comp 2
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
cells and organelles, body tissues
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
List the functions of a cell (4 marks)
to metabolise and produce energy
to synthesise molecules
communicate with other cells and surrounding environment
to divide, reproduce and pass genetic information
Draw the plasma membrane and label its structural components. What are three functions it possesses?
phospholipid bilayer (hydrophilic and hydrophobic), cholesterol (45-50%), carbs (4-8%), proteins (45-50%), glycocalyx
encloses intracellular content
controls and regulates substances moving in/out of cell
establishes resting membrane potential
Organelles suspend within cytoplasm. What does cytoplasm also contain and describe what this includes
cytosol - fluid mixture of ions and proteins with water
contains cytoplasmic inclusions: microtubules, microfilaments, intermediate-filaments
Draw a simple diagram of the nucleus, including all of its components (4). What is its main function? (2 marks)
controls movement and activity within cell
carries the code for structural and functional characteristics for cell
Ribosomes are produced by the nucleolus. What does it do?
site of protein synthesis, combines amino acids into chains of protein
Draw the cell and all of its main organelles
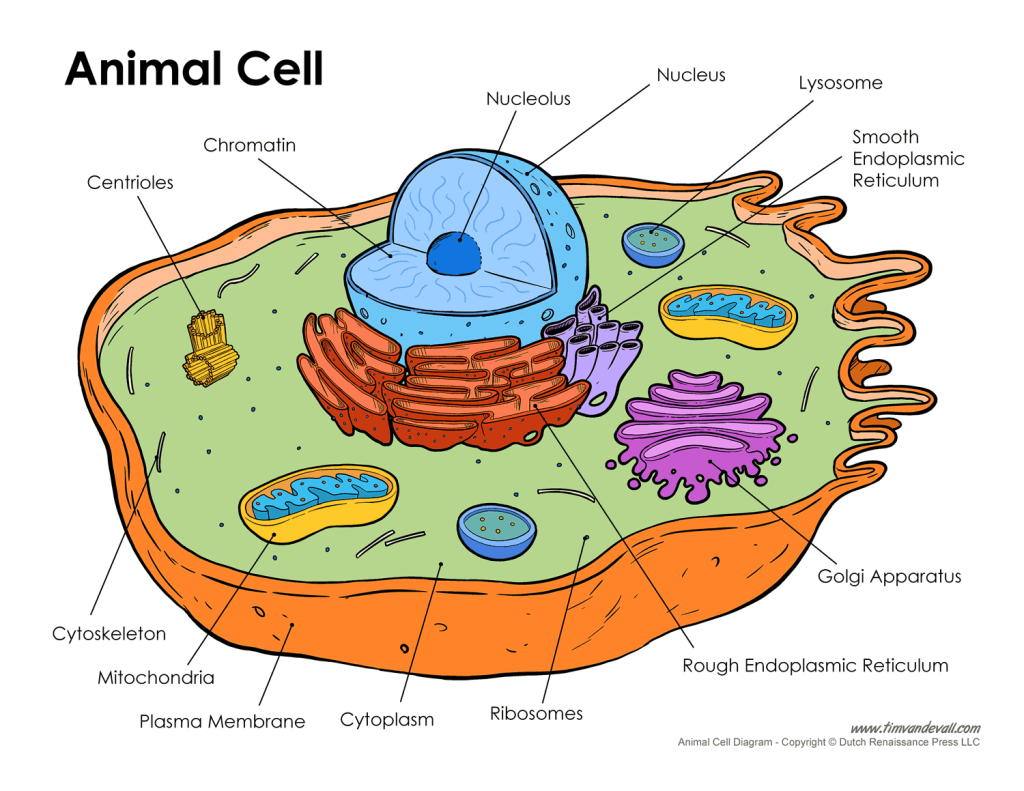
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) can be rough or smooth, differentiate between the function of the two.
rough ER - joins amino acids together to form proteins; synthesises and modifies proteins
smooth ER - site of lipid, steroid and carb synthesis, detoxifies harmful substances
Draw the golgi apparatus with its cisternae and secretory vesicles. What is its main function?
modifies, packages and distributes proteins and lipids from rough ER for secretion via lysosomes
What is the function of lysosomes?
contains enzymes which breaks down wastes within cell
What is the function of centrioles?
cell division
Mitochondria consists of two structures: the outer and inner membrane, and a matrix in between. What is the purpose of mitochondria?
mainly produces and supplies ATP
What’s the difference between cilia, microvilli, flagella
cilia: large extensions, moves substances across surface of cell
microvilli: smaller extensions, increases surface area
flagella: one long projection, enables motility
What is the purpose of cytoskeleton and how does it differ from cytosol
cytoskeleton: moves organelles and changes cell’s shape
cytosol: fluid portion of cytoplasm with a mixture of ions and proteins
histology
the study of tissues
Epithelial tissue are able to regenerate, are avascular but innervated. It’s purpose is to cover and protect structures, but what are the characteristics that it is made of? Draw a diagram
free surface, basal layer, lateral surface
Simple squamous epithelium is a single layer of flattened cells. What does it allow and where is it commonly found?
diffusion, filtration
alveoli, nephron serous membrane of pleura (lungs)
Simple cuboidal epithelium are cubed-shaped and some can have microvilli/cilia. This type of epithelium can be found in kidney tubules and terminal bronchioles, therefore what is its function?
absorption, secretion, movement
Simple columnar has a lot of cellular material, therefore cellular activity. As it allows absorption and secretion, where may it be found?
small intestines, stomach, digestive tract, lungs
Transitional epithelium can change in shape depending on the amount of fluid it holds. Where is this type of epithelium typically found?
bladder, ureter, upper part of urethra
Stratified squamous protects against abrasive due to its multiple layers. What are the two types and how are they different?
keratinised: waterproofing, eg. skin
non-keratinised: prone to abrasion, eg. vaginal canal
Stratified cuboidal is very rare and secretory, only found in ___ and ___
sweat ducts and salivary glands
Stratified columnar is a rare tissue type only found in ___ and ___
mammary gland ducts
larynx
Pseudo-stratified columnar are found in mostly the respiratory system, such as pharynx and trachea. What are its functions?
secretion and movement
What are the main characteristics of connective tissue?
few cells and lots of extracellular matrix (ground substance and fibres)
Describe three functions of connective tissue
transports, connects and binds together, supportive, provides energy
CT cells, ground substance and fibres are apart of CT composition. List the different types of connective tissue cells.
adipocytes, fibroblasts, mast cells, white blood cells (leucocytes), macrophages
CT cells, ground substance and fibres are apart of CT composition. What is the ground substance of CT?
fills space in between CT cells and where fibre is suspended
CT cells, ground substance and fibres are apart of CT composition. Differentiate between the 3 types of fibres
collagen fibres - rigid and strength
elastic fibres - stretches and recoils
reticular fibres - thin and supportive network