Concepts of health 1-5
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/49
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
1
New cards
Health
Physical health, Mental health, Spiritual health, Emotional health, Social health
2
New cards
Wellness
A positive, balanced state of physical, mental, emotional, social, and spiritual (plus environmental/ vocational) health.
3
New cards
Illness
Nonphysical ailments are often seen as less serious than physical ailments
4
New cards
Case studies
a detailed report of the diagnosis, treatment, and follow up of an individual patient or research subject
5
New cards
Case series
Combined reports of several patients with like diagnoses, treatments, or follow-ups, slightly more valid because they contain multiple people
6
New cards
Observational studies
* looking at what medical conditions occur without any intervention
* can provide important health information when large groups are studied with the right variables
* can provide important health information when large groups are studied with the right variables
7
New cards
communicable disease
* Transmitted from person to person or from contaminated objects to those who come in contact with them
* Best prevention is hand washing
* Wipe down equipment before using, use safe sex methods, avoid contact with people with communicable disease, and get vaccinated
* Best prevention is hand washing
* Wipe down equipment before using, use safe sex methods, avoid contact with people with communicable disease, and get vaccinated
8
New cards
controlled studies
One group of participants is given an experimental drug or treatment, whereas another group is given either a standard treatment for the disease or a placebo
9
New cards
double blind studies
Type of controlled clinical trail where neither the participants individuals nor the researchers know which participates and receives which treatment.
10
New cards
randomized studies
* participants are assigned by chance to separate groups that compare different treatments
11
New cards
anxiety
Chronic nervousness or anxiousness
12
New cards
shyness/ social phobia
Being afraid of people, especially people who for some reasons are emotionally threatening, such as strangers, authority figures, and potential romantic partners
13
New cards
Panic disorder
Sudden attacks of terror accompanied by a pounding heart, perspiration, weakness, faintness, or dizziness
14
New cards
lifestyle illnesses
Disease caused by our health behaviors
15
New cards
mediatation
* requires focusing on something repetitive or something unchanging
* try several times before determining if it is a good method for you
* try several times before determining if it is a good method for you
16
New cards
eustress
Stress that leads to positive response
17
New cards
distress
Stress that leads to a negative response
18
New cards
PTSD
Trouble overcoming the fear associated with a traumatic event
19
New cards
placebo effect
thinking something will help you
20
New cards
Sources of Health
Advertising, internet, family and friends, newspaper and magazine articles
21
New cards
Motivation for human behavior
Peer pressure or influence, immediate vs long term gratification
22
New cards
Fight or Flight
Heart rate increases, muscles tense, start perspiring, breathing becomes rapid and shallow, increase in alertness
23
New cards
Suicide
* a sudden worsening of school performance, such as suddenly ignoring assignments and cutting class
* A fixation with death or violence, which may be expressed through poetry, doodling, and artwork or a fascination with weapons
* Unhealthy peer relationships, such as a lack of freinds or sudden rejection
* A fixation with death or violence, which may be expressed through poetry, doodling, and artwork or a fascination with weapons
* Unhealthy peer relationships, such as a lack of freinds or sudden rejection
24
New cards
Communication and conflict resolution
* wants vs. needs
* finding a middle ground
* compromise
* finding a middle ground
* compromise
25
New cards
Interventions for stress
* a change in life situation starts the trip down the stress model road
* The goal of stress management is to keep stress levels at an optimal level, enough to pose a challenge but no so much that it overwhelms
* Eliminate unnecessary stressful life events
* The goal of stress management is to keep stress levels at an optimal level, enough to pose a challenge but no so much that it overwhelms
* Eliminate unnecessary stressful life events
26
New cards
Psychological health
Ability to express, think, and behave appropriately relative to your emotions
27
New cards
Mental illness
Refers to alterations in thinking, emotions, or behaviors that produce distress and impaired function
28
New cards
Emotional health
an ability to express emotions and feelings appropriately
29
New cards
Social health
Interact well with others, have satisfying relationships, close friends and people with whom they confide
30
New cards
Spiritual health
A clear view of meaning and purpose in life, connections with others and with nature, peacefulness, and comfort with life choices
31
New cards
Tobacco Use
* one of the unhealthiest of behaviors
* accounts for more than 18% of deaths in United States
* Higher education decreases the likelihood of smoking cigarettes
* accounts for more than 18% of deaths in United States
* Higher education decreases the likelihood of smoking cigarettes
32
New cards
Sedentary lifestyle
* Physical activity can help prevent or postpone heart disease, stroke, and other causes of early disability or death
* Helps with depression and anxiety
* 39% of American adults are inactive
* Helps with depression and anxiety
* 39% of American adults are inactive
33
New cards
Nutrition
* Many pay too little attention to what they eat
* Need less fat, sugar, refined grain, sodium and saturated fat
* Need more whole grains, vegetables, fruits, milk, oils, fiber, potassium, vitamin D, and calcium
* Need less fat, sugar, refined grain, sodium and saturated fat
* Need more whole grains, vegetables, fruits, milk, oils, fiber, potassium, vitamin D, and calcium
34
New cards
Sexual Behavior
don’t be stupid and don’t get an STD
35
New cards
Internal Locus
You believe you can do things to improve your life
36
New cards
External Locus
You believe how your life turns out is a matter of luck, chance, fate or will be determined by others
37
New cards
Habits
Behaviors that are accepted as normal because you have been doing them for so long
38
New cards
Values
* something in which you believe strongly as well as what you act on
* competing values cause you to have to decide which one is more important
* competing values cause you to have to decide which one is more important
39
New cards
Risk Perception
Believing that a behavior is worth change because of some risk, being convinced that the risk will occur without change, being convinced that the change would avoid the risk
40
New cards
Culture and Family
culture in which you live may cause you to be more or less worried about health based on the values of the culture
41
New cards
Advertisers
* serve companies, not consumer
* No guarantee what they are promising is true
* Small print
* No guarantee what they are promising is true
* Small print
42
New cards
Internet
* lots of information available
* not necessarily accurate or current
* many websites are trying to sell you something
* not necessarily accurate or current
* many websites are trying to sell you something
43
New cards
Newspaper and Magazine
* May not give the article enough space to completely analyze information
* Articles in a professional journal can be trusted
* Articles in a professional journal can be trusted
44
New cards
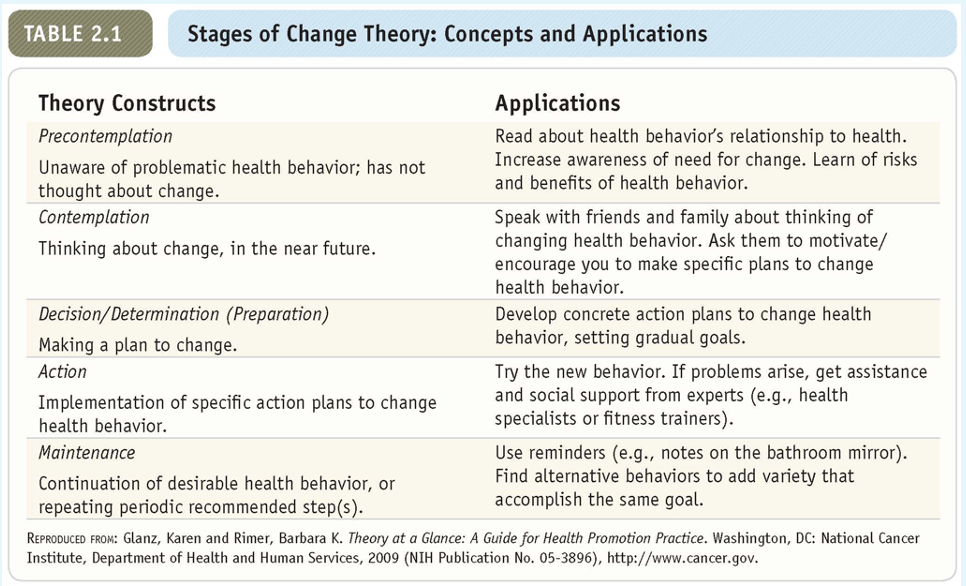
Stages of change theory
* Recognizes that people are at different stages
* suggests different strategies to change health behavior
* suggests different strategies to change health behavior
45
New cards
Health belief model
Weighting perceived susceptibility and perceived severity to determine whether or not you will act
46
New cards
Social Learning Theory
Acknowledges the relationship between the environment and the indivi
47
New cards
Low self esteem
How high a regard or opinion you have of yourself
48
New cards
Depressoin
A mood disorder in which feelings of sadness loss, anger, or frustration interfere with everyday life for a long period of time
49
New cards
Religion
* a formal organized activity that involves beliefs, practices, and rituals related to a supernatural being, god, or ultimate truth
* Usually describes what happens after death and guide moral behavior
* Usually describes what happens after death and guide moral behavior
50
New cards
Spirituality
something people define for themselves, devoid of the rules, conventions, and responsibilities of typical religions