Russia - The end of Tsardom 3.1
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Give some examples of issues which made Russia hard to rule (size)
Russia was so big with it being able to fit Britain nearly 100 times inside of it
how was life like in 1900s for peasants
peasants- 84% of the population, 400,000 people died in 1891 when crop failure hit and other diseases, not enough land to go around so peasants had to be serfs owned by there masters
give some issues to govern russia 1900s (communication)
Communication was difficult as outside the main cities there werent many paved roads so in rain it would turn into mud making it impossible to travel around.
Railways were very limited with Russia only having as many miles of track as britain by the 1900s
Only line of communication with the eastern part of Russia was the Trans Siberian Express opened in 1904 which took more than a week to go from moscow to Vladivostok
give some issues to govern russia 1900s (cultures)
15 other nationalities in Russia, most of them not speaking Russian so had to go through Russification
how was life like in 1900s for nobility and middle class
1 % of population, owned almost quarter of the land for nobility
life was very good for the middle class and lived very lavish lifestyle. link between rich businessmen and governemtn was strong
how was life like in 1900s for workers
often lived in dromitories for up to 30 workers or minute rooms sleeping several families with no privacy
give facts about the new tsar
Nicholas II crowned in 1894. He was an autocrat so he had absolute power. Believed to be chosen by God. Good deal of bribary in the lower groups and corruption. No way of getting peoples views across. Okhrana was secret police to prevent opposition and those found were exiled to siberia. Cossacks stopped any demonstrations with great brutality
what was the role orthodox church
Branch of christianity that was key for russia. tsar and church both supported each other. this is why peasants and workers often thought of the tsar as the “little father”
problem in 1900s which made it hard to govern(population)
population rapidly increase by 50% between 1860 and 1897 so made land even more scarce
benefits and disadvantages of how russia was governed
disadvantages - whole thing could collapse if the peasants stopped believing in him. Whole country would suffer just because of one man’s decision
advantages - church and secret police allowed him to stay in power
Was Nicholas II the right man for the job?
yes - family man and cared about Russia
no - spends time with family rather than deal with governmental issues. anti jewish (pogroms). his answer was always violence. Did not know much about his people.
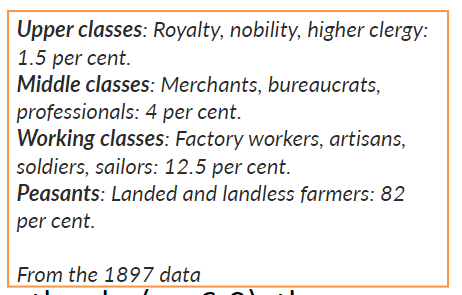
what were all the different classes in Russia
who were the revolutionary oppositions
Socialist revolutionaries - radical movement, aim was to get land from te nobility and give it to peasants. Took violence to change like 2 assassination of 2 gov officials and killed large number of okhrana
Social democratic party - smaller party but more disciplined. In 1903 it split into 2 parties bolsheviks and mensheviks. Bolsheviks wanted revolution but mensheviks thought russia wasnt ready for revolution
what was bloody sunday
peaceful protest in january 1905 and 200,000 protesters marched through streeets of st petersburg towards the winter palace for petition for change. Soldiers panicked and opened fire killing atleast 100
protests facts in 1905
just under 14000 strikes took place against the Tsar in 1905
what was the october manifesto
issued october manifesto to stop more protests and offered the creation of the duma ( an elected parliaments) giving right for free speech. But this divided opponents and then he was able to crush the peasant rebellions in countrysides and working class rebels in cities
other reasons for revolution in 1905
economic problems - living and working conditions were terrible. Heavy tax for government to improve russia. Starving of peasants in 1902 because of poor harvests. Gov used violence to stop this
russo japanese war- war in japan in 1904. Because tsar thought victory in short war would stop criticism to his gov but this caused worse conditions with prices rising and shortages of food
bloody sunday
what are the first parts to the 1905 revolution
by the end of january more than 400,000 workers were on strike.
in feb strikes spread to othe cities, workers demanded 8 hour day , higher wages and better conditions. On feb 4th the tsars uncle was assasinated Grand Duke Sergei
shameful defeats of in war with japan
middle cla liberal demanded elected parliament , freedom of speech and right to form political parties
middle parts to road to revolution in 1905
in september a peace trety was signed between russia and japan and thousands of troops now free to put down unrest and paid them and make better conditions to make them loyal to tsar
october another strike in moscow with all opposition groups together. barricades were put up
26 october st petersburg soviet of workers deputies was formed. representatives from factories met to coordinate strike. great threat to tsar
Final parts of road to revolution 1905
october manifesto on 30th october which promised duma elected by people, civil rigts, uncensored papers and rights to form political parties
now all soldiers back in russia he used force to close down the st petersburg soviet and crush an armed uprising in moscow and took revenge on people who rioted against him in december
Describe dumas
first meeting in 1906 but tsar continued to rule without taking notice of them. first and second dumas critical of the tsar by it lasted less than a year and nicholas sent them home. Tsar in 1907 made new voting rule so none of his oppositions cannot be voted in.
third duma lasted till 1912 mainly cause less critical than previous 2 about the tsar but by 1912 even this loyal duma became critical of the tsars ministers and policies but still nothing effected the tsar
dumas favoured nobles 1 in 2000 nobles but only 1 for 90,000 workers
changes after 1905 revolution
continued violent disturbances in countryside in 1906. tsar appointed peter stolypin to deal with this who had reputation for being tough.
military courts which could hang people on the spot. thousands were executed by these courts and known as stolypins necktie
okhrana still very active with thousands of informers and still articles being censored or fined
Stolypins policies stick and carrot
over 20,000 strikers exiled over 1,000 hanged on stolypins neck tie killing off opposition - stick
win over peasants by giving land and gave peasants ability to loan to get land and use modern methods to produce more to make new class called kulaks which were rich preasants who would be loyal to government
statistics on benefits of stolypins policies
between 1910 and 1913 col production increased by 10 mil tonnes and grand production increased by 20 million tonnes. Economic growth best between 1908 to 1911
ww1 stats
battle of tannanberg august 1914- 78 thousand killed or wounded compared to germany were only 12 thousand killed or wounded
battle of Masurian lakes september 1914 - Russia 125 thousand killed or wounded compared to 10 thousand killed or wounded in german forces
most important factors and stats leading to tsar’s abdiction
tsar took command of armed forces in september 1915 so tsar responsible for all defeats but also tsarina in charge who was suspected to be spy cause shes german and shes close with rasputin
after tsar took control brusilov offensive which had 500 thousand to a million expected casualties in the defeat against austria hungary and germany
average workers salary was 5 roubles a day which couldnt even buy you a kg of meat due to all the unemployment and bad economy during the war
Rasputin
rumours of affairs between alexandra and rasputin
he got murdered in december 1916
reputation was as a sex maniac
influenced tsarinas decisions
steps to revolution to abdicate tsar
winter 1916 railway lines so iced up so barely any food or fueld into petrograd so prices went sky hgih
march 7th in petrograd 40 thousand workers from the giant putilov engineering works went on strike for higher wages
12th march soldiers in petrograd refused to fire on crowds and shot their officers in the demonstration
15th march