Psychology motivation and emotion
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
motivation
The process that initiates, guides, and maintains goal-oriented behaviors. It is the driving force behind human actions and influences the intensity and direction of effort.

drive-reduction theory
A psychological concept that suggests motivation arises from the desire to reduce internal tensions caused by unmet biological needs, leading to behaviors that fulfill those needs.
homeostasis
The theory that motivation arises from the need to maintain physiological balance, whereby behaviors are driven by the desire to reduce internal tensions caused by unmet biological needs.
incentive theory
A theory suggesting that behavior is motivated by external rewards and stimuli, emphasizing the role of incentives in driving actions.
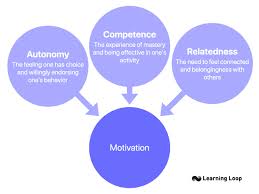
self-determination theory
A theory of motivation that emphasizes the importance of intrinsic motivation and the role of autonomy, competence, and relatedness in driving human behavior.
intrinsic motivators
elements that arise from within an individual, such as personal satisfaction, interest, or the joy of learning.

extrinsic motivators
Factors originating from outside an individual, such as rewards, recognition, or other external incentives that drive behavior.
arousal theory
a theory suggesting that individuals are motivated to maintain an optimal level of arousal and that this level varies based on the task at hand.
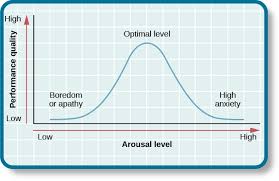
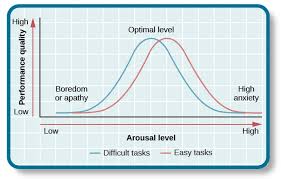
yerkes-dodson law
the principle that performance is affected by arousal levels, suggesting that there is an optimal level of arousal for peak performance.
instinct theory
a psychological theory that suggests behaviors are driven by innate instincts or biological urges, influencing motivation and actions.

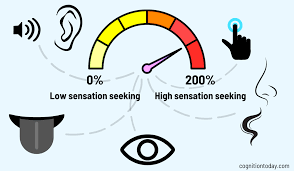
sensation-seeking theory
a theory emphasizing the pursuit of experiences that are novel and intense, suggesting that individuals have varying thresholds for arousal and seek out activities that match their needs.
motivational conflicts
situations where a person faces opposing drives or incentives, often leading to stress or difficult decision-making.
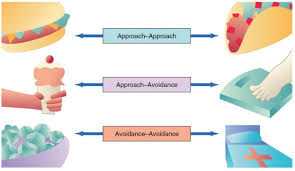
approach-approach
conflict involving two appealing options where choosing one option means losing the other.

avoidance-avoidance
conflict involving two undesirable alternatives, where choosing one means facing the other.

approach-avoidance
conflict involving a single option that has both positive and negative aspects, leading to indecision.

affiliation/belongingness theory
This theory posits that humans have a fundamental need to form and maintain personal relationships, and that social connections are vital for emotional well-being.
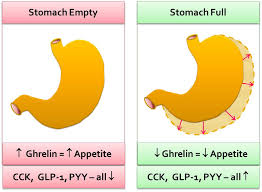
hunger
the physiological need for food, which drives the desire to consume.

ghrelin
A hormone that stimulates appetite and signals hunger to the brain.
leptin
A hormone produced by adipose (fat) tissue that helps to regulate energy balance by inhibiting hunger, thereby helping to maintain body weight.
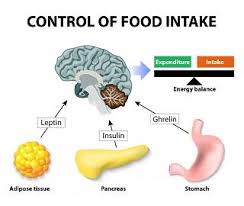
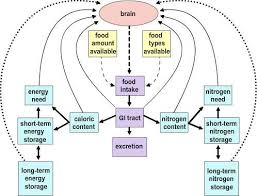
hypothalamus role in eating
The hypothalamus regulates hunger and satiety by responding to hormone signals like ghrelin and leptin, influencing food intake and energy balance.
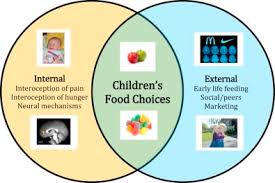
external factors on eating
Influences such as social settings, environmental cues, and cultural norms that affect food choices and eating behaviors.
emotion
A complex psychological state that involves three distinct components: a subjective experience, a physiological response, and a behavioral or expressive response.

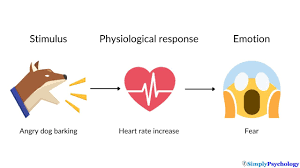
physiological arousal, then emotion theory
A theory suggesting that physiological arousal occurs first in response to a stimulus, and that emotion is experienced as a result of interpreting that arousal.
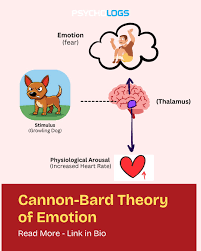
physiological arousal and emotion simultaneously theory
The theory suggesting that physiological arousal and emotional experience occur at the same time and are interrelated, influencing each other in the experience of emotions.
two-factor theory
The theory that emotion is based on two factors: physiological arousal and cognitive interpretation of that arousal.
Lazarus emotion theory
This theory posits that cognitive appraisal of a situation precedes emotional responses, emphasizing the role of thought in shaping emotions.

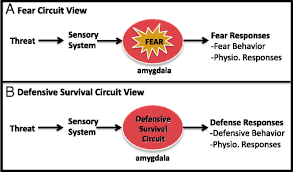
Ledoux emotion theory
The theory that emphasizes the role of neural pathways in the processing of emotions, particularly emphasizing the amygdala's role in fear responses.
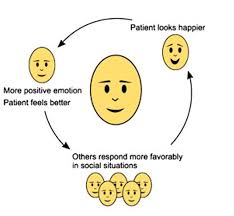
facial feedback effect
The hypothesis that facial expressions can influence emotional experiences, suggesting that our facial movements can impact how we feel.
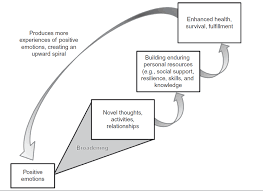
broaden-and-build theory
A theory proposing that positive emotions expand cognitive resources and promote personal growth, leading to increased resilience and well-being.
display rules
Culturally specific guidelines that govern the expression of emotions in social situations, influencing how and when emotions are shown.

universal emotions
Emotions that are recognized and experienced across all cultures, including happiness, sadness, fear, disgust, anger, and surprise.
