Photosynthesis and cellular respiration
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
What is photosynthesis?
The process of trapping radiant energy from the sun and converting it into chemical energy, and storing it as glucose. Occurs in the chloroplast
What is cellular respiration?
The process of acquiring and breaking down chemical energy stored in the bonds of glucose into ATP (Occurs in the Mitochondria)
What is an anabolic pathway?
Pathways that make large molecules from small ones. They require energy (Endothermic)
Catabolic?
Turns large molecules into smaller ones. They release energy (Exothermic)
What do plant cells have that animal cells don’t
Vacuoles (To store water) Chloroplast (Preform photosynthesis) Cell wall (Provides support)
What does the chloroplast do
The site of photosynthesis,
What are thylakoids?
Flattened interconnected sacs that contain chloraphyll. They are responsible for trapping solar energy. They are contained in the Stroma
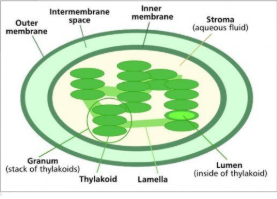
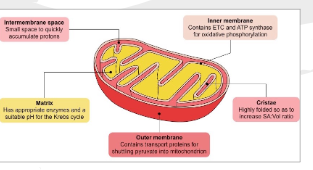
What is the Mitocondria?
The site of cellular respiration ( The fluid filled space of the inner membrane is called the Matrix) It contains proteins that break down glucose
What is the formula for photosynthesis?
CO2 + H20 ———→ C6H12O6 + O2
What is a light dependant reaction
Generates high energy molecules (ATP and NADPH)
What is a light independent reaction?
Transforms high energy molecules into G3P Which is used to create glucose
Where do light dependant reactions happen
Inside the thylakoid within the chloroplast
Where does the light independent reactions happen?
Inside the stroma of the chloroplast
What is the first step of photosynthesis
Light dependant reactions because they require sun to start
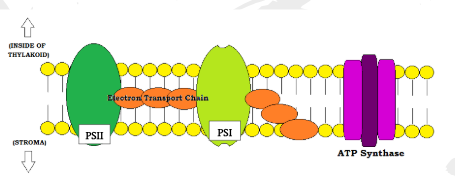
What are the two categories within light dependant reactions
Photosystem 1 and Photosystem 2
What are the steps for light dependant reactions in photosystem two
Step 1: Light energy from the syn strikes a chlorophyll molecule in photosystem two, a molecule embedded in the thylakoid membrane. This causes the election to become excited. 2: The excited electron leaves phtotsystem two and is passed down the electron transport chain. With each transfer down the chain a small amount of energy is released into the thylakoid. 3: Water molecules are split through a series of chemical reactions called photolysis inside the thylakoid. Hydrogen ions build up in the thylakoid oxygen is released and the electron that is generated by these reactions is used to replace the electron that left PS2 Step 4: The hydrogen that has been building up in the thylakoid is pushed into the stroma by the energy that was released by the ETC is step 2. This is chemiosmosis. Step 5: Hydrogen ions enter the stroma througha molecule known as ATP synthase. As it enters the stroma, H+ is used to reduce ADP to ATP. Atp is one of the main products of the light dependant reactions. it will later be used in light indepedant reactions.
Steps for light dependant reactions in photosystem one
Step 6: While the events in PS2 are taking place, light energy also excites an electron in PS1, leading to a similar series of events. The excited electron leaved PS1 and is passed down a second ETC, releasing energy along the way. The electron that leaves PS1 is replaced by the original electron that left PS2 in the first 2 steps Step 7: The electron from PS1 is then received by an electron carrier in the Stroma which is then releasing hydrogen which reduces NADP+ to NADPH. NADPH is another main product of the light dependant reactions, it will then be used in the light independent reactions.
What is the end result of the Light dependant reaction?
Production of ATP and NADPH
What happens in the light independent reaction?
Once there is enough ATP and NADPH in the stroma of the chloroplast, the energy from these molecules can be used to synthesize glucose. This process is known as the Calvin cycle. Does not rely on excitation of electrons. Happens all day.
What are the steps for the light independent reaction to occur
Carbon dioxide fixation
Activation and reduction
Replacement of RuBP
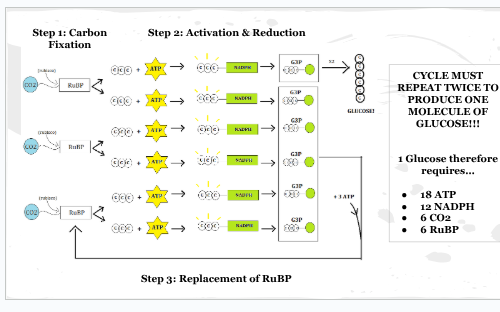
What happens during carbon Fixation
-3 CO2 molecules are required to initiate the cycle
-Each CO2 binds to a molecule of RuBP in the stroma with the help of rubisco
-This creates an unstable 6 carbon compound, which immediately breales down into two three carbon compounds called 3-PGA
End result= 3-PGA
What happens during activation and reduction
-Each 3-PGA molecule binds to a molecule of ATP. This causes each 3-PGA molecule to become activated. (gains energy)
-The six activated 3-PGA molecules each bind to a molecule of NADPH. This creates G3P.
Two G3P molecules combine to form one glucose
End result= 6 molecules of G3P
What happens during replacements of RuBP
Of the six molecule of G3P produced in step 2, five are required to replace RuBP. Replacement of RuBP also requires an additional 3 ATP molecules
What is the formula for cellular respiration
C6H12O6 + 6O2————> 6CO2 + 6H2O + ATP
What is aerobic respiration?
Cellular respiration without oxygen
What is Anaerobic Respiration
Without oxygen
What are the main steps for cellular respiration
Glycolysis
Linking reaction and Kreb Cycle
ETC
What is glycolysis?
The first step in Cellular respiration
Splits glucose into two molecules of pyruvate
Process is done without oxygen
Occurs outside the Mitochondria in the cytoplasm
What is required to start Glycolysis
2 molecules of ATP (This causes glucose to be broken down into G3P
G3P reduces NAD+ into NADH. (Will be used later in the Kreb Cycle)
The reduction of NAD+ leads to create 2 ATP by each G3P
Through reduction G3P turns into pyruvate (Required for Kreb Cycle)
What is the linking Rection (Pre Kreb)
If oxygen is present cells will move to the KC, loosing one carbon
The remaining carbon bond to make Acetyl CoA
This reaction also causes NAD+ to reduce into NADH
*Acetyl CoA enters the KC
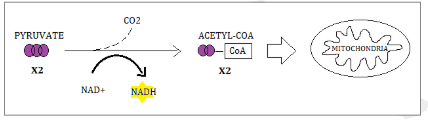
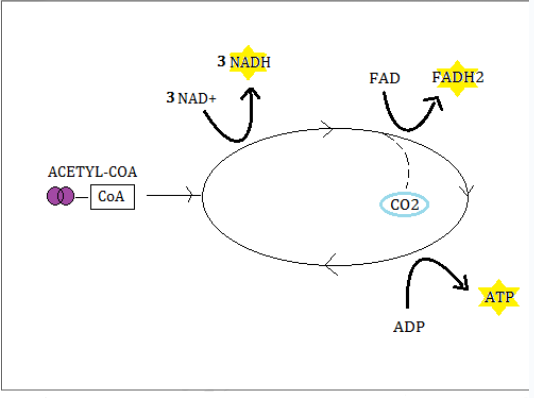
What is the main purpose of the Kreb Cycle?
Produce even more High energy compounds (NADH, FADH2) for step three
What happens in the Kreb cycle
Acetyl CoA enters the KC to generate THREE molecules of NADH from NAD+, ONE molecule of ATP from ADP and ONE molecule of FADH2 from FAD
CO2 is released as a by product
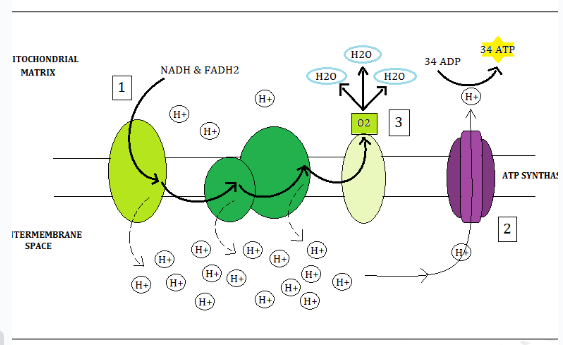
What is the ETC
The majority producer of ATP. Taking place across the inner membrane of the Mitocondria
What Happens in the ETC
Electrons that are passed down release energy (This energy pumps H+ ions across the membrane into the inter-membrane space)
High to low concentration gradient (High to low of H+ in the IMS) forces H+ ions through the ATP synthase creating ATP
O2 is the last electron acceptor. It bond with electrons and H+ creating water
What is anaerobic cellular respiration?
The same as the ETC but instead of O2 as the final receptor it is either sulfate, nitrate, or CO2
Generates similar amounts of ATP but releases different by products
What is fermentation?
Glycosysis goes as normal but when pyruvate is formed it undergoes a different set of reactions that do not require oxygen. So it does not enter the KC
Fermentation takes place only in the Cytoplasm