COSC 310 final
1/46
Earn XP
Description and Tags
The questions and answers from the first two exams :(
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
The term priority in a priority queue means that:
the lowest-priority items are deleted first
True or False: Pushing and popping items for a stack and inserting and removing items from a queue all take O(N) time
False
What is the big O for an algorithm who's running time is given by the function:
T(N) = 35N + 4.5(N-1) + 2N*N
O(N^2)
Ordered arrays, compared with unordered arrays are
quicker to search
The maximum number of items that must be examined to complete a binary search of an array of 300 elements is:
8 comparisons
Which of the following is true?
In both the stack and the queue, items removed in sequence are taken form increasingly higher index cells in the array.
The top of a stack corresponds to the rear of a queue.
The contents of a queue can wrap around, while those in a stack cannot.
The pop operation on a stack is considerably simpler than the remove operation on a queue.
The contents of a queue can wrap around, while those in a stack cannot.
Given the following statement in infix notation:
A / B - C * D
What would it be when converted to postfix. Use a single space between characters.
A B / C D * -
True or False: If there are N items, the bubble sort makes exactly NxN comparisons.
False
True or False: When you delete an item from an unordered array, in most cases you shift other items to fill in the gap.
True
Given the following segment of code what would the big O value be for running the segment?
for i in range(N):
for j in range(N):
for k in range(N):
print(i + j + k)
O(N³)
What does LIFO mean?
Last In First Out
Shifting a group of items left or right requires repeated ________.
Copies/copying
Inserting an item into a priority queue takes what Big O time on average?
O(log(N))
A stack or a queue often serves as the underlying mechanism on which an array data type is based.
False
O(1) means that a process operates in _____________ time.
Constant
Given the following segment of code what would the big O value be for running the segment?
def avePos(a,b):
N = 0
total = 0
if(a > 0):
total += a
N += 1
if(b > 0):
total += b
N += 1
return N, total
O(1)
What is the result of the following postfix expression:
2 4 + 8 2 / *
24
What is the output of the following code:
stack = Stack(10)
stack.push("one")
stack.push("two")
print(stack.pop())
stack.push("three")
print(stack.peek())
print(stack.pop())
print(stack.isEmpty())
print(stack.pop())
print(stack.isEmpty())
two, three, three, False, one, True
Suppose you push the values 12, 23, 45, 61, and 13 onto the stack in that order. Then you pop three items, and peek at the stack. What value do you see?
23
The bubble sort always ends up comparing every possible pair of items in the initial array.
False
Given the following code:
def BinarySearch(numbers, numbersSize, key):
mid = 0
low = 0
high = numbersSize - 1
while (high >= low):
mid = (high + low) // 2
if (numbers[mid] < key):
low = mid + 1
elif (numbers[mid] > key):
high = mid - 1
# Fix Code Here
return -1 # not found
def main():
numbers = [ 2, 4, 7, 10, 11, 32, 45, 87 ]
NUMBERS_SIZE = 8
i = 0
key = 0
keyIndex = 0
print("NUMBERS: ")
for i in range(len(numbers)):
print(numbers[i]," ")
print()
print("Enter a value: ")
key = int(input())
keyIndex = BinarySearch(numbers, NUMBERS_SIZE, key)
if (keyIndex == -1):
print(key," was not found.")
else:
print("Found ",key," at index ",keyIndex,".")
main()
Answer for blank # 1: elif (numbers[mid] == key):
Answer for blank # 2: return keyIndex
Use the following code block to create a function that can swap values in a python list.
def swap(values, index1, index2):
values[index1], values[index2] = values[index2], values[index1]
A colleague asks for your comments on a data structure using an unordered array without duplicates and binary search. Which of the following comments makes sense?
Because the array is unordered, a binary search cannot guarantee finding the items being sought.
In the selection sort,
a minimum key is repeatedly discovered.
Why is it important to use private instance attributes like __nItems in the definition of data structures?
From our notes: # Encapsulation
Note that the only way that you can access data in the above class is using the methods of the class
* This is going to keep underlying in the __a list private. This practice is known as encapsulation
* Note you can break the above code by trying to stuff too many things into the array “
Arrange the following in the order of slowest to fastest growth rates:
O(N^2), O(N log(N)), O(N), O(N^4), O(1), O(log(N))
O(1) – Constant time
O(log N) – Logarithmic time
O(N) – Linear time
O(N log N) – Linearithmic time
O(N²) – Quadratic time
O(N⁴) – Quartic time
How many references must be set or changed to insert a link in the middle of a singly linked list?
2
Insertion and deletion in a binary search tree require what Big O time? Assuming N nodes in the tree, and use Big O notation in your answer.
O(log(N))
Draw the binary search tree that is created from the sequence of keys:
10, 5, 15, 22, 3, 12, 17, 9, 6
When answering place the values separated by a "," and a single space in increasing order in the blank.
In Blank #1 place the keys for the leaf nodes.
In Blank #2 place the key for the root node.
In Blank #3 place the keys for all internal nodes.
Answer for blank 1: (3,6,12,17)
Answer for blank 2: (10)
Answer for blank 3: (5,9,10,15,22)
Python generators:
are useful for creating iterators.
What does it mean for a method to be recursive?
The method will call itself
A subtree of a binary tree always has
fewer nodes than the main tree.
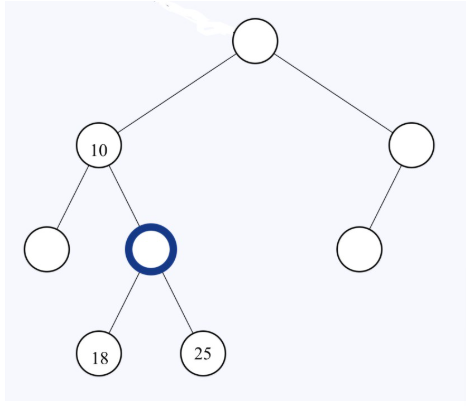
Given the binary tree above. State all potential integer key values separated by a comma for the node that is boldly circled.
(19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24)
Write a recursive routine in python that could be used to raise a value to a power. Calling the function should look like:
power(value, exponent)
and return the value raised to the specified exponent. This must be a recursive routine. You can not use python ** operator to achieve the functions goal.
def power(value, exponent):
if exponent <= 1:
return value
else:
return value * power(value,exponent-1)
When compared with storing data in an array, the main benefit of storing it in a binary search tree is
not having to copy data when inserting or deleting items.
being able to search for an item in O(log(N)) time.
He accepted both answers for this question. The bolded one is the one he chose for the auto grader
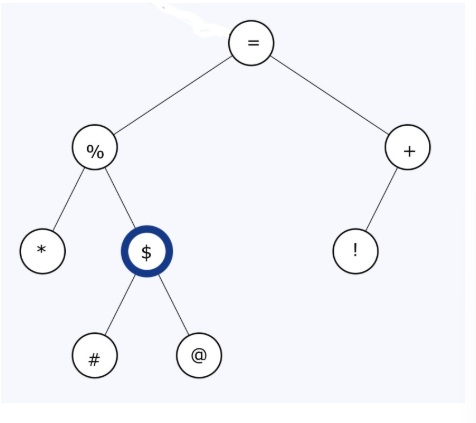
Given the binary tree above:
Blank #1 What node key has the largest value?
Blank #2 What node key has the smallest value?
Blank 1: +
Blank 2: *
The Shellsort works by
partitioning the array into two parts.
Access to the links in a linked list is usually though the ___________ link.
First
other acceptable answers: Beginning, front, head node, etc.
Answer the question provided in the python code below. Be sure to copy and paste your work into the text box provided.
""" Write a function that will create the sequence
f(1) = 1
f(2) = 2
f(3) = 6
f(4) = 24
and so on ...
Note your function should be recursive.
"""
def function(n):
if n == 1:
return 1
else:
return n * function(n-1)
An abstract data type
defines the kinds of data that are represented and the operations that can be performed on them.
Which of the following is not a characteristic of recursive routines?
when a smaller version of the problem is too complex, control passes back to the caller to try a different approach.
If you traverse a tree and print the path to each node as a series of the letters L and R for whether the path took the right child or left child at each step there could be some duplicate paths.
False
Lists differ from arrays in that:
to get the Nth item in a list, a program must follow N links, whereas in an array, the program can compute the position of the item from N.
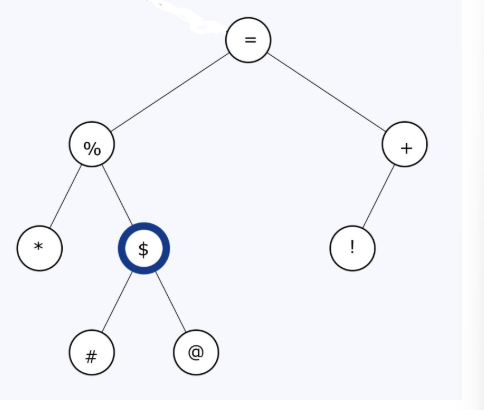
Given the following binary tree:
Blank #1: What is the "in-order" traversal of this tree?
Blank #2: What is the "pre-order" traversal of this tree?
Blank #3: What is the "post-order" traversal of this tree?
Answer for blank 1: * % # $ @ = ! +
Answer for blank 2: = % * $ # @ + !
Answer for blank 3: * # @ $ % ! + =
Traversing tree data structures
can be implemented using recursive functions or generators.
A binary tree is a search tree if
every left child has a key less than its parent and every right child has a key greater than or equal to its parent.
To transition the insertion sort into the Shellsort, which of the following do you "not" do?
change directions of the indices in the inner loop of the sort.