PRD 132: Alginate/Gypsum
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
Gypsum
A naturally occurring material consisting of calcium sulfate and water molecules
Type 1 impression plaster
Mounting stone
Type 2 impression plaster
Model plaster
Type 3 dental stone
Study casts, micro stone, yellow color we use
Type 4
high strength low expansion Die stone
Type 5
high strength high expansion dental stone
Calcination
the process of driving a specific amount of water out of gypsum to create specific plasters, stones, or investment die stones
Increased water
Less strength, more porosity, less expansion, increased setting time
Less water
More strength, less porosity, more expansion, decreased setting time
Increasing spatulation
Shortens the setting time
Exothermic
Setting reaction of gypsum is
Room temperature increasing
Will increase the rate of reaction and shorten set time
Closed container/imbibition
All gypsum products should be in a ______ to avoid
Less Setting time
Hot water, less water, increased spatulation time, use of slurry water
More setting time
Cold water, more water, decreased spatulation time
Vibrator
Must be used w/ gypsum to overcome surface tension and bubbles (doesn't work w/ alginate sets too fast)
Vaccuum mixer
Mixes both gypsum and alginate
Alginate
Irreversible hydrocolloid material used for taking preliminary impressions
Hydrocolloid
A mixture within water
Colloid
Particles of one substance that are evenly dispersed throughout another substance
Mucous extract
Alginate has ______ from brown seaweed
Active ingredient
Potassium alginate is the active ingredient (water soluble salt) derived from seaweed
15%
Potassium alginate amount
Calcium sulfate
Reacts w/ potassium alginate to form the gel (insoluble calcium alginate)
16%
Calcium sulfate amount
Tri-Sodium Phosphate
Slows the reaction time for mixing (reacts preferentially w/ calcium sulfate as a retarder)
Diatomaceous earth
Filler for built of material (primary ingredient) in alginate
60%
Primary ingredient diatomaceous earth amount
Potassium titanium fluoride
Added for surface strength in alginate
3%
Amount of potassium titanium fluoride
Sol/Gel Phases
Phases of alginate setting
Replicate teeth and soft tissue (vestibule and palate) although INACCURATE
What is the purpose of diagnostic impression
Pleasant odor, biocompatible, cheap, elastic, adequate strength
Advantages of alginate
Cold water
Maximizes working time for alginate
Do not move
After seating the tray
30 seconds
Mix alginate/water
1 minute
Working time
1:30
Setting time
Imbibition
Absorption of water, causing an object to swell
Syneresis
Loss of water, causing something to shrink
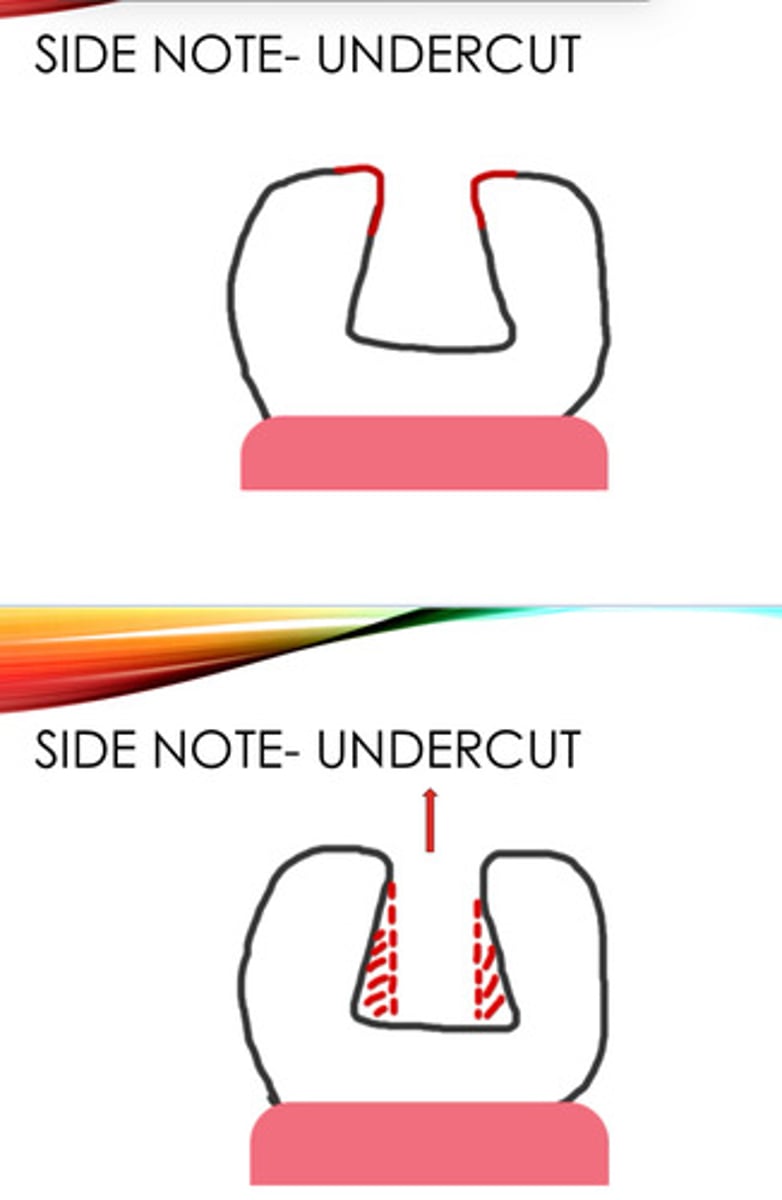
Undercut
Can make impression harder to remove
Treatment planning, dental legal records, provisional restoration
Why do we make mounted study models
Treatment planning
Patient doesn't have to be present, identify teeth position/occlusion, treatment presentation to patient
Provisional restorations
You use study models to set the putty matrix fabrication for crowns
Once
Alginate impressions can only be poured
Alginate
Pink in color
Micro stone
Yellow in color
Mounting stone
Blue in color (not used in this impression lab)
Maxillary
Four scoops of alginate
mandibular
Three scoops of alginate
Alginate to water ratio
1:1
Room temp water
Recommended so it doesn't take too long or too quick to set
Fluffed
Alginate powder should be ____ not dense and level it off
Maxillary
Load the tray in one scoop
Mandibular
Load the tray in two-three scoop
Occlusal surfaces
Before placing the tray, smear alginate on ____ to prevent bubbles
12 o clock
Maxillary you want to stand
9 if right 3 if left
Mandibular you want to stand
2 minutes, fingernail
Gelatin process takes ____, you can test w/ ur ____ to make a clean cut
40 ml water
For the micro stone, you add first
60 degrees
Hold impression at ____ on vibration platform and flow the gypsum slowly into the tray
10-15 minutes
The stone sets in