14. Vascular Pathophysiology
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
How does the body measure blood pressure?
The body senses BP as Mean Arterial Pressure (MAP) via Baroreceptors located in the aorta and carotid arteries.
What does the heart generate?
Hydrostatic pressure
What is systole?
Phase when heart muscles contracts and hows that healthy aorta is compliant.
What is Diastole?
Phase where heart muscles are relaxed and shows that healthy aorta has recoil.
What are is the function of microcirculation?
To deliver gases, nutrients, and fluid exchange between capillaries, interstitium, and lymphatics.
What determines microcirculation?
Starling-forces. Hydrostatic pressure and oncotic/osmotic pressure.
What does the starling equation determine?
The amount of filtration and absorption.
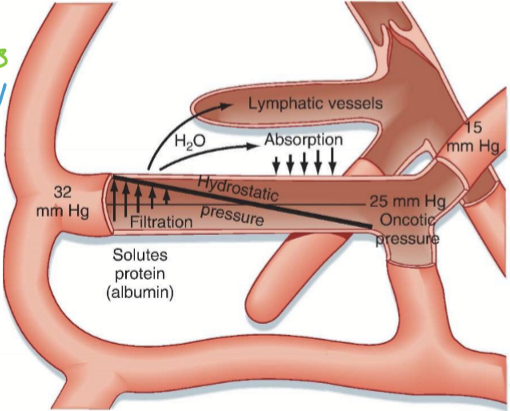
What is the starling equation?
A mathematical formula that describes the movement of fluid across capillary membranes, accounting for hydrostatic and oncotic pressures.
Jv= net filtration out of vessel (+ meaning going out to interstitium; - meaning going into BV)
Kf= vascular permeability coefficient
Pc= hydrostatic pressure in capillary
Pisf= hydrostatic pressure in interstitium
πcap= oncotic pressure in capillary
πisf= oncotic pressure in ISF
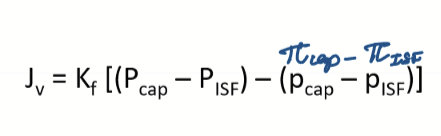
What can increase Kf /vascular permeability coefficient?
Inflammation and diabetes mellitus
What increases Pc/hydrostatic pressure of capillaries?
HTN, poor venous outflow, and local vasodilation
What decreases πcap/oncotic pressure in the capillaries?
Low protein (from malnutrition, liver disease), low salt, overhydration
What increases πisf/oncotic pressure of ISF?
Inflammation (can be systemic or local)
What are the primary etiologies of Macular Edema?
Diabetes
Hypertension
Inflammation
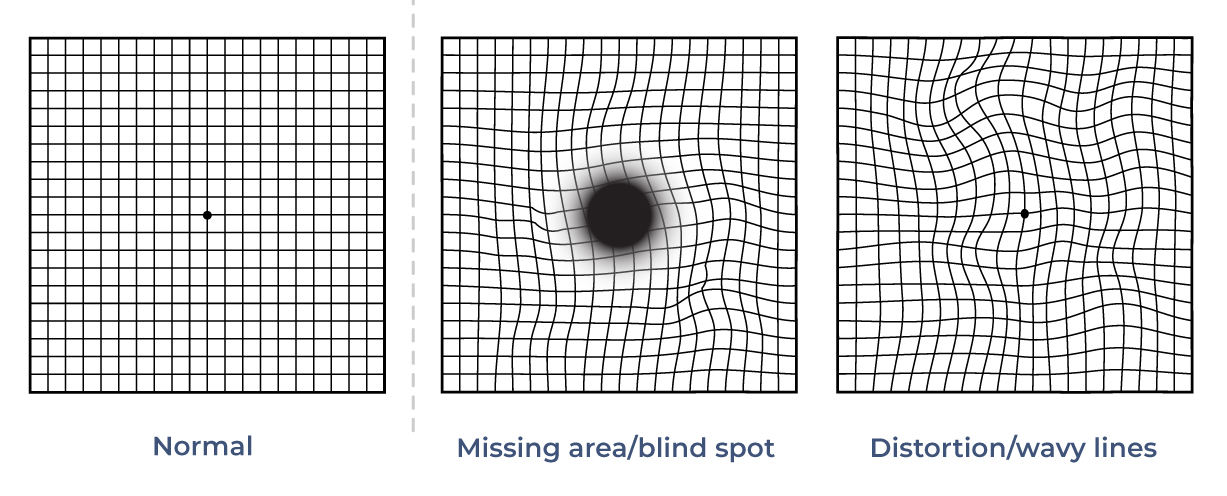
What is used to detect macular edema?
Amsler grids

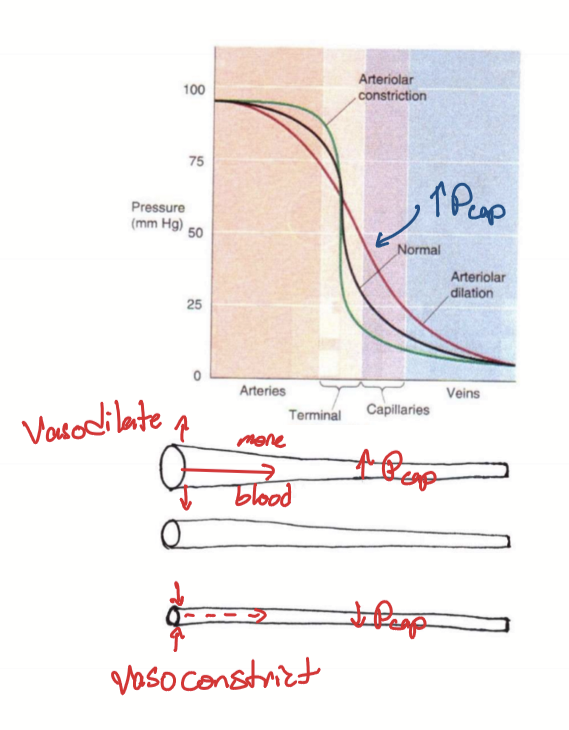
What can change capillary hydrostatic pressure?
Artery/arteriole vasodilation
Artery/arteriole vasoconstriction
What does artery/arteriole vasodilation cause?
Decreases pressure in artery/arteriole
Increases pressure in capillaries as more blood flows into capillaries
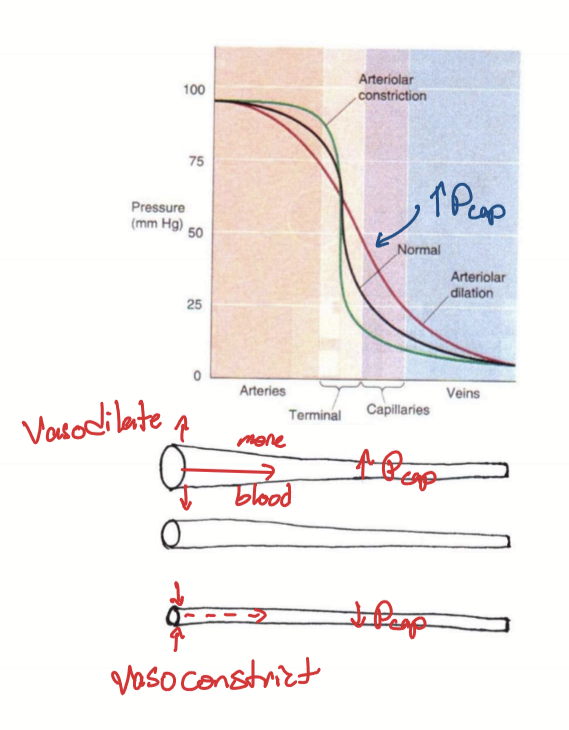
What does artery/arteriole vasoconstriction cause?
Increases pressure in artery/arteriole
Decreases pressure in capillaries as less blood flows into capillaries
What is lymphedema?
Edema caused by occlusion or removal of lymph nodes.
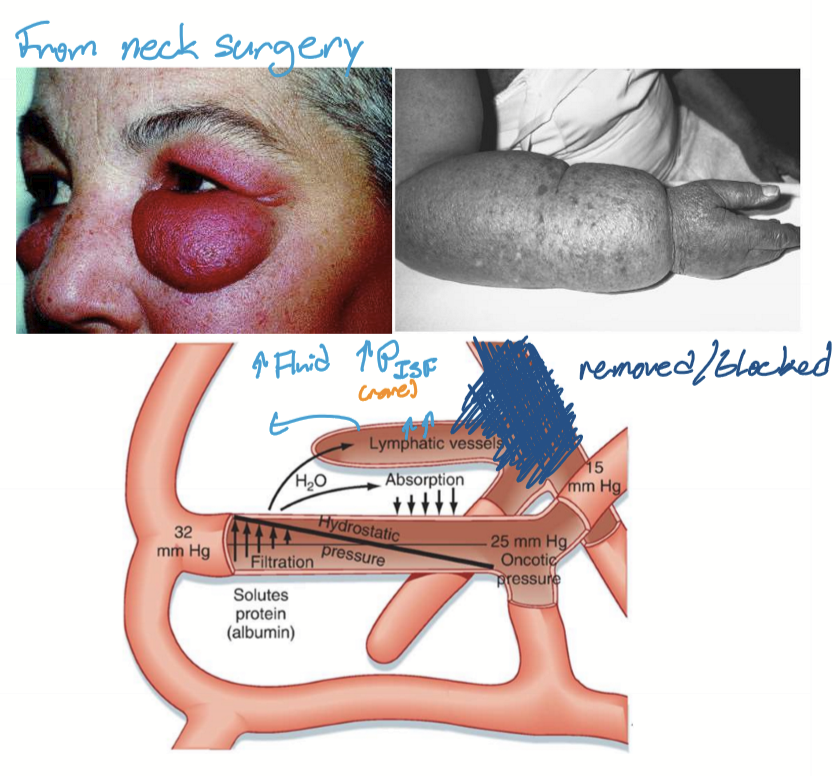
What is the pathogenesis of lymphedema?
Poor lymph outflow due to occlusion or removal of lymph nodes
Increased pressure in lymphatics
Fluid from lymph into ISF
Fluid into capillary (absorption)
What should one avoid when placing IV in?
Avoid placing IV in areas that can develop lymphedema.
How is the blood flow in blood vessels controlled?
Vascular smooth muscles in the tunica media
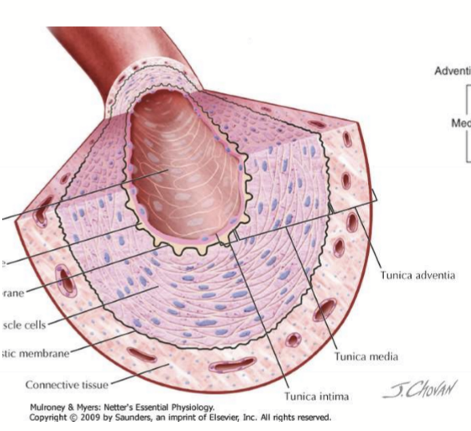
What regulates smooth muscles?
ANS, hormones, metabolic factors, inflammatory mediators
What smooth muscles have reciprocity?
Iris
What smooth muscles do not have reciprocity?
Blood vessels
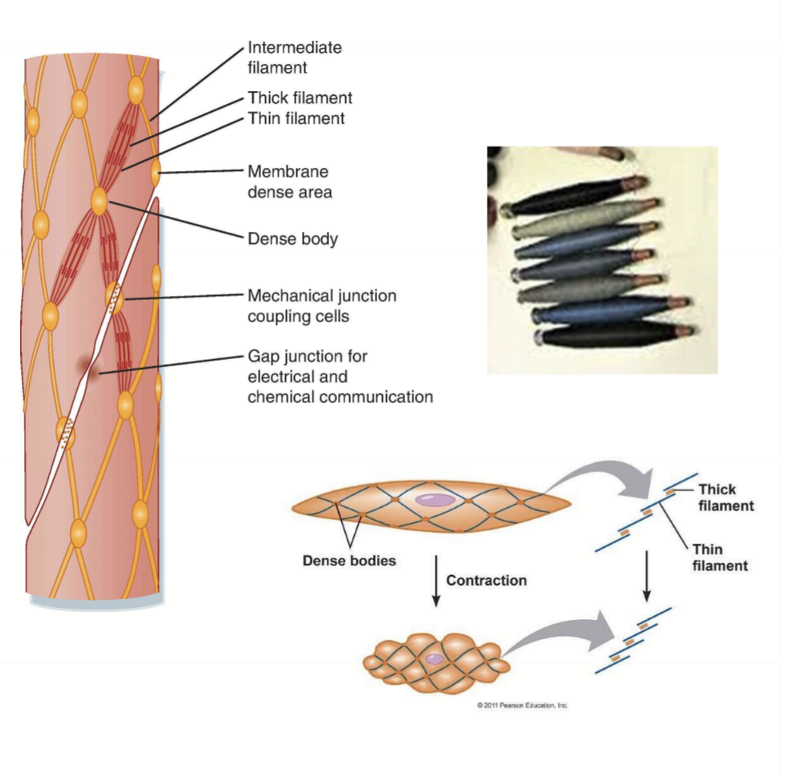
What characteristics are unique to Smooth Muscles?
Line hollow organs
Not striated
spindle-shaped
no sarcomeres
No troponin, just regulated myosin
What controls smooth muscle relaxation?
NO-sensing Guanylate cyclase, cGMP, and myosin light chain phosphatase
Activating Gs, cAMP, and inhibiting phosphorylation
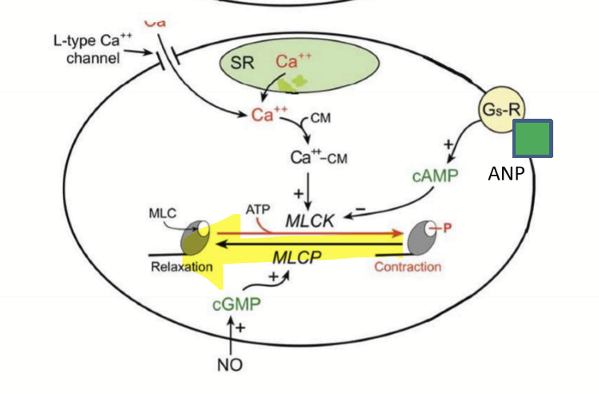
What controls smooth muscle contraction?
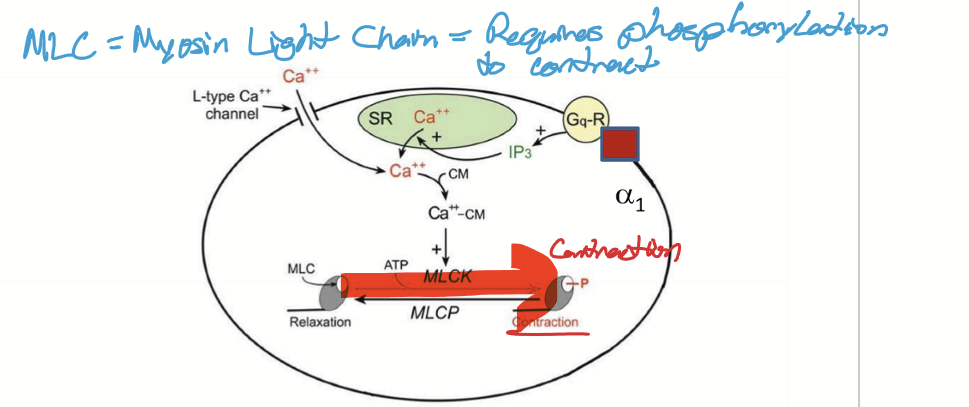
Activating Gq, IP3, and phosphorylating myosin light chain
What does it mean when cells are "able to latch”?
They can stay contracted without further input.
What are the types of regulation for smooth vascular muscle?
Autoregulation: myogenic
Local control: due to metabolic/nutrient demand or inflammation
Systemic regulation: neural and hormonal regulation to control Blood Pressure
How does autoregulation of blood vessels work?
Mechanism not well understood, but constricts if there is an increase in blood flow and dilates if there is a decrease in blood flow.
Which regulation is able to override other regulation methods?
Local regulation, as it is the most important mechanism for meeting local metabolic demands
What metabolic factors contribute to local blood vessel regulation?
↓O₂
↑CO₂
↓pH (from increased metabolic activity)
Adenosine (a by-product of ATP degradation)
How do inflammation and allergies affect local blood vessel regulation?
They promote vasodilation and increased permeability through mediators like:
Bradykinin
Prostaglandins
Leukotrienes
Histamine
How does local regulation work?
When there is a low metabolic demand, vasoconstriction causes decreased perfusion downstream. When there is a high metabolic demand, vasodilation causes increased perfusion downstream.
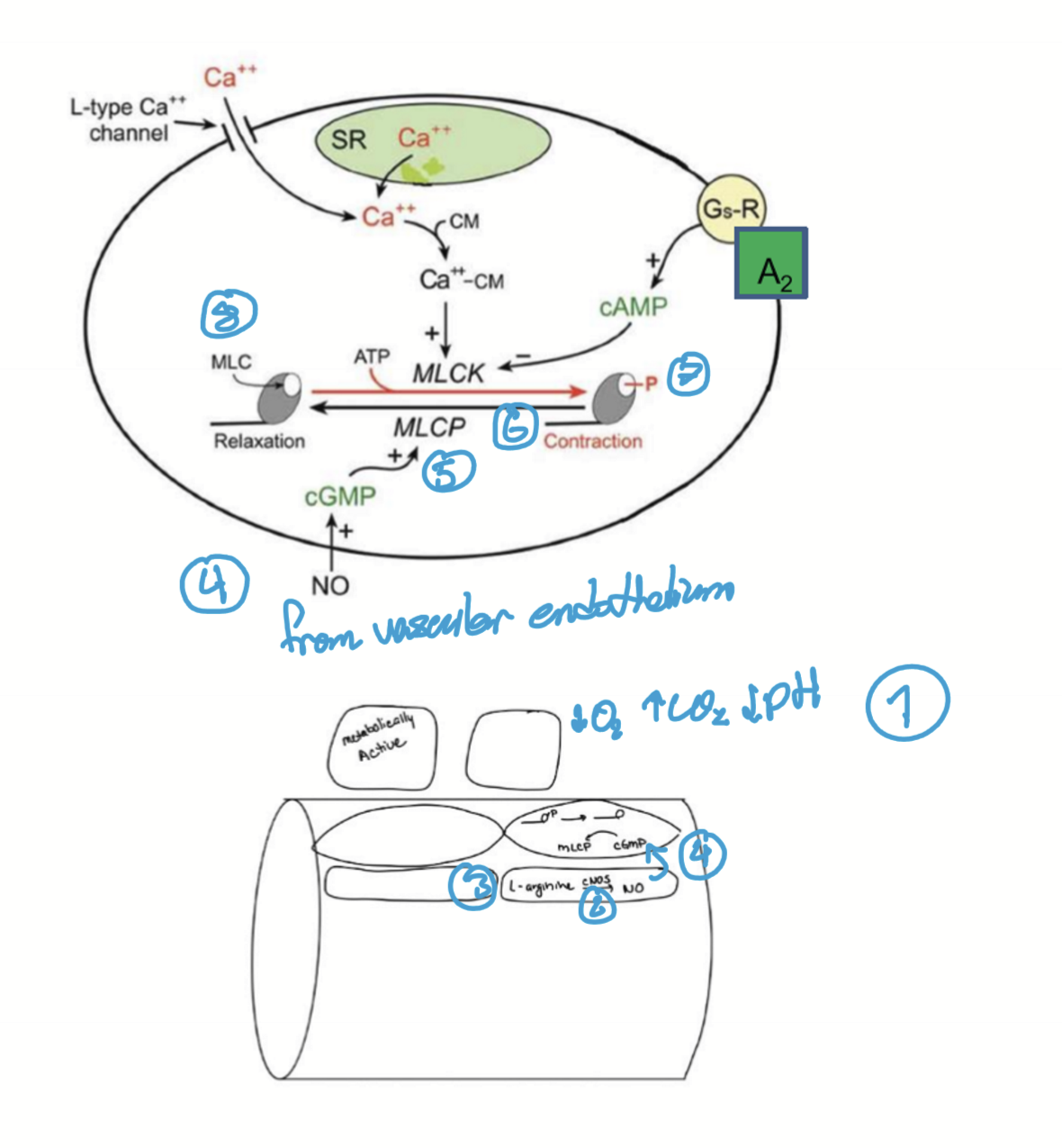
How does NO cause vasodilation?
High metabolic factors or high sheer stress (low O2, high CO2, low pH)
Increases cNOS (constitutive nitric oxide)
cNOS converts L-arginine into Nitric Oxide (NO)
NO diffuses into VSM
Increases cGMP
Increased MLC phosphatase
Dephosphorylation of myosin
Relaxation and vasodilation to increase blood glow
How does Inflammation cause vasodilation?
Inflammatory mediator and LPS on Gram negative bacteria causes vasodialtion via NO.
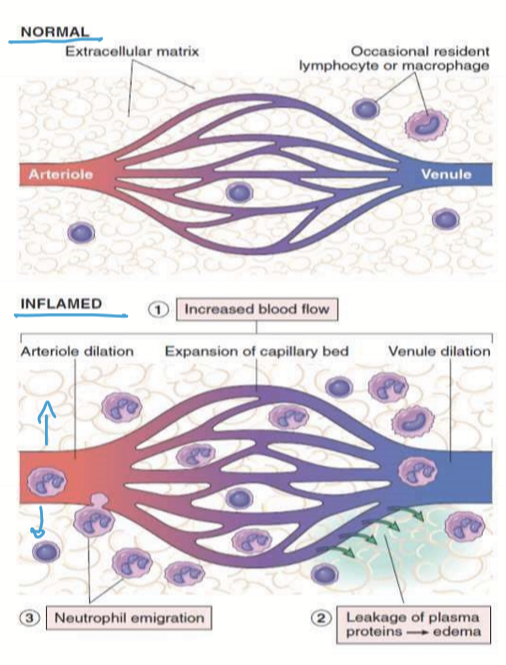
What are the mechanisms for vasodilation via inflammation?
Inflammation
inflammatory factors: histamine, bradykinin, prostaglandin (PGE2, PGD2), substance P
increases cNOS
increases NO → vasodilation
Increased blood flow brings WBCs
Gram negative infection
LPS present on Gram negative
Stimulates iNOS (inducible NO Synthase)
Increase NO → Vasodilation
Increased blood flow brings WBCs

What are the two main ways blood vessels control blood pressure (BP)?
Directly by changing vessel diameter (resistance)
Indirectly by controlling blood volume via renal vessels
How does the brain and hormones affect blood pressure?
They are mostly set up to increase BP:
SNS activation & hormonal stimulation causes vasoconstriction, increasing BP
SNS inhibition & hormonal inhibition causes vasodilation, decreasing BP
How does atherosclerosis and/or arteriosclerosis affect blood pressure?
Narrows vessel lumen → increases resistance → ↑ BP
Body compensates with vasodilation via hormones and neuron inhibition
Treatment for hypertension: promote vasodilation, often by inhibiting vasoconstriction
What happens to blood vessels during increased and decreased SNS activity?
↑ SNS (α₁ receptors) → vasoconstriction
↓ SNS → vasodilation
How do skeletal muscle vessels respond to SNS activation?
Vessels with β₂ receptors (e.g., in skeletal muscle) dilate during ↑ SNS activity
This ensures increased blood flow to muscles during fight-or-flight
How is blood volume controlled?
Starling forces in the kidney regulates the volume of blood.
Vasodilation of the BV in the kidneys increases urine production, decreasing blood volume, decreasing BP.
Vasoconstriction of the BV in the kidneys decreases urine production, increasing blood volume, increasing BP.
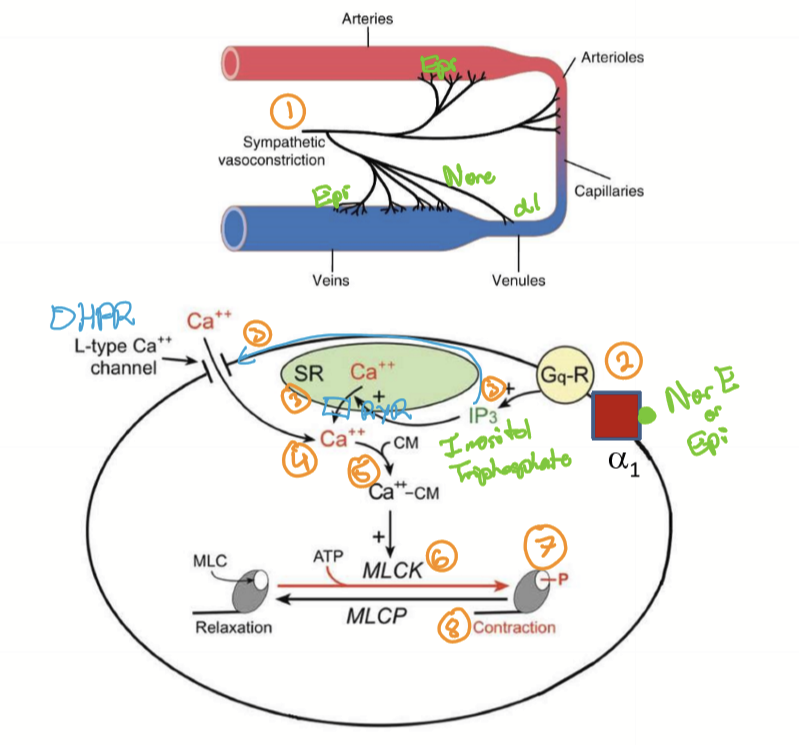
What are the steps taken for smooth muscle contraction?
SNS stimulation
NorE or Epi binds to alpha1 adrenergic receptors to activate G1-coupled proteins (G proteins)
IP3 (inositol triphosphate) produced which opens calcium channels called Ryanodine receptors (RyR). May also open DHRPR
Calcium enters ICF from SR and/or ECF
Calcium binds to calmodulin (CM)
Calcium-calmodulin complex activates myosin light chain kinase (MLCK)
MLCK phsophorylates Myosin Light Chain (MLC)
Myosin active: crossbridge
Stronger stimulation causes more IP3 = stronger contraction
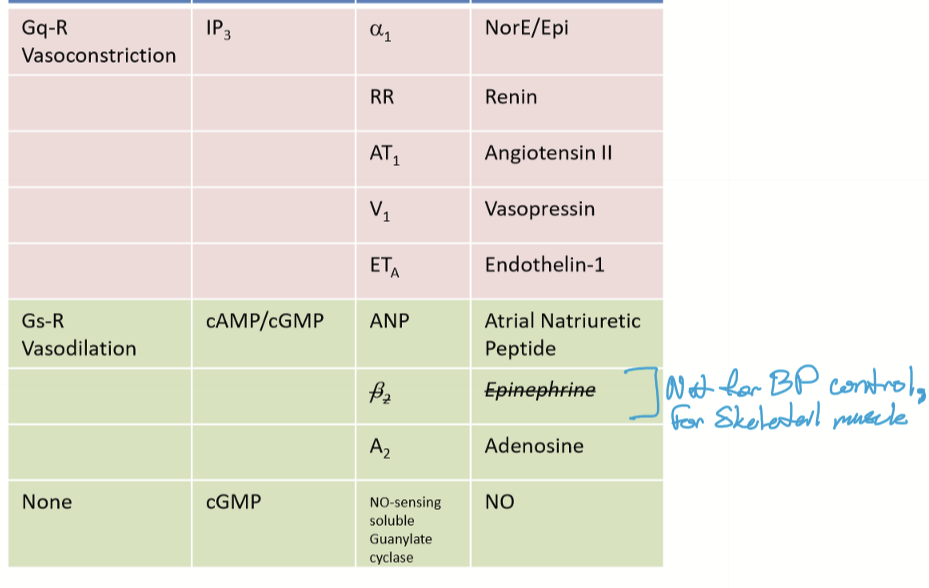
What biological agonists can cause vasoconstriction?
NorE/Epi (SNS only) to alpha 1 with Gq-R and IP3 as secondary messengers
Endocrine
Renin
Angiotensin II
Vasopressin
Endothelin-1
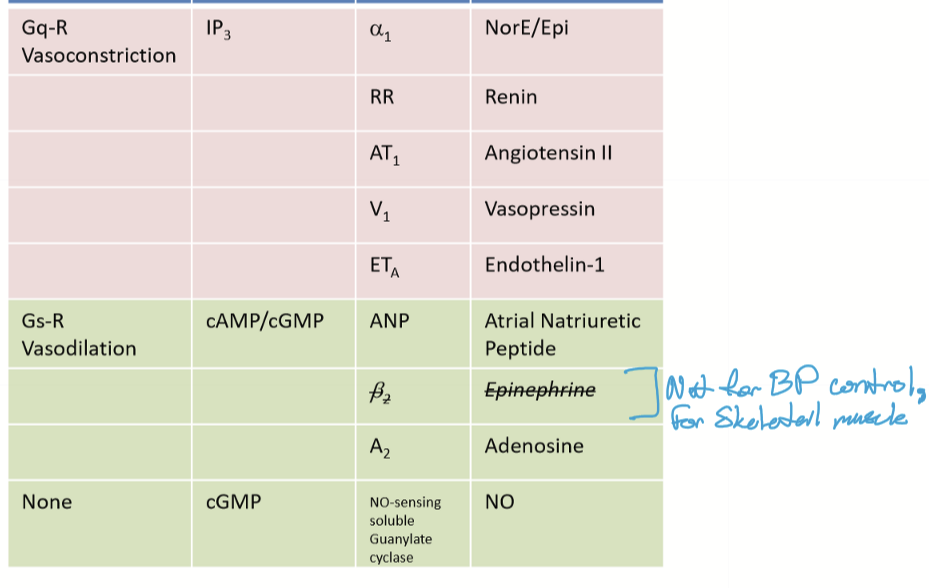
What biological agonists can cause vasodilation
Atrial Natriuretic peptide (ANP) with cAMP/cGMP as second messengers and Gs-R proteins
Adenosine on A2 receptors
NO with cGMP as secondary messengers
What are some pathways/methods do anti-hypertensives use to reduce BP?
Blocking calcium in smooth muscle
inhibiting vasoconstrictors
stimulating vasodilators
What are some calcium channel blockers that cause vasodilation?
Non-DHPR: Benzothiazepine (Diltiazem)
DHPR: Dihydropyridine (Amlodipine)
What are the types of drugs that vasodilate by inhibiting Gq?
alpha 1 blockers: Terazosin (Hytrin)
Renin inhibitors
ARB (AngII Rec blocker): Losartan
ACE inhibitor: benzapril (Lotensin)
Vasopressin Inhibitor: Vaptan
Endothelin Rec Blocker
Calcium Channel Blockers: Benzothiazepine (diltiazem) and Dihydropyridine (Amlodipine)
What are the types of drugs that vasodilate by stimulation?
ANP receptor agonists
Adenosine receptor agonists
Nitrodilators (increase cardiac perfusion)