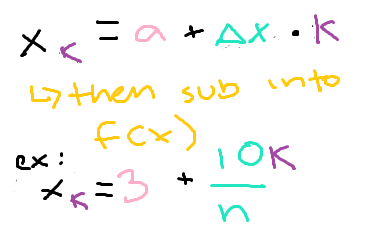BC Calculus Unit 6- Things to Memorize
1/44
Earn XP
Description and Tags
All of the rules/properties/etc. that you need to memorize for Unit 6 Integration
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
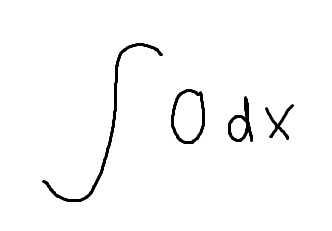
The integral of 0
A constant C

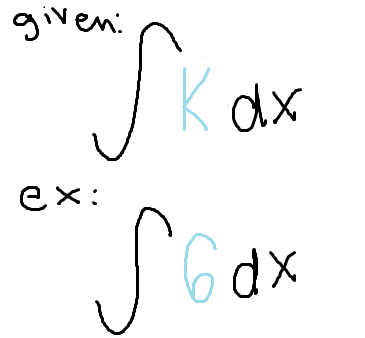
The integral of a constant
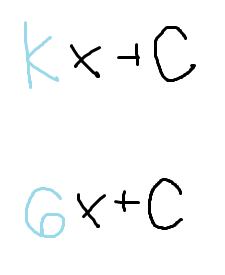
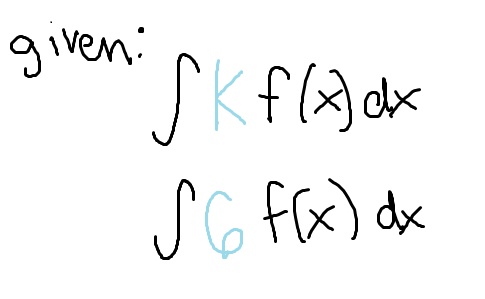
To simplify the integral of a constant multiplied by a function…
The constant can come out of the integral
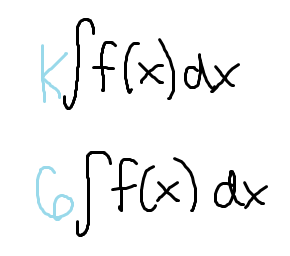
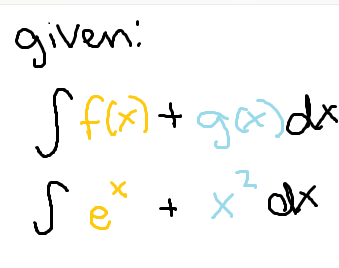
To simplify the integral of the sum of two functions
note: this also works with subtraction
The functions may be split up into separate integrals that are then added
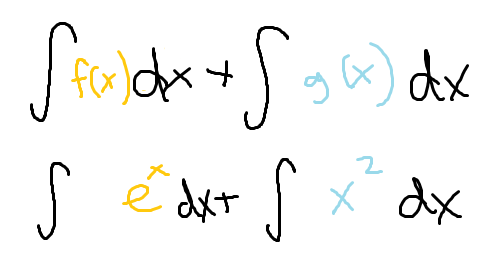
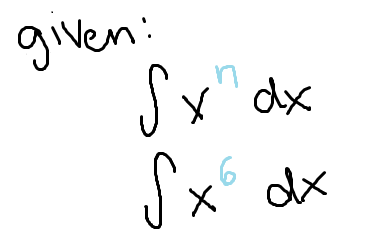
The integral of x raised to the power of a number n
note: n cannot equal -1
Increase the power by 1, then divide by that new exponent
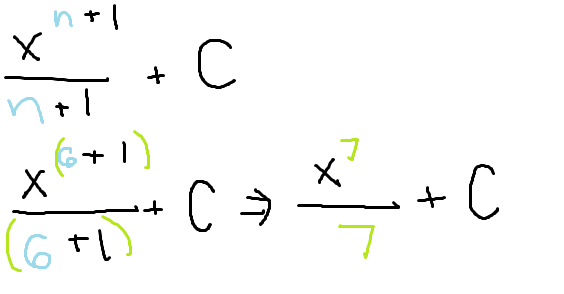
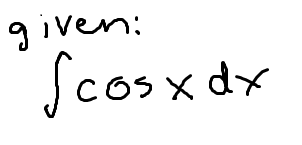
The integral of cos(x)
(note: this is the same as cos(u))
sin(x)+C
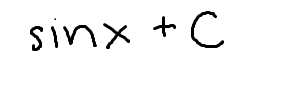
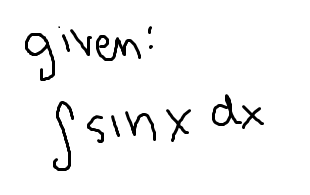
The integral of sin(x)
(note: this is the same as sin(u))
-cos(x)+C
(don’t forget the negative!)
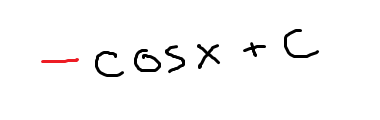
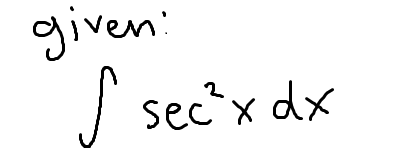
The integral of sec2(x)
tan(x)+C
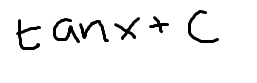
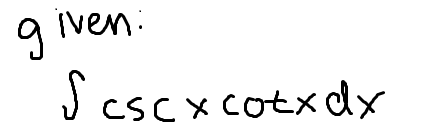
The integral of csc(x) times cos(x)
-csc(x)+C
(don’t forget the negative!)
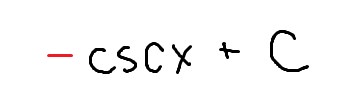
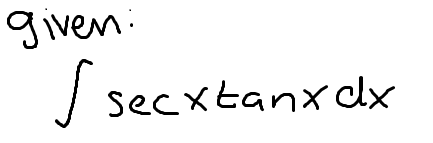
The integral of sec(x) times tan(x)
sec(x)+C
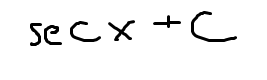
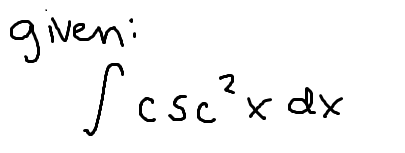
The integral of csc2(x)
-cot(x)+C
(don’t forget the negative!)
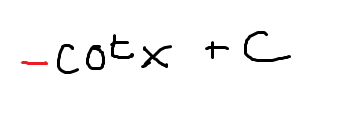
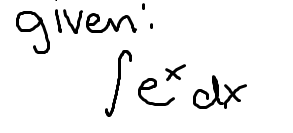
The integral of ex
(note: this is NOT the same as eu)
ex+C
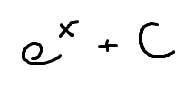
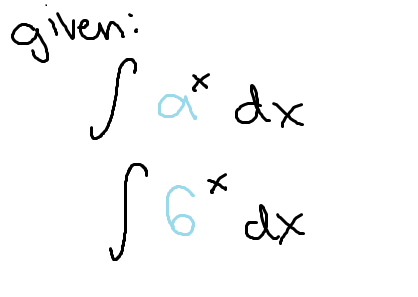
The integral of a number to the power of x
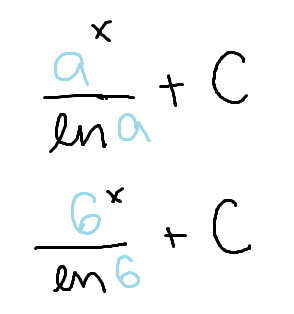
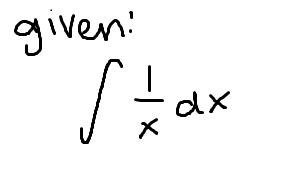
The integral of 1/x
(note: this is NOT the same as 1/u)
ln|x|
(note the absolute value)
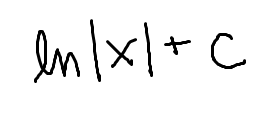
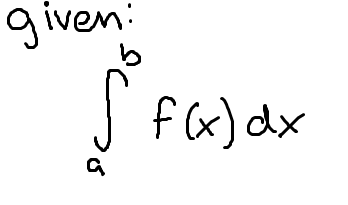
To find the value of a definite integral (Fundamental Theorem of Calculus- Part II)
F(b)-F(a)
(note that it is big F: the original function with derivative f(x))
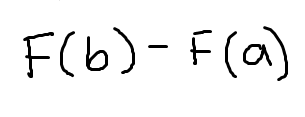
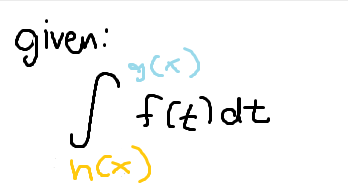
“Shortcut“ for the Fund. Theorem of Calculus
Upper sub in for t times derivative of the upper bound minus lower sub in for t times derivative of the lower bound
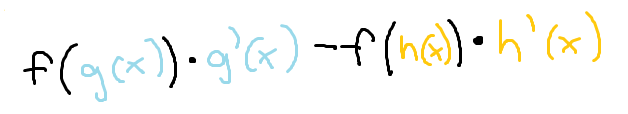
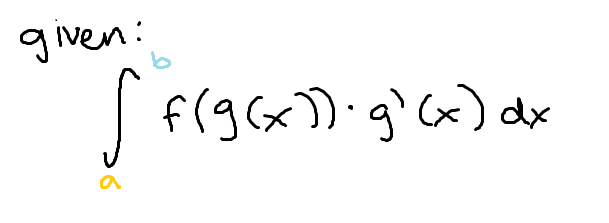
To use u substitution for a definite integral…
The upper and lower bounds of the integral must be subbed in for the function assigned to u and replace those as the bounds
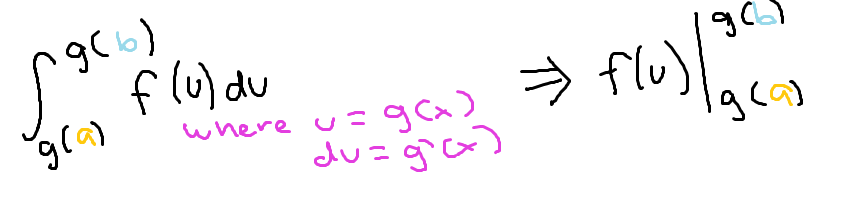
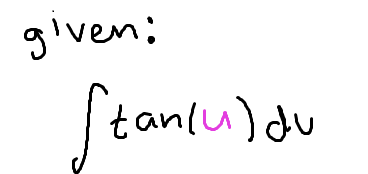
The integral of tan(u)
-ln|cos(u)|+C
(don’t forget the negative!)
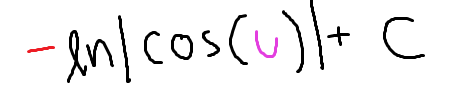
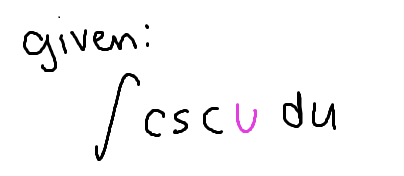
The integral of csc(u)
-ln|csc(u)+cot(u)|+C
(don’t forget the negative!)
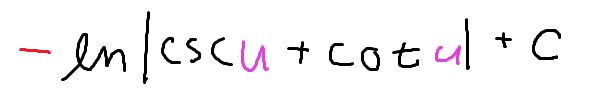
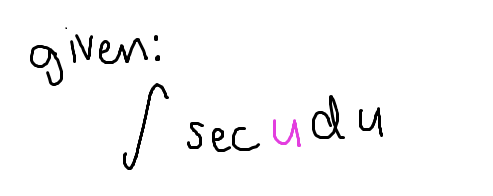
The integral of sec(u)
ln|sec(u)+tan(u)|+C
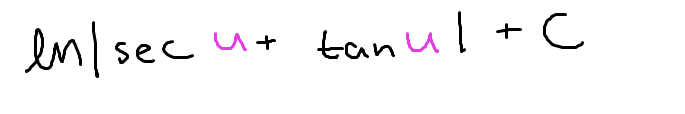
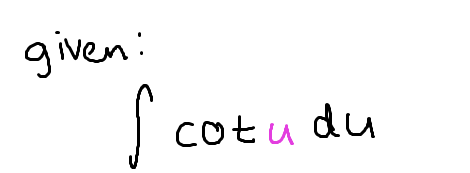
The integral of cot(u)
ln|sin(u)|+C
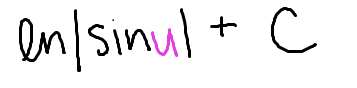
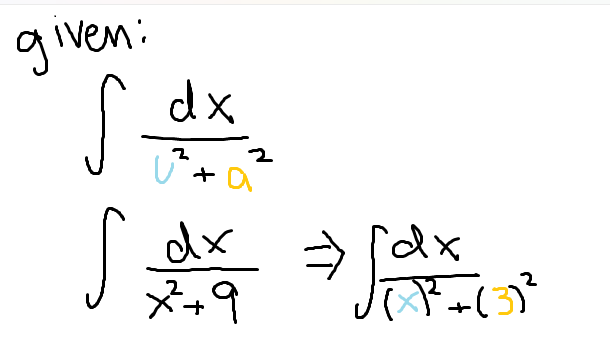
The integral of 1 divided by the sum of two perfect squares
arctan
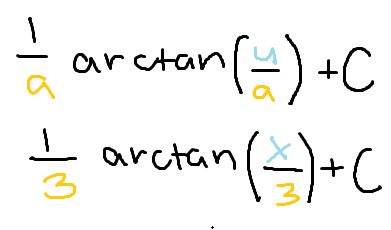
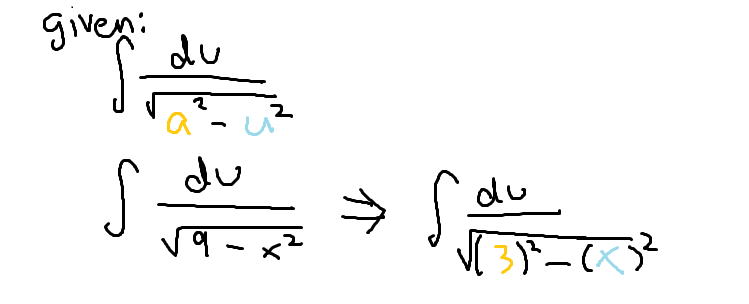
arcsin
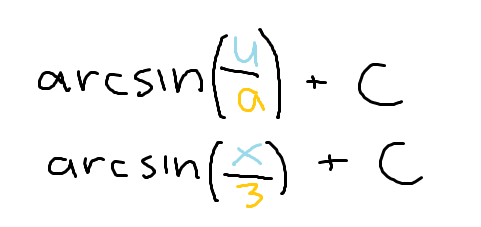
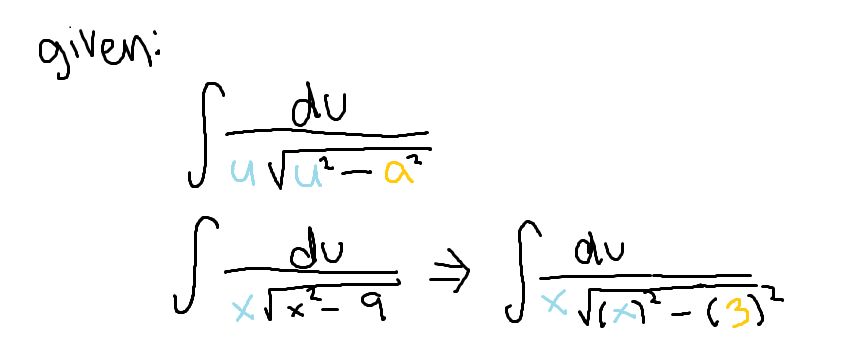
arcsec
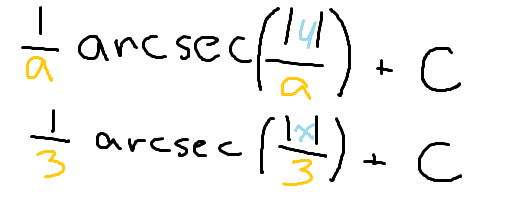
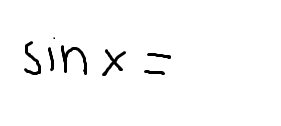
3 identities for sin(x)
ERROR: the third identity should say cos2x, not cosx
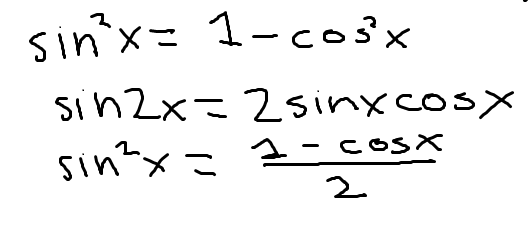
3 identities for cos(x)
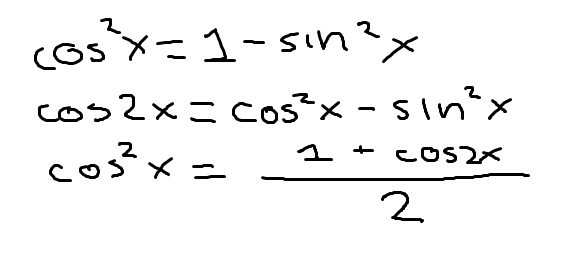
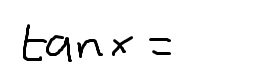
1 identity for tan(x)
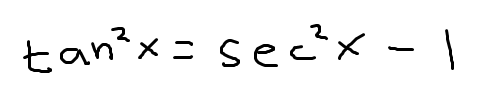
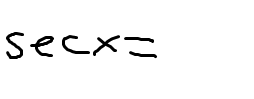
1 identity for sec(x)
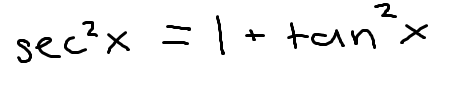
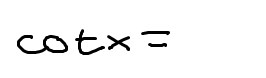
1 identity for cot(x)
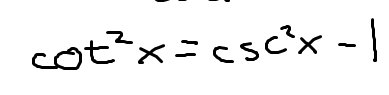
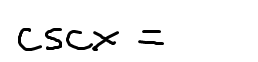
1 identity for csc(x)
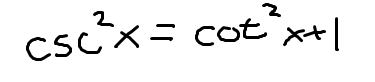
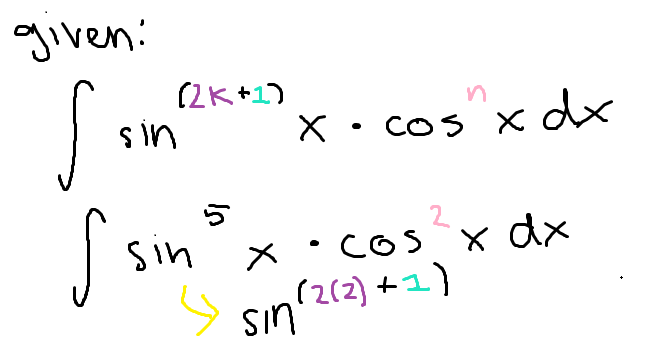
To simplify an integral involving a product of sine and cosine if either power is an ODD integer… (first step)
(note: for this example I used sine but it works the same way for cosine)
split the sin(x) into sin(x) to an even power times sin(x)
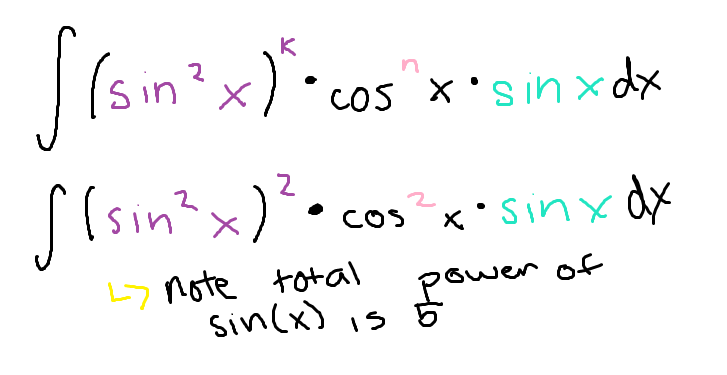
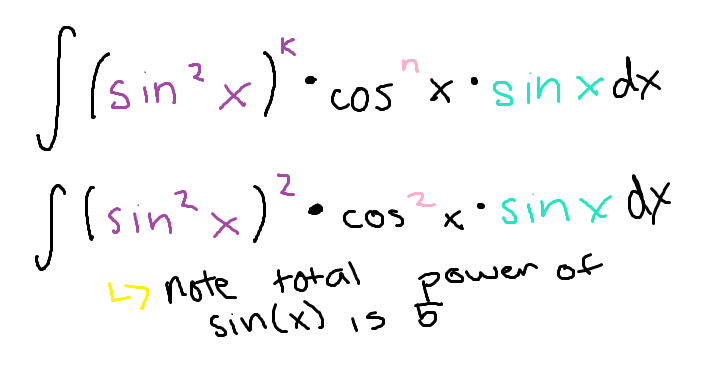
To continue simplifying an integral involving a product of sine and cosine if the power of sine is an ODD integer… (second step)
(note: for this example I used sine but it works the same way for cosine)
Sub in using the identity, then sub in using u=cos(x) (or u=sin(x) if cosine was the one split up and substituted)
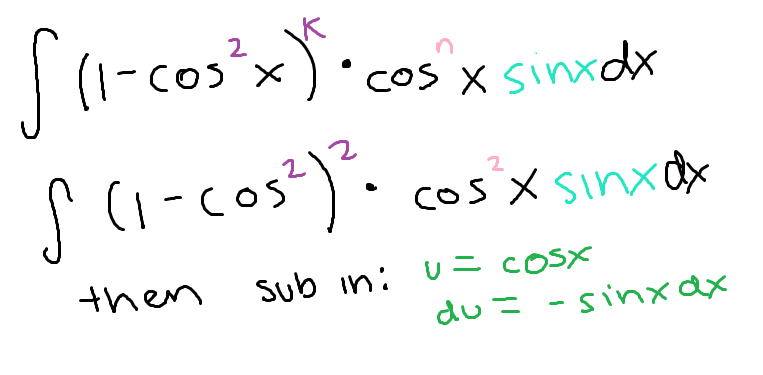
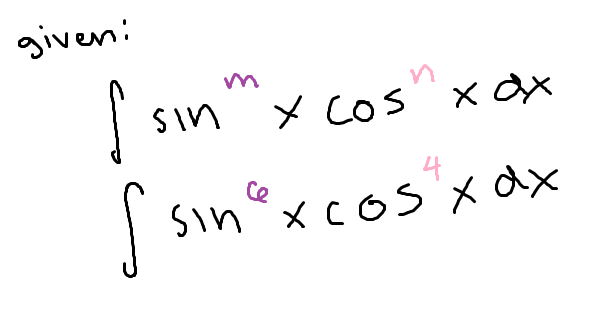
To simplify an integral involving a product of sine and cosine if the power of both are EVEN…
Use the half angle identities
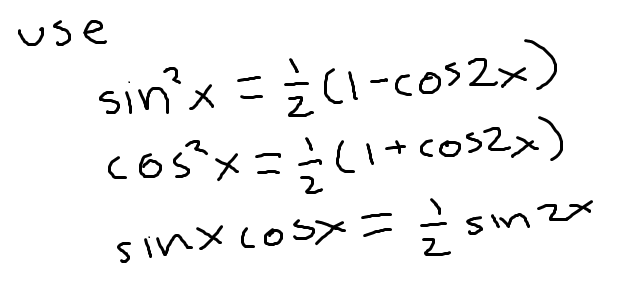
LIATE
Logarithmic, inverse trig, algebraic, trigonometric, exponential (the GENERAL order of priority for choosing a u value when doing integration by parts)
The formula for integration by parts
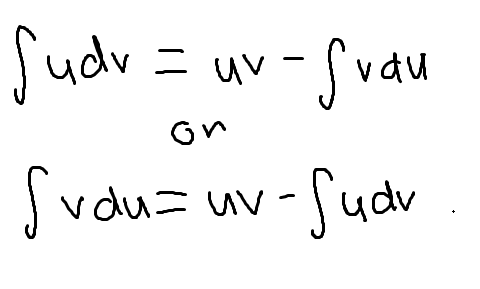
The three different cases for Type I improper integrals (upper and/or lower bound is infinity)
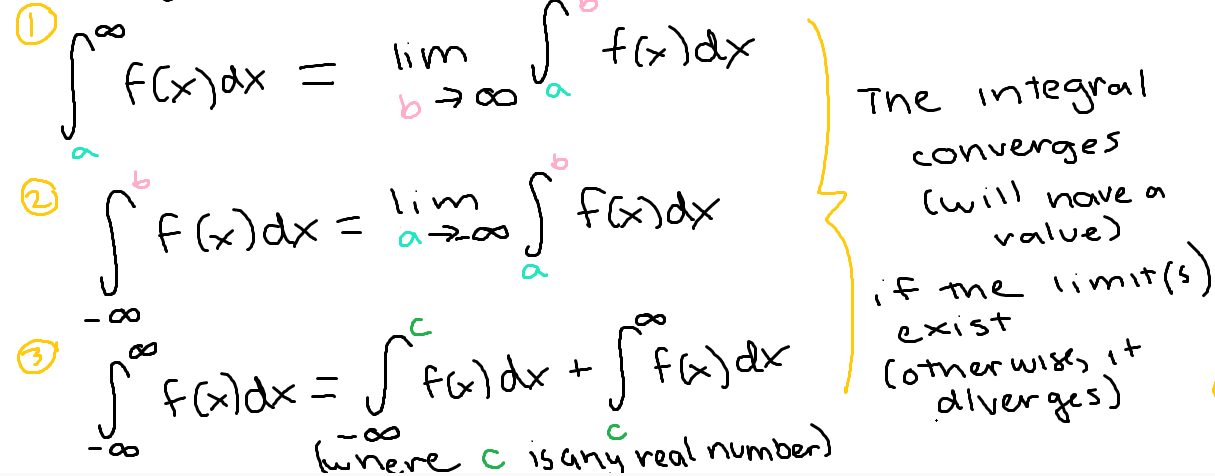
The three different cases for Type II improper integrals (have an asymptote)
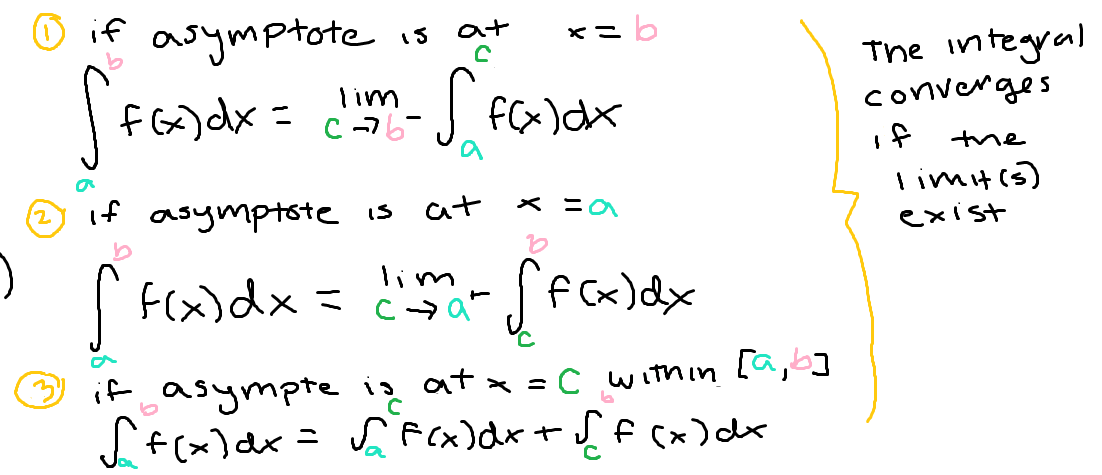
Behavior of left-hand Riemann sums
If the function is increasing: underestimate; if the function is decreasing: overestimate
Behavior of right-hand Reimann sums
If the function is increasing: overestimate; if the function is decreasing: underestimate
Right Riemann sum in summation notation
k-values go from 1 to n
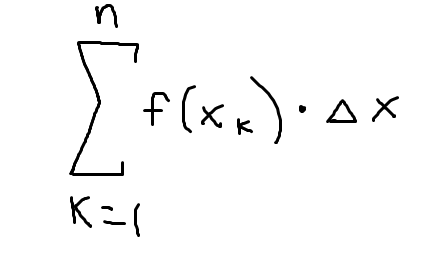
Left Riemann sum in summation notation
k-values go from 0 to n-1
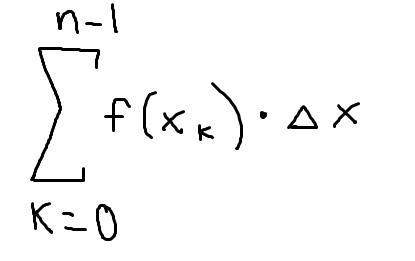
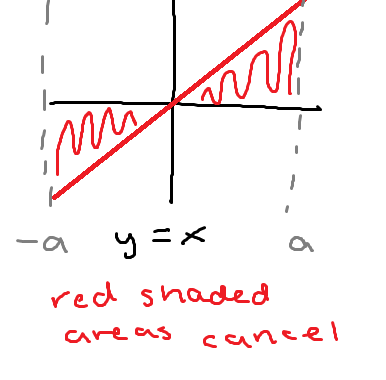
When a function is odd and the bounds are [-a, a]…
The area is 0
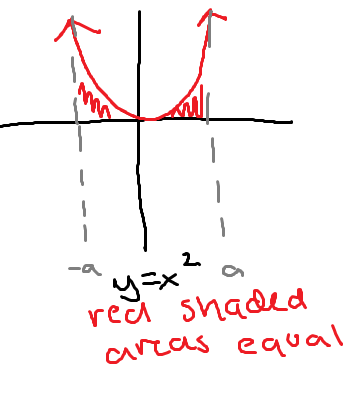
When a function is even and the bounds are [-a,a]
The integral can be split at x=0 into two equal parts
When solving an integral, which trig functions will have a negative in the answer?
sin, tan, and csc (all sine-related functions)
to find f(xk) for Riemann sums:
lower bound + rectangle width * k, then sub into f(x)