Chemistry ✿ Atomic structure and the periodic table
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
what does the nucleus consist of?
protons and neutrons
the number of protons can also tell you the number of _________
electrons
ion
an atom that has lost or gained electrons
how to find the number of neutrons in an elements?
mass number - atomic number
elements
a substance that only has one type of atom
isotopes
different forms of elements which have the same number of protons but different number of neutrons
compounds
a substance that has two or more elements that are chemically combined
mixture
a substance that has two or more different elements, not chemically bonded
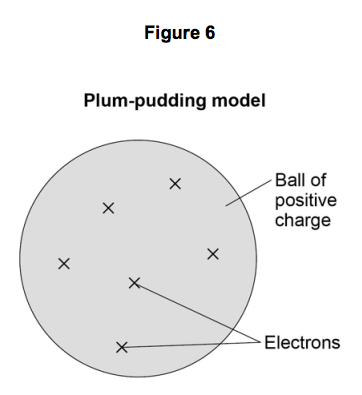
state 3 features the plum pudding model
a solid sphere of positive charge
mass was spread out
negative electrons embedded
In the alpha scattering model, what where the results and what did it say about the atom? which model did it lead to?
particles were deflected → because of positive nucleus
particles went straight through → empty space in atom
particles were reflected → mass is concentrated in the centre
led to the nuclear model
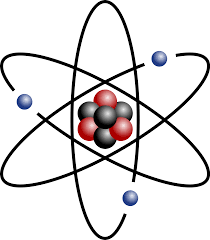
state 3 features the nuclear model
mass is concentrated in the centre
electrons orbit nucleus in shells
positive charged nucleus
who found the existence of neutrons?
James chadwick
who found the existence of the nucleus?
Rutherford
who found the existence of shells?
Neil Bohr
the period number shows how many ______ there are in the element
shells
the group number shows how many _______ there are on the outer shell
electrons
insoluble
cannot dissolve in liquid
soluble
can dissolve in liquid
what charge do atoms have overall? why?
neutral
positive protons and negative electrons cancel each other out
Non metals are located at the _____ side of the periodic table
right
give 3 properties of a metal
metallic bonding
high boiling/ melting point
conduct heat and electricity
give 3 properties of non metals
no metallic bonding
low density
brittle
what are the group 1 elements called?
alkali metals
name 3 trends in group 1 as you go down
increasing reactivity
decreasing melting/ boiling points
what is the radius of the atom?
0.1nm (1 × 10-10 m)
what is the radius of the nucleus?
10,000 times smaller than atom (1 × 10-14 m)
How do the alkali metals react with oxygen? what do they produce?
act vigorously as you go down the group and tarnish
produce a metal oxide
How do the alkali metals react with chlorine? what do they produce?
act vigorously as you go down the group and tarnish
produces metal chlorides
What do the alkali metals produce when they react with water?
metal hydroxide
How does lithium react with water? [3]
fizzes
produces hydrogen gas
floats and moves above water surface
How does sodium react with water? [2]
fizzes vigorously
floats and moves above waters surface quickly
How does potassium react with water? [3]
produces lilac flame
fizzes vigorously
floats and moves above waters surface quicky
why does the reactivity increase as you go down the group 1 metals? [3]
as you go down the group, the outermost shell is further away from the nucleus
there is less attraction between the nucleus and the electron
so the electron is lost easily
what does the reactivity of a metal of an element depend on?
the ability to lose an electron on the outermost shell
what does the reactivity of a non-metal of an element depend on?
the ability to gain an electron on the outermost shell
what are the group 7 elements called?
halogens
name 3 trends in group 7 as you go down
atoms increase in size
boiling and melting point increase
reactivity decreases
why does the melting and boiling point increase as you go down the group 7 gases? [3]
as you go down group 7, atoms increase in size
stronger intermolecular forces between atoms
more energy is required to break the forces
why does the reactivity decrease as you go down the group 7 gases? [3]
as you go down group 7, the outermost shell is further away from the nucleus
there is less attraction between the nucleus and the electron
so the outermost shell is is less likely to gain an electron
how do the halogens (group 7) react with a metal and a non-metal?
gain an electron when they react with metals and form ionic bonds
share one pair of electrons when they react with non-metals and form covalent compounds
displacement reaction
reaction where a more reactive element replaces the less reactive element in a compound
What are the group 0 elements called?
noble gases
state 3 properties of the noble gases
inert
stable arrangement of electrons
8 electrons in outermost shell (except helium)
Why does boiling point increase as you go down group 0? [3]
as you go down group 0, atoms increase in size
there is stronger intermolecular forces between atoms
so more energy is required to break the bonds