The Nervous System and Senses in BIOS 101
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
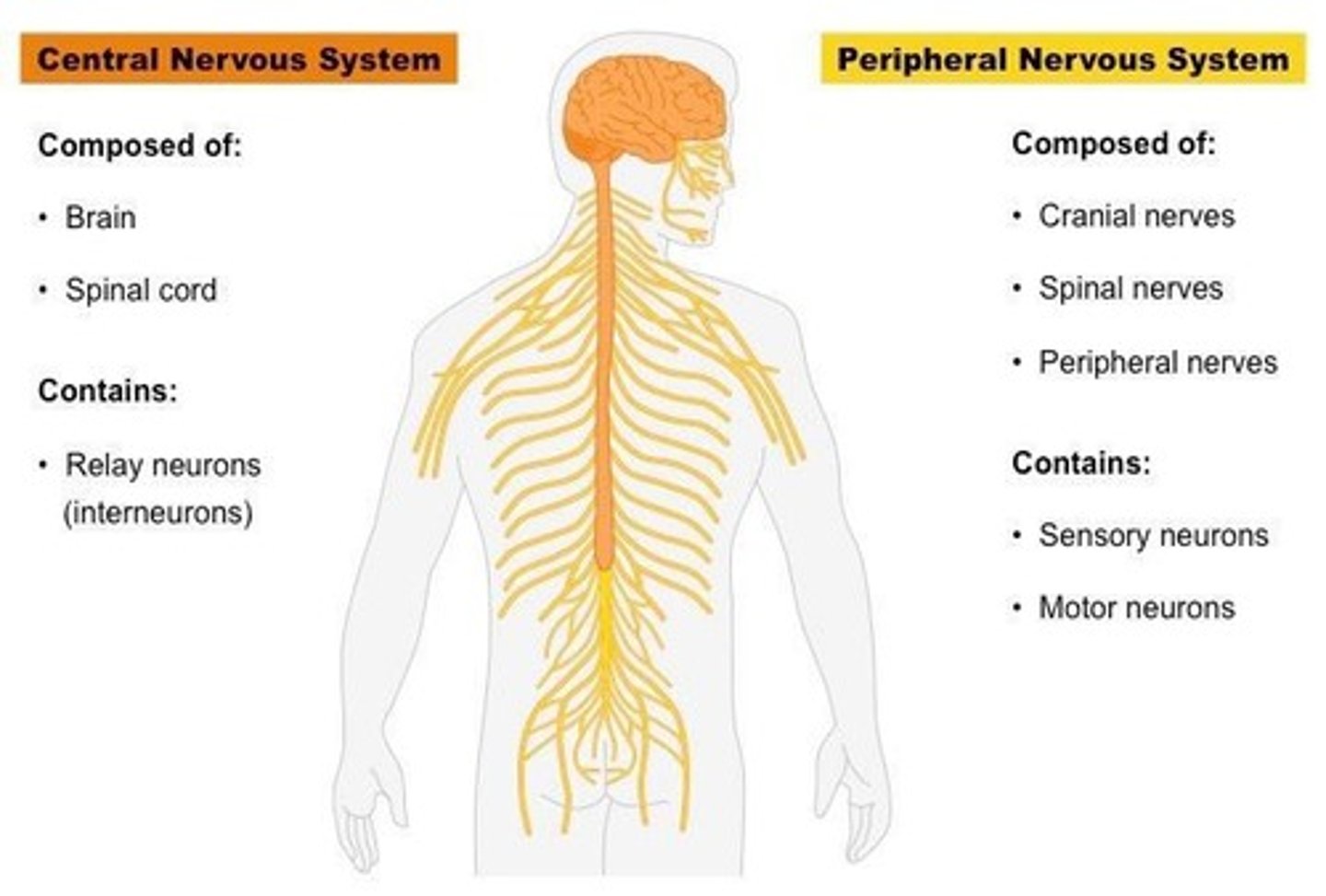
What are the two main divisions of the nervous system?
The central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS).
What is the function of association neurons (interneurons)?
They link sensory and motor neurons and are located in the CNS, providing complex reflexes and higher associative functions.
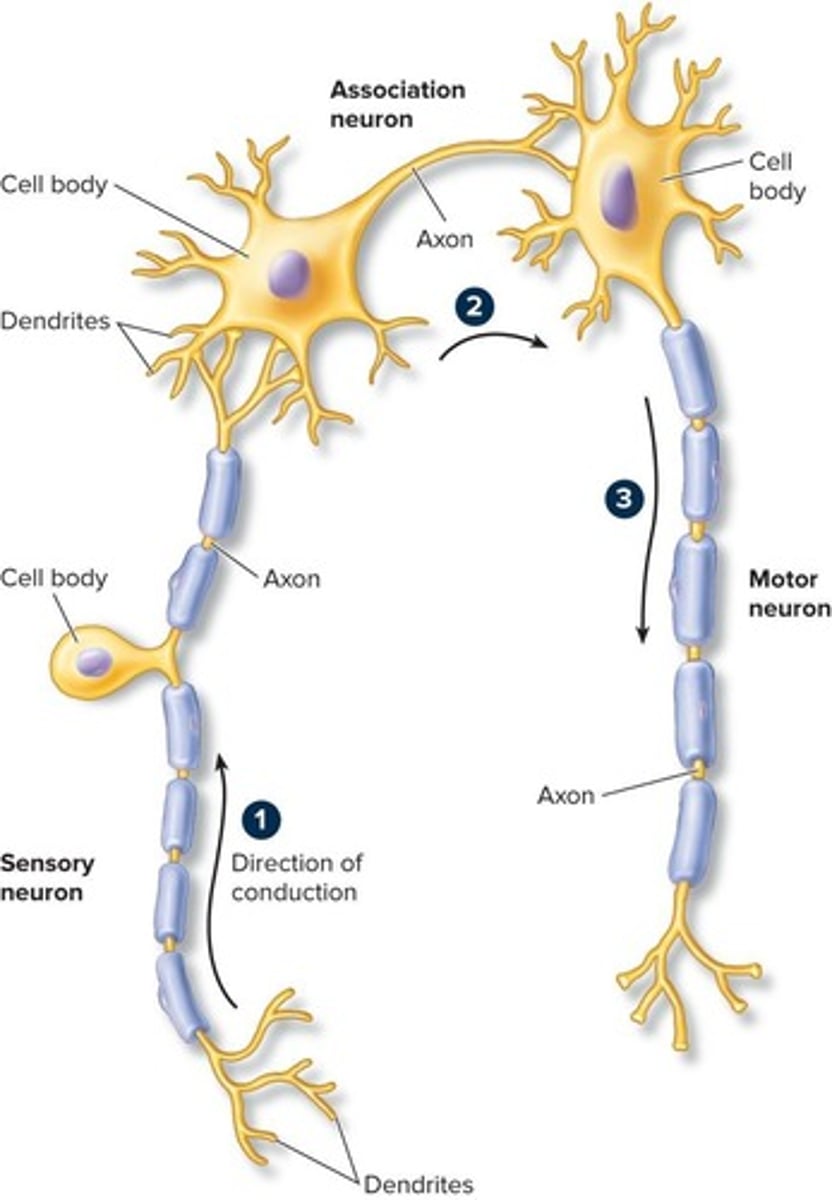
What do sensory neurons do?
They carry impulses from sensory receptors to the CNS and are located in the PNS.
What is the role of motor neurons?
They carry impulses away from the CNS to effectors such as muscles and glands, and are located in the PNS.
What are the basic structural components of all neurons?
Cell body, dendrites, and axon.
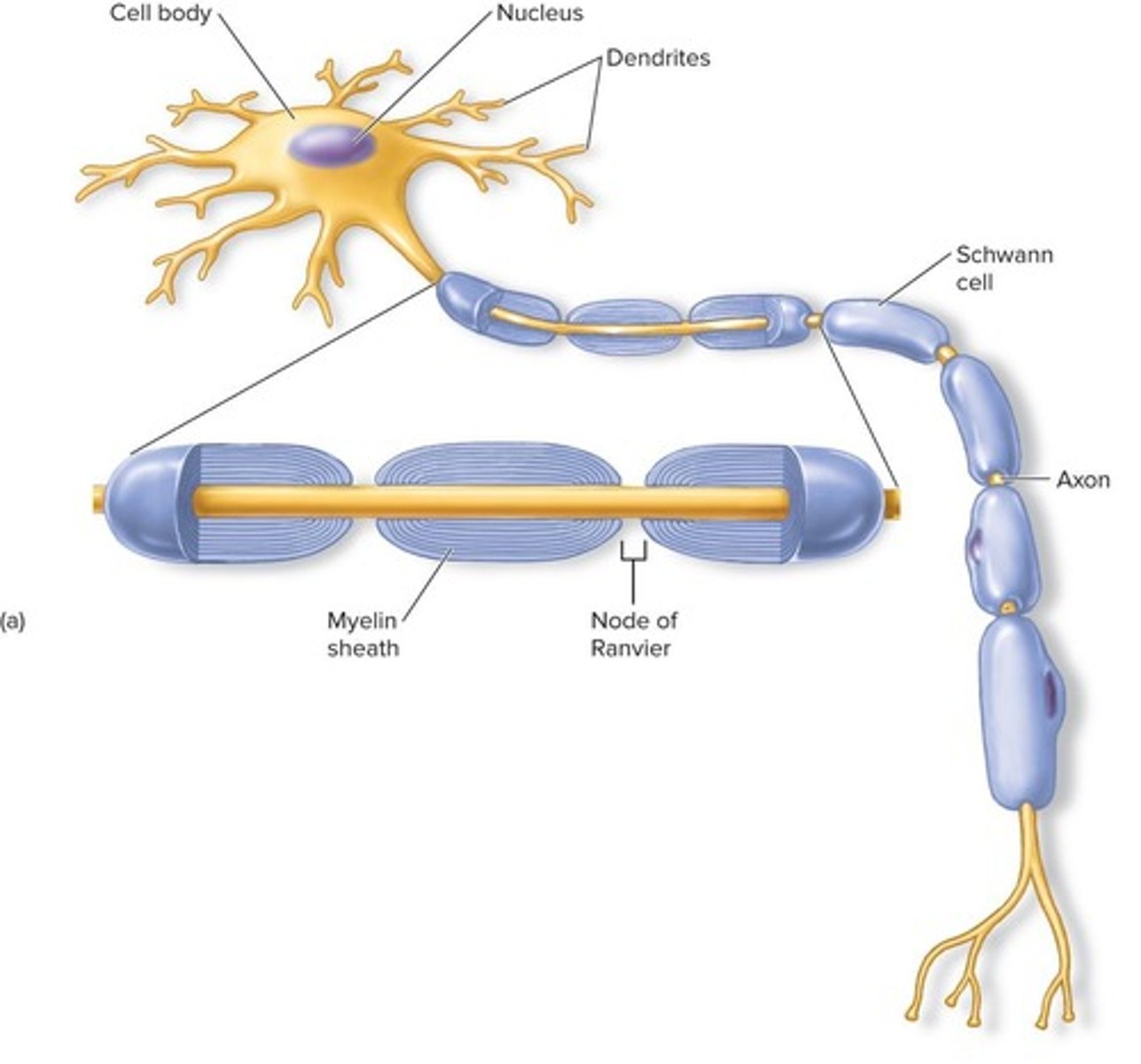
What is the function of myelin?
Myelin acts as an electrical insulator for axons.
What is an action potential?
The opening of ion channels that allows ions to move into the neuron, changing the electrical current.
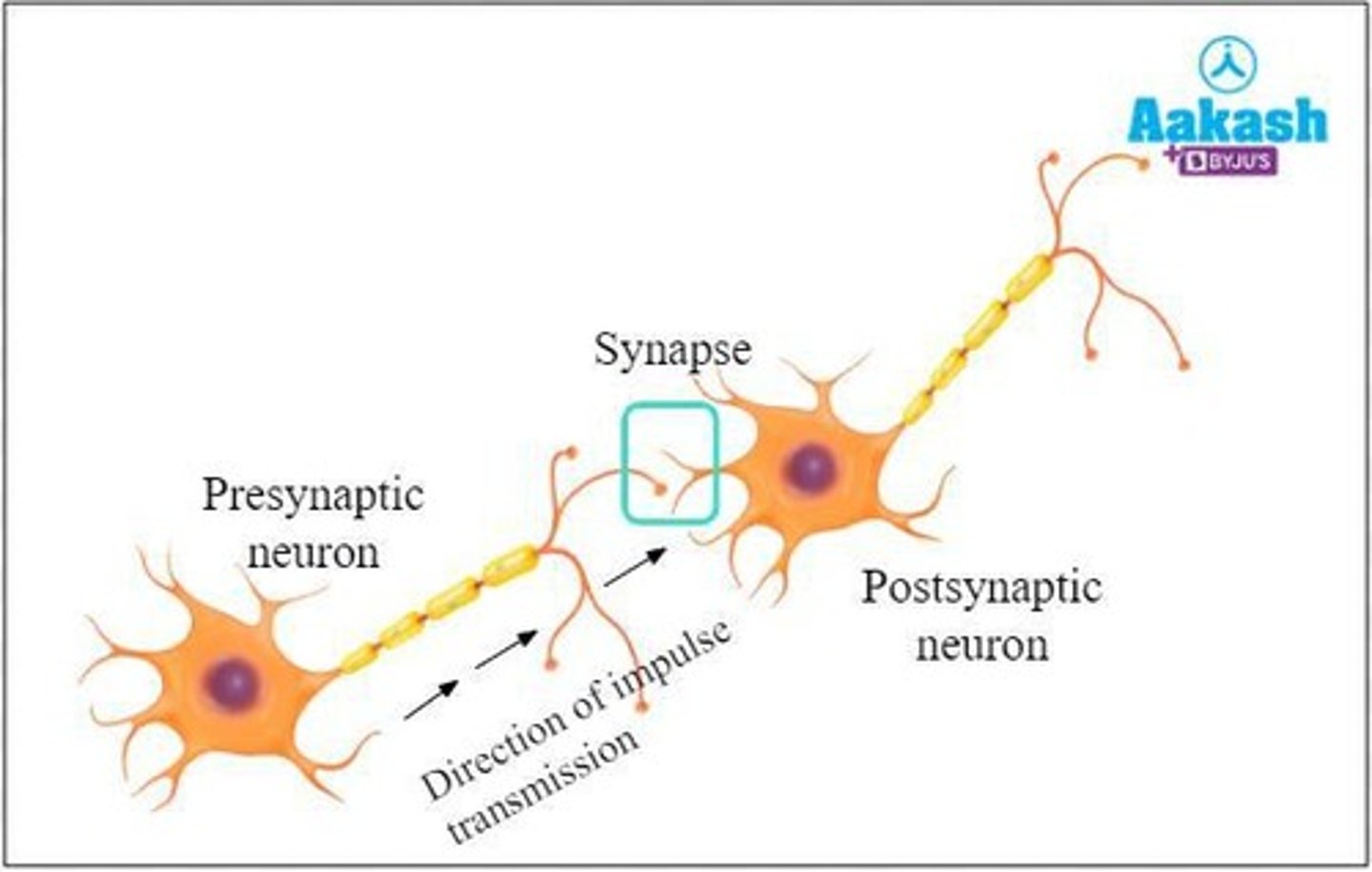
What is the synaptic cleft?
A narrow gap that separates the axon tip from the target neuron or tissue.
What are neurotransmitters?
Chemical messengers that carry signals across the synapse.
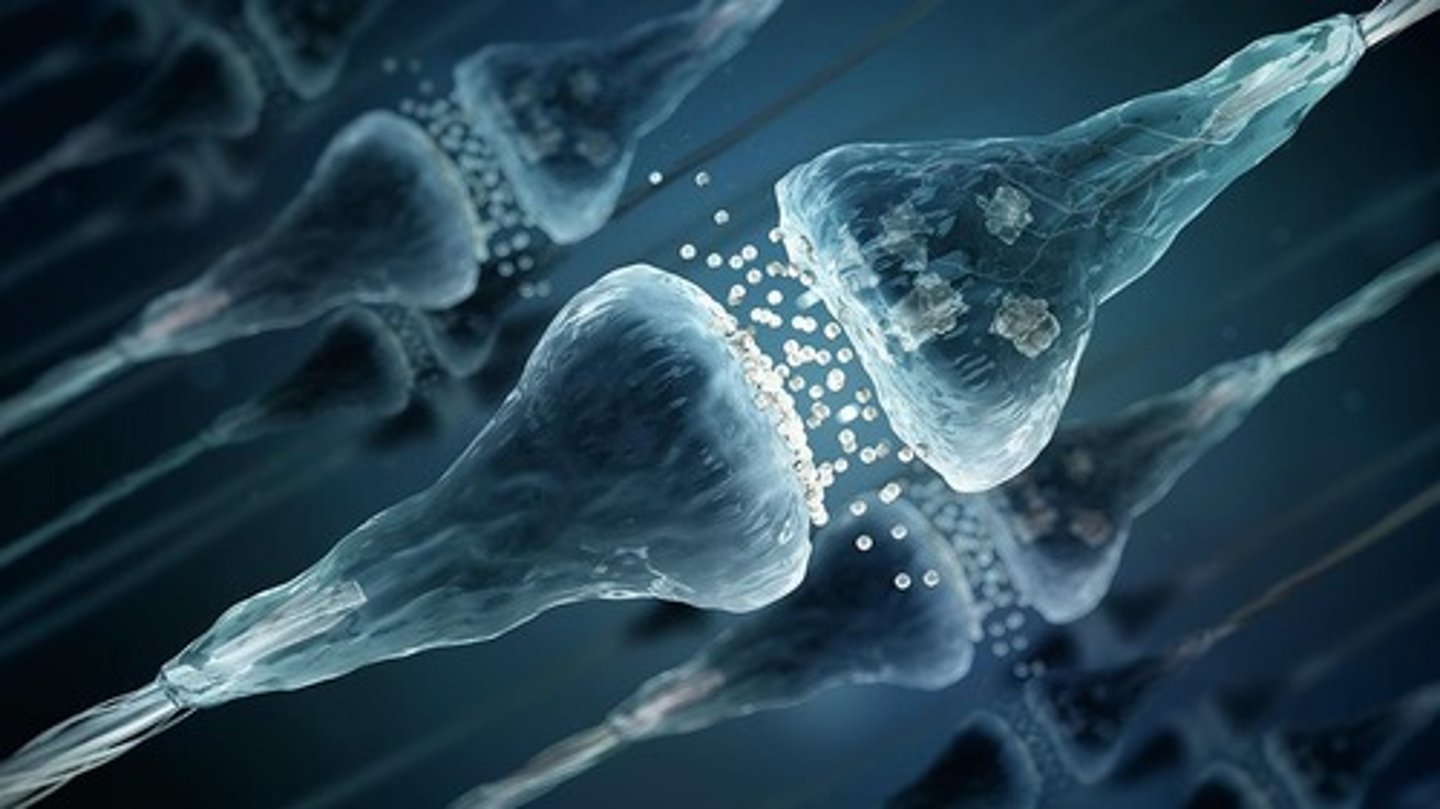
What happens when a nerve impulse reaches the end of an axon?
Vesicles release neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft.
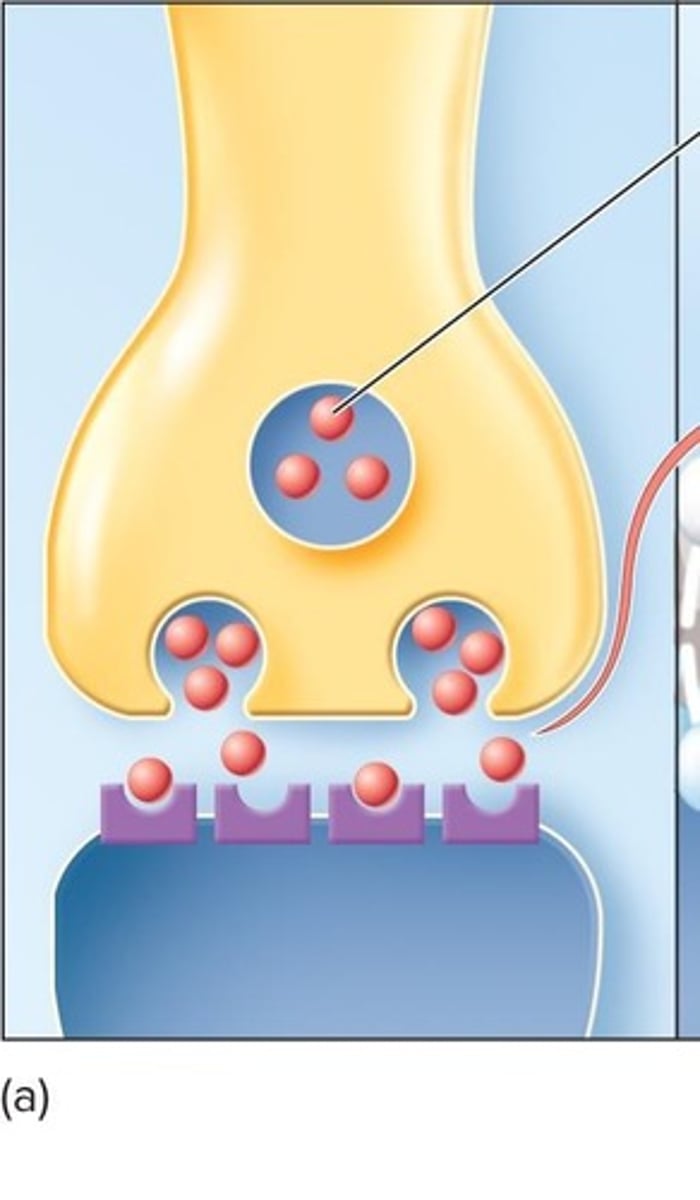
What distinguishes excitatory synapses from inhibitory synapses?
Excitatory synapses can lead to an action potential, while inhibitory synapses do not.
How do addictive drugs affect chemical synapses?
They act on neurotransmitter systems that influence emotional states.
What are the three basic divisions of the brain?
The hindbrain, midbrain, and forebrain.
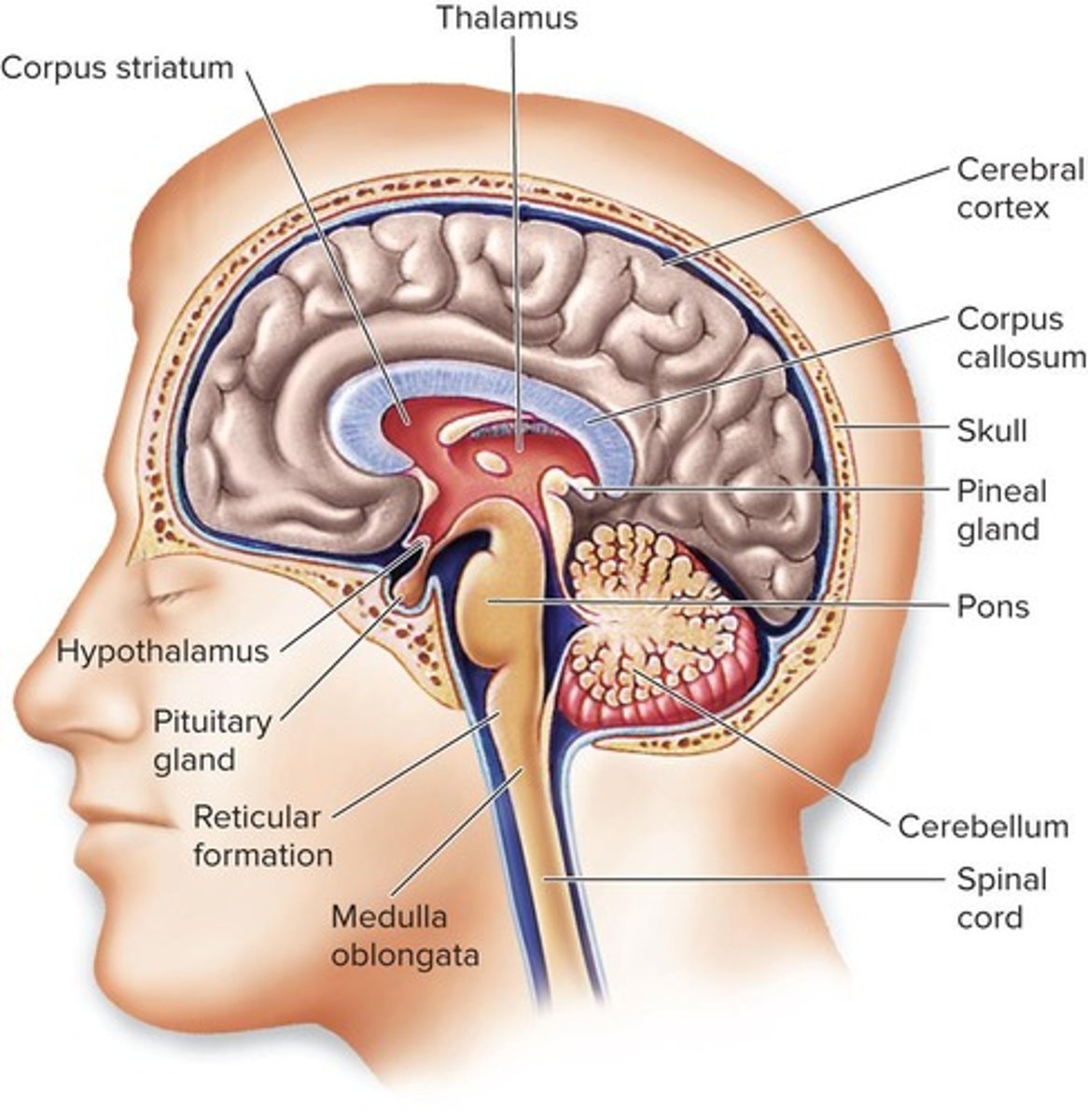
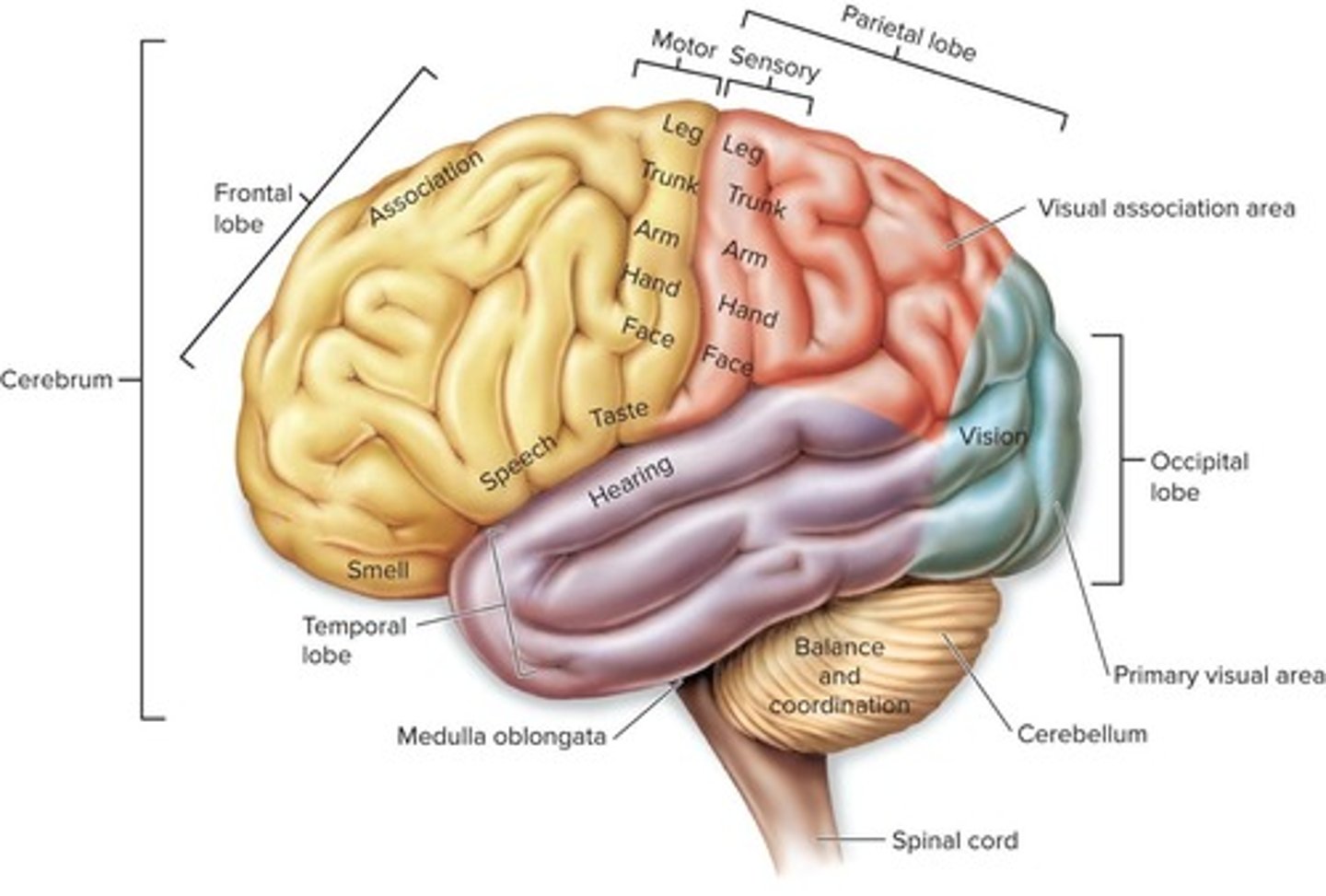
What is the primary function of the cerebrum?
It is the center for thought and association.
Why is the cerebral cortex gray?
It is densely packed with cell bodies.
What is the role of the thalamus?
It is the major site of sensory processing in the brain.
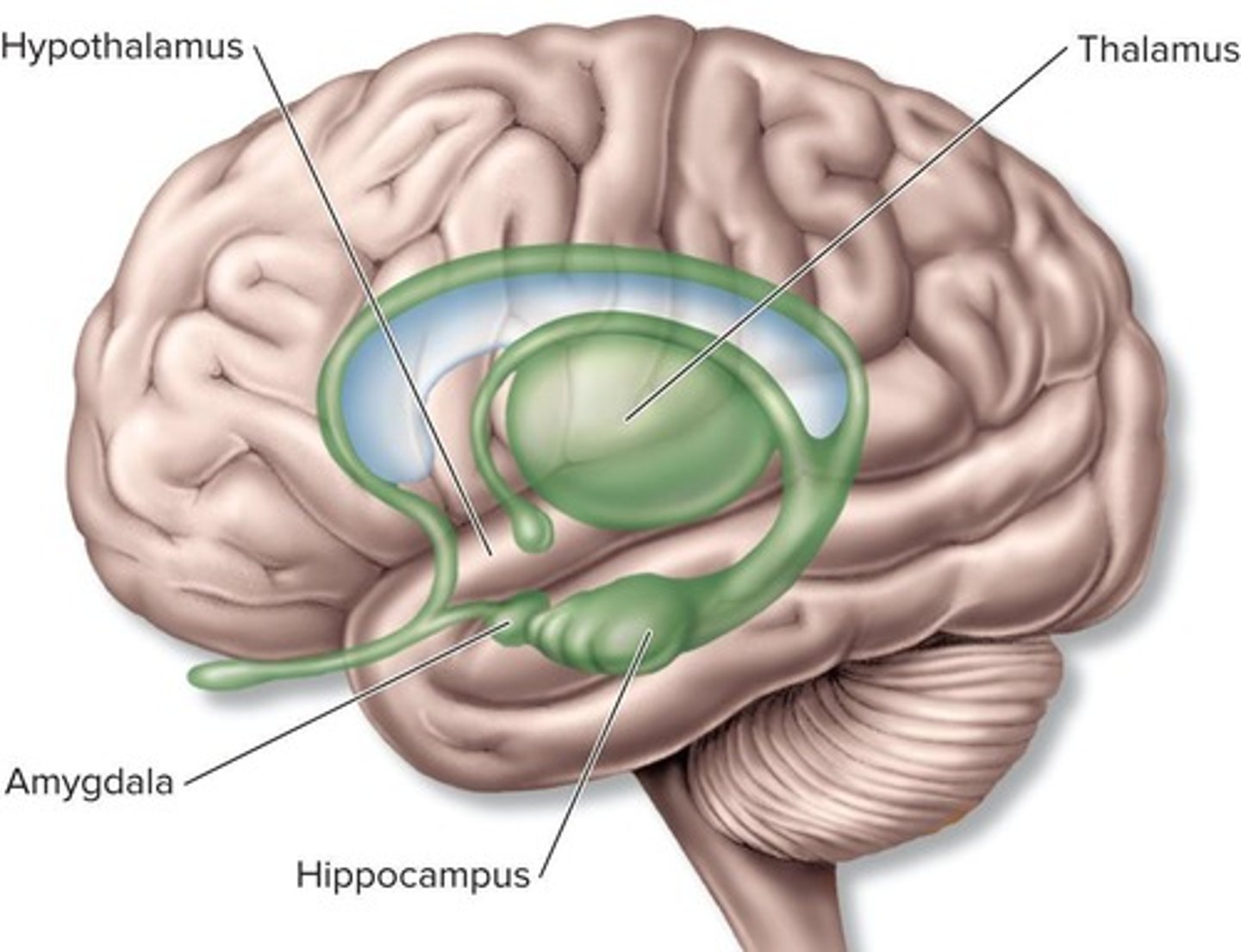
What does the hypothalamus control?
It regulates internal activities such as heartbeat, temperature, blood pressure, and respiration rate.
What is the limbic system responsible for?
It governs deep-seated drives and emotions such as pain, anger, sex, hunger, thirst, and pleasure.
What functions does the cerebellum control?
Balance, posture, and muscular coordination.
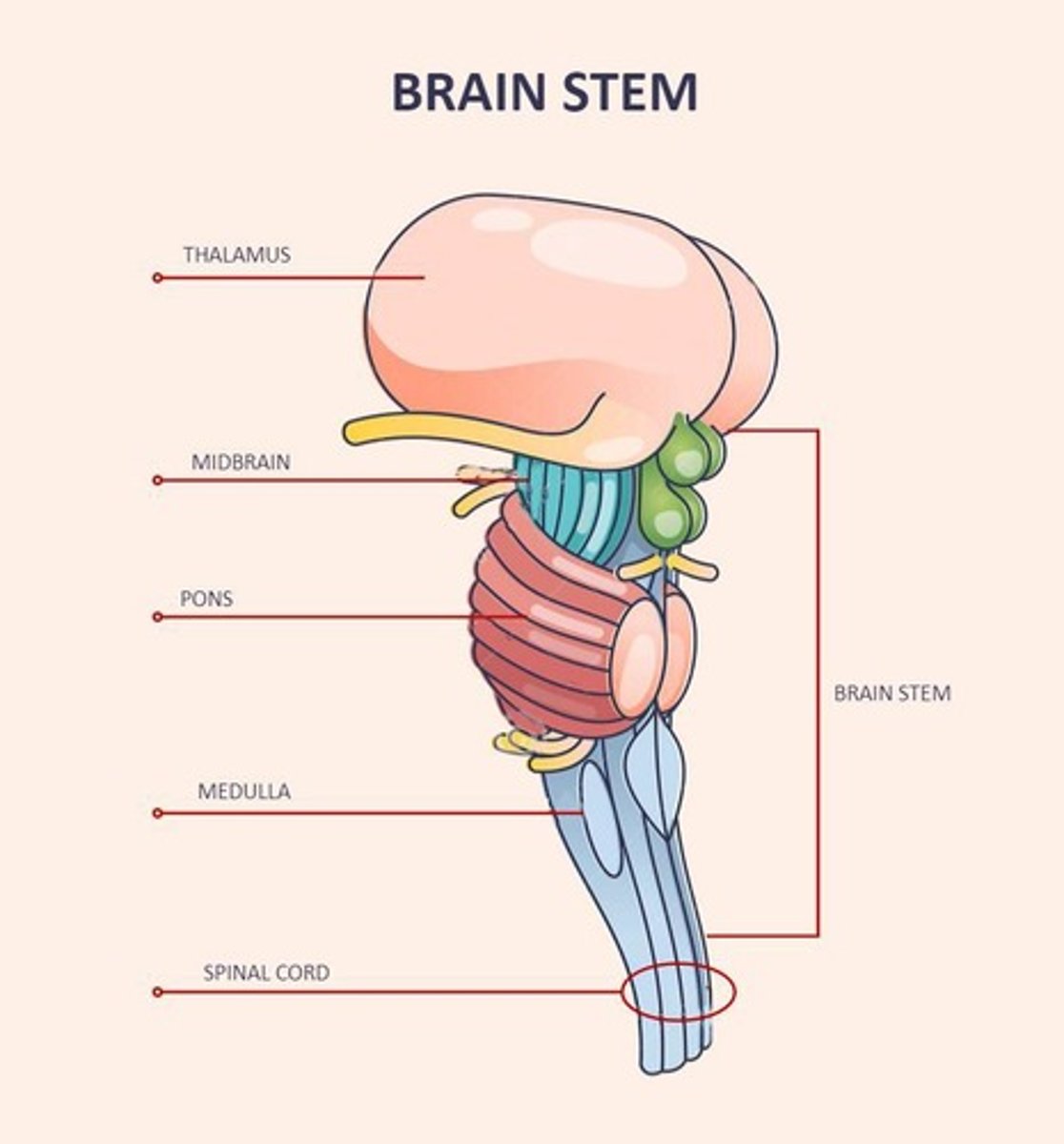
What is the brain stem's role?
It connects the brain to the spinal cord and controls vital functions like breathing and heartbeat.
How do the two hemispheres of the brain differ in function?
The right hemisphere controls the left side of the body, while the left hemisphere controls the right side.

What is the spinal cord?
A cable of neurons extending from the brain down through the backbone.
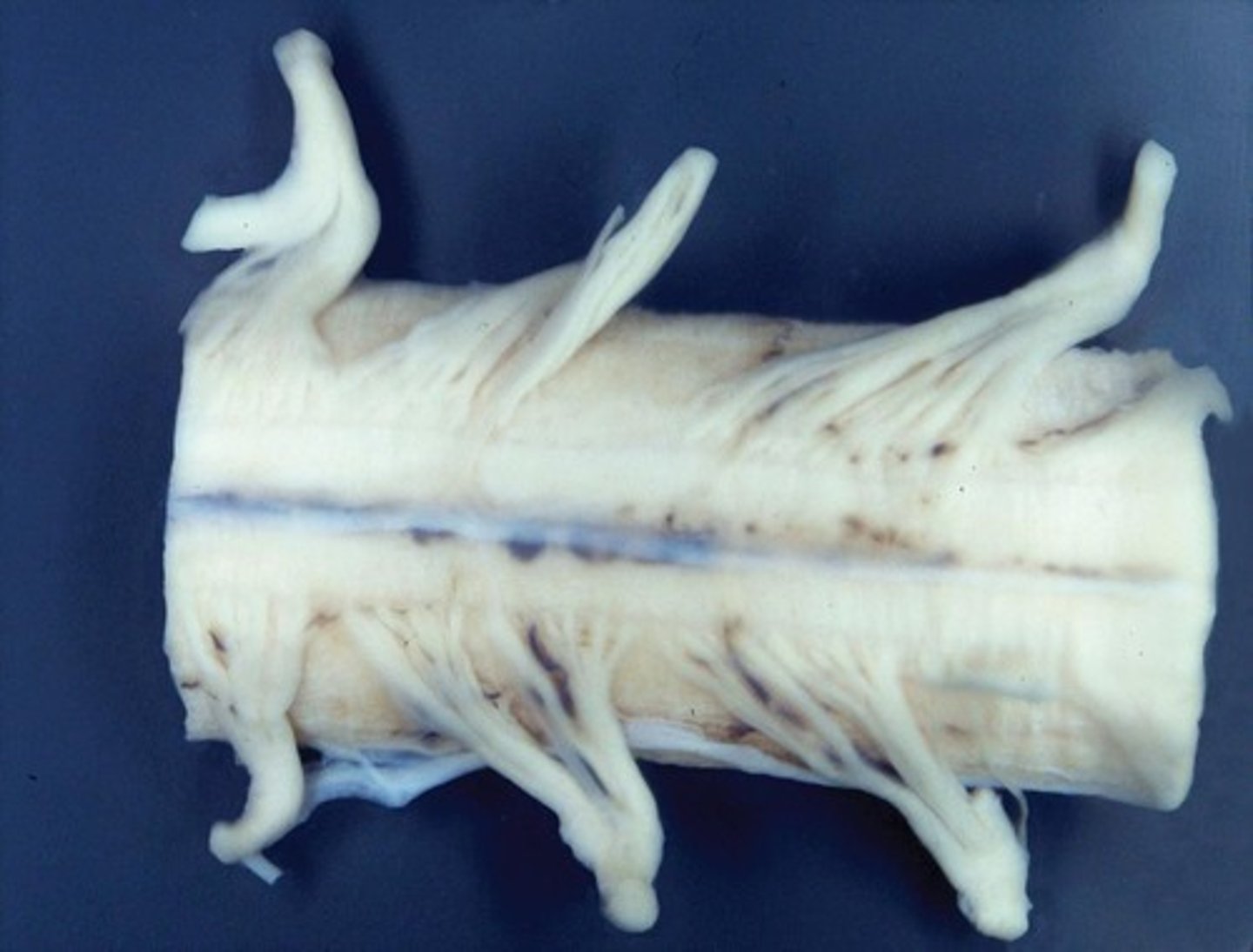
What is paralysis and what commonly causes it?
Paralysis is the loss of ability to move, often caused by damage to the nervous system, particularly the spinal cord.
What are the two components of the autonomic nervous system?
The sympathetic nervous system, which dominates in stress, and the parasympathetic nervous system, which conserves energy.
What is the purpose of a reflex?
To produce a rapid motor response to a stimulus, allowing quick reactions in dangerous situations.
What does the somatic nervous system control?
It relays commands to the skeletal muscles.
What is the primary role of the autonomic nervous system?
To maintain the body's homeostasis.
What happens during the 'fight or flight' response?
The sympathetic nervous system is activated, increasing stress responses, while parasympathetic activity decreases.