Basic Economics
1/46
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
scarcity
there is a limited amount of resources on the planet to meet the unlimited wants of people
economics
the study of how people use their resources (or make choices) to deal with the problem of scarcity
positive economic statement
based on facts and not opinions
normative economic statement
include opinions
opportunity cost
when we make decisions in life, there are trade-offs or other possible options
factors of production
the resources used to produce goods and perform services (land, labor, capital [physical/human])
entrepreneur
person who puts together the factors of production to create goods and services
production possibilities curve (ppc)
a graphic representation of how much can be produced by an economy and the opportunity cost of producing that good or service
assumptions of the production possibilities curve
1) represents full employment/productivity
2) only producing 2 different goods
3) resources can be used for both goods
4) resources and technology are fixed (ceteris paribus)
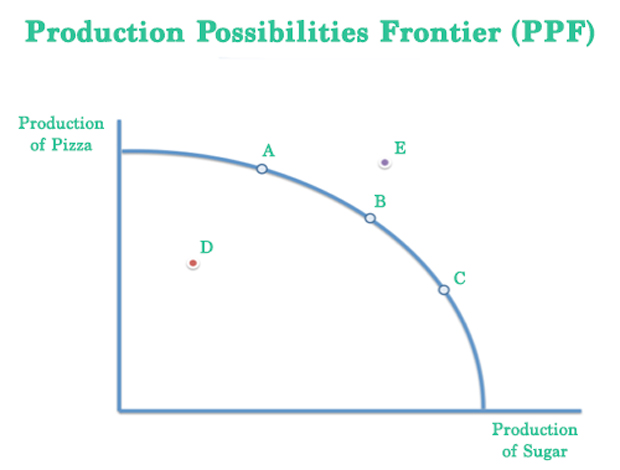
graph of production possibilities curve
points A, B, and C: efficient, max output using resources
point D: underutilization, unemployment, natural resource depletion
point E: impossible to produce, not enough resources
law of increasing costs (ppc)
as production switches from one good to another, the opportunity costs increase
growth (ppc)
when an economy can produce more than it previously could, the ppc shifts outward
reasons an economy can grow
1) acquiring new resources
2) better technology
3) trade with other economies
consumer goods
goods that satisfy our wants/needs directly, produced for personal consumption
capital goods
goods that help create consumer goods more efficiently
decline
when an economy can produce less than it previously could, the ppc shifts inward
reasons an economy can shrink
1) weather or natural disaster destroys natural resources
2) war destroys resources
economic system
how a society allocates its resources
market economy
an economic system where decisions on how to allocate resources are decided by voluntary exchanges of individuals on markets
market
consumers buy the goods and services from products
product market
consumers buy the goods and services from producers
factor market
producers buy the factors of production to make more goods or services for the product market
economic freedom
consumers buy whatever they want at whatever price they want and producers make whatever goods they want at whatever price they want to sell it at
laissez faire
“let them do as they please”
invisible hand (Adam Smith)
the economy guides itself and needs little government intervention, it shifts and adapts
price
direct resource usage by producers and they are determined, how consumers and producers communicate
competition
producers struggling against one another to get consumers to buy their goods and services
what competition gives us
1) choice and variety in goods and services produced
2) innovations
3) efficiency as producers produce a better product or cheaper products
private property
people have the right to control their possessions as they wish; the government does not control the factors of production
downsides to a free market economy
1) wealth is not evenly distributed
2) individual interests are more important than overall public well-being
3) lack of safety net for economic failure
4) competition brings out best and worst in people
socialism
philosophy based on the belief that society as a whole should control the factors of production and evenly distribute goods and services throughout society
communism
government plans and controls entire economy, centrally planned
downsides of a command economy
1) no economic freedom
2) lack of competition
3) lack of efficiency: if doctors and janitors are getting paid the same, why didn’t they have to do the same amount of school or work?
mixed economy
economic system which combines a free market economy and socialism, limited government control over some programs, but individuals make most choices
absolute advantage
the ability to produce more of a given product using a given amount of resources
comparative advantage
the ability to produce a given product more effectively (lowest opportunity cost)
in an input problem…
it shows the amount of resources required to produce 1 unit of the product, we use the lower number
to find the opportunity cost of producing ____, the amount of resources it takes to produce that product goes above the number of resources it takes to produce the product we are comparing it to
in an output problem…
it shows the amount of resources we can produce within a given amount of time, use the higher number
to find the opportunity cost of producing one ____, the number of ____ we can produce in one hour goes under the number of the compared product that can be produced in that same time
optimal allocation
finding how much to produce of a good to make consumers happy
marginal analysis
weighing marginal benefit vs marginal cost
marginal benefit
economic benefit gained from consuming or producing one more unit
marginal cost
economic cost from consuming or producing one more unit
utility
amount of satisfaction a consumer gets from consuming a good or service (unit=UTILS)
total utility
sum of all utility received from consuming a certain quantity of goods and services (add up all UTILS)
marginal utility
additional satisfaction or utility a consumer receives from consuming one more marginal good or service
law of diminishing marginal utility
the amount of utility gained from consuming each additional unit of a good decreases with each additional unit consumed (the more utility a person receives from a good or a service, the more they are willing to pay for that good or service)