Unilateralism, Multilateralism & International Institutions
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
Unilateralism, Multilateralism & International Institutions
Unilateralism: action taken by a single state
Multilateralism: coordination among 3 or more states in pursuit of a shared goal
International institutions: anything that shapes, constrains, guides and/or patterns the behavior of states
Why Cooperate?
Increasing state contact and interdependence
Transnational issues
Increase legitimacy of actions in world affairs
Increase leverage for smaller-power states
INTER-GOVERNMENTAL ORGANIZATIONS (IGOS)
aka ‘International organizations’ (IOs)
Consist of 3 or more states with activities in several states
Formal multilateralism
Consist of their own organizational structures and forms of decision-making
Examples
United Nations (UN)
Bretton Woods institutions (World Bank and the International Monetary Fund)
World Trade Organization (WTO)
North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO)
European Union (EU)
REGIONAL IGOS
Europe
-EU, Organization for Security Cooperation in Europe (OSCE)
Africa
-AU, Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS), Southern African Development Community (SADC), East African Community (EAC)
The Americas
-Organization of American States (OAS), MERCOSUR
Asia
-Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN), Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC), Shanghai Cooperation Organization (SCO)
The Middle East
-Arab League, Gulf Cooperation Council
The United Nations (UN)
A central component of world politics and governance
A truly global IGO
193 members
Central to world peace and stability
Functions
Provides the global security system
Creates international laws and principles
A forum for debate and knowledge sharing
Involved in international development efforts
Sponsors global conferences
The ‘UN SYSTEM’
Principle Bodies
General Assembely
Security Council
Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC)
Secretariate
International Court of Justice (ICJ)
Specialized Agencies
Includes WHO, ILO, UNESCO, FAO, etc.
Funds & Programmes
Includes UNICEF, UNDP, UNHCR, WFO, UN Women, UNEP, etc.
THE UN SYSTEM Pt.2
General Assembely
The international ‘hub’
-Sets the global agenda
Security Council
Core of the global security system
-15 members, 5 are permanent (P-5)
Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC)
Central forum for economic and social issues and development policy
-54 members
Secretariate
The UN’s administration
-Headed by the Secretary-General
International Court of Justice (ICJ)
World Court’
Constraints on The United Nations
Contradictions with state sovereignty
Competing interests in world politics
-Leads to ineffectiveness and inaction
Lack of sufficient funding
Ongoing and new transnational
issues
INTERNATIONAL ‘LAW’?
Law: mechanisms put in place to regulate interactions and settle disputes
There is much debate regarding whether international law is ‘law’
Nicaragua-US example
International Law Pt.2
A core international institution
“[...] the body of principles, customs and rules regulating interactions among and between states, IOs, individuals and in more limited cases, multilateral organizations” (Boyer et al, 2019, 259)
International law is consent-based
-Sovereignty is central
INTERNATIONAL LAW & DOMESTIC LAW
International law exists in a condition of anarchy
There are multiple sources of international law
International law lacks centralized, consistent enforcement
International law is consent-based
International law is more facilitative than controlling
Politics precedes and constrains international law to a greater extent
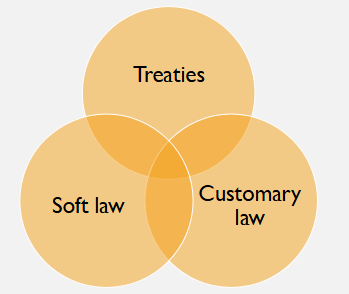
Sources of International Law
Treaties
Soft Law
Customary law