Unit #5 - Erythrocytes
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
A set of flashcards based on key concepts, definitions, and facts about erythrocytes to aid in exam preparation.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
What will a CBC measure alongside the WBC population?
Erythrocytes and thrombocytes.
Define MCV.
Mean cell (corpuscular) volume – a direct measure of the cell size.
What does MCH stand for and what does it measure?
Mean corpuscular hemoglobin – the amount of hemoglobin in the red cells.
What is the definition of MCHC?
Mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration – the average percent measurement of hemoglobin concentration in each red blood cell.
What does RDW stand for?
Red-cell distribution width – indication of the variation in the mean cell volume of erythrocytes, reported as a percentage.
What is HCT?
Hematocrit or PCV (packed cell volume), given as a percent.
What is a polychromatic cell?
An immature RBC that is slightly larger, stains pale blue and has no nucleus.
What percentage of polychromatic cells is considered normal in cats and dogs?
1-2%.
Should polychromatic cells be seen in circulation in horses or cows?
No, maturation of RBC happens in the marrow.
What is the name for a nucleated erythrocyte?
Metarubricyte.
What are the three parts of an erythrocyte?
Hemoglobin, RBC membrane, biconcave disc.
What is the function of hemoglobin?
It carries oxygen.
What does the RBC membrane help facilitate?
deformable/flexible gives the ability to pass through small vessels, biconcave disc-high surface area to deliver O2
What does the RBC enzyme system help facilitate?
provides energy for Na+ pumps, maintains hemoglobin and membrane function, facilitates 02 release into tissue
What is Rouleaux formation?
RBC’s that lack the zeta potential, causing them to stick together; may be due to inflammatory proteins.
Name the two possible ways RBC’s get removed in the body where does this mainly occur?
Extravascular Hemolysis- most common
Intravascular lysis
What is the primary site for extravascular hemolysis?
Liver and Spleen-Phagocytosis by macrophages (most common)
Is conjugated bilirubin water soluble?
yes
What does yellowing of the eyes and mucus membrane indicate in a dog?
Abnormal breakdown of RBC’s resulting in excess bilirubin in the blood, causing jaundice.
Where on a blood smear do we examine erythrocytes?
Monolayer – in the body of the blood film.
Define macrocytosis, microcytosis, and anisocytosis.
Macrocytosis - larger than normal; Microcytosis - smaller than normal; Anisocytosis - variation in size beyond expected.
What color classifications of RBCs are there?
Polychromatophilic- shades of blue to blue grey when stained
normochromic,- normal color
hypochromic- pale RBC due to a decrease in hemoglobin
hyperchromic- increased color due to increased hemoglobin (there are no conditions that cause an increase in hemoglobin, you can only push so much hemoglibin into an RBC, usually due to spherocytes present, (thicker cell)
What is poikilocytosis?
A term for abnormally shaped red blood cells.
What are the three parts an old RBC breaks into after breakdown?
Iron
Hemoglobin (which splits into heme and globin),
Unconjugated bilirubin.
What protein carries oxygen in a RBC?
Hemoglobin.
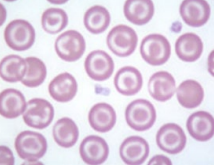
Name
Target cell
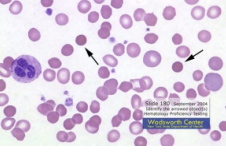
Name
Spherocytes
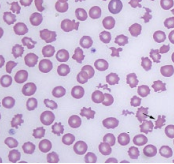
Name
Shistocytes