Cardio/Renal 13 - Rheumatic Fever, Bacterial Endocarditis, Premedical Prophylaxis (Dr. Shaikhi)
1/115
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
116 Terms
what strep species are a part of our normal flora?
α-hemolytic Streptococcus
Streptococcus Viridans

what is the invading bacteria species that Causes Strep. Throat/pharyngitis?
Streptococcus pyogenes/ Group A β-hemolytic streptococcus

Incubation period of group A strep pharyngitis is approximately :
2 to 5 days

Pt presents with sudden onset of sore throat, fever, myalgia dysphagia (difficulty swallowing), odynophagia (painful swallowing), swollen and painful anterior cervical lymph nodes and tonsillar exudate
Streptococcal Pharyngitis (Strep Throat)

t/f: coughing is a symptom of a Streptococcal pharyngeal/throat infection
false, more common with viral pharyngitis

couching, watery eyes and runny noes is associated with:
viral pharyngitis (!!!!!!)

b-hemolytic strep. Infection can also cause:
scarlet fever (with typical scalatiniform rash)

Diagnosis of streptococcal pharyngitis is confirmed with a:
Rapid Antigen Detection Test (RADT)

the GOLD STANDARD for diagnosing streptococcal pharyngitis is ____________
throat culture test

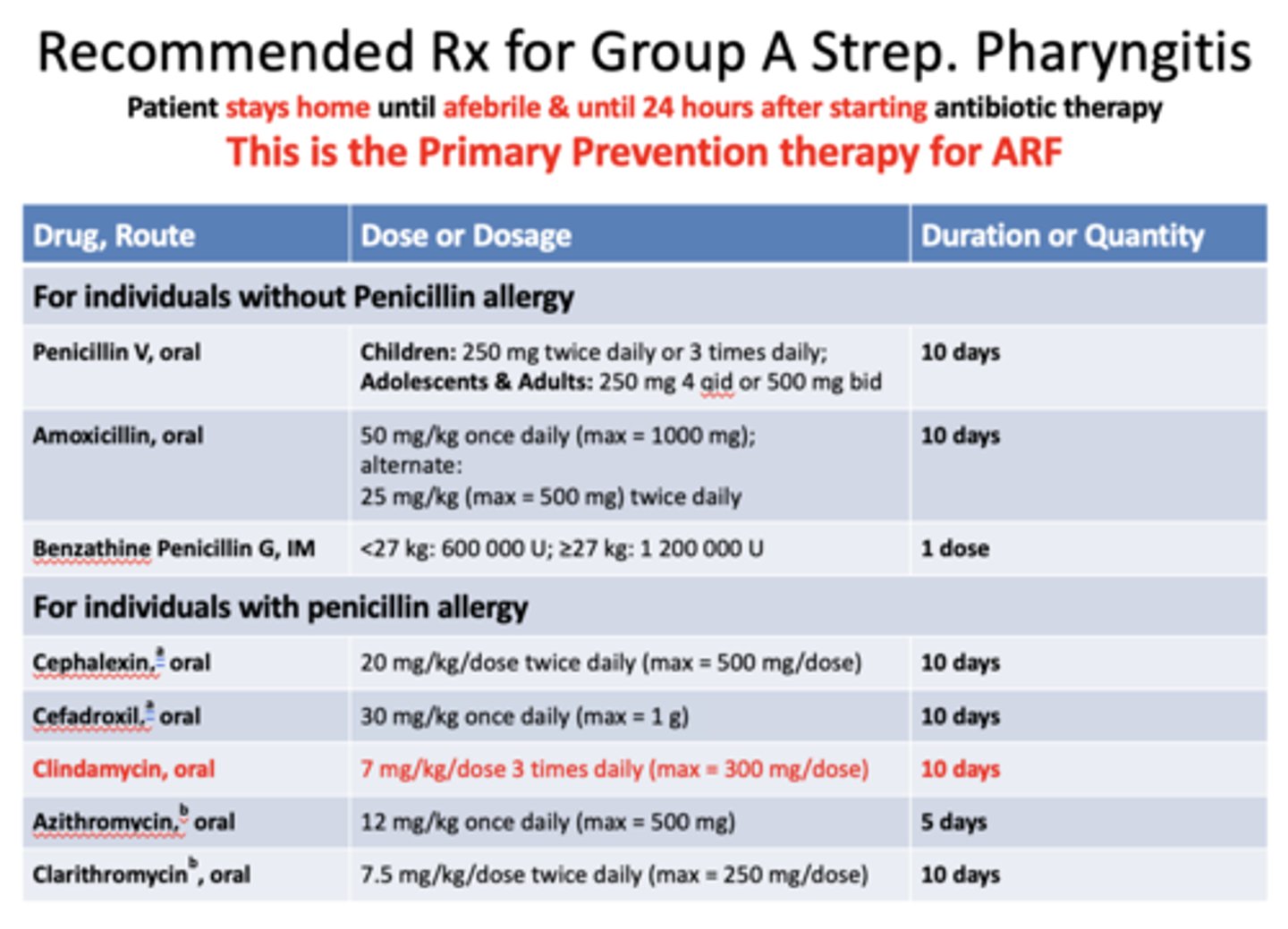
What is the recommended Rx for Group A Strep. Pharyngitis?
patient stays home until afebrile & until 24hrs after starting antibiotic therapy
(This is the Primary Prevention therapy for ARF)
Peritonsillar abscess, retropharyngeal abscess, cervical lymphadenitis and mastoiditis are all __________ complications of group A strep infections
suppurative

Acute rheumatic fever/ARF and Post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis are __________ complications of group A strep infections
non-suppurative

Complications of group A strep pharyngitis occur ______ original infection resolves
after

_________ is a non-suppurative acute inflammatory response to a PAST untreated or partially treated Group A, b hemolytic streptococcal infection
Acute Rheumatic Fever (ARF)
Acute Rheumatic Fever occurs ______ after an untreated / partially treated b-hemolytic streptococcalinfection
3-4 weeks

Strep. infections are more common in what patient populations?
low income, high density populations
age most affected by Acute Rheumatic Fever (ARF):
5-15 years
Acute Rheumatic Fever (ARF) is uncommon for ages ____ and below
3 years
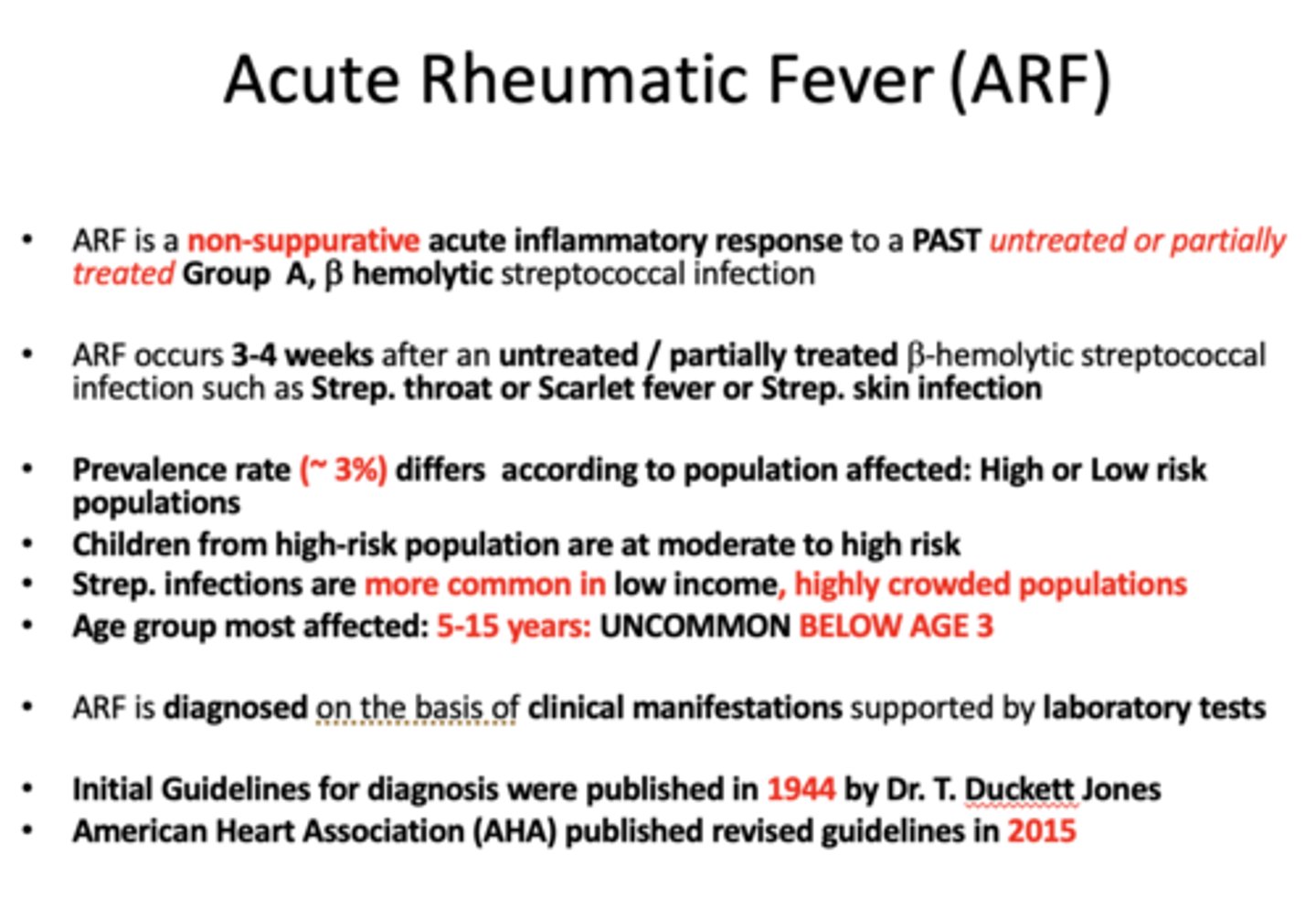
ARF is an antigen-antibody reaction that affects
peri-arteriolar connective tissue
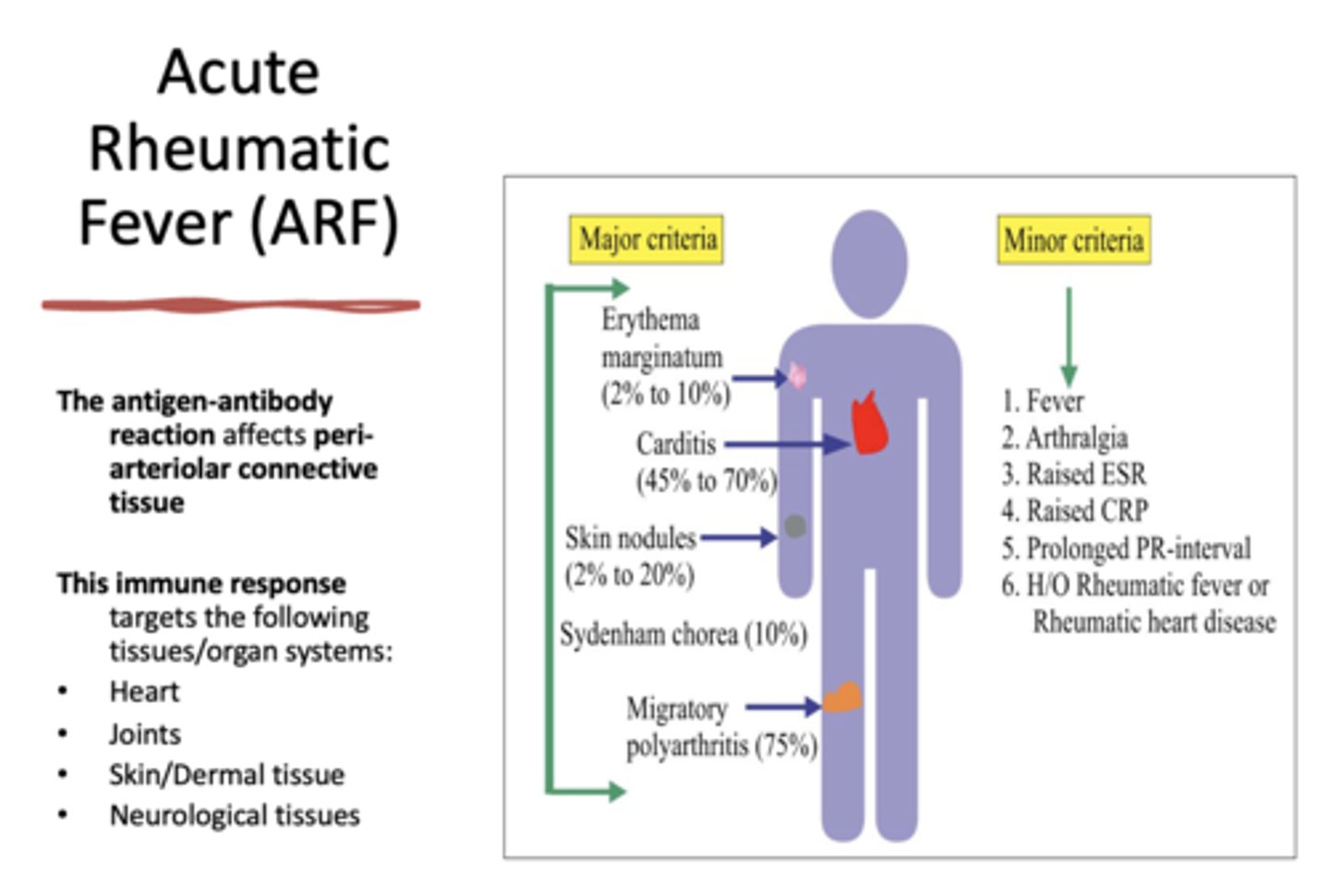
Fever is considered _______ criteria for diagnosing Acute Rheumatic Fever (ARF)
minor

Pain in the Right Upper Abdominal Quadrant (RUQ) is considered _______ criteria for diagnosing Acute Rheumatic Fever (ARF)
minor

Elevated Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR) is considered _______ criteria for diagnosing Acute Rheumatic Fever (ARF)
minor

Increased C-reactive protein (CRP) is considered _______ criteria for diagnosing Acute Rheumatic Fever (ARF)
minor

Antibody titer Tests is considered _______ criteria for diagnosing Acute Rheumatic Fever (ARF)
minor

EKG & Doppler echocardiography as tools to diagnose cardiac involvement is considered _______ criteria for diagnosing Acute Rheumatic Fever (ARF)
minor

Erythema marginatum is considered _______ criteria for diagnosing Acute Rheumatic Fever (ARF)
major
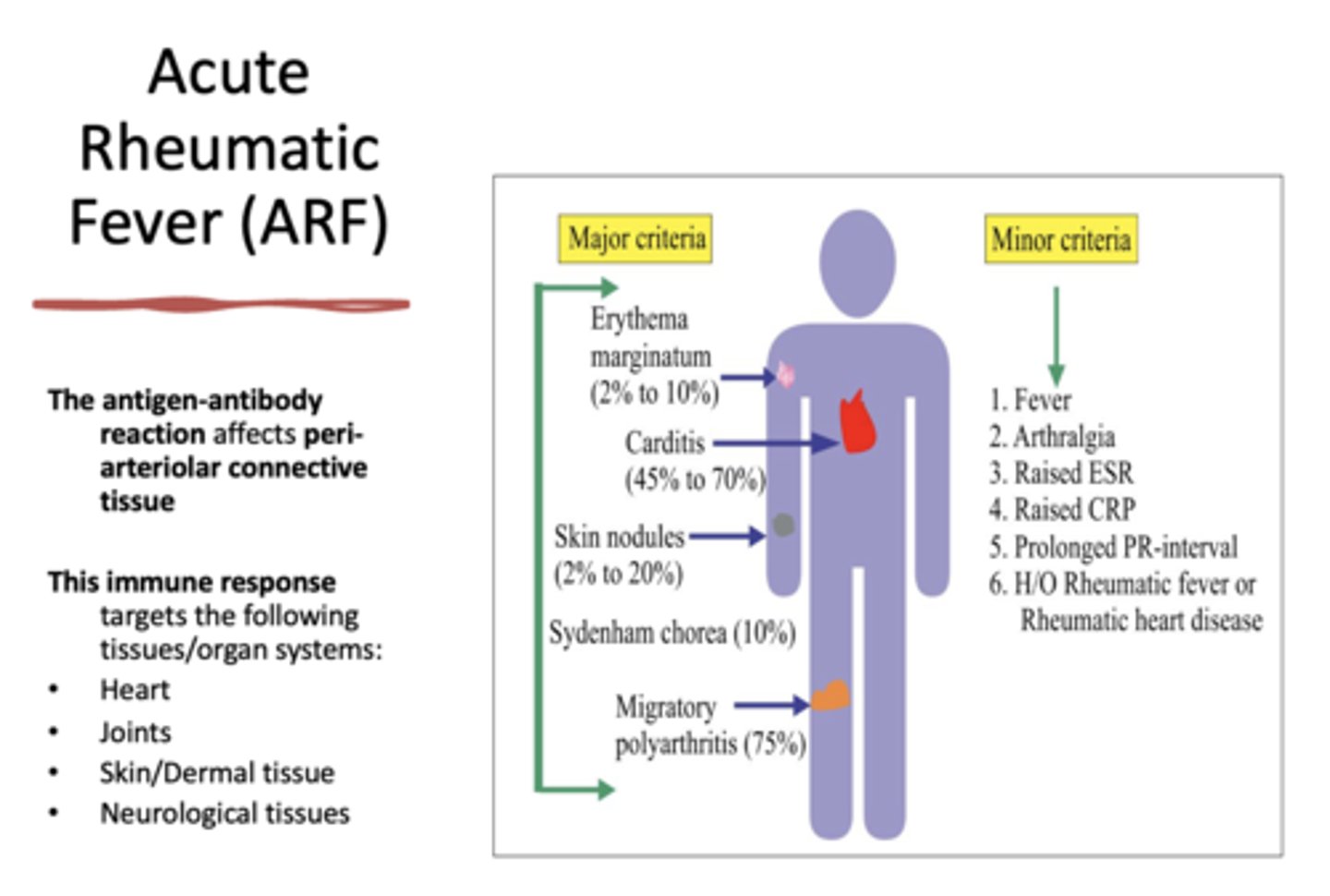
Carditis is considered _______ criteria for diagnosing Acute Rheumatic Fever (ARF)
major
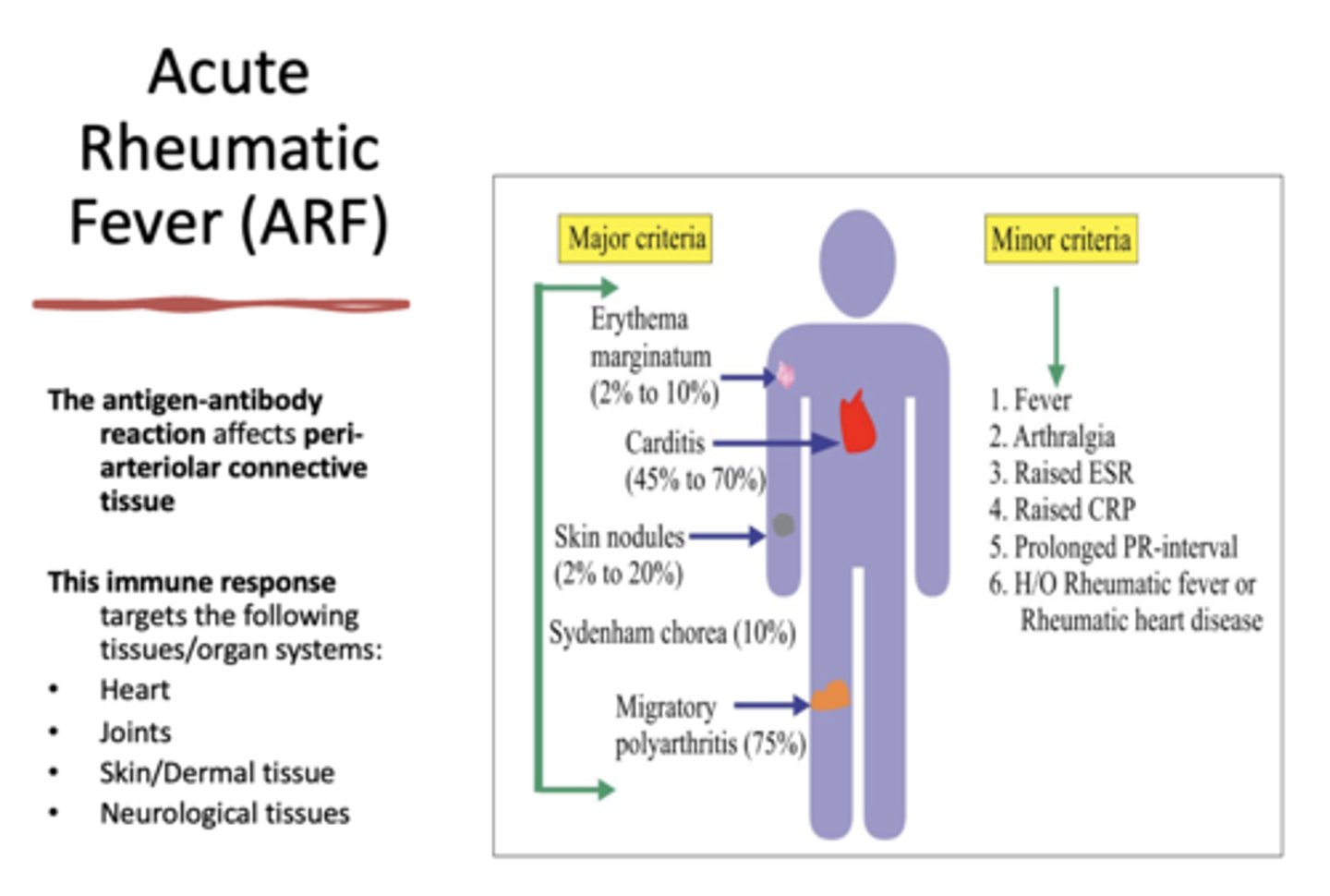
Skin nodules is considered _______ criteria for diagnosing Acute Rheumatic Fever (ARF)
major
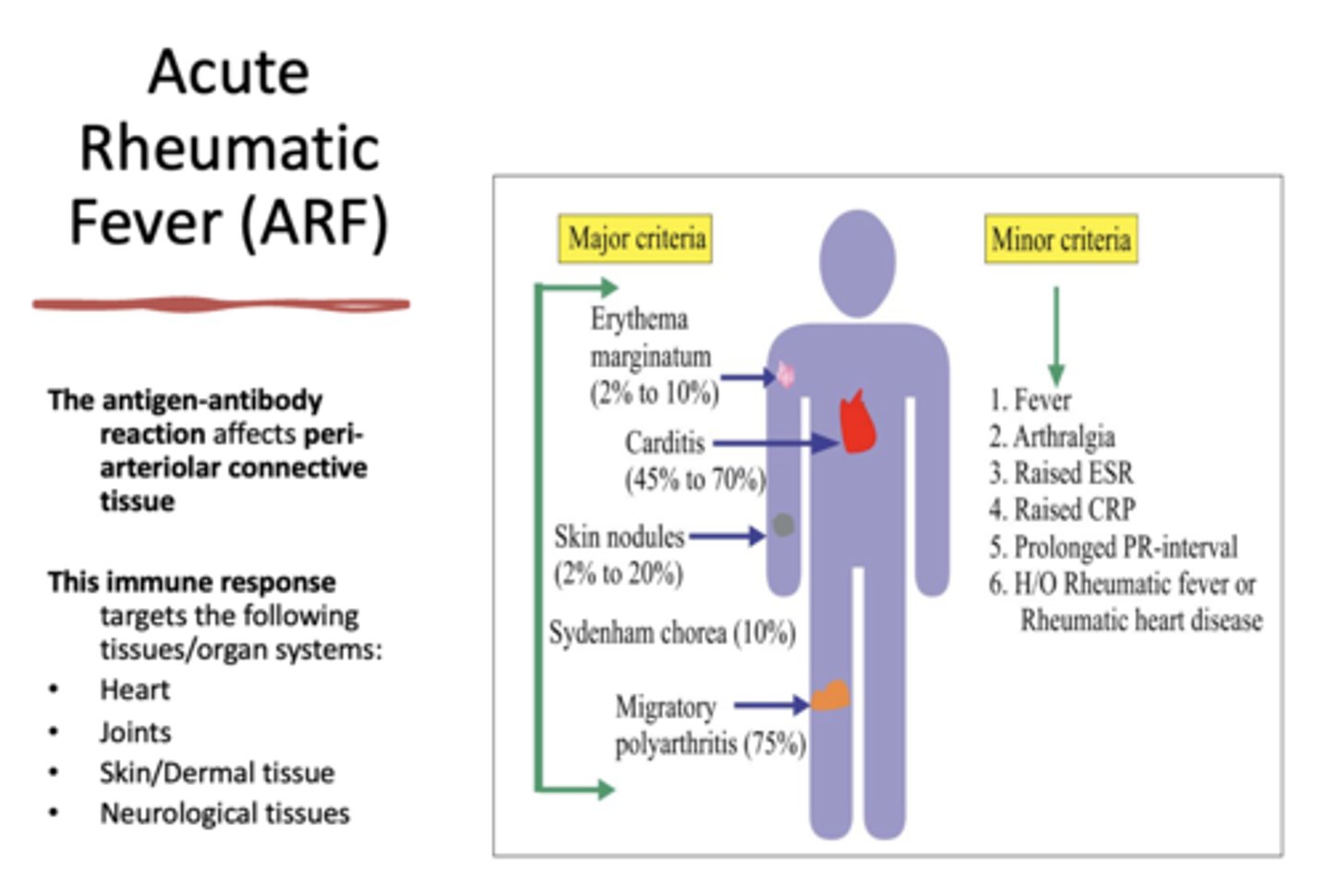
Sydenham chorea is considered _______ criteria for diagnosing Acute Rheumatic Fever (ARF)
major
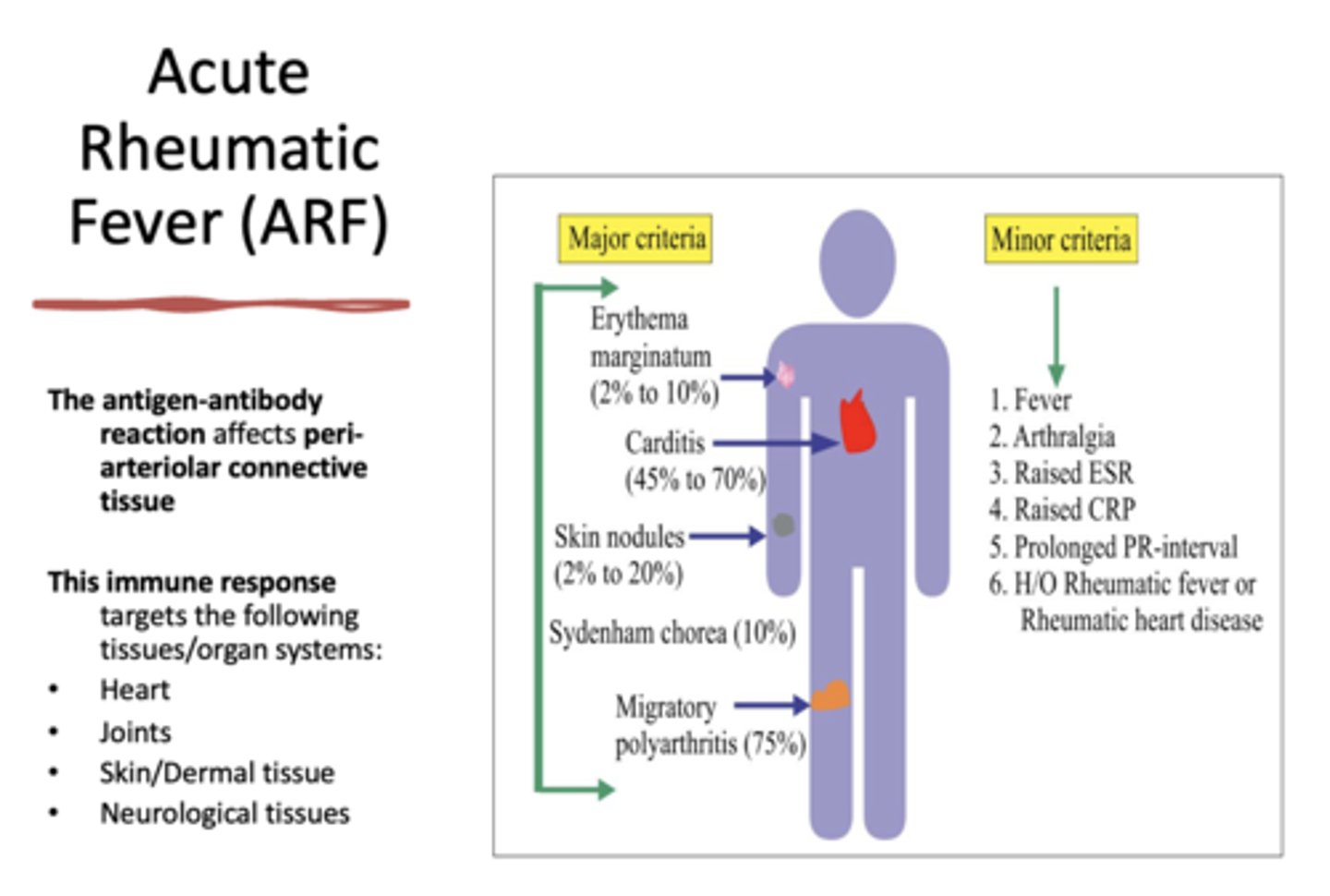
Migratory polyarthritis is considered _______ criteria for diagnosing Acute Rheumatic Fever (ARF)
major
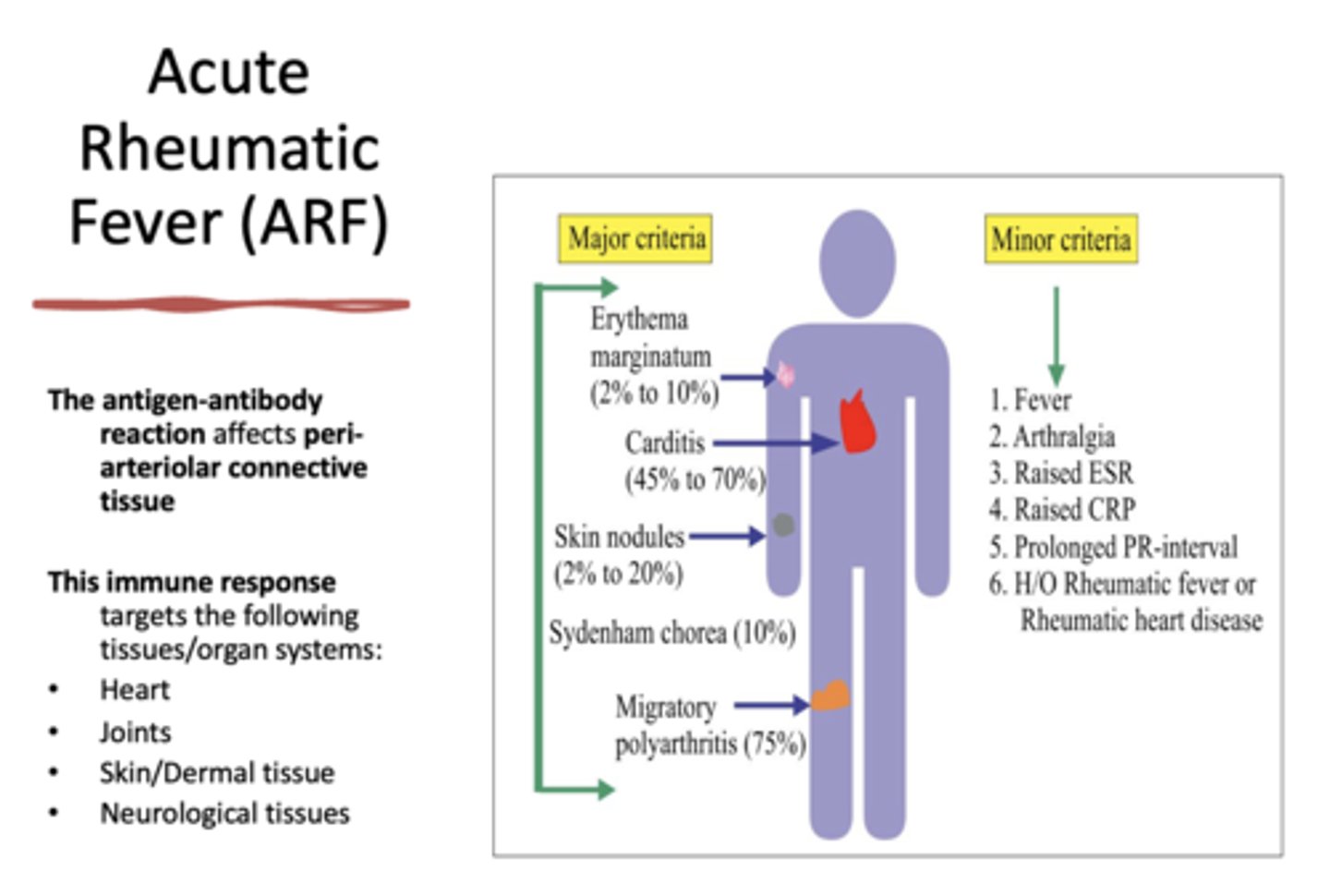
Acute Rheumatic Fever (ARF) Diagnostic Criteria
The patient must have..
2 major criteria or 1 major & 2 minor

Rheumatic arthritis is seen most commonly in _______
children (rare in adults)

What presents with the following characteristics:
•Major joints are affected bilaterally
•Joints are swollen, painful & filled with aseptic fluid: An aseptic arthritis
•Resolution of joint swelling occurs in a few weeks
•Following recovery, NO residual joint deformity persists
Rheumatic arthritis

If other causes, like rheumatic arthritis are excluded, what could qualify?
Polyarthralgia

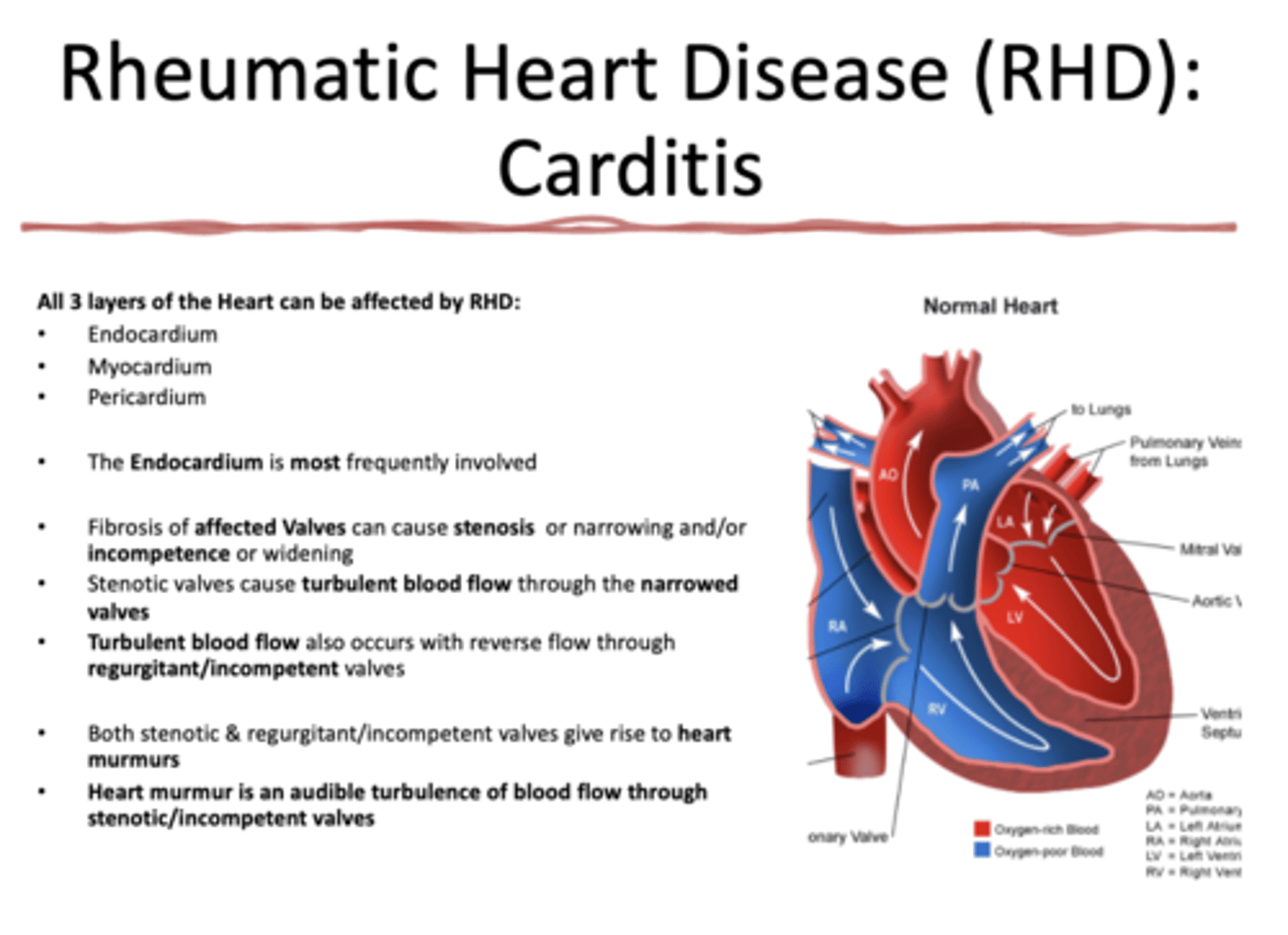
What layers of the heart can be affected by Rheumatic Heart Disease?
all 3 layers (endocardium, myocardium, pericardium)
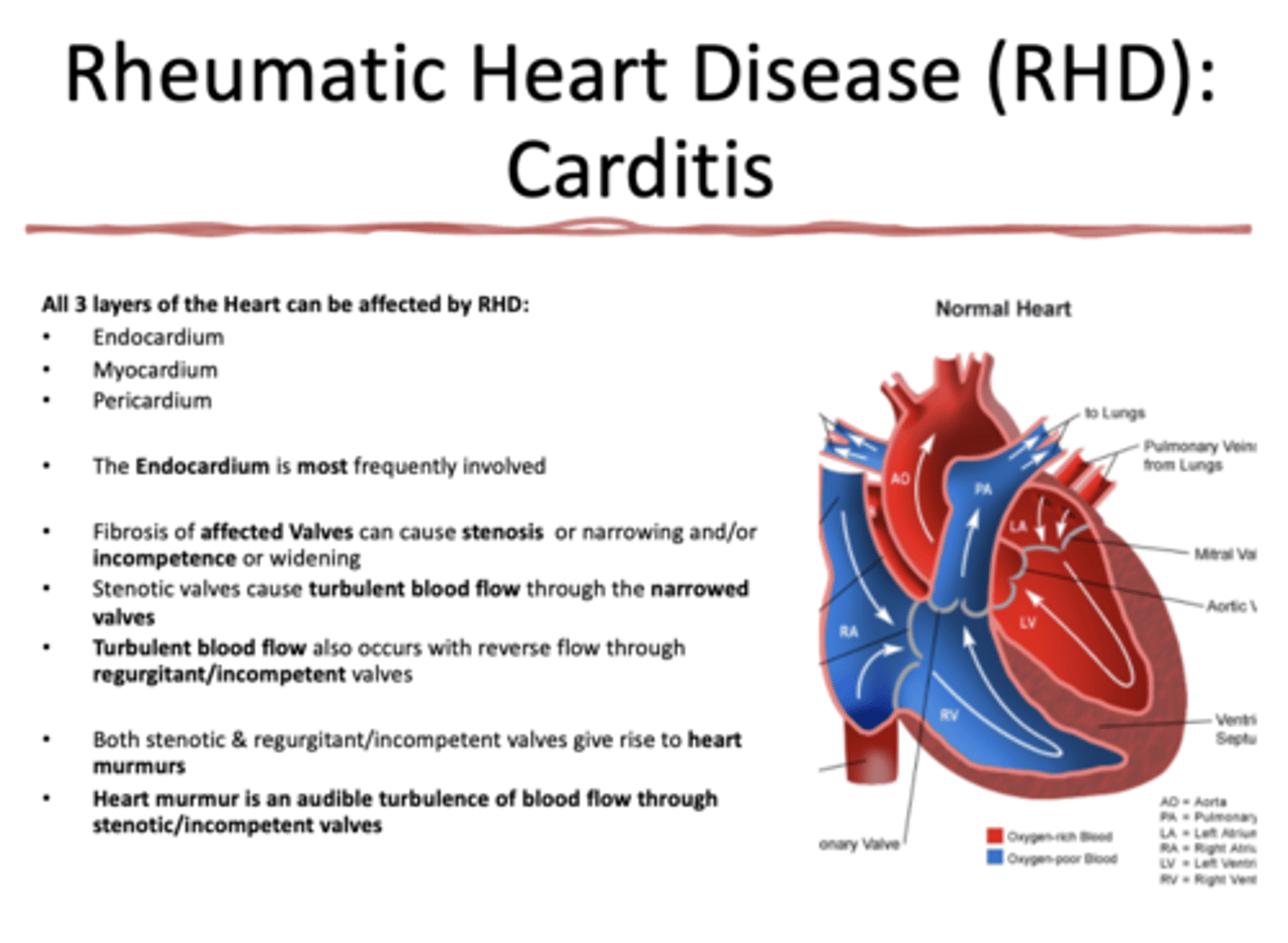
what layer of the heart is MOST affected by Rheumatic heart disease?
endocardium
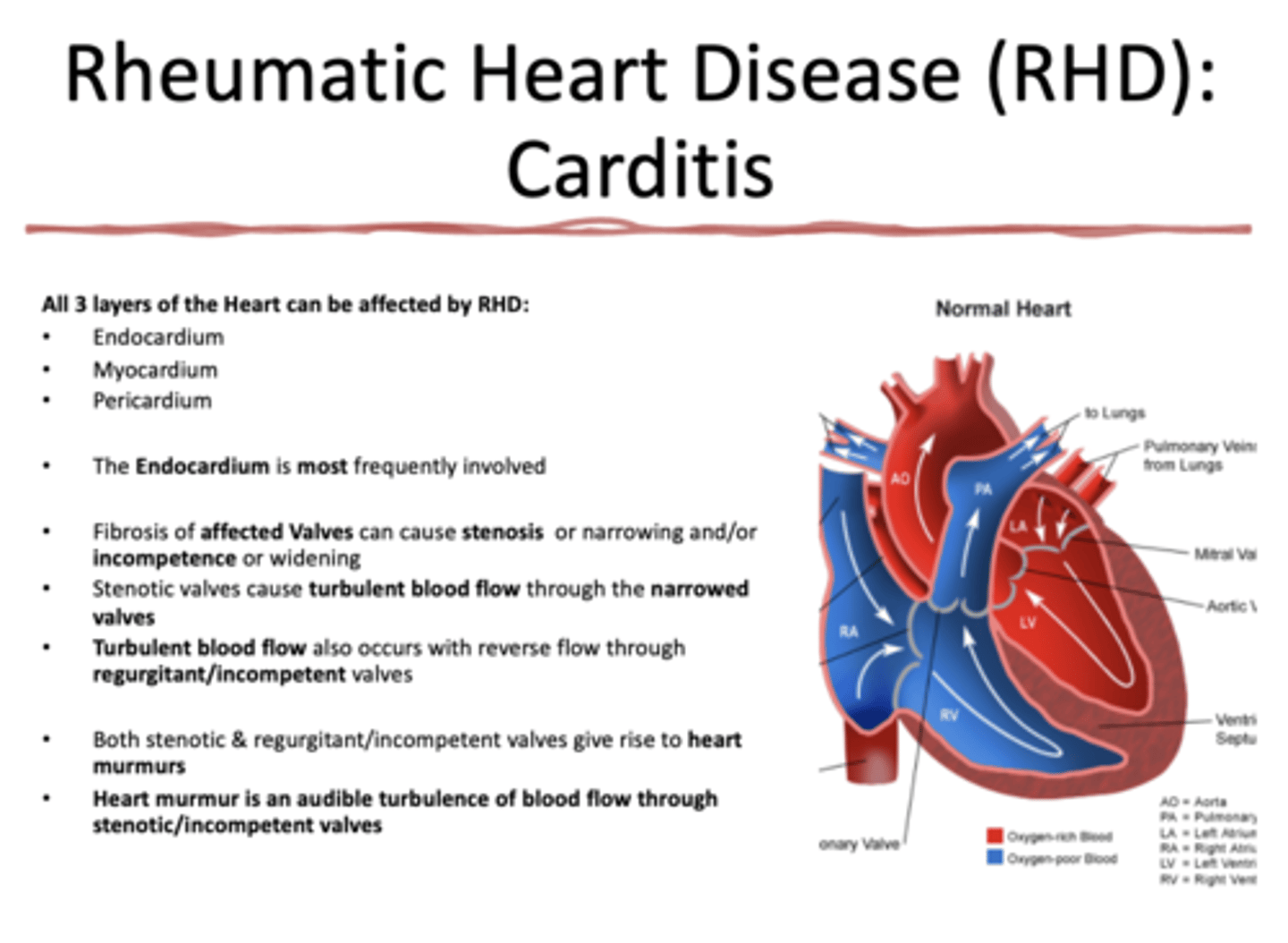
What presents with the following characteristics:
•Fibrosis of affected Valves can cause stenosis or narrowing and/or incompetence or widening
•Stenotic valves cause turbulent blood flow through the narrowed valves
rheumatic heart disease (RHD)
Both stenotic & regurgitant/incompetent valves give rise to ___________
heart murmurs
___________ is an audible turbulence of blood flow through stenotic/incompetent valves
heart murmur
Turbulent blood flow also occurs with reverse flow through
regurgitant/incompetent valves
in children with Rheumatic heart disease, which valve is most commonly affected?
mitral valve (mitral stenosis/incompetence)
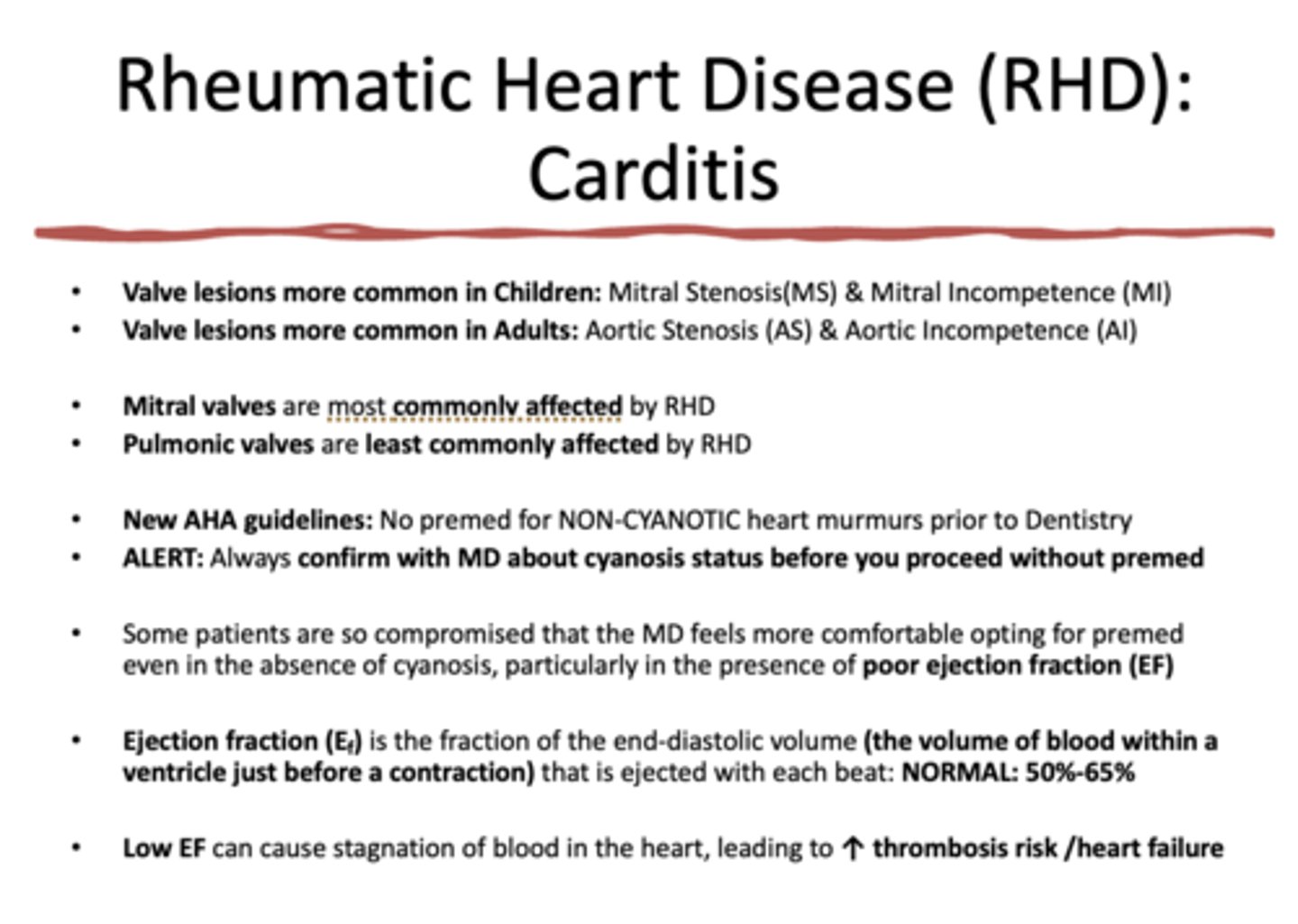
in adults with Rheumatic heart disease, which valve is most commonly affected?
aortic valve (aortic stenosis/incompetence)
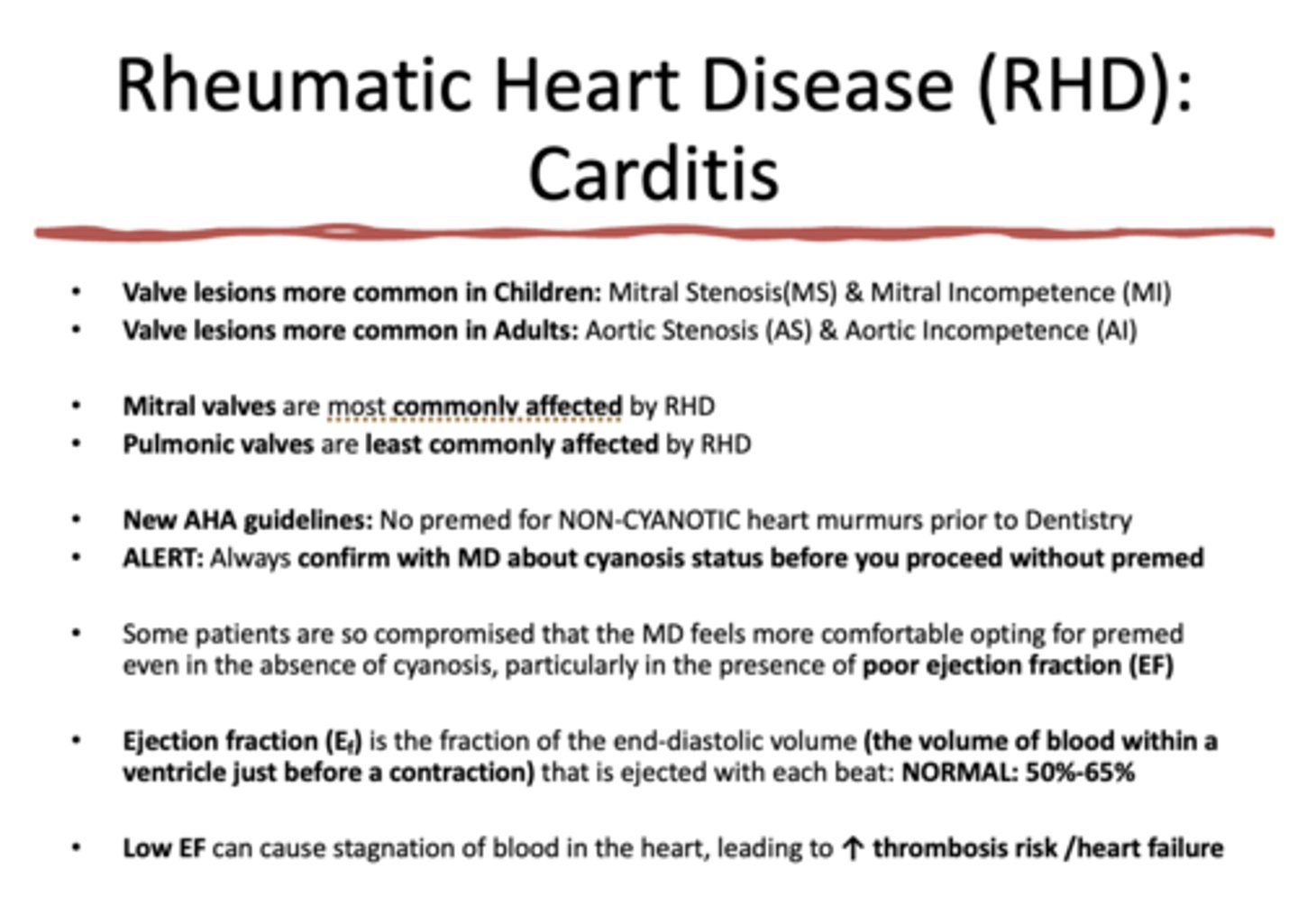
which valve is most commonly affected by RHD
mitral valve
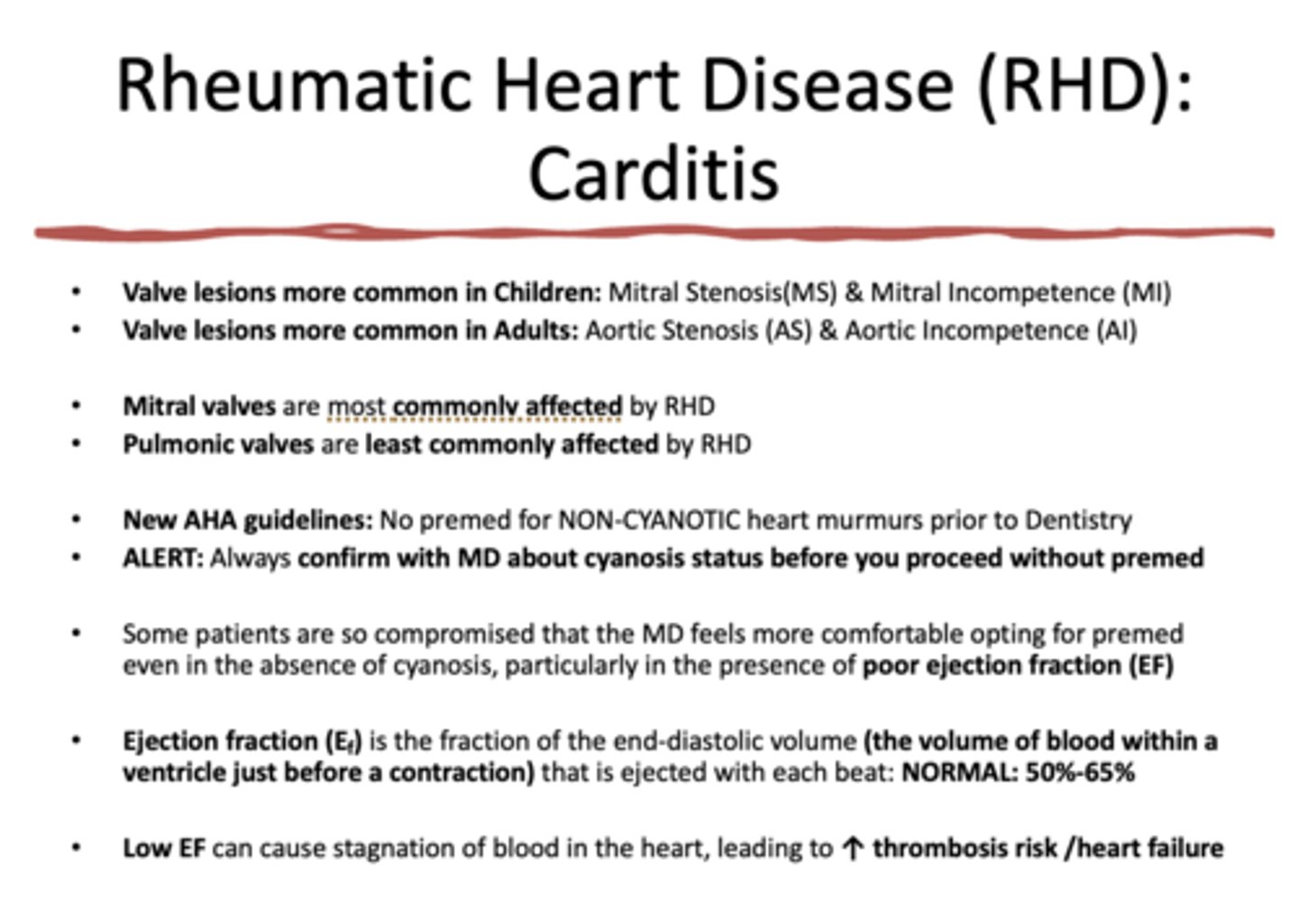
the __________ is LEAST commonly affected by RHD
pulmonic valve
No premed for _________heart murmurs prior to Dentistry
Non-cyanotic
________ is the fraction of the end-diastolic volume (the volume of blood within a ventricle just before a contraction) that is ejected with each beat: NORMAL: 50%-65%
ejection fraction
Low/high Ejection fraction (EF) can cause stagnation of blood in the heart, leading to increase thrombosis risk and heart failure
Low
Ejection fraction (Ef) is the fraction of the end-diastolic volume (the volume of blood within a ventricle just before a contraction) that is ejected with each beat. What is the normal ejection fraction percentage?
50-65%
Low EF can cause stagnation of blood in the heart, leading to ___________ thrombosis risk /heart failure
Increased
In RHD, involvement of the myocardium is ___________
rare
in RHD, Pericardial involvement is common in ___________
children
Does Cardiomyopathy/enlarged heart require Premedication?
no
does ARF with/without Rheumatic Heart Disease require premedication?
no
What presents with the following characteristics:
•Exclusively a childhood disorder of the central nervous system/CNS
•Characterized by rapid, irregular, involuntary movements of arms, legs, trunk & facial
•Movements are absent during sleep
•Females are affected more than Males
•Emotional distress worsens the movements
Sydenham's Chorea/St. Vitus' dance

Which of the following statements regarding Sydenham's Chorea/St. Vitus' dance is false?
A. Chorea can occasionally strike up to 6 months after the fever or infection has cleared
B. typically resolves in 2-3 months with no long-term adverse effects
C. stress management during dentistry is extremely helpful
D. It is exclusively found in adults
D. It is exclusively found in adults

Rx for Sydenham's Chorea/St. Vitus' dance:
- Bed rest
- Barbiturates
- Benzodiazepines
- Valproic acid

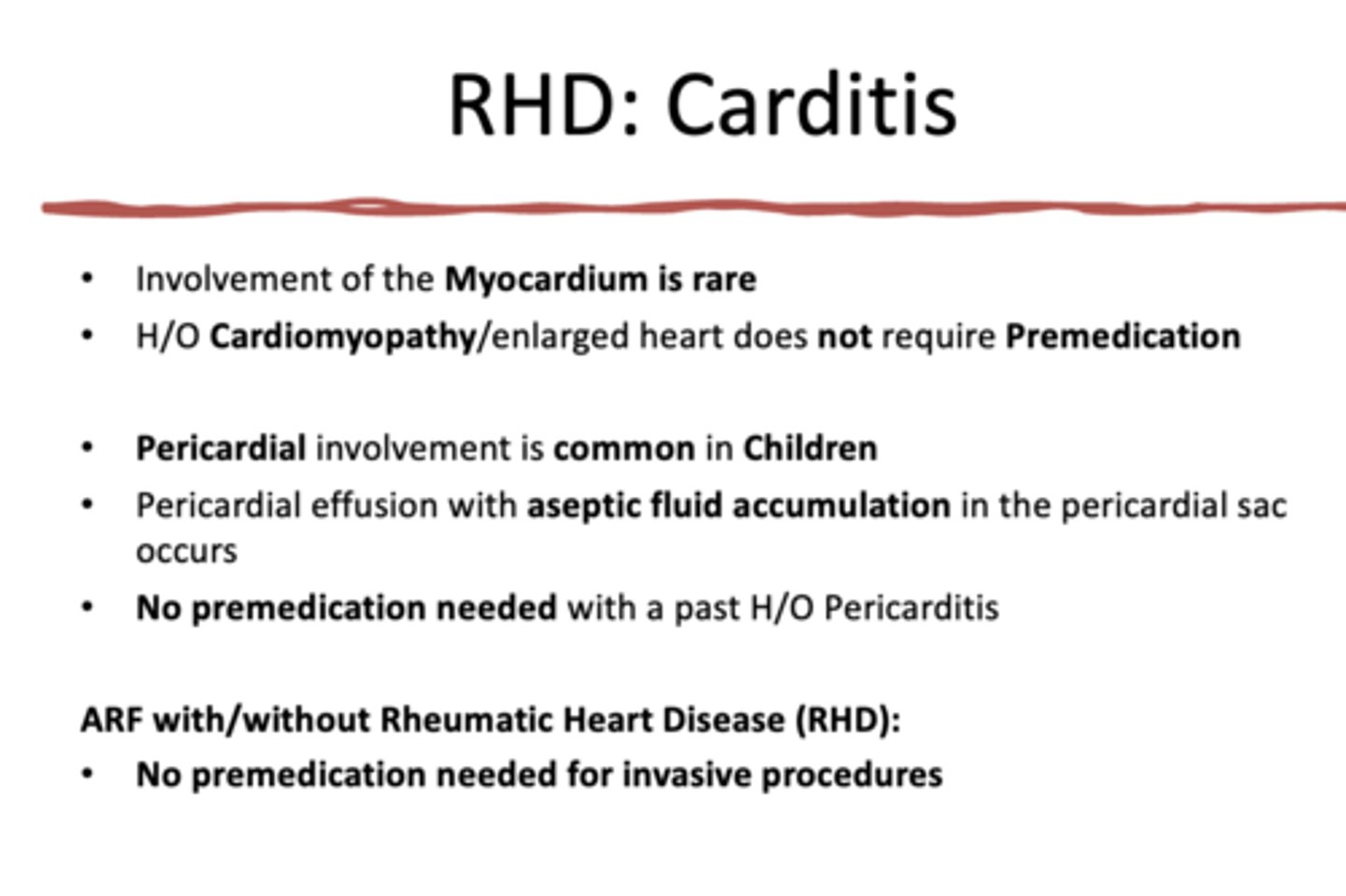
_____________ is a rash that is a RARE finding with the following characteristics:
- Lighter skin pts only show rash
- Presence of rash diagnostic of RF
- Doughnut shaped serpiginous spreading rash
each rash lesion has a pale center and dark margins
- Rash begins on lower trunk and migrates upwards
Erythema Marginatum
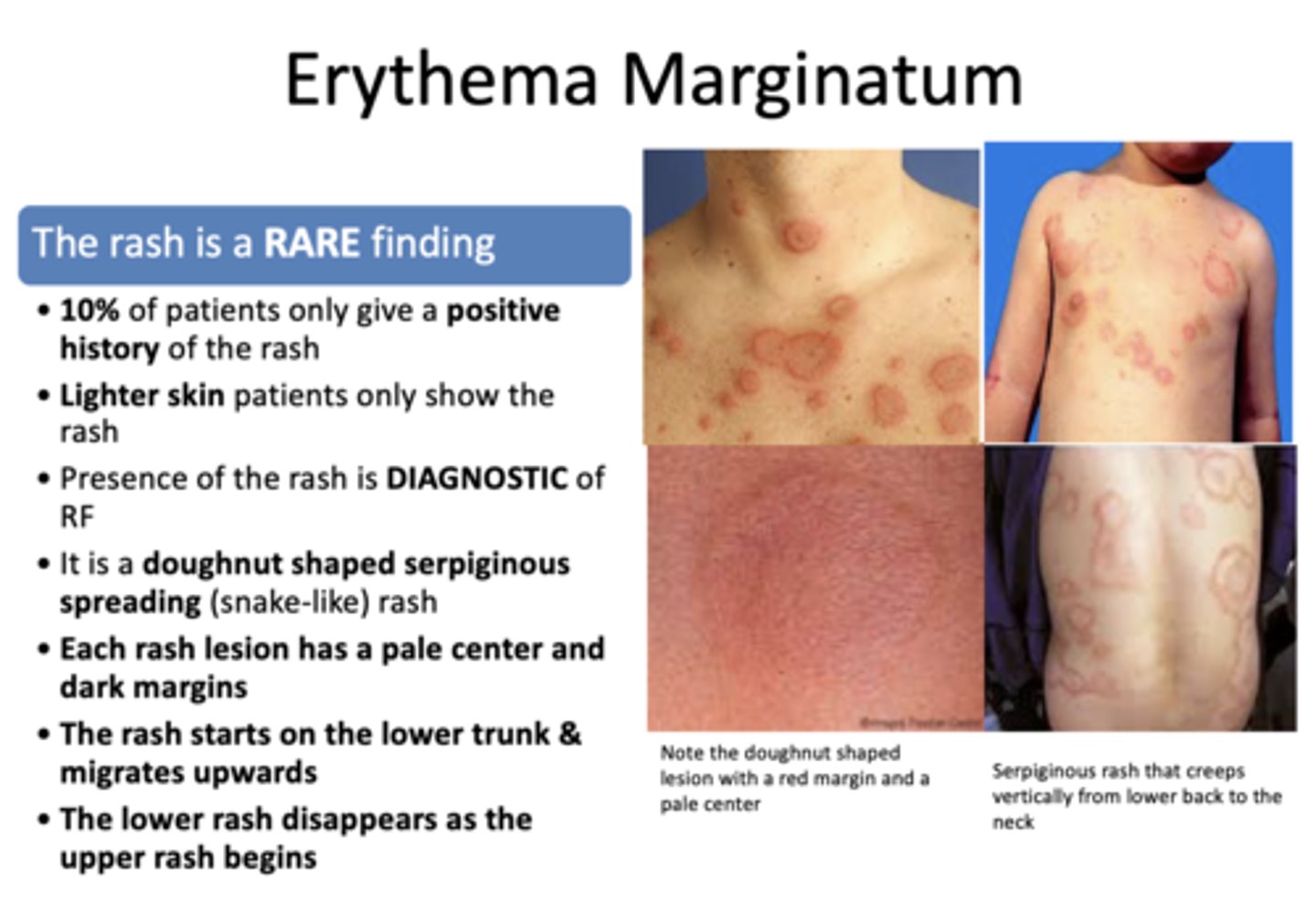
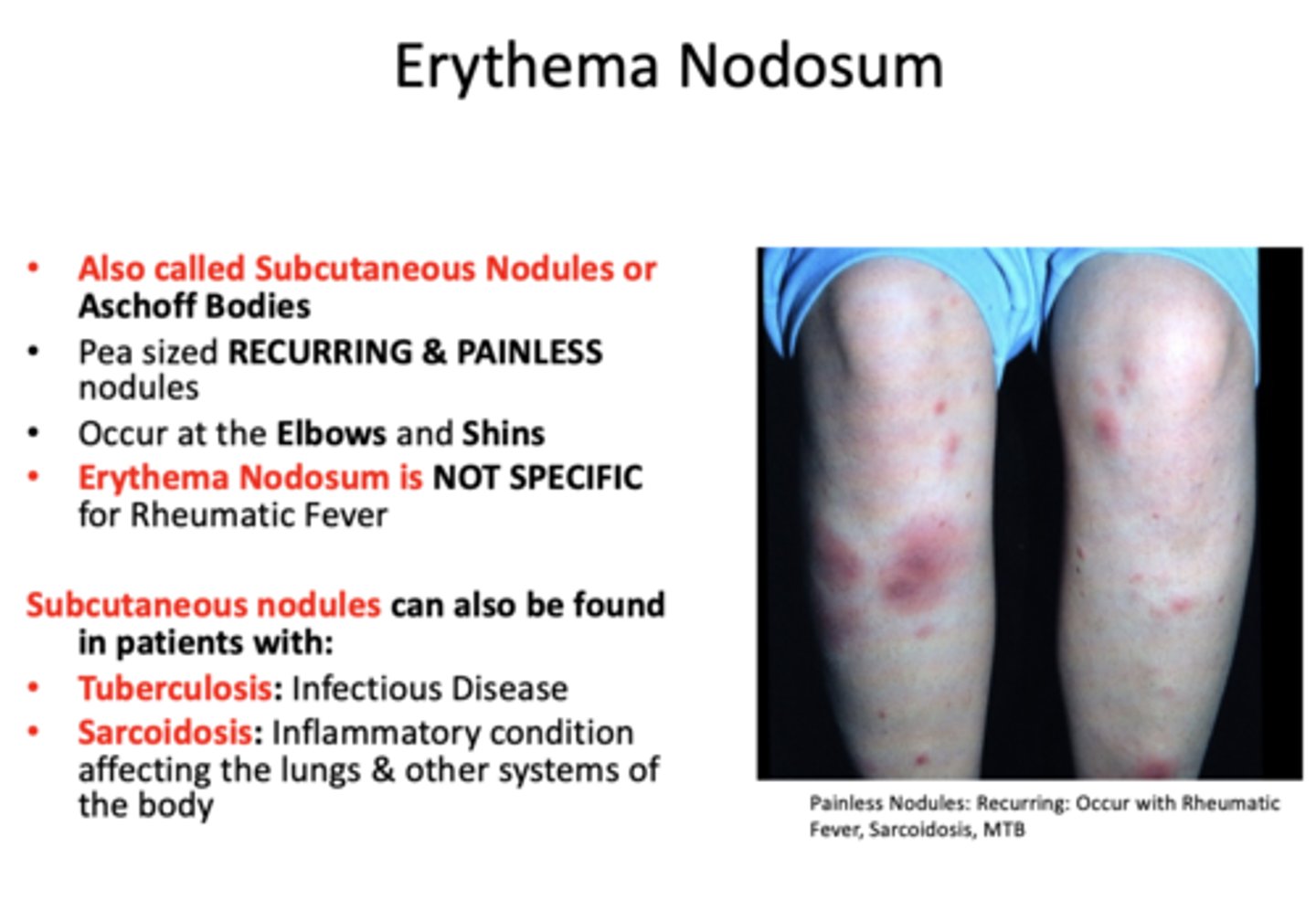
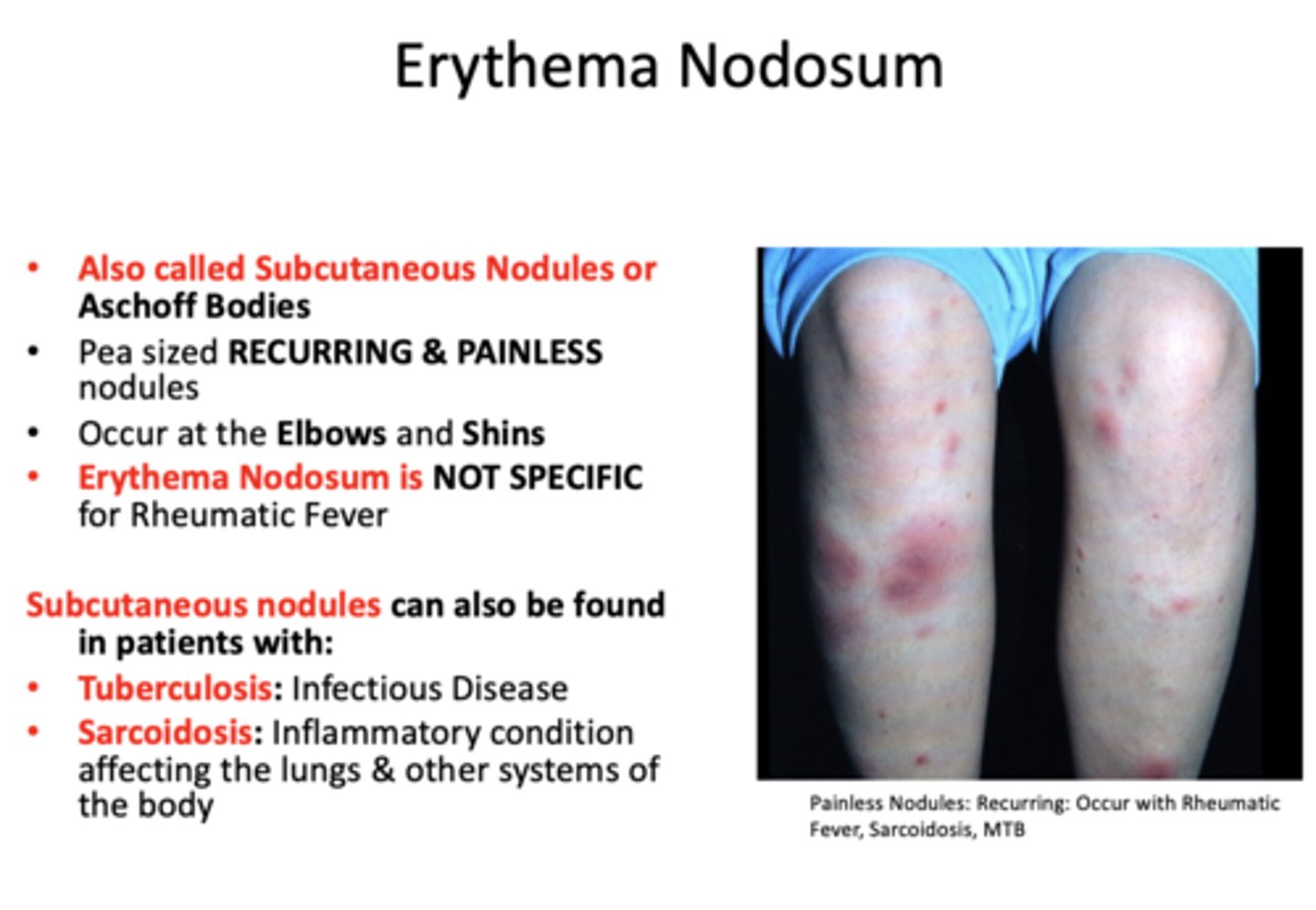
Subcutaneous nodules, Erythema Nodusum, can also be found in patients with: (3)
- Tuberculosis
- Sarcoidosis
- Rheumatic fever
What has the following characteristics:
- Pea sized RECURRING & PAINLESS nodules
- Occur at the Elbows and Shins
Erythema Nodosum
What are three strep antibody tests to detect group A beta-hemolytic strep infections?
• Anti-streptolysin O titer (ASO) Test
• Anti-deoxyribonuclease-B titer (anti-Dnase-B, or ADB) Test
• Streptozyme Test

Throat cultures are of no value about _____-_____ weeks after initial infection
2-3

_______ is an indicator of inflammation
Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR)
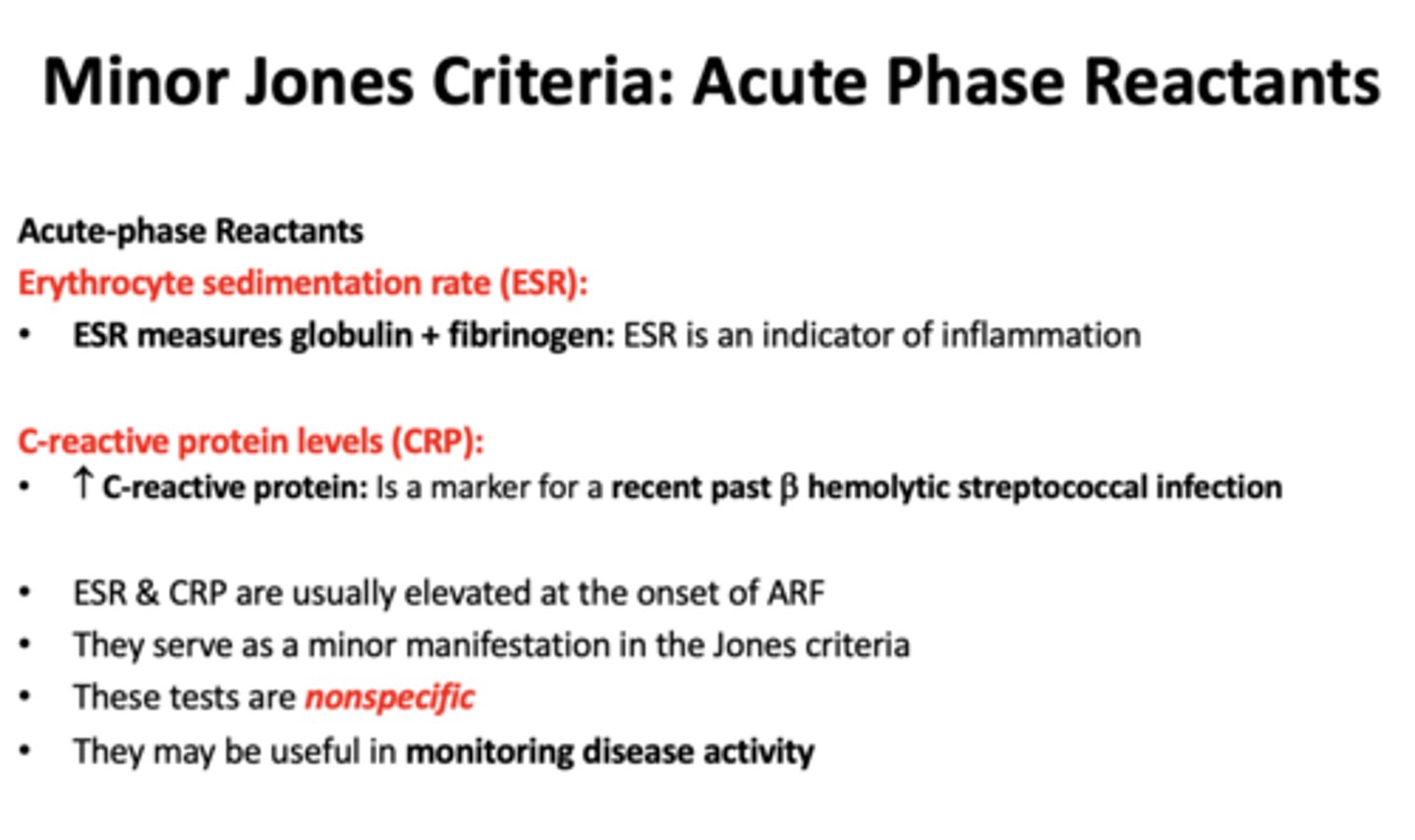
a marker for a recent past B-hemolytic streptococcal infection is...
increase in C-reactive protein
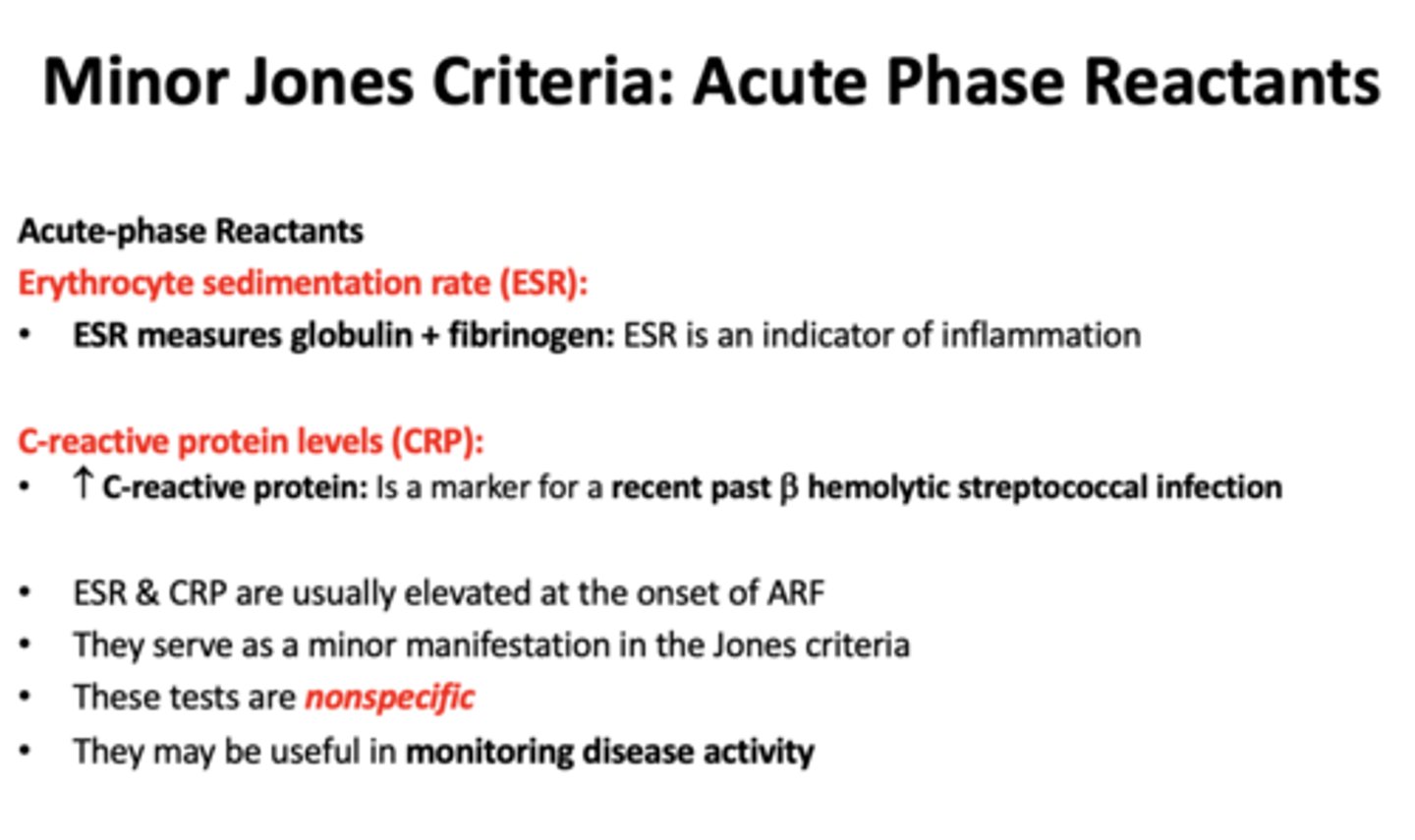
recurrent joint pains with no joint swelling or deformity
arthralgia
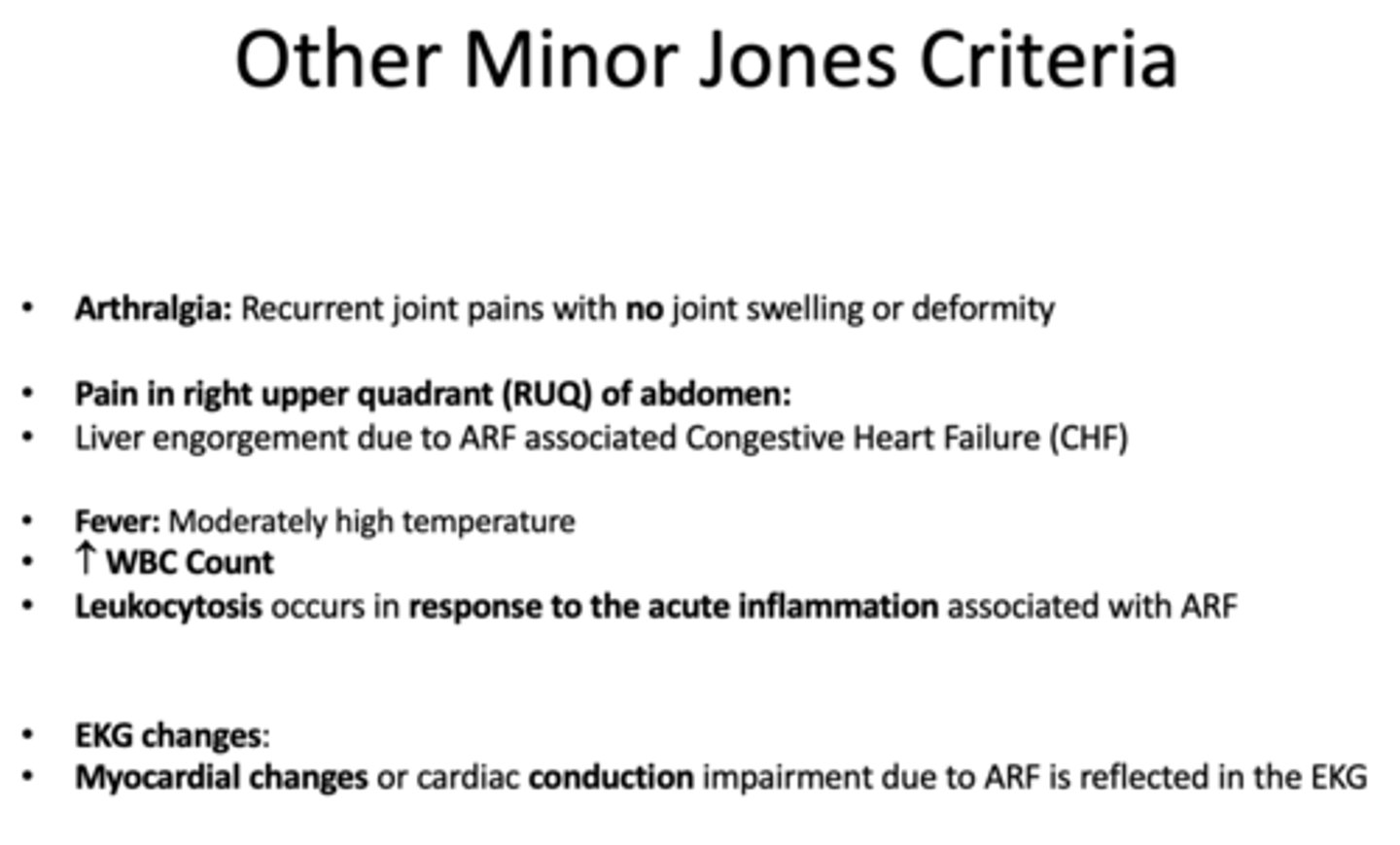
Liver engorgement due to ARF associated with ________
Congestive Heart Failure (CHF)
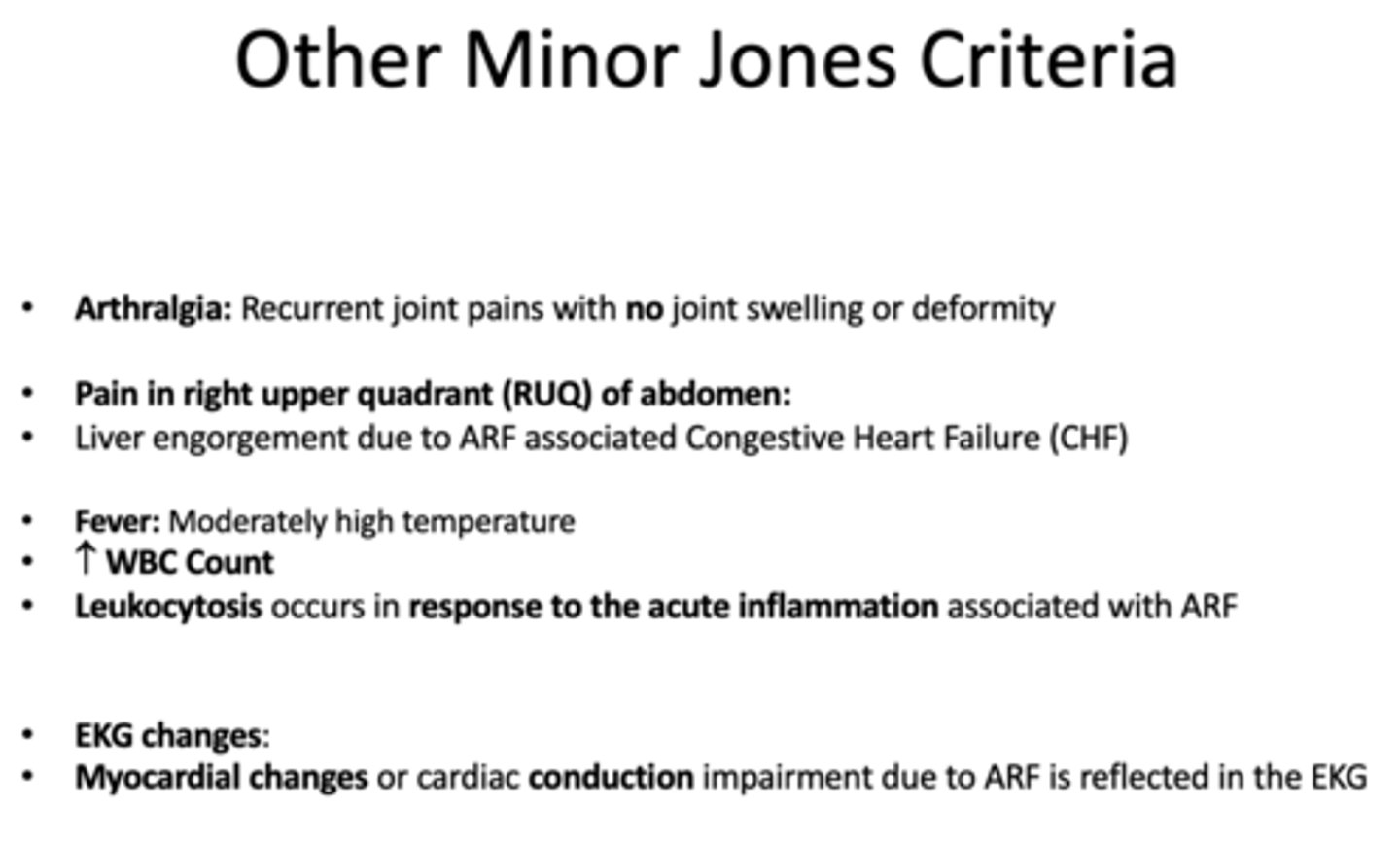
____________ occurs in response to the acute inflammation associated with ARF
Leukocytosis
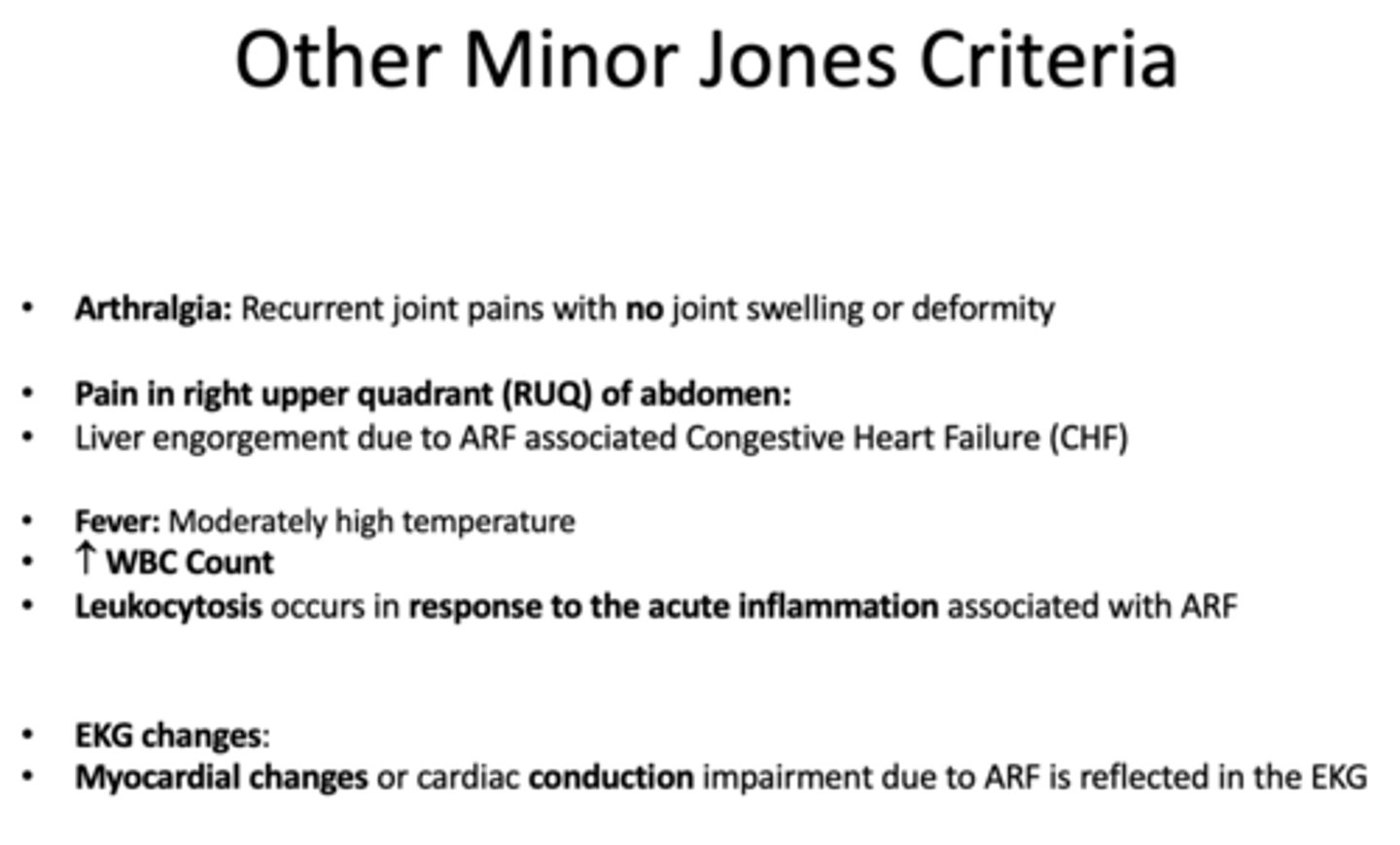
What are the phase treatments of rheumatic fever?
- Acute phase treatment
- Secondary prevention prophylaxis treatment
When providing premeditation for say, a Prosthetic valve during the phase of Preventive therapy:
Select a premedication antibiotic from ANOTHER FAMILY

Keep __ hours between the 2 antibiotics during acute rheumatic fever secondary prophylaxis therapy
6

Endothelial trauma can occur with what three things?
• Valvular Regurgitation
• Valvular Stenosis
• High pressure gradients due to Atrial Septal Defect (ASD)/Ventricular Septal Defect (VSD)
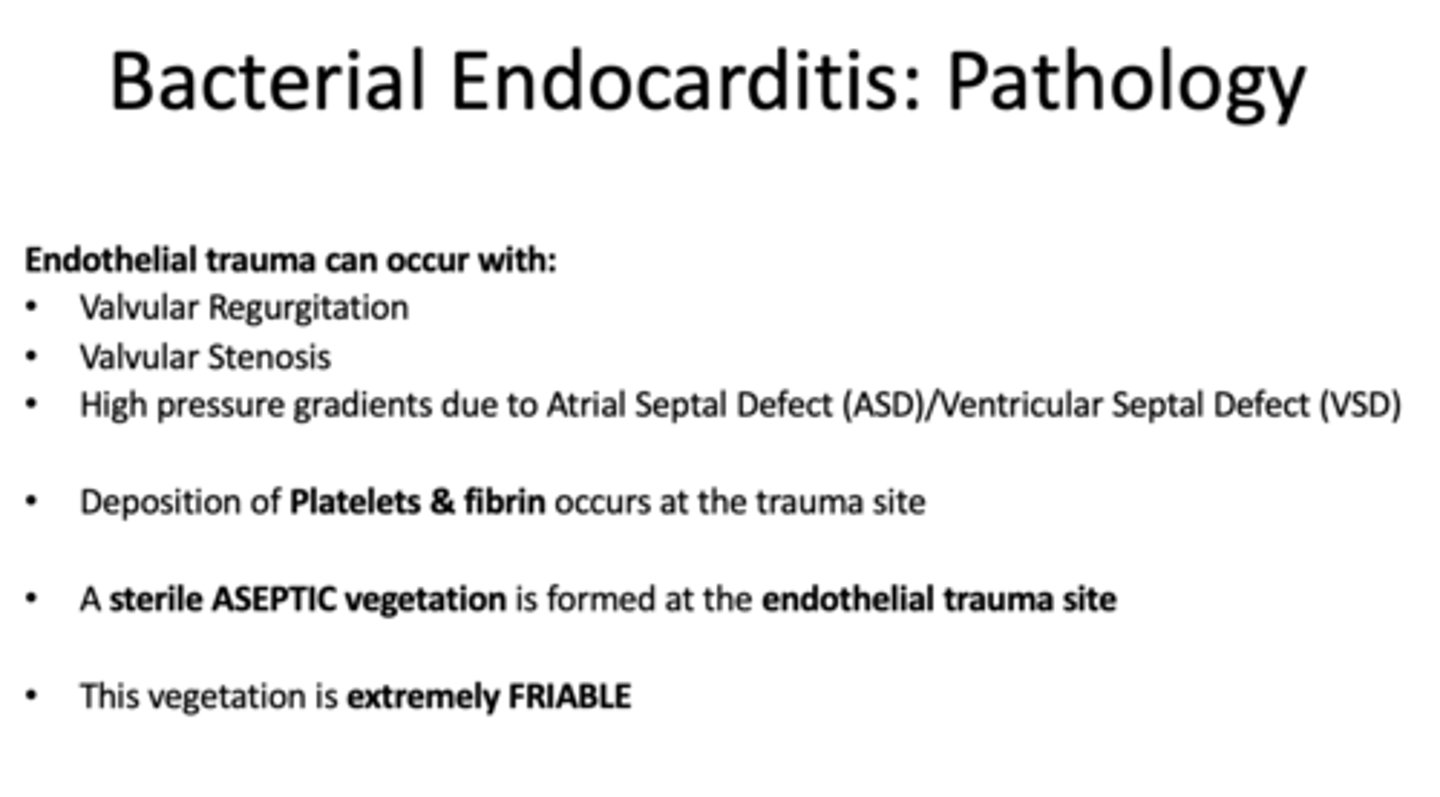
deposition of platelets and fibrin occurs at the trauma site in _______________
bacterial endocarditis
In bacterial endocarditis, a __________ is formed at the endothelial trauma site, this vegetation is extremely FRIABLE
sterile ASEPTIC vegetation
The following can cause what?
- Invasive treatment causes bacteremia (introduces bacteremia)
- The aseptic vegetation can thus become SEPTIC
- Friable septic thrombus can dislodge into the circulation
Bacterial endocarditis
which type of endocarditis is more common, acute or subacute?
sub-acute endocarditis (SBE)
acute endocarditis is caused by what type of infections?
•Staphylococcus
•Viral
•Fungal
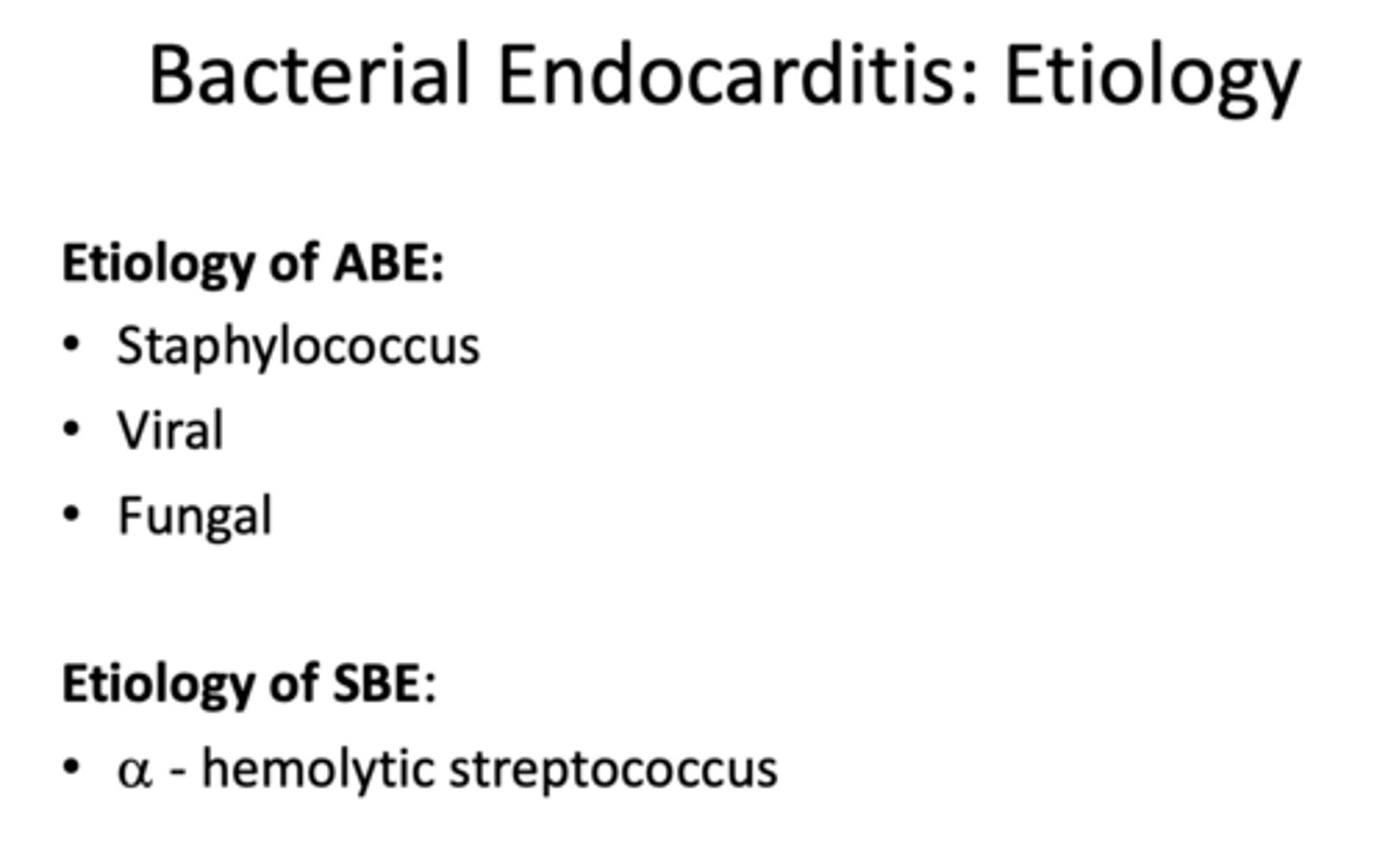
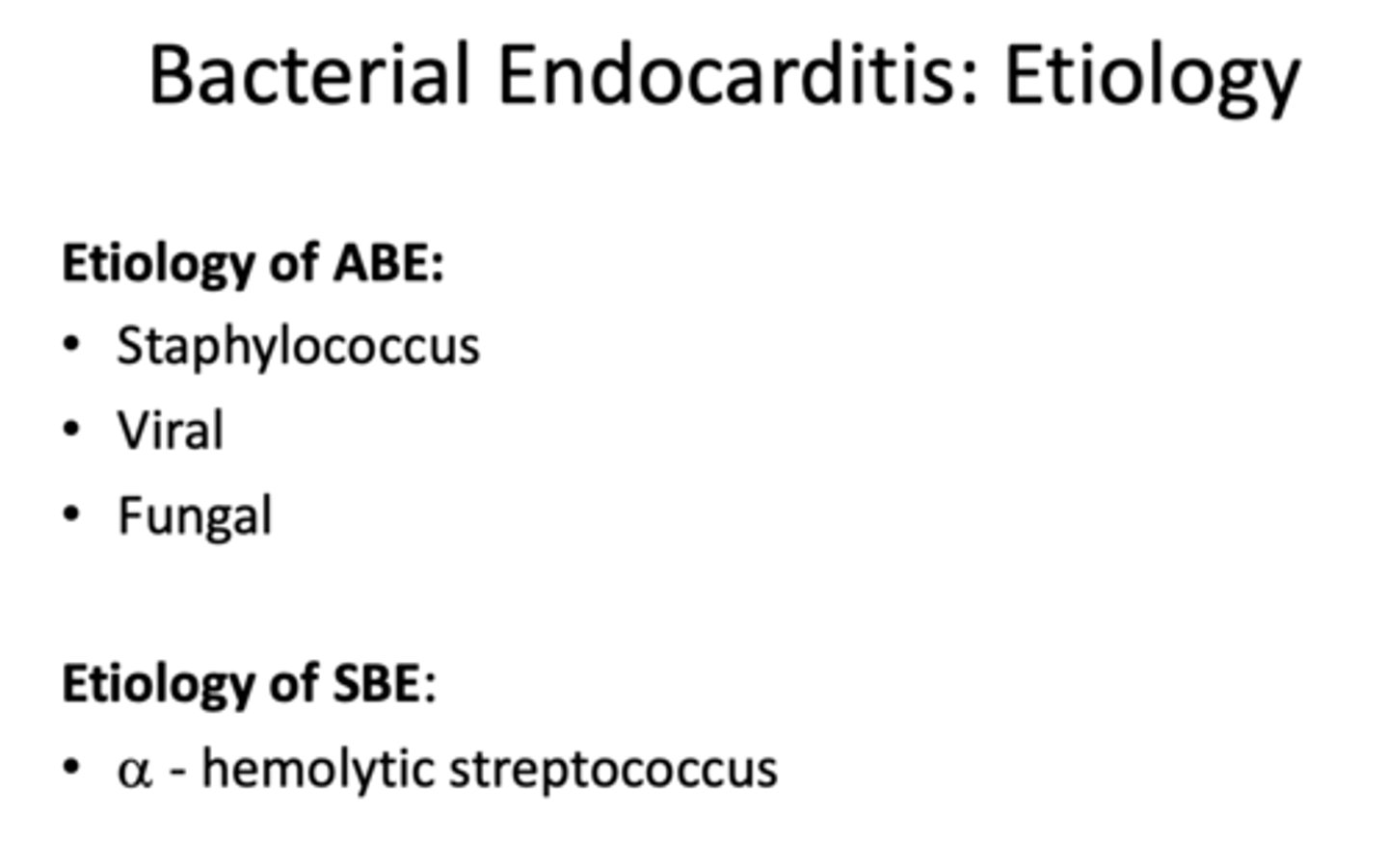
sub-acute endocarditis is caused by what type of infections?
a - hemolytic streptococcus
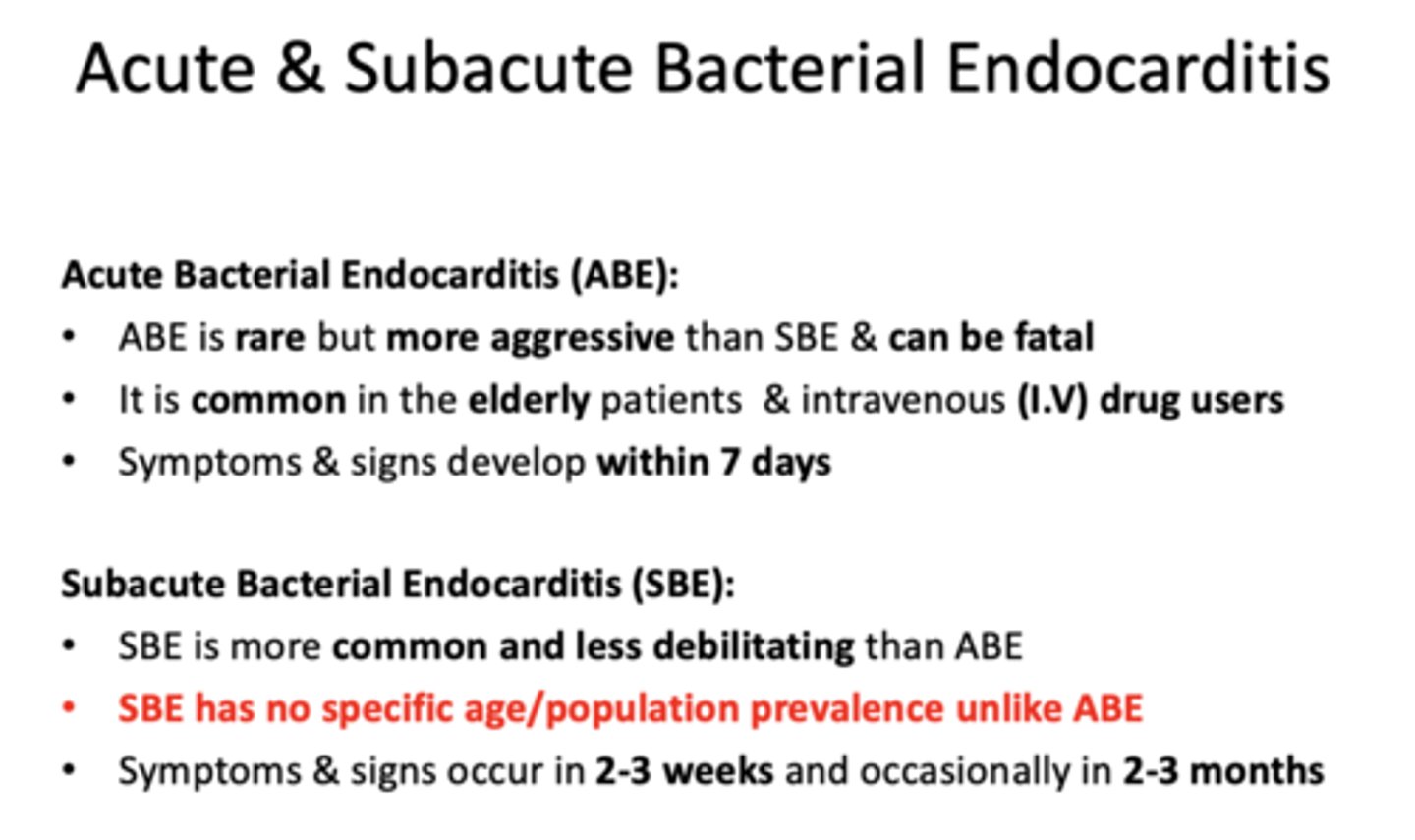
What type of endocarditis?
- It is common in the elderly patients & intravenous (I.V) drug users
- Symptoms & signs develop within 7 days
- is rare but more aggressive, can be fatal
acute endocarditis
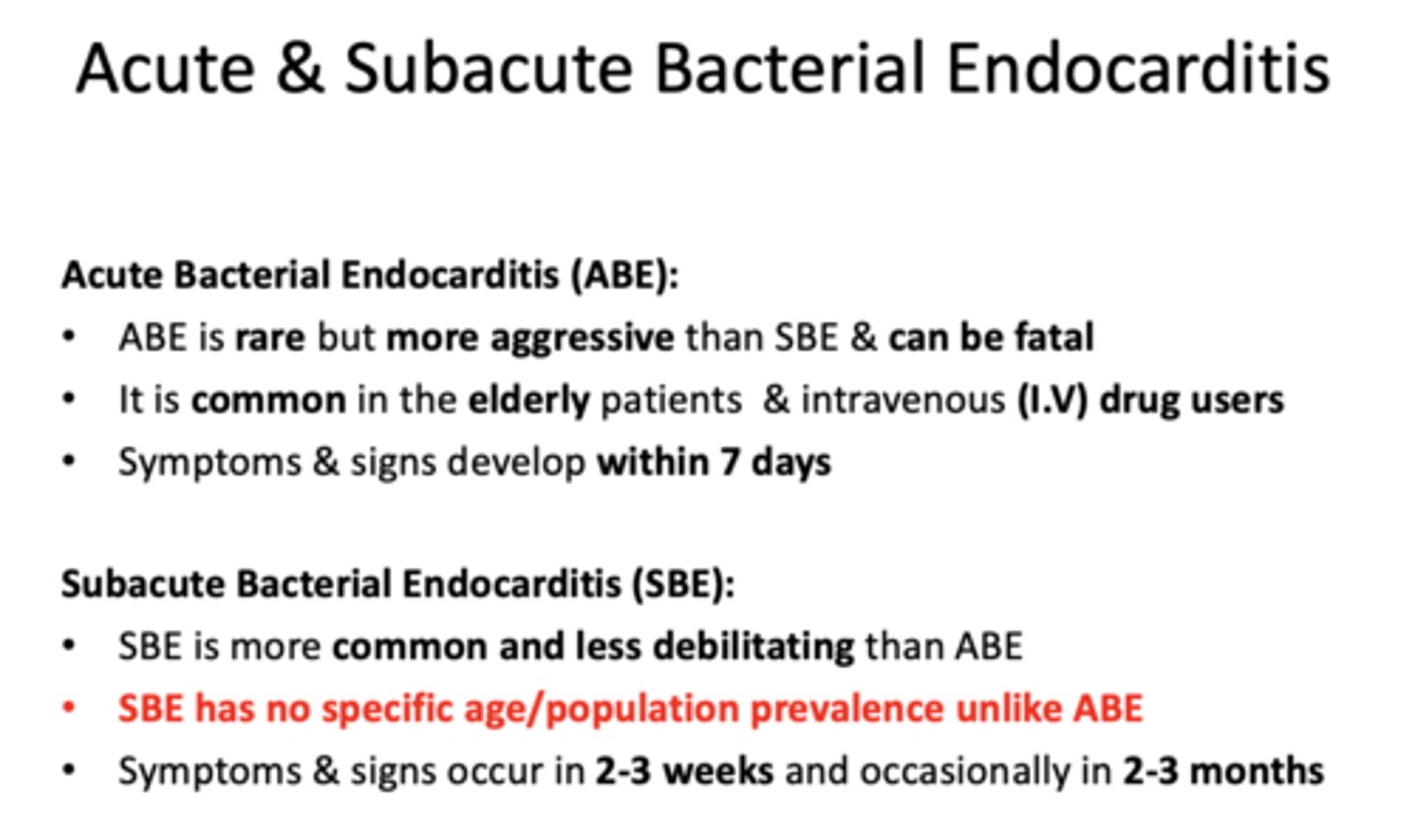
What type of endocarditis?
- Is more common and less debilitating than ABE
- Has no specific age/population prevalence unlike
- Symptoms & signs occur in 2-3 weeks and occasionally in 2-3 months
sub-acute endocarditis
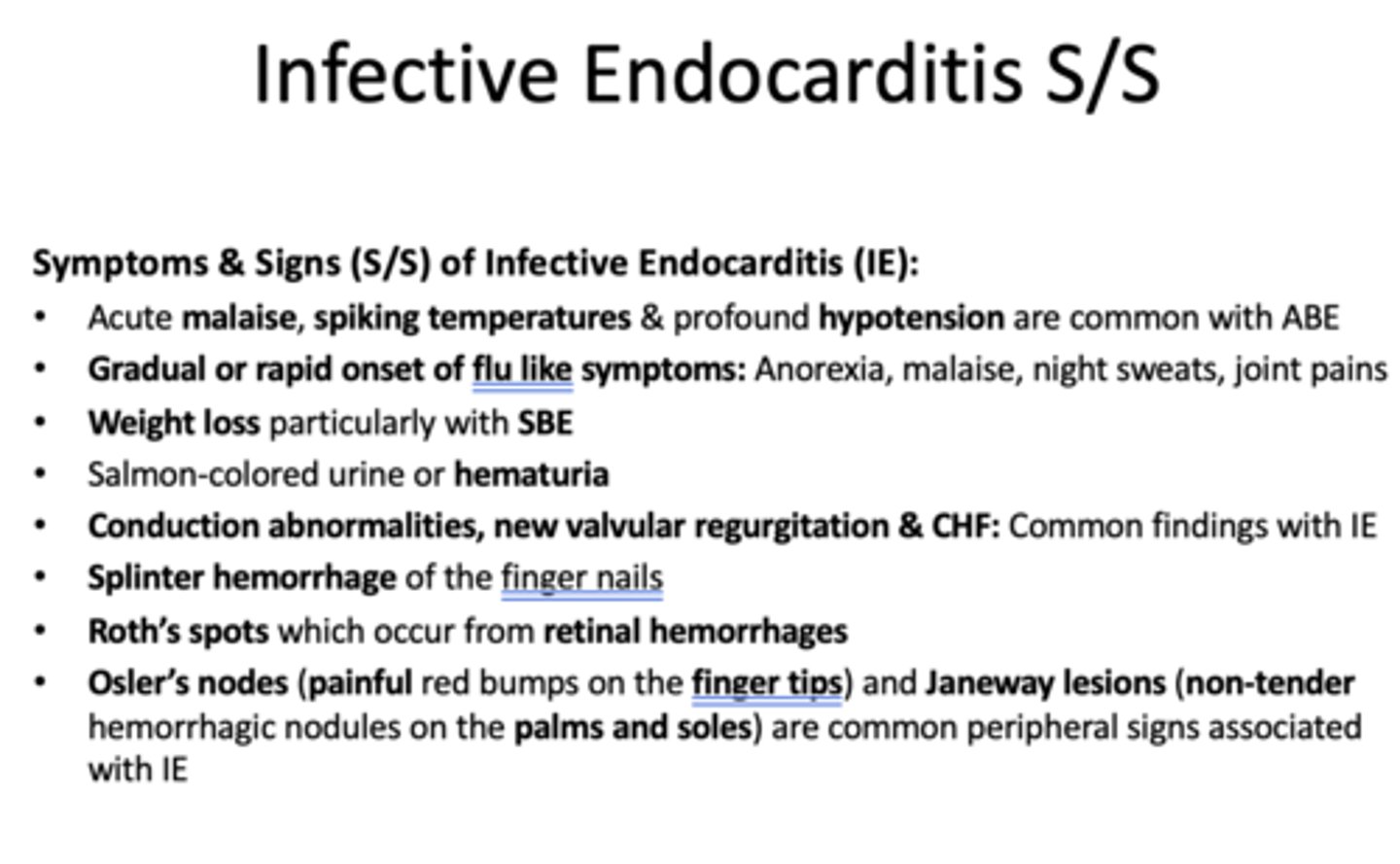
The following are symptoms and signs of what?
- Acute malaise, spiking temperatures & profound hypotension are common with ABE
- Gradual or rapid onset of flu like symptoms
•Weight loss particularly with SBE
- Salmon-colored urine or hematuria
- Conduction abnormalities, new valvular regurgitation & CHF
- Splinter hemorrhage of the finger nails
- Roth’s spots which occur from retinal hemorrhages
- Osler’s nodes (painful red bumps on the finger tips) and Janeway lesions (non-tender hemorrhagic nodules on the palms and soles) are common peripheral signs associated with IE
Infective Endocarditis
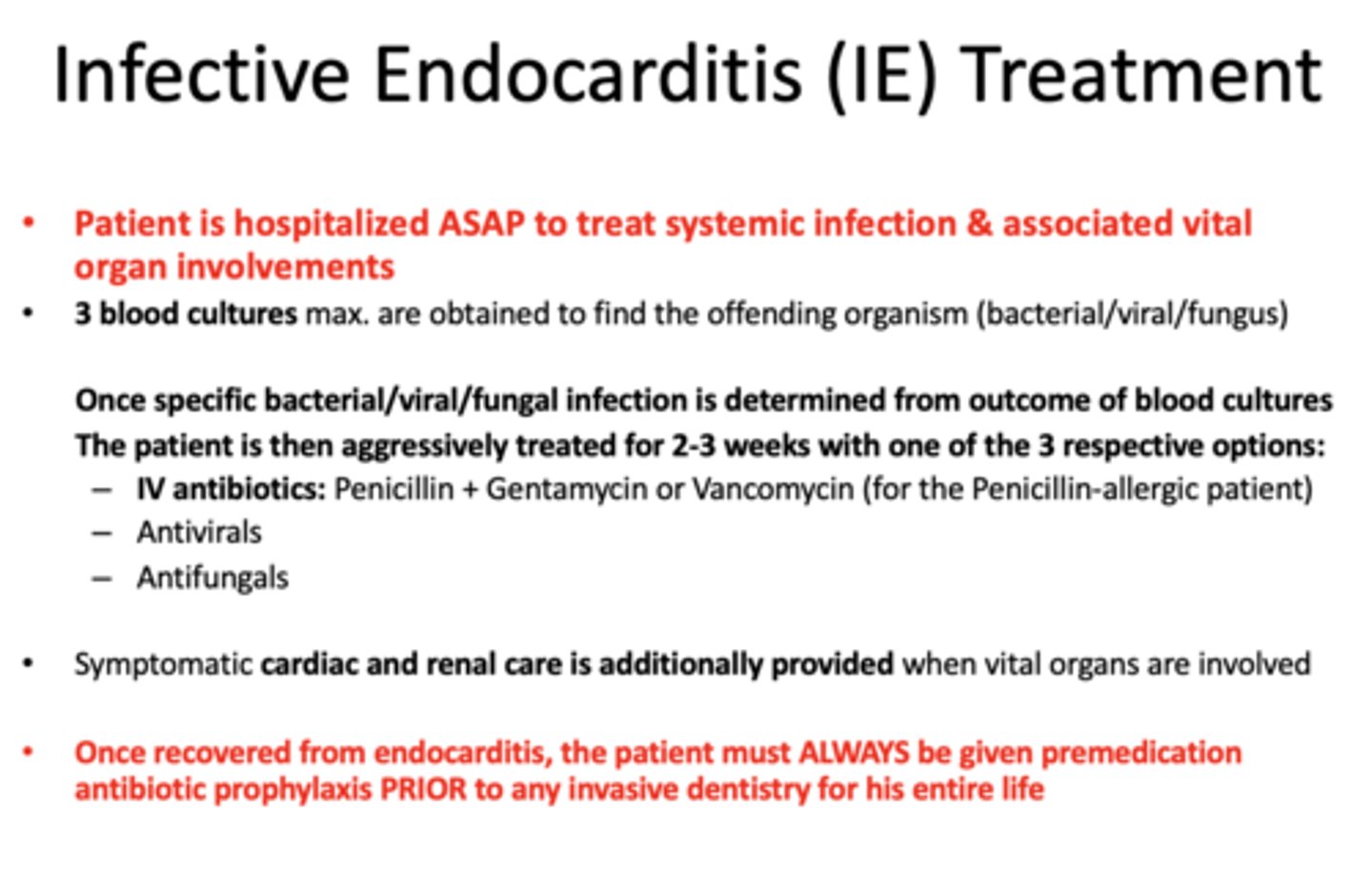
What is the treatment of infective endocarditis (IE)?
Patient is hospitalized ASAP to treat systemic infection & associated vital organ involvements
do patients that recover from endocarditis need to take premedication antibiotic prophylaxis?
yes
t/f: Once recovered from endocarditis, the patient must ALWAYS be given premedication antibiotic prophylaxis PRIOR to any invasive dentistry for his entire life
true
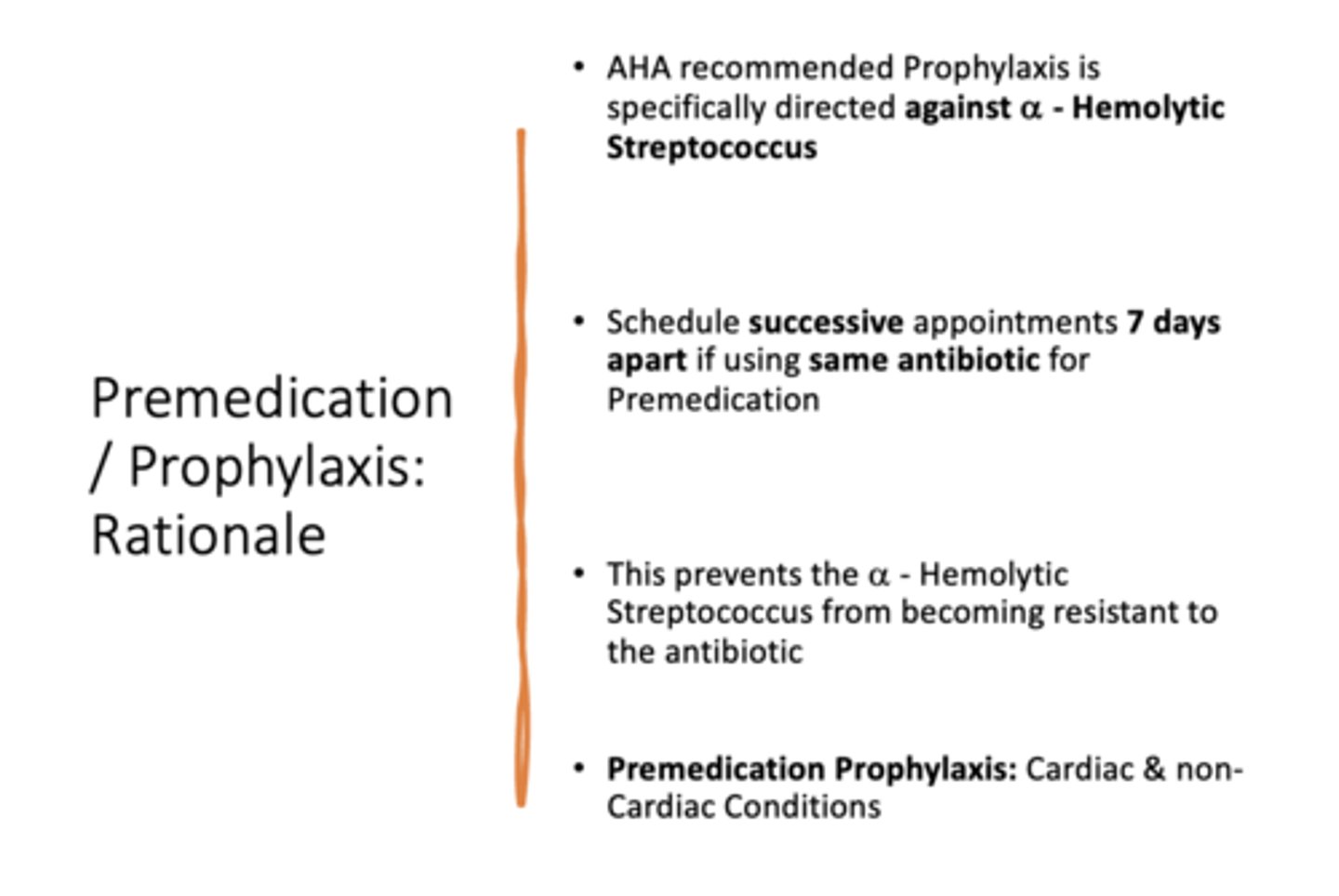
AHA recommended Prophylaxis is specifically directed against ___________
alpha - Hemolytic Streptococcus
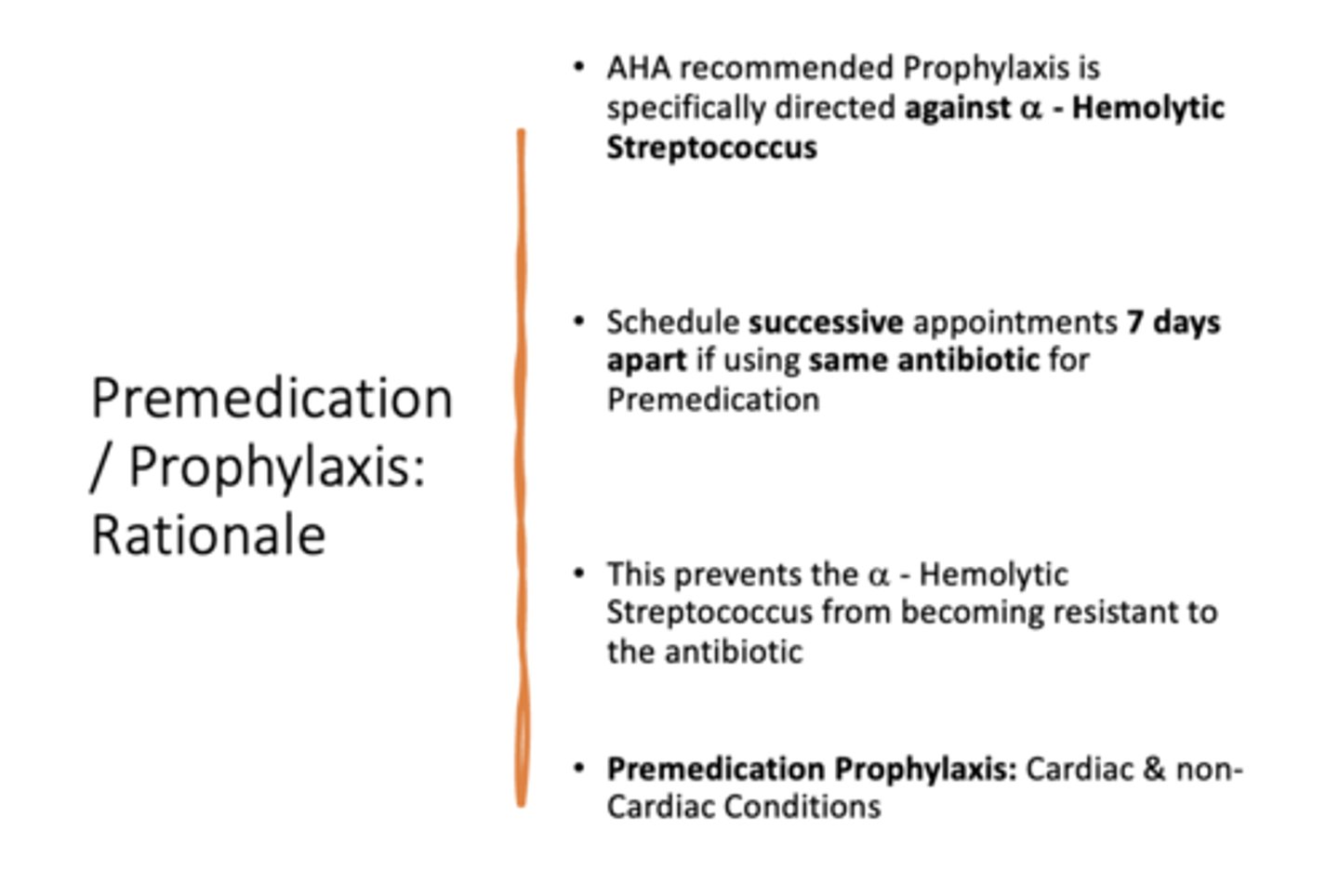
AHA recommended Prophylaxis is to schedule successive appointments _______ days apart if using same antibiotic for Premedication. This prevents the alpha - Hemolytic Streptococcus from becoming resistant to the antibiotic
7
What are four underlying conditions for which antibiotic prophylaxis is suggested?
-Prosthetic cardiac valve or material
-Previous, relapse, or recurrent infective endocarditis (IE)
-Congenital Heart Disease (CHD)
-Cardiac transplant recipients who develop cardiac valvulopathy

t/f: Implantable devices such as pacemakers & stents do NOT require antibiotic prophylaxis
true

What are "high-risk" states associated with joint prothesis?
- Congenital/Acquired immunocompromised states
- Chronic inflammatory joint diseases
- History of Joint Prosthesis associated draining Fistula
- Multiple Joint Prosthesis
- Past history of Joint Prosthesis infection
- Congenital bleeding disorders
- Severe Periodontitis &/or 1/> odontogenic abscesses
- Large Chronic oozing Skin sores: Psoriasis/eczema

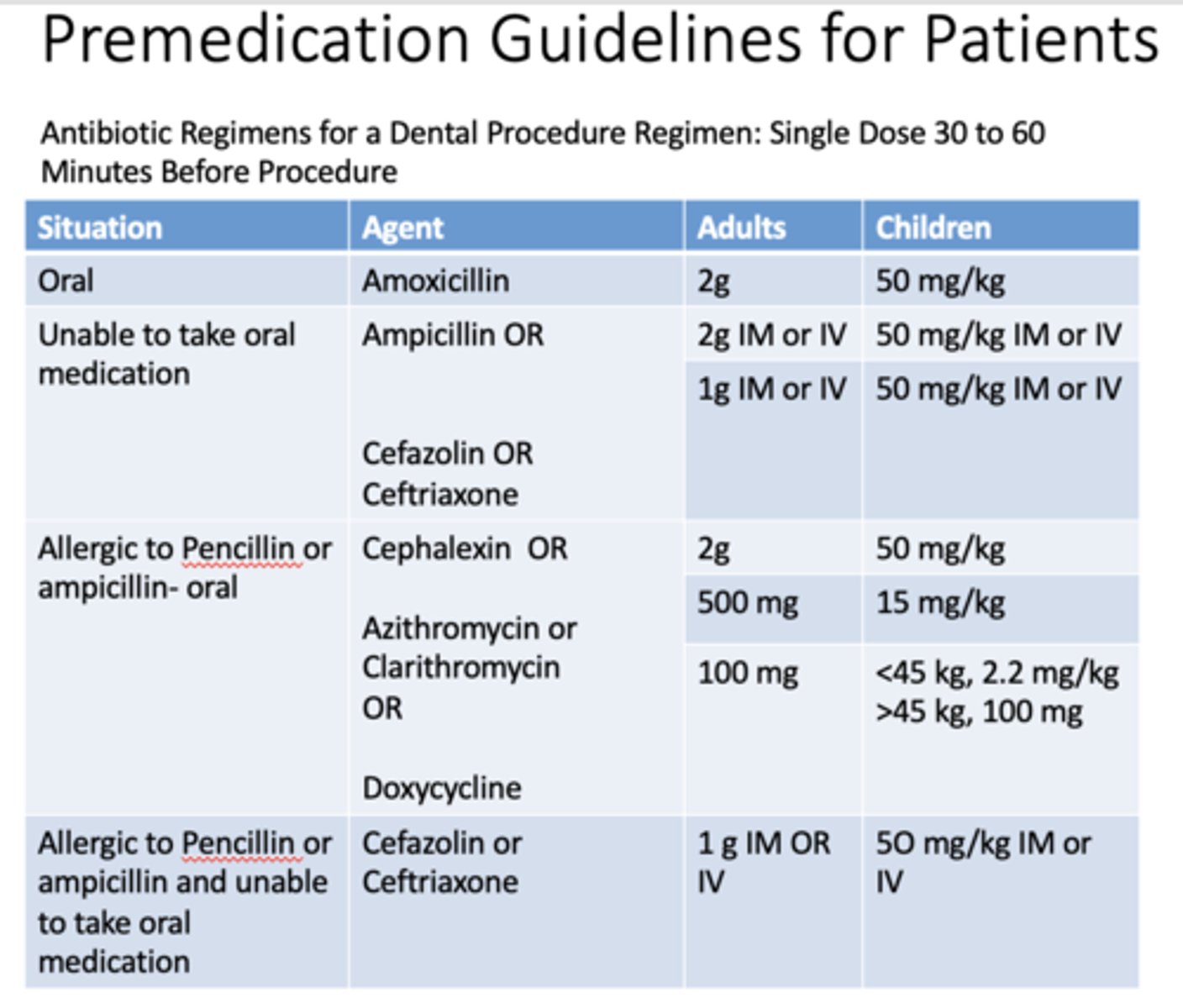
Antibiotic Regimens for a Dental Procedure Regimen: Single Dose _______ to _______ Minutes Before Procedure
30-60
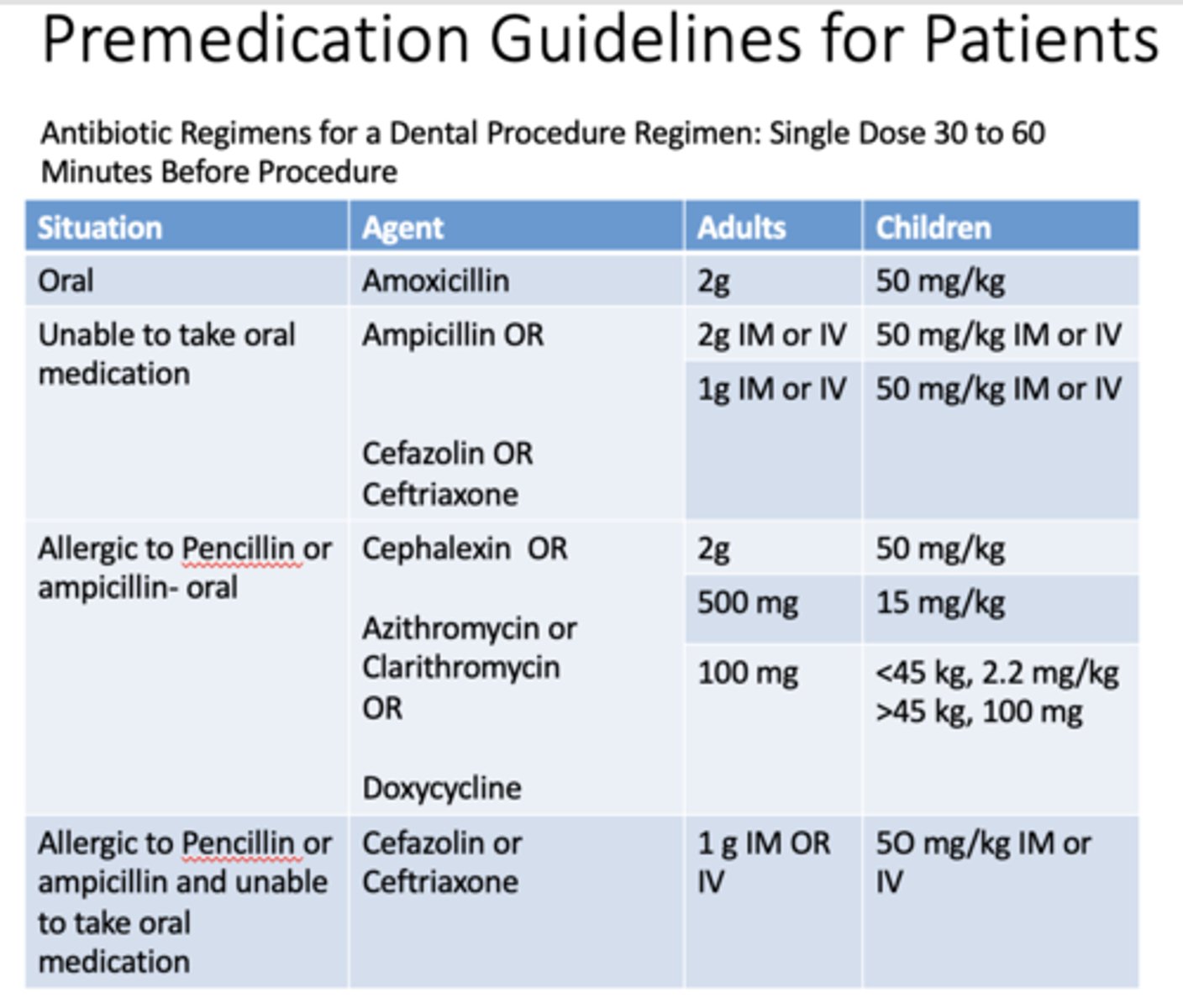
If a patient is taking oral medication, what are the doses for adults and children for amoxicillin?
Adults: 2g
Children: 50 mg/kg
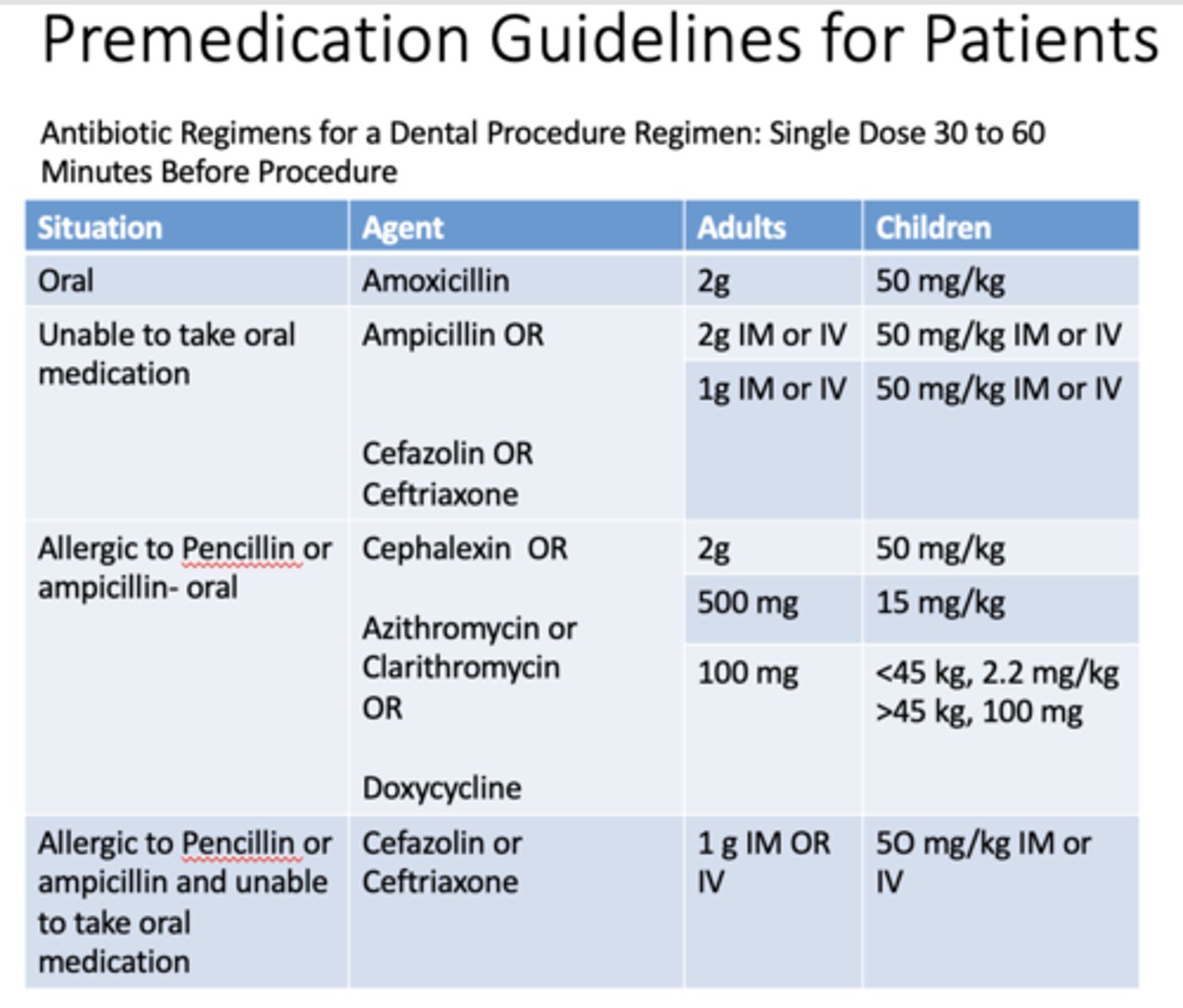
If a patient is unable to take oral medication, what are the doses for adults and children for ampicillin?
Adults: 2g IM or IV
Children: 50 mg/kg IM or IV
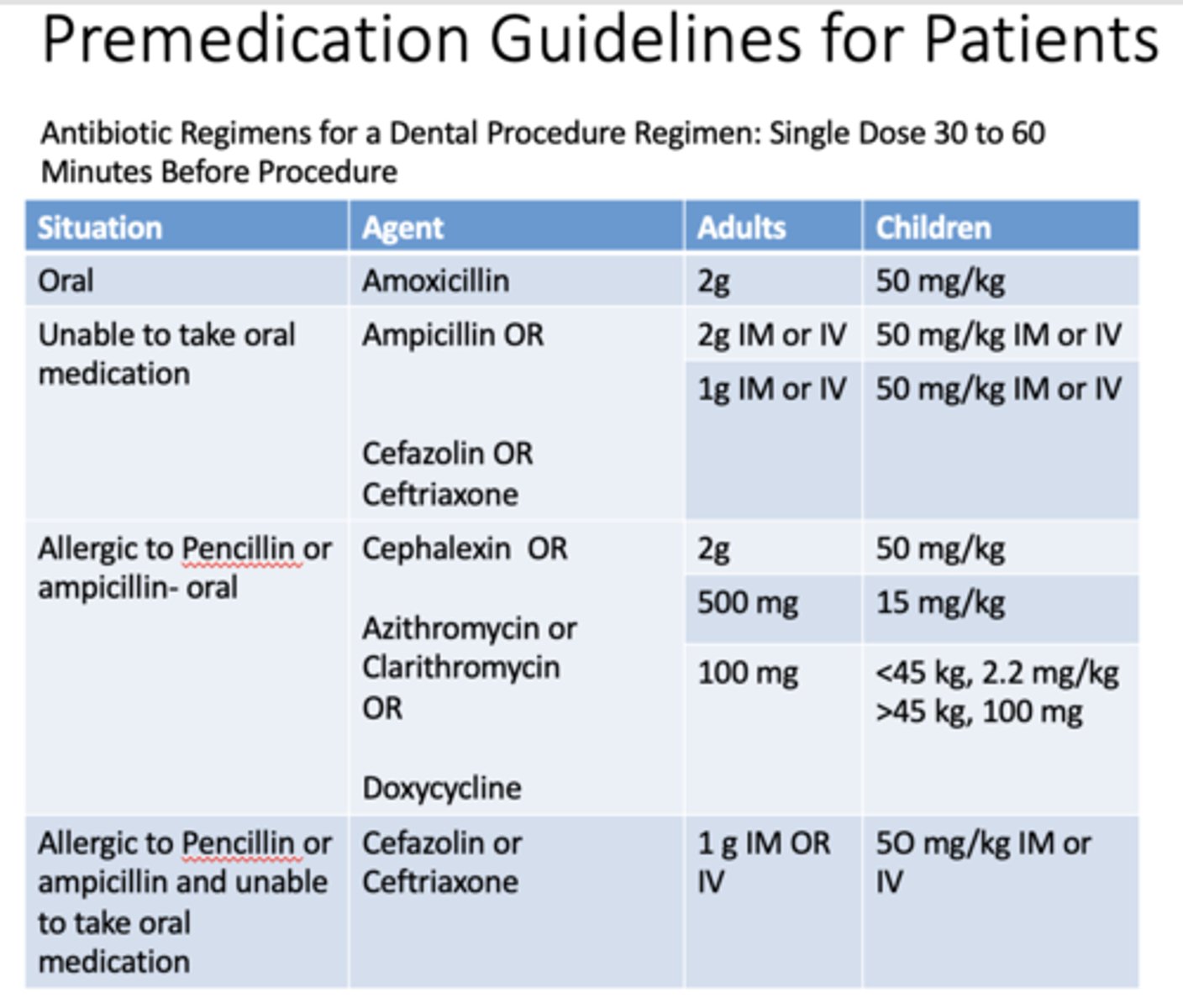
If a patient is unable to take oral medication, what are the doses for adults and children for cefazolin OR cefriaxone?
Adults: 1g IM or IV
Children: 50 mg/kg IM or IV
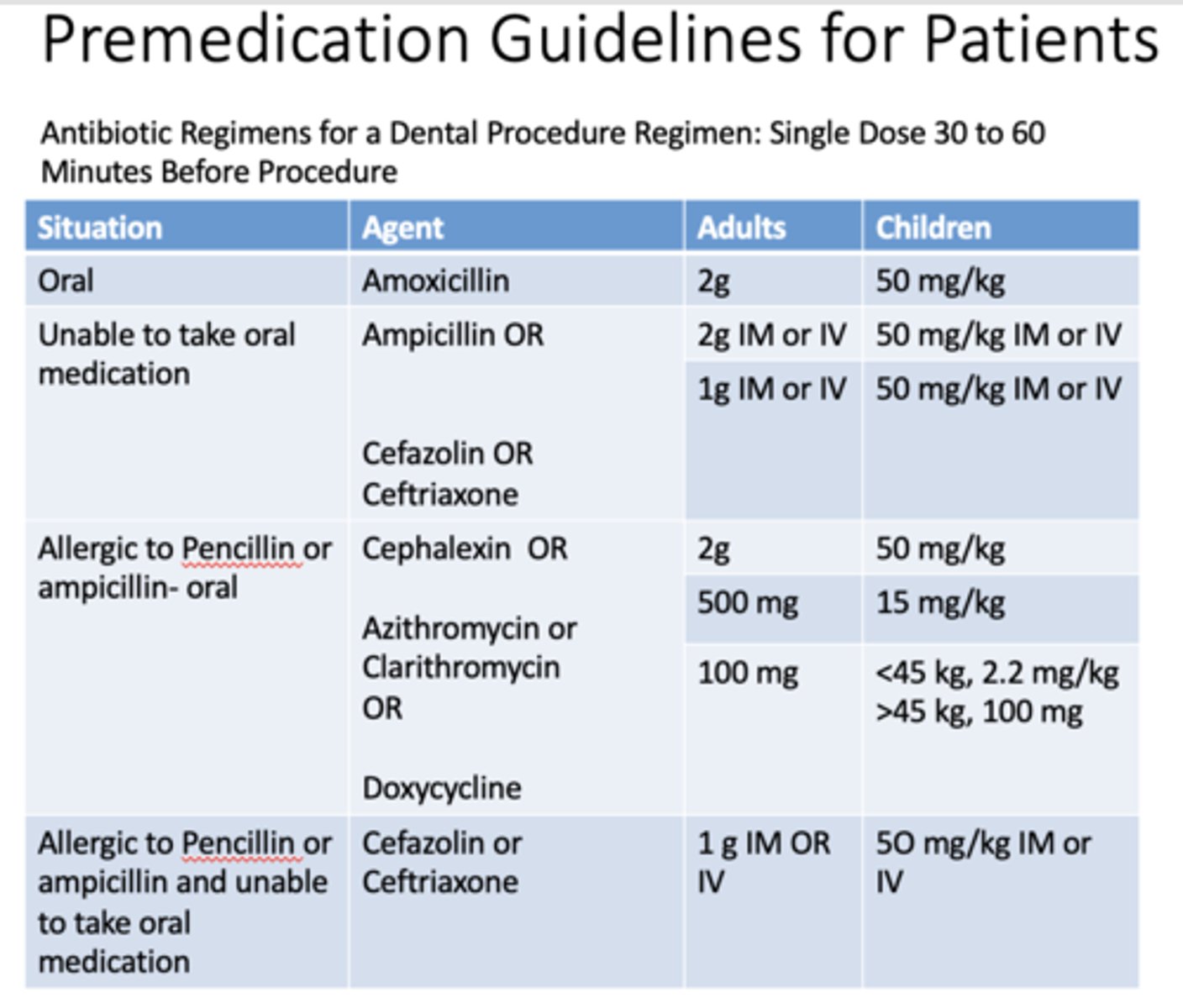
If a patient is allergic to penicillin or ampicillin and taking medication orally, what are the doses for adults and children for cephalexin?
Adults: 2g
Children: 50 mg/kg
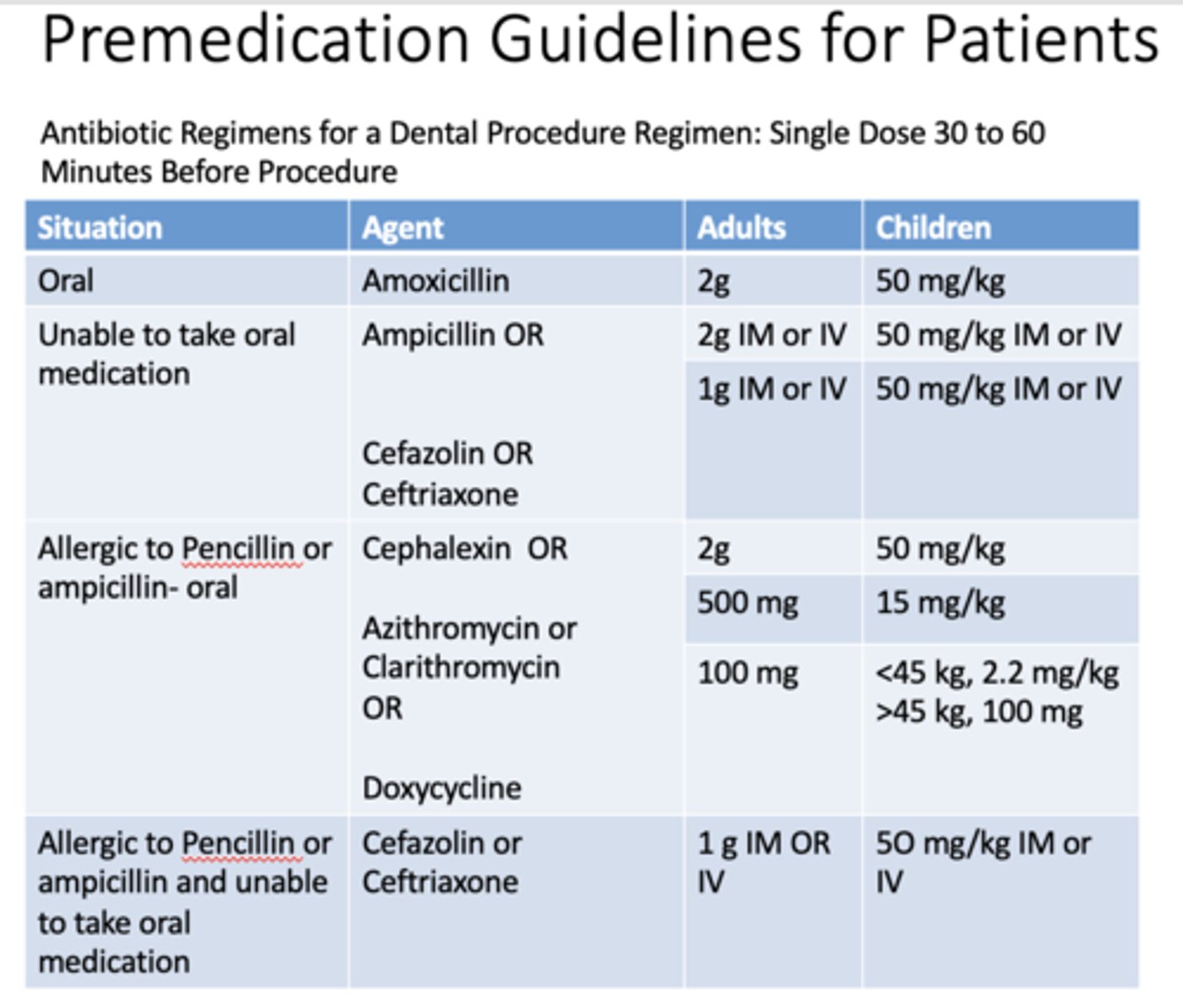
If a patient is allergic to penicillin or ampicillin and taking medication orally, what are the doses for adults and children for azithromycin or clarithromycin?
Adults: 500mg
Children: 15 mg/kg
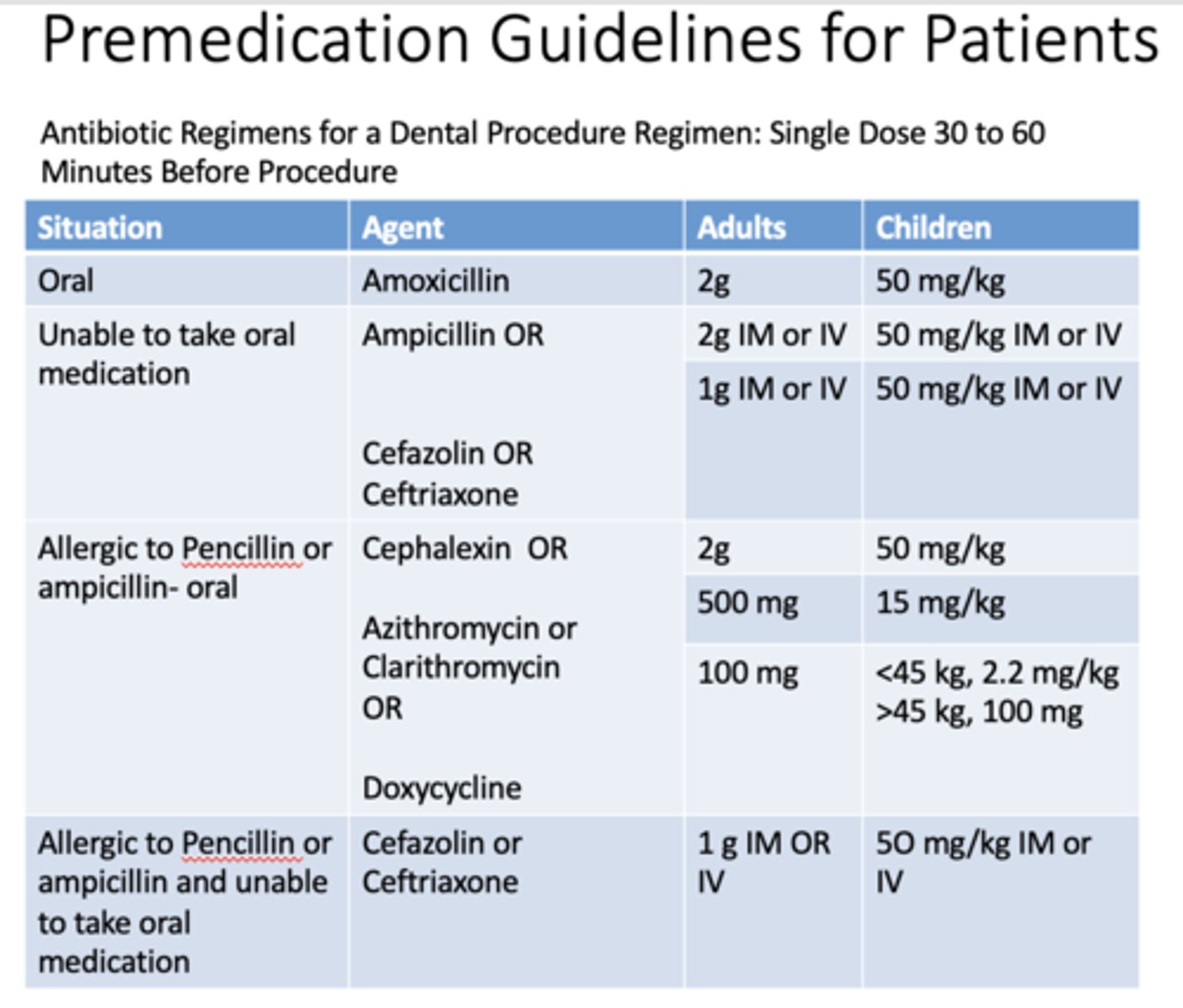
If a patient is allergic to penicillin or ampicillin and taking medication orally, what are the doses for adults and children for doxycyline?
Adults: 100mg
Children: <45 kg, 2.2 mg/kg, >45kg, 100mg
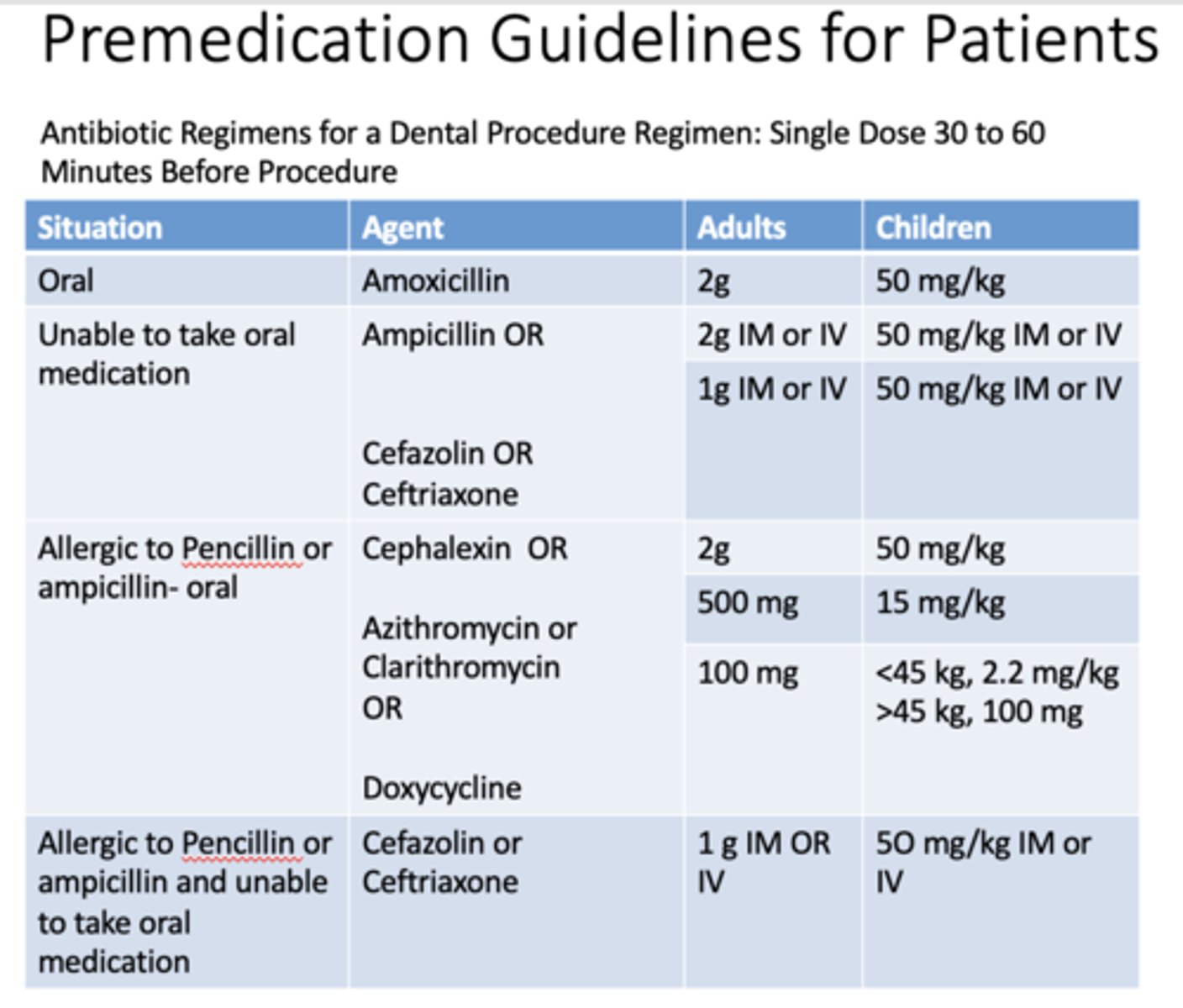
If a patient is allergic to penicillin or ampicillin and unable to take medication orally, what are the doses for adults and children for cefazolin or cefriaxone?
Adults: 1g IM or IV
Children: 50 mg/kg IM or IV
Is clindamycin recommended for patients who are allergic to penicillins & for antibiotics prophylaxis for a dental procedure?
no

What antibiotic should not be used in an individual with a history of anaphylaxis, angioedema, or urticarial with penicillin or ampicillin?
Cephalosporins

which types of artificial valves require endocarditis Prophylaxis prior to invasive dentistry?
both

What are the 3 sources for Bio-prosthetic valves?
- Pig
- Bovine
- Human cryo-preserved heart valves (longest lifespan)

Bio-prosthetic valves in general have a ______ risk for clot formation
low
