History Review Booklet #1
4.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 10:04 PM on 6/16/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
1
New cards
Tariffs
Tariffs are taxes imposed by a government on imported or exported goods. They are used to protect domestic industries, raise revenue, and regulate trade. Tariffs can be specific (a fixed amount per unit) or ad valorem (a percentage of the value of the goods). Tariffs can also be used as a tool in international trade negotiations.
2
New cards
Assimilation
Assimilation refers to the process of individuals or groups adopting the cultural norms, values, and behaviors of a dominant culture. This can occur voluntarily or involuntarily, and can involve changes in language, religion, dress, and other aspects of culture. Assimilation has been a controversial topic throughout history, with some arguing that it leads to the loss of cultural diversity and others arguing that it is necessary for social cohesion and integration.
3
New cards
Treaties
Negotiations and terms made by each party which were signed and said not to be broken
4
New cards
Stalemate
When both party’s have no improvement and stuck where they are
5
New cards
Partisan
To support a cause or a political party
6
New cards
Pemmican
A type of food which was used for trading which had bison, berrys and various other things
7
New cards
Rep. by Pop.
representation by population which meant that votes were not taken by seat they were taken by how many people voted and who they voted.
8
New cards
Provisions
the action of providing or supplying something for use.
9
New cards
Amnesty
an official pardon for people who have been convicted of political offenses.
10
New cards
Immigration act
primarily focused on ensuring the safety of immigrants during their passage to Canada and protecting them from exploitation upon their arrival.
11
New cards
Manitoba School Act
The Act eliminated provincial funding for Catholic and Protestant denominational schools, establishing instead a system of tax-supported, nonsectarian public schools. This prohibition would ultimately lead to the reduction of Catholic schools, as many Catholic parents were unable to pay for schooling.
12
New cards
Millitarism
the belief or desire of a government or people that a country should maintain a strong military capability and be prepared to use it aggressively to defend or promote national interests.
13
New cards
Conscription
compulsory enrolment for service in a country's armed forces
14
New cards
Refugee
a person who has been forced to leave their country in order to escape war, persecution, or natural disaster
15
New cards
What is history and why do we study it?
Faults and achievements which have been taken in the past.
we study it so that we know how to encounter them, to educate ourselves with were we came from.
we study it so that we know how to encounter them, to educate ourselves with were we came from.
16
New cards
Who were the first people, and how did they structure their world?
The original people of north america, they were said as caretakers of the world, which there relation with the world was a give or take.
17
New cards
Why did the French and other Europeans come to North American?
trying to find the northwest passage, to establish settlements.
18
New cards
How did the French and other Europeans interact with First peoples?
first good then bad
19
New cards
How did First Peoples and europeans interact in the northwest and what were the results?
there interactions where simply first trading but then it turned into a havoc as there were partnerships with rival groups, etc.
20
New cards
How did British colonial rule change from 1763-1867?
Well Canada’s fur trade was increasing then the 13 colonies became america
21
New cards
What impact did the change in British colonial rule have on life in north America from 1763-1867?
the impact was on the first nations as they lost more land and they were never apart of the 13 colonies separation.
22
New cards
How did the fur trade, European settlement, and the rise of the Metis nation transform life for the peoples of the Northwest?
Fur Trade
Fur Trade
The fur trade was a great way to get tools and get familiar with the other world for the first nations. fur trade was also how they were introduced to liquor which was not a good thing
23
New cards
How did the fur trade, European settlement, and the rise of the Metis nation transform life for the peoples of the Northwest?
European Settlement
European Settlement
Many first nations were pushed off there land and lost rights of having any say about there land. they were also seen as a minority as the European settlements increased.
24
New cards
How did the fur trade, European settlement, and the rise of the Metis nation transform life for the peoples of the Northwest?
Rise of the Metis Nation
Rise of the Metis Nation
The natives life’s changed because of the metis were being seen by the goven. but they were not
25
New cards
Why did the Metis resist the westward expansion of Canada, and what were the consequences?
The reason they resisted was because they had the land, they had started settlements there which was being surveyed without their permission and then they were sold to incoming immigrants because they did have proper papers for them to keep there land, despite all the letters they had sent to the governments asking for proper papers
26
New cards
What were the three main causes of confederation and give two examples for each?
* Great Britain not wanting anything to do with the government
* Didn’t want to deal with many of the issues there, such as the Metis complaints
* Was also at war with France again and all there focus was there
* The fear of attack by the States
* Taking over Rupert land
* open threats
* civil war in the mood for fighting
* Railway
* Great Britain promised to help build the transcontinental railway
* Didn’t want to deal with many of the issues there, such as the Metis complaints
* Was also at war with France again and all there focus was there
* The fear of attack by the States
* Taking over Rupert land
* open threats
* civil war in the mood for fighting
* Railway
* Great Britain promised to help build the transcontinental railway
27
New cards
How was the Dominion of Canada established as a confederation of British colonies in 1867? Give the four main events?
* Great britain not wanting anything to do with canada
* open threats from US
* Political deadlock
* economic status
* open threats from US
* Political deadlock
* economic status
28
New cards
How did territorial expansion, immigration, and industrialization change life for men and women in Canada?
Territorial Expansion
Territorial Expansion
men:
more jobs, land rights
women:
working on farms with men
more jobs, land rights
women:
working on farms with men
29
New cards
How did territorial expansion, immigration, and industrialization change life for men and women in Canada?
Immigration
Immigration
men:
less land
women:
seen as just baby produces
less land
women:
seen as just baby produces
30
New cards
How did territorial expansion, immigration, and industrialization change life for men and women in Canada?
Industrialization
Industrialization
more jobs!
Territorial expansion, immigration, and industrialization had significant impacts on the lives of men and women in Canada. Industrialization led to the growth of urban centers and the rise of factory work, which provided new employment opportunities for both men and women. However, women were often paid less than men for the same work. Immigration brought new cultures and traditions to Canada, but also led to discrimination and prejudice against certain groups. Territorial expansion displaced Indigenous peoples and disrupted their way of life, leading to ongoing struggles for Indigenous rights and reconciliation. Overall, these changes brought both opportunities and challenges for men and women in Canada.
Territorial expansion, immigration, and industrialization had significant impacts on the lives of men and women in Canada. Industrialization led to the growth of urban centers and the rise of factory work, which provided new employment opportunities for both men and women. However, women were often paid less than men for the same work. Immigration brought new cultures and traditions to Canada, but also led to discrimination and prejudice against certain groups. Territorial expansion displaced Indigenous peoples and disrupted their way of life, leading to ongoing struggles for Indigenous rights and reconciliation. Overall, these changes brought both opportunities and challenges for men and women in Canada.
31
New cards
How did Canada’s relationship with First nations, metis and inuit peoples change after confederation?
became more harsh
32
New cards
How was Canada’s identity as a nation shaped by the first world war?
they were brave and courageous
\
The First World War played a significant role in shaping Canada's identity as a nation. Canada's contribution to the war effort, particularly at the Battle of Vimy Ridge, helped establish Canada as a respected military power. The war also brought about changes in Canadian society, including increased industrialization and urbanization, and a greater sense of national unity and pride. Additionally, the war helped to solidify Canada's relationship with Britain, while also asserting its independence as a nation.
\
The First World War played a significant role in shaping Canada's identity as a nation. Canada's contribution to the war effort, particularly at the Battle of Vimy Ridge, helped establish Canada as a respected military power. The war also brought about changes in Canadian society, including increased industrialization and urbanization, and a greater sense of national unity and pride. Additionally, the war helped to solidify Canada's relationship with Britain, while also asserting its independence as a nation.
33
New cards
How was Canada’s identity as a nation shaped by its changing relationship to Great Britain and the world?
Canada's identity as a nation was shaped by its changing relationship to Great Britain and the world in various ways. Initially, Canada was seen as a British colony, but over time, it gained more autonomy and became more independent. Canada's participation in World War I and II helped to establish its reputation as a strong and capable nation. Additionally, Canada's multiculturalism and diverse population have contributed to its unique identity as a nation. Overall, Canada's relationship with Great Britain and the world has played a significant role in shaping its national identity.
34
New cards
How has Canada been shaped by technological change?
railway
35
New cards
Who was Gabriel Dumont and what did he do?
he wanted justice for his people and got riel
Gabriel Dumont was a prominent Métis leader and military commander who played a key role in the North-West Resistance of 1885. He was a skilled buffalo hunter and horseman, and led the Métis forces in several battles against the Canadian government's military forces. Despite his tactical brilliance, the Métis were ultimately defeated and Dumont fled to the United States. He later returned to Canada and lived out his life as a farmer and community leader.
Gabriel Dumont was a prominent Métis leader and military commander who played a key role in the North-West Resistance of 1885. He was a skilled buffalo hunter and horseman, and led the Métis forces in several battles against the Canadian government's military forces. Despite his tactical brilliance, the Métis were ultimately defeated and Dumont fled to the United States. He later returned to Canada and lived out his life as a farmer and community leader.
36
New cards
Do you think that Gabriel Dumont was a “rebel”? Why or why not, and justify your answer?
he was but for the right cause
37
New cards
Locate the following places on the map below?
Upper Canada
Lower Canada
Rupert’s Land
Upper Canada
Lower Canada
Rupert’s Land
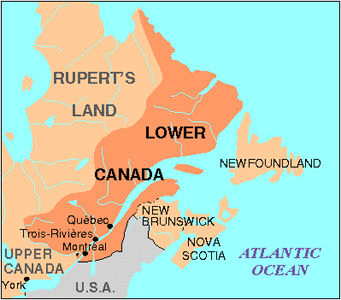
38
New cards
Describe Sir John A. from a political, social, and personal point of view?
potical view: Get more people and be connected to britain
socail: rude but good at convining people
personal: didnt like the metis and natives
socail: rude but good at convining people
personal: didnt like the metis and natives
39
New cards
Explain the significance of Cartier’s Death?
Cartier also brought British Columbia into the Canadian fold in 1871. He had negotiated with the colony's leaders promising them a railway to the Pacific it they joined the Dominion.
40
New cards
Explain the significance of Thomas scott’s death?
he was an orangeman who thought that the Metis shouldn’t get any say and that the provisional government will not work and then riel told his people to execute him
reil was a hero and a villan
reil was a hero and a villan
41
New cards
How did other countries view Canada between 1869-1915?
a baby country with lots of immigrants
42
New cards
what was the one invention that caused and industrial boom in Canada in 1909?
hydroelectricty
the automobile, the airplane, and the radio
railway
the automobile, the airplane, and the radio
railway
43
New cards
What effects did industrialization have Canada in the 20th century?
First, economic and social activities were transformed from agriculture and natural resource extraction to manufacturing and services. Second, economic and social activities shifted from rural cottage industries to urban industrial pursuits
44
New cards
Who was sir Wilfred Laurier?
prime mister who loved canada
Sir Wilfred Laurier was a Canadian politician and the seventh Prime Minister of Canada, serving from 1896 to 1911. He is known for his policies of conciliation, expanding the country's territory, and promoting immigration. He also played a key role in the development of Canada as a nation, including the creation of the Royal Canadian Navy and the Canadian Navy.
Sir Wilfred Laurier was a Canadian politician and the seventh Prime Minister of Canada, serving from 1896 to 1911. He is known for his policies of conciliation, expanding the country's territory, and promoting immigration. He also played a key role in the development of Canada as a nation, including the creation of the Royal Canadian Navy and the Canadian Navy.
45
New cards
Who is Nellie McClung and what did she do?
* apart of the famous five
* activist for womens vote
* put on a play
Nellie McClung was a Canadian feminist, politician, and social activist who played a significant role in the women's suffrage movement. She was one of the "Famous Five" who fought for women's rights and helped to secure the inclusion of women as persons under Canadian law. McClung was also a successful author and public speaker, advocating for women's rights and social justice.
* activist for womens vote
* put on a play
Nellie McClung was a Canadian feminist, politician, and social activist who played a significant role in the women's suffrage movement. She was one of the "Famous Five" who fought for women's rights and helped to secure the inclusion of women as persons under Canadian law. McClung was also a successful author and public speaker, advocating for women's rights and social justice.