Chapter 5 Interactions Among Branches of Government
Congress
Congressional Structure
- Congress: the bicameral legislature for writing laws
- Oversees bureaucracy, clarifies and codifies policy, represents citizens, build consensus
- House of Representatives: a 435-member house, with members apportioned by each state’s population (designed to represent population)
- Senate: a 100-member house, with 2 members per state (designed to represent states equally)
- Census: a survey taken every 10 years to count population and determine the number of congressional districts each state has
- Redistricting: the redrawing of district boundaries to ensure each district has an equal population done by state legislature
- Gerrymandering: drawing district boundaries to give the majority party a future advantage
- Does not apply for Iowa; uses an independent commission to draw district lines
- Helps incumbents
- Some states have such small populations that the entire state becomes a district
- Each state is guaranteed one seat in the House
Congressional Elections
- Elections for the House of Representatives are every two years
- Representatives must live in the district they represent and be a citizen of the state, and must be 25 years old
- Elections take place within each district
- Constituencies are smaller than senators’
- Incumbent election rates are very high (>90%)
- Less competitive
- Elections for the Senate are every two years
- Each term is six years
- Senators must be at least 30 years old
- More competitive, expensive, and high profile
- Draw candidates from other offices
- %%Baker v. Carr (1962)%%: Charles Baker sued Tennessee for not redrawing its state legislative districts because his county’s population had grown but not gained representation
- Violated 14th amendment (equal protection of the law)
- Ruled in 6-2 decision that the government can force states to redistrict every 10 years
- Led to the development of the “one person, one vote” doctrine
- Gave federal courts the right to weigh in on redistricting
- %%Shaw v. Reno (1993)%%: white voters living in North Carolina’s 12th district sued the state for gerrymandering to isolate African Americans into the 12th district
- Ruled in 5-4 decision that the state was using racial bias in its redistricting
- Violated equal protection clause
- Any racial gerrymandering required a compelling state interest
Congressional Districts and Representation
Voting Rights Act of 1965: encouraged states to increase minority representation in Congress
- Initially made little change
- 1982 amended to make states create majority-minority districts (concentrating minority populations into districts)
- Made it easier for minority candidates to get elected
- Many states redistricted after the 1990 census, resulting in an increase of minority representation
- District shapes were weird
- Legislators in NC, GA, TX, and other states have been accused of gerrymandering
- Black and Hispanic voters are majority Democrat, Republican-controlled legislatures were accused of trying to remove racial minority Democrats from districts to ensure more Republicans get elected
- Packing: isolating minorities in a district
- Cracking: dividing minorities across many districts
- Population shifts gave more seats in the House to Southern states but took away seats from other regions
- Suburban representation has increased, but both rural and urban have decreased
- Hijacking: redrawing two districts in a way that forces two incumbents to face each other in a single district
- Kidnapping: moving an incumbent’s home into another area after redistricting
Congressional Powers
- The Constitution lists out the responsibilities of Congress in more detail than the other branches
- Both houses have unique powers that require them to work together, including taxing, borrowing money, regulating commerce, raising an army, creating/making rules for courts, establishing naturalization laws, creating post offices, building a militia, and making laws
- Taxing and spending clause (Article 1, Section 8, Clause 1): gives Congress much control over budgetary spending
- “Power of the purse”: gives Congress power to influence others by preventing access to funds or adding conditions
- Can be used positively to fund programs or negatively to harm an agency
- House of Representatives can start spending bills and tax laws
- House of Ways and Means Committee: oversees spending laws and taxing
- Senate can approve presidential nominations to court and ambassadors to other countries
- Must also ratify all treaties the president signs
Non-legislative Tasks of Congress
Congress primarily writes laws
Oversight: reviews federal agencies’ work (checks executive branch), investigates charges of corruption, holds hearings (experts and citizens discuss government issues and propose solutions)
- All committee chairs can subpoena (legally compel) witnesses to show and testify
- Confirms members of presidential cabinet
- Approves nominees for federal court
Public education: floor debates and committee hearings increase awareness of government/social issues and help to focus national attention
Representing constituents within the government: politicos (representatives of electorates, Congress members) help constituents with the government and vote on laws; can act on complaints about federal services/agencies, sponsor those who seek contracts, and seek suggestions on improvement
- Delegate Model (representational view): consider themselves delegates who mirror the views of their districts
- Trustee Model (attitudinal view): some consider themselves trustees who should think about constituents’ views but use their judgement when making decisions
Constitutional amendments: can propose amendments by 2/3 vote in both houses or by a convention called by 2/3 of state legislatures
Electoral duties: House can elect next president if neither candidate gets 270 votes, Senate picks VP
Impeachment: House has power over impeachment; if majority votes to impeach an official, the Senate runs the impeachment trial and convicts/removes the official from office with 2/3 of Senate votes
Confirmation duties: Senate can approve both presidential appointments and federal officials
Ratification: only Senate can ratify treaties if 2/3 votes
- Senate can influence international relations and foreign policy
Investigation: can be conducted by either a standing or committee and may last months while members gather evidence and witnesses
- Majority lead to new legislation to address the issue, changes in programs, or officials’ removal from office
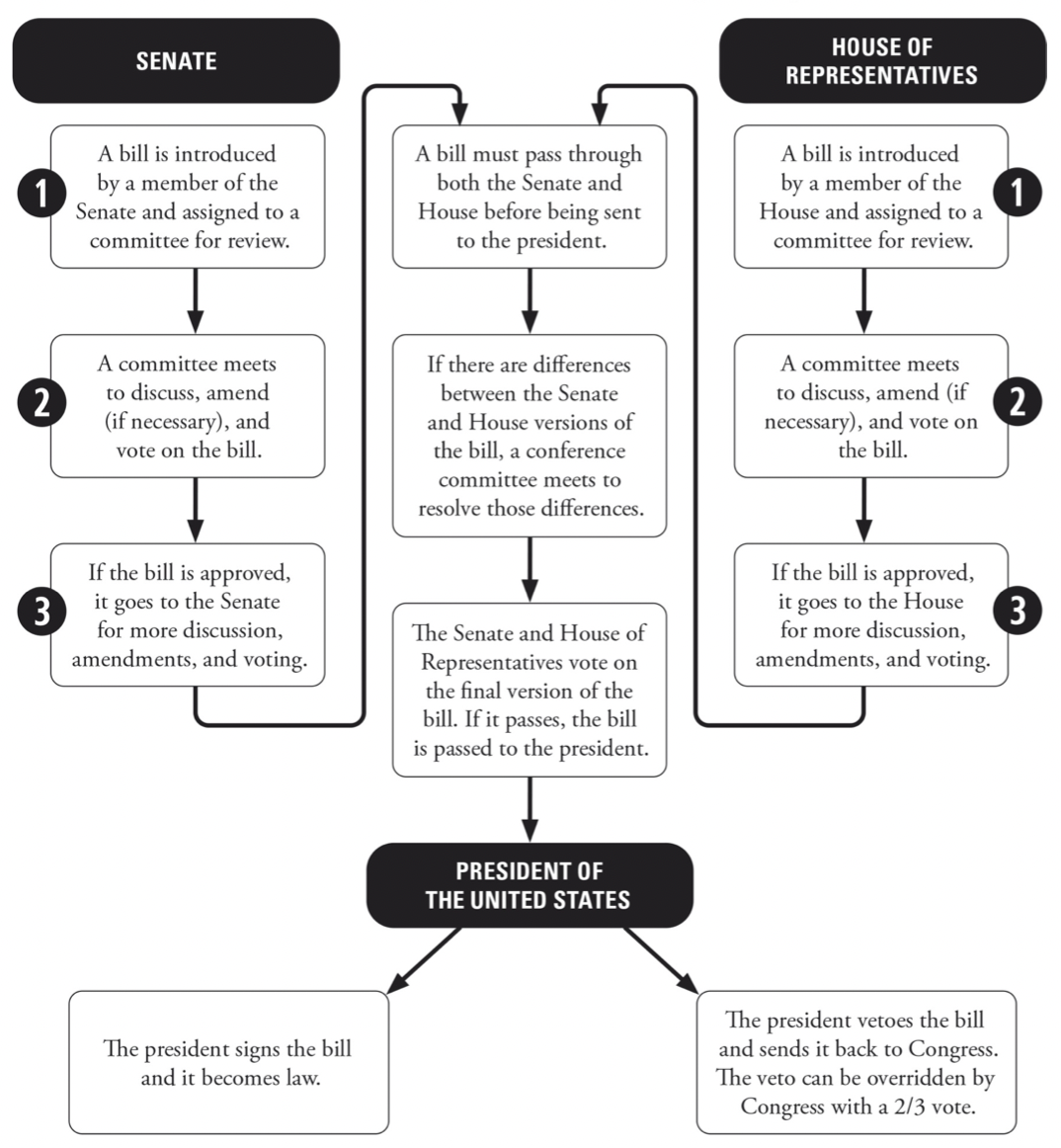
Legislative Process
Slow and complicated
- Prevents decisions from being made too quickly
- Facilitates compromise and communication between both sides
Bills
- 10,000 bills introduced every year
- Some written by Congress members and staff
- Others are written by executive branch and introduced by Congress members
- Many are written or suggested by interest groups + lawyers
- Can only be proposed by a Congress member (the sponsor of the bill)
- Requires two houses to work together
- Both houses must pass the same bills
- Different debate and voting processes
- House of Representatives:
- Debates about bills are limited in House of Representatives (too many people)
- Rules Committee: determines how long a bill will be debated and whether open or closed rules for amending bills are allowed
- Open rules allow amendments
- Closed rules forbid amendments
- Republicans (majority) in 1994 promised open rules for most bills
- Considered most powerful committee in House
- Can kill a bill by postponing vote or make it easy for an opponent to add killer (poison-pill) amendments
- Can bring bills up for immediate vote
- Senate:
- Does not strictly control debate, no time constraints
- Filibuster: used to delay bill’s vote and tie up Senate’s work, usually by a senator making a very long speech
- Can happen without speeches
- Senate majority may require a traditional filibuster if needed
- Cloture: the vote which is the only way to end a filibuster, requires votes of 60 members
- No closed rules
- Riders: amendments, do not have to be relevant to bill, allow senators to add amendments
- Pork barrels: “pet project” riders created to get money to a home state
- Earmark: provisions in legislation that allot money to a project (appropriation and authorization bills)
- Not allowed by House
- Conference committee: committee each house’s version of a bill is sent to which come from the committees of each house that wrote the bill
- Attempts to negotiate compromise bill
- Compromise bill returns to both houses for voting
- Failure to pass a compromise bill will kill it
- Sent to White House if passed for presidential approval
- President:
- Bill becomes law after 10 days if president does nothing regardless of signature
- Bill is pocket vetoed if president doesn’t sign every bill into law and congressional session ends during 10 days
- President can veto entire bill if congressional session doesn’t end in 10 days and gives reasons for vetoing
- Both houses can override veto by a two-thirds vote
- Houses can also make any required changes
- If house of origin does nothing with veto, bill is dead
- Line-item veto: given to President Clinton in 1996 by Congress, allowed the president to veto certain parts of a bill
- Clinton v. City of New York (1998): the Supreme Court struck down the line-item veto as an unconstitutional power of the president
- Congress has tried to give itself veto power over the president
- Wrote legislation giving Congress ability to void presidential actions by a vote of the houses
- INS v. Chadha (1983): Supreme Court declared legislative veto unconstitutional
Legislation by Committee
- Most legislative activities by Congress are in committees
- Committee members are determined by many factors
- Majority party of each house holds all committee chairs
- Also holds most seats on each committee (2/3 on important committees)
- Oldest/most experience member of majority party is chair and senior member from minority party is ranking member
- Ranking member becomes chair if minority party becomes majority party
- Assignments determined by House and Senate leaders + both parties’ caucus
- Try to get on committees that will help them help the constituents the most and with reelection
- Investigate and debate bills that otherwise wouldn’t be considered due to time
- Call interested parties and expert witnesses (often lobbyists)
- Congress can subpoena witnesses
- After investigations committees amend and rewrite parts of bills in meetings known as markup sessions
- Often first assigned to subcommittee for consideration
- Often determine how money is spent
- Most die because of lack of interest
- Membership of committee and subcommittee is crucial
- Bills written to appeal to certain committees
- Can refuse to vote a bill out
- Pigeonholed: a bill stuck in a committee
- Discharge petition: the way to force a bill out of committee for a floor vote
- Oversee bureaucratic agencies and departments
- Heads of agencies often appear before congressional committees
- Can subpoena witnesses (legally requires individuals to appear or produce requested documents)
- Can hear testimony from agency heads asking for money or people
- House has more committees and are more specialized because each member serves on fewer committees
- Types of committees:
- Standing committees: permanent, specialized
- Ex. House Ways and Means, Senate Judiciary, Senate Armed Services
- 17 in the Senate, 20 in the House
- Joint committees: made up of members of both houses
- Normally used for investigations or communicating with the public
- Select committees: temporary committees created in each house for a special reason
- Usually carry out investigations to write special bills
- Ex. House Watergate Committee, Senate Select Committee on Unfair Practices
- Conference committee: temporary committees made up of members from committees of both houses who wrote a bill
- Try to create compromise bills, then submit to both houses
- Disbanded once a compromise bill is negotiated
Congressional Leadership
The House
- The leader is the speaker
- Chosen by the majority party in an election
- Can direct floor debate and has influence over committee assignment and the Rules Committee
- Can control which bills are assigned to certain committees
- Majority leader is in charge of party members, determines party policy and agenda
- Minority leader is in charge of minority party members, determines party’s agenda
- Majority and minority whips help their leaders keep members loyal to the agenda, coordinate members, and get support for legislation
The Senate
- President of the Senate is the vice president, only official responsibility
- Only votes to break a tie
- President pro tempore is the temporary president when the VP is absent
- Mostly honorary position
- Usually given to oldest member of the majority party
- Majority leader controls agenda and acts as policy initiator and power broker
- Minority leader is similar, not policy initiator or agenda controller
Why Do They Vote That Way?
- Pressure to influence vote from own party and opposition
- President jawbones (tries to influence) and colleagues logroll (mutual help)
- PACs, constituents, and interest groups donate to try to influence votes
- Judgment can be affected by personal ideology and religion
- Party affiliation is most important factor
Notable Legislation
National Growth, Expansion, and Building Institutions
- Northwest Ordinance (1787, 1789): created by the Articles of Confederation, provided guidelines for settling new territories and creating new states, reaffirmed in the Constitution in 1789
Government and Industry Regulation
- Pendleton Act (1883): got rid of the spoils system for government job selection, set up exam-based merit system for candidates
- Sherman Anti-Trust Act (1890): gave Congress the power to regulate and disassemble monopolies in the US, abused to break up labor unions
- Hatch Act (1939): let government employees vote in elections but prevented them from participating in partisan politics
- Freedom of Information Act (1966): let the public view government documents
- Air Quality Act (1967) and Clean Air Acts (1960s-1990s): regulated environmental impacts by establishing standards for factories and cars
- Federal Election Campaign Acts (1971, 1974): created the FEC and required contributions and expenditures to be disclosed, created limits on presidential election expenditures and contributions, created subsidies for presidential candidates
- War Powers Act (1973): put limits on presidential power to use troops overseas, created time limit, gave Congress power to withdraw troops; all presidents have declared act unconstitutional since 1973
- Budget and Impoundment Control Act (1974): created Congressional Budget Office and congressional budget committees, gave Congress authority to prevent president from refusing to fund congressional initiatives
- Gramm-Rudman-Hollings Bill (1985): created budget reduction targets to balance the budget; failed to eliminate loopholes
- No Child Left Behind Act (2001): states must adopt education accountability standards, requires annual progress testing, and sanctions schools that fail to meet the yearly progress goals
- Unfunded Mandates Reform Act (1995): Congressional Budget Office must analyze impact of unfunded mandates on states, must have separate congressional vote on bills that impose them
Rights and Freedoms
- Espionage Act (1917), Sedition Act (1918): greatly reduced rights of Americans during war and increased federal government’s power to control public activity; repealed by Congress in 1921
- Immigration Act (1924): limited number of immigrants entering the US and set strict standards for entry
- Voting Rights Act (1965): eliminated literacy tests, let federal officials register voters, prevented states from changing voting procedures without the government’s approval; let federal officials count ballots and make citizens vote
- Age Discrimination in Employment Act (1967): prevented age discrimination in jobs unless job is affected by age
- Civil Rights Act or Fair Housing Act (1968): Title II prevented discrimination in public places based on race, color, national origin, or religion, Title VII banned employment discrimination based on gender
- Title IX Education Act (1972): banded gender discrimination in federally funded education
- Americans with Disabilities Act (1990): protected disabled Americans’ rights and required accommodations to public facilities; prohibited job discrimination if accommodation could be made, required access to facilities for the disabled, allowed non-paid leave of absence without fear of firing
- National Voter Registration Act (1993): AKA The Motor Voter Act, allowed people to register to vote when receiving driver’s licenses
- Patriot Act (2001): After 9/11, Congress permitted police authority to federal, state, and local governments to interdict, prosecute, and convict suspected terrorists; known as the USA-PATRIOT (Uniting and Strengthening America by Providing Appropriate Tools Required to Intercept and Obstruct Terrorism) Act
Government Aid to the People
- New Deal Legislation (1933-1939): expands role of government in society and the economy; created Social Security, the Tennessee Valley Authority, and the Securities and Exchange Commission; expanded role and size of government
- Personal Responsibility and Work Opportunity Reconciliation Act (1996): Welfare Reform Act signaled change in national role with states, tried to increase role of personal responsibility in welfare recipients, shifted many responsibilities to state governments for welfare provision, ended federal entitlement status of welfare, replaced with block grants to states; recipients of grants had to work within 2 years and could not get benefits > 5 years
- Bipartisan Campaign Reform Act (2002): AKA McCain-Feingold Bill; banned soft money to national political parties and raised hard money limits to 2,000 dollars; SCOTUS struck down several parts of this law in %%Citizens United v. FEC%%, especially parts related to donations made by corporations
The President
The Formal Powers of the Presidency
- Article II, Section 2 of the Constitution
- Responsible for serving as the ceremonial head of state, handling foreign policy, and enforcing laws
- Administrative head of government
- Can force Congress into session, brief Congress on State of the Union, veto legislation
- Must cooperate with Congress (checks and balances)
- Can appoint federal judges, SCOTUS justices, ambassadors, and department secretaries that must be approved by the Senate
- Negotiates treaties that must be ratified by 2/3 of the Senate
- Executive agreements do not require Senate approval, agreements between country leaders
The President as Commander in Chief
- Commander in chief of the armed forces
- Only Congress can declare war, but president can make war
- Can mobilize armed forces
- Chief strategist and director of military
- Relies on Congress for money
- Gulf of Tonkin Resolution (1964): gave president broad powers to bring unlimited troops for unlimited time to Vietnam
- War Powers Act (1973): passed in an attempt to make president get congressional approval before making war, limiting president to 10,000 troops or 60 days and 30 additional days to withdraw
The Informal Powers
- Build morale
- Lead legislation and build coalitions
- Set legislative agenda
- Important when government is divided
- Chief of party
- Influence on party’s agenda, issues, policy, strategy, and direction
- Divided government: when the president and majorities in houses are not from the same political party
- Unified government: when the house majorities and the president are from the same political party
- Persuade policy and communicate to Congress and the country
- Bully pulpit lets the president speak with the American people and helps them to pressure Congress
- Theories about how the president chooses to use power:
- Literalist doctrine: president only has the powers listed in Article II of the Constitution and should not use power that is not granted; not followed by any president 1920s
- Stewardship doctrine: gives the president the ability to use power in multiple ways and arenas; free to use any power not denied to them by the Constitution; increases power of president
- Unitary executive theory: gives executive branch nearly unlimited power to develop any policy that is necessary
Executive Office of the President
- Helps carry out president’s administrative responsibilities
- Made up of agencies involved in the White House, divided into domestic, foreign, and military areas
- Chief of staff: top aid to the president; very trustworthy and known for a long time; considered extremely powerful, manages Executive Office, controls access to president (+ information received by president)
- National Security Counsel (NSC): headed by national security advisor, direct access to president in situations related to the military or foreign policy; involved during national emergencies, free from congressional oversight, favored by president
- Domestic Policy Counsel: helps the president create policies related to agriculture, education, energy, natural resources, drug abuse, crime, health, the economy, and welfare
- Office of Management and Budget (OMB): prepares US budget and used to control/manage executive agencies; very powerful because it is able to fund cabinet departments and control the department’s effectiveness
- Council of Economic Advisors: helps the president make economic policy; made of economists to advise president
- US trade representative: negotiates trade and tariff agreements with help from the White House
The Cabinet
- Created through custom and usage, not by the Constitution
- Cabinet departments created by acts of Congress to control executive branch responsibilities
- Cabinet secretaries appointed by president + approved by Senate
- Able to be dismissed by president
- Run departments, carry out policies
- Used to deflect criticism and explain/promote policy
- Fight for their own department => friction between departments
- Presidents don’t usually hold full cabinet meetings
- 15 cabinet departments in total (latest: Department of Homeland Security, created after 9/11)
Impeachment
- Gives Congress the ability to remove president for crimes
- Crimes undefined by Constitution-- up to legislative branch to decide
- House of Representatives impeaches president (brings charges) by majority vote
- Senate holds trial with Chief Justice presiding if impeachment passes w/two-thirds vote to remove president
- Political disagreement over when impeachment should be used
- Every impeachment has divided Congress between parties
- No president has been removed from office
- House impeached Andrew Johnson for violating Tenure in Office Act, Senate fell one vote short of removing him from office
- Watergate scandal caused Richard Nixon to resign before impeachment could begin
- Impeachment of Bill Clinton for lying under oath was political, slim chance of Senate conviction
- Donald Trump impeached for abuse and power and obstruction of Congress, but not convicted by Senate
- Federal judges can only be removed by impeachment and have lifetime terms
- Only 8 have ever been removed
The Judiciary and the Law
American Legal Principles
- Equal justice under the law
- Due process of law
- Substantive due process: whether laws are fair
- Bill of Rights, 14th Amendment, Constitution
- Procedural due process: whether laws are applied fairly
- Adversarial system
- Both sides must be represented
- Opposite = inquisitorial system
- Presumption of innocence
- Innocent until proven guilty
Types of Law
- Most legal cases involve civil law or criminal law
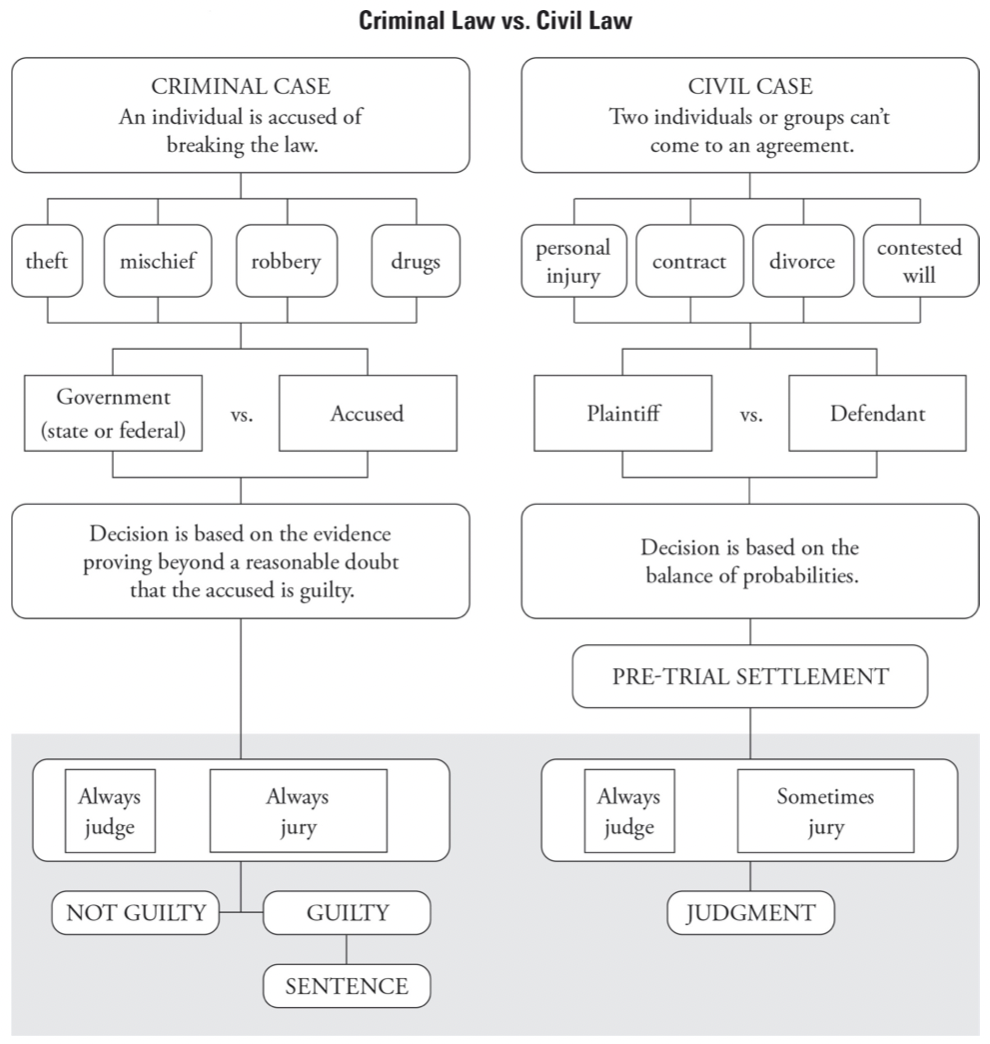
- Criminal law involves crimes that harm others
- Suspect arrested and to be indicted by grand jury (24-48 jurors, decide whether or not trial should begin
- If accused is indicted they have the option of plea bargaining with the prosecution to agree to a less serious crime and sentence
- Most cases end in plea bargains
- State/US opposes accused in criminal trials
- Prosecution should prove guilt beyond a reasonable doubt
- Held before petit juries (12 people), decision known as verdict
- Guilty verdict only returned if all 12 jurors vote to convict
- Split jury = “hung jury”, results in a mistrial
- Civil law solves conflicts over custody, contracts, property, or issue of liability
- Government is not involved unless it is being sued
- No prosecution
- Plaintiff vs. defendant in civil court
- Case moves forward if judge/jury thinks complaint has merit, settlement is used to avoid trial
- Settlement = how much each party is willing to give up
- Plaintiff only needs to show that a preponderance of evidence favors their side (~51% of evidence)
- Juries can be made of as few as 5-6 members
- Winning can result in payment of monetary damages or equity (loser forced to stop doing something that was annoying or harmful)
Structure of Jurisdiction
- Federal courts responsible for interpreting/settling disputes from federal law
- State courts responsible for interpreting/settling disputes from state law
- Three levels of federal courts:
- Federal District Courts: have original jurisdiction
- Federal Circuit Court of Appeals: hear cases on appeal from District Courts
- Supreme Court: hears appeals of cases dealing with the constitution from Circuit Courts and suits between states or cases involving foreign ministers
- No jury
- Collegial court - decisions made by 9 justices
- Acts in appellate jurisdiction, can only decide issues of law and not facts of a case
- 94 Federal District Courts
- Inferior to Supreme Court
- Civil and criminal cases in original jurisdiction
- Trial court that determines guilt/innocence is court of original jurisdiction
- Heat evidence and use juries to decide verdict
- dDecide liability in civil cases with monetary losses
- Also have juries
- Defendant can ask judge to decide a case, but a judge can refuse and force the defendant to have a jury trial
- 13 Circuit Courts of Appeals
- Hear cases on appeal from Federal District Courts or state Supreme Court
- Someone has to claim that a federal constitutional right has been violated
- Decide issues of law and not fact
- No juries - decisions made by panels of appointed judges
- Court of last resort, Supreme Court almost never hears cases appealed from the Circuit Courts
- Origins of most Supreme Court justices
The Politics of the Judiciary
- All judges are appointed by the president for life
- Must go through confirmation process in Senate
- Impeachment is only method of removal
- Appointments have become political
- Some presidents have required potential appointees to fill out a questionnaire to determine political/judicial ideology
- Nominees almost always of same party as president
- In nomination hearings before Senate Judiciary Committee, both parties try to determine how appointees would rule in cases dealing with their issues
- American Bar Association evaluates nominee’s qualifications and interest groups often show their opinions
- Senators in a state where an appointee will sit have exercised senatorial courtesy - submit a list of acceptable nominees to president
- Expected only when president and senators are the same party
- Ideological changes in Court’s makeup has resulted in new precedents and rejection of old precedents
- More precedents overturned since 1950s than in 150 years
- Courts are seen as the least democratic, when they overturn an act of legislature they are overruling the people’s will
- Judges who are hesitant to overturn legislature practice judicial restraint
- Liberals see judges as constitutional interpreters who reflect the people’s values
- Judicial activist: a judge who will readily overturn an act of legislature
Process by Which Cases Reach the Supreme Court
- Not part of the Constitution
- Supreme Court will not grant an appeal until all other opportunities in lower courts have been exhausted
- Often refuses to hear appeal because it agrees with lower court decision
- If 4 justices agree to review lower court’s decisions, court issues a writ of certiorari - document used to request lower court transcripts of case
- Only rules in cases that involve an actual legal dispute (justiciable)
- Places limits on who can bring cases before it - petitioner must have interest in case outcome (have standing)
Judicial Review
- Not in the Constitution
- %%Marbury v. Madison (1803)%%:
- Chief Justice John Marshall established judicial review
- John Adams commissioned William Marbury as Justice of the Peace in DC in the last hours of his presidency, approved by Senate; President Jefferson ordered Secretary of state to not deliver commission
- Article III, Section 2 of Constitution - what is the extent of the Supreme Court’s power regarding judicial review?
- Ruled that the part of the Judiciary Act allowing the Supreme Court to grant the position of Justice of the Peace was unconstitutional
How the Court Hears Cases
- Both sides submit summaries of their arguments (briefs) and legal foundations
- Interest groups affiliated with both side of the case submit their own briefs
- Amicus curiae briefs: effort to sway the justices, can be very influential
- From October to April, court hears oral arguments for cases
- Lawyers for each party have 30 minutes to present their arguments before the justices
- Federal government will often take one side, solicitor general can argue on the government’s behalf
- Known as the “tenth justice”
- Second-ranking member of the justice department
- Often makes appearances before the high court
- Justices meet for a secret meeting after the oral arguments, cast votes, and write opinions
- Four types of opinions:
- Unanimous opinion: all justices agree, carries most force in future legal cases, ex. Brown v. Board of Education
- Majority opinion: the opinion with the most votes, decides the case
- Concurring opinion: justices may vote with majority but take issue with legal reasoning
- Dissenting opinion: written by justices in the minority, questioning the winning side
- Power of Supreme Court limited through:
- Constitutional amendments
- Judicial appointments/confirmations
- Legislation that changes court jurisdiction
- Legislation written to counteract Supreme Court decisions
- President and states refuse to comply with Supreme Court decisions
The Bureaucracy
Ensures that policies and programs created by Congress and executive branch are carried out
Considered part of the executive branch
Supposed to function above partisan politics
Bureaucrats operate under merit system - hires and promotes people based on skills and experience
15 cabinet secretaries and heads of independent agencies appointed by president and approved by Senate
Most people who work for the government work for one of the executive departments or other “cabinet level” agencies
Department of Defense: largest department, administered by Secretary of Defense
- Reports directly to president
Each military service is led by a uniformed chief of staff
- Work together as the Joint Chiefs of Staff, carry out defense policy and report directly to president and Secretary of Defense
Policy implementation: primary role of the bureaucracy, determines the process for implementing policy once passed
- Must act within constitutional limits and agency jurisdiction
- Can develop rules to govern policies and procedures
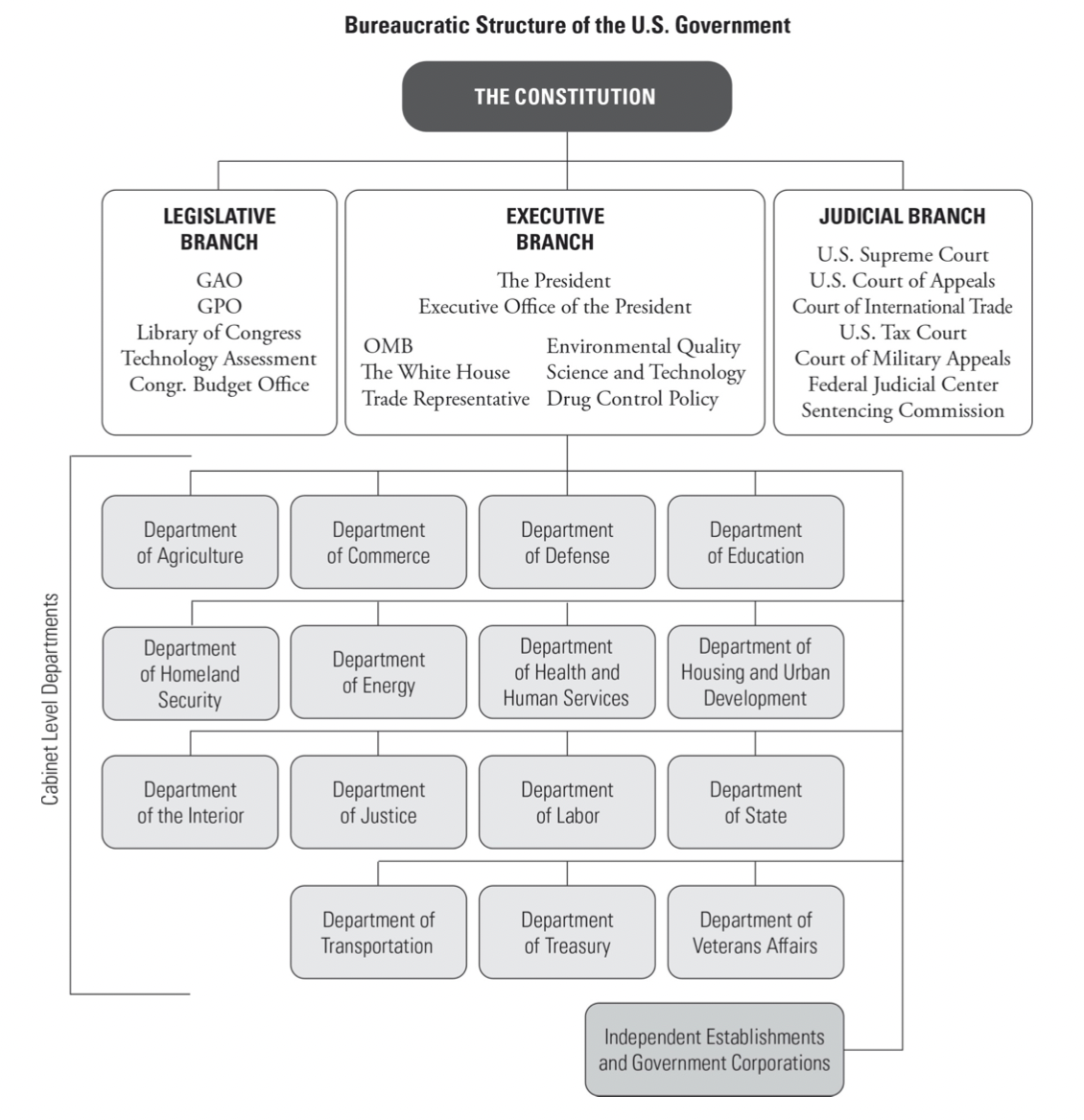
Secretary of department at head of each “pyramid”
- Appointed by president, approved by Senate
- Undersecretary is direct subordinate, appointed by president without Senate approval
- Both undersecretary and secretary replaced at the end of president’s term
- Personnel of Senior Executive Service below the secretaries, including appointed and non-appointed
- Do not need Senate confirmation
- Responsive to White House policy goals and help bureaucrats implement president’s policy preferences
Government Corporations
- Hybrid organizations, private business corporation + government agency
- Freedom of action and flexibility, produce revenue to support themselves
- Ex. Amtrak
- USPS was originally created as a cabinet position but has become a government corporation
- Corporation for Public Broadcasting produces and airs television and radio
- PBS funding comes from private and government subsidies
- Most programming related to public affairs, news, and culture
Regulatory Agencies and Commissions
- Not within 15 cabinet departments
- Two categories:
- Independent agencies: generally normal bureaucracies with presidential oversight
- Regulatory agencies/independent regulatory commissions: more independence, act as watchdogs over federal government; Congress and president are not supposed to interfere
- Writing legislation is complex and often beyond lawmakers’ abilities and expertise - often written in general terms with many gaps
- Quasi-legislative agencies: independent agencies who fill in gaps and write rules
- Quasi judicial agencies: rule enforcement, punish violators
- Bureaucrats often has answers for Congress
- Asked for advice and expertise
- Often ignored because of interest groups’ pressure
- Write and enforce rules that regulate environment, economy, or industry
- Examples of regulatory agencies:
- Federal Trade Commission: prevents fraud in marketplace, prevents price fixing and deceptive advertising
- Securities and Exchange Commission: protects investors by regulating stock markets and preventing corporations from false and misleading claims of profits
- Nuclear Regulatory Commission: controls how power companies design, build, and operate nuclear reactors
- Federal Communications Commission: assign broadcast frequencies, license radio/TV stations, regulate use of wireless communication
- Food and Drug Administration: inspect food supply, regulate sales of over-the-counter drugs and patent medicines
- Federal Energy Regulatory Commission: prevent price fixing and price manipulation in energy
- Occupational Safety and Health Administration: ensures a safe work environment for workers
Who Runs Regulatory Agencies?
- Run by Board of Commissioners (panels of administrators)
- Appointed by president with Senate approval
- Terms usually overlap president’s term, intended to minimize White House political pressure
- Term is 3-14 years
- Ex. Federal Reserve Board: policies affect public’s buying power - regulates banks, monetary value/supply, and interest rates
- Policies can conflict with president’s policies
Who Controls the Bureaucracy?
- Political considerations always play a part in the appointment process, but presidents and boards/commissions vary regularly
- Rank-and-file bureaucrats are permanent, but they do not like political interference
- Presidents can promote supporters and use budget to change agency’s influence while in office
- More congressional power over bureaucracy than presidential
- Senate affirms/rejects appointments
- Congress can destroy agencies or change jurisdiction
- Final say over funding
Rule Setting, Alliance Building, and Iron Triangles
- Regulatory agencies set rules and regulations that industry must follow
- Participatory process, industry involved in determining rules
- Hold public hearings for testimony and advice
- Law requires agencies to consult with industry in most cases before rules/regulations can go into effect
- Iron triangle: informal alliance made of three groups: particular industry + lobbyists, congressional committee dealing with that industry, and the agency that is affected
- Groups that make iron triangle work together to create and implement policy
- Lobbyists representing industries promote their agendas by claiming it is in the best interest of the American people
- Special interests contribute money to congressional campaigns, large donators ask for help from representatives
- Alliance/issue network: a close working relationship formed when issues affect many groups by pro/con coalitions of interest groups, Congress members, and bureaucrats
- Regulatory agency writes/publishes rules after input and debate opportunities have been exhausted
- Industry can sue regulatory agency if it objects to regulation
- Deregulation: removing government restrictions and regulations
- Those in favor claim that competition of marketplace is all that is needed
- Regulation is expensive and time-consuming
Civil Service and Maintaining Neutrality
- Civil service system: Office of Personnel Management is bureaucracy’s employment agency, administers civil service examination, publishes job opening lists, and hires based on merit
- Established in 1883 by the Pendleton Act, which ended the patronage system (giving government jobs for political support)
- Intended to create a competent, professional bureaucracy
- Merit Systems Protection Board investigates charges of agency corruption, protects whistleblowers
- Hatch Act (1939): passed to ensure bureaucratic neutrality; permits bureaucrats right to vote but not the right to campaign for political candidates, run for office, or work for parties
- Revision of 1993 is less restrictive - bureaucrats can join political parties, make campaign contributions, and display political advertising (buttons/bumper stickers)
- Still cannot run for public office, solicit campaign funds from subordinates, or make political speeches