar
______ is shoulder/arm pain with tingling/numbness along _______ nerve distribution (C8/T1)
b/w ant. and med. scalene
clavicle and 1st rib
pec minor
Malignancies
For possible ______ (breast cancer or lung cancer), look for hx of CA and get lab work to rule out metastases
systemic signs: fever, weight loss, incr. temp, fatigue
Yellow/Red Flags
______ include:
pain decr. with sleeping on involved side
no difficulty sleeping
shoulder pain is not eased by rest
insidious onset and pain cant be reproduced
systemic s/sx
Upper Crossed Syndrome
_____ is when pecs/upper traps/levator scap muscles are tight and deep neck flexors and scap stabilizers are weak
shoulder elevation
if _______ is not achievable due to incr. kyphosis or poor posture, individual will use lower thoracic and lumbar spine to elevate arms
Scapulohumeral Rhythm
Motions to watch for regarding ___________:
tipping
winging
dumping
shrugging
Dumping
_____ is the lack of eccentric control of the lower traps and SA as the scap comes down from elevated position
Shrug Sign
______ is when there is a torn RTC and the patient cannot elevate their arm
Scapular Winging
_____ is with weak SA + Lower Trap, tight Pecs, tight RTC mms
infraspinatus, teres minor, winging
In IR, the_____ and _____ will pull scap with them and cause ______ → posterior capsule is tight
Scapular Anterior Tilt
_________ is from tight pec minor, tight biceps, weak middle/lower traps, and weak SA
Force Coupling
_______ in the shoulder involves Upper and Lower traps working with SA to create scapular upward rotation
Scapular Downward Rotation
_____ involves weak Upper/Lower traps/SA with tight Levator/Rhomboids/Pec Minor
Upper Limb Tension Test, median
______ (ULTT1 or UTTLA) look at the ______ nerve with:
shoulder depression/abd
elbow extension
forearm supination
wrist extension
finger extension
contralateral cervical SB
Upper Limb Tension Test, ulnar
_______ stretches the _____ nerve with:
shoulder depression/abd
elbow flexion
forearm pronation
wrist extension/radial deviation
finger extension
shoulder ER
contralateral cervical SB
Upper Limb Tension Test, radial
_______ stretches the ______ nerve with:
shoulder depression/abd
elbow extension
wrist extension/ulnar deviation
finger flexion
shoulder IR
contralateral cervical SB
active
During _____ motion we are assessing any change in symptoms, neuromuscular control, and looking for any compensations to achieve full ROM
resisted
during _____ motion we are looking at myotomes, neuromuscular control and integrity, changes in symptoms, and any differences b/w sides
passive
during ______ motion, we are assessing end feel, change in symptoms, and differences b/w sides
Impingement Syndrome (SAIS)
_____ is either:
mechanical compression of structures in subacromial space (usually supraspinatus)
degeneration of tenon and/or bursae secondary to overuse and aging
roof
the _____ of the subacromial space is:
inf. acromion surface
coracoacromial ligament
coracoid process
AC jt
floor
the _____ of the subacromial space is:
greater tuberosity
humeral head
subacromial space
the ___________ contains the supraspinatus, subacromial bursa, long head of biceps, and joint capsule
One, 25
Stage ___ of Neer’s classification is edema/hemorrhage of bursa and cuff in people less than ______
fibrosis, tendonitis
Stage Two of Neer’s classification is _____ and _____ of the cuff or bursa in 25-40 y.o.
Three, partial/full tears, bone spurs
Stage ____ of Neer’s classification involves ____/_______ _____ of the rotator cuff and ______ in those over 40 y.o.
direct compression
Primary SAIS is _________ of RTC and biceps bursa and the cause is either intrinsic or extrinsic
GH instability, Glenoid labral tear
Secondary SAIS is caused by another pathology like _______ or ______
age, AC joint, bicep tendinitis, dyskinesias
Primary Impingement involves ______ (>50yo.), degenerative changes, DJD of ______, bursitis/tendinitis/tendinosis, _________, and scap ______
30, repetitive OH, labrum, cuff
Secondary Impingement involves those <____yo., experiencing ant/anterolateral pain especially with _______ use → issue with static stabilizers (capsule/_____) while dynamic stabilizers (____) are weak and fatigued
Intrinsic Causes of SAIS
_______ = “Within the tendon”
degeneration or inflammation of tendon/bursa
overuse from stress on tissue overtime
age related like vascular or metabolic changes
weak motor control of RTC leads to disruption of force couple of deltoid with ER/IR
from overuse, aging, bad ST jt kinematics, poor posture
humeral head
If the motor control of the RTC is weak then the deltoid increases ________ superior translation during shoulder elevation and ER/IR
Scapular muscles
Extrinsic Causes of SAIS: Weakness of motor control issues of the _______ can cause tendon breakdown, instability of ST articulation, faulty GH kinematics, poor posture
Postural dysfunctions
Extrinsic Causes of SAIS: _______ in the C spine and T spine create issues in kinematics of different areas of the spine and scapula working together
Posterior Capsule Tightness
_______ involves increased humeral head sup/ant translation and causes changes in GH + scapular kinematics → increased infra tone
inf. post. glide would help shoulder get to full elevation
Posterior Shoulder Tightness
_____ is usually measured in supine and passive IR
stop just before ant lift of shoulder from table → scap substitution
compare bilaterally
scaps, 94
With horizontal ADD with scap retraction, the pt is supine and retracts their _____ and horizontally ADD their arm with a normal value of ___ deg
Altered Kinematics
Extrinsic causes of SAIS: ______ like scap dyskinesis and humeral dyskinesis can be related to reduced subacromial space
Scapular Dyskinesia
_____ is decreased protraction, ER, and upward rotation during GH elevation
Humeral Dyskinesia
_______ is increased ant. and sup. humeral head translation during GH elevation
Acromial Morphology
Extrinsic causes of SAIS: ________ is related to the bony changes of the acromion → 3 types (flat, smooth, hooked)
RC tears, SAIS
Acromial Angle (b/w scap spine and acromion) is associated with ______ and ______
OS Acromiale
______ is the unfused distal epiphysis
tendons, AC joint, bursae
Overtime, ______ and the _____ degenerate and ______ thicken
full thickness, age
Older patients are more likely to have _______ RC tears so it is important to consider _____ when looking at SAIS
GH instability, labral tears
Younger pts are more likely to have _____ or _______ and may require surgery
overhead, insidious, local, C5-C6
SAIS medical history:
associated with sports/work activities that are repeatedly _____
_____/slow onset of symptoms
pain with activity or provocative positions
pain = ______ but can refer to _______ dermatomes
local, sharp, limited
SAIS Examination:
pain = _______ and possibly at C5,6 dermatome
pain = _____ with provocative mov’ts (OH, cross body, behind back)
TTP at RC tendons at muscle belly and insertion
AROM and PROM are ______ d/t p! with ROM, acute edema, or length of symptoms
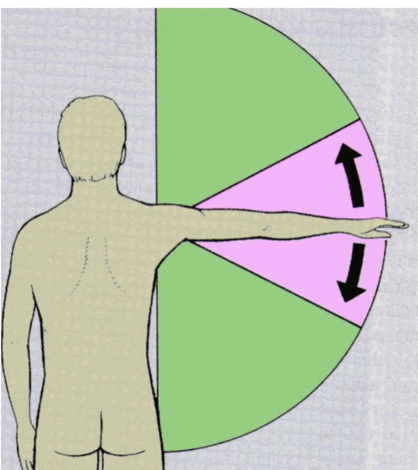
Painful Arc
Painful Arc, SAIS, RC tear, AC jt, SAIS, RC tears
_____ occurs during elevation of arm
p! + sx @ 60-120 deg = ______ and _____
p! + sx @ 160/170-180 deg = _____ or _____ or _____
resisted
SAIS will have pain with _______ ABD + ER and posture will be fwd head, T spine FL, and scap
decreases, impingement
When a lidocaine injection into the subacromial area ______Sx it is a sign of ______