2.4 Stem Cell Dilemmas
Adult stem cells in medicine:
To treat burns (adult skin stem cells from patient’s own body so that they are not rejected)
To treat leukaemia (adult blood stem cells taken from willing donors). The donors must match.
Embryonic stem cells in research:
A lot more controversial (as embryos cannot ‘give permission’)
Embryos from IVF (that are no longer needed) are usually used
Legal in the UK, but very restricted
Possibilities to treat diabetes and paralysis
Embryonic stem cells | Adult stem cells | |
|---|---|---|
Advantages | Can differentiate into any specialised cell Can be accepted without rejection | From willing, consenting donors Well tested and reliable |
Disadvantages | Ethical issues Development of therapies is slow, expensive and difficult to control | Possibility of rejection Can only differentiate into certain cells |
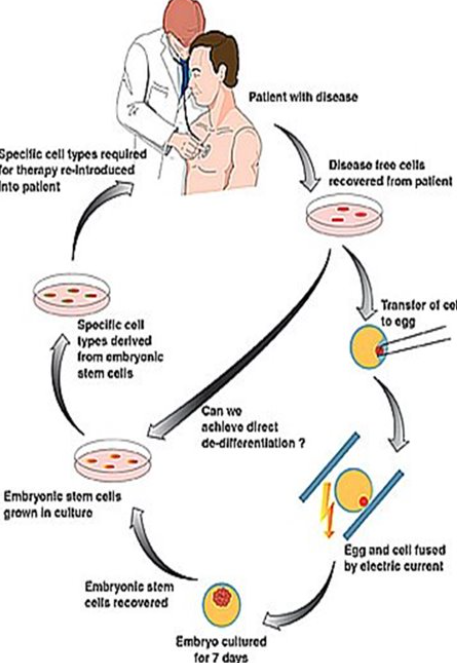
Therapeutic cloning:
Disease-free cells are taken from the patient (to avoid rejection)
An egg is transferred to the cells
Cells that can be used for treatment are formed