Interphase and Metaphase Chromosomes
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
Interphase Chromosomes
Is the compaction level of interphase chromosomes uniform or not?
Not completely uniform
Interphase Chromosomes
Therefore, what are the 2 types of regions in interphase chromosomes?
Euchromatin
Heterochromatin
Interphase Chromosomes
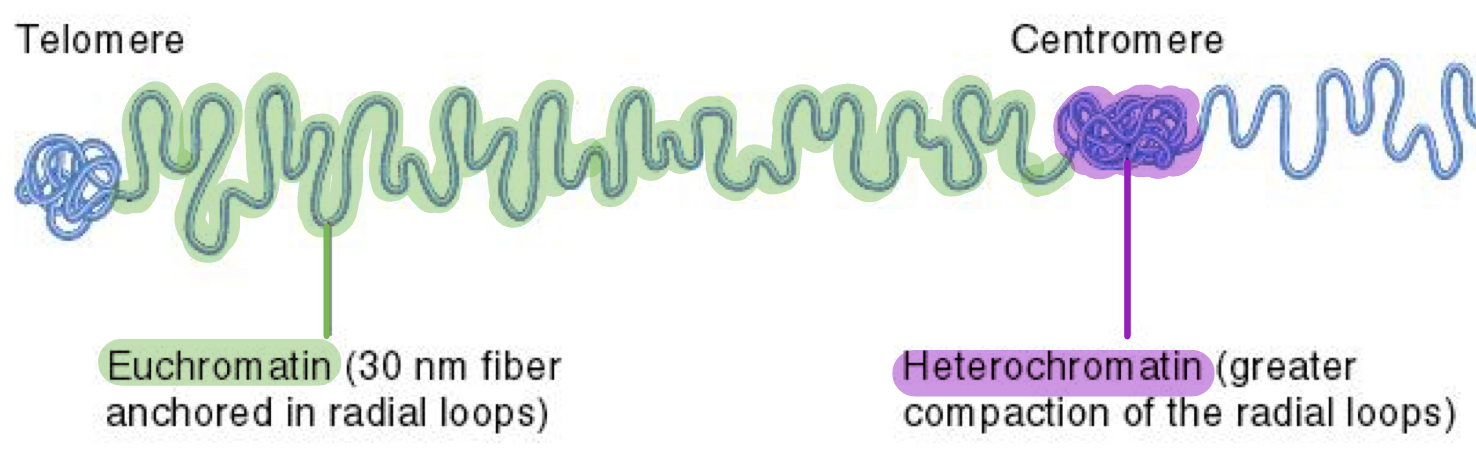
Euchromatin vs Heterochromatin
Level of compactness
Transcriptionally active or inactive
Radial loop domains
Euchromatin:
Level of compactness: Less compacted
Transcriptionally active or inactive: Active
Radial loop domains: Regions where 30nm fiber forms radial loop domains
Heterochromatin:
Level of compactness: Tightly compacted
Transcriptionally active or inactive: Inactive (in general)
Radial loop domains: Compacted even further
Interphase Chromosomes
What are the 2 types of heterochromatin?
Constitutive heterochromatin
Facultative heterochromatin
Interphase Chromosomes
What is the difference between constitutive and facultative heterochromatin?
Constitutive: Always heterochromatic
Which means it is permanently transcriptionally inactive
Facultative: Can interconvert between euchromatin and heterochromatin
EX: Barr body
Interphase Chromosomes
However, during interphase chromosomal regions are mostly?
Euchromatic
Metaphase Chromosomes
What happens to the level of compaction?
It changes dramatically
Metaphase Chromosomes
At the end of prophase, sister chromatids are entirely?
Heterochromatic
Metaphase Chromosomes
Therefore, if they are highly condensed, what is their level of transcription?
Highly condensed = little gene transcription
Metaphase Chromosomes
How are metaphase chromosomes are highly compacted?
Because radial loops are highly compacted and stay anchored to a scaffold
Scaffold is formed from nuclear matrix
Metaphase Chromosomes
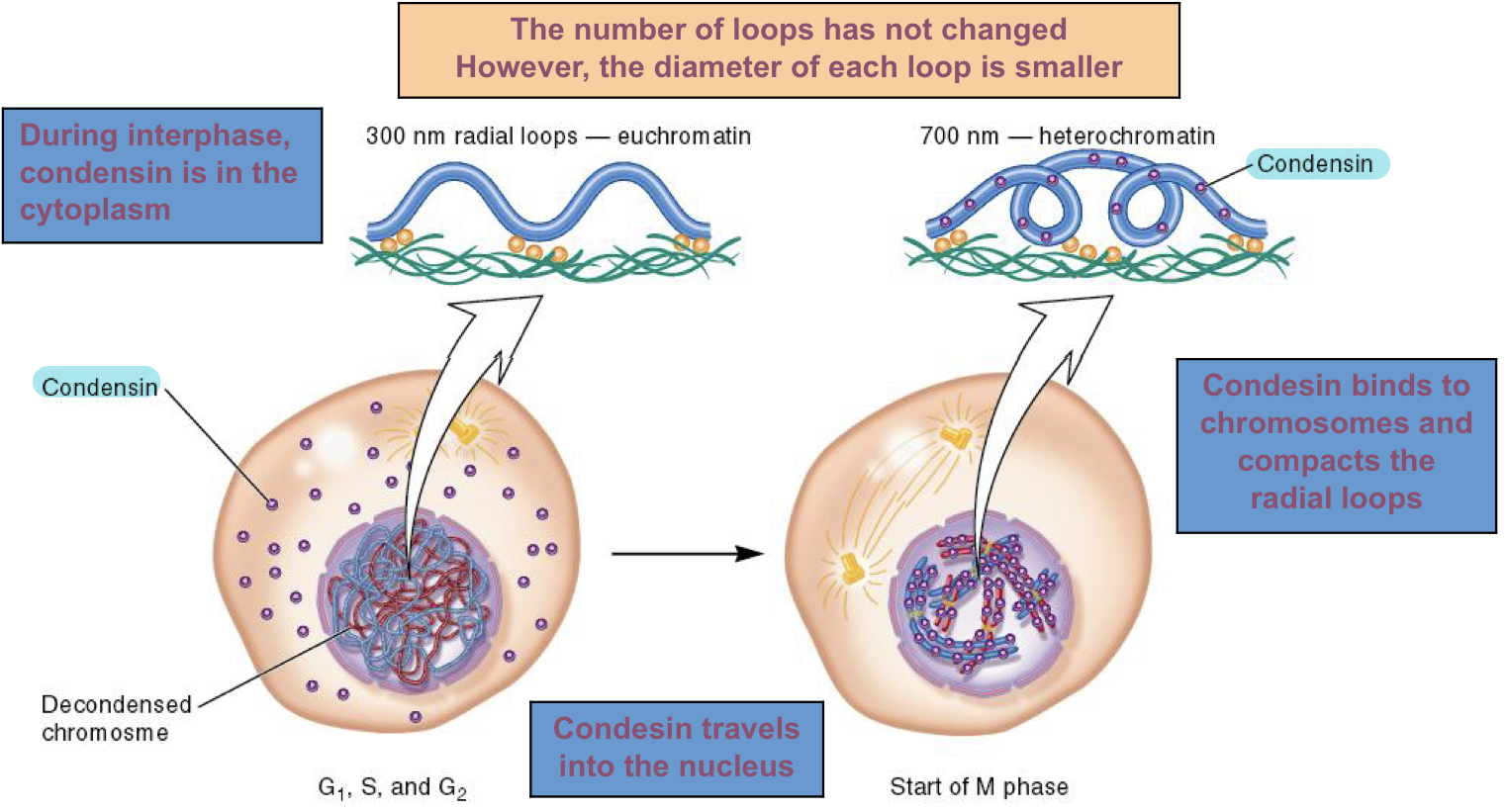
When chromosomes are compacted, do the number of loops change?
Number of loops don’t changed BUT diameter of each loop gets smaller

Metaphase Chromosomes
Mutltiprotein Complexes
What 2 multiprotein complexes help form and organise metaphase chromsomes?
What are their roles
Both contain what
What multiprotein complexes:
Condensin
Cohesion
Roles:
Condensin: In chromosome condensation
Cohesion: In sister chromatid alignment
Both contain: SMC proteins that uses ATP energy
Structural Maintenance of Chromosome
Metaphase Chromosomes
How does condensin work?
During interphrase, condensin is in the cytoplasm
After G2 phase, it travels into nucleus
Where it binds to chromosomes and compacts the radial loops
Metaphase Chromosomes
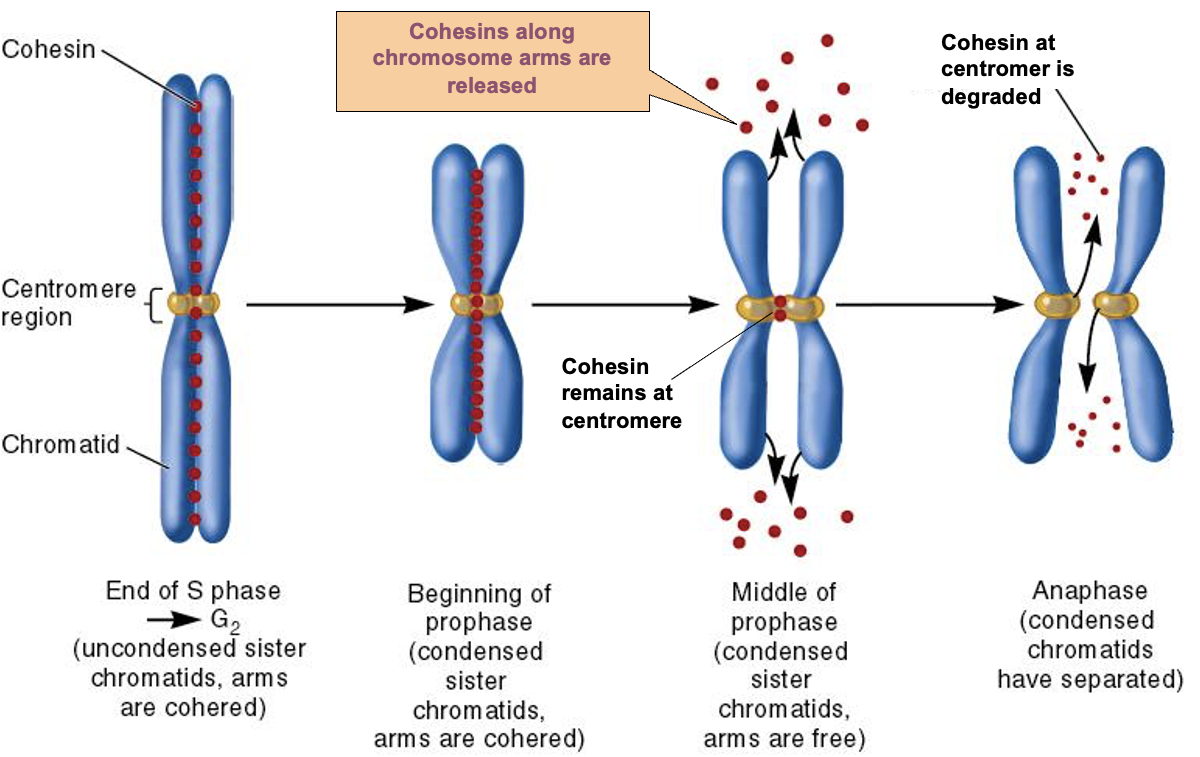
How does cohesions work?
Beginning of prophase: Cohesions are along the chromosome arms
Middle of prophase: Cohesions are only at centromere
This means the chromosome arms are free
Anaphase: Cohesion at centromere is degraded
This means that condensed chromatid have separated