3 - GI physiology three
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
what form is fat digested in?
triclyglycerol
what is fat digested by
pancreatic lipase in small intestine
what is lipase
water soluble enzyme
why is fat digestion slow?
digestion can only take place at surface of triclyglycerol droplet
what is emulsification
breaking down of large fat droplets into smaller droplets
why is emulsification important?
increases surface area and accessibility to lipase speeding up fat digestion
what does emulsification require
mechanical disruption
emulsifying agent
what is mechanical disruption
large droplets to small droplets - smooth muscle contractions to grind and mix - lumen contraction
emulsifying agents purpose
prevention of small fat droplets reforming into large droplets
what are emulsifying agents made of?
bile salts and phospholipids
prevent small droplets reforming into large droplets
what type of molecule are emulsifying agents
amphipathic - non polar part and polar part
how is fat absorption enhanced
formation of micelles
what are micelles
bile salt + monoglycerides + fatty acids + glycerol
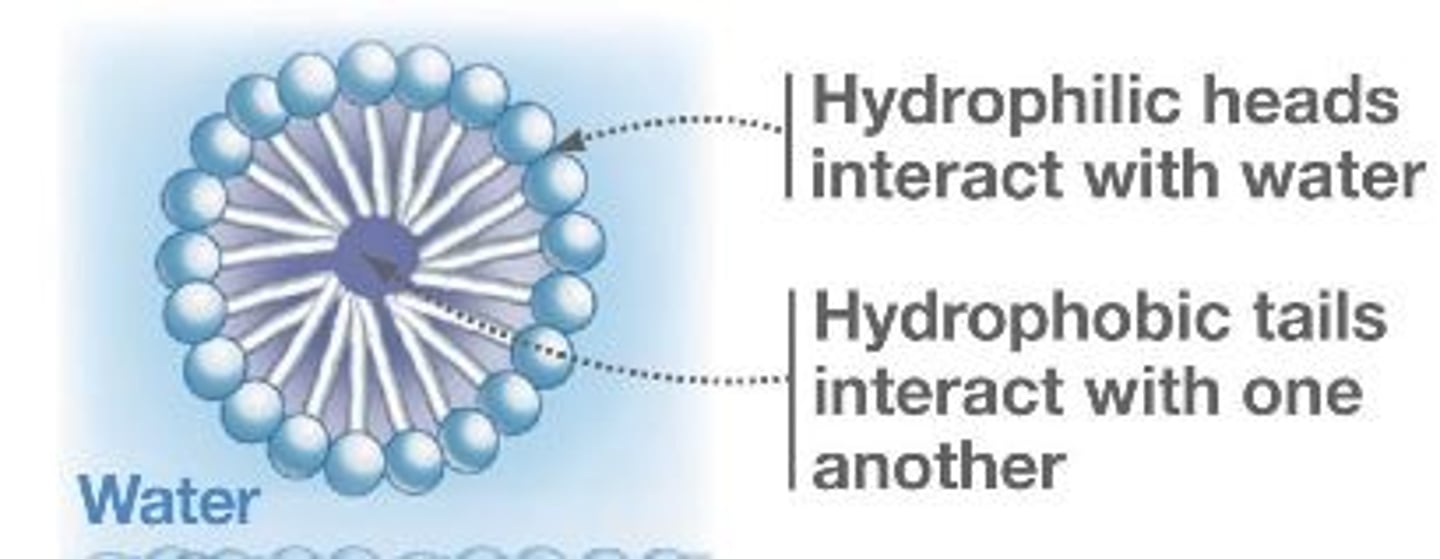
fatty acid micelle structure
HYDROPHOBIC
- fatty acids and monoacylglycerols in interior
- bile salts on exterior
micelle breakdown 2 steps
release small amount of free fatty acids and monoglycerides into solution
diffusion across plasma membrane of absorbing cells
micelles are not.... during fat absorption
ABSORBED
why is dynamic equilibrium important between fatty acids and monoglycerides in solution and in micelles
retains most of fat products in solution while constantly replenishing supply of free molecules for absorption
after entering epithelial cells where do fatty acids and monoglycerides go?
enter smooth endoplasmic reticulum
what happens to fatty acids and monoglycerides within SER
reformed into triacylglycerols by enzymes
what happens to triacylglycerols in SER
coated with amphipathic coating for emulsification
where do triacylglycerols go after SER modification
droplets transported through cell in vesicles to be processed by golgi and exocytosed into ECF at serial or basolateral membrane
what are extracellular fat droplets called
chylomicrons (smallest one)
what do chylomicrons contain
phospholipids
cholesterol
fat soluble vitamins - ADEK
what to chylomicrons pass to and why?
pass into lacteals between endothelial cells as they cannot pass through capillary basement membrane
2 classes of vitamins
fat soluble
water soluble
how are fat soluble vitamins absorbed
Same way as fats with them
how are water soluble vitamins absorbed (B,C and folic acid)
diffusion (passive) or by carrier mediated transport
what is vitamin B12
large charged molecule
How is vitamin B12 absorbed?
binds to intrinsic factor in stomach
froms B12 complex
absorbed via specific transport mechanism in distal ileum
B12 deficiency
pernicious anemia - failure of RBC maturation
how is iron absorbed?
iron transported across brush border membrane via DMT1 into duodenal enterocytes
incorporated into ferritin to create protein-iron complex as an intracellular iron store
unbound iron transported across serosal membrane into blood
hyperaemia
increased ferritin levels - more iron bound in enterocytes - haemochromatosis
anaemia
lack of iron due to decreased ferritin
what percent of daily ingested iron absorbed crosses the intestine into the blood
10%
Which Vitamin enhances iron absorption
Vitamin C
reduces ferric (3+) to become ferrous (2+) which is absorbed
Heme iron
from meat & fish
10% food iron, 25% absorbed
non heme iron
from veg, milk, egg
90% food iron
10% absorbed